Respiratory Histology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Describe the cells that lines the Respiratory System
Lined by respiratory epithelium – pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
Mucus producing cells (Goblet)
Mucus traps particles
Ciliated cells
Moves thin layer of mucus
Describe how the cellular composition changes as you go from conducting to respiratory zone
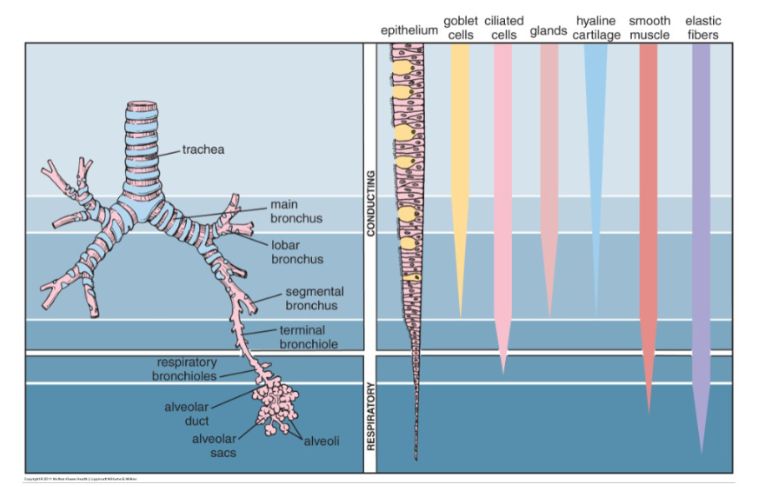
Describe what happens to the Respiratory Epithelium as you go from the start towards the end of the conduction zone
Where are Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium present?
Transition:
as you go towards the respiratory zone:
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated with goblets → simple columnar → simple cuboidal epithelium
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium:
In areas exposed to rapid airflow (ex: Vocal Folds)
In areas prone to other abrasions (Ex: epiglottis)
Describe the characteristics of these cells associated w/ respiratory
epithelium:
Ciliated columnar cell
Goblet (mucous) cell
Brush Cell
Basal Cell
Neuroendocrine Cell
Ciliated columnar cell:
Each cell has hundreds of cilia on its apical surface that move mucus along the epithelial surface.
Cillia is attached to microtubules
Goblet (mucous) cell:
apical region of the cell is filled with polysaccharide-rich mucus droplets
Brush cell:
apical surface is covered with microvilli.
Acts as sensory receptors
Basal (stem) cell:
rounded cells that sit on the basal lamina
regenerative cells, capable of dividing and differentiating into other cell types of the epithelium
Neuroendocrine cell:
cells of diffuse endocrine system that are located on the basal lamina and have numerous granules
may regulate the mucous and serous secretions of other cells
Define Squamous Metaplasia
How can this occur
consequences?
DEF: reversible process in which an epithelial tissue transforms to a different type of epithelial tissue
Cause:
chronic presence or accumulation of toxins that occur with heavy cigarette smoking or industrial air pollution
Consequences:
Immobilization of cilia → failure to clear mucus containing filtered material → exacerbates problem → squamous metaplasia of the epithelium
change from pseudostratified ciliated columnar to stratified squamous epithelium → precancerous cell dysplasia
Describe the Nasal Mucosa:
Cells of Respiratory epithelium
Basement Membrane
What happens to the mucus
Respiratory epithelium = pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar
Contains Goblet Cells
Lamina propria rich in blood vessels, serous and mucus glands
Mucus is propelled to pharynx by cilia where it is swallowed or expelled
Describe the Olfactory Epithelium:
Location?
What does it lacks?
Describe Olfactory cells
Type of Cells
What kind of receptors?
Where does it send signals to?
Location:
Superior nasal concha and superior portion of the nasal septum
Cellular Composition:
Lacks goblet cells and motile cilia
Olfactory cells (OC):
Specialized sensory bipolar neurons
Dendrites extends to epithelial surface ending in a knob with cilia
Non-motile cilia contains olfactory receptors that bind odor molecules
Axons project from the cell base to olfactory bulb forming Cranial Nerve 1
In the olfactory epithelium, Describe:
Sustentacular cells
Characteristic/Function
Basal cells
Sustentacular cells:
has microvilli on apical surface and form junctional complexes w/ each other and w/ OC
Function: Support & electrically insulate olfactory cells
Basal Cells:
Replace and proliferate both olfactory cells and sustentacular cells
***one of the few instances in adult where nerve cells can be replaced***
Describe Olfactory Glands
AKA?
Function?
Olfactory Glands (Bowman’s Glands):
Produce a serous secretion that traps and dissolves odiferous substances → Constant Flow = remove
old scents and permits detection of new scentssecretory portion found in basement membrane, deep to olfactory epithelium and their ducts open on the epithelial surface
Describe the Lymphoid tissue in the nasal pharynx
Function?
Bulge?
Component of…?
Function: acts as immune surveillance against inhaled antigens
May bulge into lumen (that is called adenoid)
Component of Waldeyer ring of lymphoid tissue protecting openings of respiratory and GI
Describe the two folds of the larynx; Seperated by?
What is the function of vocalis muscles
Folds:
Upper false vocal cord
Lower true vocal cord
Separated by ventricle – narrow cleft
Vocalis muscle controls pitch of sound by moving true cord
Describe the epiglottis:
Lining?
Core?
During respiration/swallowing
Lining = Stratified squamous epithelium; changes to respiratory epithelium at base of laryngeal surface
Elastic cartilage core
Respiration: epiglottis is in a vertical position and uncovers the laryngeal opening
Swallowing: epiglottis moves to a horizontal position covering the larynx
Describe the Trachea:
Basal Cells Function?
