BSC 114 - EXAM 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/330
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:06 PM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
331 Terms
1
New cards
eukaryotic cell vs. prokaryotic
eukaryotic:
- nucleus
- linear DNA
prokaryotic:
- no nucleus
- circular DNA
- nucleus
- linear DNA
prokaryotic:
- no nucleus
- circular DNA
2
New cards
zygote
development of fertilized cell
3
New cards
cell division does
1. development from fertilized cell
2. growth
3. maintenance and repair of tissues
2. growth
3. maintenance and repair of tissues
4
New cards
chromatin types of structure
- tight or loose
easier to move DNA when tightly packaged
** when condensed, genes aren't always turning on
easier to move DNA when tightly packaged
** when condensed, genes aren't always turning on
5
New cards
somatic cell
any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells.
6
New cards
gametes
Humans = sperm and egg cells
Plants = pollen and ovum
** reproductive
Plants = pollen and ovum
** reproductive
7
New cards
Goal of mitosis
splitting up genetic material
8
New cards
meiosis goal
make offspring have little bit of genetic difference
9
New cards
cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm to produce two genetically identical daughter cells
10
New cards
cells not always identical
in mitosis
11
New cards
2 Big Phases of Cell Cycle
M phase: mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis)
Interphase
Interphase
12
New cards
G1 phase
receiving of environmental signals
- signal transduction pathway
- a cell receiving its job
- cell growth
- signal transduction pathway
- a cell receiving its job
- cell growth
13
New cards
S (DNA synthesis) phase
spend energy on making second copy of DNA
- need nucleotides to make DNA
- S-cyclin promotes
- need nucleotides to make DNA
- S-cyclin promotes
14
New cards
G2 phase
receiving signals from environment
- "is it ok to divide?"
- cell growth
- need ATP to power through
- "is it ok to divide?"
- cell growth
- need ATP to power through
15
New cards
Signal transduction pathways control
shifting between different phases of cell cycle
16
New cards
Mitosis 5 Phases
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
17
New cards
Nucleolus starts dissolving in G2 of interphase
allows chromosomes to condense up
- nuclear envelope dissolves 50% during prometaphase **
- nuclear envelope dissolves 50% during prometaphase **
18
New cards
metaphase plate
where sister chromatids split in half
- half to souther and northern poles
- half to souther and northern poles
19
New cards
plant cell cytokinesis
DONT PINCH INWARD
- vesicles that form cellulose, lines up to form cell plate, and grows bigger between cells to help divide them
- vesicles that form cellulose, lines up to form cell plate, and grows bigger between cells to help divide them
20
New cards
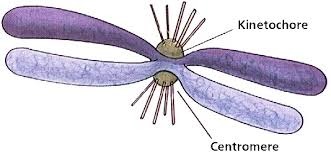
kinetochore
proteins that anchor the chromatids
- site for spindle fibers to pull sister chromatids apart in anaphase
- site for spindle fibers to pull sister chromatids apart in anaphase
21
New cards
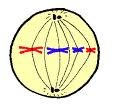
metaphase
all spindle fibers should be attached to kinetochore part of chromosome
- cell is circular (One half going north/south)
- cell is circular (One half going north/south)
22
New cards
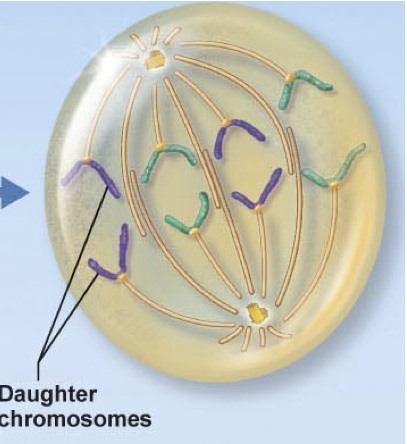
anaphase
asters getting further apart and spindle fibers are getting shorter ... separating two sister chromatids (cell becomes semi ovular)
23
New cards
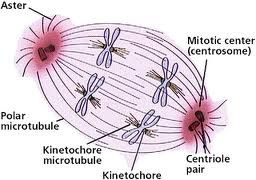
aster
A radial array of short microtubules that extends from each centrosome toward the plasma membrane in an animal cell undergoing mitosis.
24
New cards
Telophase and Cytokinesis
chromosomes hit opposite ends of cell; you get two new nuclei and two new cells start to form
25
New cards
cytokinesis in animal cell
cleavage furrow
- contractile ring forms and pinches off into two new cells
- contractile ring forms and pinches off into two new cells
26
New cards
checkpoints in cell cycle
G1
G2 --> chromosomes condensed together; no turning on genes
M --> mitosis checkpoint
G2 --> chromosomes condensed together; no turning on genes
M --> mitosis checkpoint
27
New cards
G0 checkpoint
NON-DIVIDE STAGE
cell isn't giving signals ... won't reproduce anymore
- can pop out of G0 and go back into cell cycle
cell isn't giving signals ... won't reproduce anymore
- can pop out of G0 and go back into cell cycle
28
New cards
checkpoints are controlled by ...
cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk)
- G1/S-cyclin promote G phase
- increase concentrations move through cell cycle
- G1/S-cyclin promote G phase
- increase concentrations move through cell cycle
29
New cards
cyclin
cell cycle protein activated by joining ... then protein turned on
30
New cards
meiosis makes
four cells with half amount of DNA; DNA should be different in each one
- plants, humans, any eukaryotes
- plants, humans, any eukaryotes
31
New cards
growth factors
released by certain cells and stimulate other cells to divide
32
New cards
density-dependent inhibition
crowded cells stop dividing
- need room to grow so take cells and put them in a new bottle
- need room to grow so take cells and put them in a new bottle
33
New cards
anchorage dependent
wants to be stable on something
- in order to divide they must be attached to a substratum
- in order to divide they must be attached to a substratum
34
New cards
Cancer cells
have some form of inhibition but very little
- have growth were you shouldn't have growth
- feed themselves growth factors
- have growth were you shouldn't have growth
- feed themselves growth factors
35
New cards
transformation
normal cell converted to a cancerous cell
36
New cards
benign tumor
abnormal cells at original site
37
New cards
malignant tumor
invade surrounding tissues and metastasize
- export cancer to other parts of body
- export cancer to other parts of body
38
New cards
Biggest advantage to cancer treat
"personalized medicine"
- sequence own human genome for under $1000
- sequence own human genome for under $1000
39
New cards
prokaryotic cell development
binary fission
1. double amount of DNA
2. two origins of replication
3. cell splits in half (two genetically identical)
- every 18 mins; also die very fast
1. double amount of DNA
2. two origins of replication
3. cell splits in half (two genetically identical)
- every 18 mins; also die very fast
40
New cards
cell division
continuity of life is based on reproduction of cells
- distribution of identical genetic material (DNA) to two daughter cells
exception: meiosis
- distribution of identical genetic material (DNA) to two daughter cells
exception: meiosis
41
New cards
genome
cell's DNA; genetic info
- prokaryote = single DNA
- eukaryote = number of DNA
- prokaryote = single DNA
- eukaryote = number of DNA
42
New cards
somatic cell count
46 chromosomes 2 sets of 23
- first is X/Y = sex-linked
- first is X/Y = sex-linked
43
New cards
sister chromatids
joined copies of original chromosome
- each sister chromatid has a centromere
- each sister chromatid has a centromere
44
New cards
Interphase accounts for
90% of cell cyle
- G1, S, G2
- cell grows during all phases but chromosomes only replicated during S
- G1, S, G2
- cell grows during all phases but chromosomes only replicated during S
45
New cards
spindle apparatus consists of
- kinetochore microtubules --> bind to centromere associated protein
- overlapping nonkinetochore microtubules --> interact via motor proteins
- astral microtubules (asters) --> extend from each centrosome
- centrosomes --> remain attached to spindle microtub
- overlapping nonkinetochore microtubules --> interact via motor proteins
- astral microtubules (asters) --> extend from each centrosome
- centrosomes --> remain attached to spindle microtub
46
New cards
prometaphase
nuclear envelope breaks down; chromosomes undergo active movement as they begin process of aligning at equator
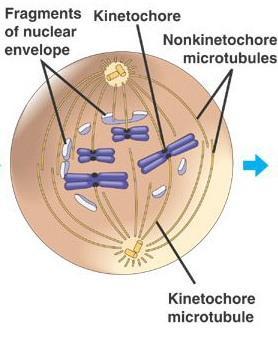
47
New cards
prophase
replicated chromosomes condense
- outside nucleus microtubule spindle assembles between two centrosomes
- outside nucleus microtubule spindle assembles between two centrosomes
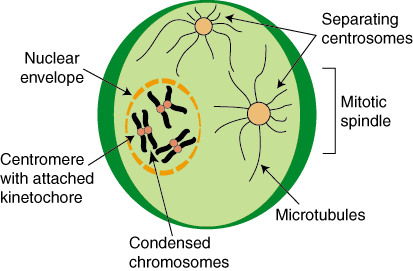
48
New cards
cell checkpoints regulated by
internal and external signals
49
New cards
Cdk activity controlled by
protein kinases
protein phosphatases
non-enzyme proteins regulating cyclin-Cdk activity
protein phosphatases
non-enzyme proteins regulating cyclin-Cdk activity
50
New cards
heredity
transmission of traits from one generation to the next
51
New cards
haploid cell
diploid zygote
52
New cards
genes
units of heredity and made up of segments of DNA
53
New cards
n
haploid
54
New cards
2n
diploid
55
New cards
sex of baby is determined by
sperm's DNA
56
New cards
ploidy level of original cell
diploid
57
New cards
ploidy level of final cell
haploid
58
New cards
prophase I
crossing over
- synapsis; recombination
- chiasmata = sites of crossover
- synapsis; recombination
- chiasmata = sites of crossover
59
New cards
metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up on metaphase plate
- one chromosome at each pole
- microtubules from one pole attached to kinetochore
- one chromosome at each pole
- microtubules from one pole attached to kinetochore
60
New cards
anaphase I
pairs of homologous chromosomes separate
- one chromosomes moves toward opposite poles
- one chromosomes moves toward opposite poles
61
New cards
telophase & cytokinesis
each half of cell has a haploid set of chromosomes
- cleavage furrow forms (animal)
- cell plate form (plant)
