Asynchronous Intro to Patho/Pharm
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Health: state of complete
physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely as the absence of disease or infirmity
Disease:
a biologic or psychologic alteration that results in a malfunction of a body organ or system
Illness:
a sickness or deviation from a healthy state; the term has a broader meaning than disease
Illness Terminology
Acute
Typically
Patient recovers back to
Subacute
Longer than
Chronic
Present for
May have periods of
May include
We have seen a shift from
Acute
Typically short lived, self-limiting, and responds to specific treatment
Patient recovers back to their previous health status (full recovery), typically in a predictable sequence
Subacute
Longer than a few days but shorter than several months
Chronic
Present for longer period of time
May have periods of worsening (can be acute or subacute)
May include permanent disability, long-term medical management of physical/cognitive problems
We have seen a shift from communicable chronic diseases to non-communicable
Etiology
disease causation
idiopathic
unknown cause
iatrogenic
effect of medical treatment
pathogenesis
how disease develops
Signs
Symptoms
These are
Signs
what can be seen and measured
Symptoms
what the patient describes
These are manifestations of disease
Syndrome
groups of signs and symptoms that occur together
remission
manifestations occur
exacerbation
manifestations of an existing disease/condition increase
Psychosocial Aspects of Illness
Personality type will play a role in recovery (independent vs. dependent)
Fear, anxiety, denial
Disability
An individual with a disability is defined by the ADA as a person who has a
_____, _______ domains
Not all disabilities are _____
An individual with a disability is defined by the ADA as a person who has a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities, a person who has a history or record of such an impairment, or a person who is perceived by others as having such an impairment.
Physical, cognitive domains
Memory, executive function, processing issues, ability to learn, problem solving, behavior issues
Not all disabilities are visible
Health state of an individual
Factors:
genetic influence
cognitive abilities
age
sex
environment, life style
geographic location
culture
religion
standard of living
health beliefs, practices
previous health experiences
support systems
Role of PT in Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
Primary
Disease prevention
Who may be susceptible to a given disease?
Risk factor assessment
Wellness activities
Removing or reducing risk factors
Role of PT in Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
Secondary
Tertiary
Secondary
early disease detection
Screening programs
Tertiary
limiting the impact of established disease
Genetic Aspects of Health and Disease
Individual
Impact of
Genetic variations may make one more susceptible to certain
We need to be prepared to
Individual genetic differences/variation
Impact of family history on acquiring disease and disease progression
HTN
Stroke
Alzheimer disease
Parkinson disease
OA
Genetic variations may make one more susceptible to certain diseases/severity of disease/disease progression/response to physical therapy interventions
We need to be prepared to support our patients with hereditary disease patterns and or/that undergo genetic testing
Epigenetics
Looks at how biology and the
Looks at how biology and the environment exert their effects on a person and how genes express themselves
SDOH
Lifestyle choices
Other variations in client presentation
Race and ethnicity
Gender
Race and ethnicity
Biology is not the causative factor as to why some groups experience some diseases more commonly
Related more to social and cultural influences
Gender
Are some biological differences, but epigenetics also play a large role
Gender as a social construct
What is a child exposed to at an early age?
Stigma of LGBTQ status and stress
Other Epigenetic Influences
Nutrition
Obesity
Physical activity levels
Smoking/Tobacco/ETOH/Other drugs
What does this mean for us as physical therapists?
