HESI A2 BIOLOGY
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
kingdom
largest and most inclusive category
species
most restrictive category
hierarchic organizational system
kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genius, species
steps to an experiment
1. observation
2. hypothesis
3. experiment
4. conclusion
observation
data is observed and recorded/ previous data is studied
hypothesis
a statement or explanation of certain events or happenings
experiment
repeatable procedure of gathering data to support or refute the hypothesis
conclusion
where the data and its significance are fully explained
aqueous
water based
water molecule consists of
two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to one oxygen atom
most significant aspect of water is
the polarity of its bonds that allows for hydrogen bonding between molecules
specific heat
the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 1 gram of that molecule 1 degree celsius
water has high specific heat due to
the extent of hydrogen bonding between water molecules, which allows waters to resist shifts in temperature (ability of oceans or large bodies of water to stabilize climates)
cohesion
the ability of a molecule to stay bonded or attracted to another molecule of the same substance (water running together on a newly waxed car)
adhesion
the ability of water to bond to or attract other molecules or substances (when water is sprayed onto the wall, some of it sticks to the wall)
when water freezes it forms
lattice crystals; causing the molecules to spread apart, resulting in the phenomenon of ice floating
polarity of water allows it to act as an
versatile solvent (used to dissolve a number of different solvents)
carbohydrates
longs chains, or polymers of sugar
-used for storage, structure, and energy
-the backbone of important molecules such as DNA and RNA
lipids
known as fats, but specifically they are fatty acids, phospholipids, and steroids
fatty acids
Vary greatly but simply are grouped into two categories: saturated and unsaturated
saturated fats
contain no double bonds in their hydrogen tail
-solids at room temp
-lead to cardiovascular problems associated with diets
unsaturated fats
have one or more double bonds
-liquid at room temperature
phospholipids
-consist of two fatty acids of varying length bonded to a phosphate group
-phosphate group is charged and therefore polar and soluble in water
steroids
-component of membranes
-precursors to significant hormones and drugs
proteins
-most significant contributor to cellular function
-polymeres of 20 molecules called amino acids
-complex, consist of several structural types and are the largest biological molecule
enzymes
particular types of proteins that are used to catalyze different reactions or processes
(physical factors such as temperature and pH can alter the activity because they have an effect on the shape)
*enzymes speed up reactions
