Psyc121 Final Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:56 AM on 6/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
What is a paradigm?
a set of shared assumptions, agreed methods and ways of thinking commonly accepted by members of a group
2
New cards
Who was the key figure involved in the psychodynamic perspective? What are its key principles/basic assumptions? Main contributions to modern psychology?
Sigmund Freud. Conscious + unconscious forces interact to control thoughts and behaviour. Awareness is like an iceberg, bulk of processes occur at an unconscious level. Obtain information through case studies of the client. Ego, superego and id. Main contributions: dreams, importance of childhood experiences.
3
New cards
Differentiate the ego, superego and id in the psychodynamic perspective
ego: rational mind. superego: moral component. id: innate, pleasure principle.
4
New cards
Criticisms of the psychodynamic perspective?
Unfalsifiable, uses qualitative data only.
5
New cards
Who was a key figure involved with the behaviourist perspective? What are its basic principles/metaphors/findings?
B.F Skinner. Aims to understand how the environment shapes behaviour. Metaphor: Humans + Animals are mechanistic. This means certain responses can be elicited through environmental stimuli. Primary contributions: Classic conditioning (involuntary eg. pavlov's dog) and operant conditioning (voluntary, eg. teaching a dog to fetch with rewards).
6
New cards
Criticisms of the behaviourist perspective?
Focus solely on nurture, dismisses internal workings of humans
7
New cards
culture
The shared rules that govern behaviour, the filter through which we understand reality. Includes shared values, norms, behaviours, and beliefs that distinguish one group from another.
8
New cards
cultural psychology
Examines how how cultural practices, norms, values, meanings, and social structures shape individuals. Does not assume universal properties to culture.
9
New cards
cross-cultural psychology
focuses on how culture influences human behaviour, aiming to explain the similarities and differences in how people think, feel, and behave across cultures.
10
New cards
emic perspective
A research approach that involves focusing on a specific cultural group and examining particular psychological aspects of that group. (cultural psychology)
11
New cards
etic perspective
A research approach that involves the search for commonalities or differences across cultures. (cross-cultural psychology)
12
New cards
cross-cultural comparison study
Research that involves comparing two or more different cultures in relation to a particular psychological variable.
13
New cards
cross-cultural study
Research that examines whether a psychological variable in one culture can be applied and have meaning in another
14
New cards
unpackaging study
Studies that try to explain why cultural differences occur, looking at the range of variables that might account for divergence in a particular aspect.
15
New cards
three methods of cultural and cross-cultural research
1. The study of individual cultures to determine relationships between the structures, values, belief sys- tems, language and practices of a culture and the behaviour of people living within that culture.
2. The comparison of human behaviour across different cultures.
3. The study of the interaction between cultures that co-exist in a larger societal context.
16
New cards
challenges of cultural psychology
research methods, equivalent samples, interpreting results, researcher bias, sensitive issues, WEIRD
17
New cards
WEIRD
White, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, Democratic
18
New cards
individualism-collectivism continuum
the extent to which cultures favour individual goals compared to communal goals and how this influences psychological processes - most popular way of measuring cultural variability
19
New cards
six dimensions of culture
time, emotion, interpersonal space, context, tight vs. loose, individualism vs. collectivism
20
New cards
monochronic cultures
divide time into closely regulated, linear segments - people are expected to be punctual, and activities are scheduled at specific and regular intervals
21
New cards
polychronic cultures
have a more fluid and less regulated perspective of time - people are not expected to be punctual, and pay less attention to observing strict deadlines or schedules
22
New cards
emotion and culture
cultures differ in relation to rules on the appropriateness of displaying certain emotions in particular social circumstances
23
New cards
interpersonal space and culture
intimate, social, and public zones of space. involves how people interact with spaces, and the cultural expectations of what distances are appropriate
24
New cards
high-context culture
pay close attention to nonverbal signs and conversational differences to decode the true meaning behind words or actions - emphasise interpersonal relationships and rely more on intuition and interpretation over logic
25
New cards
low-context culture
interpret what people say and do literally without regard for accompanying circumstances - rely on fact and logic, saying exactly what they mean
26
New cards
tight culture
expect members to closely adhere to cultural norms and expectations, deviation from group norms is not tolerated
27
New cards
loose culture
involve relaxed social norms where deviance to a degree is tolerated
28
New cards
individualist culture
an emphasis on the primacy of the individual over the group - people define themselves in terms of individual attributes and view their individual identity and needs as more important than group identity and needs.
