cytoskeleton
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
microtubules
component of cytoskeleton
regular, non-branching polymers of tubulin
recall “polymer”
hollow tubes (diameter 20-30 nm, inner diameter 14 nm)
highly dynamic, microtubules can be polymerized and depolymerized rapidly
“grow” from the microtubule organizing center (MTOC)
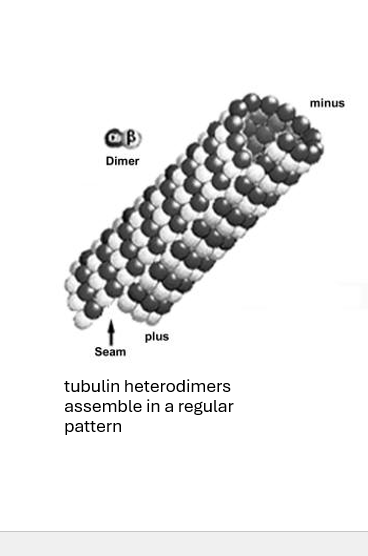
what are tubules exhibiting? meaning?
they exhibit dynamic instability
meaning they are constantly remodeling
what is control of polymerization and depolymerization dependent on?
temperature
presence of GTP and Mg2+
presence of microtubule association proteins (MAPs)
what do microtubules do?
serve as infrastructure for molecular motor proteins (dyeins and kinesins)
mitotic spindle
cell elongation and migration
movement of cilia and flagella
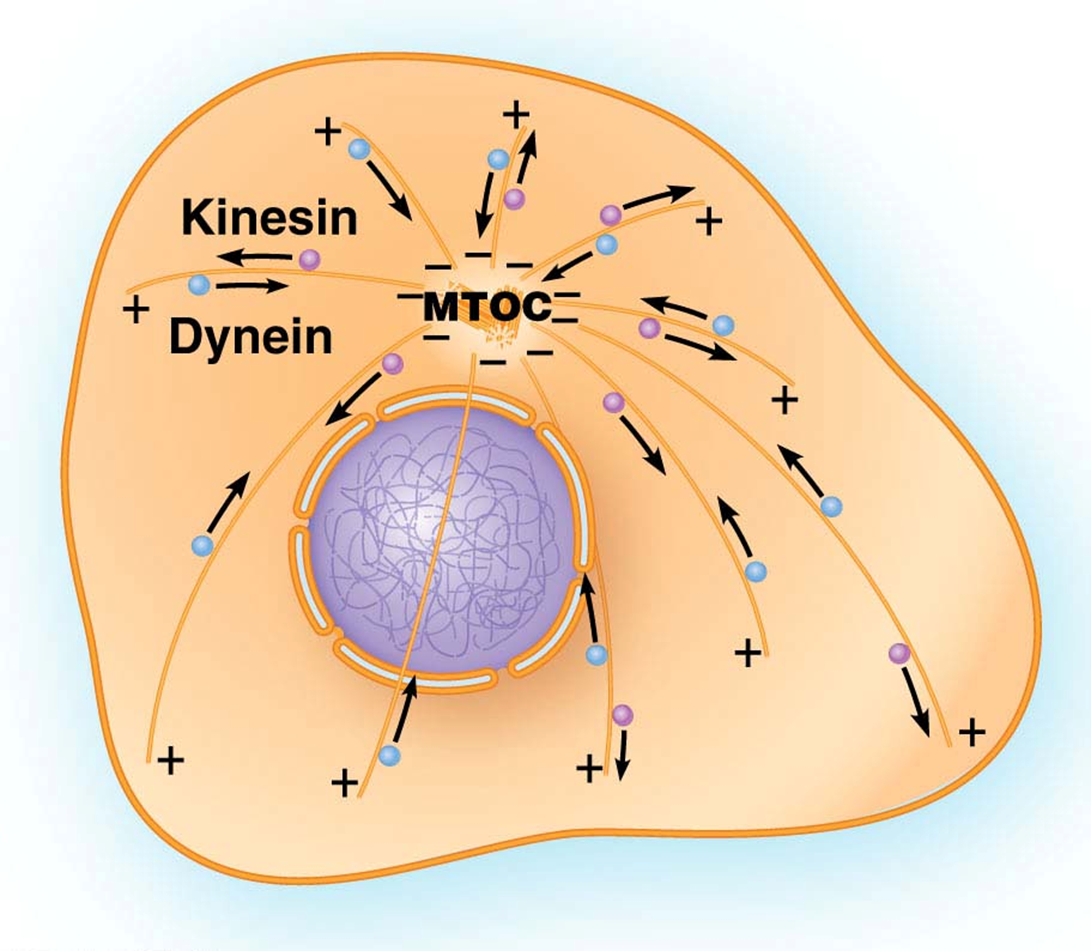
where do kinesin and dyein move
kinesin moves toward positive end towards outside of cell away from MTOC
dynein moves toward negative end towards MTOC
describe structure of actin filaments and talk ab what cells have them. differences bn microtubules
all cells have actin
actin molecules polymerize to form actin chains, two chains wrap around eachother forming actin filament (6-8 up in diameter)
they are thinner, shorter, and more flexible than microtubules
what are actin filaments called when free or polymerized? what must be present for polymerization? what does ABP do?
