AP Biology UNIT-6
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
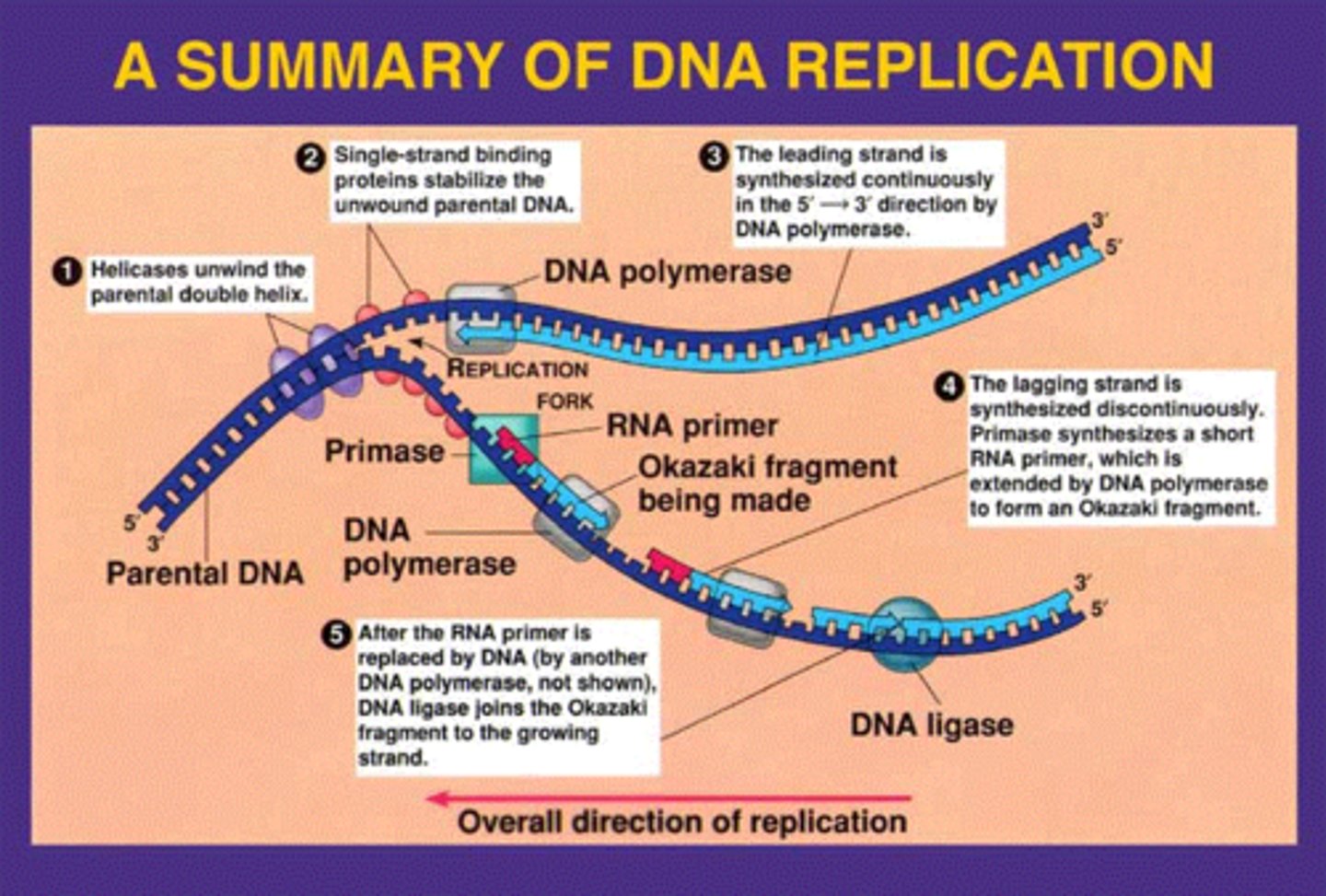
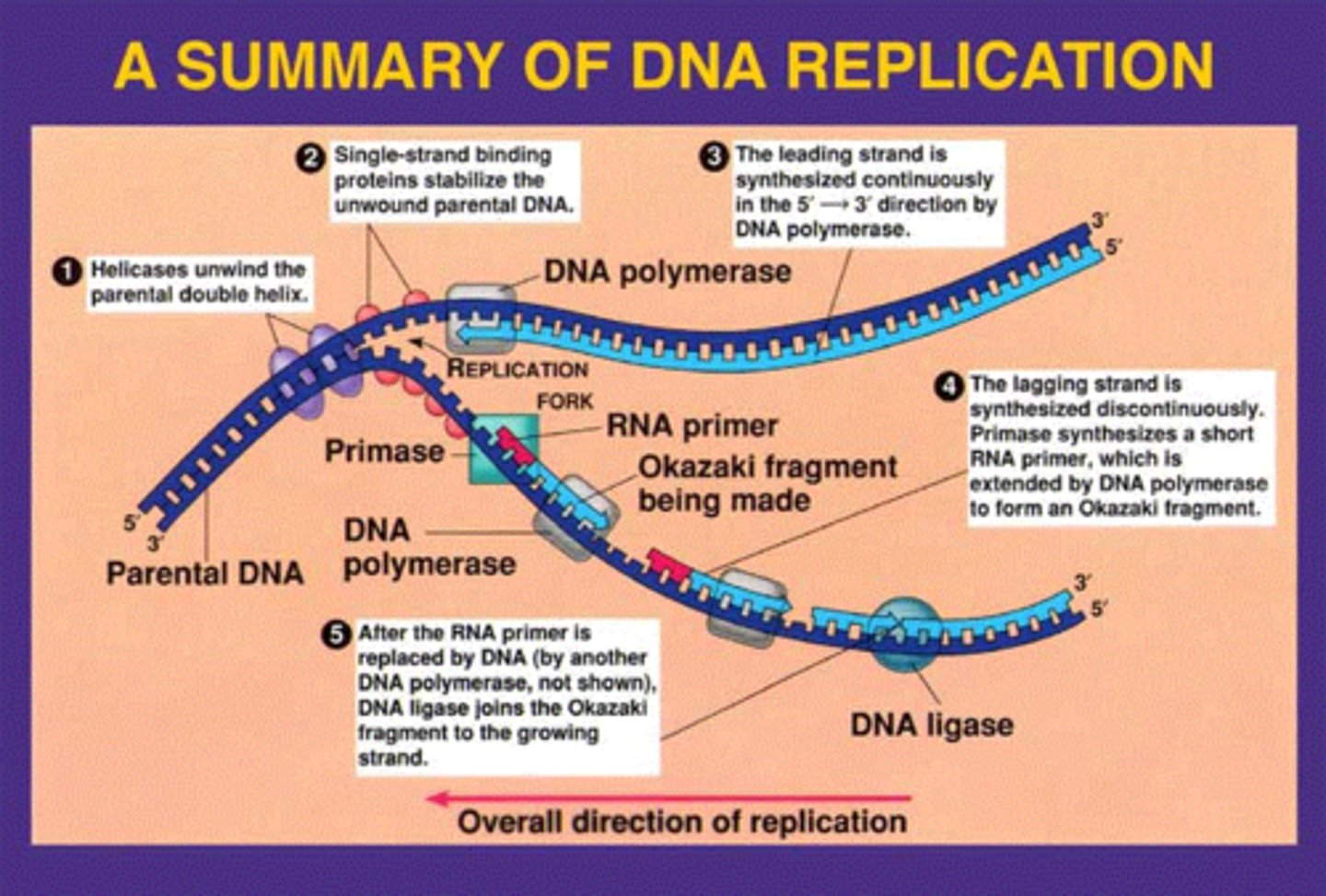
DNA Replication
process of copying DNA
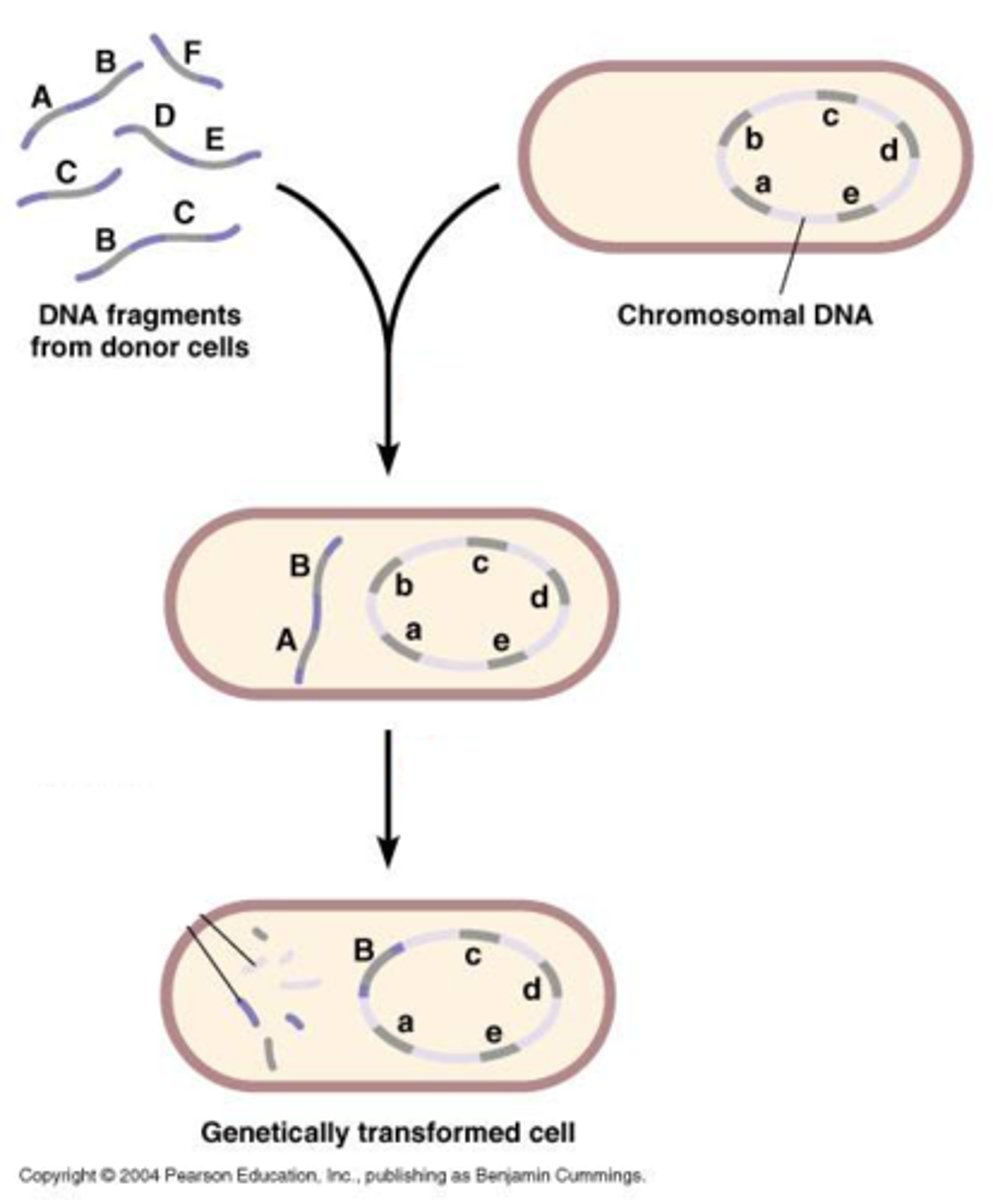
Transformation
A change in genotype and phenotype due to the assimilation of external DNA by a cell.