Need to understand how disease and the
Need for
Need to understand how disease and the movement system are related, and how this may change across the lifespan
Need for individualized attention and prescription for our patients
Person centered care
Understanding the role of the patient’s physical, social, emotional, psychological systems and how we can best support the patient on all levels
Understanding how cultural beliefs may alter therapy (ie. No blood transfusions for Jehovah witnesses; fasting for religious reasons)
Reasoning for learning about pharmacology
Your patients/clients may be taking over the counter or prescription medications
Want to avoid adverse interactions between medications and PT interventions
Timing of sessions with respect to drug administration for optimal participation
Pharmacology subgroups
Pharmacotherapeutics
Toxicology
Pharmacotherapeutics subgroups
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
how the body deals with the drugs
Pharmacodynamics
what the drug does to the body
Pharmacokinetics subgroups
Absorption
Distribution
Elimination
Also includes administration and metabolism
Pharmacodynamics subgroups
Systemic effects
cellular effects
Example: Ibuprofen
Pharmacotherapeutics:
Pharmacokinetics:
Pharmacodynamics:
Pharmacotherapeutics: reduces hormones to decrease pain and inflammation
Pharmacokinetics: p.o. administration; absorbed in stomach; excreted through metabolism and urine
Pharmacodynamics: decrease in pain, fever, inflammation
Drug Nomenclature
Chemical name
Generic name (official name)
Trade name (brand name)
Chemical name
(RS)-2-(4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl)propanoic acid
Generic name (official name)
ibuprofen
Trade name (brand name)
Advil TM
Motrin TM
Prescription vs. Over-the-Counter
Prescription
Requires order and dispensing by
Over-the-Counter (OTC)
Non-
Consumer can
Usually for more
Can still be
We need to be asking about what patients are
Prescription
Requires order and dispensing by authorized practitioner
MD, dentist, APRN, PA to name a few
Over-the-Counter (OTC)
Non-prescription
Consumer can directly purchase
Usually for more minor issues and have less toxicity risk
Can still be abused
We need to be asking about what patients are taking and educating them appropriately
***WE CANNOT PRESCRIBE OR ADMINISTER OTC DRUGS***
Common Abbreviations
bid
hs
q
qid
tid
prn
p.o.
bid
twice daily
hs
at bedtime
q
every/each
qid
four times daily
tid
three times daily
prn
as needed
p.o.
by mouth
Concepts in Drug Therapy
We need the drug to be able to reach the
Then, the drug needs to be able to
Need to give enough drug so that the
….but don’t want too much of the drug and have
_____-_____ RELATIONSHIP
We need the drug to be able to reach the target cell or tissue
Then, the drug needs to be able to exert its effect on that tissue
Need to give enough drug so that the benefit of the drug can be exerted….
….but don’t want too much of the drug and have toxic effect
DOSE-RESPONSE RELATIONSHIP
Dose Response Curve
Dose/Dosage
Enough to
Minimal
Ceiling effect or maximal efficacy
No greater
Dose/Dosage
Enough to do the job intended
Minimal toxic effects
Ceiling effect or maximal efficacy
No greater effect of the drug is noted if dosage is increased
Potency
Potency is related to the dose that produces a given response in a specific amplitude.
A smaller dosage of the blue drug will be needed to reach the desired response than the green or red drug.
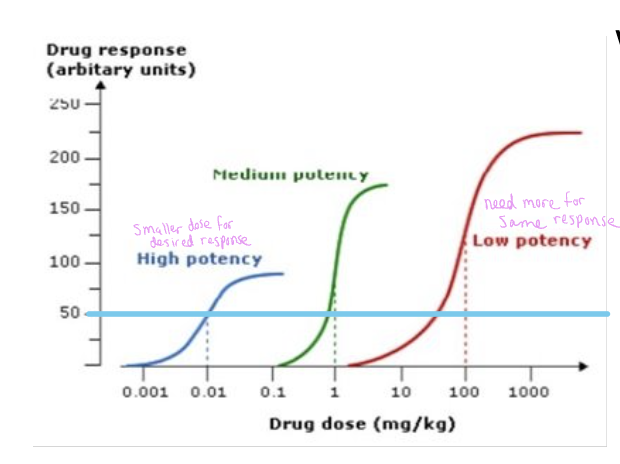
Therapeutic index
TI is used to calculate
Drugs such as chemo have a
In some cases of drugs with a low TI, blood levels may be monitored to decrease risk for
TI is used to calculate drug safety; higher TI = safer drug
Drugs such as chemo have a low TI, but in most cases the benefits of taking it outweigh the potential negative effects
In some cases of drugs with a low TI, blood levels may be monitored to decrease risk for toxicity