PHEO 678 Exam 1: Key Terms in Medicine & Definitions
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Definition of Ergonomics
- law of work
- fitting the job to the worker and not the worker to the job
4 goals of ergonomics
- efficient production
- improve quality of work life
- improve product quality
-optimize health & safety
core science in ergonomics
anatomy, engineering, physics, psychology, anthropology, physiology, medicine, and epidemiology
Fredrick Taylor
-Father of scientific management
-1st management consultant
-systematic observational & study
-Bethlehem Steel (shoveling)
Frank & Lillian Gilbreth
- time and motion studies
- movement and reducing fatigue
- Therbligs
Bernardino Ramazzani
- industrial hygiene
- study occupational diseases
Fredrick Bartlett
- studied pilot stress
- fit man to job (FMJ)
What does human factors put more emphasis on
integration of human consideration into total system design process
Benefits of Ergonomics
1. safer job with fewer injuries
2. increased efficiency & productivity
3. improved quality & fewer errors
4. improved morale
levels of prevention
primary, secondary, tertiary
primary prevention
prevention of disease before it happens
secondary prevention
early detection of asymptomatic disease
tertiary prevention
reduce long-term dysfunction
occupational variables are associated with what?
increase incidence in diseases/case
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders
the adverse health effect that arise from repeated exposure to mechanical stresses in occupational settings
epidemiological evidence of WMDS
- no single comprehensive surveillance data system providing necessary data to link MSDs and work
- with no system, it is necessary to examine elements of the association, as represented on several incomplete, somewhat overlapping data source
Theories of causation of WMDS
- exposure-specific task elements
- dose-magnitude of biomechanical & physiological stress
- dosage pattern of temporal loading (duration & repetition)
- excessive biomechanical stress
- normal tissue respond with adaptive or degenerative changes
- excessive dosage leads to pathology