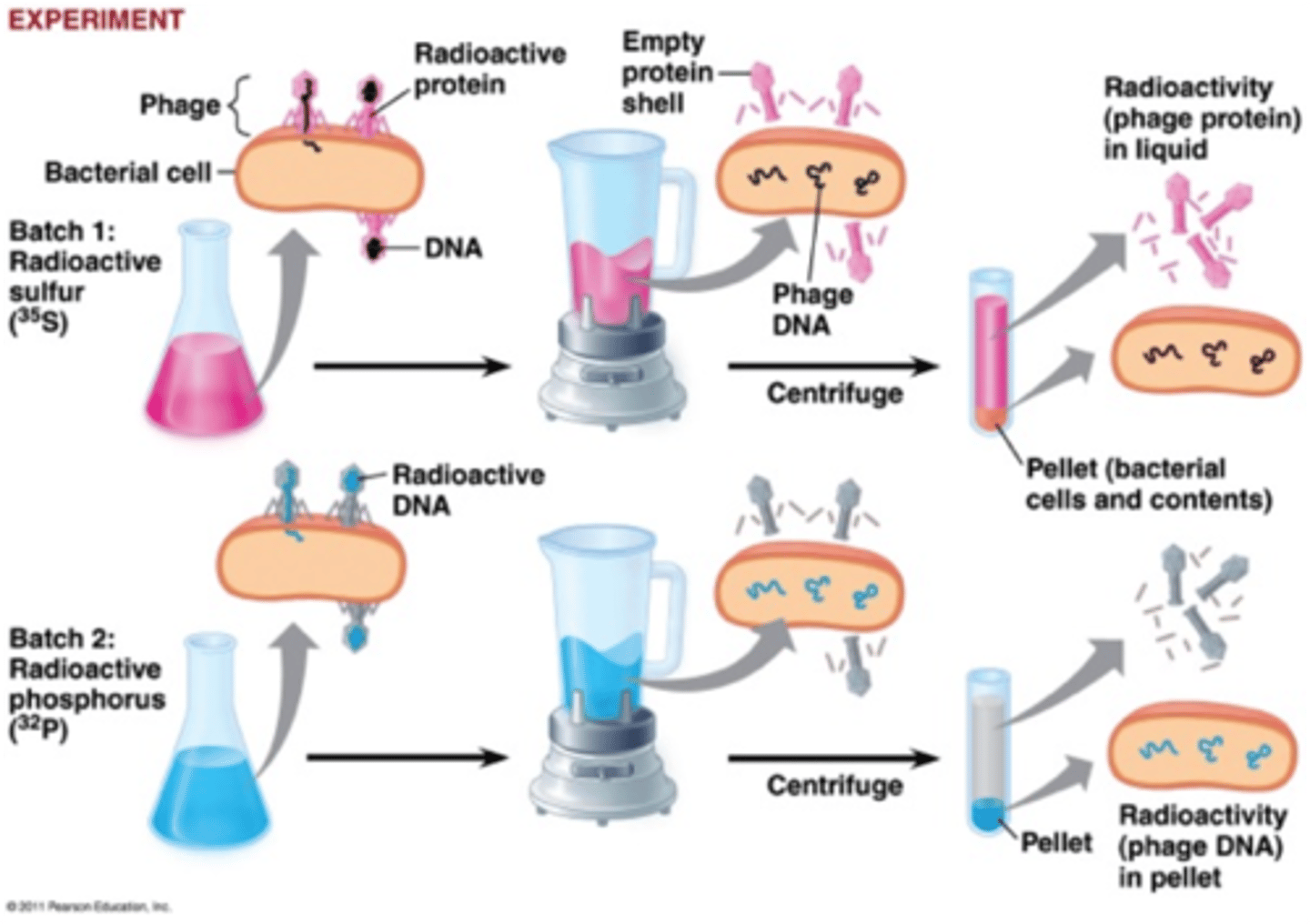
Hershey and Chase
DNA is the genetic material, not protein; blender experiment.
T.H. Morgan
genes are on chromosomes(fruit flies); tested whether genes are protein or DNA
Transforming Factor
The DNA responsible for bacterial transformation.
Rosalind Franklin
Woman who generated x-ray images of DNA.
Watson and Crick
Developed the double helix model of DNA.
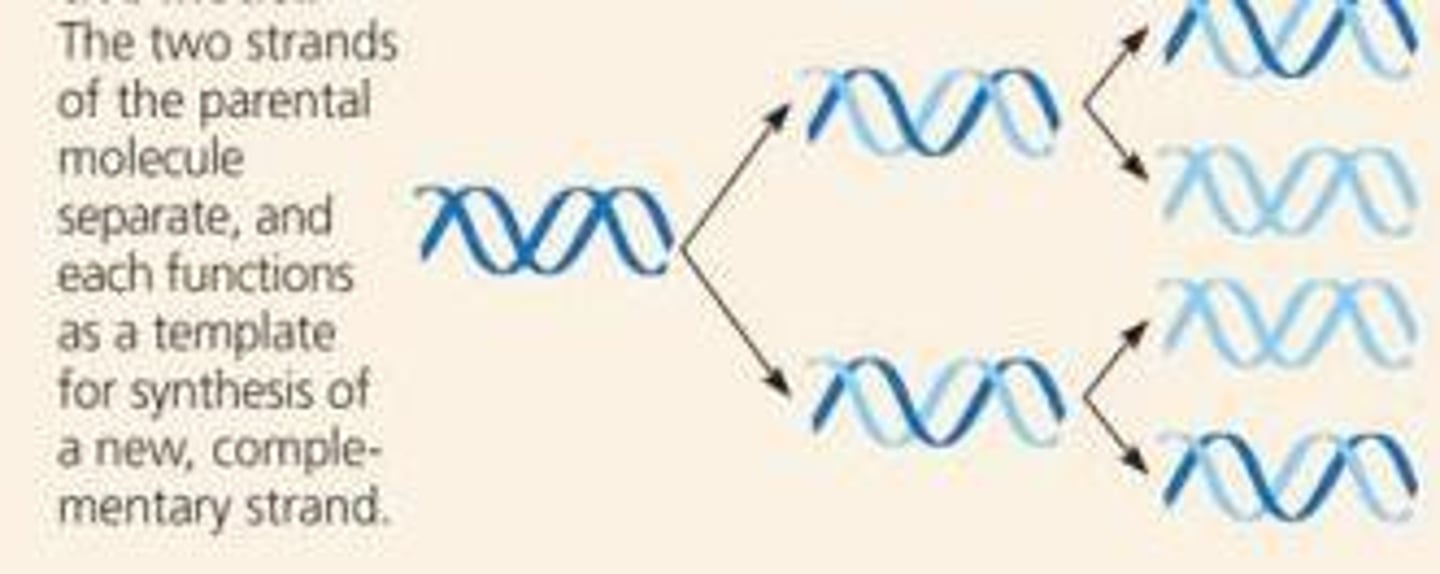
Semi Conservative Replication
in each new DNA double helix, one strand is from the original molecule, and one strand is new
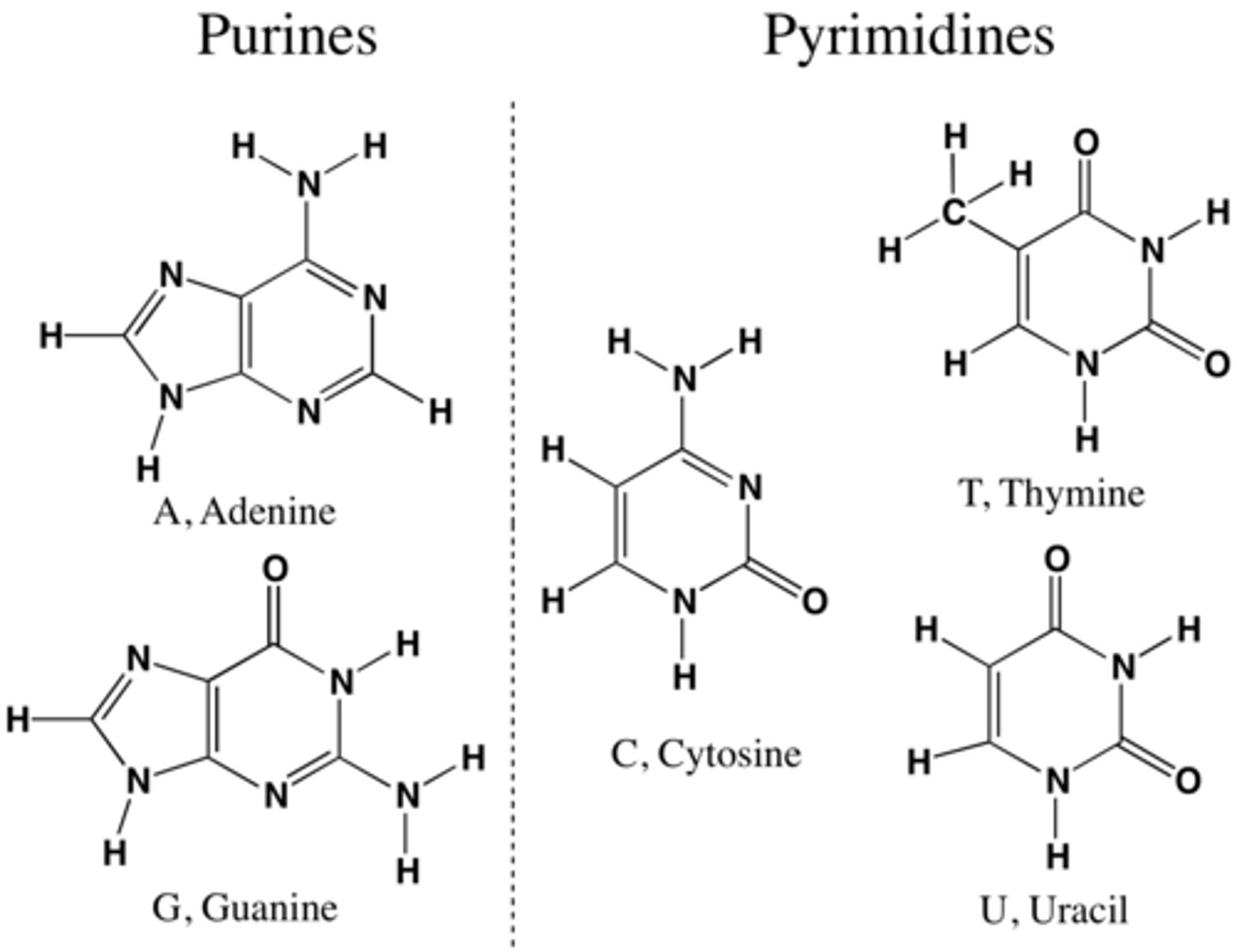
Why does adenine bond with thymine?
