12- interim restorations
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Why do we use interim restorations?
Needs to function for extended period- can be weeks or months- must be adequate to maintain health
Lab delays
Patient unavailable
Delay placing definitive restoration due to TMJ disorder factors or perio disease
What are the biological requirements
Protect pulp
Maintain periodontal health- facilitate plaque removal, good marginal fit, contours, smooth surface
Provide occlusal compatibility
Maintain tooth position
Protect against fracture
what are mechanical requirements
Resists functional loads, removal forces
Maintain interabutement alignment- don’t want abutments to move
Condense slides 10, 11 about function
How do we prevent tooth displacement after prepping tooth?
Referent interim resto quickly
Small space between them- luting agent has lower strength then regular cements- cannot withstand added force if big space
Removal of reuse
What are aesthetic requirements?
Easily contourable
Colour compatibility and stability overtime
Translucency
Material matches colour of adjacent teeth, interim restoration is a guide to know what they want- specific feedback
What are indications of fiber-reinforced interim restorations?
Long span posterior FDP
Long treatment time
Can’t avoid excessive forces on prosthesis
High masticatory muscle strength
Freq breakage history
Models used in making interim restorations consist of…
External surface form (esf)- 2 catergoirss- custom, preformed
Tissue surface form (tsf)- divided into indirect, direct and indirect-direct procedure
Slide 19
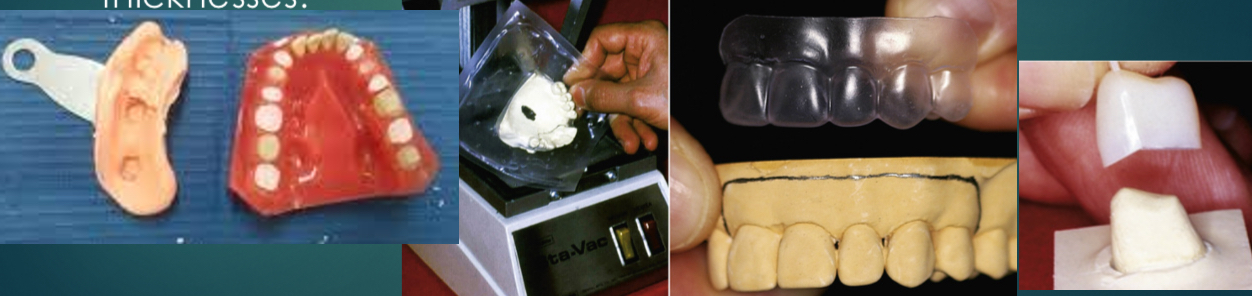
What is a custom ESF?
Negative reproduction of either patients teeth before prop or modified diagnostic cast
Obtain from impression- mouldable putty popular- can trim easily for accurate reseating
Use thermoplastic sheets
Fill in with autopolymerising resin or acrylic
Indirect procedure of indirect procedure (prpepared outside mouth)- adva
Impression of prepared teeth- pour it with quick setting material
No contact of free monomer- can cause allergic reaction or damage gingiva or tooth
Teeth aren’t effected by heat from polymerising resin
Can be retained for multiple uses
Won’t shrink
Direct procedure disadvs
Tissues trauma from polymerising resin and poor marginal fit
Indirect- direct procedure
Condense slide 31
Advantages vs disadvantage of indirect-direct procedure?
Low chair time
Less heat generated in mouth- less resin used during lining
Minimal contact of resin monomer and tissues
Need to constantly adjust to seat shell completely in prepared tooth
Ideal properties of interim restorative materials
Good working time, easy moulding, rapid setting time
Biocompatible
Dimensional stability- during solidification
Easy to add to or repair
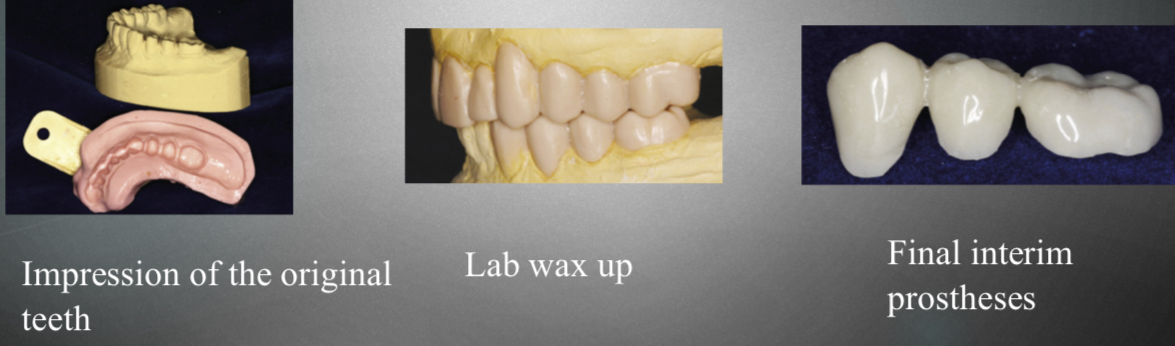
Custom indirect method- best
Impression of teeth
Lab wax up
Form final interim procedure
Not done with patient- easier
What is useful for making interim restorations in single anterior teeth and premolars?
Polycarboxylate crown
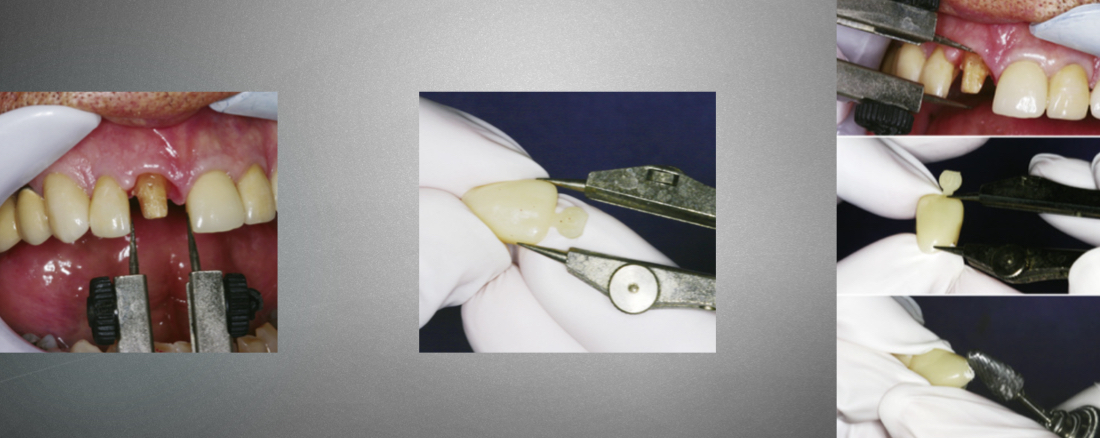
How can we provide interradicular retention for a tooth with no sound structure?
Cast metal post and core restoration
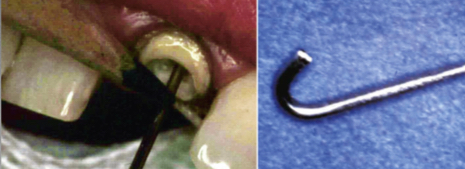
Place wire in post space and fill down with interim resin
What is the primary function and characteristics of interim luting agents?
Provide seal, prevents marginal leakage and pulp irritation
Low strength
Luting agents seals margin, easy to clean