different types of MSD
- impingement syndrome
- epicondylitis
- carpal tunnel syndrome
impingement syndrome
irritation of the rotator cuff at the tendon
medinal epicondylitis
- small tear of the muscle/tendon unit on the inside of the elbow
- also known as golfer elbow or little league elbow
lateral epicondylitis
tennis elbow
- microscopic tears in tendon
- extensor muscles of arm
- inflamed or injured tendon tissue
Trigger Finger
formation nodule in tendon from repeated trauma
definition of anthropometric
measurement & analysis of human dimensions
anthropometric in ergonomics
to create the best possible situation on the job relative to:
- welfare of workers physical & mental health
- efficiency of production
- quality of product produced
Anthropometric basic design philosophies
- design for average
- design for extreme
- design for range
(5th to 95th percentile accommodates 90% of population)
Design principles
- design for largest person (clearance)
- design for smallest person (reach)
- design for average person (other)
- design for adjustability
types of anthropometry
- static (structural): body feature measurement are taken w/ body in fixed position
- dynamic (functional): dimensional obtained with body involved in physical activity
external dimensions
dimensions must be related to physical landmarks
What do most investigators assume with anthropometric data?
data is normally distributed
anatomical position
- universal "starting point"
- all joints are considered to be in a neutral position
- no movement has occurred yet
- arms slightly to side
- standing erect, palms and feet facing forward
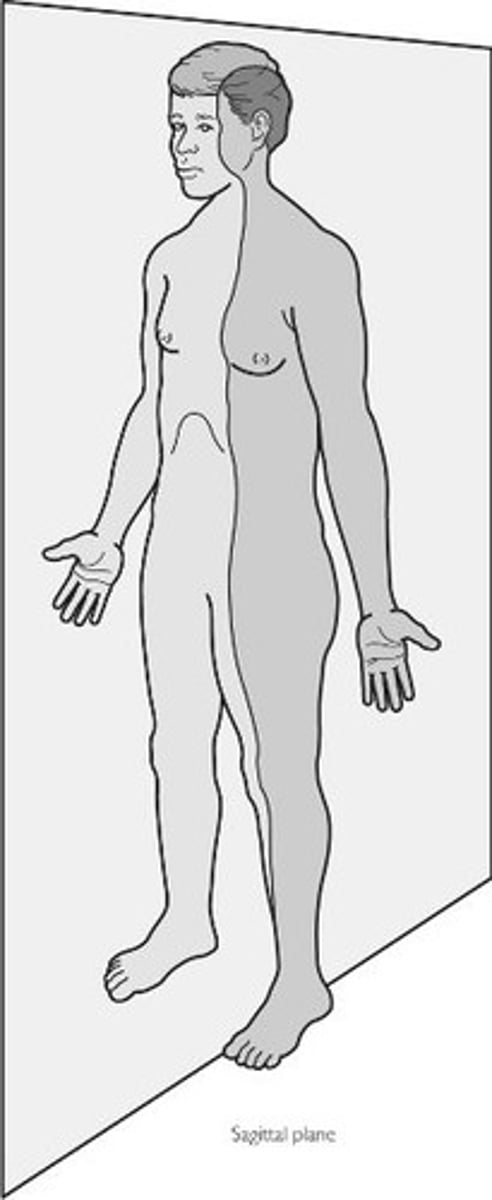
sagittal plane
the plane that creates a right and a left side of the body passing from the front to the back
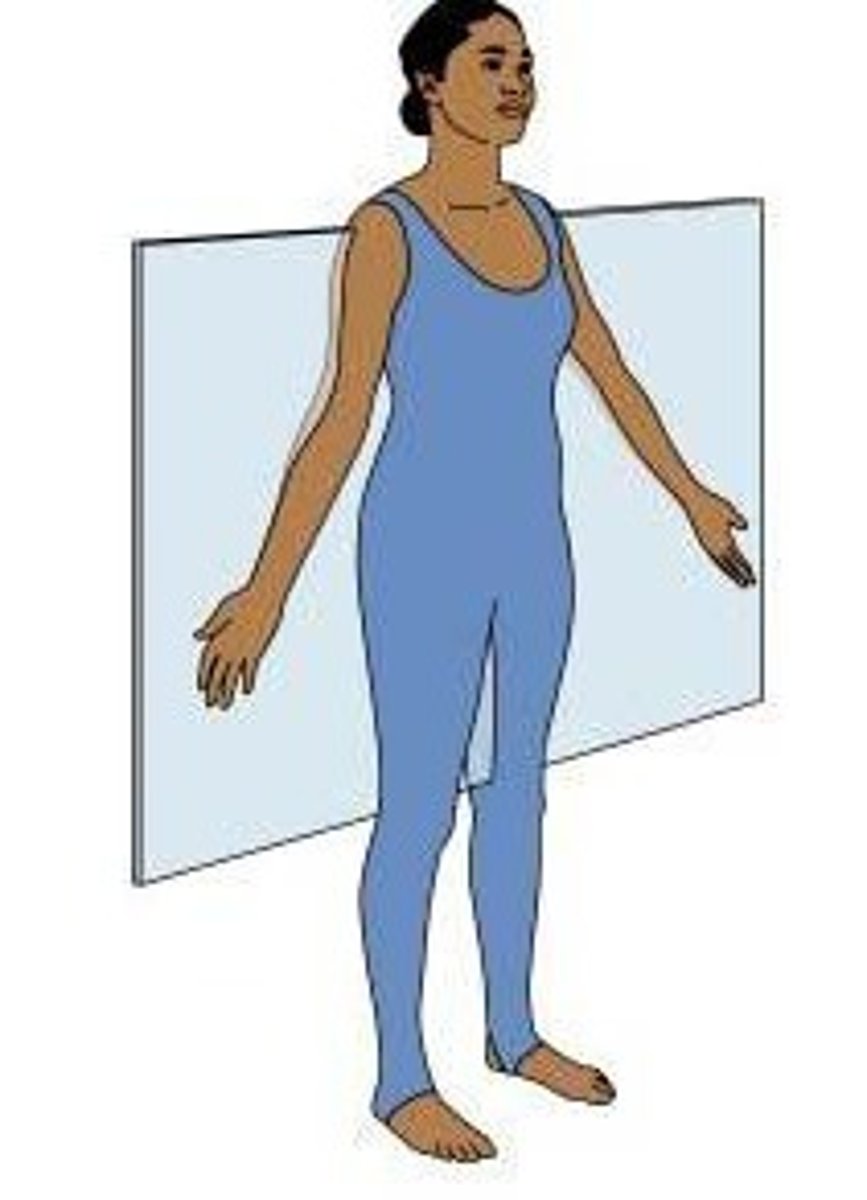
horizontal plane
also called the transverse plane, create a top and a bottom
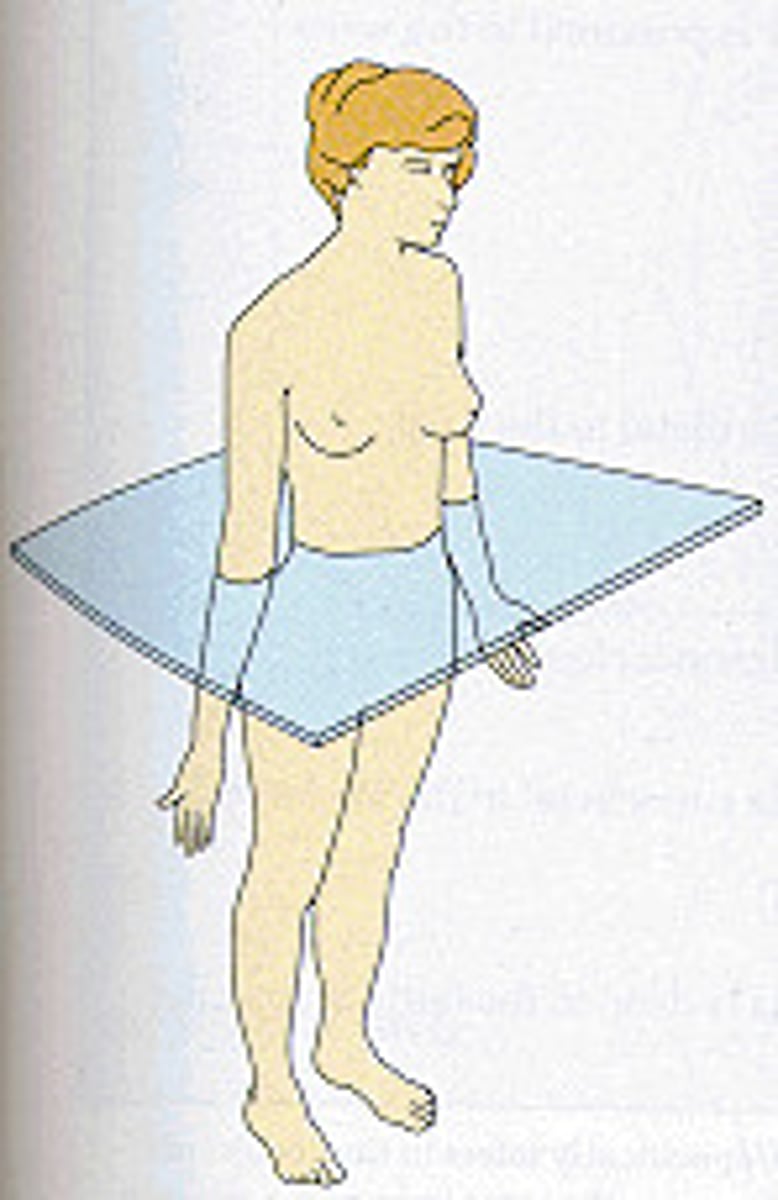
frontal plane
also called lateral plane, create a front and a back side as it passes from one side of the body to another
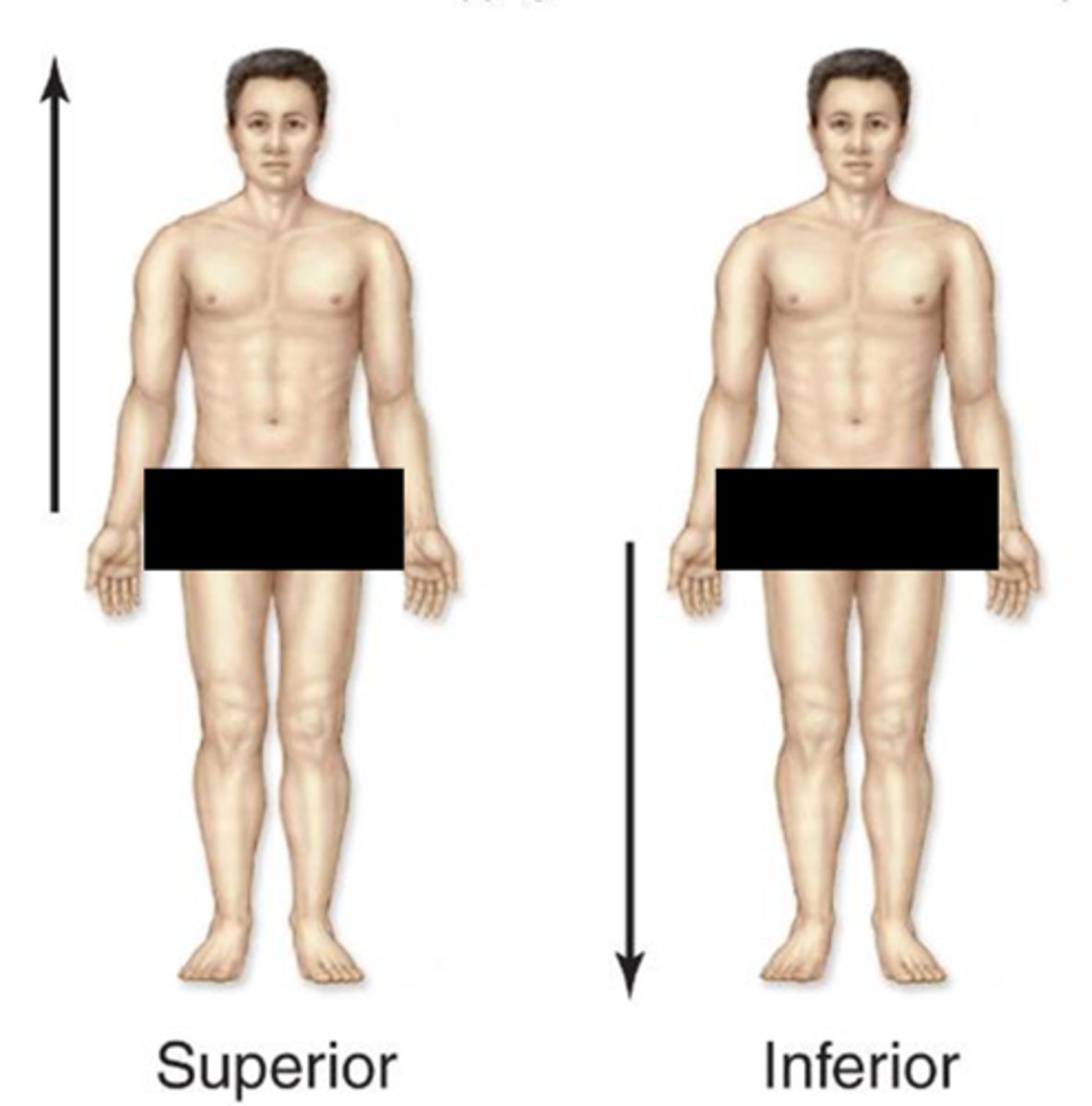
Superior
refers to something that is above or higher than another structure