Nucleic Acids
-components of the molecules of inheritance
-DNA and RNA
DNA deoxyribonucleic acid
unique molecule specific to a particular organism and contains the code necessary for replication
RNA ribonucleic acid
used in transfer of information from DNA to protein level and as a messenger in most species of the genetic code
metabolic pathways
progressing from a standpoint of high energy to low energy.
metabolism
sum of all chemical reactions that occur in an organism
prokaryotic cells
lack a defined nucleus and do not contain membrane bounded organelles
(prokaryote: bacteria and cyanobacteria)
eukaryote cells
have a membrane inclosed nucleus and a series of membrane bound organelles that carry out the functions of the cell as directed by the genetic information contained in the nucleus
(eukaryote: all living organisms except eubacteria and archaebacteria)
nucleus
contains the DNA of the cell in organized masses called chromosomes
chromosomes
contain all the genetic information for the regeneration (repair and replication) of the cell, as well as all instructions for the function of the cell
ribosomes
organelles read the RNA produced in the nucleus and translate the genetic instructions to produce proteins
-found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (bound ribosomes) and the cytoplasm (free ribosomes)
endoplasmic reticulum
membranous organelle found attached to the nuclear membrane and consists of 2 continuous parts (smooth ER and rough ER)
rough ER
-covered with ribosomes
-responsible for protien synthesis and membrane production
smooth ER
-lacks of ribosomes
-it functions in the detoxification and metabolism of multiple molecules
golgi apparatus
transports proteins from the ER throughout the cell
lysosomes
-intracellular digestion takes place here
-hydrolyze proteins, fats, sugars and nucleic acids
-acidic environment (ph of 4.5)
vacuoles
membrane inclosed structures that have various functions depending on cell types
phagocytosis
uptake food through the cell membrane creating a food vacuole
vacuole in plant cells
functions as storage, waste disposal, protection, and hydrolysis
two distinct organelles that produce cell energy
1. mitochondria (eukaryotic cells and are the site of cellular respiration/energy)
2. chloroplast (found in plants and are the site of photosynthesis)
cellular membrane
-consist of a bilayer of phospholipids with proteins, cholesterol, and glycoproteins peppered throughout
-phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, creating a hydrophobic region between the two layers making it selectively permeable
Adenosine triphosphate ATP
used as the energy currency of the cell
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH
-acts as a reducing agent and is a vehicle of stored energy
-used as a precursor to produce greater amounts of ATP in the final steps of respiration
glycolysis
