NCM 109 (Unit 5): Nsg Care of Patients with Specific Disturbances in Reproduction and Sexuality
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Reproductive and Sexual Disturbances in Infants
phimosis
hypospadias
epispadias & exstrophy complex
cryptorchidism
hydrocele
Reproductive and Sexual Disturbances in Adolescents
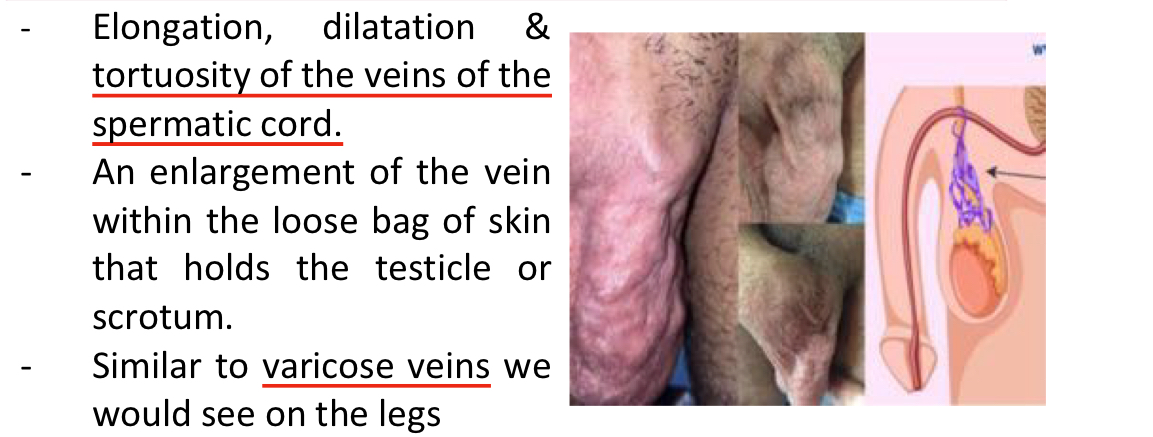
Varicocele
Reproductive and Sexual Disturbances in Adult Women
breast cancer
fibrocystic breast
Fibroadenoma of the Breast
Dysmenorrhea
Imperforated Hymen
Premenstrual Syndrome
Menopausal Syndrome
Reproductive and Sexual Disturbance in Adult Men
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Phimosis
The inability to retract the foreskin from the glans of the penis
Can occur naturally or be a result of scarring
A tight foreskin is common in baby boys who aren’t circumcised, but usually stops being a problem by the age of 3
3 yrs old
Age or period when a tight foreskin common in baby boys who aren’t circumcised usually stops being a problem
Balanitis
inflammation of the phimotic foreskin or;
inflammation of the glands or head of the penis due to infection or other causes
Can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful, but it is not usually serious
can be relieved with topical medication
N/C of Phimosis
● Proper hygiene
● Do not forcibly retract the skin or else other problems might occur such as Paraphimosis
Paraphimosis
a urologic emergency in which the retracted foreskin of an uncircumcised male can’t return to its normal anatomical position
Can result in gangrene and amputation of the glans penis
TTT of phimosis
Steroid cream
Circumcision
Hypospadias
Abnormal ventral placement of the urethral opening on the underside of the penis instead of the tip
This is common and doesn’t cause difficulty caring for this infant
Surgery usually restores the appearance of the child’s penis.
S/sx of hypospadias

