Nurse cheung: chemical reactions Teas
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
chemical reactions
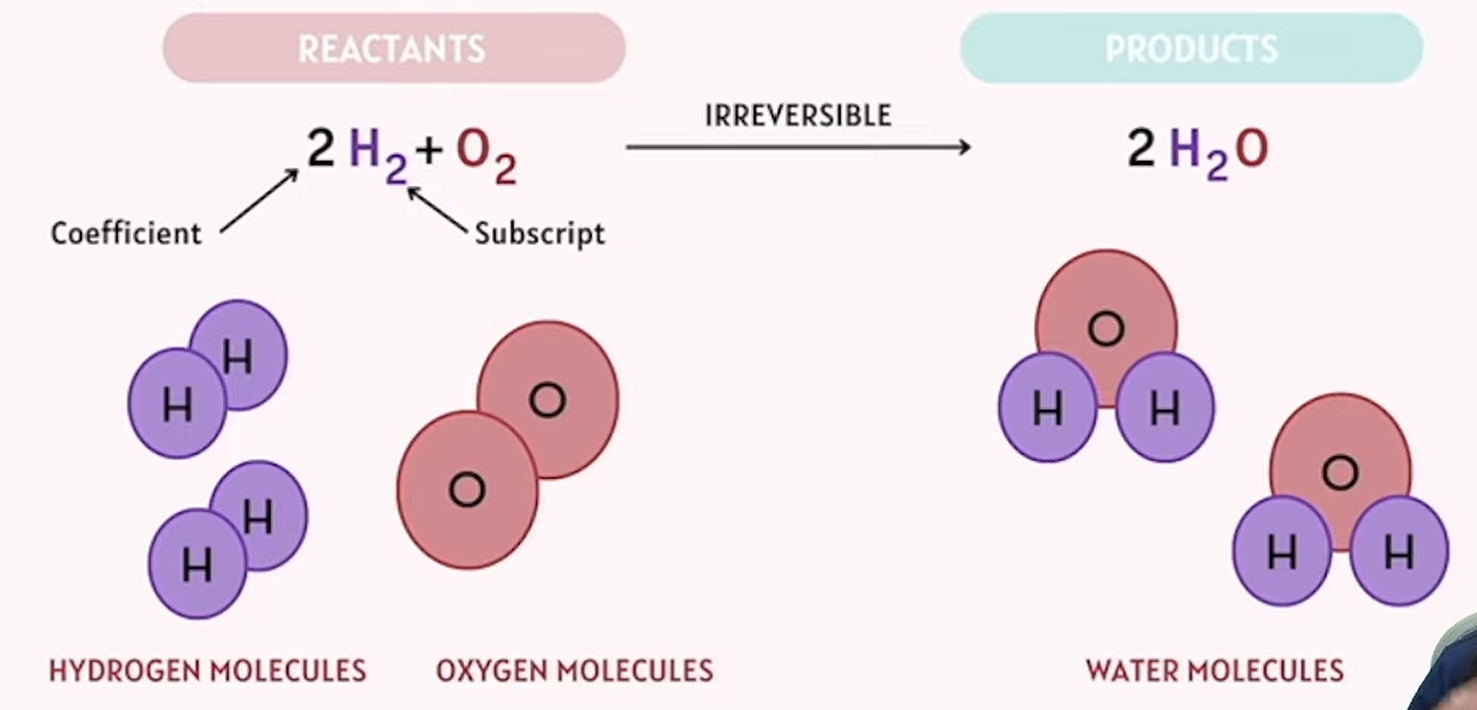
one or more substances, known as reactants, that are transformed into different substances called products
reactants
substances present at the start of a chemical reaction that participate in the reaction
