L18: Shigella and Salmonella
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
negative
are these gram positive or negative?
1. S. dysenteriae
2. S. flexneri
3. S. boydii
4. S. sonnei
what are the four species of Shigella?
IS, hemorrhagic dysentery
shigella (is/is not) host restricted to humans and higher primates, causing ___ ___ in humans
shiga toxin encoding phage
shigella is invasive like E. coli and S. dysenteriae is a source of ___ ___ ___ ___ found in enterohemorrhagic E. coli
Bacillus cholera-suis, Salmonella cholerasuis
Dr. Salmon discovered ___ ____ form a pig suffering from hog choera 1885, later renamed ___ ___
Salmonella enterica and Salmonella bongori
what are the two true species of Salmonella?
Salmonella enteric sbsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium, 2600
Salmonella enterica has 6 ubspecies, the most important being... comprising over ____ serovars
O, H, and Vi antgens
what antigens are included in the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor scheme for Salmonella
False; only 1/3 of the outbreaks are due to food
T/F: salmonella outbreaks are only due to food-boune outbreaks
virulence from acquired plasmid
the top serotypes of salmonella food borne infections may changes due to added ..
go listen ot what he said at like 1:12 about slide 9
protects from antibiotic and bile salts
the O-antigen lipopolysacchardide has what function?
1. motility
2. phase inversion expression for phase 2 repression and phase 1 expression
function of the H- antigen
1. type 3 secretion system
2. lipopolysaccharide
3. fimbrae
4. flagelline
5. bacterial DNA
both S. typhimurium and S. typi express..
S. typhi
S. paratyphi C
S. Dublin
the Vi antigen is exclusive expressed in which S. species?
by repressing flagellin and LPS expression
how are the Vi expressing species able to circumvent the innate immune system?
inflammation
what is the driver of non-typhoidal Salmonella?
Typhoidal Salmonella
___ ___ down regulated immune response to avoid immune system
invade the host's intestinal epithelial cells and persist within Salmonella-containing vacuoles
invasion and intracellular survival enable Salmonella to efficiently ....
Salmonella biofilm formation on gallstones or lineing of gallbladder
what causes persistant shedders of Salmonella?
liver and shed into intestinal tract via flow of bile from liver
Since horses do not have gall structures, how are they shedders of salmonella?
self-limiting
the broad host range of salmonella diseases is ____ causing acute gastroenteritis and watery diarrhea
diarrhea
nausea
vomiting
intestinal cramps
fever
when contracting salmonella, the hosts inflammatory response is responsible for clinical signs including...
reduced milk or egg production
reduced weight gains
persistant carriers
what are some subclinical symptoms of salmonella disease?
1. S. typhimurium
2. S. enteritidis
3. S. newport
4. S. infantis
5. S. kentucky
what subspecies are considered to have a broad host range for salmonella
localized signs in unusual locations like the chest wall or thyroid abscess
most times in non-preferred hosts, they are subclinical. What are some clinical signs when it does cause infection?
S. Bublin in cattle and S. Cholerasuis in pigs
what subspecies are considered to have a host adapted for salmonella
typhoid or typhoid like disease
for host specific salmonella, there is a very narrow host range with usually only one host and causes ____ ____ ___
S. typhi
S. gallinarum
S. Abortusovis
S. typhisuis
S. abortusequi
what subspecies are considered to have a host specific salmonellaosis?
15% reported HAI
What is the rate of hospital aquired infection of Salmonella, considering it is the fourth highest HAI?
asymptomatic shedders
___ __ of salmonella pose risk for nosocomial infections and zoonotic infection
5.73% in dogs, 30% of those shed after consuming bones/raw diet
prevalence of salmonella in dogs
20-48.7% of farms have at least 1 positive cow
prevalance of Salmonella at dairy farms
ither horizontal transfer to the egg/shell membrane or vertical transfer through the oviduct sections
for transmission of S. enteritidis in poultry, explain the process.
