Redo of US, CT, MRI Better
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
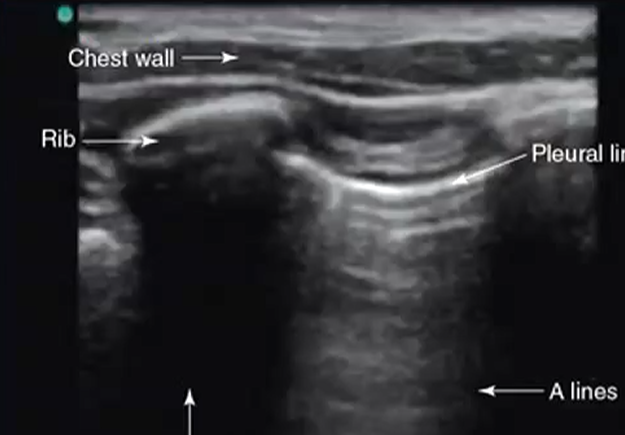
Bottom line
Acoustic shadow
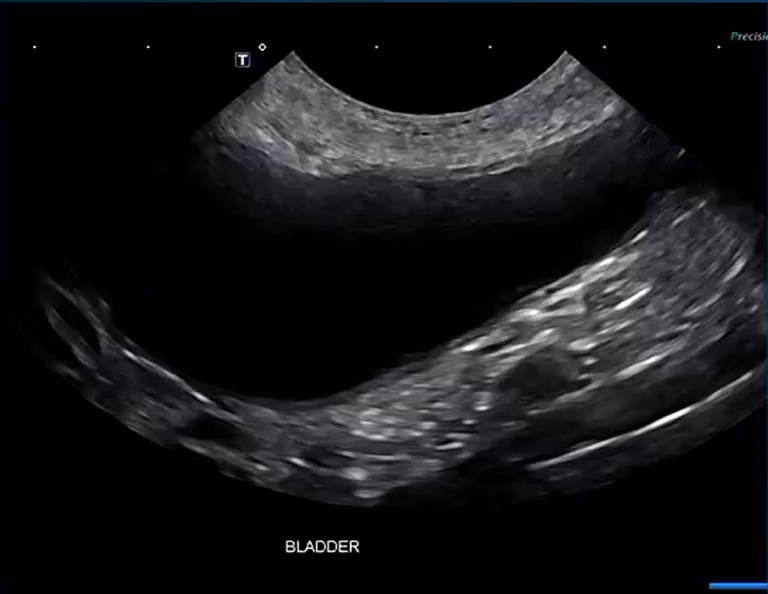
Anechoic
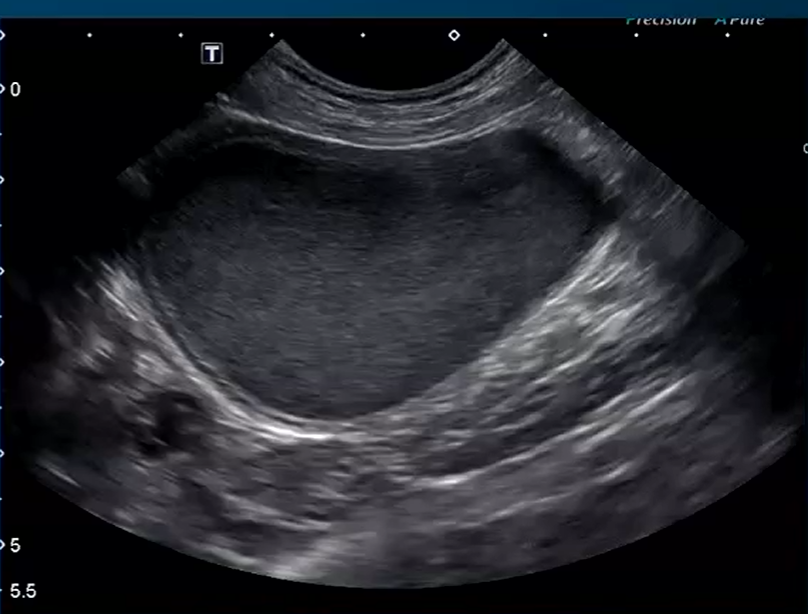
Echogenic
What does the doppler pobe tell you?
What fluid is traveling towards you and what is away from you
Red is towards. Blue is away
What on US can help you identify a thrombus?
Doppler
What technology does echocardiograms use?
Ultrasound
What is M-mode?
It lets you graph out a tissue over time with an ultrasound. Useful for examining the heart with echocardiogram
What is nuclear scintigraphy?
Inject radioactive drug to target a specific ACTIVE tissue. Camera can be used to detect areas of increased metabolic activity like infection or neoplasia
What is the usefulness of nuclear scintigraphy?
Functional imaging that is highly sensitivity but has a low specificity
Describe the view of nuclear scintigraphy
Not cross sectional
Poor spatial and contrast resolution
What imaging modality has the best spatial resolution?
Radiographs
What imaging modalities use x-rays?
Radiographs and CT
How are radiographs formed?
x-rays
What is the risk of x-ray exposure?
Stochastic and deterministic effects
What is the indication for a radiography?
Usually a first line of defense for imaging
What are the limitations of a radiograph?
Making 3D animals into 2D images causes superimposition
Border effacement occurs due to soft tissue and fluid having the same opacity or because two soft tissue opacities are next to each other
What imaging modalities removed superimposition?
Ultrasound, MRI, and CT because they are cross sections
What does ultrasound have the best contrast resolution for?
Soft tissue
What is the spatial resolution of ultrasound?
Good, but not as good as radiographs
How does ultrasound form images?
Sending out soundwaves and letting them bounce back
What is acoustic impedance?
Difficulty for a soundwave to go through a tissue
What is the reason why bone is not visible on ultrasound?
The acoustic impedance is really high
What is acoustic shadow?
Area deeper than bone on ultrasound that is just black
What does anechoic mean?
Term for when sound waves do not bounce back on ultrasound
What does echogenic mean?
Term for when sound waves do bounce back
What is a dynamic imaging technique?
Ultrasound
What are the limitations of ultrasound?
Lots of training and limited views
What opacities are limited with ultrasound?
Bone and gas
What do you use for contrast with MRI?
Paramagnetic IV materials like gadolinium
What is MRI best for?
Soft tissues like brain and spine
How does MRI work?
Uses magnetic resonance and radiofrequency
What is the safety of MRI?
Extremely strong magnetic field formed by a superconducting magnet makes it impossible to have metal nearby
What term do you use for MRI instead of opacity?
Intensiry
What are the limitations of MRI?
Takes 30 or 90 minutes so always needs general anesthesia
Why is CT able to differentiate soft tissue from liquid?
Liquid is more hypoattenuated than soft tissue with CT
What contrast agent do you use for CT?
Iodinated agents like iohexal
What is dose of CT?
100x that of an xray so more risk for stochastic and deterministic effects
What term is used instead of opacity in CT?
Attenuation
What are the indications for a CT?
Trauma, met check, vascular shunt, bony disease, non neurogenic skull problems
What are the limitations of CT?
Only takes 30ish seconds but still usually needs general anesthesia or a heavily sedated patient