reactants are your ingredients (flours, sugar, eggs)
products
substances that are formed as a result of a chemical reaction
products are what you end up with after the reaction (cake)
example of reactants (irreversible) products
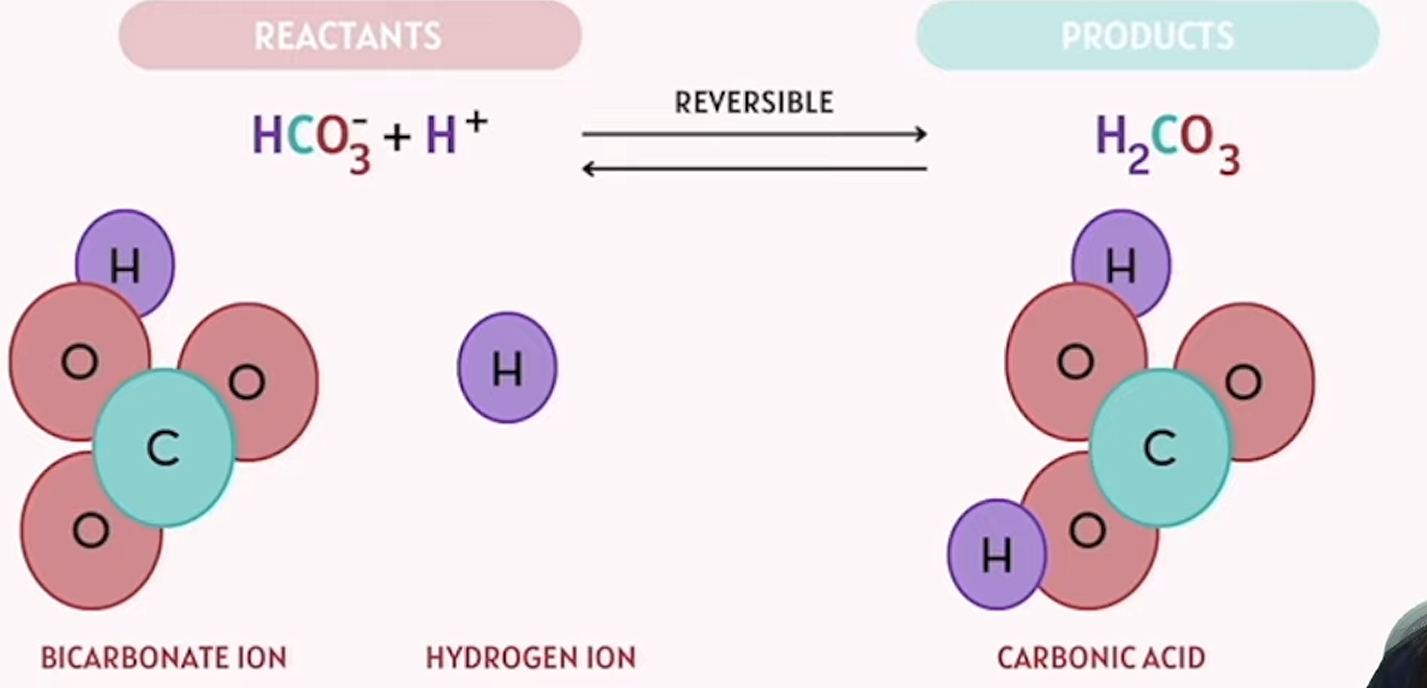