Components of Basement Membrane?
Submucosa contains?
What is more common in upper trachea
Basal cells
Part of diffuse neuroendocrine system
Stem cells can divide and replace other cell types
Lamina propria – loose, vascular supporting tissue
Submucosa contains numerous serous and mucinous glands
Goblet and basal cells more common in upper trachea
Describe Tracheal rings:
Composed of?
Cartilage prevents?
Function of Trachealis Muscle?
Tracheal rings:
Composed of fibroelastic tissue and C shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
Cartilage prevents collapse during inspiration
Trachealis muscle: joins rings posteriorly
Contraction during coughing
Describe the changes as we move towards:
Main Bronchus
Segmental Bronchus
Bronchiole
Terminal Bronchiole
Changes in Main Bronchus:
contains less goblet cells
Submucosa contains fewer glands
Upper lamina propria contains more elastin
SM seperates Lamina propia and submucosa
Cartilage support by plates not rings
Segmental Bronchus:
Sparse submucosal glands
Occasional cartilage plates
Completely encircled by smooth muscle
Bronchiole:
No cartilage or submucosal glands
Abundant smooth muscle
Neuroendocrine cells secrete serotonin
Regulates muscle tone in bronchial and vessel wall
Terminal Bronchiole:
Goblet cells replaced by Clara (club) cells-columnar cells
Produce components involved in maintaining alveolar patency
Act as stem cells
Synthesis of enzymes believed to degrade certain inhaled toxins
Differentiate between Pulmonary Lobule/acinus
Pulmonary lobule:
Terminal bronchiole
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar ducts
Alveolar sacs
Alveoli
Pulmonary acinus:Functional unit of gas exchange
Respiratory bronchiole
Alveolar duct
Alveolar sac
Alveoli
Describe Respiratory bronchiole:
Structure?
Composition
Respiratory bronchiole:
initial segment of the respiratory portion
Structurally: similar to terminal bronciole
except for the presence of a few alveoli projections
Composition:
cuboidal cells and Clara cells
Describe Alveolar ducts:
Divides into?
Composed of?
Alveolar ducts:
Divides into alveolar ducts (AD) that ends in alveolar sacs (AS)
Composition:
bundles of smooth muscle, collagen and elastin fibers form alveolar rings
Smooth Muscles function:
Regulates air movements
What is the alveolus
Lining?
Cell types?
Alveolus:
Functional unit of the pulmonary acinus
has a thin wall lined by simple squamous epithelial cells forming a part of air – blood barrier
Cell Types:
Type 1 alveolar cells
Type 2 alveolar cells
Describe Alveolar Capillaries
Describe its lining
What does its endothelial cells contain?
Alveolar Capillaries:
Lined by continuous endothelial cells juxtaposed to Type I alveolar cells through a dual basal lamina produced by these two cells
Endothelial contains: ACE
Angiotensin II constricts blood vessels
Describe the Alveoli:
What does it provide?
Describe the characteristics of Type1 and Type2 cells
What is Kohn?
Alveoli:
Provide a large surface area for gas exchange
Consists of pocket lined by pneumocytes
Type1: Flat
Type2: Rounded- typically at branch points
Secrete surfactant
has Lamellar bodies
membrane bound vesicles of concentric surfactant
Can divide and replace type 1 cells
Kohn:
Alveolar pore between each alveoli → equalizes pressure between air sacs
What is the function of surfactant
What is it composed of
Function:
Decreases surface tension of alveoli
Allows normal inflation of alveoli at birth
Allows reinflation of alveoli which collapse after airway obstruction
Keeps alveoli open
Composition:
phospholipids, particularly palmitoyl phosphatidylcholine
[REVIEW] NRDS

Describe Alveolar wall:
Composed of?
Elastin Forms?
Composed of:
simple squamous epithelium, capillaries and fibroelastic
supporting meshwork
Elastin forms supportive ring at opening of alveoli
What three membrane forms the Blood-Air barrier
Alveolar epithelial cells
Basement membrane formed by fusion of epithelial cell basal lamina + capillary endothelial cell basal lamina.
Capillary endothelial cells
Describe Pulmonary macrophage:
Location
Function
Pulmonary macrophage
Found in alveolar spaces and connective tissue of alveolar septum
Remove foreign material (mostly carbon from exhaust and smokers and bacteria)
Carbon is expelled into mucus or remains in lung
Recognized as anthracotic pigment
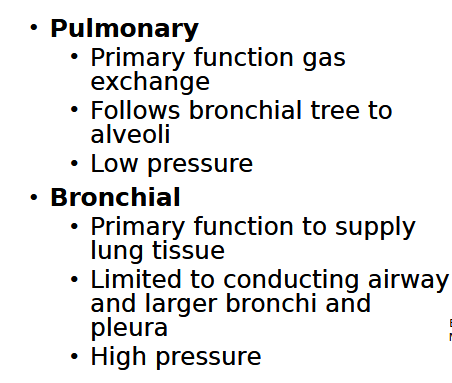
[REVIEW] Pulmonary vs Bronchial vasculature
****Bronchial Arterial branches follow the bronchial tree until the level of the respiratory bronchioles, at which point the network of continuous capillaries is formed****
[REVIEW] Parietal vs Visceral Pleura

How can lymph vessels cause pleural effusion
pulmonary lymphatics run in fibrous septa and empty into the pleural cavity
If lungs = edematous (heart failure, cirrhosis) → lymphatics can move fluid into pleural space causing pleural effusion
it can also carry bacteria that cause this as well