soil fertility 3rd midterm
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
phosphorous deficiency symptom
purple coloration
stunted growth, delayed maturity
lack of germination
lack of initial root development
reduced overall plant growth and stunted plants
phosphorous functions in plant tissues
structural component
DNA and RNA
phosphilipds in membranes
energy transfer
ATP and ADP conversion
starch and sugar utilization
required for starch remobiization
concentrats in the seed
which P compound is concentrated in the seed?
phytate
effects of P deficiency
smaller leaf area, less leaf development, shoot growth impaired
P present in plant tissue
mostly phosphate (PO43-) form
present in vaculoes
highly mobile inside plants, but compartamentalized
no redox reactions in plant tissue. Only one oxidation stage for P:5+
retranslocation within the plant: when? why
when and why plant tissues leak out P?
How is P delivered to the surface of plant roots
diffusion
slow P diffusion to root surface is due to (Challenge of P uptake)
precipitation, adsorption, microbial immobilization
How plants adapt to low P availability
grow more roots and root hairs
release organic acids (citrate) ad phosphatase to mobilize P in rhizosphere
high affinity P carriers (transporters)
association with mycorrhizae
why and how root hairs are important for P uptake
root hairs are physically capable of bridging small air gaps to scavenge P
P uptake happens ver close to the root surface
P transport
the protein carrier at the plasmelemma is a symporter (both elements are moving in the same direction)
most of the P as phosphate
most of the P in the vacuole
in which range of nutrient concentrations in the soil high affinity carriers and the low affinity carriers operate
high affinity: low Km values (do best with low nutrient concentrations)
low affinity: within a range of Km values (best with high nutrient concentrations)
mycorrhizae mutualism
barley, wheat, perenials are open to mycorrhizae infestation.
ratio of N:P in plant tussues
usually 10:1
manure: 2:1
too much P
50
Case: Using manure in terms of supplying balance N & P nutrients
Let’s assume that a crop will require 70 units of N and 10 units of P
In the case of using manure with a N:P ratio of 2:1 as a nutrient source, an initialcalculation would be supplying 10 units of total Pand 20 units of total N from adding manure, and the rest of the N (50 units) can come from other N source (e.g., synthetic fertilizer such as urea).
Of course we know that only some of the manure-N and manure-P are available in the first growing season (e.g., 50% of N becomes available, and 20% of P becomes available), and some of that good stuff stays residual for future seasons. Therefore, only these mineralizableN and Pto be released from the manure addition need to be accounted for; these availabilities can be quantified or estimated.
E.g., using these availability assumptions (20% of P and 50% of N), then 10 units of available Pand 50 units of available N would be sourced from manure, and the rest of the N (only 20units) could come from urea.
What is Km?
Michaelis constant. Measure of the affinity an enzyme has for its substrate (nutrient)
low km = high affinity: carrier binds its substrate eailt
high km = low affinity. Enzyme binds nutrient less easily
How does P help other nutrients flow too?
P fuels ATP needed to power uptake of other ions
_____ (aluminium sulphate) is effective in reducing ___ solubility in manures, thereby slowing accumulation of labile P in soils under repeated manure applications
alum, P
saturating the P retention capacity of soils can result in the ______ of water
eutrophication
what are the environmental risks of N
volatilization of ammonia
dentrification as nitrous oxide
nitrate leaching into gw
what are the environmental risks of P
P in surface runoff
leaching into gw
how much P is available in solid manure in the first year
20%
2nd: 12%
3rd: 6%
rock phosphate (apatite) fertilizer must be finely ground, and it is better when incorporated on ____ soils.