example of reactants (reversible) products
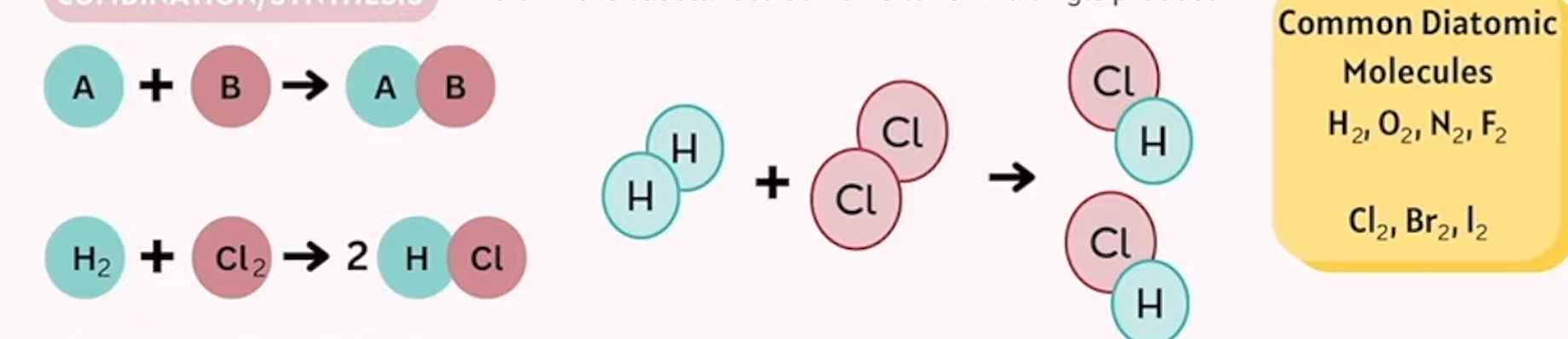
combination/ synthesis
2 or more substances combine to form a single product
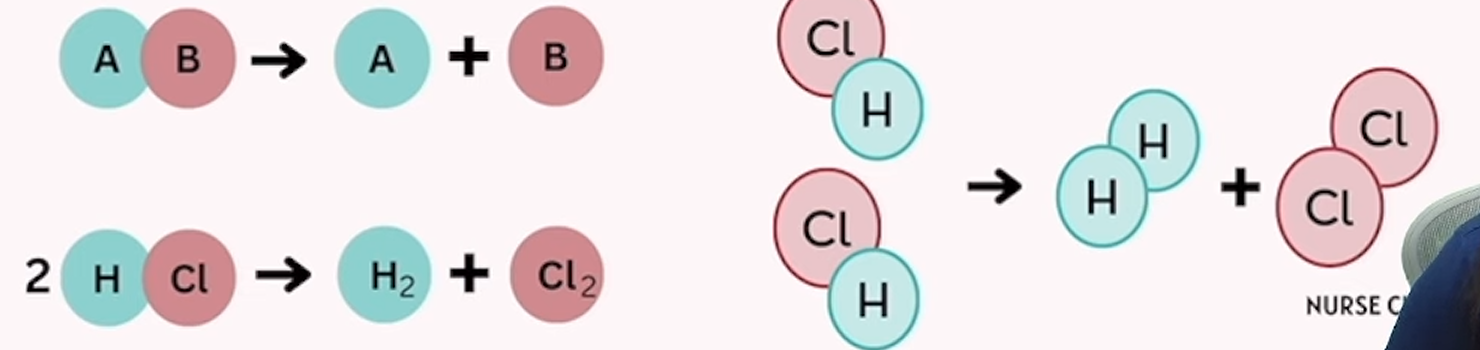
decomposition
a single substance breaks down into 2 or more simpler substances
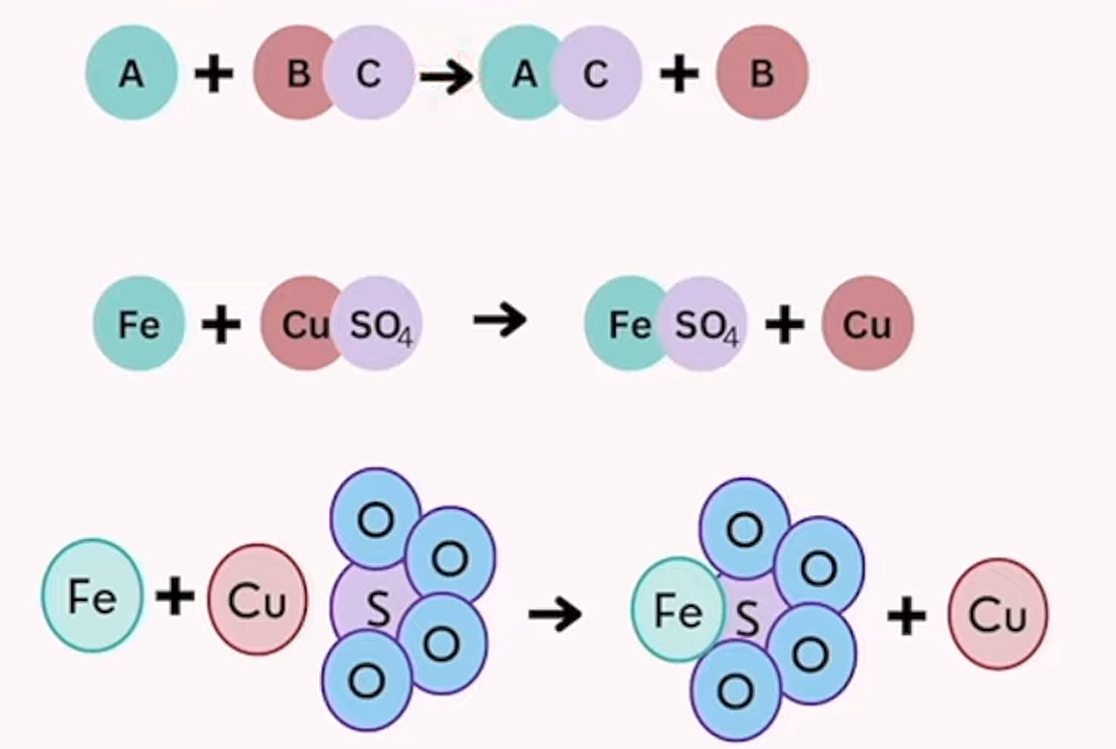