-first step of metabolism of food cellular energy is the conversion of glucose to pyruvate
-takes place in the cytosol of the cell and produces two molecules of ATP, two molecules of pyruvate and two molecules of NADH
citric acid cycle (Krebs Cycle)
-in step 2 the pyruvate is transported into a mitochondrion and used in the first of series of reactions
-takes place in the mitochondria
-two ATP molecules, 6 molecules of carbon dioxide and 6 NADH molecules are produced
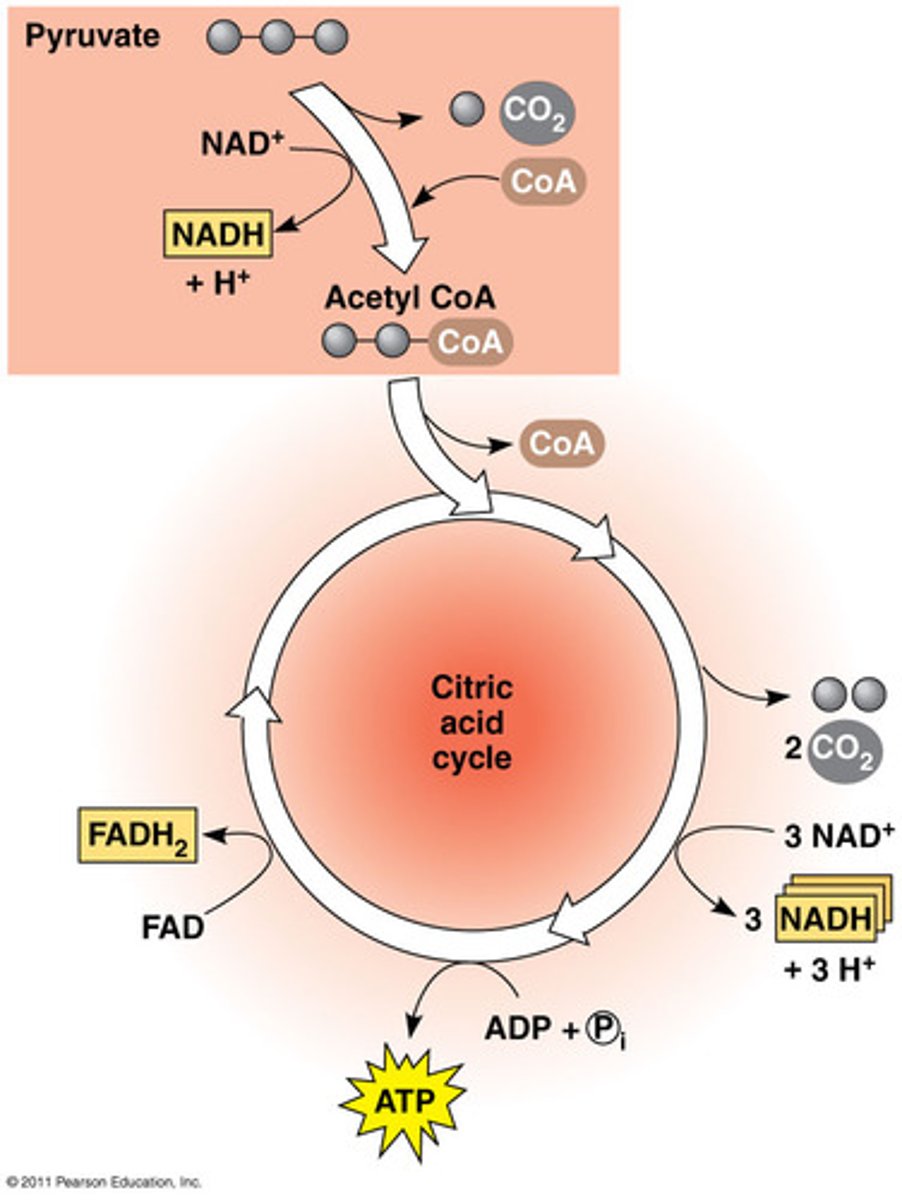
electron transport chain
3rd step begins with the oxidation of the NADH molecules to produce oxygen and finally to produce water
-for every glucose molecule 28-32 ATP molecules can be produced
cellular respiration ATP overall production
32-36 ATP
(C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O)
photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O + light --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Light reaction in photosynthesis
those that convert solar energy to chemical energy
-the cell accomplishes the production of ATP by absorbing light and using that energy to split water molecules and transfer the electron thus creating NADPH and producing ATP (these molecules are then used in the Calvin Cycle to produce sugar)
Asexual reproduction
1. binary fission
2. mitosis
binary fission
*involves bacteria
chromosomes bind to the plasma membrane where it replicates
-then as the cell grows it pinches into two producing two identical cells
