Mitosis and Meiosis - 2.1.6 Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2.1.6 Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What does mitosis produce?
Two genetically identical daughter nuclei that are also identical to the parent cell nucleus.
How many main stages are there in mitosis?
Four main stages.
Name the four main stages of mitosis.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
What happens to chromosomes during prophase?
Chromosomes condense and become visible.
What are sister chromatids?
Two identical chromatids joined together at the centromere.
What is the role of spindle fibres during mitosis?
They attach to chromosomes and help in their movement during cell division.
What is the nuclear envelope's status during prophase?
It breaks down into small vesicles.
What occurs at the metaphase plate?
Chromosomes line up at the equator of the spindle.
What is independent assortment?
The random positioning of maternal and paternal chromosomes along the spindle equator.
What happens during anaphase?
Sister chromatids separate at the centromere and are pulled to opposite poles.
How does telophase conclude the process of mitosis?
Nuclear envelopes reform, and chromosomes begin to decondense.
What is meiosis?
A form of nuclear division that results in the production of haploid cells from diploid cells.
What are gametes?
Sex cells produced by meiosis for sexual reproduction.
What is a bivalent?
A pair of homologous chromosomes arranged side by side.
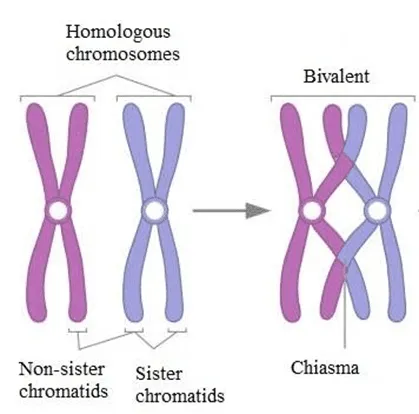
What occurs during crossing over in Prophase I?
Non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material at points called chiasmata.
What is the function of the spindle in meiosis I?
To help separate homologous chromosomes.
What happens during telophase I of meiosis?
Nuclear envelopes form around two groups of chromosomes and nucleoli reform.
What is cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm after mitosis or meiosis.
How does meiosis II compare to mitosis?
Meiosis II is almost identical to the stages of mitosis.
What is produced by the end of meiosis II?
Four haploid cells.
What are the stages of Mitosis?
The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
What happens during Prophase of Mitosis?
During prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope begins to break down, the nucleolus disappears and the spindle fibres form.
What happens during Metaphase of Mitosis?
During metaphase, chromosomes align at the metaphase plate, and spindle fibers attach to the centromeres.
What happens during Anaphase of Mitosis?
During anaphase, sister chromatids separate at the centromere and are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell, spindle fibres contract.
What happens during Telophase of Mitosis?
During telophase, chromosomes decondense, and the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes.
What is Cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis is the process of cytoplasmic division that occurs after mitosis, resulting in two separate daughter cells.
What are the stages of Meiosis I?
The stages of meiosis I are prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, and cytokinesis.
What happens during Prophase I of Meiosis?
During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair and exchange genetic material through crossing over at the chiasmata.
