UNIT 4 CHEM AFTER REACTION PATHWAYS
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Macromolecules/Monomers/Polymers Definition
- Monomers: Small covalent molecules
- Macromolecules (polymers) is made when monomers are joined by covalent bonds
- Polymers,ers could be made from a single monomer or two or more different monomers.
Name the synthetic polymers, their monomers and examples:
Polymer: Polyalkene
Monomer: Alkene
Example: Polythene
Polymer: Polyester
Monomer: carboxylic and hydroxyl functional groups (ester)
Example: Polyester
Name the Natural Polymers, their monomers and examples:
Polymer: Polypeptide
Monomer: Amino Acid
Example: Protein, Enzyme
Polymer: Polysaccharide
Monomer: monosaccharides (sugars)
Example: Starch, cellulose (carbohydrates)
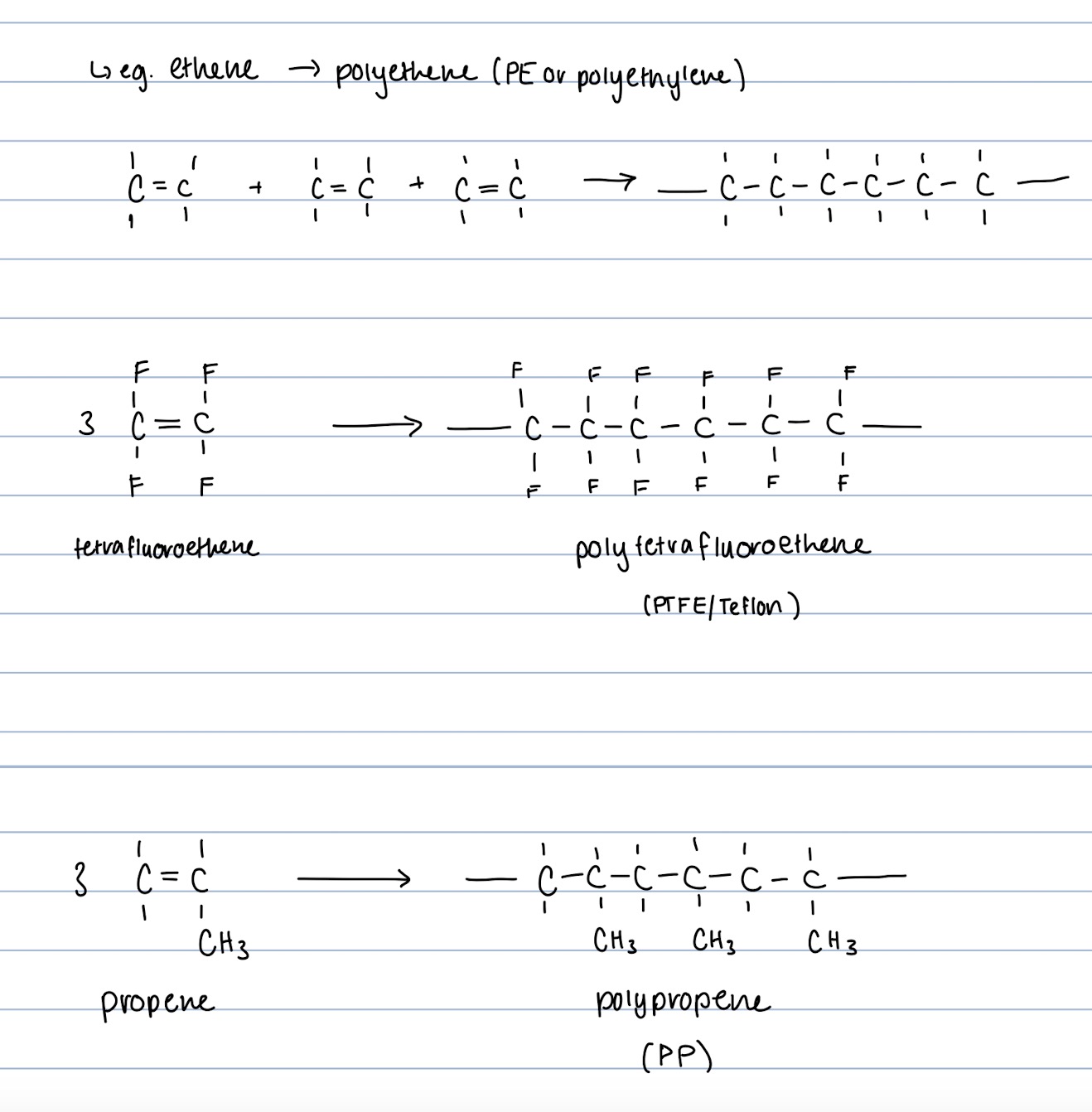
How is a Polyalkene Formed?