Adenine, a purine, and thymine, a pyrimidine, bond with each other because they both have two hydrogen bonds
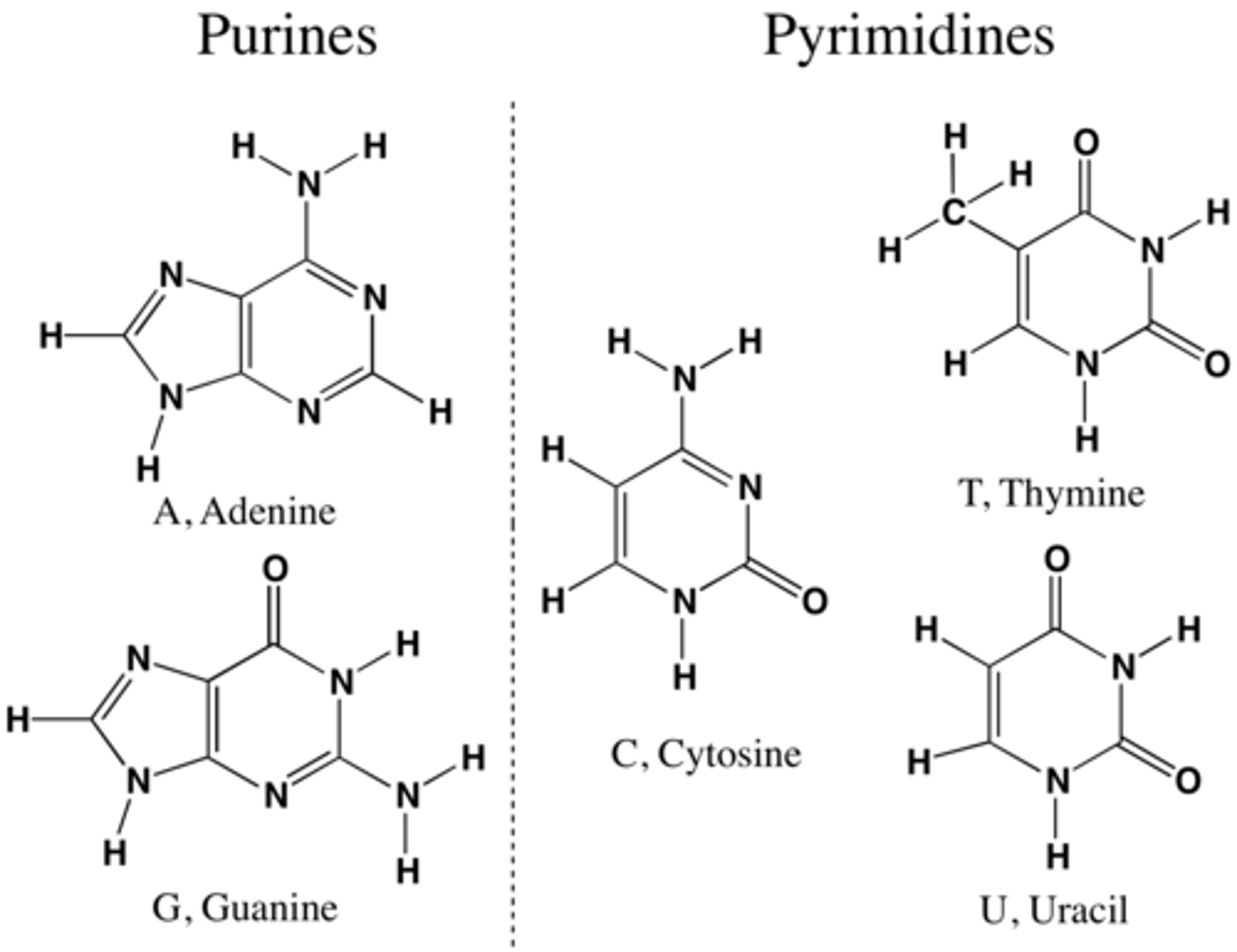
Why does guanine bond with cytosine?
Guanine, a purine, bonds with cytosine, a pyrimidine, because they both have three hydrogen bonds
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines
Cytosine and Thymine
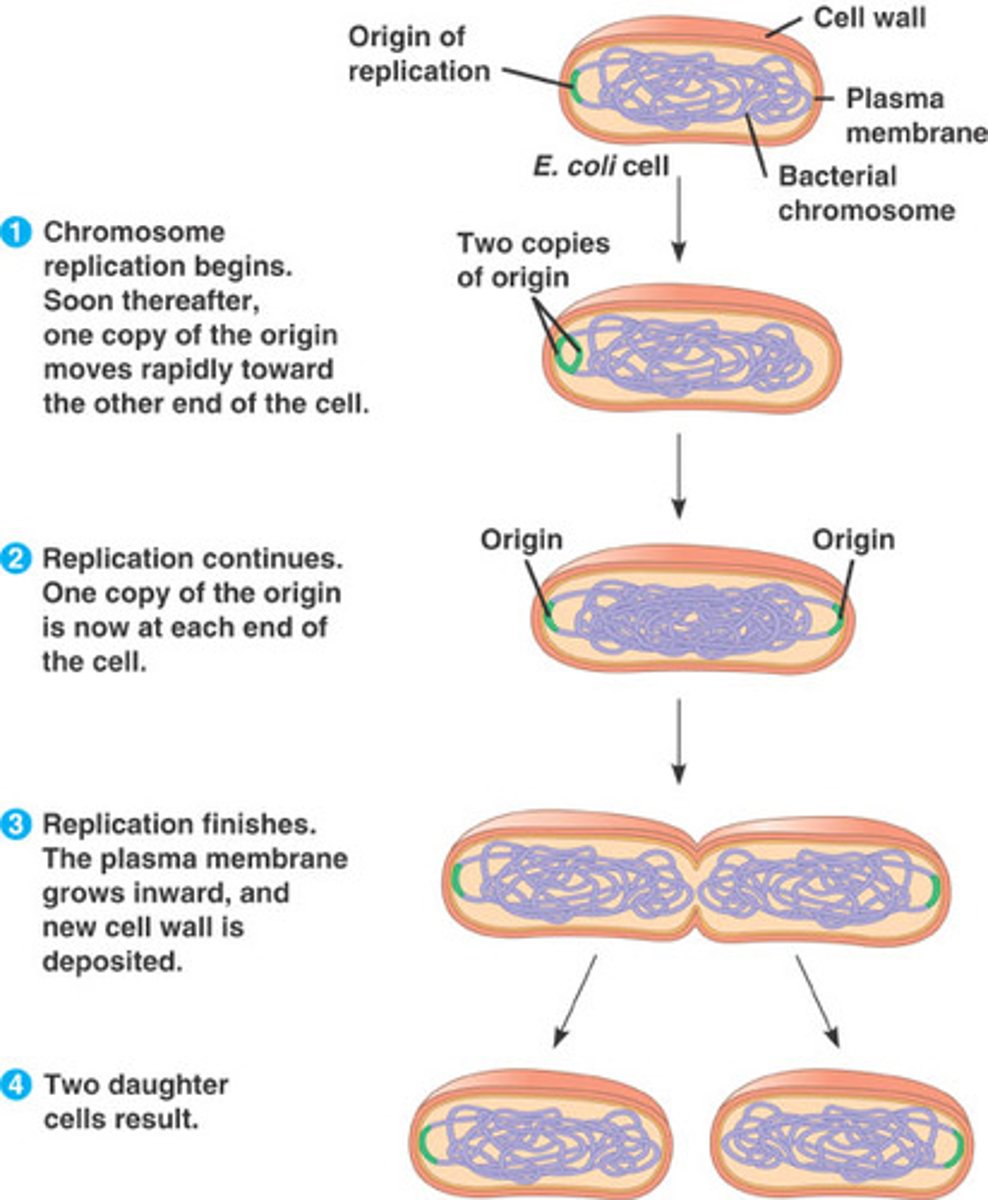
How is bacterial DNA replication accomplished?
Replisome (helicase, topoisomerases and DNA polymerase III) directs bidirectional DNA replication from a single origin of replication.