(basically whatever happens in prophase in mitosis)
The chromosomes are arranged side by side in homologous pairs (bivalents)
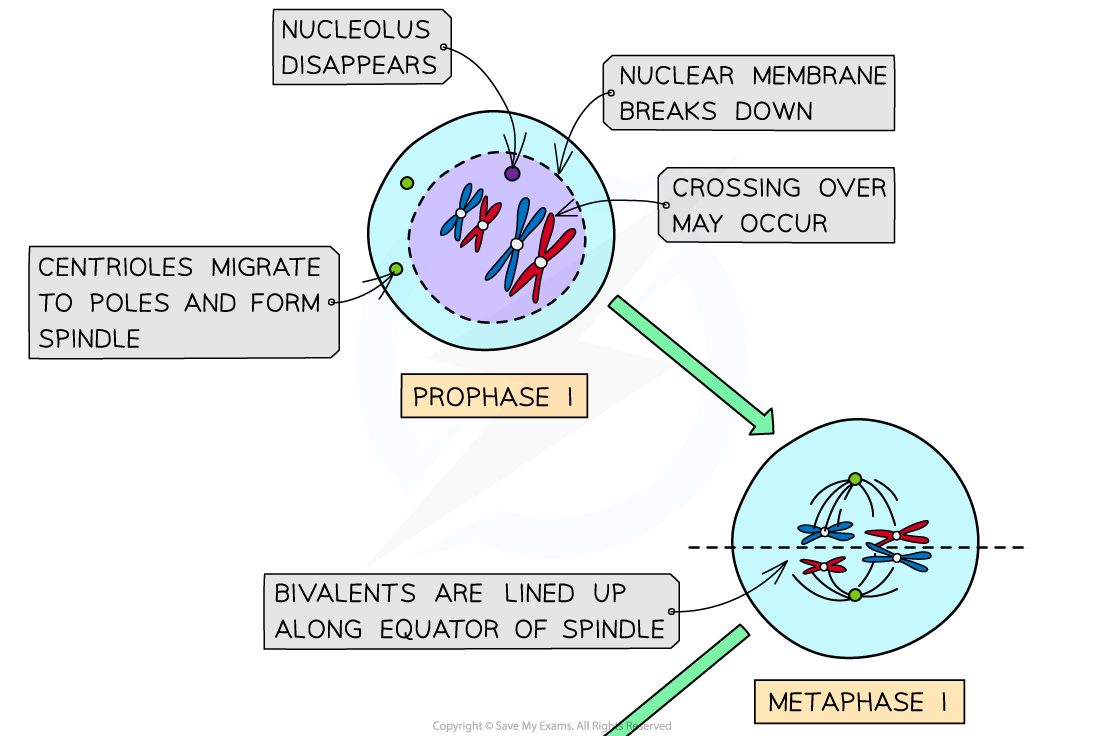
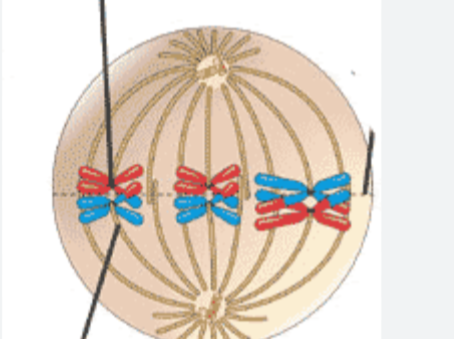
What happens during Metaphase I of Meiosis?
During metaphase I, homologous chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate.
with the spindle fibres attached to the centromeres
The maternal and paternal chromosomes in each pair position themselves independently of the others
this is independent assortment
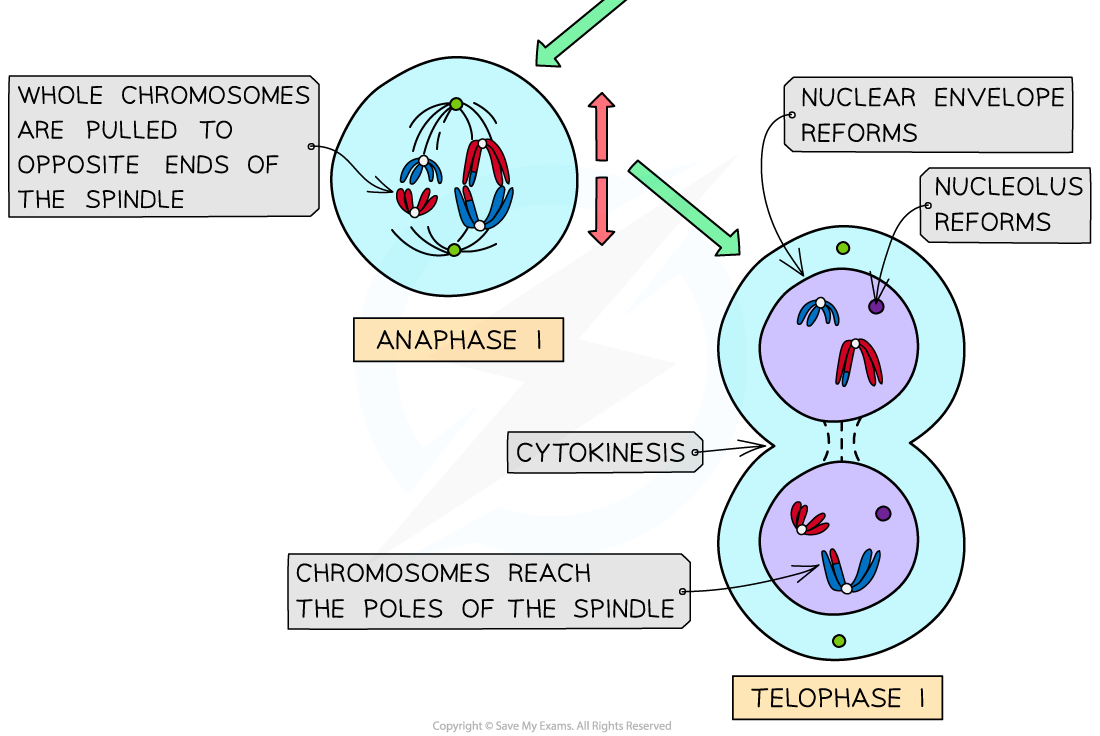
What happens during Anaphase I of Meiosis?