Chordee
Downward curvature of the penis
Exstrophy
Referred as ‘turned inside out’
Epispadias
All boys with bladder exstrophy also has this disorder and occurs on its own
Orchiopexy
done at 6-24 mos. of life
Surgical procedure in which the undescended testicle is moved down to its proper place in the scrotum
Types of hydrocele
Communicating hydrocele
Non-communicating hydrocele
Varicocelectomy
Surgical procedure that removes the enlarged veins and it is done to restore proper blood flow to the reproductive organ
TTT of breast cancer
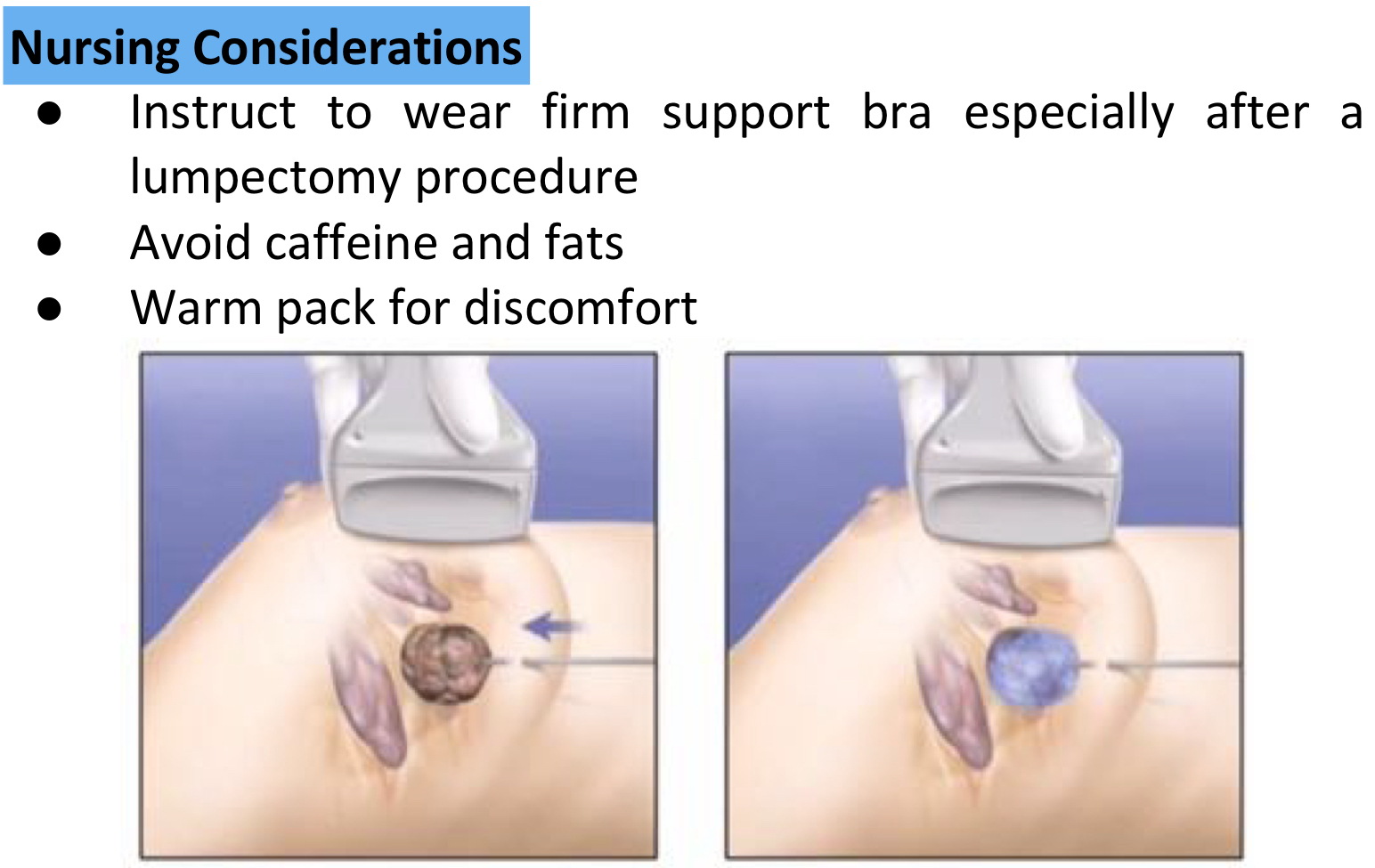
lumpectomy
mastectomy
chemotherapy
radiation therapy
Estrogen
Etiology of fibrocystic breast
Diagnostic tests for fibrocystic breasts
Clinical and Self Breast Exam
Mammogram
UTZ
Types of fibroadenoma
complex fibroadenoma
juvenile fibroadenoma
giant fibroadenoma
Cryoablation
A minimally invasive procedure;
Treatment of cancer by killing cancer cells with extreme cold
Primary dysmenorrhea
due to prostaglandin release
8-48 hours from the start of the first day of menstruation
Secondary dysmenorrhea
due to pathologic condition
Dull pain that radiates to buttocks and thighs
N/C of hypospadias

Anticholinergic (Oxybutynin)
Used to treat Bladder spasm for patient with hypospadias
Med for hypospadias

