De-Extinction and Genetic Engineering Concepts
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of flashcards covering key vocabulary related to de-extinction, genetic engineering, and environmental science as presented in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
De-extinction
The scientific process of reviving extinct species through genetic engineering techniques such as cloning, selective breeding, and advanced DNA manipulation.
The goal is to reintroduce these species into their original habitats.
Nuclear transplantation
(Also known as somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)
A method where nuclei from preserved specimen samples are inserted into donor cells, used to create an embryo with a nucleus from a somatic cell.
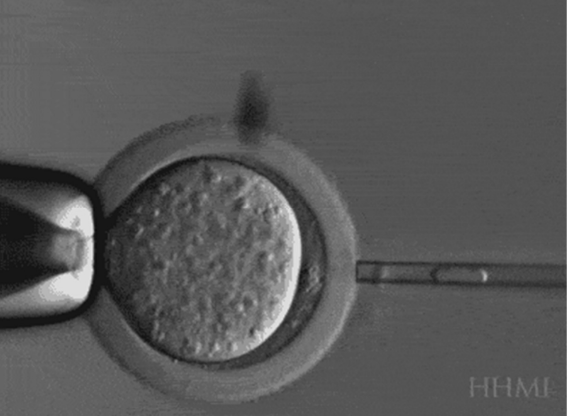
what is the only temporarily de-extincted mammal?
The Pyrenean ibex (Capra pyrenaica pyrenaica) was one of 4 subspecies of the Iberian ibex and endemic to the Pyrenees
• The last Pyrenean ibex died in January 2000 –skin biopsies preserved before death
• SCNT (from fibroblasts) used to produce a living specimen with a Spanish ibex/goat hybrid as the surrogate parent
• The offspring was born alive but died after a few minutes due to a lung defect
• Thus, the Pyrenean ibex has the dubious distinction of being the only animal to have gone extinct twice

What is the goal of de-extincting the woolly mammoth?
To create a cold-resistant elephant with all of the core biological traits of the woolly mammoth, an important ecosystem engineer.
Aims for it to move, resemble & sound like a woolly mammoth
Be able to inhabit the same ecosystem previously abandoned by the mammoth’s extinction i.e Wrangel island
Due to their natural environment, many mammoth samples are well preserved
What happens to DNA after death?
DNA begins to degrade, breaking down into smaller fragments due to exposure to nucleases, microbial decomposition
This degradation can affect the ability to extract and analyze genetic material from remains.
how can DNA decay be slowed naturally?
Occasionally DNA is spared this fate:
• Rapid dessication
• Low temperatures
• Anaerobic conditions eg in boglands
• High salinity which limits some microbial activity and nucleic acid degradation.
what is depurination?
The process in which purine bases (adenine and guanine) are removed from DNA, leading to strand breaks and potential mutations.
what is deamination?
The process where an amine group is removed from a nucleotide bases, converting cytosine to uracil and adenine to hypoxanthine, which can result in mutations.
what is the age limit of using useful DNA
Increasing time → increasing degradation → decreasing utility
• 100,000 to 1,000,000 years considered the age limit for DNA to yield useful sequence
why is SCNT not possible for de-extincting the wooly mammoth genome?
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) is not possible for de-extincting the wooly mammoth genome because suitable, viable cells from preserved specimens are scarce & instead required changing DNA of a relative to be more mammoth-like
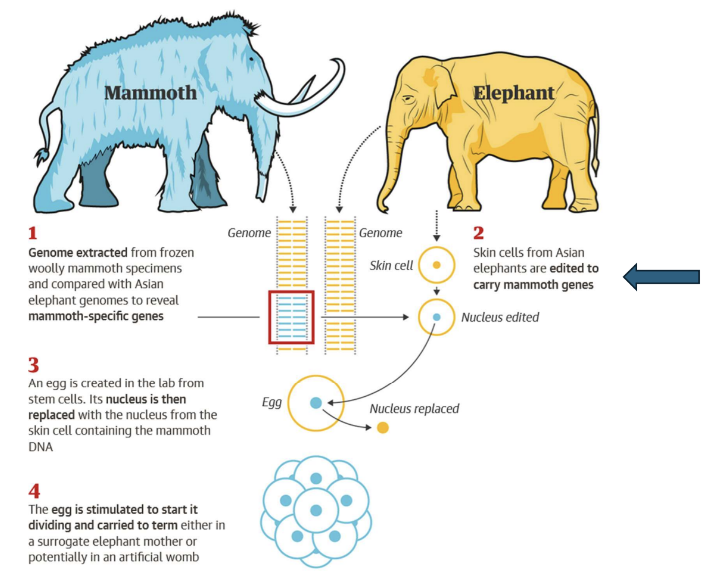
how could the wooly mammoth be “de-extincted”?