It is for long-term build up strategy, and can be partially _____ to increase P availability
it is the P source (raw material) for many P fertilizers, including triple superphosphate, MAP, and DAP
acidic, acidulated
synthetic phosphrous ferts
ammonium phosphates
manufactured by NH3 + H3PO4
P uptake is enhanced by presence of N
monammonium phosphate
diammoniu phosphate
most widely used P fert
may cause seed damage if too much seed is places - salt effect and acidifying
calcium orthophosphates
single superphosphate
7-9.5% of P off which all is availabe
triple superphosphate
17-23% P of which all is availabe
ammonium polyphosphate
can be applied in liquid form
potassium phosphate
phosphoric acid
used to manufacture other fertilizers
What is the most widely used P fert, and what is one of the warning about it?
DAP - diammonium phosphate
can cause seed damage. Salt effect and acidifying
triple __________ is high analysis, widely used and safer than DAP or MAP
superphosphate
ammonium _______ can be applied in liquid form, and sometimes reacted with urea to increase N content
polyphosphate
phosphorous and zinc ferrilization interaction
Zn fert helps when also adding P
added P is precipitated and removed from the soil solution any existing zn when no zn was added
only having both nutrient additions led to the highest yield
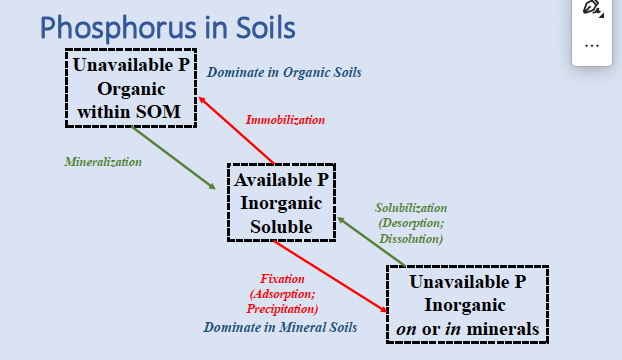
p cycle
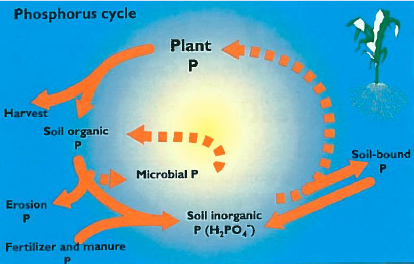
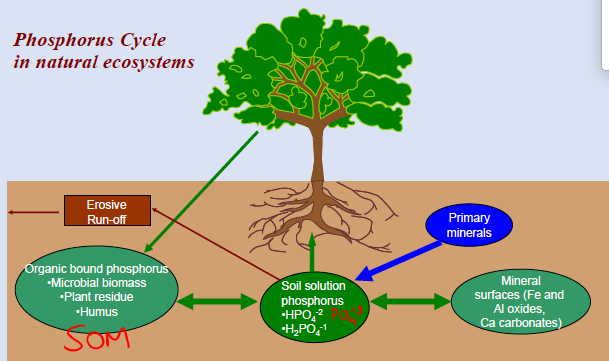
soil factors and P bioavailability
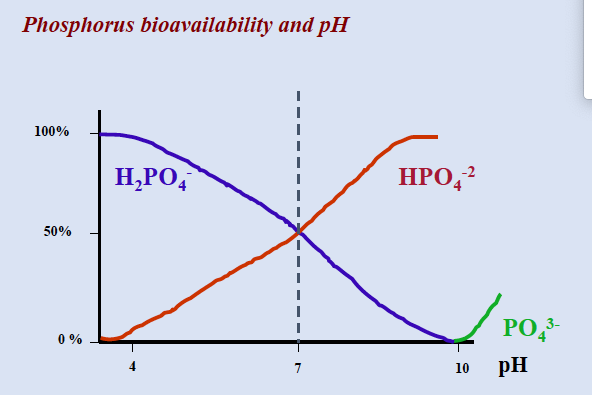
pH: max availability ~6.5
mineraology
acid soils controlled by al and fe compounds
neutral and alkaline soils controlled by ca and mg
buffer capacity
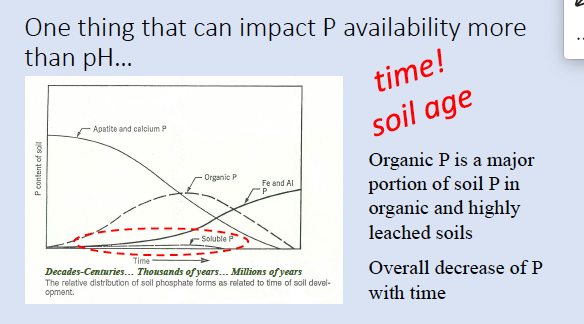
soil “age” or time (weatherin)
total amount of P present and form (organic vs inorganic)
phosphorous bioavailibility and pH
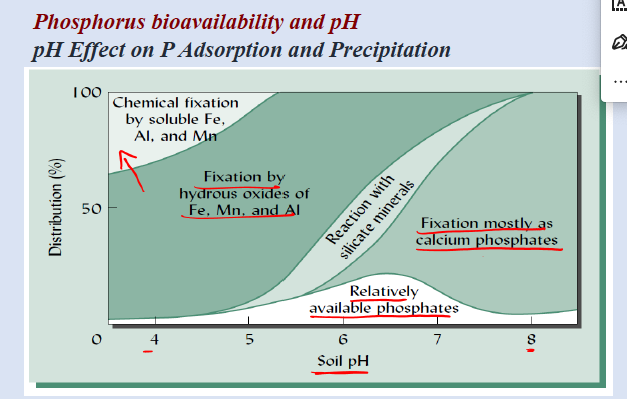
phosphorous bioavailability and pH
pH effect on P adsorption and precipitation
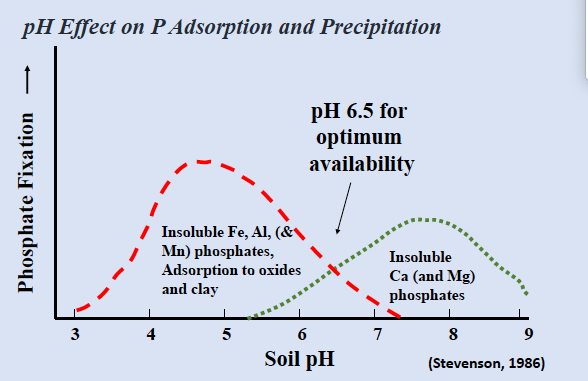
the least adsorption and precipitation at intermediate pH
