(PART 3) ASEXUAL & SEXUAL SPORES
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Asexual Spores
Are produced by mitosis and cell division without nuclear fusion.
Conidiospore
Sporangiospore
Two types of asexual spores:
Conidiospore (Conidium)
- A unicellular or multicellular spore that is not enclosed in a sac.
- Produced in a chain at the end of a conidiophore.
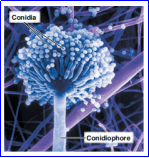
Penicillium
Aspergillus
Examples of Conidiospore (Conidium)
Arthroconidia
Blastoconidia
Chlamydoconidium
TYPES OF CONIDIA
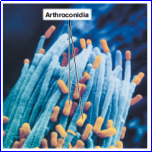
Arthroconidia
TYPES OF CONIDIA
Formed by the fragmentation of septate hypha into single, slightly thickened cells.
Coccidioides immitis
Example of Arthroconidia
Blastoconidia
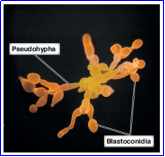
TYPES OF CONIDIA
Formed from the buds of its parent cell.
Candida albicans
Cryptococcus
Example of Blastoconidia
Chlamydoconidium
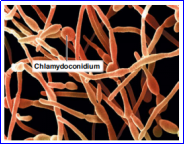
TYPES OF CONIDIA
A thick-walled spore formed by rounding and enlargement within a hyphal segment.
Candida albicans
Example of Chlamydoconidium
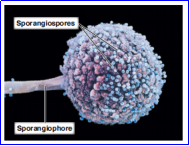
Sporangiospore
- Formed within a sporangium (sac) at the end of an aerial hypha called a sporangiophore.
- A single sporangium can contain hundreds of sporangiospores.
Rhizopus
Example of Sporangiospore
1. Plasmogamy: A haploid nucleus from a donor cell (+) penetrates the cytoplasm of a recipient cell (-).
2. Karyogamy: The (+) and (-) nuclei fuse, forming a diploid zygote nucleus.
Meiosis: The diploid nucleus undergoes meiosis, producing haploid nuclei (sexual spores), which may include genetic recombinants
Sexual spores result from sexual reproduction, which involves three phases:
Plasmogamy
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
A haploid nucleus from a donor cell (+) penetrates the cytoplasm of a recipient cell (-).
Karyogamy
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
The (+) and (-) nuclei fuse, forming a diploid zygote nucleus.
Meiosis
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
The diploid nucleus undergoes meiosis, producing haploid nuclei (sexual spores), which may include genetic recombinants.
Phyla
The type of sexual spores characterizes the fungal?
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
In clinical settings, asexual spores are primarily identified using microscopic examination, as most fungi display only asexual spores in lab conditions.
Chemoheterotrophs
Fungi absorb nutrients rather than ingesting them like animals.
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
Fungi is the same from bacteria in their environmental requirements and nutritional characteristics.
5
Fungi grow better in environments with a pH of about?
(which is too acidic for most common bacteria)
Molds
Mostly aerobic.
Yeasts
Mostly facultative anaerobes.
osmotic pressure
Fungi are more resistant to _______________ than bacteria, allowing growth in high sugar or salt concentrations
low moisture content
Fungi can grow on substances with ________________, conditions that are generally unsuitable for bacterial growth.
less nitrogen
Fungi require _______________ than bacteria for the same amount of growth.
carbohydrates
Fungi can metabolize complex __________ (e.g., lignin, a component of wood) that most bacteria cannot use for nutrients.
- Bathroom walls
- Shoe leather
- Discarded newspapers
Due to their nutritional adaptability, fungi can grow on unlikely substrates such as: