Vascular study guide
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
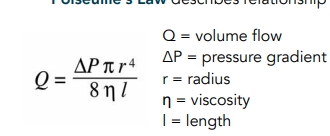
What does Poiseeuilles law describe
relationship of resistance, pressure gradient and flow.
Increase pressure gradient = Increase volume flow
Increase resistance = Decrease volume flow
decreasing diameter increases resistance but decreases flow.
If a vessel is vaso-constricted, what does that mean in terms of Diastole.
less diastole, higher resistance, smaller radius and less volume. If its vaso-dilated it has a larger radius, more diastole and more volume with less resistance.
( think of why the ICA is bigger than the ECA)
What is the Bernoulli effect
describes the relationship of pressure and velocity when radius changes. Pressure and velocity are inversely related. For example: Where there is a narrowing ( stenosis) the velocities increase and the pressure drops
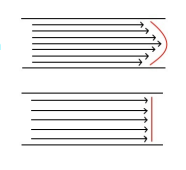
What’s the difference between parabolic and plug flow.
They’re both types of laminar flow but parabolic is the most common type, highest velocities found in the center of vessel and lowest next to the walls.
Plug flow: Found at origin of vessels where all layers move at the same velocity.
What is turbulent flow, where is it found?
Abnormal, disorganized flow. Flow patterns become disturbed and form swirling patterns. Occurs when there’s a sudden change in resistance and elevated velocities. Usually seen distal to stenosis or tortuous vessels.
What is Reynolds number used for ( add picture)
Predicts when flow becomes disorganized or turbulent
CRITICAL VALUE = >2000
The 2 main factors are radius and velocity. Both DIRECTLY RELATED The larger the vessel and higher the velocity will increase the Reynold’s # and more likely there will be turbulent flow
Ex: “Post-stenotic turbulence” = AFTER stenosis when vessel diameter is larger but velocity is increased. Spectral broadening indicates turbulence.
Draw out the stenosis profile