-Monomer is alkene
- Addition Reaction—> Double bond of each monomer breaks, and a new C-C bond is formed between two adjoining monomers until all monomers are used up.
-Examples include: Polypropene, Polyethene, Tetra Fluroethene
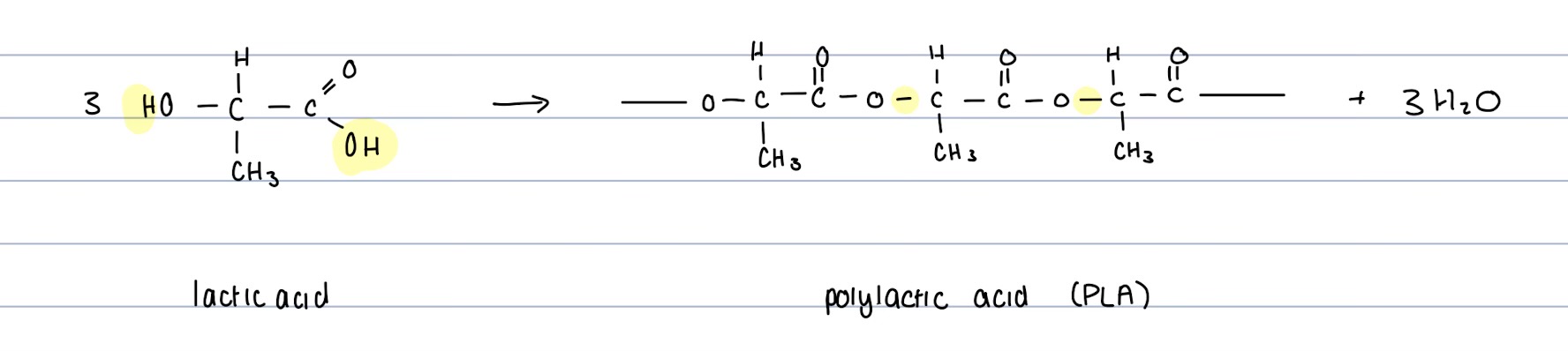
How are Polyesters formed?
Formed By condensation Rections
Esterification between carboxylic and hydroxyl function groups
A new covalent bond is formed between C and O of the carboxylic and hydroxyl functional group respectively
Byproduct of Water
There are two ways for this to form, either:
Both carboxyl and hydroxyl functional groups are present in two different molecules
OR
One molecule has two carboxyl function groups (dioc acid), and the other has two hydroxyl groups (diol).