29
New cards
collectivist culture
emphasise the group over individuals - people define themselves in terms of group attributes and see themselves primarily as part of a group and focus on the groups needs and identity
30
New cards
colonisation
involves the invasion of an area by a new group who often takes control and asserts sovereignty over the area and its people. cultural, economic, and political control
31
New cards
coloniality
refers to the continuation of the dynamics of colonialism in the present - ways of being, strategic relations of power, and the systems of knowledge that have roots in the colonial period and persist long after the end of colonial rule
32
New cards
multiculturalism
where multiple cultures exist within a country, and where the number of inhabitants representing those minority cultures is significant
33
New cards
pluralism
where there is a general acceptance not just of the existence of many different cultural and ethnic groups, but also their right to retain their cultural heritage and coexist
34
New cards
culture shock
the feeling of disorientation and anxiety that occurs as people from one culture encounter and adapt to another culture's practices, expectations and rules.
35
New cards
1. honeymoon phase
36
New cards
2. disenchantment phase
37
New cards
3. beginning resolution phase
38
New cards
4. effective functioning stage
39
New cards
acculturation
the changes that groups and individuals undergo when they encounter another culture - a process of integration where people adopt and adapt aspects of the new culture they enter, whilst retaining aspects of their cultural heritage
40
New cards
assimilation
absorption of the receiving culture and abandonment of home culture
41
New cards
integration
retaining home culture whilst also participating in the receiving culture
42
New cards
separation
retaining home culture with minimal engagement with the receiving culture
43
New cards
marginalisation
little connection with both the home and receiving culture
44
New cards
ethnic identity
where members of an ethnic group identify 'us' in relation to 'them' using aspects of shared culture, language or religion - ethnicity involves a shared sense of personhood
45
New cards
personal identity
the sense of who we are as individuals - reflects what we feel is unique about us and the combination of our personal values, traits, abilities, likes, aspirations, and life history
46
New cards
social identity
sense that we are part of a larger social group with salient attributes including values, meanings and goals - it is common to have multiple social identities, and feel a shared sense of belonging within these social groups
47
New cards
ethnocentrism
the tendency for a person's own culture to influence the way they view the rest of the world, people view the values, standards attitudes and behaviours of their culture as the 'norm' - a groups 'self-centeredness'
48
New cards
xenophobia
the fear or hatred of foreigners, or anything foreign or unfamiliar - based on a broad stereotype about any cultures different from your own
49
New cards
whiteness
'white' is a form of dominant expression of normative systems - whiteness represents a turn towards understanding power and privilege a how it is maintained in different domains
50
New cards
prejudice
an unreasonable and negative stereotype about members of another group - negative assumption made on the basis of their group membership
51
New cards
racism
the pervasive and systematic assumption of the inferiority of certain groups, and the different and unfair treatment of those groups on the basis of assumed inferiority
52
New cards
discrimination
the behavioural manifestation of prejudiced attitudes
53
New cards
a culturally skilled psychologist should:
be aware of their own cultural background, heritage and biases, and the differences that exist between themselves and those of other cultures. understand and respect the values, attitudes, and worldviews of other cultures, and the socio-political circumstances that impact certain groups
54
New cards
cultural competence
effectiveness in communicating and behaving appropriately with people from another culture, both in terms of understanding and being understood
55
New cards
contextual competence
requires considering the various other factors which might impact on health-related issues including the historic, family, economic and social contexts in which individuals are situated
56
New cards
cultural safety
involves healthcare professionals delivering safe, accessible and responsive healthcare in culturally appropriate ways that are free from racism
57
New cards
cultural responsiveness
critical reflexivity, anti-racism and cultural humility, which includes examining our own cultural beliefs, assumptions, privilege, power, and social location
58
New cards
Key figures of the humanist perspective? What are the basic principles/metaphors?