Prokaryotes
No membrane-bound nucleus
Eukaryotes
contain membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
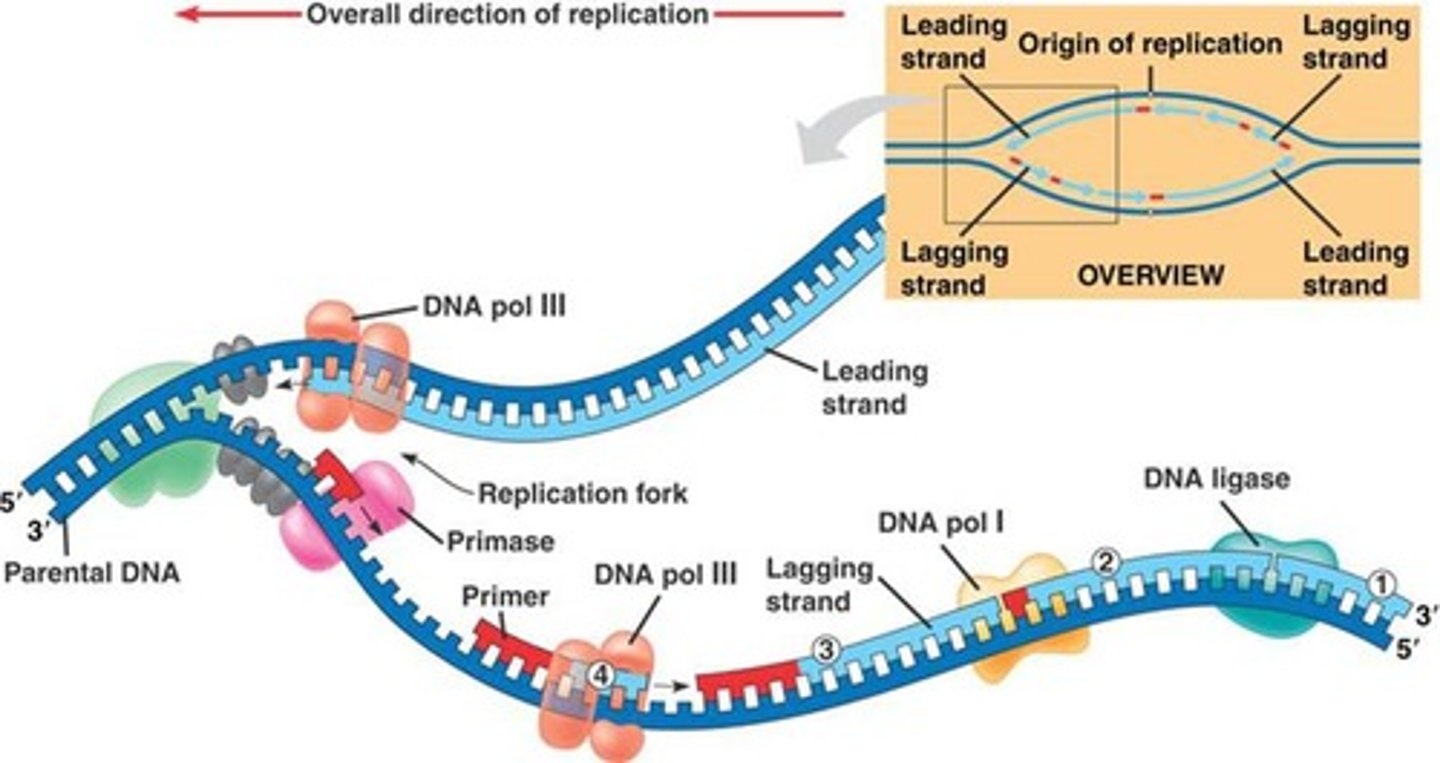
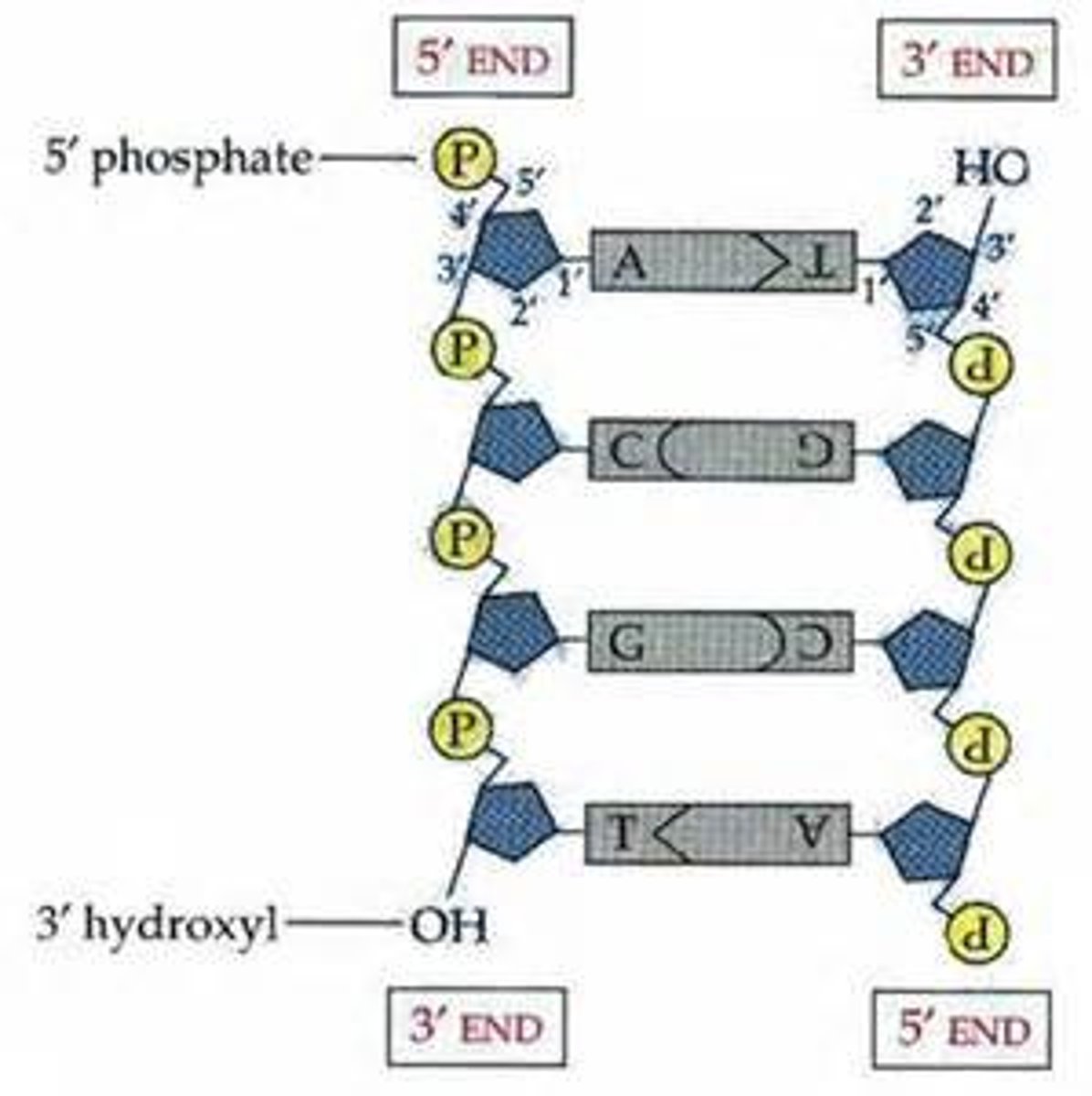
DNA is antiparallel
strands run in opposite direction and replication is semiconservative- each strand acts as a parent strand for the new molecules
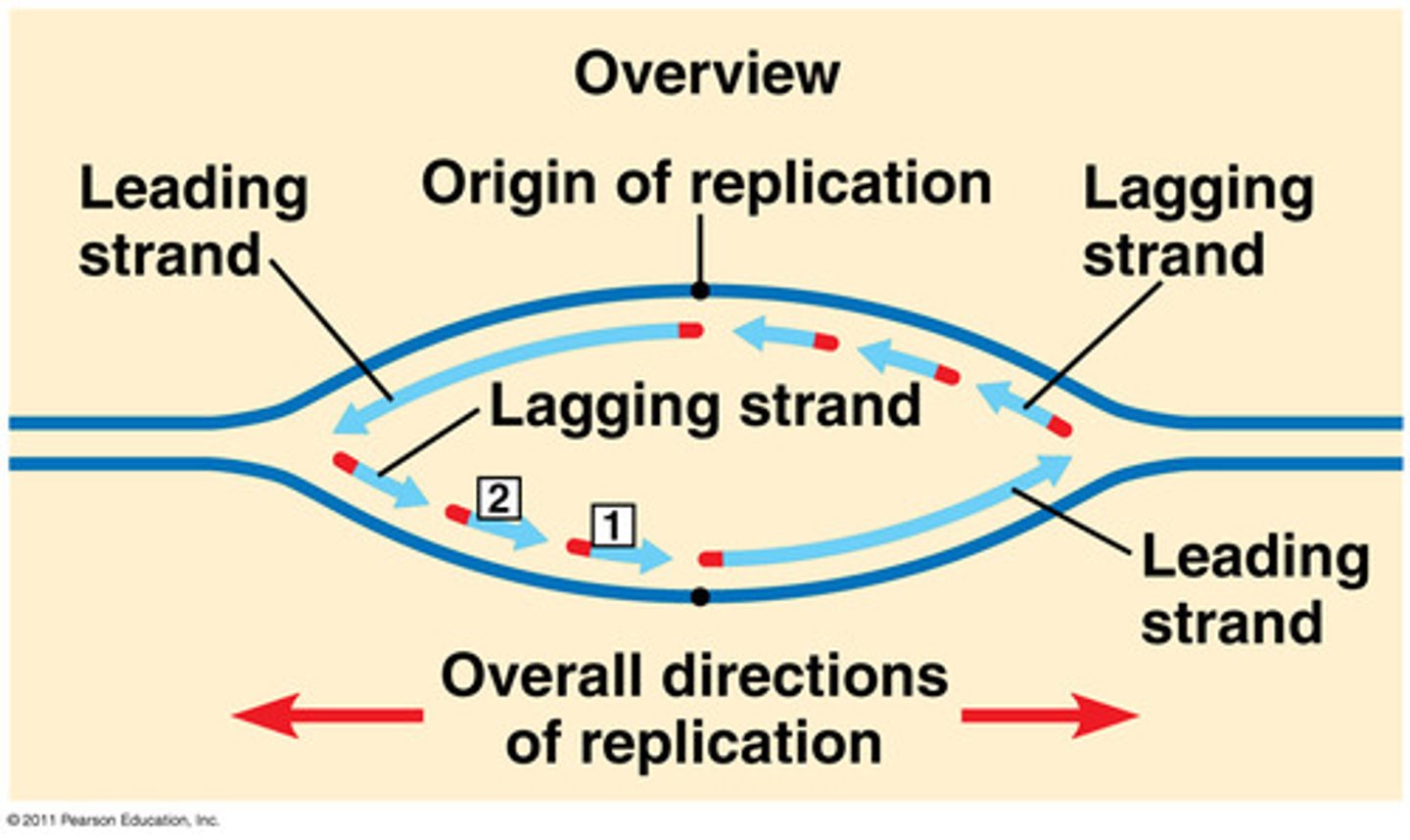
Leading Strand
synthesized continuously
Lagging Strand
The strand that is synthesized in fragments using individual sections called Okazaki fragments
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase.