single displacement
one element in a compound is replaced by another element
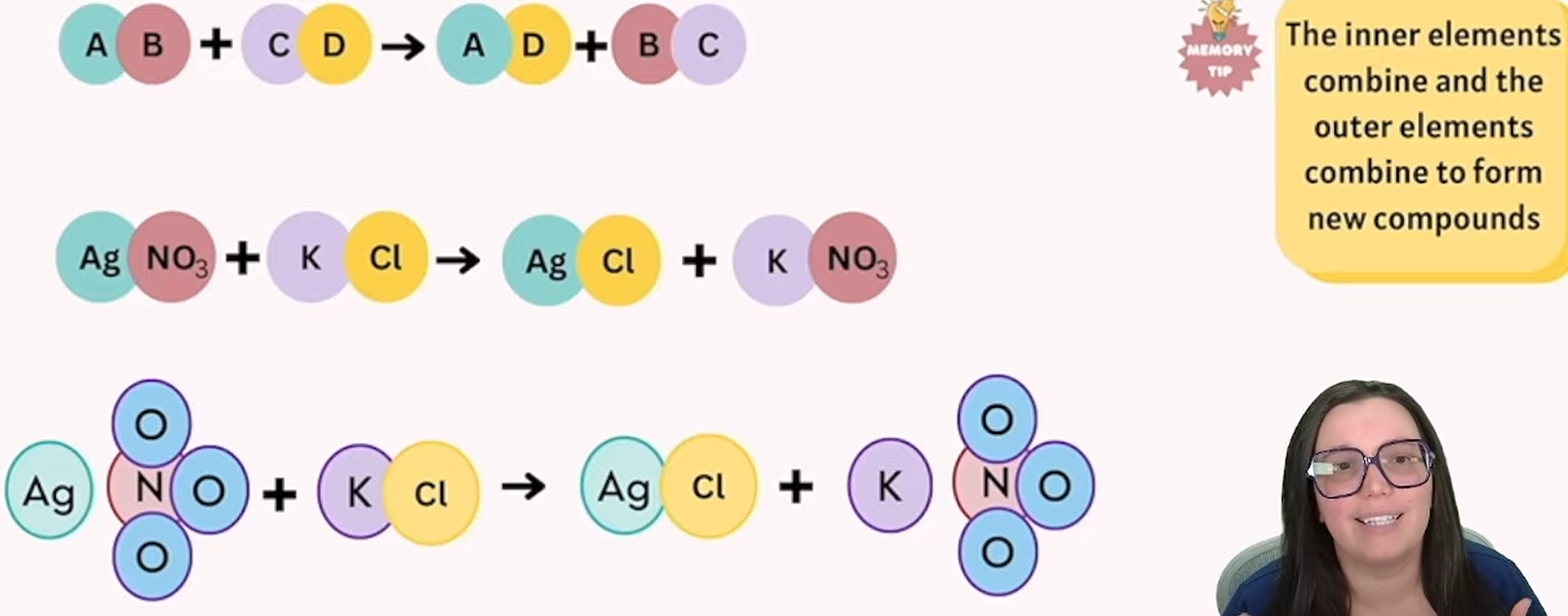
double displacement
elements in 2 different compounds swap places with each other to form 2 new compounds
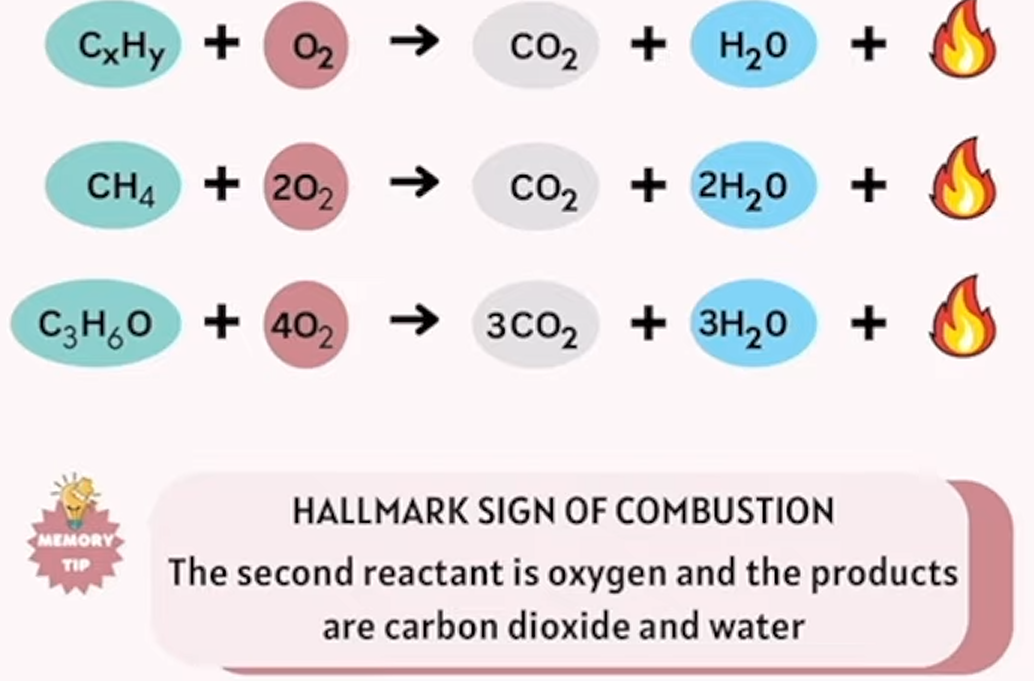
combustion