Maslow+Rogers. Emphasises the uniqueness of the individual, and individuals are motivated towards self actualisation. People experience problems when there is a difference between their ideal self and self-concept. Free will+determination.
59
New cards
Criticisms of the humanist perspective?
Are all people inherently good (eg. jails)? Rejection of lab methods - is it scientific? Do we even have free will?
60
New cards
Describe the key features of the cognitive perspective.
Focus on how people process, store + retrieve information. metaphor of the mind like a computer (Information processing model). Uses experimental methods to INFER underlying mental processes (i.e. perception, attention, memory, learning, etc.)
61
New cards
What are the basic principles/assumptions of the evolutionary perspective? What is a criticism of this theory?
Behaviours and mental processes evolved because they helped our ancestors survive + reproduce. Focus primarily on nature. Darwinian origins. A criticism of this theory is that we cannot go back in time and observe the process of evolutionary adaption.
62
New cards
What are the two major debates in psychology paradigms?
Free will vs. Determinism, Nature vs. Nurture
63
New cards
What is the modern 'paradigm' used in psychology now?
Biopsychosocial approach/model. Draws on positive aspects of individual paradigms and combines them eg. importance of childhood from psychodynamic theory.
64
New cards
What is motivation
the driving force behind behaviour, leading us to pursue some things and avoid others.
65
New cards
Psychodynamic perspective of motivation
Emphasis on the fulfillment of the basic drives of self-preservation (also referred to as aggression) and sex. Motives that reflect these drives can be unconscious.
66
New cards
Behaviourist perspective of motivation
Motivation is the result of conditioning, when reinforcement and reward is desired. Primary drives that produce behaviours in order to fulfill them are hunger, thirst and sex. Secondary drives are learnt through conditioning, like wanting to earn money.
67
New cards
Drive-reduction theory
Unfulfilled needs lead to drives, motivation stems from these drives.
68
New cards
Cognitive perspective of motivation
Motivation is a result of what value an individual places on an outcome, and the extent to which they believe they can attain it.
69
New cards
Humanistic perspective of motivation
People are motivated by the desire for personal growth. Emphasises the importance of Maslow's hierarchy of needs in motivation.
70
New cards
Evolutionary perspective of motivation
Most motivated behaviour in humans is a result of instincts, that maximise reproductive success.
71
New cards
What are psychosocial motives
Acheivement, power, self-esteem, affiliation.
72
New cards
What is emotion
A positive or negative feeling that includes physiological arousal, subjective experience and behavioural expression.
73
New cards
What is affect
A pattern of observable behaviour that expresses ones emotion
74
New cards
What is the physiological component of emotion
Visceral and voluntary reactions to a stimulus.
75
New cards
James-Lange theory vs the Cannon-Bard theory
James-Lange: Emotions originate in the peripheral nervous system responses, that the central nervous system interprets. Cannon-Bard: Emotion inducing stimuli elicits both an emotional and physiological experience simultaneously.
76
New cards
What are the 5 areas of happiness (PERMA)
Pleasure, engagement, relationships, meaning, accomplishment
77
New cards
What are the universally recognised emotions
Surprise, fear, anger, disgust, happiness, sadness
78
New cards
What is positive affect
Pleasant emotions
79
New cards
What is negative affect
Unpleasant emotions
80
New cards
Role of hypothalamus in emotion
Converts emotional signals generated by the brain, into autonomic and endocrine responses.