Reversible Reaction
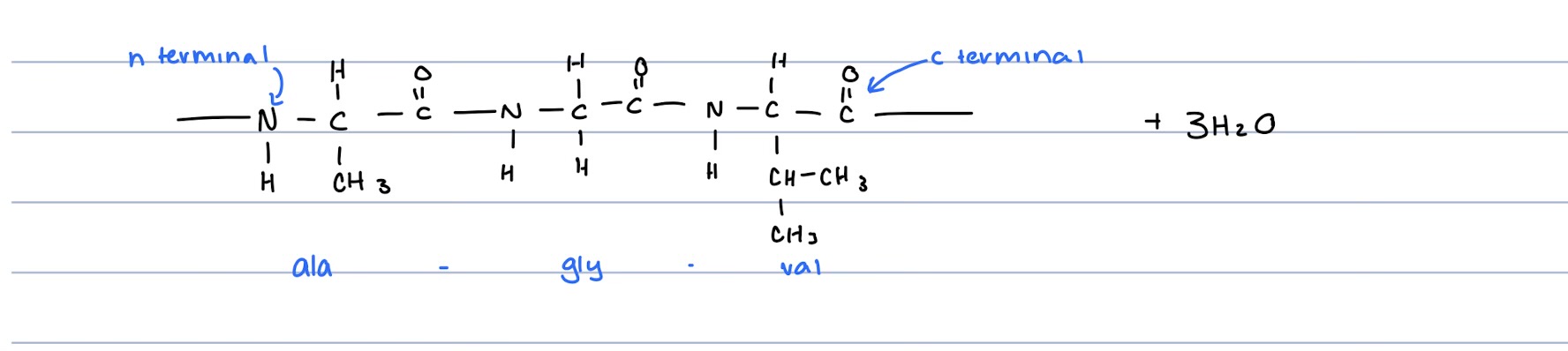
How are Polypeptides formed?
Monomer: Amino Acid
The Amino Acid has a carboxyl functional group, an amino functional group and a hydrogen atom bonded to the same carbon atom
The side chain(R) attached to the same carbon atom could vary.
Condensation reaction take place between carboxyl functional group of one amino acid, and amino functional group of second amino acids.
A peptide bond (amide bond) is formed between adjoining amino acid molecules
For each peptide linkage formed, a water molecule is also formed
What is a monosaccharide
Monosaccharide is a monomer molecule, also know as sugar
The names do all monosaccharides end in “ose” Eg. Ketose, Aldose
Chain structure is in equilibrium with cyclic structure in aqueous solution
How to name monosaccharides
In cyclic structure, the carbon atom next to the O atom (clockwise) is C(1) In glucose and galactose and C(2) in fructose and the OH group attached to it is;
pointing down and opposite side to C(6) it is an Alpha isomer
pointing up and same direction as C(6), it is a Beta isomer.
The three monosaccharides are:
Glucose
Galactose
Fructose
How are disaccharides formed
The condensation between OH group of C1 of the first monosaccharide and the OH group which is closest to it on the second monosaccharide.
This bond formed is called a glycosidic bond
The glycosidic bond is written in order of < alpha or Beta — atom number of the second sugar + glycosidic bond >
Eg. alpha 1-4 glycosidic bond, Beta 1-4 glycosidic bond, alpha 1-4 glycosidic bond
There are three types of Disaccharides;
Maltose, Lactose and Sucrose
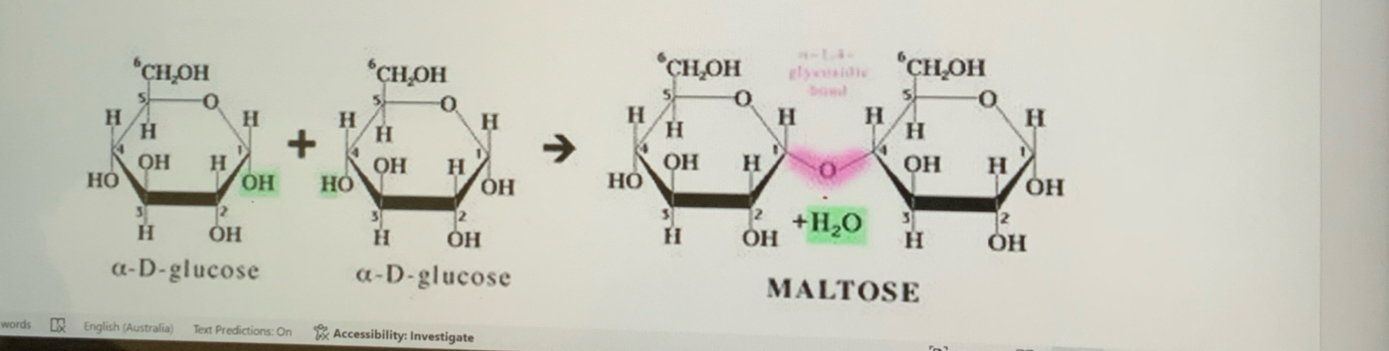
What is maltose
alpha glucose+ alpha glucose—> Maltose +H2O
Forms alpha 1–4 glycosidic bonds.