free = G-actin (globular actin)
polymerized = F-actin (filamentous)
F-actin has fast growing end (+ barbed) and slow growing end (- pointy)
ATP, Mg2+, K+ required for polymerization
actin binding proteins influence structure and function of actin filaments
microfilament roles
anchorage and movement of membrane protein
comprise the core of microvilli (a cell modification for absorptive cells, especially intestinal cells)
locomotion of cells and migration via lamellipodia
(cells crawl)
extension of filopodia
intermediate filaments: size, dynamicism, role
heterogenous group of similarly sized filaments
subunits are diverse but size remains the same
less dynamic that actin filaments or microtubules
between microfilaments and microtubules in size
role is structure and anchoring (keep membranous organelles in place)
what is the MTOC? centrioles and their structure
MTOC region in cytoplasm surrounded the centrioles where microtubules originate
centrioles observable under light microscope as paired short cylinders
comprised of 9 microtubule triples
structure of MTOC
tubulins
microtuble
pericentriolar matrix
gamma-tubulin ring
nucleus
- end and + end
nucleus-basal body connector (NBBC)

centriole axoneme structure
9+2 arrangement
cell surface specializations`
cilia and flagella (sperm)
what is the mechanism of axoneme movement
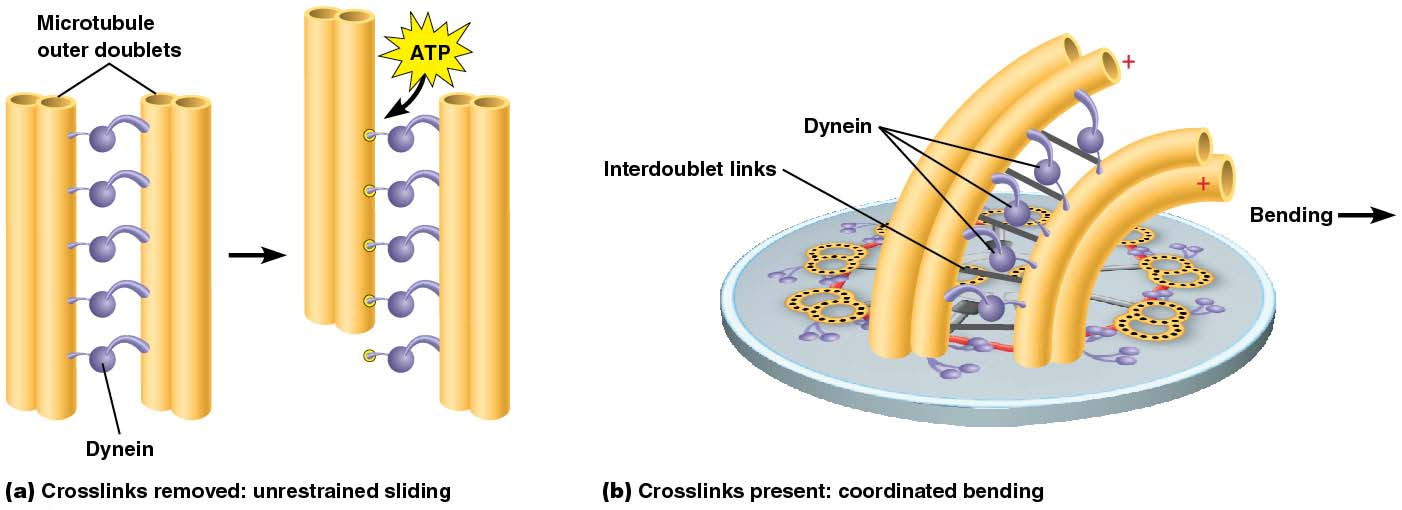
what is immotile cilia syndrome?
defect in ciliary dynein
respiratory tract infections
male infertility