Networks
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
System security
a set of measures taken to protect a computer from harm to its data/software
Cyber attack
an attempt to gain unauthorized access or to control a network
Data loss
An unintentional loss of information that may impact vital data.
e.g. family photos
Unauthorized data change
entering a computer system to steal data or destroy a network
can be stolen or leaked
e.g. product designs, floorplans
data theft
to steal data in order to take advantage of it
e.g. sales info, virtual money
Computer virus
A piece of malware that infects a computer & replicates itself to pass onto another computer
Penetration testing
Ethical hacking where hackers attempt to break into a network to identify possible security threats
Network forensics
monitoring, recording and analysis of network events
e.g.
software to analyze unusual activity
network policies to prevent problems occuring
acceptable use policy
rules that network users must agree to follow to be able to use
disaster recover policy
procedures that the organization will follow to restore normal network operations
anti-malware software
used to detect and remove malware such as viruses
has a database of virus signatures and looks for its behaviors
firewall
a piece of software or hardware that
monitors traffic in and out of networks
can allow or block data from entering/leaving
user access levels
a manager controls the level of access people have to networks
encryption
a method of changing the original numbers and characters so they are hidden or disguised.
network
two or more computers connected together so that they can share resources
pros of networks
improved communications
improved security
hardware and software shared
back-up is possible
LAN(local area network)
a network that is confined to a relatively small geographical area
general one building or site
they have their own infrastructure & hardware
LAN charecteristics
small area
single site
cheap to build/run
cables, wireless, infra-red from organisation
WAN(wide area networks)
connect to larger geographic areas that are at least a mile apart
many joined together using routers
external hardware/infrastructure
WAN characteristics
covers a wide geographical area
many buildings
more telecommunication links from external companies
EXPENSIVE
NIC(network interface controller)
used to convert data from original form to something that can be transmitted via the network
Functions of NICs
prepares data for sending over the network
controls flow of data from computer to the transmission medium
sends data
Transmission mediums
optional fibers for fiber optics
air for wireless
metal for CATS cables
Hubs
simple network devices that allows multiple computers to communicate
Switches
Hubs with more intelligence
inspect data packets
only sends data to intended computer, reducing data amounts and increasing speed
Wireless access points
uses a radio transceiver to allow wireless connections to a network
Routers
used to send data signals across the internet
network topology
When connections are made between two or more nodes to transfer data signals or backup information
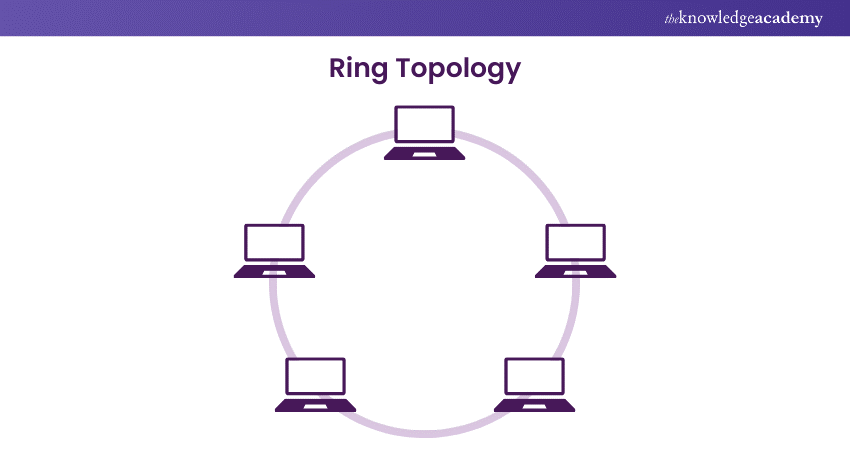
Ring topologies
each device is connected to 2 other devices, forming a ring for signals to travel around.