a substance (usually a hydrocarbon) reacts with oxygen to produce heat, light, and typically produces carbon dioxide and water
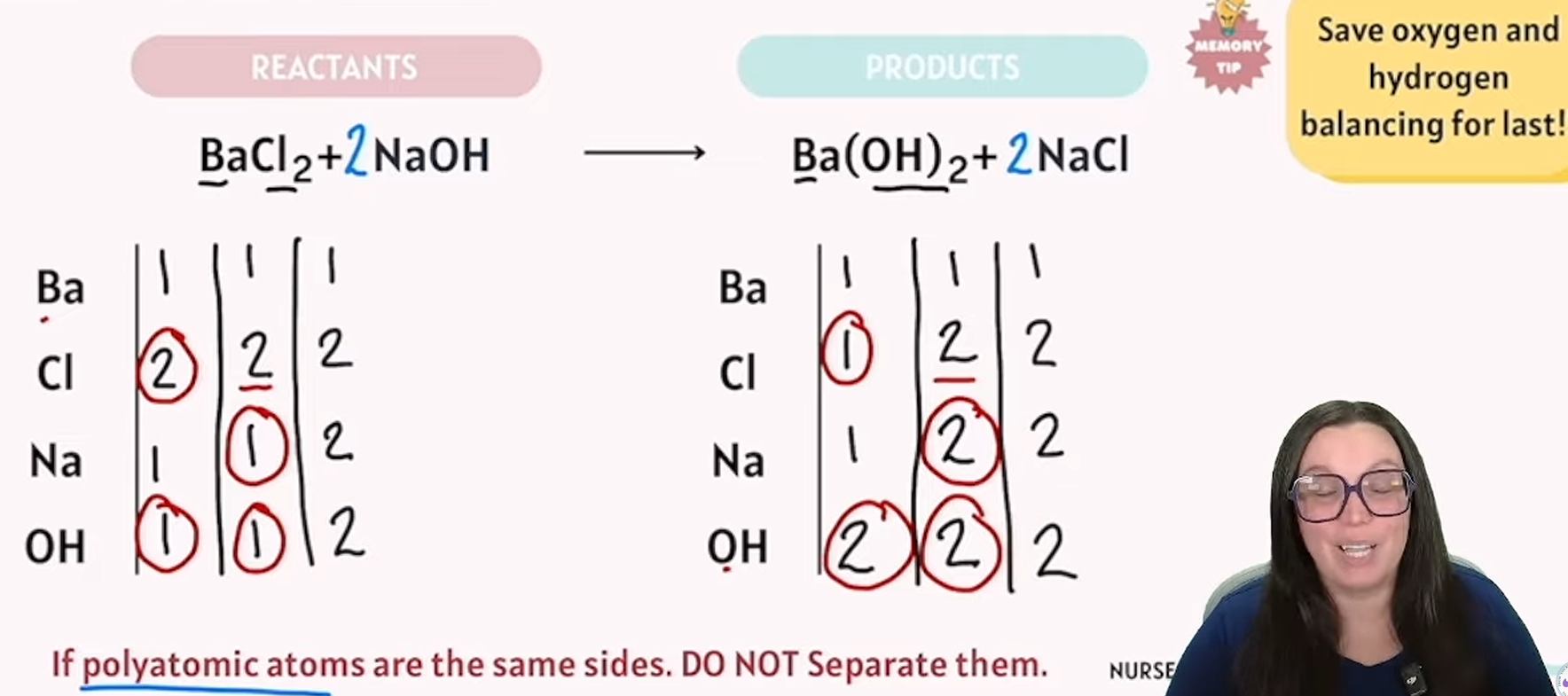
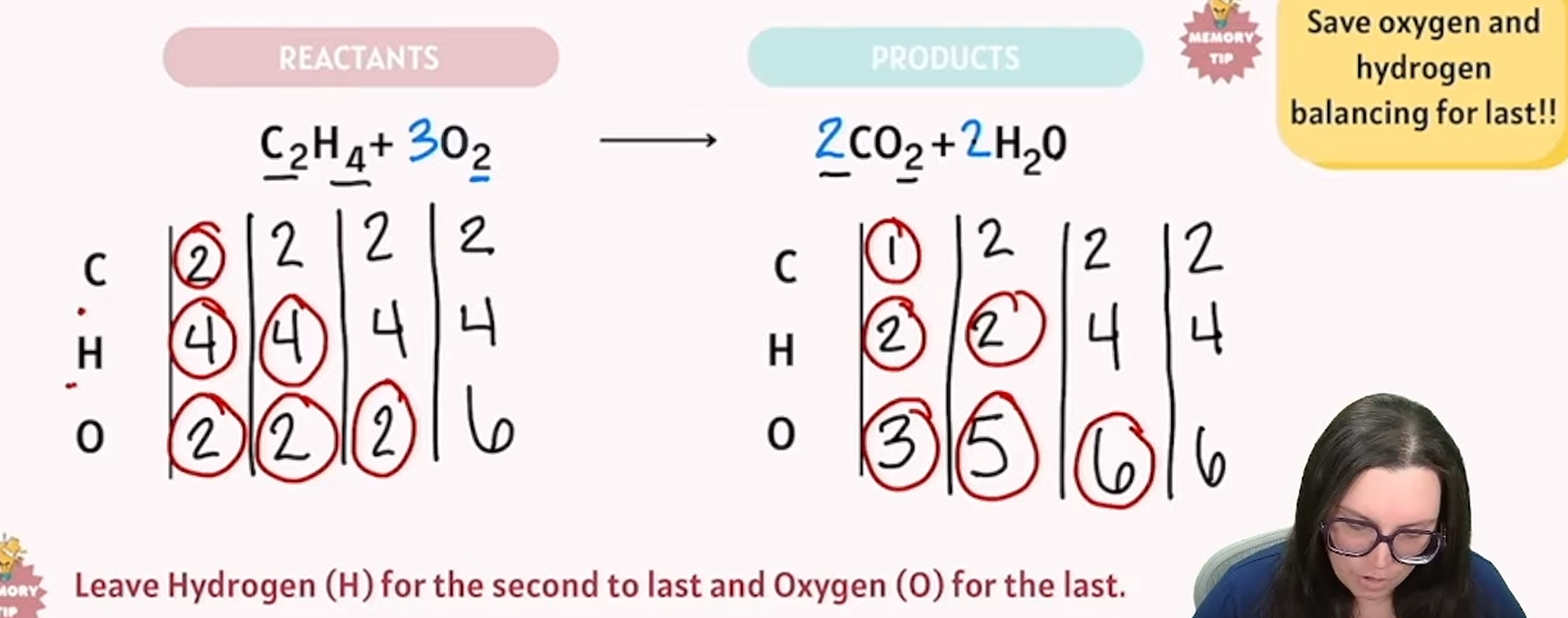
balancing chemical reactions
reactants are the same exact numbers as your products
another example of balancing chemical reactions
mole