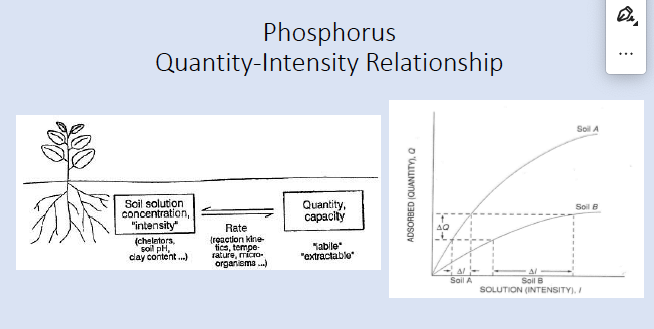
buffer capacity (quantity/intensity)
ratio between changes of nutrient concentrations in soluble vs solid states during nutrient additions or removals
mostly affected by soil states that exchange rapidly with soluble state (adsorbed) but also by precipitated and organic states
the two ways to model isothermms
freundlich
langmiur
what does P sorption depend on
the more clay the more sorption, but it also depends strongly in the type of clay present
buffer capacity of P - low P
when there is little P in the soil, there are many adsorption sites that are unoccupied, so a high proportion of P is adosrbed
buffer capacity: medium P
when P is added to a soil, the adsoprtion sites become more occupied with some of this P, and hence a higher proportion of P remains in the solution
buffer capacity high P
when there is a lot of P in a soil, the adsorption sites may become fully occupied (saturated), so no more P adsorption
the buffer capacity of potassium and phosphorous
20, 200
about _____ % of total p in agricultual soils is in inorganic form; however, only _____ in forest soils
75, 25
how much soil P
soils contain 500-2500 lbs p/acre
phosphours in soil solution usually <1 mg P L-1
remaining P (which is nearly all of it) is tied up in OM and minerals that are relatively insoluble
75% of total P in agricultural soils in in inorganic form; 25% in forest soils
available P is in what form in soils
inorganic soluble (mineralized)
how does pH affect adsorption-desorption of inorganic P
«5.5 —> greater density of positively charged exchange sites —> greater P adsorption in very acidic soils
»7.5 greater density of carbonate sites (Ca
greater P adsorption in very basic soils
adsorption-desorption is dependent on
surface density of Al and Fe oxides
kinds of clays
allophae and imogilite > 1:1 clays > 2:1 clays
soil organic matter effects
temperature (higher temp —> more rapid reactions of sorption)
precipitation-dosolution
soluble P concentrations are in dynamic equilibtrium with Ca,___ and __ phosphate minerals
Al, Fe.