During anaphase I, homologous chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite poles.
N.B. centromeres DON’T DIVIDE!! Whole chromosomes pulled to opposite sides of the cell
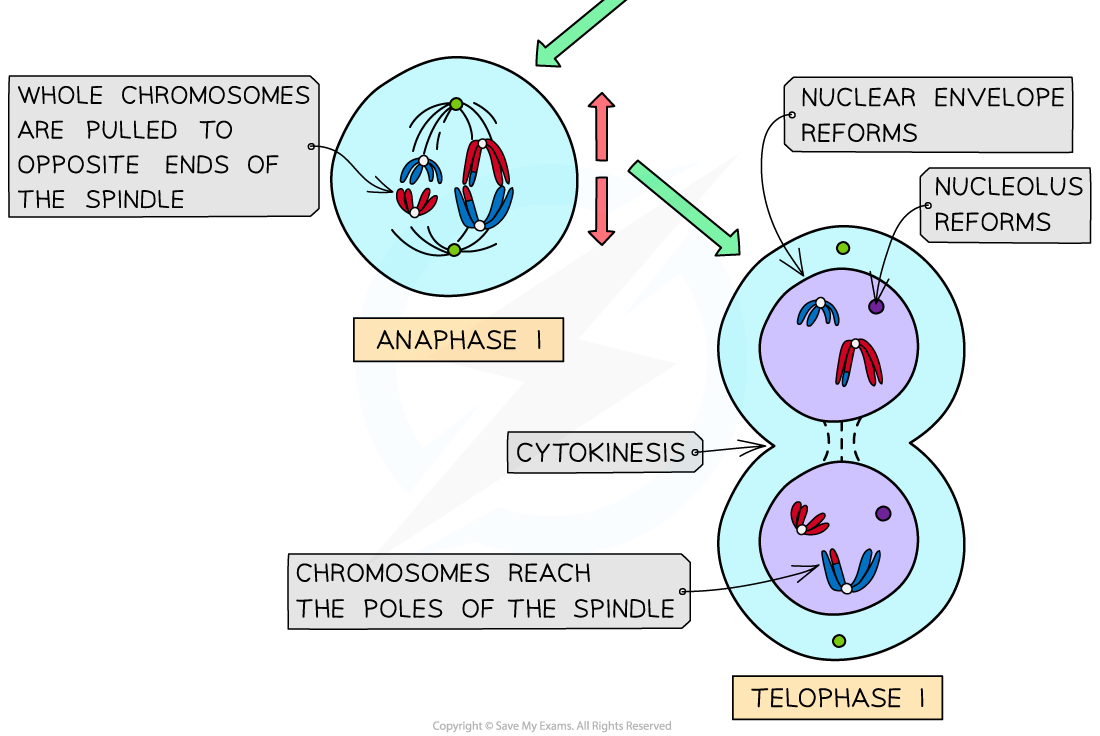
What happens during Telophase I of Meiosis?
During telophase I, the cell prepares to divide, and the nuclear envelope may reform.
Spindle fibres start to break down
Describe how cytokinesis occurs in animal cells
In animal cells: the cell surface membrane pinches inwards creating a cleavage furrow in the middle of the cell which contracts, dividing the cytoplasm in half
Describe how cytokinesis occurs in plant cells
In plant cells, vesicles from the Golgi apparatus gather along the equator of the spindle (the cell plate).
The vesicles merge with each other to form the new cell surface membrane
What is the end product of cytokinesis in meiosis I?
The end product of cytokinesis in meiosis I is two haploid cells
What are the stages of Meiosis II?
The stages of meiosis II are prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II, and cytokinesis.
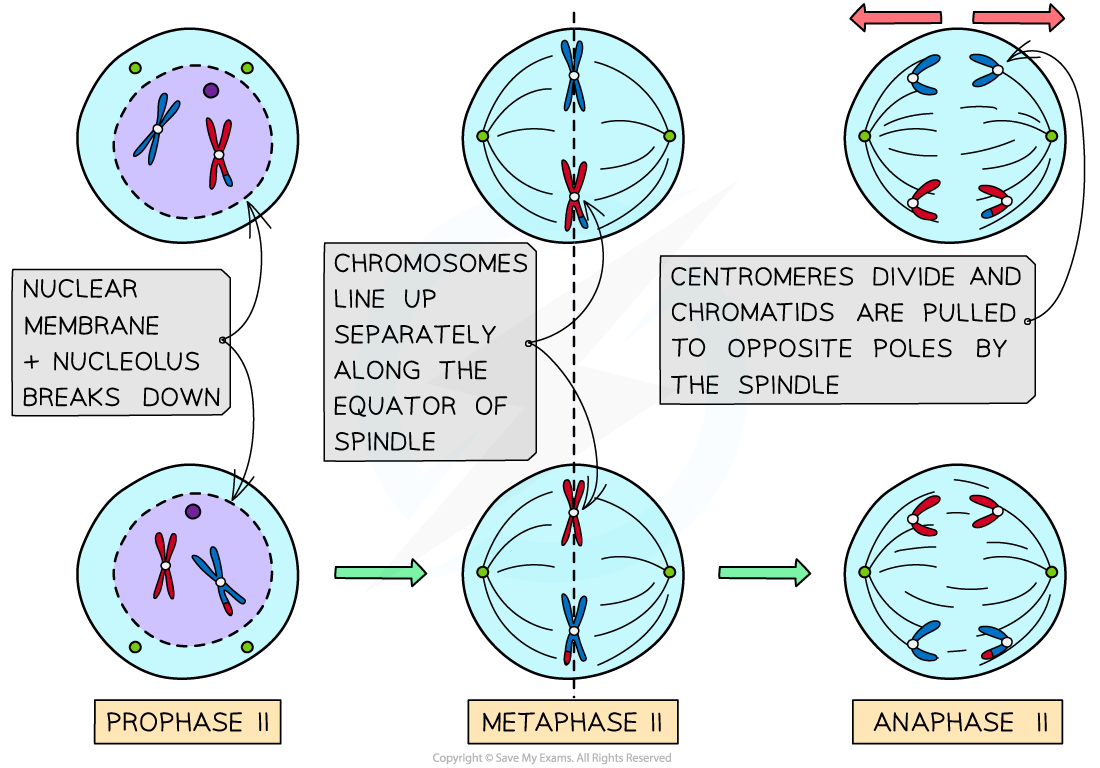
What happens during Prophase II of Meiosis?
During prophase II, the nuclear envelope breaks down if it reformed, and spindle fibers begin to form.
