Variation and evolution
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is variation?
The differences in the characteristics of individuals in a population
What are the three main causes of varation?
Alleles individuals have inhereited - genetic
Enviroment
A combination of genes and the enviroment eg height (genetics on how tall we can grow and enviroment on how much calcium we coonsume)
What are mutations?
Random changes to DNA
What is a phenotype?
The observable characteristics of an organism, resulting from its genotype and interactions with the environment
What can mutations lead to?
New phenotypes (adapt)
What is evolution?
The change in the inherited characteristics of populations over time through the proccess of natural selection
What are the step of evolution in natural selection?
Every organism has a slightly different combination of alleles that is inherited from its parents
This means some organisms in the same species are better adapted to certian conditions then others
If there is a sudden change in the enviroment, organisms which have inhereited alleles that suite the enviroment will survive and reproduce while other who havent got this enviroment die
This means their offspring may inherit the desiered allele and go on to live
Over generations this allele will pass down the generations
What can evolution lead to?
A species spliting off into two species as their alleles become to different
If the two species were to reproduce they would produce unfertile offspring
Why may a organism be selectivly bread?
To create a gentle nature
To become disease resistance
More food to be produced
To make flowers larger or unusal flowers
How is selective breading carried out?
Take a mixed population of the organism and choose two with the most presented wanted characteristics
Breed them together
The offspring will be a mixture of the two meaning the wanted characteristic is dominant
This is carried over many generations
What are the problems with selective breeding?
If we breed together closely related animals or plants it produces interbreeding
This can cause them to be prone to disease and inherited defects
What are genes? What do they do?
Genes are sections of DNA on a chromosome
Each gene codes for the amino acid sequence of a specific protien
What happens in genetic engineering?
Genes from one organism are cut out and transfered to cells of a different organism
What happens in genetic engineering?
Genes from one plants are cut out and transfered to cells of a different plants to make genetically modified crops
This produces a greater yield than normal crops
This is done to make plants more resistant or bigger
What is geno therapy?
The use of genetic modification as a way to treat inherited disorders in humans
What are the main steps in genetic engineering?
First identify the gene we want to transfer
Use enzymes to isolate this gene
Transfer the gene into a small circle of DNA called a plasmid (origanily came from bacteria and are useful for transfers) or we can use a virus - these are vectors
The desired gene is transferred into the cells of the target organisms
What is a important point on genetic engineering?
Always transfer the gene at an early stage in the organisms development so all the cells recieve the gene
What are fossils?
The remains of organisms from million of years ago which are found in rocks
What are the three ways fossils can form?
Fossils can form when parts of organisms have not decayed which happens when the conditions for decay are absent eg if its too cold
A fossil can form even if the organism decays if parts of the organisms are slowly replaced by minerals during the decay process
Fossils can be the preserved traces of organsims such as footprints and preserved place where roots were
What are the problems with fossils?
Many of the earlist forms of life were soft-bodied organisms so had no shell or skeleton
What do fossils show?
Species that have became extinct
Why do species become extinct?
Due to a catastrophic event
Enviroment changes
New predators
New diseases
A species become extinct if a new, more succesful species involves and competes with it for food or water
What organism evolves rapidly and why is this?
Bacteria
This is because it can reproduce every thirty minutes
What kills bacteria?
Antibiotics
Other then for humans, what is antibiotics used for?
To prevent diseases in animals
What is MRSA?
A common strain of antibiotic resistant
How does antibiotic resistance happen?
A mutation can make a bacterium resistant to antiobiotics in a group of bacteria
When antibiotics are used on these groups of bacteria all the bacteria get killed apart from the bacterium that is resistant to antibiotics
This bacterium survices and reproduces without competition from other bacteria and other time the resistent strain rises
The resistant strain now spreads and there is no longer effective treatment
How can we reduce the spread of resistant bacteria?
Doctors should prescribe antiobiotics appropriately
Patients should complete their course of antibiotics
Restrict the use of antibiotics in farming
Whats the problems with developing new antibiotics?
Expensive
Time consuming
How are organisms classified?
Organisms are classified into species based on their structure and characteristics
How did Linneaus classify organisms?
Firstly he organised them into two kingdoms
Animal and plant kingdom
He then divided each kingdom into smaller categories
What are the catergories? (Using a abrevation)
Kingdom - King
Phylum - Philip
Class - Came
Order - Over
Family - For
Genus - Good
Species - Soup
What is the binomial name?
The mixture of the genus and the species
What advances have been made for these catergories?
Microscopes can be used now to examine the internal structure and DNA not the internal structure
Whats the three domain system?
Archae
Found in extreme hot conditions
True bacters
Eg the kind that live in the human digestive system
Eukaryote
This includes animlas, plants and fungi (and protist)
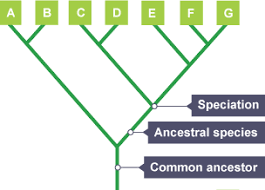
What are the function of evolutionary trees? How are they made?
Show how closely related organisms are to each other
They are made using classification data on living organsims eg their DNA
However they use fossils for extinct animals
Why can using fossil records for evolutionary trees be a problem?
Fossil records of a species may be incomplete
Example of a evolutionary tree