TTT of hypospadias

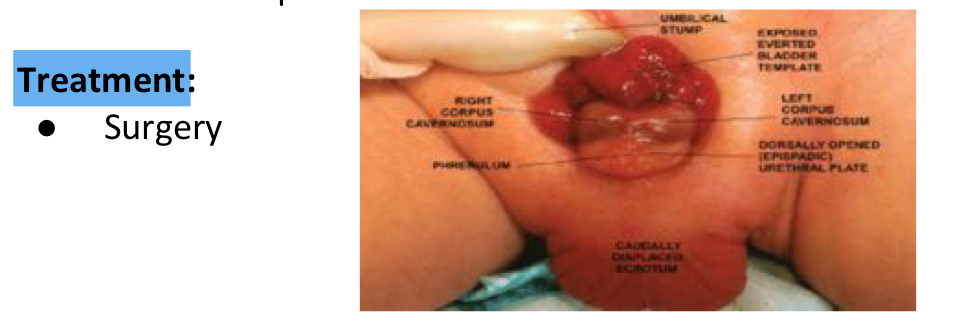
Bladder exstrophy:

Epispadias in boys

Epispadias in Girls

N/C of epispadias and exstrophy complex

TTT of epispadias & exstrophy complex
Cryptorchidism

S/sx of Cryptorchidism

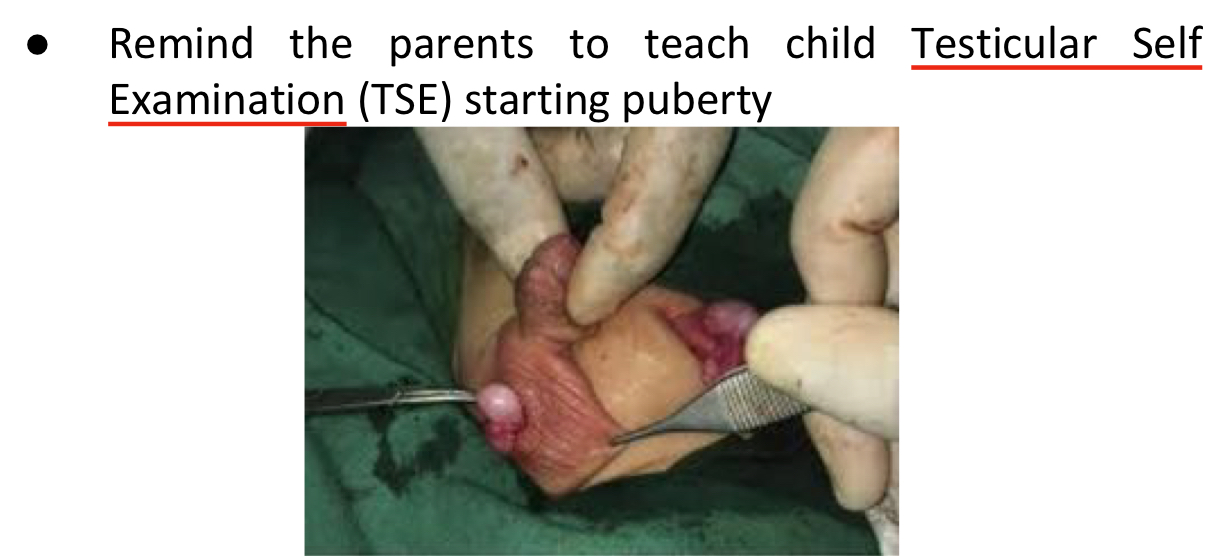
TTT of Cryptorchidism

N/C of Cryptorchidism

N/C of Cryptorchidism
Hydrocele

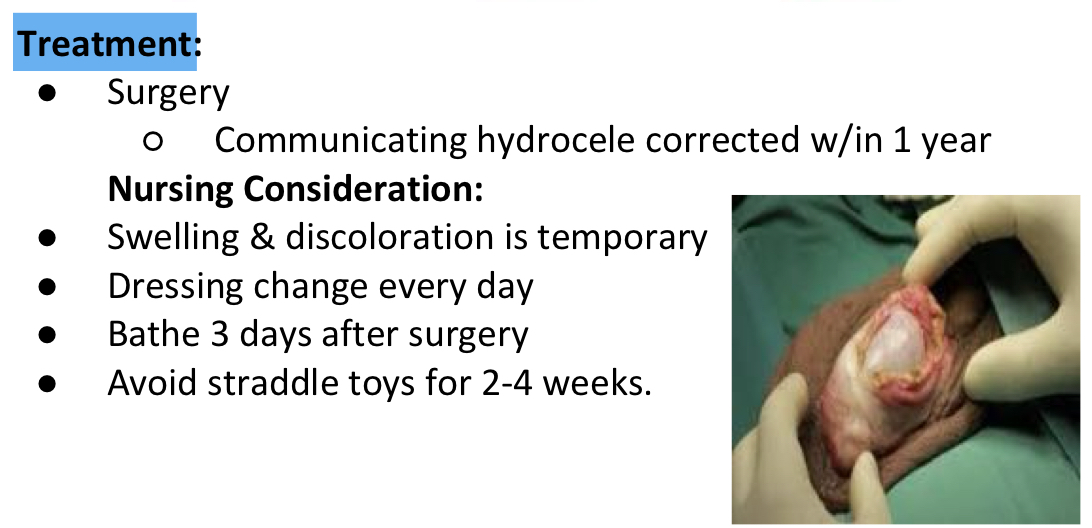
Communicating Hydrocele

No communicating Hydrocele

TTT & N/C of hydrocele
Varicocele
S/sx of Varicocele
● Wormlike mass above the testes
● Decreased testes
● Decreased dihydrotestosterone
● Rarely causes pain, but pain may vary from sharp to dull
○ Increased pain when standing or physical exertion
over long periods
○ Pain worsens over the course of the day
○ Relieves when the person lies down on his back
○ Causes impairment in fertility
Common cause of Varicocele