- cleavage furrow forms (animal)
- cell plate form (plant)
62
New cards
Prophase II
spindle apparatus forms
- later prophase II (chromosomes move toward metaphase plate)
- later prophase II (chromosomes move toward metaphase plate)
63
New cards
metaphase II
sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate
- two sister chromatids of each chromosome are no longer genetically identical
- two sister chromatids of each chromosome are no longer genetically identical
64
New cards
anaphase II
sister chromatids separate
- move as two newly individual chromosomes toward opposite poles
- move as two newly individual chromosomes toward opposite poles
65
New cards
telophase II and cytokinesis
chromosomes arrive at opposite poles; nuclear chromosomes begin condensing
66
New cards
chiasmata
site of crossing over
67
New cards
mitosis vs. meiosis
mitosis:
- no crossing over
- 2 identical cells
- metaphase = sisters line up
- 1 round cyotkinesis
Meiosis:
- don't want identical
- 4 genetically diverse
- prophase I -> genetic diff
- metaphase I -> homologous line up
- no crossing over
- 2 identical cells
- metaphase = sisters line up
- 1 round cyotkinesis
Meiosis:
- don't want identical
- 4 genetically diverse
- prophase I -> genetic diff
- metaphase I -> homologous line up
68
New cards
genetic variation
1. independent assortment of chromosomes
2. crossing over
3. random fertilization (not animals or plants)
2. crossing over
3. random fertilization (not animals or plants)
69
New cards
karyotype
ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell
70
New cards
homologous chromosomes (homologs)
two chromosomes of a pair have the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern
- X/Y = sex chromosome
- X = egg
- sperm = X or Y
- X/Y = sex chromosome
- X = egg
- sperm = X or Y
71
New cards
autosomes
non-sex chromosomes
72
New cards
synaptonemal complex
formation of zipper-like structure
- holds one homolog to other
- holds one homolog to other
73
New cards
synapsis
the DNA breaks are closed up so that each broken end is joined to the corresponding segment of the nonsister chromatid
74
New cards
3 unique events of meiosis I
1. synapsis and crossing over
2. alignment of homologous pairs at metaphase plate
3. separation of homologs
2. alignment of homologous pairs at metaphase plate
3. separation of homologs
75
New cards
locus
gene's specific individual passes all genes to offspring w/o fusion of gametes
76
New cards
fertilization
union of gametes (sperm and egg)
- fertilized egg = zygote
- one set of chromosomes from each parent
- fertilized egg = zygote
- one set of chromosomes from each parent
77
New cards
gametes are the only
haploid cells in animals
78
New cards
Gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote that divides by
mitosis to develop into a multicellular organism
79
New cards
daughter cell has only
half as many chromosomes as parent cell
80
New cards
Mitosis conserves the number of chromosome sets
producing cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell
81
New cards
Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from
Two (diploid) to one (haploid)
82
New cards
independent assortment
1. homologous pairs of chromosomes orient randomly at metaphase I of meiosis
2. each pair of chromosomes sorts maternal/paternal homologs into daughter cells independently
2. each pair of chromosomes sorts maternal/paternal homologs into daughter cells independently
83
New cards
crossing over
produces recombinant chromosomes
- contributes to genetic variation (combine DNA from two parents into single chromosome)
- contributes to genetic variation (combine DNA from two parents into single chromosome)
84
New cards
natural selection results in
the accumulation of genetic variations favored by the environment
85
New cards
sexual reproduction contributes to
genetic variation in a population, which originates from mutations
86
New cards
character
heritable feature that varies among individuals (flower color)
87
New cards
trait
each variant for a character (purple or white color)
88
New cards
true-breeding
plants produce only same variety as the parent plant
89
New cards
hybridization
"crossing" of two true-breeding varieties
90
New cards
P generation
true-breeding parents (parental generation)
91
New cards
Hybrid offspring
F1 generation (first "son" generation)
92
New cards
hybrids self-pollinate
F2 generation
93
New cards
alleles
alternative versions of a gene
94
New cards
homozygote
organism that inherits two alleles of the same type for a given gene
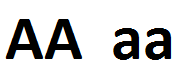
95
New cards
heterozygote
organism that inherits two different alleles for a given gene
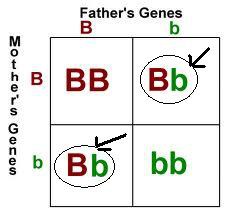
96
New cards
phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
97
New cards
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
98
New cards
testcross
Breeding an organism of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype.
99
New cards
monohybrids
where heterozygous for the one particular character being followed in the cross
100
New cards
dihybrids
individuals heterozygous for the two characters being followed in the cross