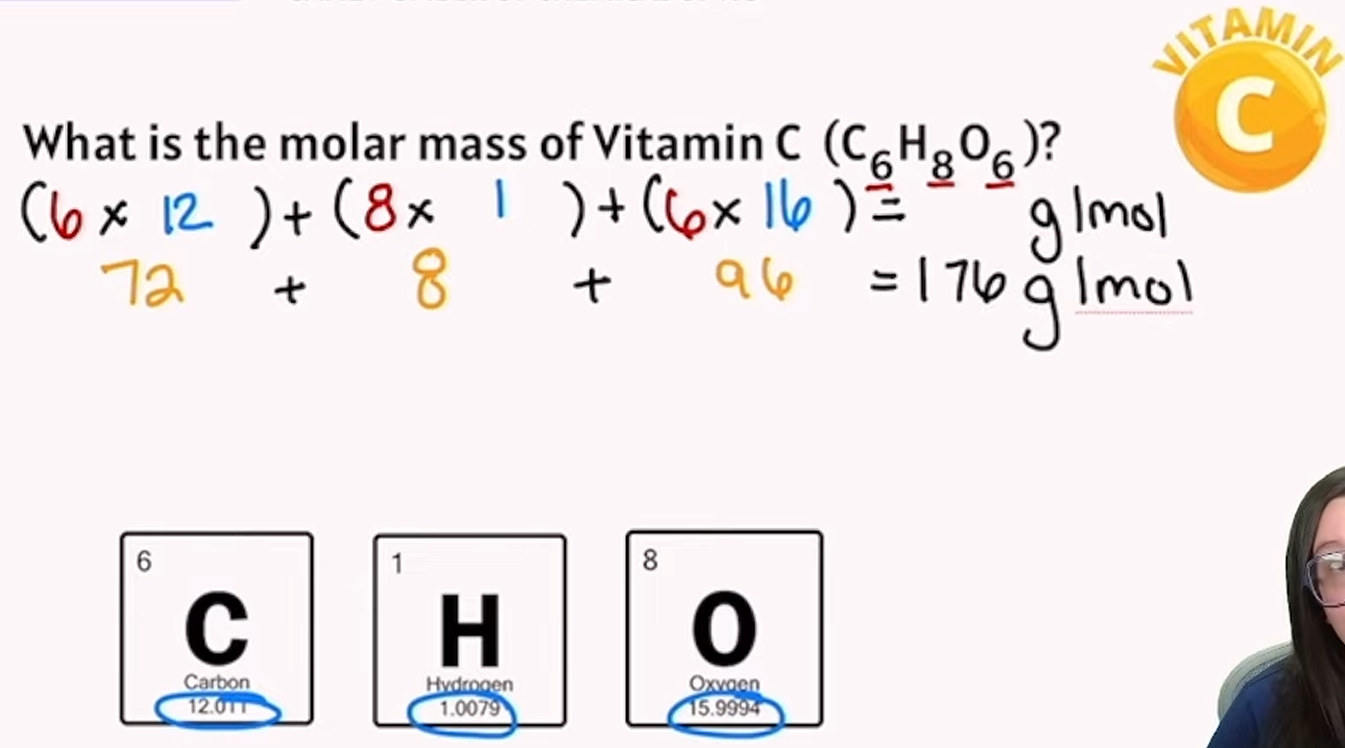
unit of measurement that is the amount of a pure substance containing the same number of chemical units
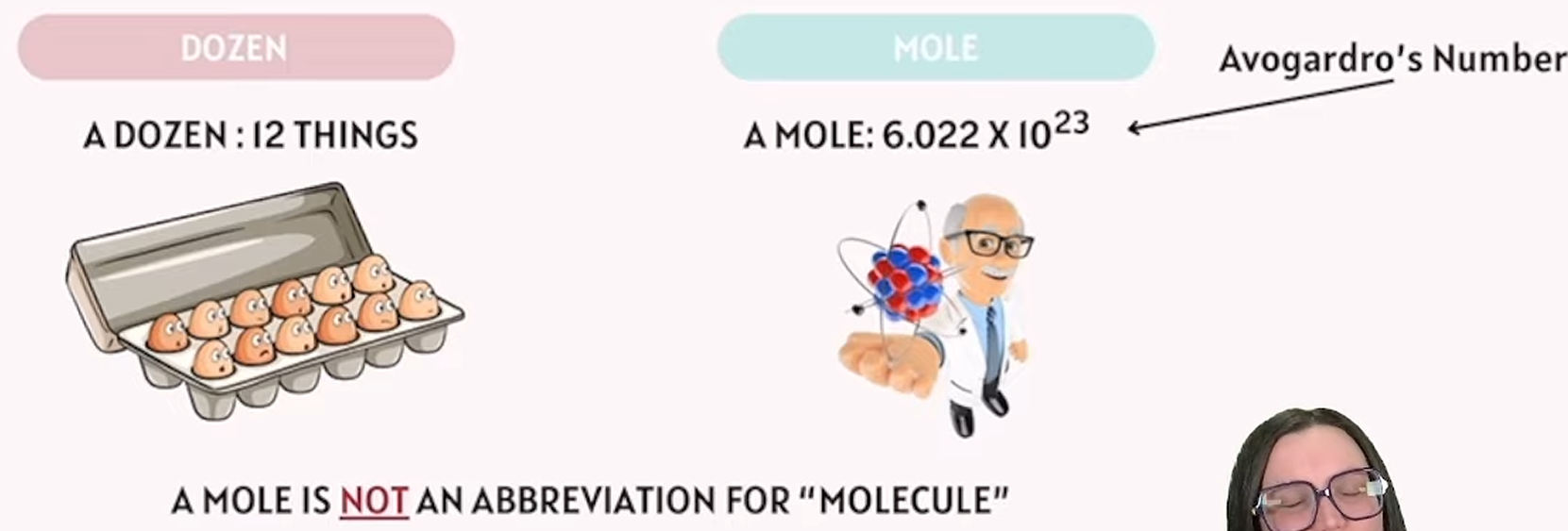
mole example
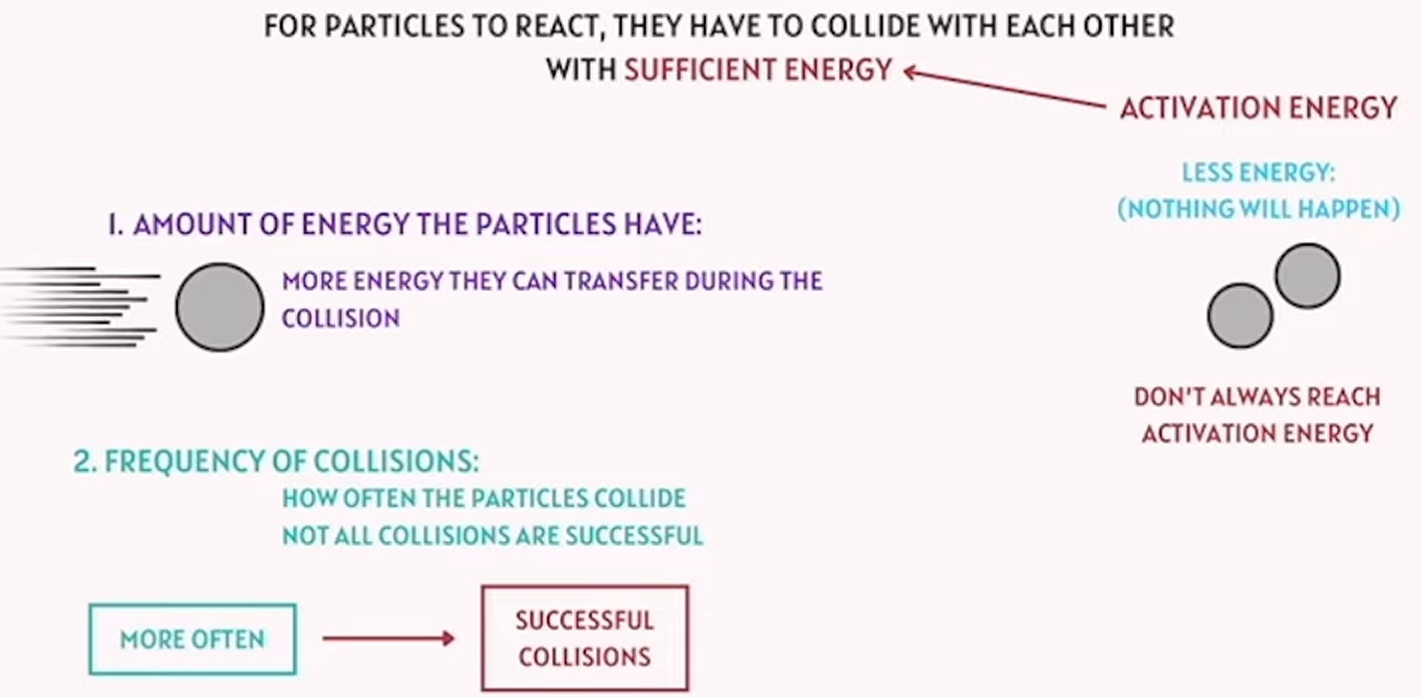
collision theory
for particles to react, they have to collide with each other with sufficient energy