TTT of Varicocele

Breast cancer

S/sx of breast cancer

Lumpectomy
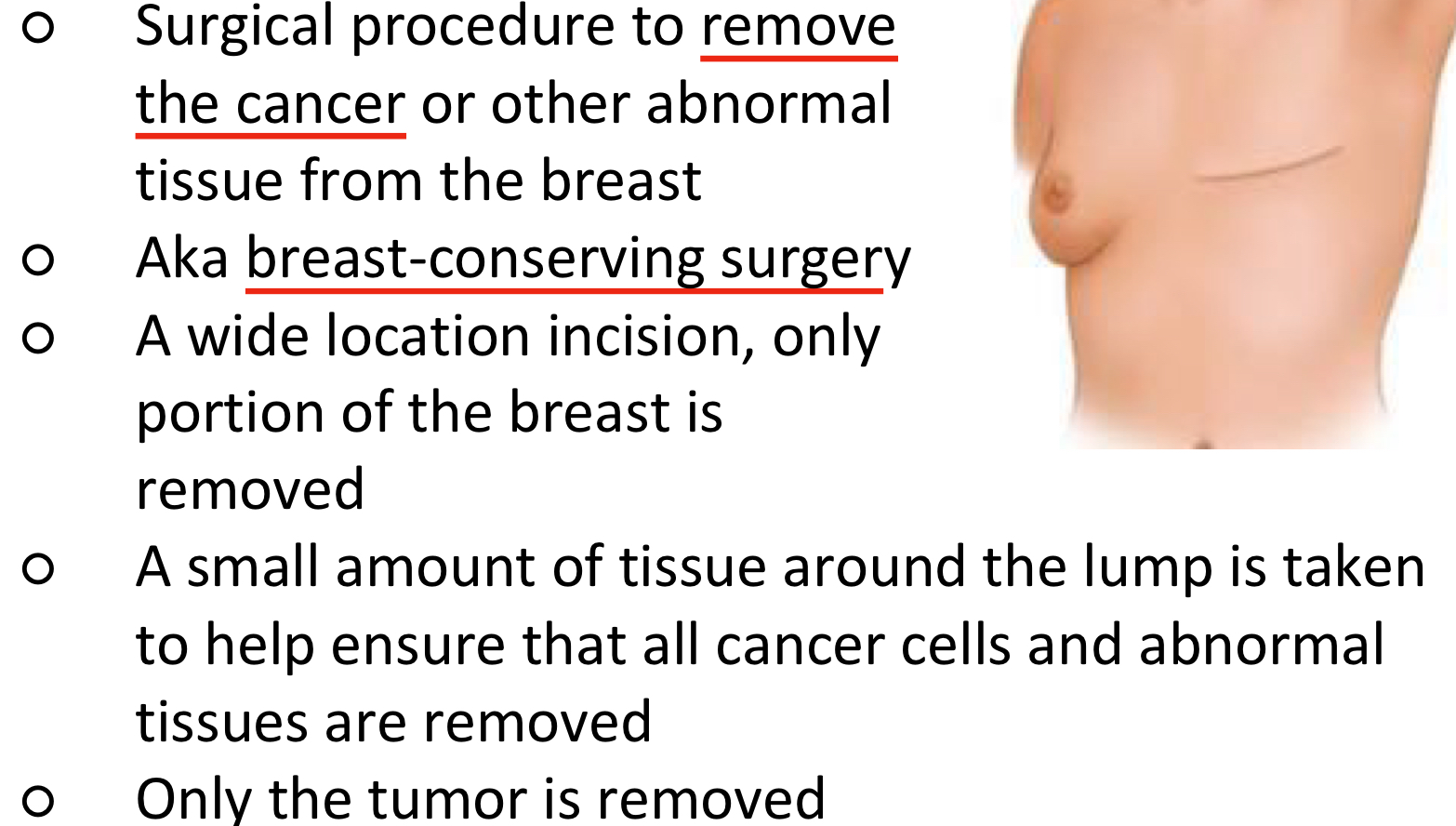
Mastectomy

Chemotherapy