mitosis
five phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telephase
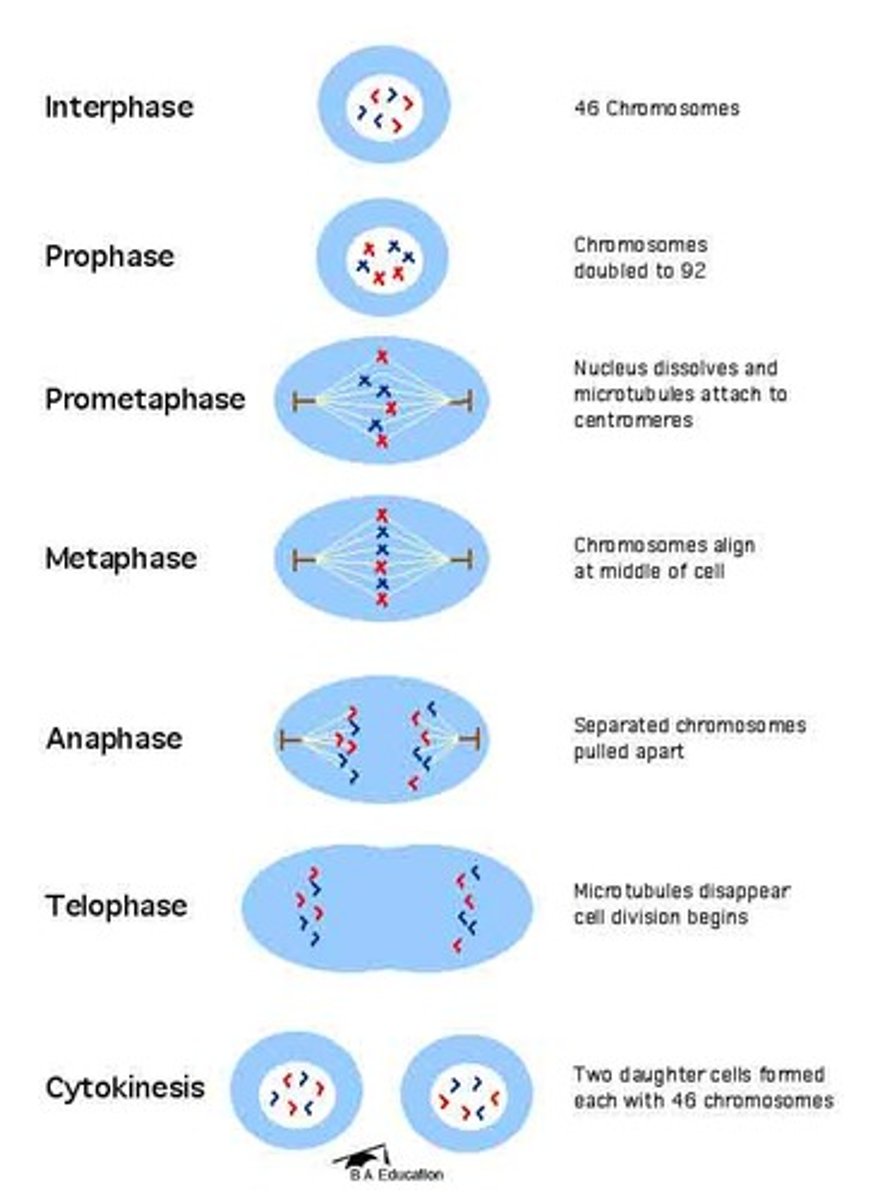
Mitosis prophase
chromosomes are visibly separate and each duplicate chromosome has two noticeable sister chromatids

mitosis pro-metaphase
the nuclear envelope begins to disappear and the chromosomes begin to attach to the spindle that is forming along the axis of the cell
mitosis metaphase
with all chromosomes aligning along what is called the metaphase plate, or the center of the cell
mitosis anaphase
begins when chromosomes start to separate
-chromtids are considered separate chromosomes
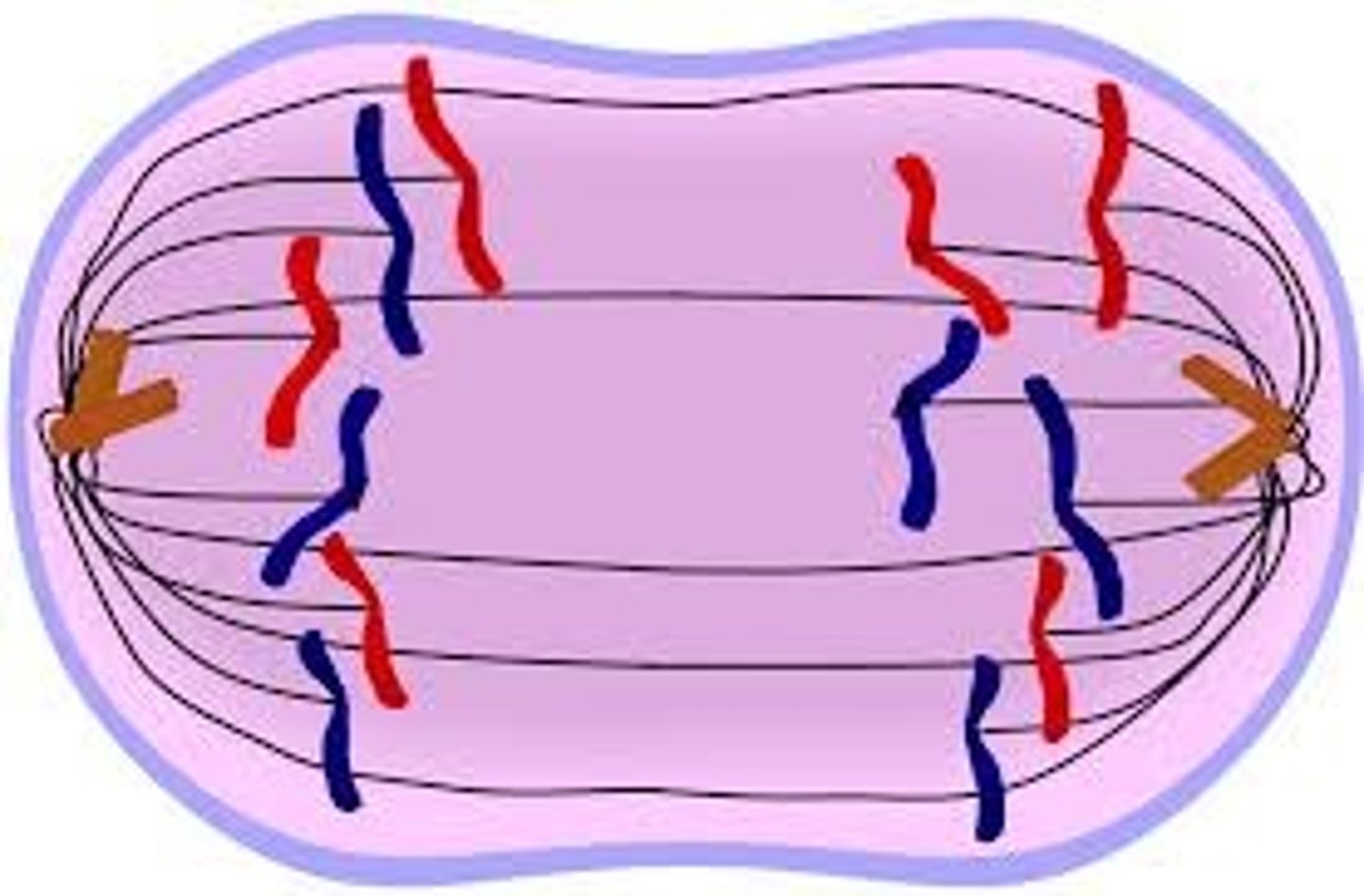
mitosis telophase
chromosomes gather on each side of the now separating cell
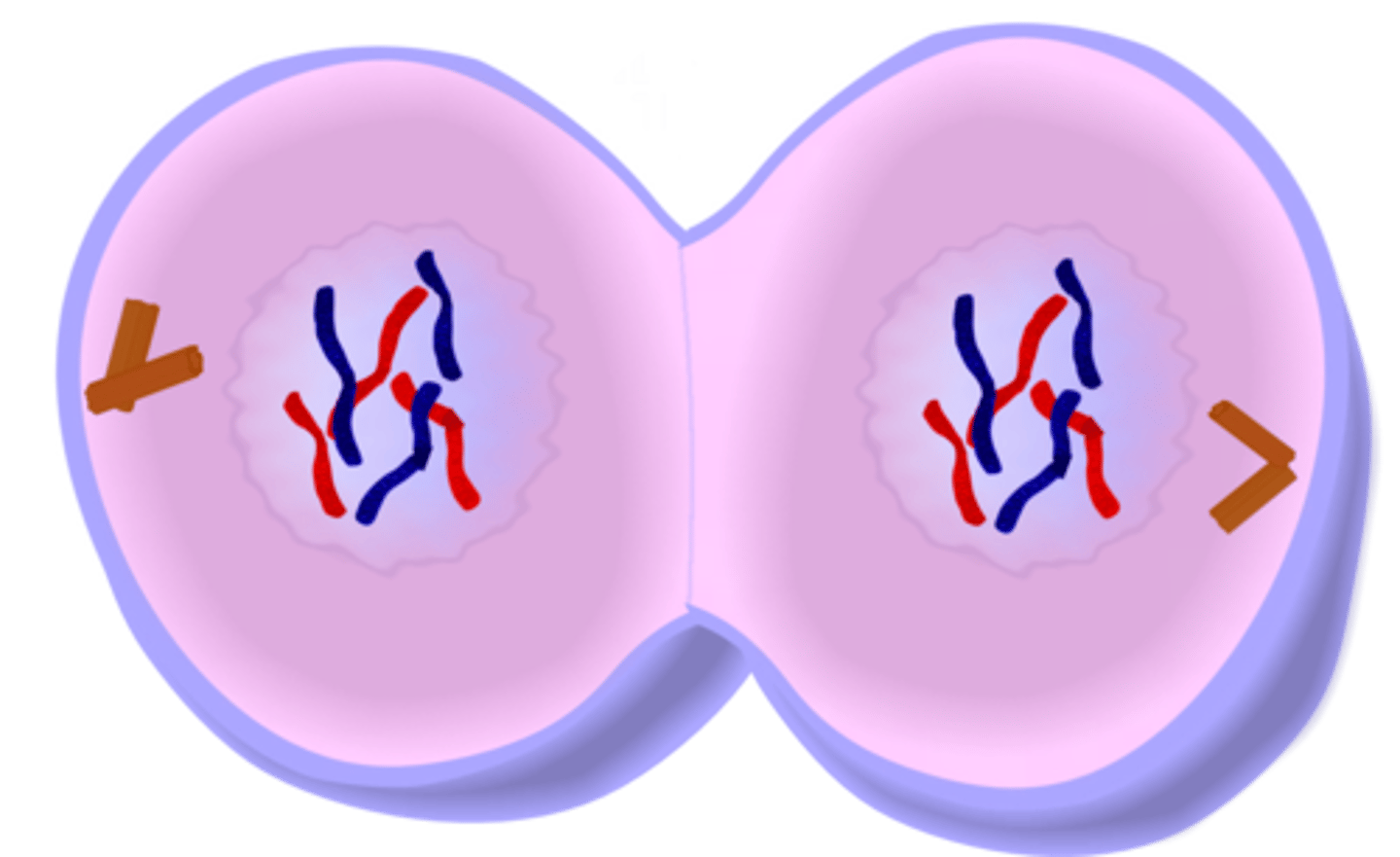
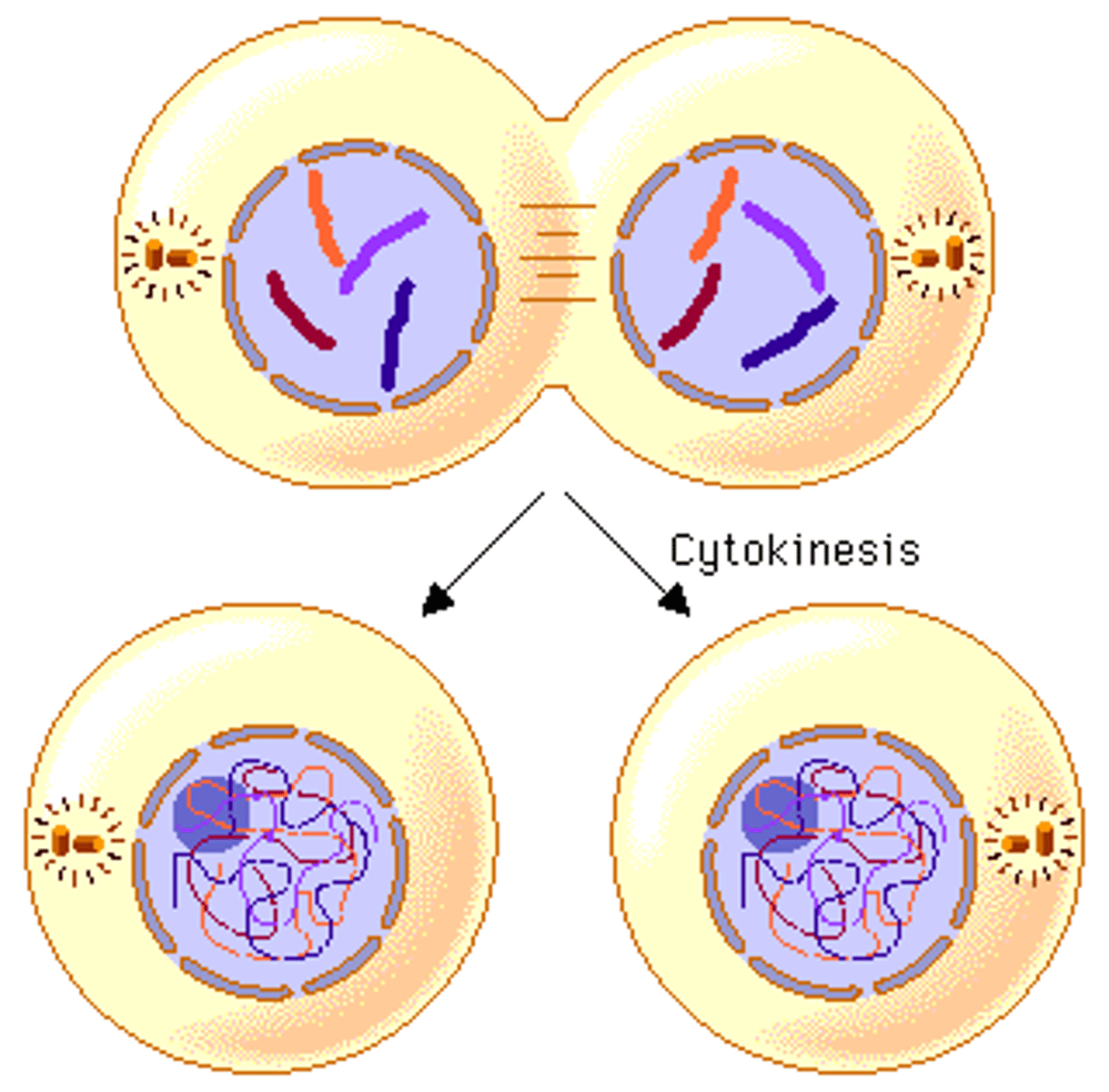
cytokinesis
separate from the phase of mitosis
-the cell pinches in two , forming two identical cells
Sexual reproduction
two cells contribute genetic material resulting in significantly greater variation
-these two cells find each other randomly making it virtually impossible for cells to be alike
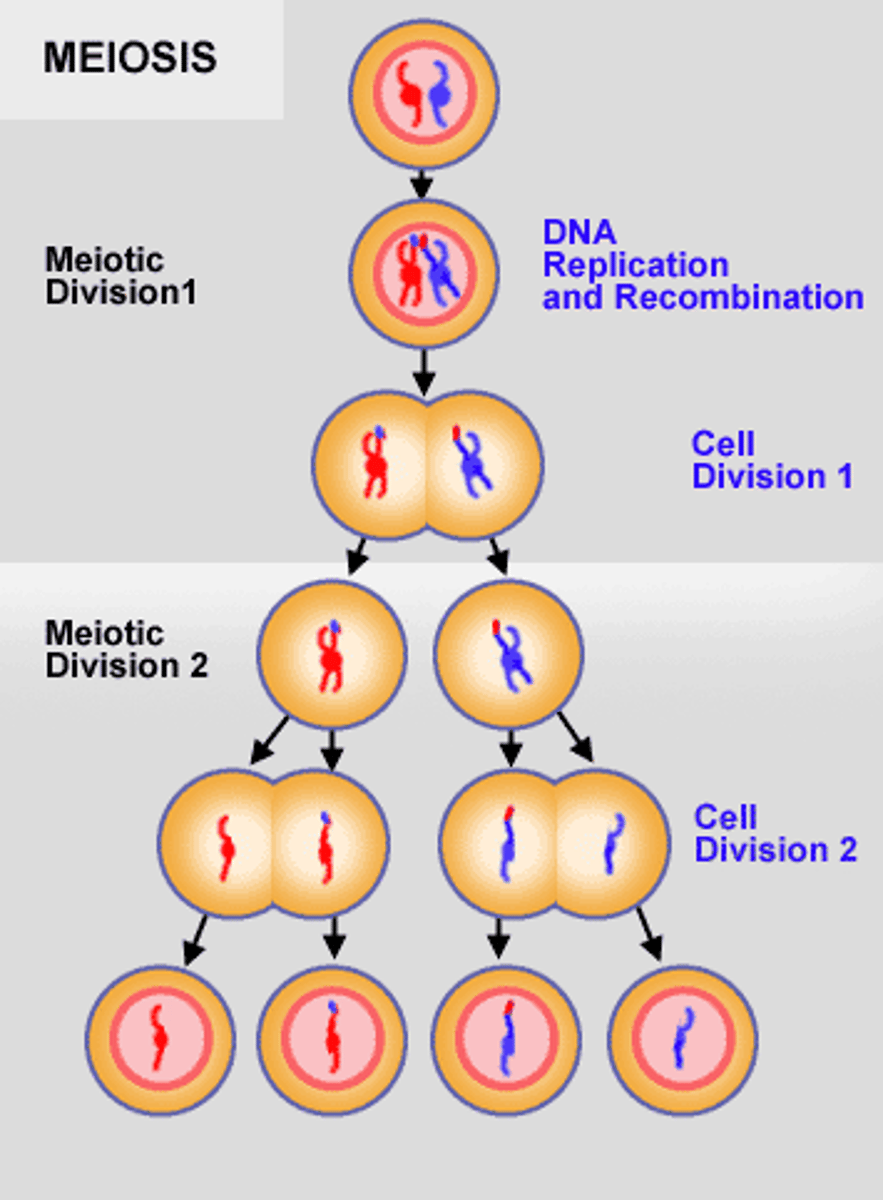
meiosis
consist of meiosis I and meiosis II resulting in 4 daughter cells
-each daughter cell contains half as many chromosomes as the parent
Gregor Mendal
discovered the basic of genetics; alleles
alleles
for every trait expressed in a sexually reproducing organism, there are at least two alternative versions of a gene
