Bio 93 Quiz 3: Energy Transfer and Metabolic Pathways in Cells
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
Energy
The capacity to cause change.
Kinetic energy
Energy associated with motion.
Heat (thermal energy)
Kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms or molecules.
Potential energy
Energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure.
Chemical energy
Potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction.
First law of thermodynamics
Energy of the universe is constant; can be transferred or transformed but cannot be created or destroyed.
Second law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe.
Entropy
A measure of disorder in a system.
Spontaneous processes
Processes that occur without energy input; they can happen quickly or slowly.
Anabolic reactions
Small molecules assembled into large ones; require energy.
Catabolic reactions
Large molecules are broken down into small ones; generate energy.
Change in free energy (ΔG)
Related to the change in enthalpy/total energy (ΔH), change in entropy (ΔS), and temperature in Kelvin (T).
Exergonic reaction
Releases energy, spontaneous, from high energy to low energy.
Endergonic reaction
Requires energy, non-spontaneous, from low energy to high energy.
ATP
Cell's energy shuttle that mediates energy coupling.
Components of ATP
Composed of ribose, adenine, and 2 phosphate groups.
Hydrolysis of ATP
Powers the three types of cellular work: mechanical, transport, and chemical.
ATP cycle
Acts like a revolving door for energy; ATP is regenerated by addition of a phosphate group to adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
Phosphorylation
ATP donates a phosphate and changes the shape of that protein.
Sodium and potassium pump
Energy derived from exergonic ATP hydrolysis is used to pump sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane.
Net ΔG
If the first reaction has a positive ΔG, it won't happen on its own; coupling it with ATP can drive the reaction forward.
Renewable energy resource
ATP is regenerated by addition of a phosphate group to ADP, with energy coming from catabolic reactions in the cell.
Catalyst
a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction
Enzyme
a catalytic protein
Activation energy (Ea)
the initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction
Substrate
reactant that an enzyme acts on
Enzyme-substrate
this is formed when the enzyme binds to its substrate
Active site
region on the enzyme where the substrate binds
Induced fit
the process where the substrate brings chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to catalyze the reaction
Cofactors
non-protein enzyme helpers
Inorganic cofactors
metal in ionic form
Coenzymes
organic cofactors, i.e., vitamins
Competitive inhibitor
binds to the active site of an enzyme competing with the substrate
Non-competitive inhibitor
binds to another part of the enzyme, causing it to change shape and making the active site less effective
Allosteric regulation
either inhibit or stimulate an enzyme's activity; occurs when a regulatory molecule binds to a protein at one site and affects the protein's function at another
Metabolic pathways
a series of reactions catalyzed by multiple enzymes
Feedback inhibition
where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream step
If ATP concentration begins to drop, respiration speeds up; when there is plenty of ATP, respiration slows down
Cellular respiration
includes both aerobic and anaerobic but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration
doesn't use oxygen and produces lactic acid as a byproduct
Glucose is still broken down but not as efficiently
Photosynthesis
generates O2, glucose, organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
Thermal energy
often supplied to the reactant molecules to start a chemical reaction
Optimal conditions
allow the most active shape for the enzyme molecule
Taq polymerase
an enzyme used in PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) that can withstand high temperatures
Lactic acid
the byproduct of anaerobic respiration that can lead to muscle fatigue or cramps
OIL RIG
Oxidation is loss, reduction is gain.
Oxidation
Loses electrons and is oxidized.
Reduction
Gains electrons and is reduced (the amount of positive charge is reduced).
Reducing agent
Electron donor.
Oxidizing agent
Electron acceptor.
Redox reactions
Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants.
NAD+ in cellular respiration
A coenzyme that functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration.
NADH in cellular respiration
The reduced form of NAD+ that represents stored energy for ATP synthesis.
Glycolysis
The process that breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, occurring in the cytoplasm. Electrons carried via NADH. Occurs in the cytoplasm.
Citric Acid Cycle
Completes the breakdown of glucose, occurring in the mitochondria. Electrons carried via NADH, FADH2
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Accounts for most of the ATP synthesis by harvesting electrons to create a big electrochemical gradient.
Energy Investment Phase
The phase of glycolysis that requires initial energy, adding 2 ATP to start the process.
uses two ATP molecules in the phosphorylation of glucose → two three-carbon molecules
Energy Payoff Phase
The second half of glycolysis that involves phosphorylation with ATP investment, produces 4 ATP and 2 NADH.