Radiation Therapy

N/C of breast cancer

Fibrocystic breast

S/sx Fibrocystic breast
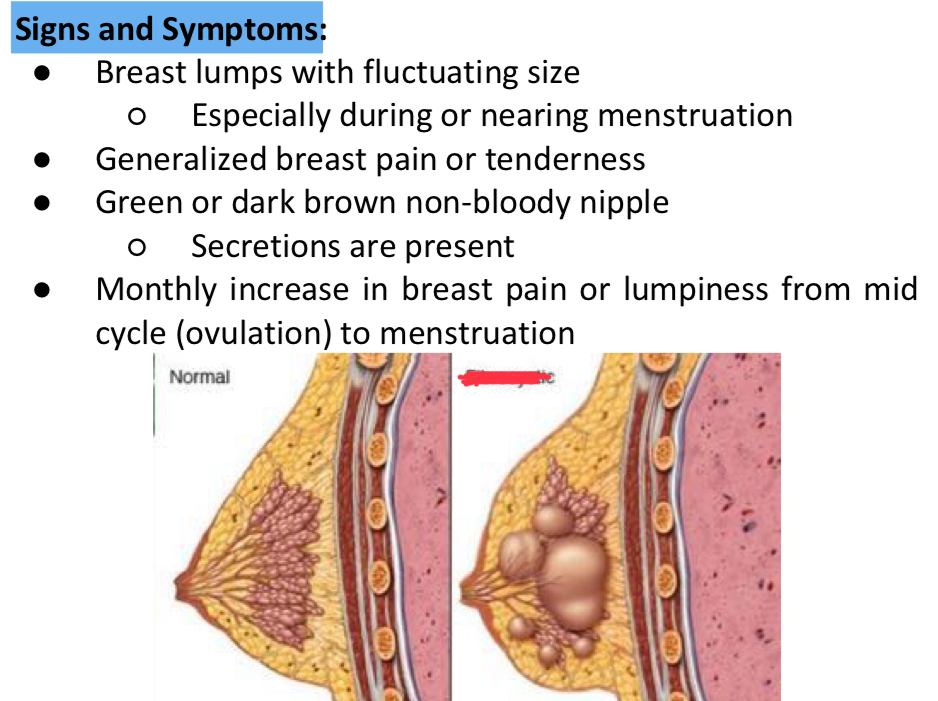
TTT Fibrocystic breast