homozygous
if both alleles are the same type
heterozygous
if the alleles are different types
punnett square
by the use of this device, it is possible to predict the genotype and phenotype of the offspring of sexual reproduction
phenotype
physical appearance
genotype
genetic makeup
DNA
the genetic material of a cell and is the vehicle of inheritance
can't be altered
watson and crick
described the the structure of DNA
-double helix structure that contains four nitrogenous bases: adenine & thymine, guanine & cytosine
transcription
RNA strand, complementary to the original strand of DNA, is produced
mRNA (messenger RNA)
functions as a messenger from the original DNA helix in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytosol or on the rough er
codon
every three bases along the stretch of mRNA
tRNA (transfer RNA)
-anticodon is located here
-carries a specific amino acid
-binds to the ribosome when its codon is sliding through the ribosome
stop codon
the chain is released into the cytoplasm and the protein folds onto itself and forms its complete conformation
phloem
conducts water, sugar, amino acids and hormones from some source (metabolically producing or taking out of storage) to rest of the plant or to a "sink" (material is used up or taken out of circulation and put into storage)
xylem
conducts water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant
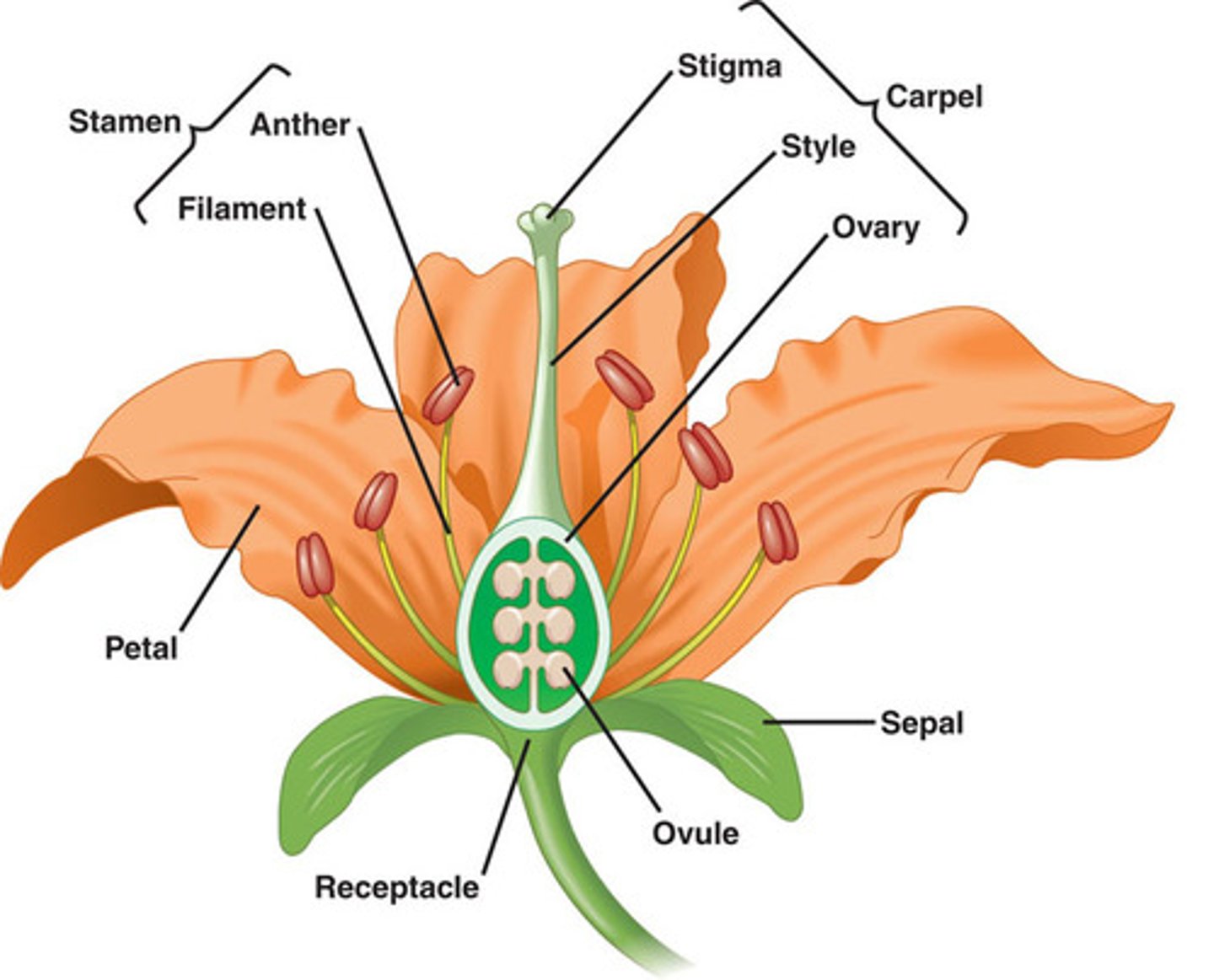