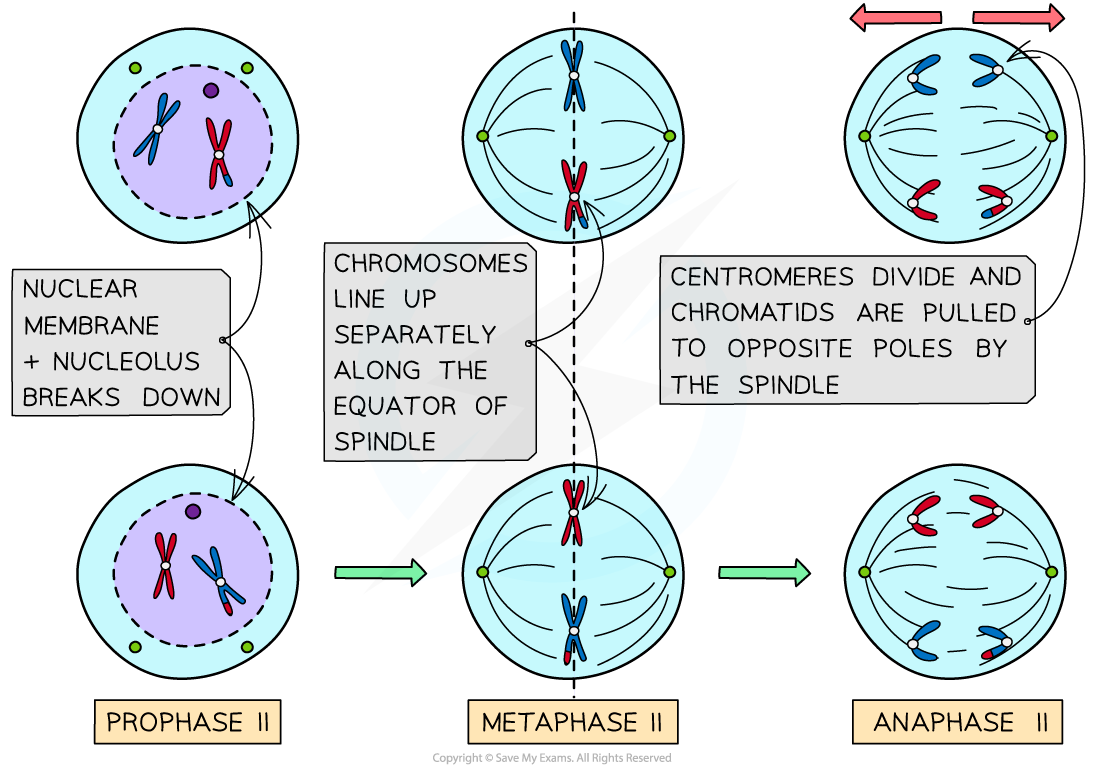
What happens during Metaphase II of Meiosis?
During metaphase II, chromosomes align at the metaphase plate again.
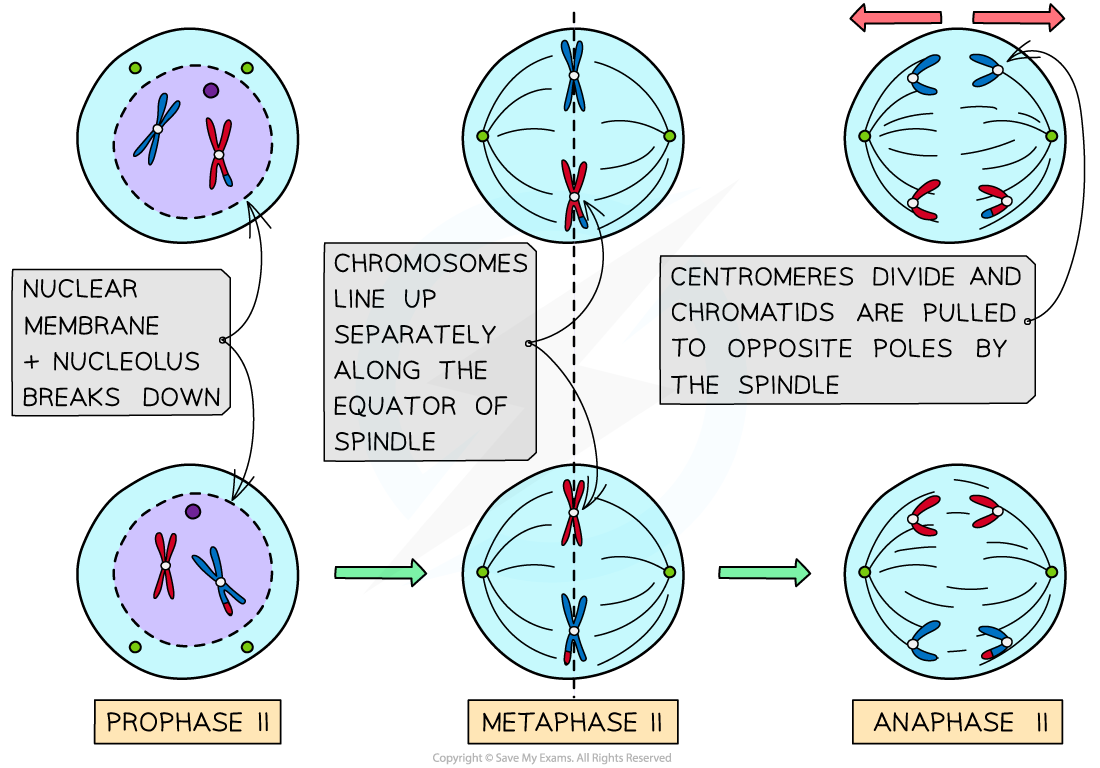
What happens during Anaphase II of Meiosis?