fibroadenoma of breast

S/sx of fibroadenoma of breast

Complex fibroadenomas

Juvenile fibroadenomas

Giant fibroadenomas

Phyllodes tumor

TTT of fibroadenoma of breast

N/C of fibroadenomas
Dysmenorrhea

Primary Dysmenorrhea

Secondary Dysmenorrhea

Risk Factors of Dysmenorrhea

N/C Dysmenorrhea

Hymen

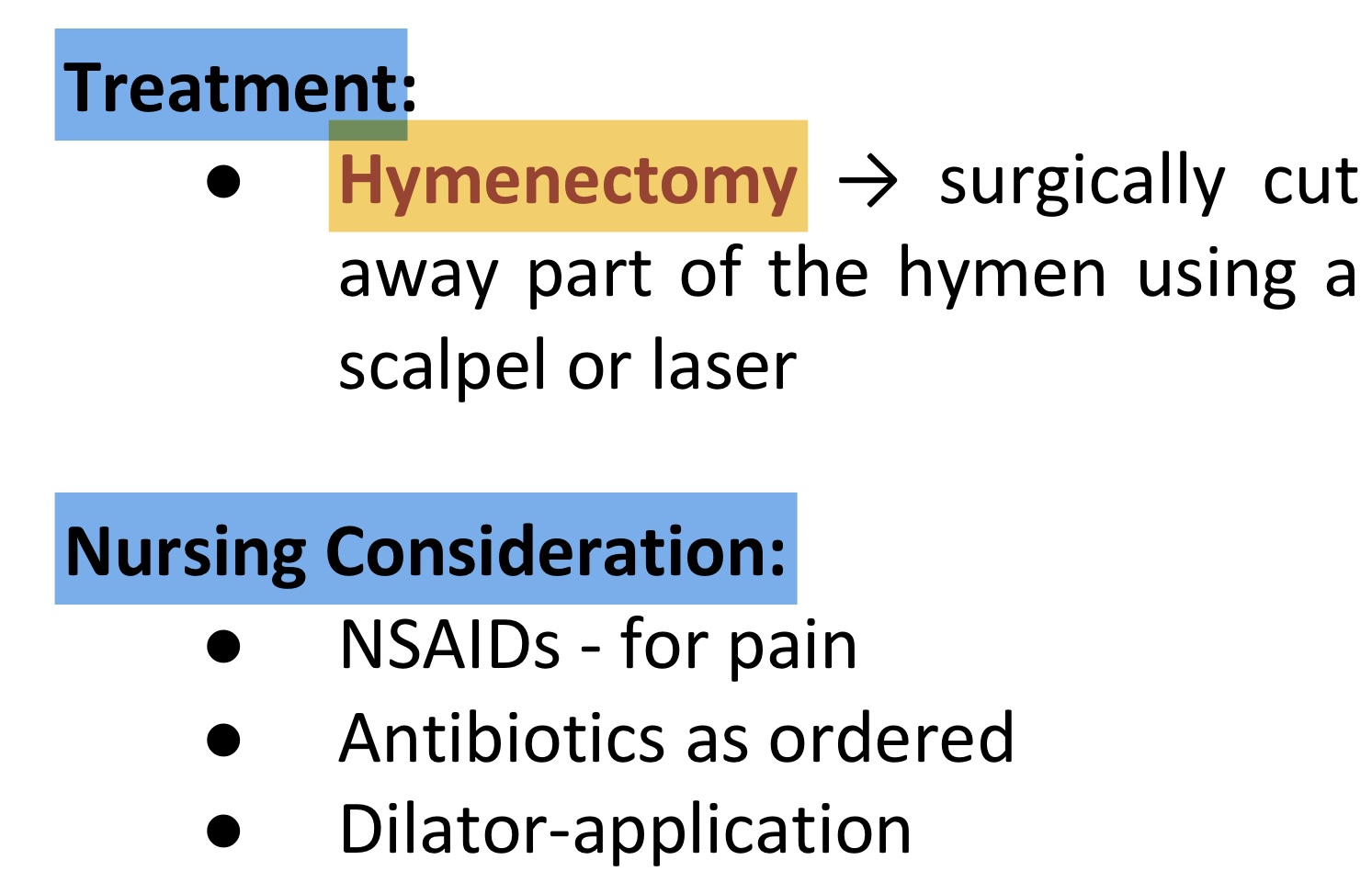
Imperforate hymen

S/sx Imperforate hymen

TTT & N/C of Imperforate hymen
Physical s/sx of PMS

Emotional and behavioral s/sx of PMS

S/Sx of Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)

Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
small number of women with premenstrual syndrome have disabling symptoms. This form of PMS is called cause significant physical and behavioral symptoms that interfere with daily living
Menopausal syndrome