Requires knowledge of mammoth genome and the relative’s genome
• Sequence mammoth genomes
• Sequence Asian elephant genome
• Identify important cold-weather genes
• Edit mammoth versions into Asian elephant cells
• Fuse into Asian elephant egg
• Implant into a surrogate Asian elephant mother.
Ancient DNA (aDNA)
DNA extracted from ancient specimens that provides insights into extinct species.
what are some examples of retrieving ancient DNA?
Quagga (extinct relative of the zebra) DNA cloned from museum specimen (Higuchi et al.1984)
2430 year-old Mummy DNA cloned (Paabo 1985) by isolating DNA and cloning into bacteria before sequencing
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) use in aDNA
An advanced sequencing method that uses DNA fragments anyways allowing analysis of fragmented ancient DNA.
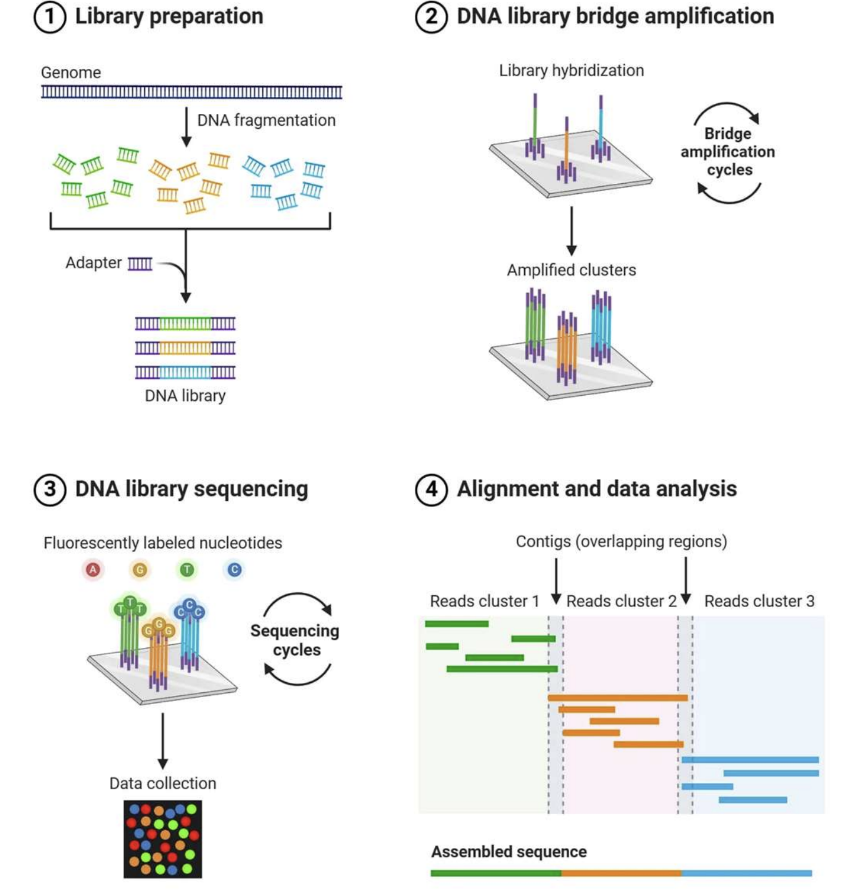
how was early mammoth genomes sequenced?
70% of (4Gbp) mammoth genome sequenced in 2008
• Preserved in ice
• Hair preserved – great for DNA
• Hard to contaminate with closely related species (modern elephants)
• DNA fragmented – but NGS sequences short fragments
how did Colossal biosciences create a high-quality sequenced elephant genome + how did it help understand differences b/w it & the wooly mammoth?
T2T (telomere to telomere) Asian elephant genome is one of the highest quality mammalian genomes in existence with only 59 gaps.