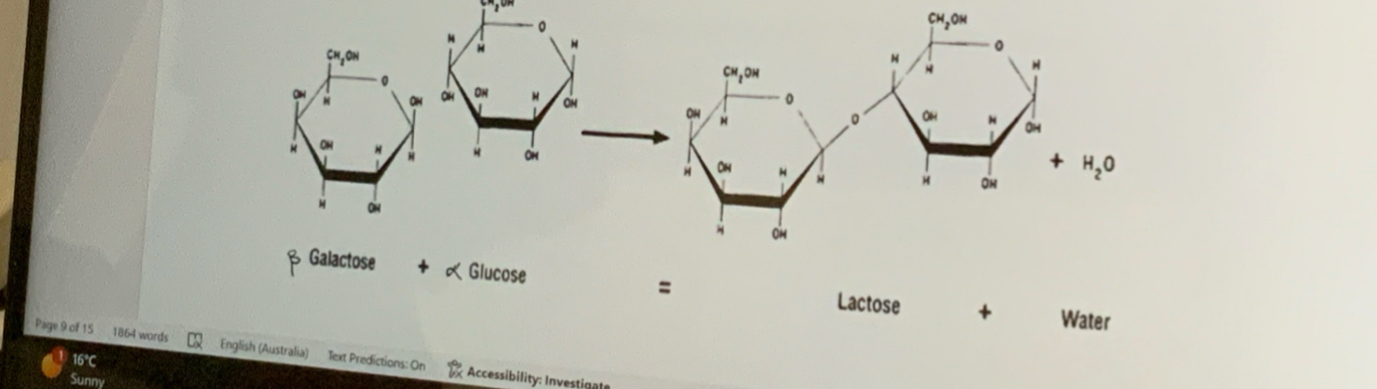
What is Lactose?
Beta-galactose + alpha-glucose—> lactose +H2O
Forms Beta 1-4 glycosidic bonds
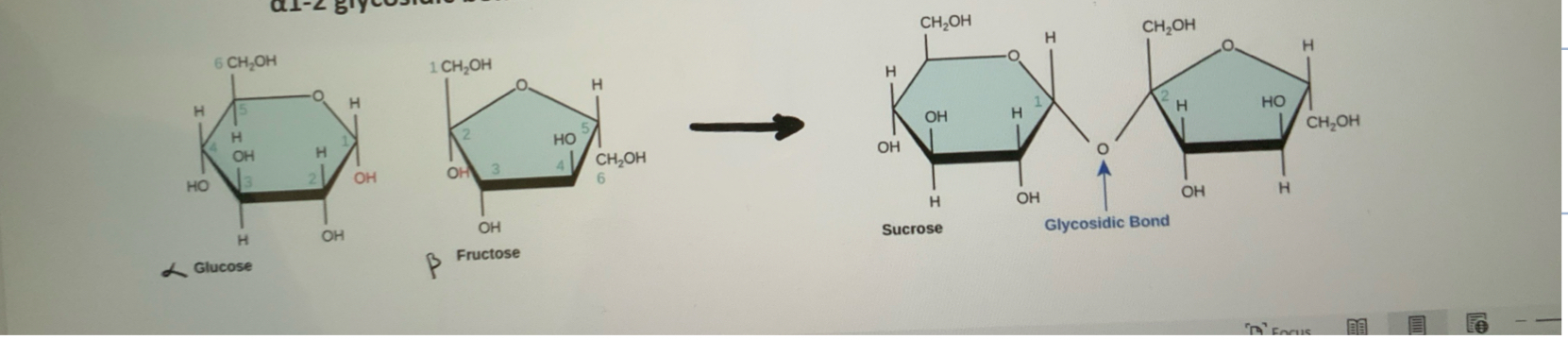
What is Sucrose?
alpha-glucose + Beta-Fructose—> Sucrose + Water
alpha 1–2 glycosidic bond is formed between two monomers
The beta fructose is inverted and switched sides to create this bond
What are Polysaccharides?