Etiology Menopausal syndrome
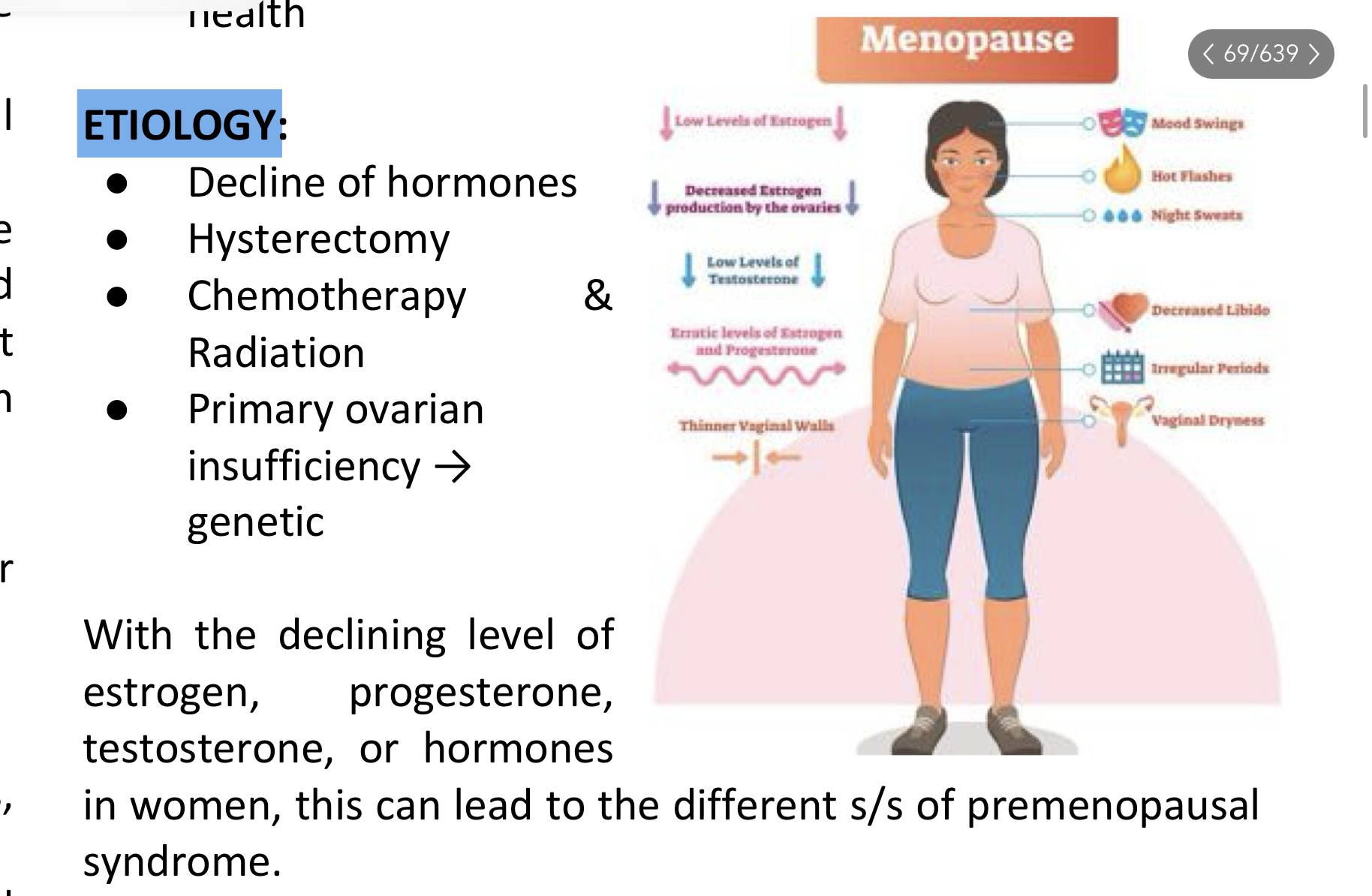
S/sx of Premenopausal

S/sx of Premenopausal
Complications of menopausal syndrome

TTT of menopausal syndromeu

Gabapentin
Med for hot flashes
Vitamin D and calcium
Supplements that prevent osteoporosis
BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA

S/sx of benign prostatic hyperplasia

Risk factors of benign prostatic hyperplasia
● Aging (60 y.o and above)
● Family history of BPH
● Diabetes and heart disease (due to the use of beta blockers)
● Obesity