This phase happens 2x for every glucose we end up splitting
Net ATP from Glycolysis
2 ATP net, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate per glucose molecule.
Acetyl CoA
The molecule that pyruvate is converted into before entering the Citric Acid Cycle.
Krebs Cycle
Another name for the Citric Acid Cycle, which completes the breakdown of pyruvate to CO2.
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
The molecule that feeds into the payoff phase of glycolysis.
Carbon dioxide release
Occurs when pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA.
Multienzyme complex
Catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
ATP synthesis
The process of producing ATP, primarily occurring during oxidative phosphorylation.
FADH2
An electron carrier produced during the Citric Acid Cycle.
Oxaloacetate
The final compound that regenerates to start the cycle again as long as pyruvate is available.
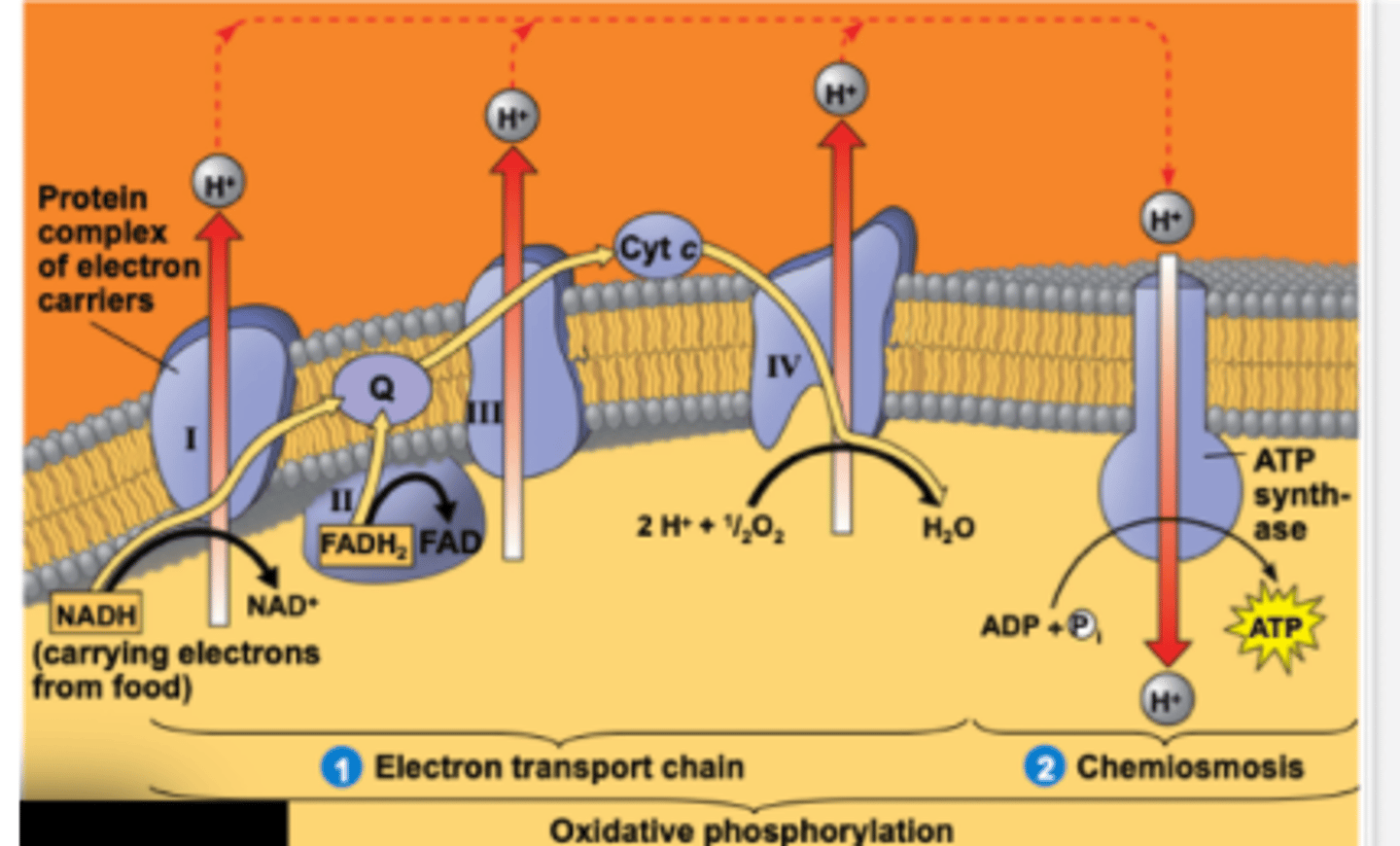
Electron Transport Chain
A series of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2.