81
New cards
Role of limbic system (amygdala) in emotion
Sensory information is associated with a pleasant or unpleasant feeling. Also assists in detecting other people's emotions.
82
New cards
Role of cortex in emotion
Considers whether a stimulus is safe or harmful.
83
New cards
Psychodynamic perspective of emotion
People can be unconscious of their own emotional experience.
84
New cards
Cognitive perspective of emotion
People's emotions reflect their subjective appraisals of a situation or stimuli.
85
New cards
Evolutionary perspective of emotion
Emotions serve an adaptive purpose. They can be a powerful source of motivation.
86
New cards
Neuron
Nerve cells. Carry information from cell to cell within the nervous system.
Sensory neurons: transmit information from sensory receptors to the brain.
Motor neurons: transmit commands from interneurons to the glands and muscles of the body, to perform actions and functions.
Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons in the spinal cord.
Sensory neurons: transmit information from sensory receptors to the brain.
Motor neurons: transmit commands from interneurons to the glands and muscles of the body, to perform actions and functions.
Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons in the spinal cord.
87
New cards
Dendrite
Receive input from other nerve cells.
88
New cards
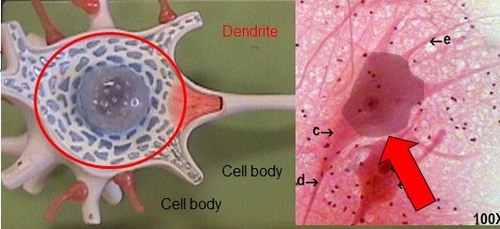
Soma
Contains the nucleus, decision making centre of the neuron.
89
New cards
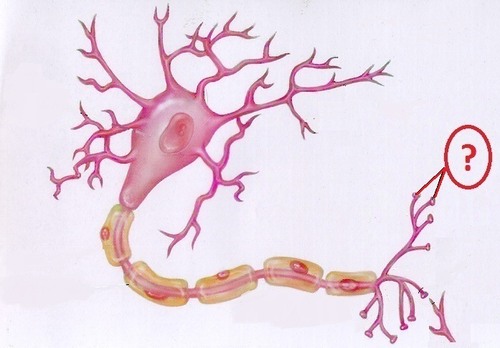
Axon and terminal buttons
The axon transmits information from the soma down to the collateral branches. Terminal buttons on these branches send signals from the neuron to other adjacent neurons, through the synapse.
90
New cards
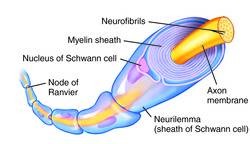
Myelin sheath
White matter, insulates the axon to increase speed of transmission.
91
New cards
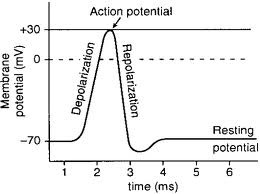
Resting potential
The membrane of the neuron is polarised, meaning the electrical charge is more negative on the inside.
92
New cards
Graded potential
Stimulation from another neuron reduces the membranes polarisation, which excites the neuron. This is caused by an influx of sodium ions. Another neuron can also increase polarisation, which inhibits the neuron. This is caused by an outflow of potassium ions.
93
New cards
Action potential
If the electrical current crosses a threshold, the neural membrane becomes totally permeable to sodium ions. This makes the charge inside the cell momentarily positive.