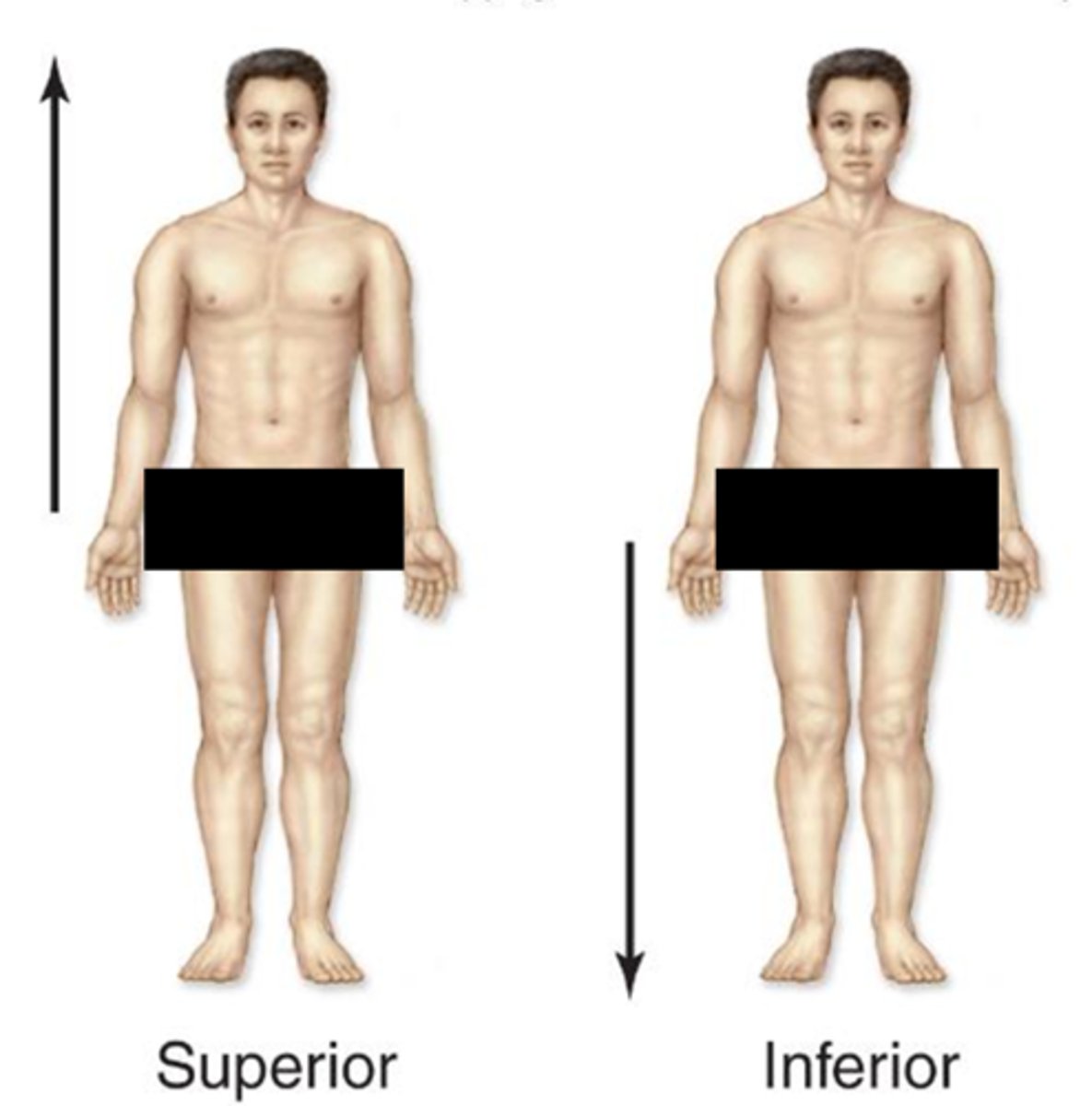
inferior
refers to something that is below or lower than another structure
lateral
refers to something farther away from the midline of the body
medial
refers to something closer to the midline of the body
anterior
refers to a structure that is in front of another structure
posterior
refers to a structure that is behind another structure
proximal
closer to the trunk of the body
distal
farther from the trunk of the body
dorsal
top side of a structure (dorsal fin)
plantar
underside of a foot
prone
means laying face down
supine
means lying face up
afferent
directed toward a center
efferent
directed away from center
central
situated or pertaining to center
