1.3.2 Databases
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Database
Simplest kind is a flat file, consisting of information about a single entity
Entity
A category of object, person, event or thing of interest about which data needs to be recorded
Relational databases
A database which recognises the difference between entities (item of interest about which information is stored) by creating different tables for each entity
Attributes
Characteristics of entities - categories about which data is collected
Flat file database
Database that consists of a single file. Most likely based around a single entity and its attributes. Typically written out as: Entity1(Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3 …)
Primary key
Unique identifier for each record in the table that is automatically indexed. Primary key is shown by underling it
Composite Primary Key
Sometimes two or more attributes are needed to uniquely define a record
Foreign key
The attribute which links two tables together. Will exist in one table as the primary key and act as the foreign key in another. Shown using an asterisk
Secondary key
Allows a database to be searched quickly
Entity relationship modelling
Tables can have different kinds of relationships, which depends on how entities are related in the real world
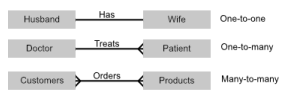
One-to-one entity relationship
Each entity can only be linked to one other entity, such as the relationship between a husband and wife
One-to-many entity relationship
One entity can be associated with many other entities, such as a mother having multiple children
Many-to-many entity relationship
One entity can be associated with many other entities and the same applies the other way round, such as students and courses - each student can enrol in more than one course and each course can have more than one student
Relationship modelling
Normalisation
Process of coming up with the best possible layout for a relational database
What does normalisation try to accomplish?
No redundancy (unnecessary duplicates)
Consistent data
Records can be added and removed without issues
Complex queries can be carried out
First normal form
There must be no attribute that contains more than a single value. No repeating groups of attributes
Second normal form
Database which doesn’t have any partial dependencies and is in first normal form can be said to be in second normal form. This can only occur if the primary key is a composite key
Third normal form
If the database is in second normal form and contains no non-key dependencies, it’s in third normal form. A non-key dependency means the attribute only depends on the value of the primary key and nothing else
Indexing
Method used to store the position of each record ordered by a certain attribute. Used to look up and access data quickly. Primary key is automatically indexed; however is almost never queried since it’s not normally remembered. Secondary keys are used to make the table easier and faster to search through on those particular attributes
Capturing data
Data can be input into the database using multiple methods depending on the context, such as Magnetic Ink Character Recognition, Optical Mark Recognition, or Optical Character Recognition
Selecting and managing data
Could involve only selecting data that first a certain criteria to reduce the volume of input. Can alternatively be managed using SQL
Exchanging Data
The process of transferring the collected data
SQL
Structured Query Language:
A declarative language used to manipulate databases
SELECT, FROM, WHERE
SELECT is used to collect fields from a given table and can be paired with FROM to specify which table the information will come from. WHERE can be used to specify the search criteria
ORDER BY
Specifies whether you want it in ascending or descending order. Values are automatically placed in ascending order
JOIN
Provides a method of combining rows from multiple tables based on a common field between them
CREATE
Allows you to make new databases
ALTER
Used to add, delete or modify the columns in a table
INSERT INTO
Used to insert a new record into a database table
UPDATE
Used to update a record in a database table
DELETE
Used to delete a record from a database table
Referential Integrity
The process of ensuring consistency. Ensures information is not removed if it is required elsewhere in a linked database and that no foreign key in one table can reference a non-existent record in a related table
Transaction
A single operation executed on data
ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability)
Atomicity: Transaction must be processed in its entirety or not at all
Consistency: Transaction must maintain referential integrity rules between linked tables
Isolation: Simultaneous executions of transaction should lead to the same result
Durability: Once a transaction has been executed it will remain so
Record Locking
Process of preventing simultaneous access to records in a database. Used to prevent inconsistencies or loss of updates. While one person is editing a record it ‘locks’ it to prevent others from accessing the same record
Problems with Record Locking
If two users attempt to update two records a situation can arise where neither can proceed, this is a deadlock
Timestamp Ordering
Deadlock prevention. When a user tries to save an update, if the read timestamp is not the same as it was when they started the transaction then another user has accessed the same object.
Commitment Ordering
Deadlock prevention. Transactions are ordered in terms of their dependencies on one another as well as the time they were initiated. Can be used by blocking one request until another is completed
Redundancy
The process of having one or more copies of the data in physically different location