This sequencing provided insights into the evolutionary differences between the Asian elephant and the woolly mammoth, including adaptations to cold climates and tusk development.
how did Colossal biosciences ‘de-extinct’ the dire wolf?
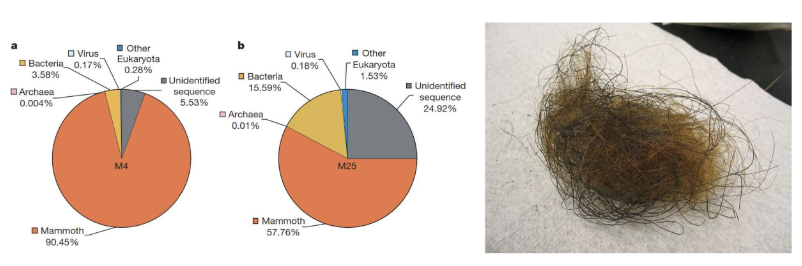
Pilot phase: examined 46 dire wolf remains for viable DNA and were able to recover 0.1% of the genome
• Extracted DNA from a dire wolf tooth (from Sheridan Pit, Ohio, that is around 13,000 years old) and an inner ear bone (from American Falls, Idaho, around 72,000 years old) obtaining 3.4x coverage genome from the tooth and 12.8x coverage genome from the inner ear bone
• Compared to grey wolf genome to see what variants might underlie dire wolf phenotype
• Identified 20 loci across 14 genes to edit, 5/20 changes are based on mutations known to produce light coats in grey wolves
• Collect grey wolf blood during a normal veterinary procedure and establish cell lines from blood epithelial progenitor cells (EPCs) less invasive
• Perform multiplex CRISPR genome editing on these
• Select cells with normal karyotypes for cloning by somatic cell nuclear transfer into donor oocytes then transfer into surrogates for interspecies gestation
what is a key locus of interest that varies from grey wolves in dire wolfs?
A key change was a dire wolf variant of a well-known gene found in
canids: Ligand Dependent Nuclear Receptor Corepressor Like (LCORL) which codes for a transcription factor—a key regulatory protein that controls the expression of hundreds of other genes related to body size and growth.
Smaller dog breeds and wolves contain an intact version of LCORL. However, in the largest breeds, a functional domain at the end of the protein has been deleted
Red wolf restoration
The conservation effort aimed at increasing the population of red wolves, a critically endangered species, through breeding programs and habitat protection.
This includes reintroduction of cloned wolves into their native range in the Gulf Coast ecosystems

what are ghost wolves?
Ghost wolves - canids, which are genetically similar to coyotes from
the Gulf Coast of the US show red wolf ancestry
• Neka Kayda was cloned from a ghost wolf with 70.8% red wolf ancestry and strong, red wolf morphometric traits.
Thylacine
Also known as the Tasmanian tiger, it is an extinct carnivorous marsupial last known to be observed in 1936.
what are some examples of surrogate species used by colossal to de-extinct mammals?
Asian elephant - closest species to wooly mammoth
Nicobar pigeon - closest species to Dodo
Fat-tailed dunnart - closest marcupial to thylacine
Genetic rescue
Conservation strategies aimed at reviving or reinforcing the genetic diversity of endangered and extinct species.
Chimeric organisms
Creatures created through genetic engineering that possess traits from multiple species.
Endangered species
Species at risk of extinction due to changes in habitat, loss of genetic diversity, or other environmental pressures.
Mammoth genome sequencing
The process of decoding the DNA of the woolly mammoth to identify genetic traits for use in de-extinction.
what are some benefits / support of de-extinction efforts?
• We have used article selection on numerous species through either
domestication or agriculture
• Conservation geneticists change the gene pool through their efforts to protect and conserve species
• Is genome editing any different?
• Learning how to do this has pure and applied research benefits e.g. medicine or verterinary genetics
what are some disadvantages / critiques of de-extinction efforts?
• You are not ‘de-extincting’ these species – just creating chimaeric examples of a species exhibiting some of their phenotypes
• The money is better spent conserving current species
• Species have evolved through selection acting on many variants in the genome and these may be co-adapted gene complexes
• Variants act in concert with environment
• Species such as wolves and elephants are social creatures. Is it ethical to raise 1 or 2 individuals. And, to what end?
• Traditional conservation genomics acts to preserve population variation –is there sufficient population variation here?