Electric Circuits & Forces – Key Vocabulary
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
30 vocabulary flashcards summarizing core terms and definitions from the lecture on electric circuits and forces.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Parallel circuit
A circuit with multiple branches where the voltage is the same across every branch but current splits between them.
Series circuit
A circuit with a singular path; the current is identical everywhere, but voltage divides across components.
Branch (in circuits)
An individual path in a parallel circuit containing one or more components through which current can flow.
Current (I)
The flow of electric charge per second, measured in amperes, detected with an ammeter.
Voltage (V)
The amount of energy the electrons have. Stays equal across branches in parallel circuits and divides in series circuits.
Ohm’s Law
The relationship V = I x R, showing how voltage, current, and resistance are connected.
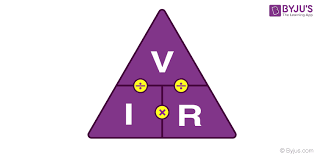
Resistance (R)
Opposition to current flow; greater resistance lowers current and causes a larger voltage drop.
Wire resistance (length effect)
Longer wires have higher resistance because electrons encounter more material.
Wire resistance (width effect)
Wider wires have lower resistance, giving electrons more paths to move through.
Light-bulb brightness in series
Adding bulbs makes each dimmer because voltage is shared among them.
Light-bulb brightness in parallel
Adding bulbs keeps brightness unchanged because each branch receives full supply voltage.
Switch in a parallel circuit
A control that opens or closes only its own branch without affecting others.
Force
A push or pull that can change an object's shape, speed, or direction; measured in newtons.
Push
A force directed away from the source (e.g., hitting a ball).
Pull
A force directed toward the source (e.g., towing a car).
Newton (unit)
The SI unit of force, measured with a force meter; arrow length often represents its size and direction.
Balanced forces
Equal and opposite forces that cancel, causing no change in motion.
Unbalanced forces
Forces that are not equal, resulting in acceleration or change in motion.
Newton’s First Law
Newton’s First Law states: An object remains in its state of motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force
Newton’s Second Law
Newton’s Second Law states: The acceleration of an object depends on its mass and the net force acting on it.
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Newton’s Third Law
Newton’s Third Law states: For every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.
Air resistance
A frictional force exerted by air that opposes the motion of objects through it.
Gravity
Attractive force between masses that pulls objects toward each other (e.g., toward Earth).
Electrostatic force
Force between electrically charged objects, either attractive or repulsive.
Tension
Pulling force transmitted through a rope, string, or cable.
Compression
Pushing (squashing) force that shortens or squeezes a material.
Friction
Force that resists motion between two contacting surfaces.
Thrust
Forward-directed push that propels an object, such as a rocket or airplane.
Buoyancy
Upward force exerted by a fluid on an immersed object.
Magnetic force
Attraction or repulsion between magnetic materials or moving charges.
Support Force
The upward force that balances the weight of an object resting on a surface, preventing it from falling.