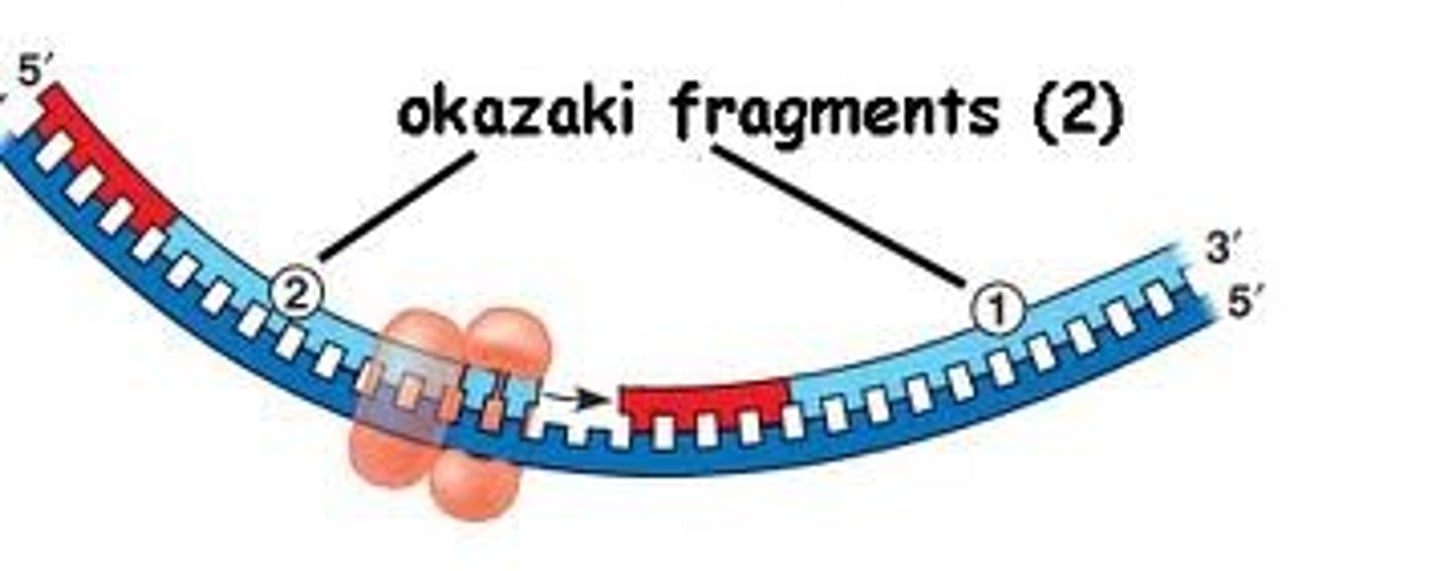
DNA Ligase
enzyme that chemically links DNA fragments together
Primer
a short stretch of RNA with a free 3' end, bound with DNA nucleotides during DNA replication
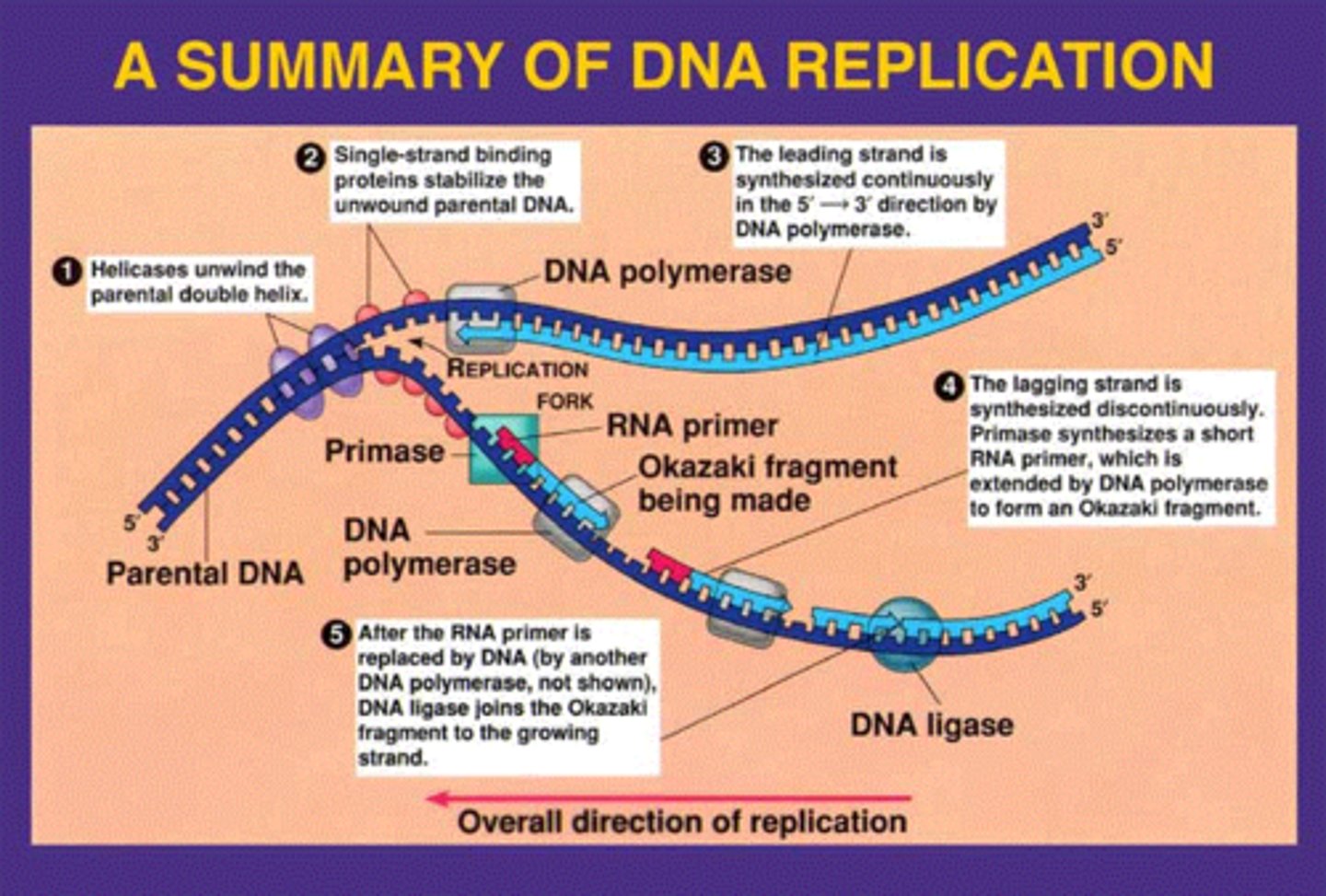
Helicase
unwinds DNA
Single Stranded Binding Protein
Binds to and stabilizes single-stranded DNA until it can be used as a template.
Topiosomerase
snips away pieces to loosen DNA strands to release tension
Primase
synthesizes RNA primer
DNA polymerase III
- used by prokaryotes
- can synthesize a new strand of DNA
- read template DNA 3' to 5'
- synthesize new strand 5' to 3'
DNA Polymerase I
removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA
Telomeres
the ends of chromosomes; their length decreases with each cell duplication.