A large number of monosaccharides (monomers) are joined by the glycosidic bonds
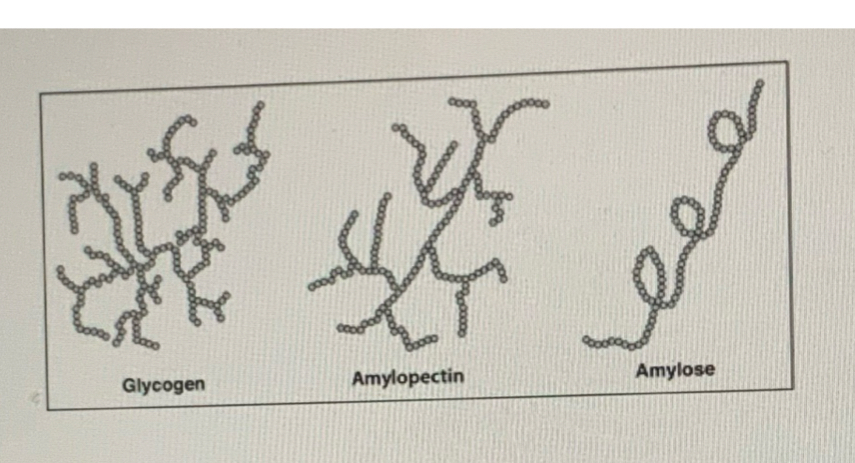
What are the two polysaccharides which make up starch?
Amylose
Amylopectin
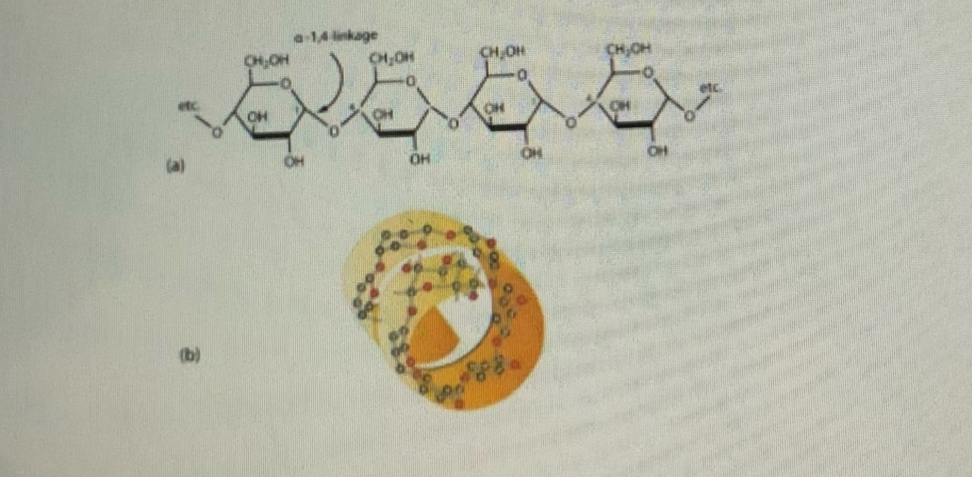
Describe the properties of Amylose:
Monomer is alpha-glucose
alpha-glucose form alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds in polysaccharide chain
Only a few alpha glucose molecules per chain
Unbranched, hence water soluble
Intra chain hydrogen bonding form spiral shape in secondary structure
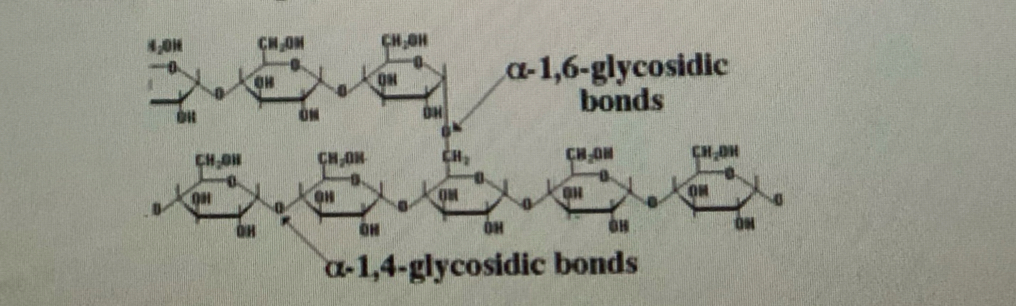
Describe the properties of Amylopectin:
many alpha glucose molecules per polymer bonded through alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds
Branched polymer forming alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Branching doesn’t allow regular hydrogen bonds to form a spiral instead forms granules