extensive bacterial growth in the yolk
an egg hoizontally infected with salmonella will experience what
1. feces
2. animal to animal
3. animal contact
4. ingestion of contaminated feed
horizontal transmission of S. dublin in cattle
intrauterine transmission mostly causing abortions or via milk
vertical transmission of S. dublin in cattle
1. decreased weight gain
2. decreased milk production
3. sterility
clinical signs of salmonella for asymptomatic/subclinic cases
1. fever
2. poor appetite
3. diarrhea bloody or mucoid
4. vomiting/abdominal pain
5. sepsis
6. colic
7. abortion
clinical signs of salmonella for animals with gastroenteritidis
1. bacterimia
2. sepsis
3. abortion
4. localized infections in bone/joint
5. infection of mammary tissue/ovaries
clinical signs of salmonella for animals with estra-intestinal infection
marked jaundice and hepatomegaly
gross necropsy findings of salmonella dublin
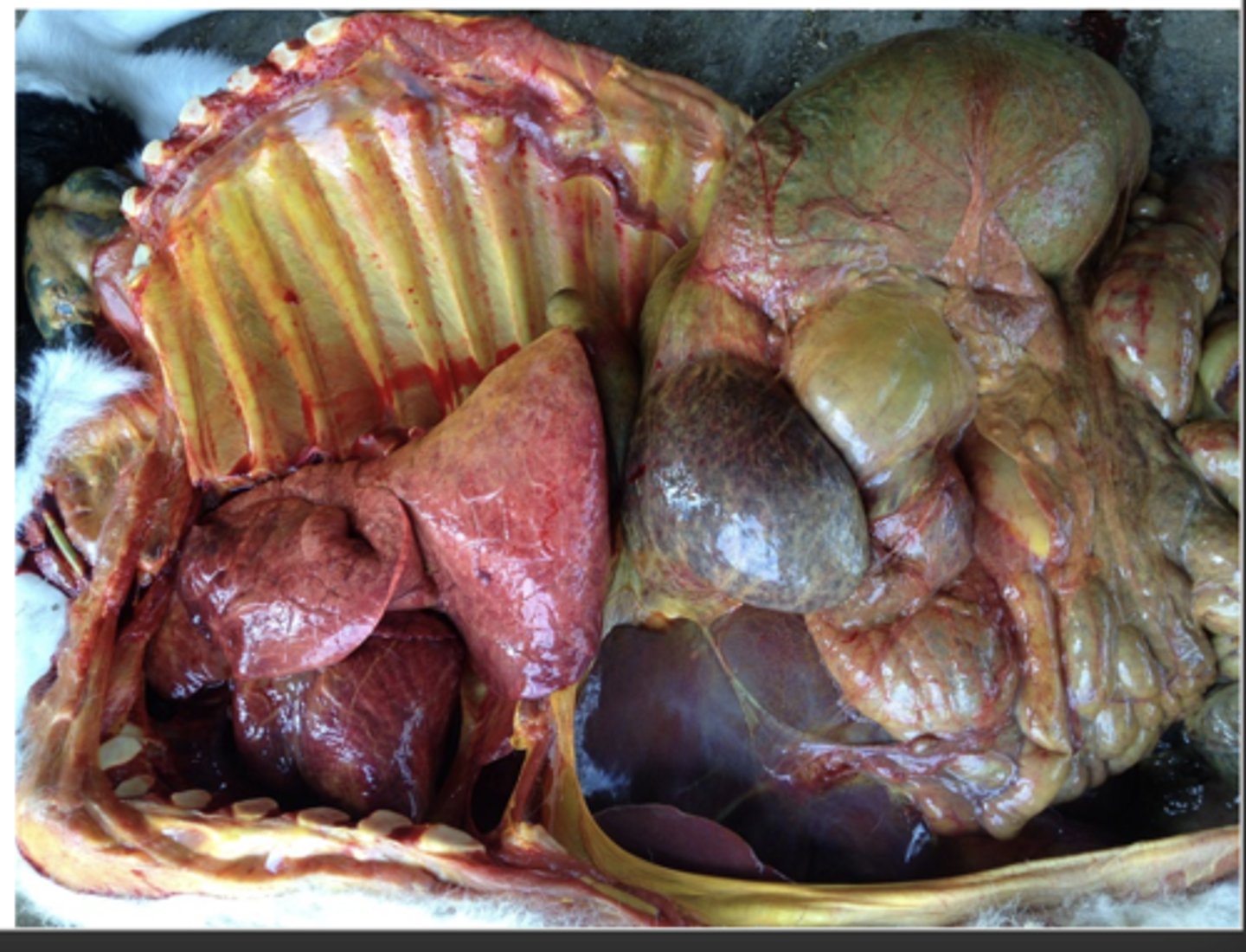
1. cyanosis
2. sever gastritis
3. severe colotis
pigs infected with Salmonella Choleraesuis
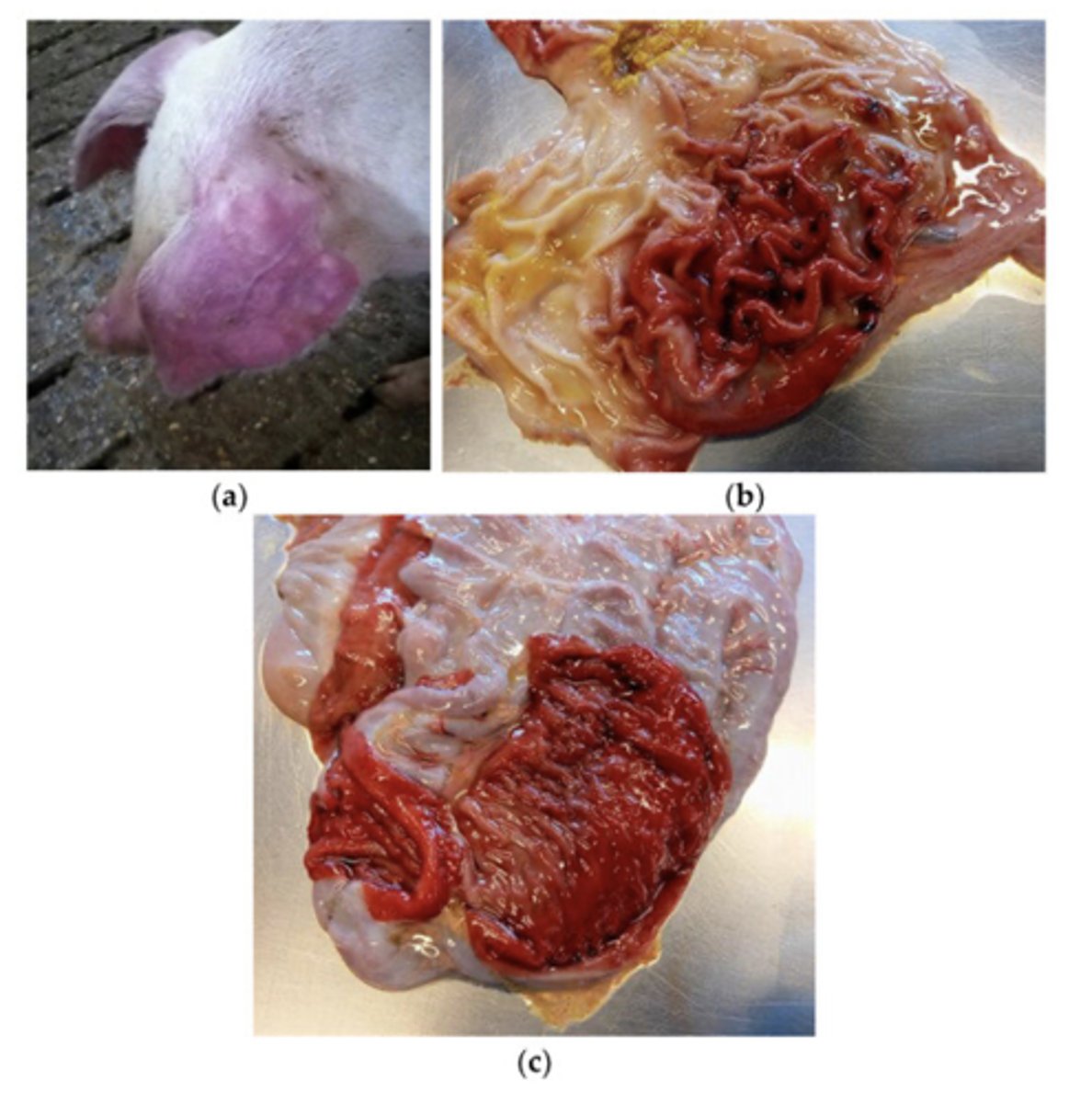
travel, age, food consumptions, exposure, new animals introduced to herd
diagnosis of salmonella is important with a medical history. include...
1. direct streak onto agar
2. enrichment broths
3. biochemical confirmation
4. serological confirmation
tests to request with suspect salmonella
supportive care is useful but antimicrobial use is controversial because of resistance and some strains are not susceptible to antimicrobials for use with septicemia (in calves)
treatment of salmonella
enrofloxacin, enrofloxacin
US isolates of S. Dublin are susceptible to ____ however use of ___ to treat S. dublin infections is extralabel which is prohibited for fluoroquinolones in food animals
isolate new animals, transport stress increases susceptibility to salmonella
preventing salmonella introduction to a herd
1. ID infected animals and recheck previous patients
2. restrict movement between herds
3. CLEAN maternity areas and disinfect buidlings
4. don't feed animal scraps to companion animals
5. education of the hazards of working with infected animals
how to limit transmission and increase biosecurity with salmonella disease?
attenuated Salmonella vaccine in pigs, cattle, and chickens
vaccine for salmonella