Telomerase
catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in germ cells
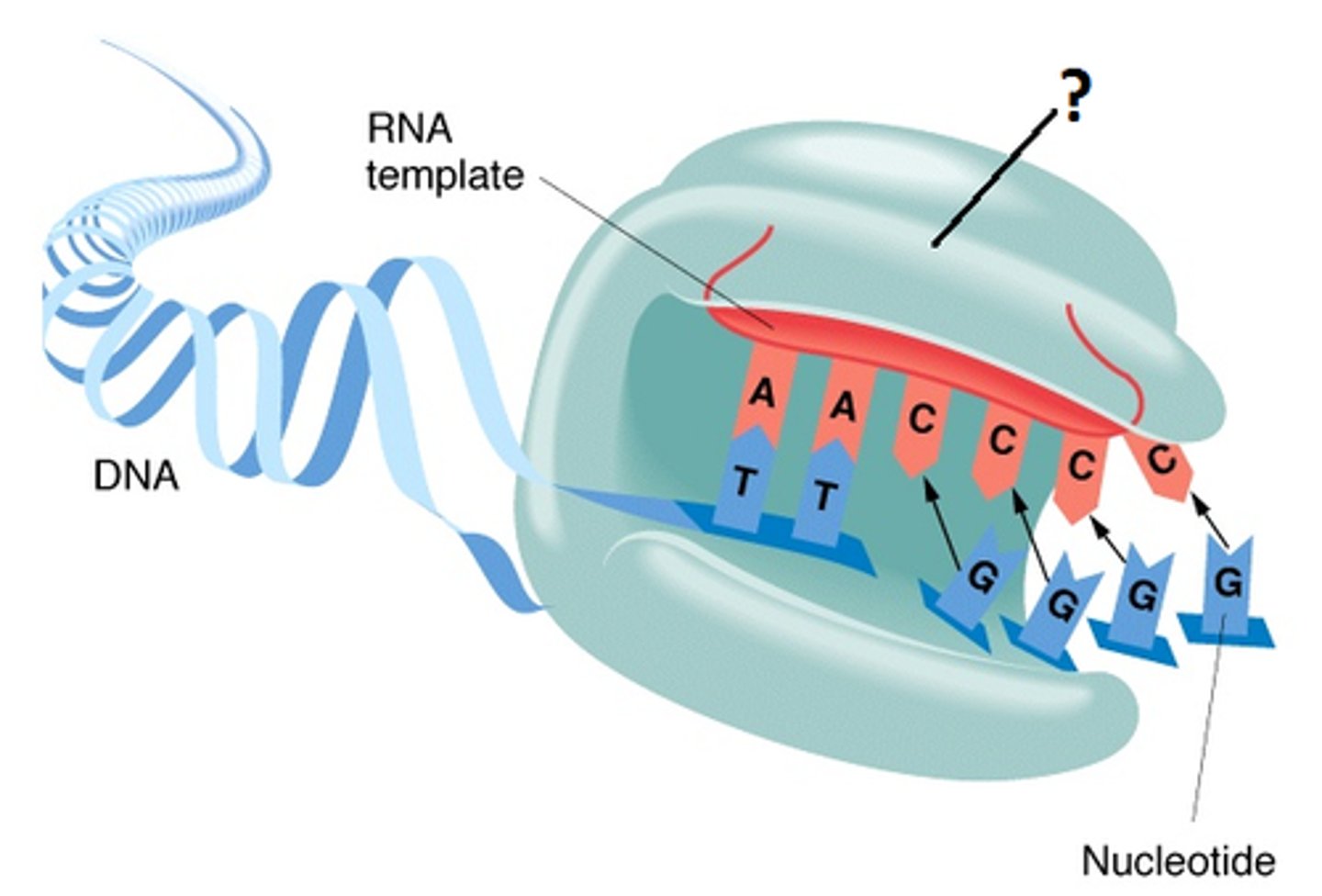
Nuclease
DNA cutting enzyme
Mismatch Repair
repair enzymes correct errors in base pairing
Bacteria Cell
Lacks nucleus, RNA produced by transcription
Eukaryotic Cells
The cell provides separate area for transcription.
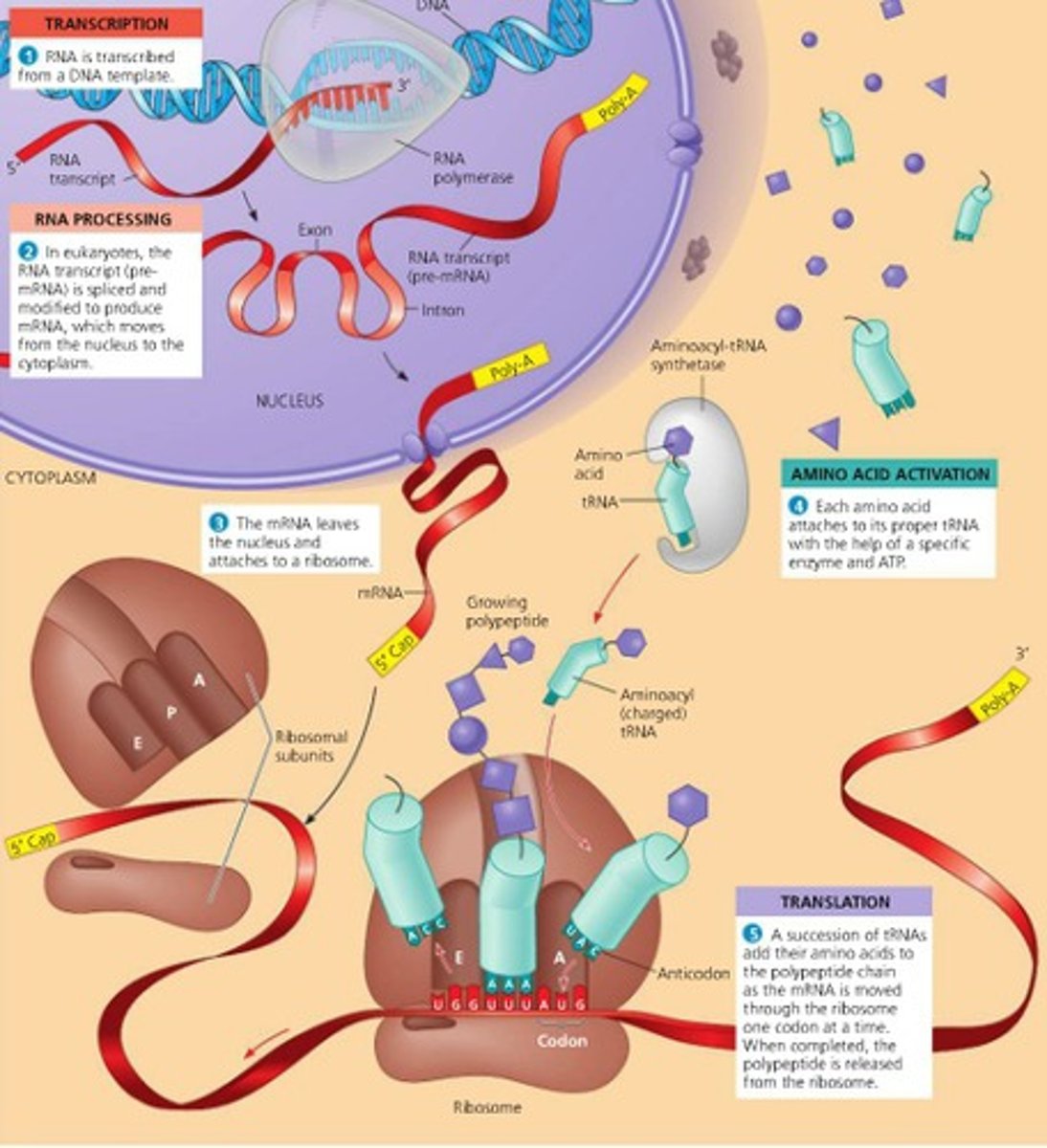
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
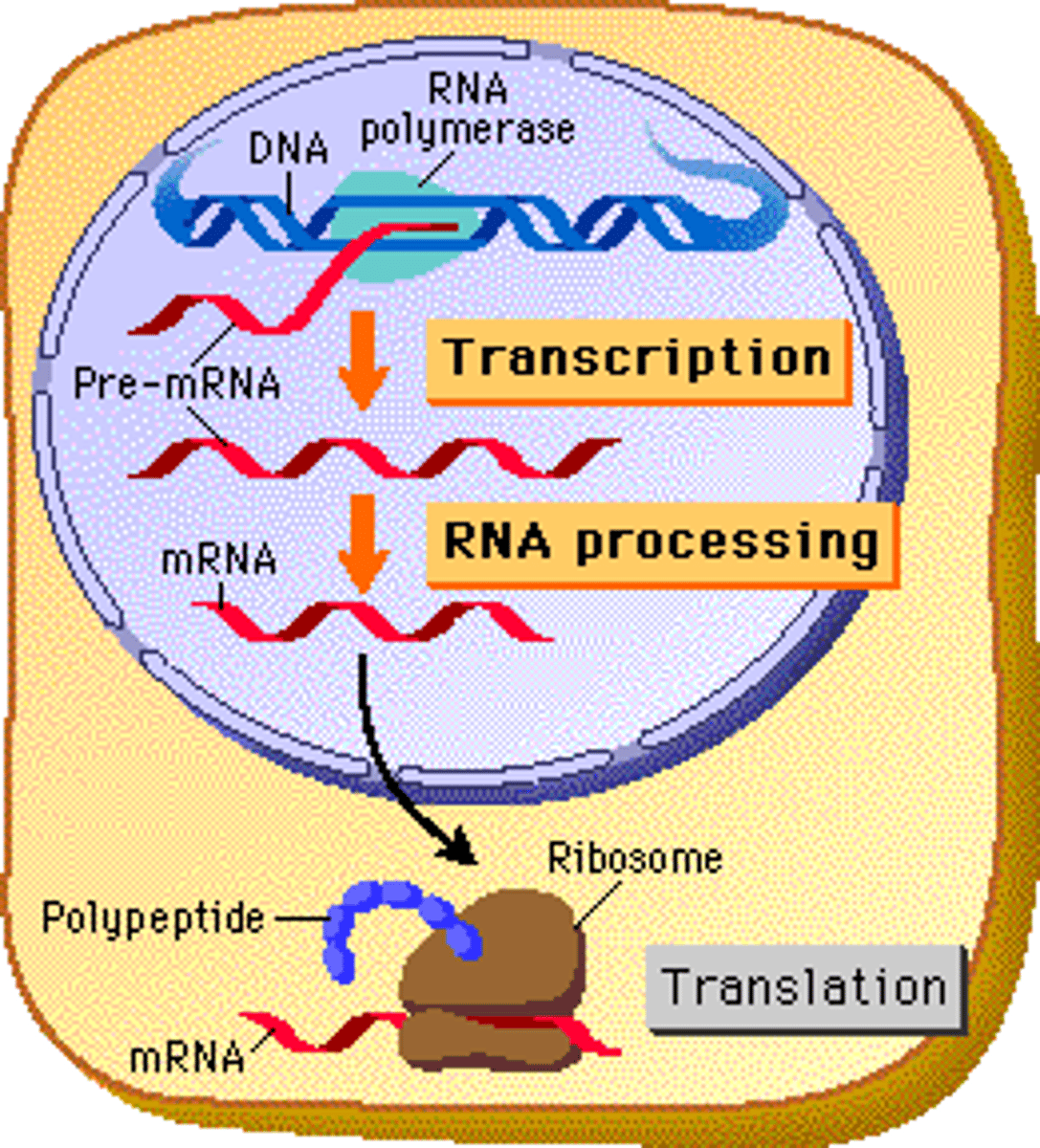
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
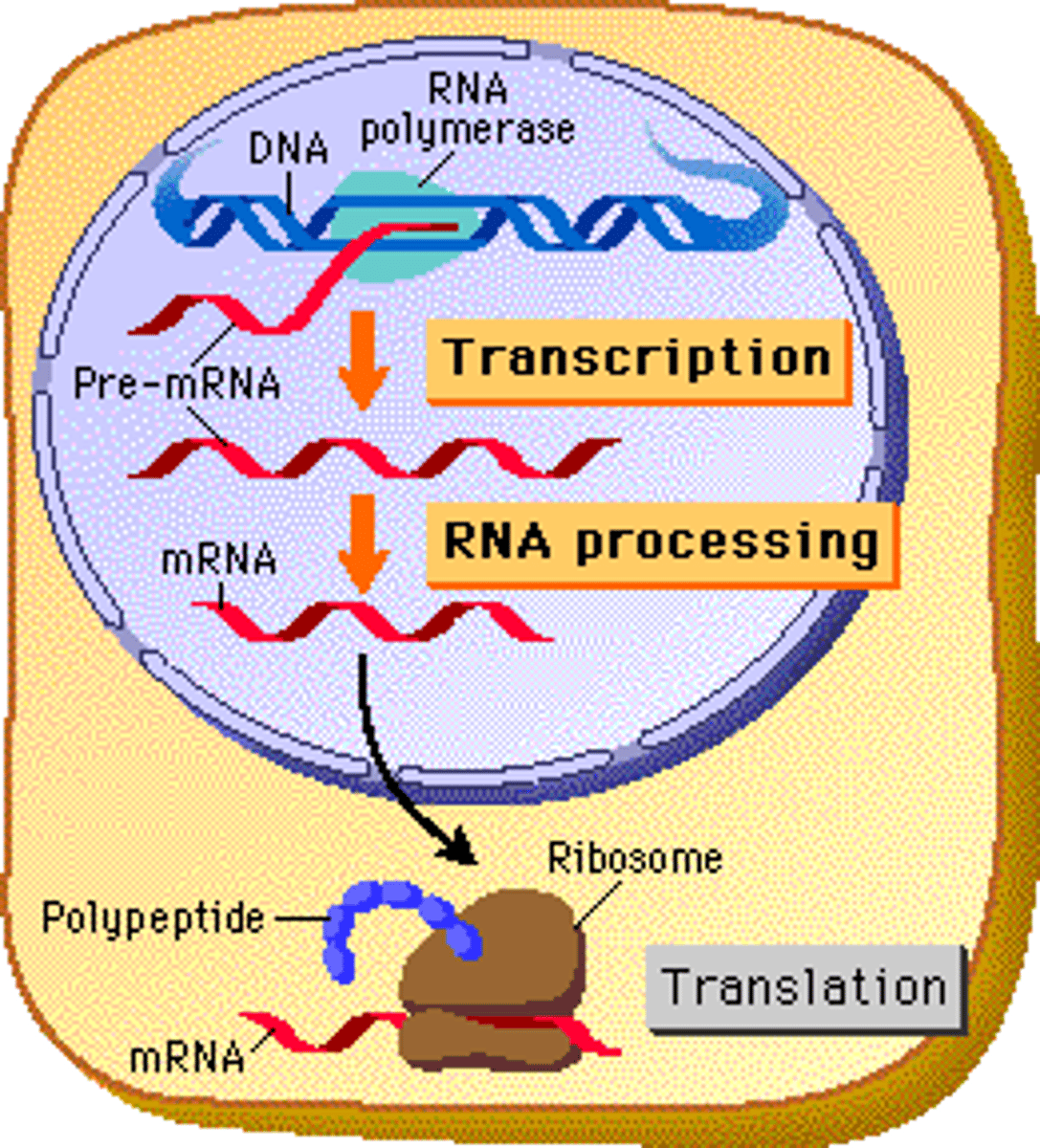
Replication
Copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA
Template Strand
the strand of DNA that specifies the complementary mRNA molecule
Codon
In mRNA, a nucleotide base triplet that codes for an amino acid or stop signal during translation
Anticodon
a nucleotide triplet at one end of a tRNA molecule that base-pairs with a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule
Reading Frame
Reading mRNA nucleotides in the correct groupings.
Prokaryotic Promoter
establishes where RNA synthesis is initiated.
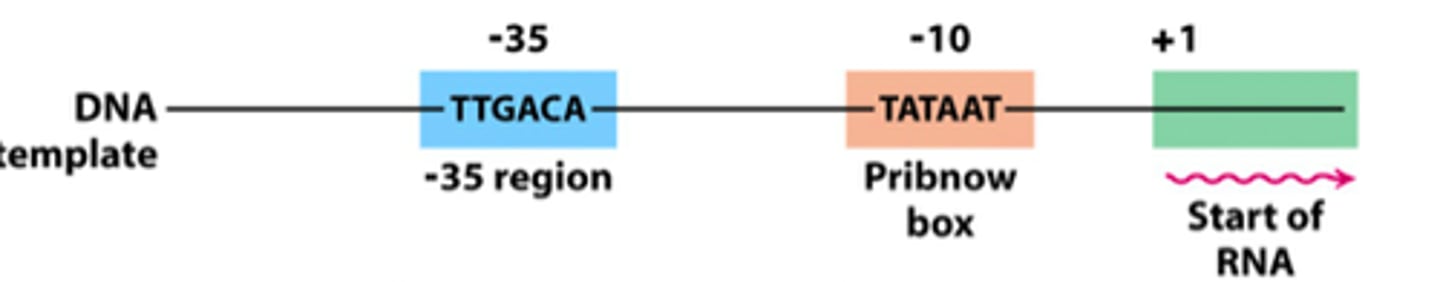
Prokaryotic Termination
Sequence of Nucleotide, marks end of gene, signals to release newly made RNA from DNA
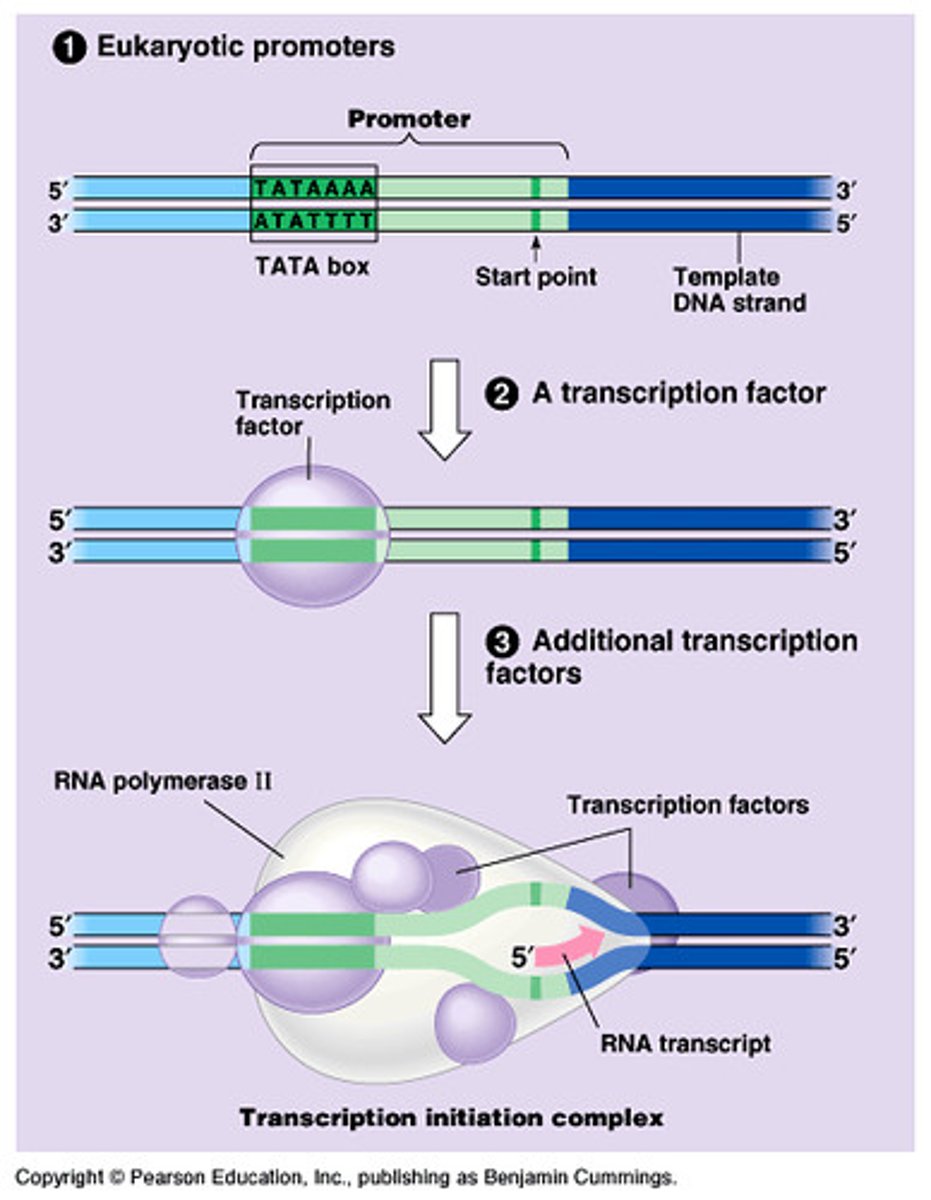
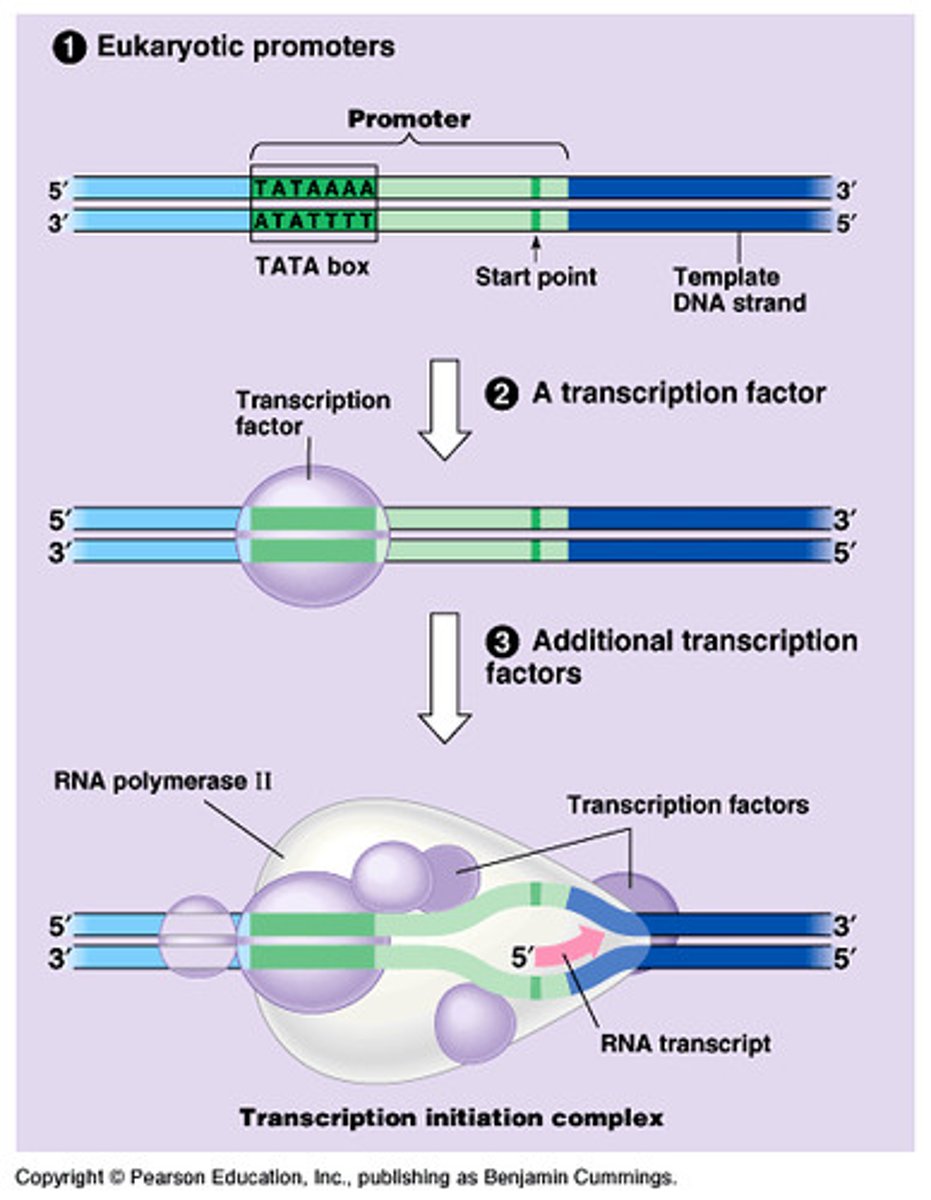
Prokaryotic Termination of Transcription
Proceeds through a termination sequence
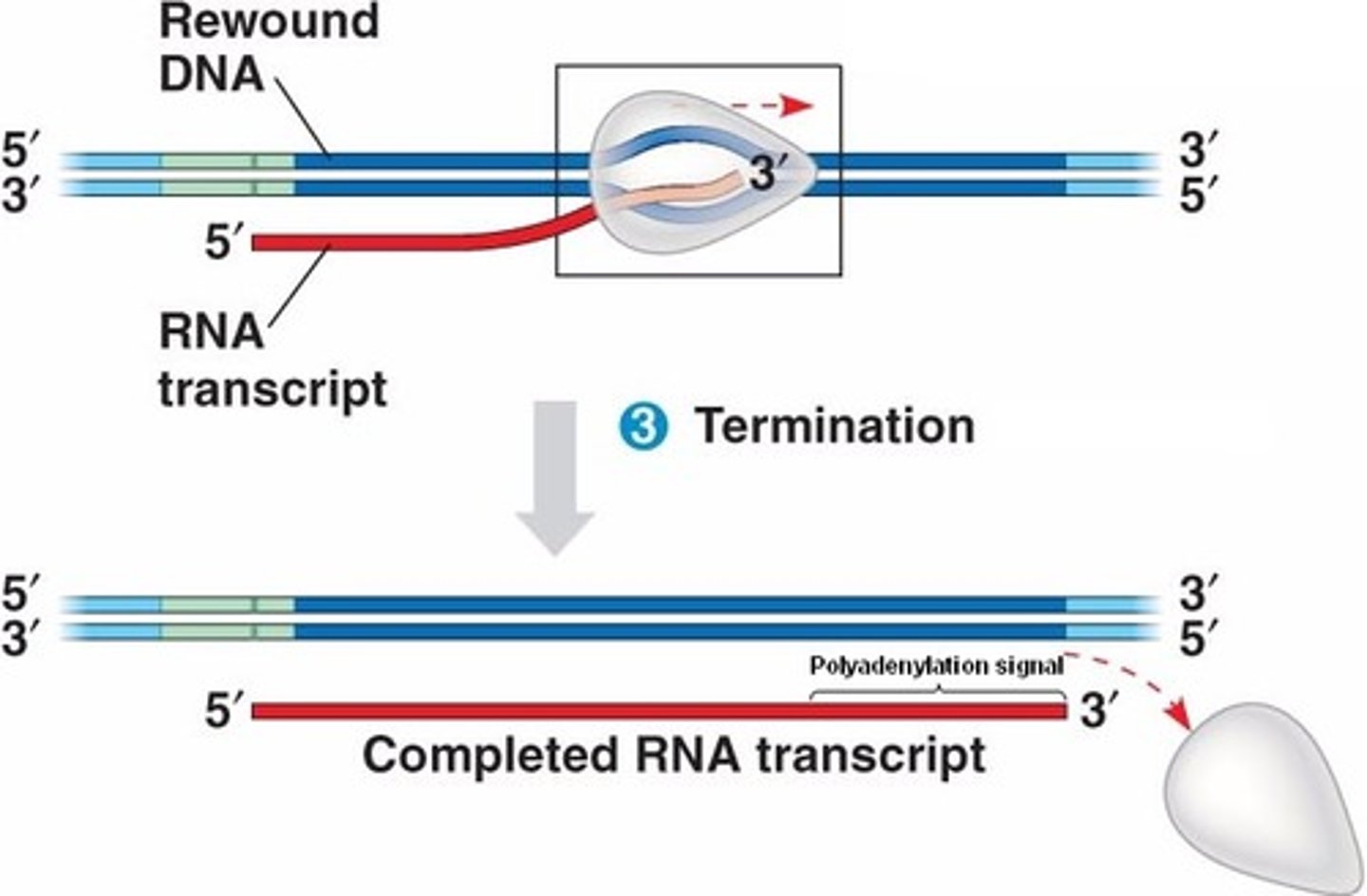
Eukaryotic Termination of Transcription
Pre mRNA is cleaved from growing RNA chains while polymerase II continues.
Why is RNA processing necessary?
RNA processing is necessary to protect message and attach to ribosome
What does adding a 5' cap and poly A tail mean ?
They protect mRNA from degradation
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
RNA splicing
removes introns and joins exons, creating an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence
Introns
Noncoding segments of nucleic acid.
Exons
coding segments of DNA