Since amylopectin is larger than amylose structure and branched, it is insoluble.
Function: storage polysaccharide
Describe the properties of Glycogen
large number of alpha glucose molecules per polymer chain
Bonded through alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds
alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds responsible for branching
More extensively branched than amylopectin
Water insoluble, suits function as storage polysaccharide
Function: to maintain blood glucose and provide energy in muscle
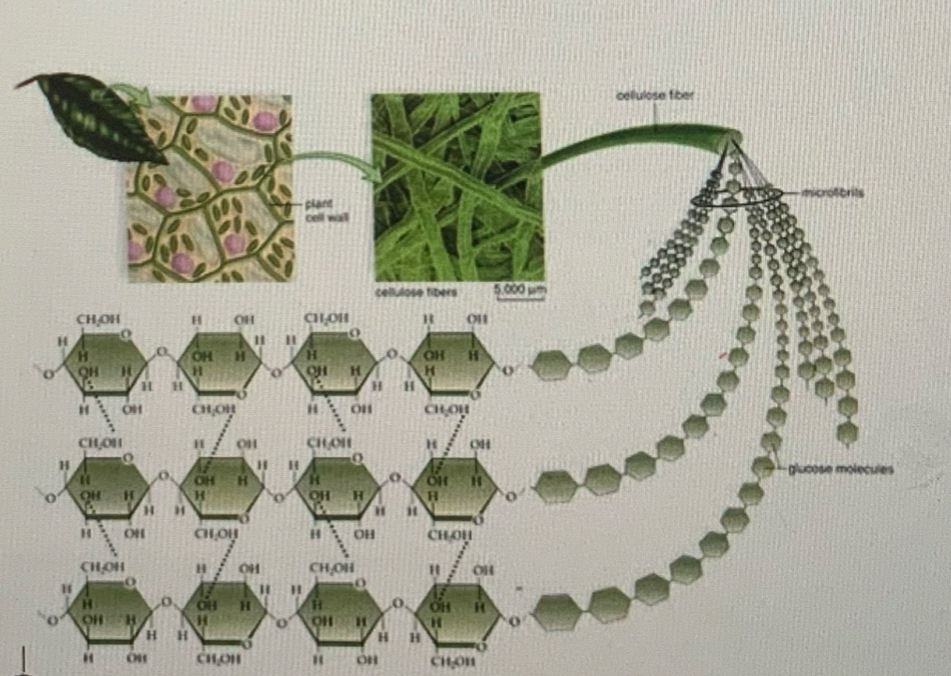
Cellulose
Unbranched hence linear polymer formed through beta glucose molecules
Formed through 1-4 glycosidic bonds
Inter chain hydrogen bonding forms between polymer chains to form microfibrils
Function: This allows for cellulose to be rigid and give physical strentgh to plants, with some animals using cellulose as a form of energy