Chemiosmosis
The process of protons moving down their concentration gradient to generate ATP.
This is where ATP Synthase is making ATP.
ATP Synthase
An enzyme that synthesizes ATP as protons flow through it, functioning like a turbine.
As electrons move down the chain, protons (H⁺) are pumped into the intermembrane space, creating a gradient. This gradient powers ATP synthase, which makes ATP — this process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
Free Energy
The energy that electrons lose as they move down the electron transport chain.
Oxygen
The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, forming water.
Without oxygen, there would be no electron transport chain, no protein gradient, no ATP synthase.
ATP Production Summary
Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, Citric Acid Cycle produces 2 ATP, and Oxidative Phosphorylation produces 26-28 ATP. Total: 30-32 ATP
Protein Gradient
A concentration gradient of protons created during oxidative phosphorylation, essential for ATP synthesis.
Alcohol Fermentation
A process where pyruvate is converted to ethanol in two steps, with the first releasing O2, used in brewing, winemaking, and baking.
Pyruvate in Alcohol Fermentation
The product of glycolysis that is converted to acetaldehyde, releasing CO₂.
Acetaldehyde
The compound that accepts electrons from NADH, converting it back to NAD⁺ and becomes ethanol.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
A process where pyruvate is reduced by NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO₂.
Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce
GLUT4
A glucose transporter stored in vesicles that fuses with the plasma membrane upon insulin binding to transport glucose into the cell.
Light Dependent Reactions
The first stage of photosynthesis occurring in thylakoids, using light energy to make ATP and NADPH.
Calvin Cycle
The second stage of photosynthesis occurring in the stroma, using energy from ATP and NADPH to make GA3P from CO₂.
Chloroplasts
Organelles where photosynthesis occurs, containing chlorophyll and found mainly in mesophyll cells.
Stomata
Microscopic pores in leaves through which CO₂ enters and O₂ exits.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that obtain their organic material from other organisms, including humans.
Fossil Fuels
Energy stores formed from the remains of organisms that died hundreds of millions of years ago.
ATP Generation in Glycolysis
Glycolysis produces a net gain of 2 ATP.
Oxygen in Photosynthesis
A byproduct of photosynthesis produced when chloroplasts split H₂O.
Chlorophyll
The green pigment in chloroplasts responsible for capturing light energy.
Located in the membranes of the thylakoids.
Where green color of leaves come from?
Mesophyll
The interior tissue of the leaf where chloroplasts are primarily located.
Light
A form of electromagnetic energy, also called electromagnetic radiation.
Wavelength
The distance between crests of waves, determining the type of electromagnetic energy.
Pigments
Substances that absorb visible light. Different pigments absorb different wavelengths
Wavelengths that aren’t absorbed are reflected or transmitted
Leaves appear green because chlorophyll reflects and transmits green light
Chlorophyll a
The main photosynthetic pigment, functioning in 'normal light'.
Accessory Pigments
Pigments such as chlorophyll b that broaden the spectrum used for photosynthesis. (“low light”)
Carotenoids
Accessory pigments that absorb excessive light that would damage chlorophyll ("bright ass light")
Excited State
The unstable state of a pigment after absorbing light.
When a pigment absorbs light, it goes from ground state to an excited state, which is unstable
Fluorescence
The afterglow given off when excited electrons fall back to the ground state and photons are given off
Photosystem
A structure consisting of a reaction-center complex surrounded by light harvesting complexes.
Primary Electron Acceptor
A component in the reaction center that accepts excited electrons and is reduced.
Solar-powered transfer of an electron from a chlorophyll a molecule to the primary electron acceptor is the first step of light reactions
Photosystem II (PSII)
The first functioning photosystem, best at absorbing a wavelength of 680nm.
P680
The reaction center chlorophyll a of Photosystem II.