Splicesome
1) assembled from snRNPs (snurps) and protein complexes
2) enzyme that carries out RNA splicing; |
3) removes introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA (splicing)
snRPS
short nucleic segments at the end of the introns that signal where it will splice.
Ribozymes
catalytic RNA molecules that function as enzymes and can splice RNA
Alternative RNA splicing
Some genes can encode more than one kind of polypeptide, depending on which segments are treated as exons during splicing
Mutation
A change in a gene or chromosome.
Point Mutation
gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed
Base-Pair Substitution
type of mutation in which a single base pair changes
Missense
a mutation that changes one amino acid
Nonsense
codon changed to a stop codon
Insertions
additions of nucleotide pairs in a gene
Deletion
removals of nucleotide pairs in a gene
Frame-shift Mutation
a mutation involving the addition or loss of nucleotides
Mutagen
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.
A summary of transcription and translation in a eukaryotic cell.
Plasmids
Circular DNA molecules that can replicate independently of the main chromosomes of bacteria
Chargaff's Rule
A=T and C=G
Direction DNA is synthesized
5' to 3'
Central Dogma of Biology
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
What type of RNA carries the instructions for making proteins to the ribosome?
mRNA Messenger RNA
What type of RNA carries the anticodon?
tRNA Transfer RNA
What type of RNA makes up ribosomes?
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
This protects the mRNA molecule from enzymatic degradation in the cytoplasm and aids in transcription termination, export of the mRNA from the nucleus, and translation
Poly-A tail
This is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. It plays a role in the stability of the mRNA molecule
GTP cap
Excision of introns & splicing and retention of exons can generate different versions of the resulting mRNA molecule. What is this called?