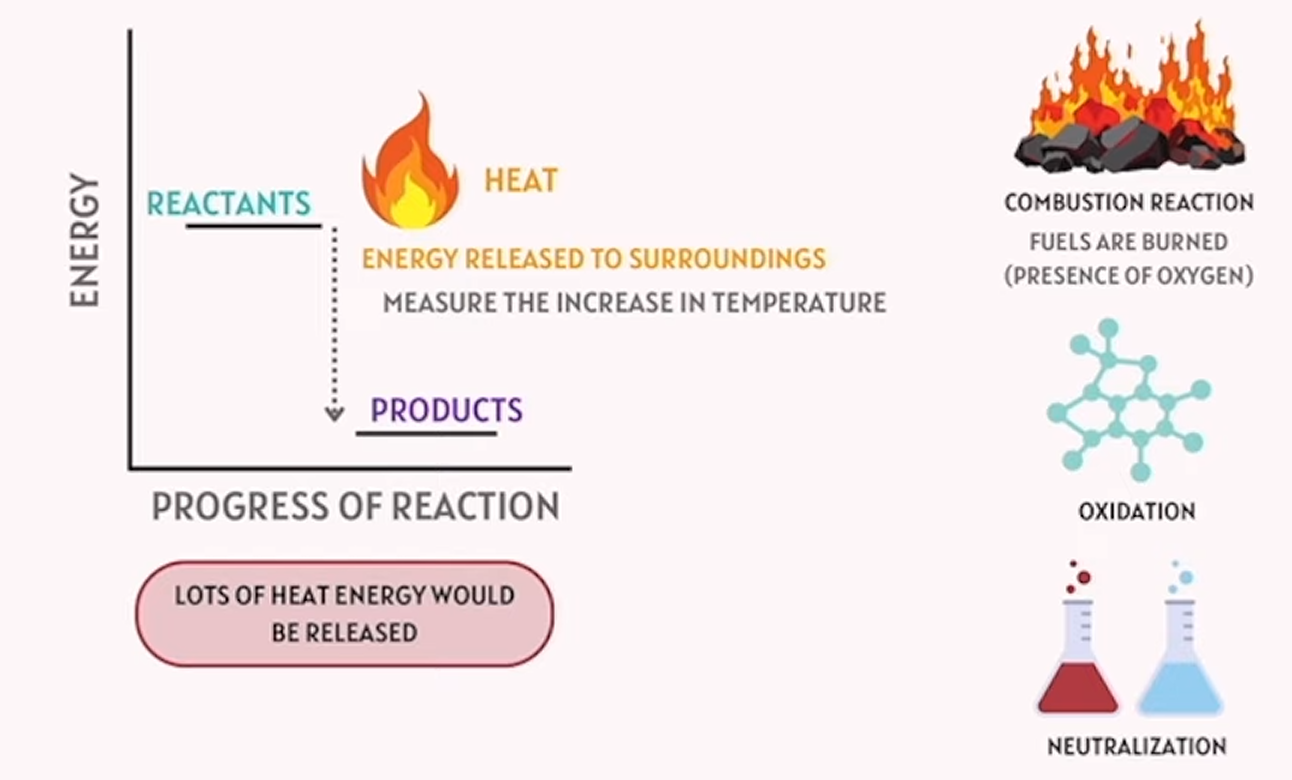
exothermic reactions
releases energy to surroundings - release heat
exothermic think “exit”. heat is exiting during this reaction
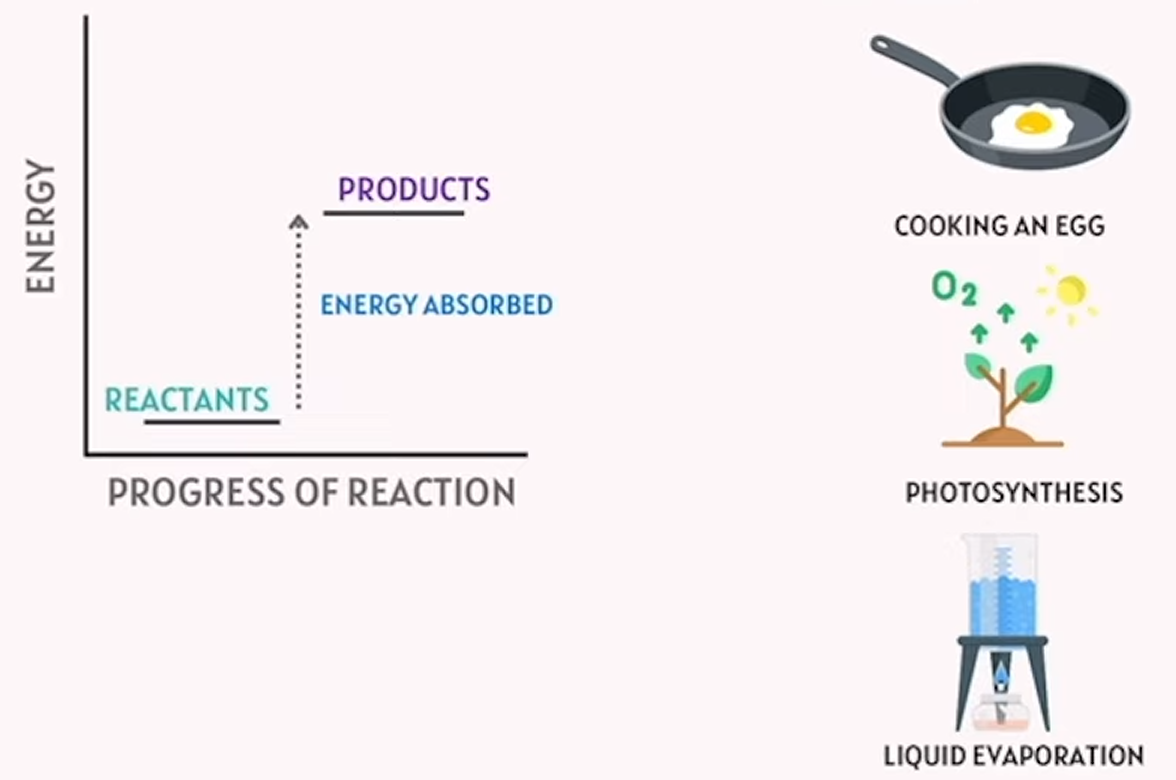
endothermic reactions
takes in heat energy from the surroundings - absorbs heat
endothermic think “enter”. heat enters/absorbs during this reaction
equilibrium
when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction in a closed system

static
the rate of the forward and reverse reactions are 0. they are static
diamonds
dynamic
the forward and reverse reactions are occurring at the same time