During anaphase II, sister chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite poles.
What happens during Telophase II of Meiosis?
During telophase II, nuclear envelopes reform around the four sets of chromosomes, leading to the formation of four haploid cells.
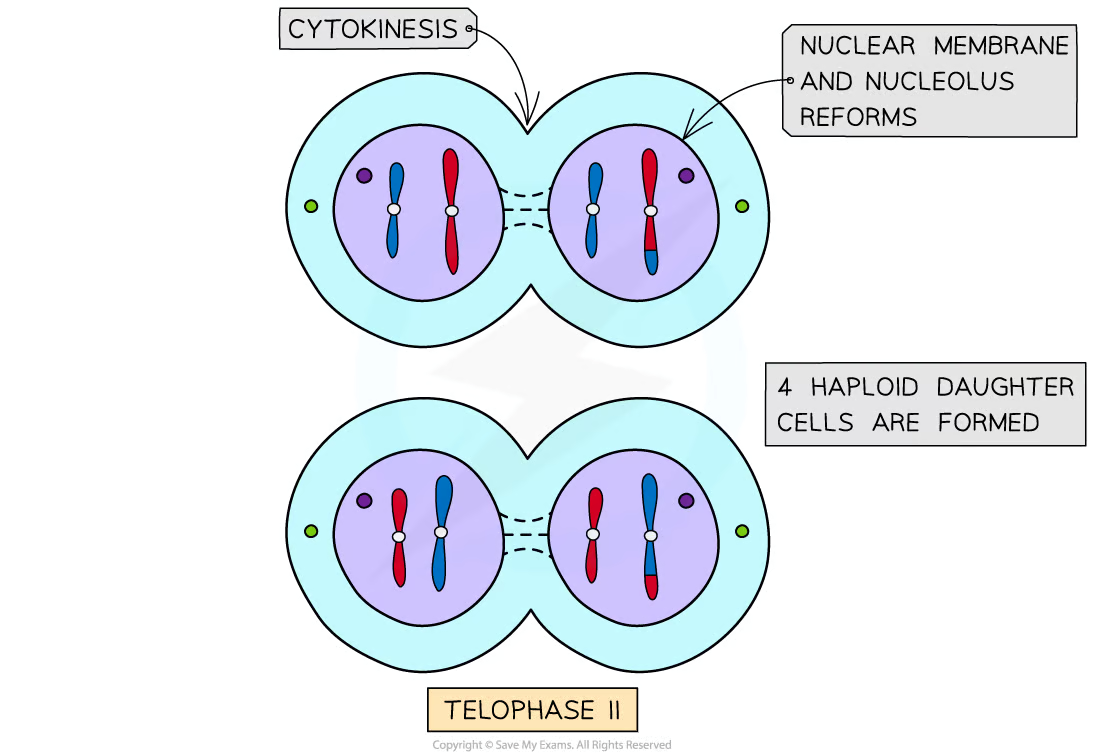
What is Cytokinesis in Meiosis?
Cytokinesis in meiosis occurs after telophase II, resulting in the division of the cytoplasm of the two cells into four haploid daughter cells.
Chromosomes vs chromatids? How to differentiate and count chromosomes?
We count chromosomes by the number of centromeres present.
So when the 46 chromosomes duplicate during interphase and the amount of DNA in the cell doubles there are still only 46 chromosomes present
because there are still only 46 centromeres present.
However, there are now 92 chromatids, which are strands of replicated chromosomes.