Alternative splicing
The first stage of translation is called
Initiation
The second stage of translation is called
Elongation
The third stage of translation is called
Termination
What causes translation to be initiated?
The mRNA start codon interacts with the rRNA in the ribosome
What forms a polypeptide chain?
Amino acids
Retrovirus
An RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA and then inserting the DNA into a cellular chromosome; an important class of cancer-causing viruses.
lac operon
the operon that controls the metabolism of lactose
Tryp operon
Repressible operon
An example of an inducible operon is the
lac operon
This is a small non-coding RNA molecule (containing about 22 nucleotides) found in plants, animals and some viruses, that functions in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression
miRNA (microRNA)
These are the primary source of genetic variation
Mutations
What is transformation?
A change in genotype and phenotype due to the assimilation of external DNA by a cell.
What is Transduction?
Viral transmission of genetic information
Conjugation
In bacteria, the direct transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined.
Gel Electrophoresis
The separation of nucleic acids or proteins, on the basis of their size and electrical charge, by measuring their rate of movement through an electrical field in a gel.
When does it mean when DNA is amplified?
Multiple copies are made of DNA fragments
What is PCR?
Polymerase Chain Reaction; a procedure used to amplify DNA
Viruses that infect bacteria are called
Bacteriophages
What type of bond joins the nitrogenous bases of DNA
Hydrogen
What type of bond joins the phosphate-sugar backbone of DNA
Phosphodiester
What determines RNA function?
Sequence of RNA bases
Structure of the RNA molecule
'Illustration' of DNA replication
What is another name for the antisense strand of DNA?
Noncoding strand
How does RNA know when to stop translation?
When it comes to a stop codon