WORKSHOP TEST 5 - ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is the Theory of Relativity?
Replacing Newtonian mechanics when dealing with particle speeds comparable to the speed of light.
What is Quantum Theory?
Understanding behavior of atoms in absorption and emission of radiation.
What is blackbody radiation?
A body that emits all radiation when hot and absorb all radiation incident on it and will reflect more thus appearing black.
What are some examples of a blackbody radiator?
Glowing filament of a lightbulb, the sun
What is a plot of intensity vs wavelength called?
The spectrum of blackbody radiation
The total power of the emitted radiation increases as…
Temperature increases
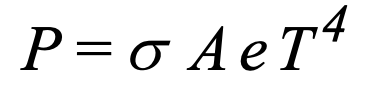
What is Stefan Boltzmann’s Law used to calculate shown?
used to calculate the power radiated by a black body in terms of its temperature
The peak of the spectra shifts towards shorter λ as…
temperature increases
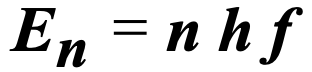
What is this equation used to calculate?
energy of the system at a particular level n
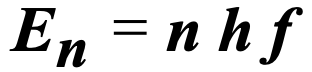
What Is the n in this equation?
the quantum number, which represents the level of energy.
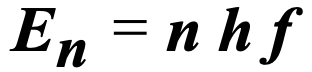
What does the h stand for?
Planck’s constant
what is Planck’s Quantum Hypothesis?
the idea that energy is not continuous but is emitted or absorbed in small, fixed amounts called quanta.
What is the photoelectric effect?
where light shining on a metal surface causes it to emit electrons. This effect helped prove that light behaves like particles, not just waves.
Photocurrent is proportional to…
light intensity
max kinetic energy of an electron is proportional to..
Frequency
max kinetic energy of an electron is NOT proportional to
Intensity of light
Electrons are ejected when
light strikes a metal surface
Quantum Mechanics =
wave mechanics
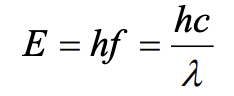
What is this equation used for?
calculate the energy of the photon
One photon ejects how many electrons?
one
What is Line Spectrum?
A gas heated in a discharge tube emits light only at characteristic frequencies.
What is E=mc²?
Energy of a particle is equal to its mass multiplied by the speed of light squared
A blackbody when cool will….
absorb all radiation falling on it.
A blackbody when hot will
emit blackbody radiation
What are the three types of radiation?
Alpha, beta and gamma rays
What kind of charge are alpha rays?
Positively charged
What kind of charge are beta rays?
negatively charged
What kind of charge are gamma rays?
neutral charge
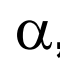
what does this represent?
alpha rays
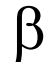
what does this represent?
beta rays
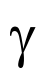
what does this represent?
gamma rays
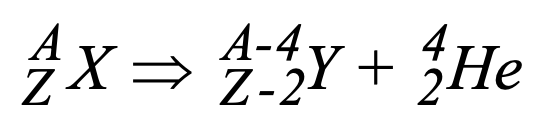
What is shown in this image?
alpha decay
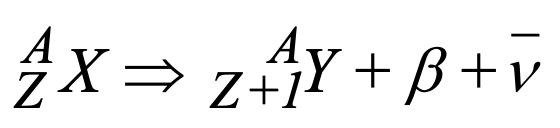
What is shown in this image?
beta decay
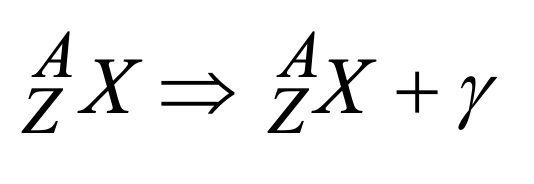
What is shown in this image?
gamma decay
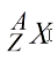
What is the Z in this represent?
Atomic Number
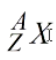
What is the A in this represent?
Atomic mass number
what is radioactive decay law?
radioactive decay means the number of atoms gets smaller and smaller over time, always cutting in half after a specific amount of time (the half-life).
number of decays is proportional to…
the period
number of decays is proportional to…
to the number of parent nuclei
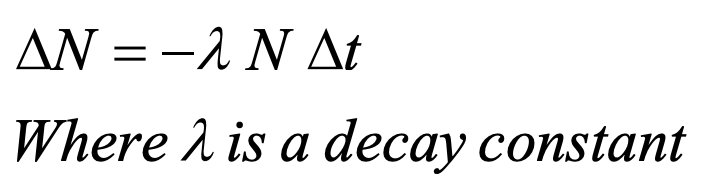
What does his equation calculate?
radioactive decay
1 Bq =
1 decay per second
Bq (becquerel) is the unit for
radioactive decay
What does h represent in E=hf
Planck’s constant
What does c represent in photon equations?
Speed of light (in a vaccum)
What is the si unit for effective dose?
Sv (sievert)
Which radiation would cause more damage to biological tissue, 1 mSv of x-ray, gamma or alpha
All would cause the same damage
Nuclear force is…
Attractive, short range
Coulomb force is…
Repulsive and long range