How ring topologies work
a small packet called a token is passed around the ring to each computer in turn.
if there is a request, the ring is modified and goes around the ring until destination is reached.
it travels in 1 direction only.
pros of ring topologies
transfers data quickly
0 collisions as it all goes in one direction
easy to increase size
no hogging on the network
cons of ring topologies
relies on one cable
must pass through every computer
difficult to locate network problems
anything faulty will cut off the network
ring topology diagram
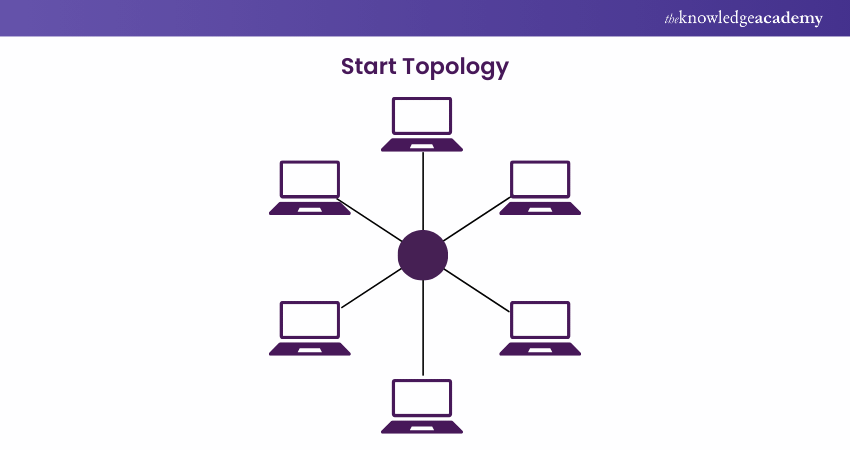
star topology
switch in the middle with cables running from it to each swtation
How star topologies work
signal is received by a hub and re-transmitted down every other cable segment
only the computer that is addressed will act upon it
pros of star topologies
fast and dedicated connection
won’t slow down as much
secure connections
easier to trace issues
easy to increase size
cons of star topologies
expensive cable costs
no other ways of sending/receiving data
complex operation
congestion may occur
management
star topology diagram
mesh network
no central connection point.
each device is connected to at least one other node and they all act as relays
node
basic unit of data structure
pros of mesh topology
received quickly
no node is isolated
operation at the same time
easy to increase size
cons of mesh topology
impractical set up due to high numbers
requires maintenance
mesh topology diagram
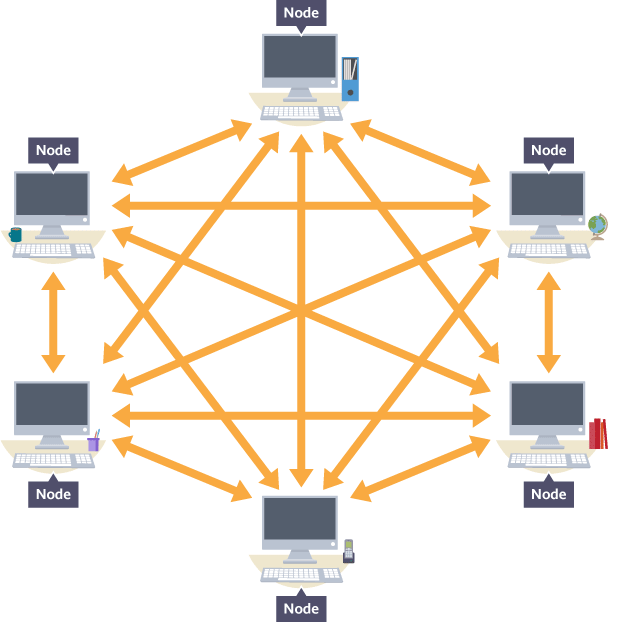
full mesh
directly connected to every other node.
partial mesh
not all nodes are connected to one another
each node is still connected with another
less routes meaning easier installation and better speed.