plant reproductive system
top: pistil
male reproductive parts (stamen)
-anther
-filament
female reproductive parts (carpel)
-stigma
-style
-ovary
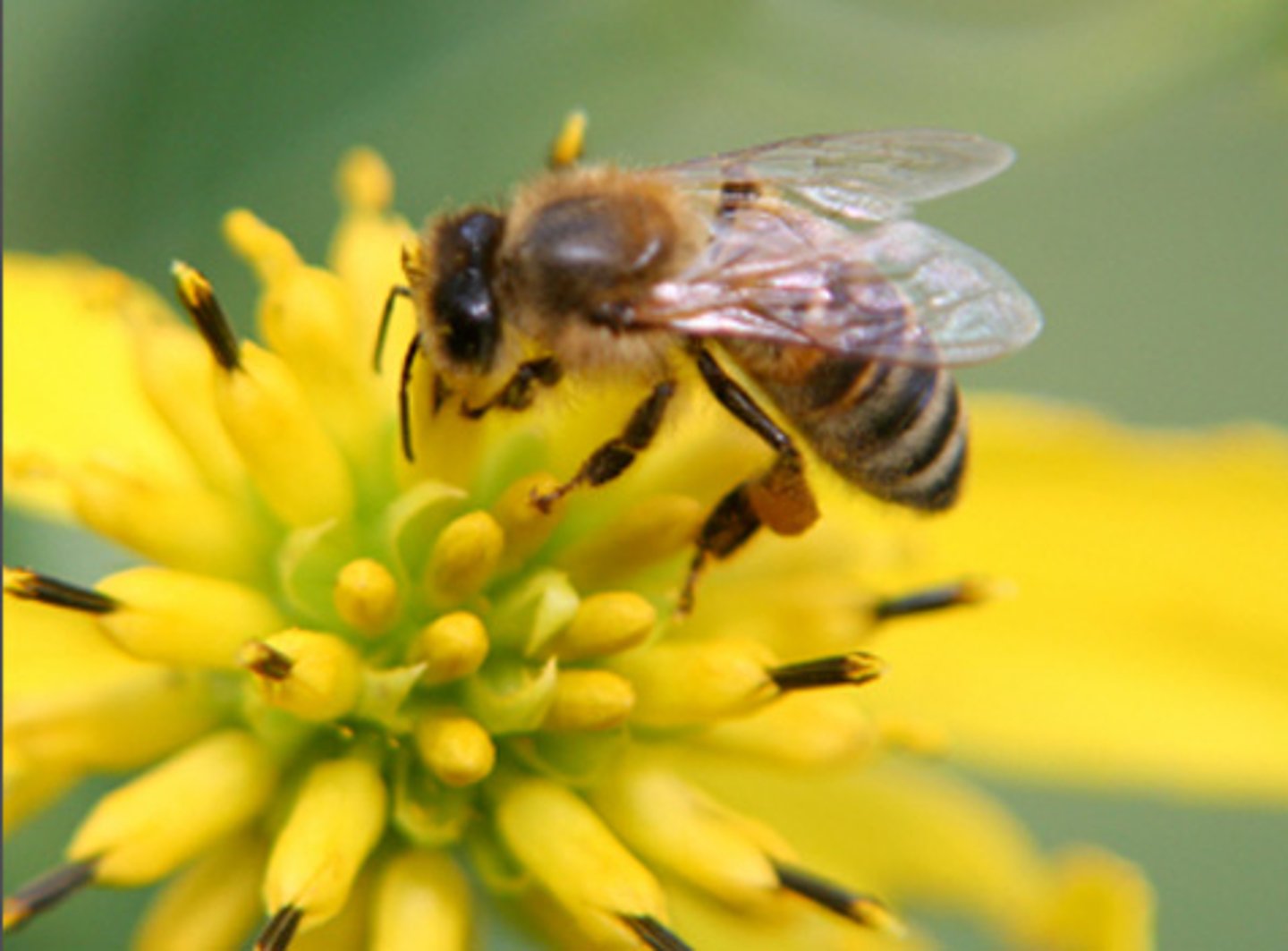
mutualism
both symbiotic organisms benefit

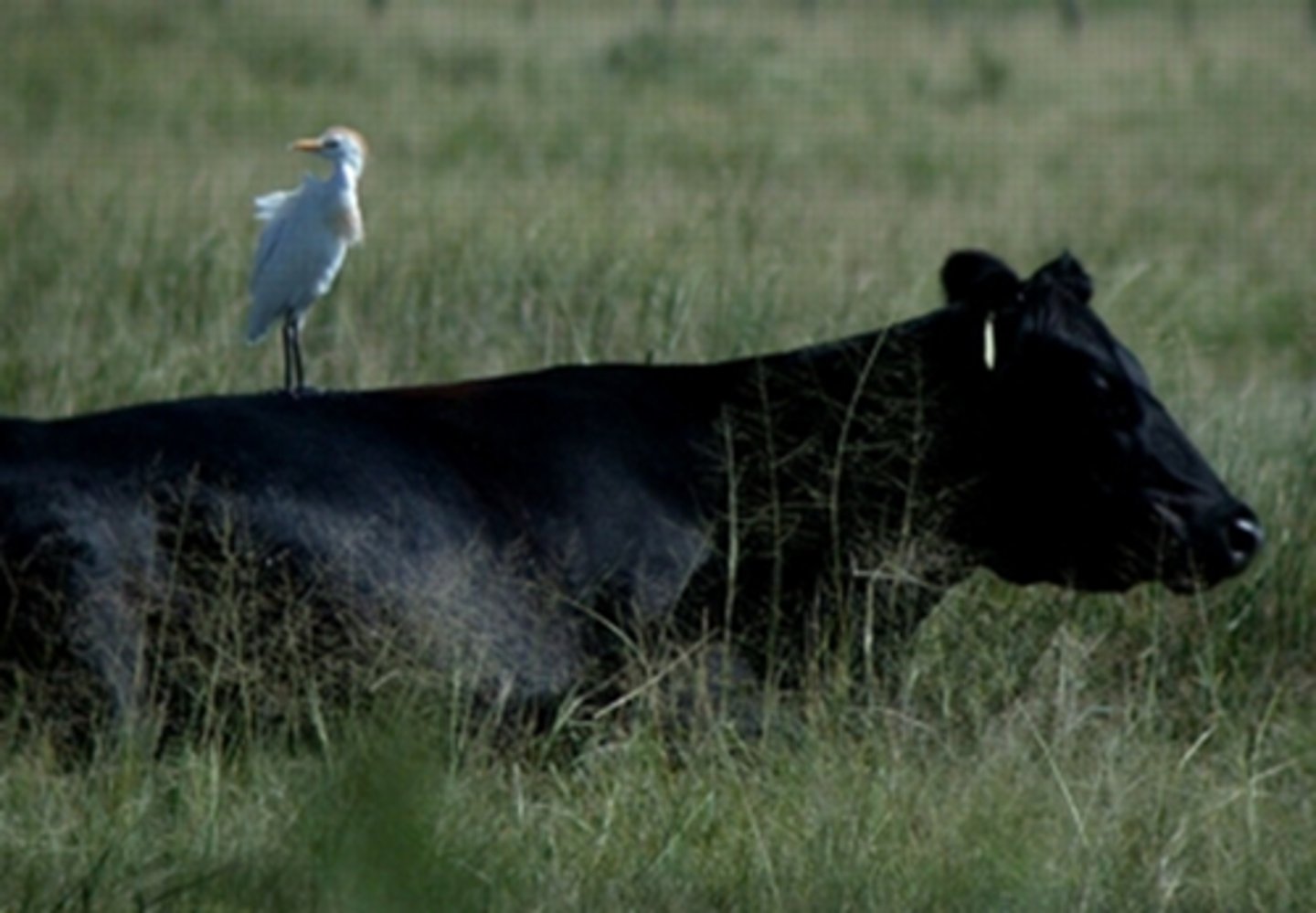
commensalism
one organism benefits while neither harming nor helping the other in any significant way

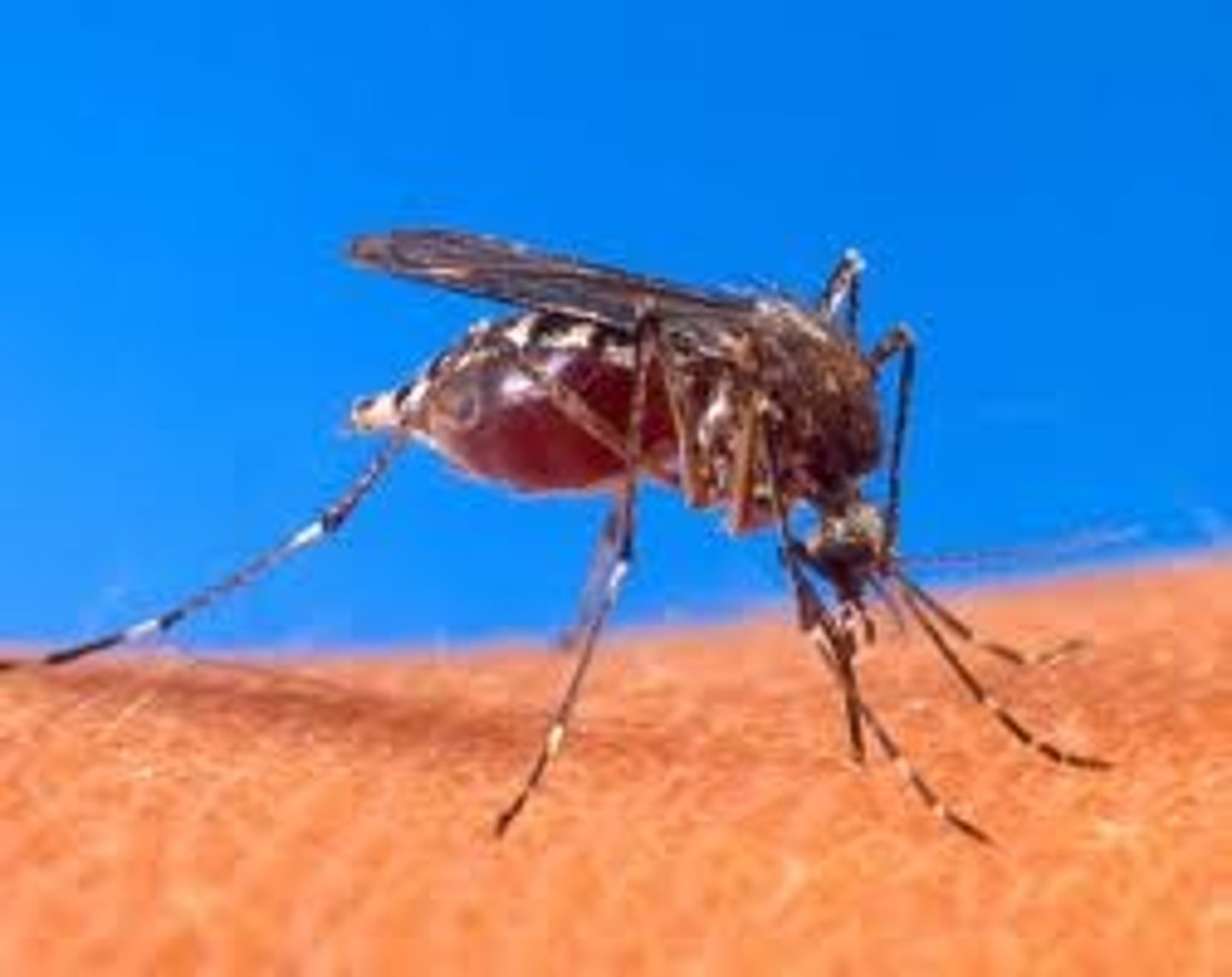
parasitism
an organism called a parasite harms but does not kill its host

steps of the water cycle
evaporation
condensation
precipitation
runoff/collection
percolation
mitosis
process cells in the tip of a plant's root undergo to increase in number
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
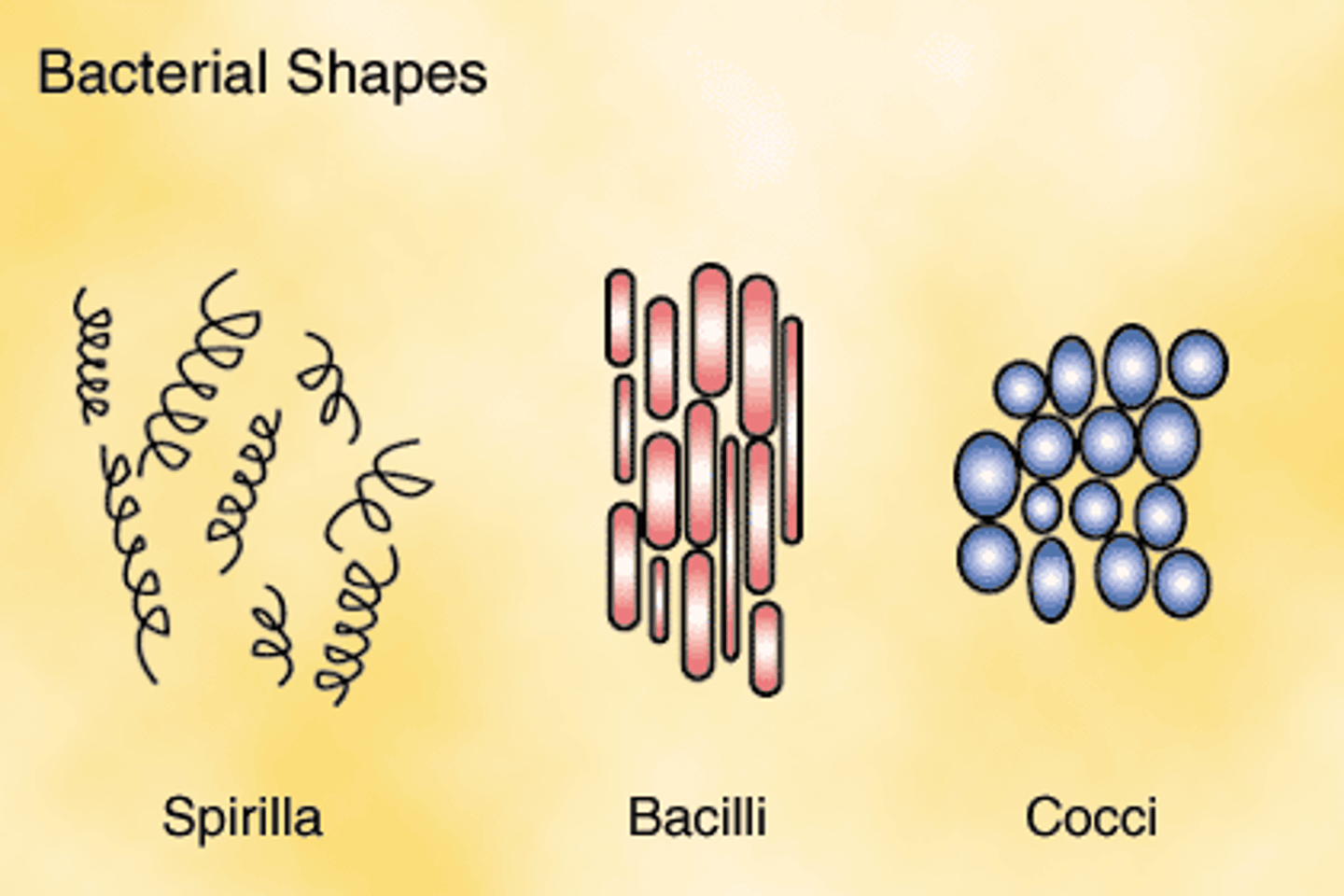
bacteria shapes
cocci (spherical) Chlamydia, spirilli (spirals) Spirochetes, bacilli (rods) Gram positive
Transpiration
the process where plants absorb water through the roots and then give off water vapor through pores in their leaves
intrachromosomal translocation
a segment breaks off the chromosome and rejoins it at a different location
hierarchy of a dog example
kingdom: animalia
phylum: chordata
class: mammalia
order: carnivora
family: canidae
genus: Canis
species: lupus
active transport
goes against its concentration gradient which means that it requires energy
low concentration to high concentration
passive transport
does not require energy
high concentration to low concentration