94
New cards
Steps of transmission of information
* the terminal buttons of the pre-synaptic neuron contain vesicles that carry neurotransmitters
* when the neuron fires, some vesicles adhere to the membrane and release neurotransmitters into the synapse
* these bind with receptors on the post-synaptic neuron
* excitatory neurotransmitters depolarise the cell
* inhibitory neurotransmitters hyperpolarise the cell
* when the neuron fires, some vesicles adhere to the membrane and release neurotransmitters into the synapse
* these bind with receptors on the post-synaptic neuron
* excitatory neurotransmitters depolarise the cell
* inhibitory neurotransmitters hyperpolarise the cell
95
New cards
Main neurotransmitters
Glutamate: primary excitatory neurotransmitter
GABA: primary inhibitory neurotransmitter
Dopamine: motivation, behaviour, mood
Seretonin: regulating mood
Acetylcholine: learning and memory
Endorphins: elevate mood, reduce pain
GABA: primary inhibitory neurotransmitter
Dopamine: motivation, behaviour, mood
Seretonin: regulating mood
Acetylcholine: learning and memory
Endorphins: elevate mood, reduce pain
96
New cards
Endocrine system
Glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Pituitary gland: hormones it releases stimulate and regulate other glands
Thyroid gland: releases hormones that control growth and metabolism
Adrenal gland: secretes adrenaline
Gonads: influence sexual development by secreting testosterone and estrogens
Pituitary gland: hormones it releases stimulate and regulate other glands
Thyroid gland: releases hormones that control growth and metabolism
Adrenal gland: secretes adrenaline
Gonads: influence sexual development by secreting testosterone and estrogens
97
New cards
Peripheral nervous system
Throughout the body, consists of neurons that convey messages to and from the central nervous system.
Somatic: transmits sensory information to the central nervous system, and carries out motor commands.
Autonomic: conveys information to and from internal bodily structures that carry out basic life processes.
* Sympathetic is activated when under threat
* Parasympathetic maintains homeostasis
Somatic: transmits sensory information to the central nervous system, and carries out motor commands.
Autonomic: conveys information to and from internal bodily structures that carry out basic life processes.
* Sympathetic is activated when under threat
* Parasympathetic maintains homeostasis
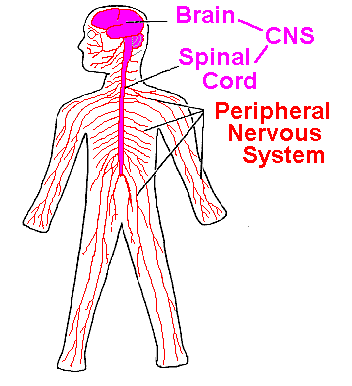
98
New cards
Central nervous system
Consists of the brain and spinal cord. The spinal cord transmits information between the brain and the body. Within the spinal cord, nerves are called tracts. The neurons in the spinal cord produce reflexes.
99
New cards
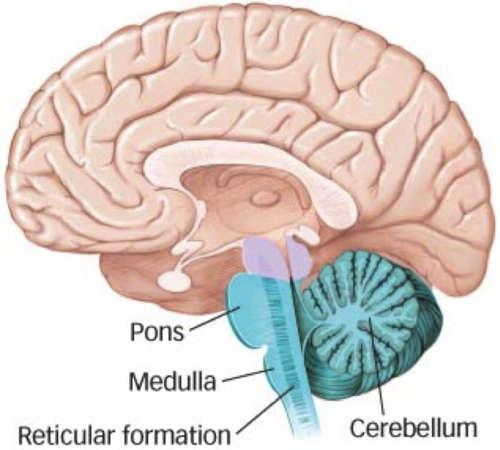
Hindbrain
Links brain to spinal cord.
Medulla oblongata: controls vital physiological functions.
Pons: respiration, movement, sleep
Cerebellum: movement, sensory and cognitive processing
Reticular formation: consciousness and arousal
Medulla oblongata: controls vital physiological functions.
Pons: respiration, movement, sleep
Cerebellum: movement, sensory and cognitive processing
Reticular formation: consciousness and arousal
100
New cards
Midbrain
Connection point between forebrain and hindbrain.
Colliculi: processing visual and auditory signals
Tegmentum: movement, pain and alertness
Colliculi: processing visual and auditory signals
Tegmentum: movement, pain and alertness