concentrations of soluble P at which equilibrium is reached depends strongly on pH
an example with a Fe-phosphate mineral is ____
strengite (FePO4)
with an acid pH, the reaction for the dissolution—-recipitation of strengite goes into _____ P form
precipitated
the Ca-phosphate mineral, dicalcium phosphate:
at a pH <7.8 forces reaction to _____ P form
soluble
ca-phosphate mineral dicalcium phosphate, pH >7.8 and in the presence of CO2, forces reaction to _____ P form
soluble
which fixed P dominates around AB?
calcium bound (ca-P)
because they are less weathered and have a high PH
weathered + low pH —> precipitated ot adsorbed (tropics)
P is rapidly fixed in soil solution by Fe, Al, Ca. In acidic soils, fixed P can occur on the surface of:
aluminum oxides and hydroxides such as _____
iron oxides and hydroxides such as _______ or ______
gibbsite
geothite, hematite
in alkaline soils, fixedP IN or ON _______ phosphate ot tricalcium phosphate or HPO42-
dicalcium
soil tests to measure available P in acidic soils
bray 1
soil test to measure available P in neutral, alkaline, or calcarous soils
olsen
mehlich 3 soil test is universal?
form of potassium in soil
nearly all K is in the inorganic form in soils
tied up as part of primary minerals (feldspar, micas)
tied up in the interlayers of clay minerals
relatively immobile in soil (some movement in sandy)
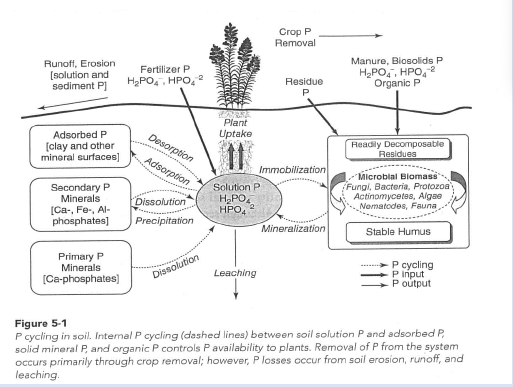
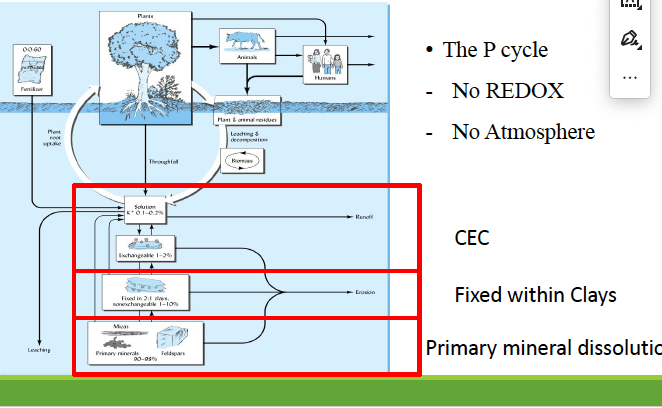
the P cycle
fixation of K+ in soil depends on the type of clays
2:1 clay
interlayer K —> slowly available K
soils that are K fixers vs non-fixers
montmorillonite
illite
vermiculate
non-fixers
OM
kaolinite
chlorite
micas
potassium slides
how soil moisture infuences k+ availability
effect on K diffusion
higher tortuosity in dry soil
diffusion path increases at low soil moisture
saturated soils decrease K uptake
How temperature influences K+ availability
plant root growth reduced at low temps
high soil temps increase K release rate from solid phase (don’t oven dry soil samples being tested for K)
how soil mineralogy and textire effects k+ availability
2:1 clays fix and release K+
nearly all K is in the ____ form in soils. It is relatively ____ (mobile/immobile) in soils
inorganic, immobile
most soil K is tied up as part. ofprimary minerals such as ______ and ______ or tied up in the interlayers of clays (illlite, montmoriilonite, vermiculite)
feldspars, micas
the P cycle has no _____ and no _____
redox, atmosphere
______ of structural Fe3+ to Fe2+ INCREASES 2:1 layer charge, fixing K+
reduction
Oxidation of sructural Fe2+ to Fe3+ ______ (increase/deceases) 2:1 layer charge releasing K+
decreases
K fixers include:
montmorillonite (smectite clay)
illite (clay-sized mica)
vermiculite (clay)
K non-fixers
OM
kaoloinite (clay)
chlroite (clay)
micas
factors influencing K+ availability
soil moisture (effect on K diffusion)
temp
soil mineralogy and texture
2:1 clays fix and release K+
long-term availaibilitty of K in soils is greater with 2:1 clays
more overall K availability with clayey soils than sandy soils
higher CEC increases K availability
less availabiity with coarse/sandy soil
what is the affinity sequency for exchangeabe sites
al3+ > H+ >Ca2+ >Mg2+ > K+
other factors that influence K availability
interactions with other nutrients
activity of base cations (Ca2+, Mg2+)
K avilaibility ratio (K+/ (Ca2+ + Mg2+)
tillage management
reduced or no till
PM
micas vs feldspars
NOT commonly deficient in prairie soils (unlike N and P) =
K+ is also responsible for _____ translocation within plants
sugar
K+ deficiency symptoms appear on ____ (older/younger) leaves
older
K+ deficiency symtpoms
yellow leaf margins
slow growth
weak root systems
brittle stems
the most widely used K fert is potassium _____, which is often known as muriate of ______ (MOP_
chloride, potash
potassium sulfate is good for ___ sensitive crops such as _____
Cl, tobacco, potato
What are the three main pools of K in soil?
mineral
fixed
exchangeable
What is the largest pool of K in soil?
structural
HowdoesK become exchangeable or fixed in soil?
weathering of primary minerals
k+ trapped in clay
Which clay types are responsible for fixing or exchanging K?
What factors influence K availability insoil?
soil texture, mineraoligy, CEC, PM, pH, moisture
What function does K have in soil?
(in plant)
regulates water balance
enzyme activation
sugar transport
(in soil)
fixed in 2:1 clays
buffer capacity, involved in cation exchange
What are different types of K fertilizers?
potassium chloride, potassium sulfate
What visual deficiency are expected for N,P,K,S?
n - yellowing
p - dark green leaves
k = browning on edges
s - yellowing
What areadvantages/ limitations of using plant visual deficiency symptoms?
Whatis‘hidden hunger’?
nutrient deficiency symptoms not visible, but lower than optimal
Whatisthecriticalnutrientconcentration?
What information can we gather from nutrient ratios?
antagonistic and synergistic relationships
17:1 wheat N:S
s needed to use N