peripheral
situated away from center
median
situated in midline of a structure
intermediate
situated between median (middle) and lateral (side)
deep
situated far beneath the surface
superficial
situated near the surface
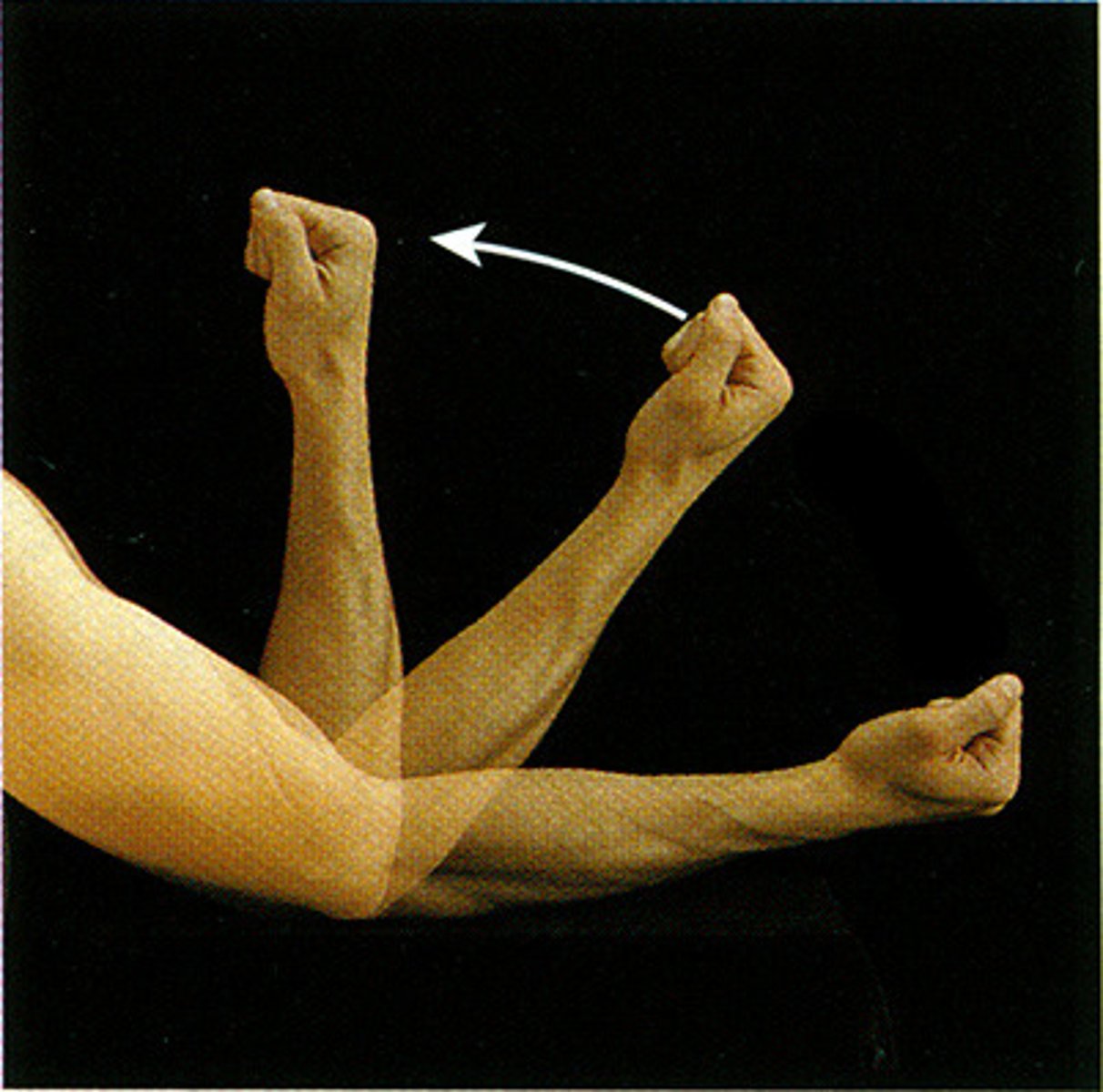
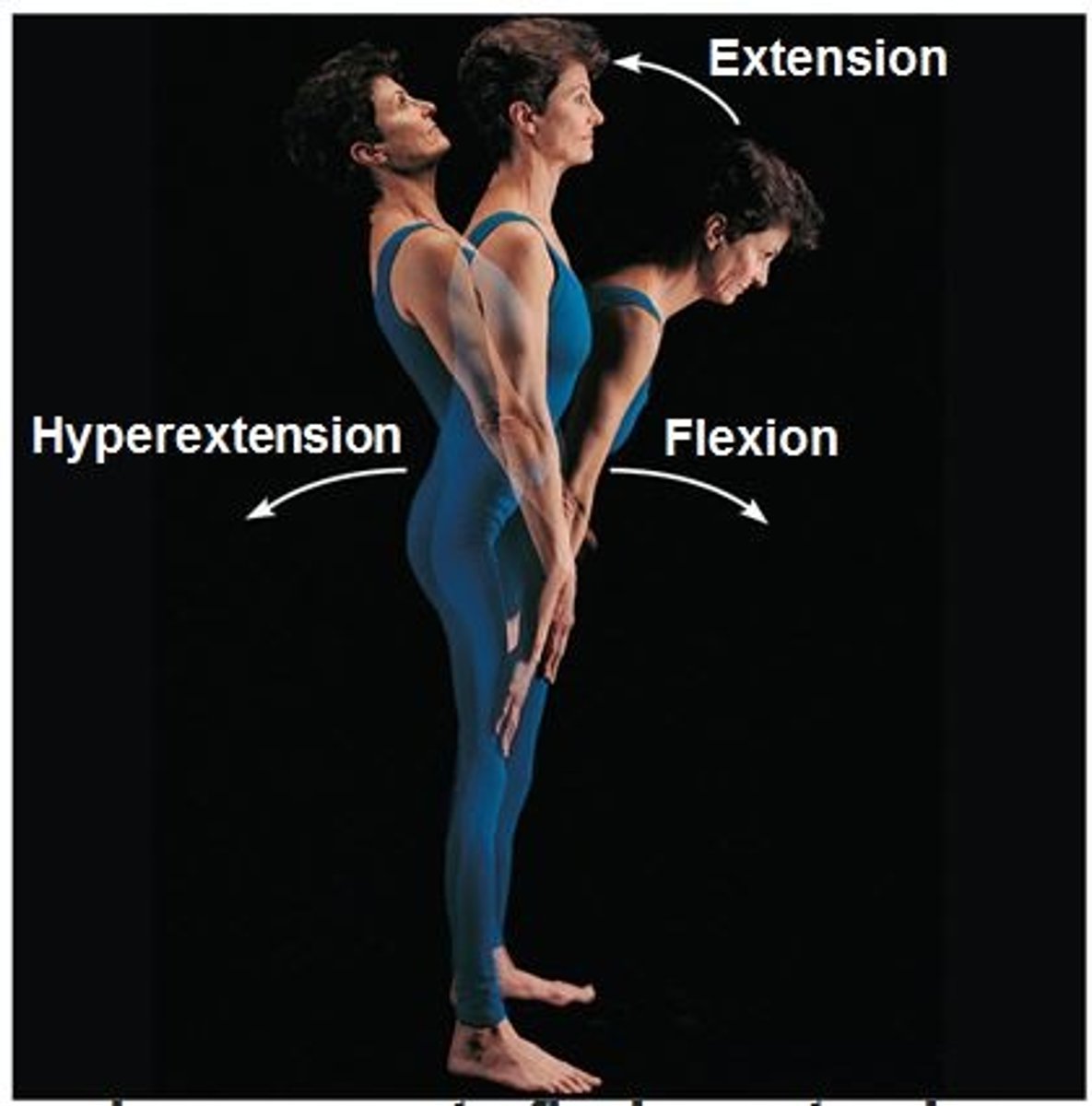
flexion
decreasing the angle formed by the bones of the joint
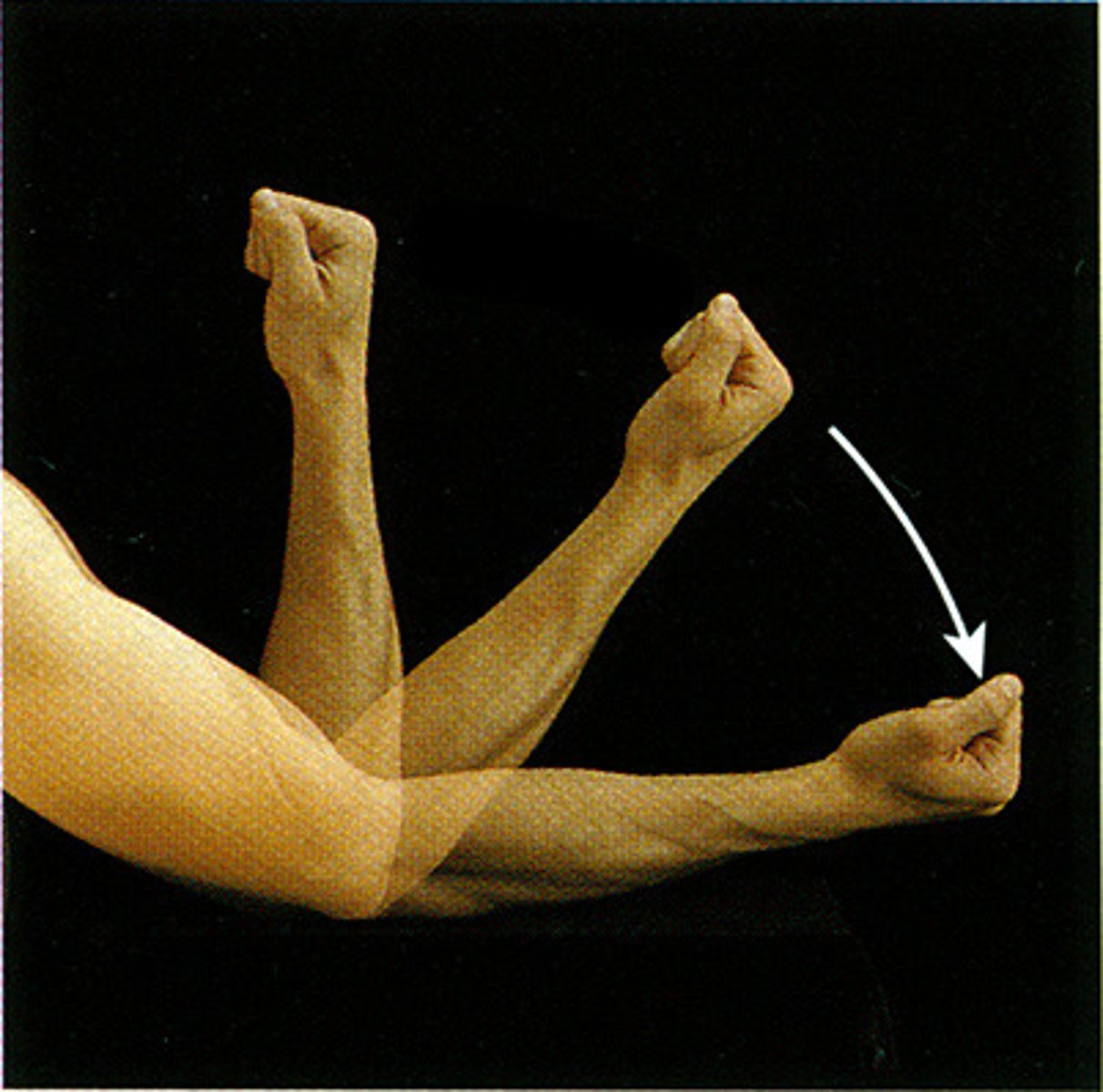
extension
increasing the angle of the joint
hyperextension
extreme or excessive straightening of a part
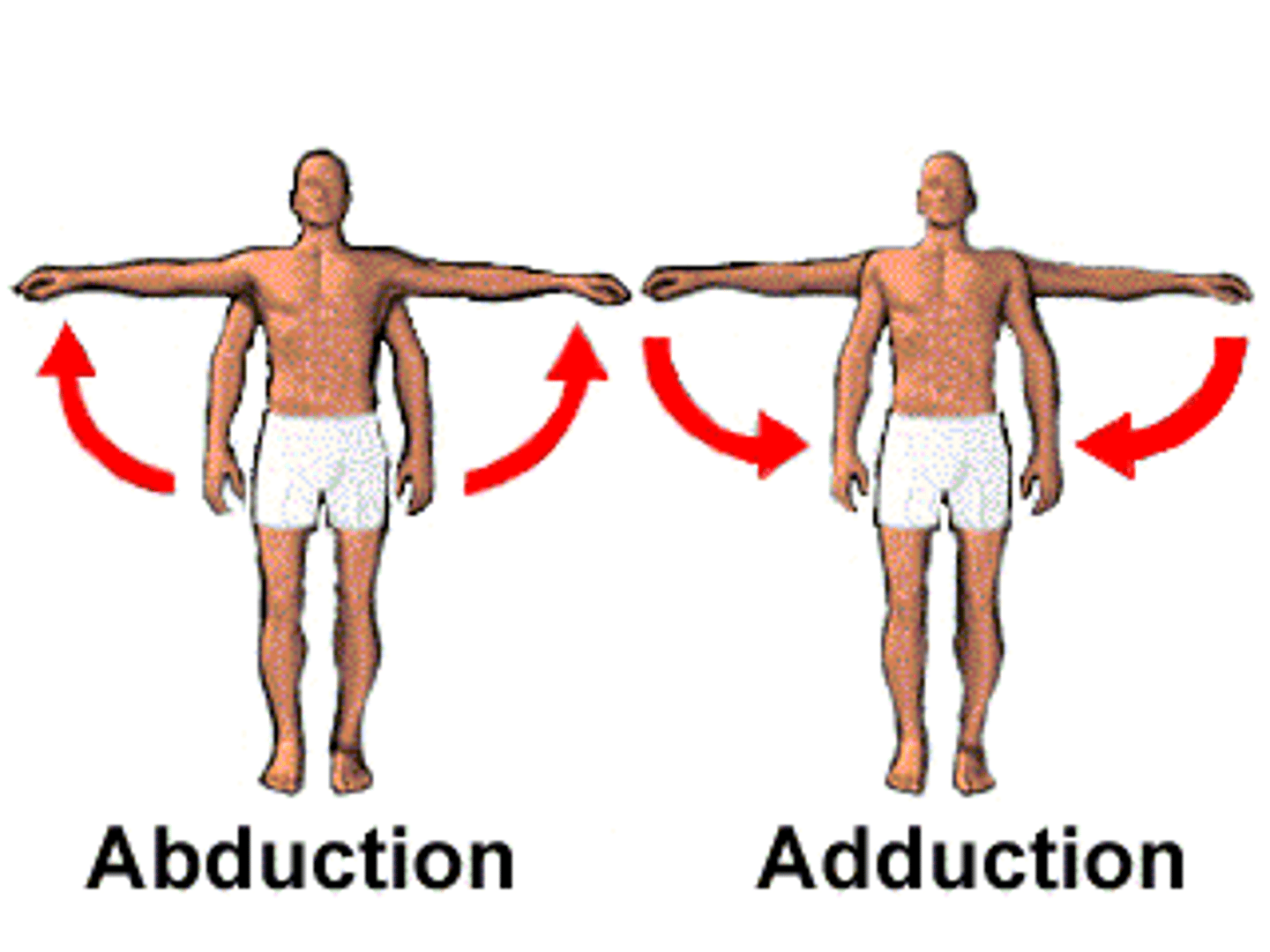
abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
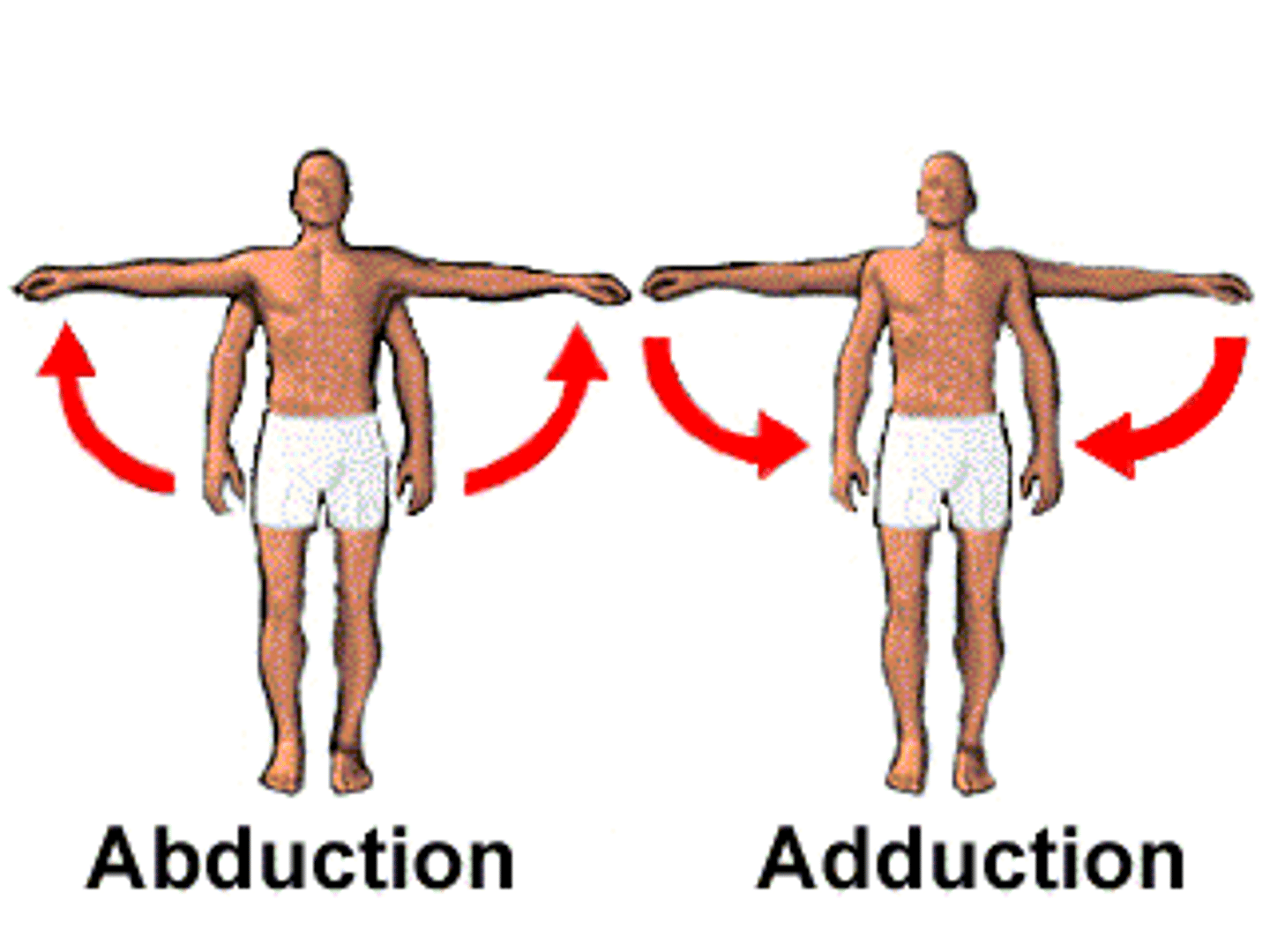
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
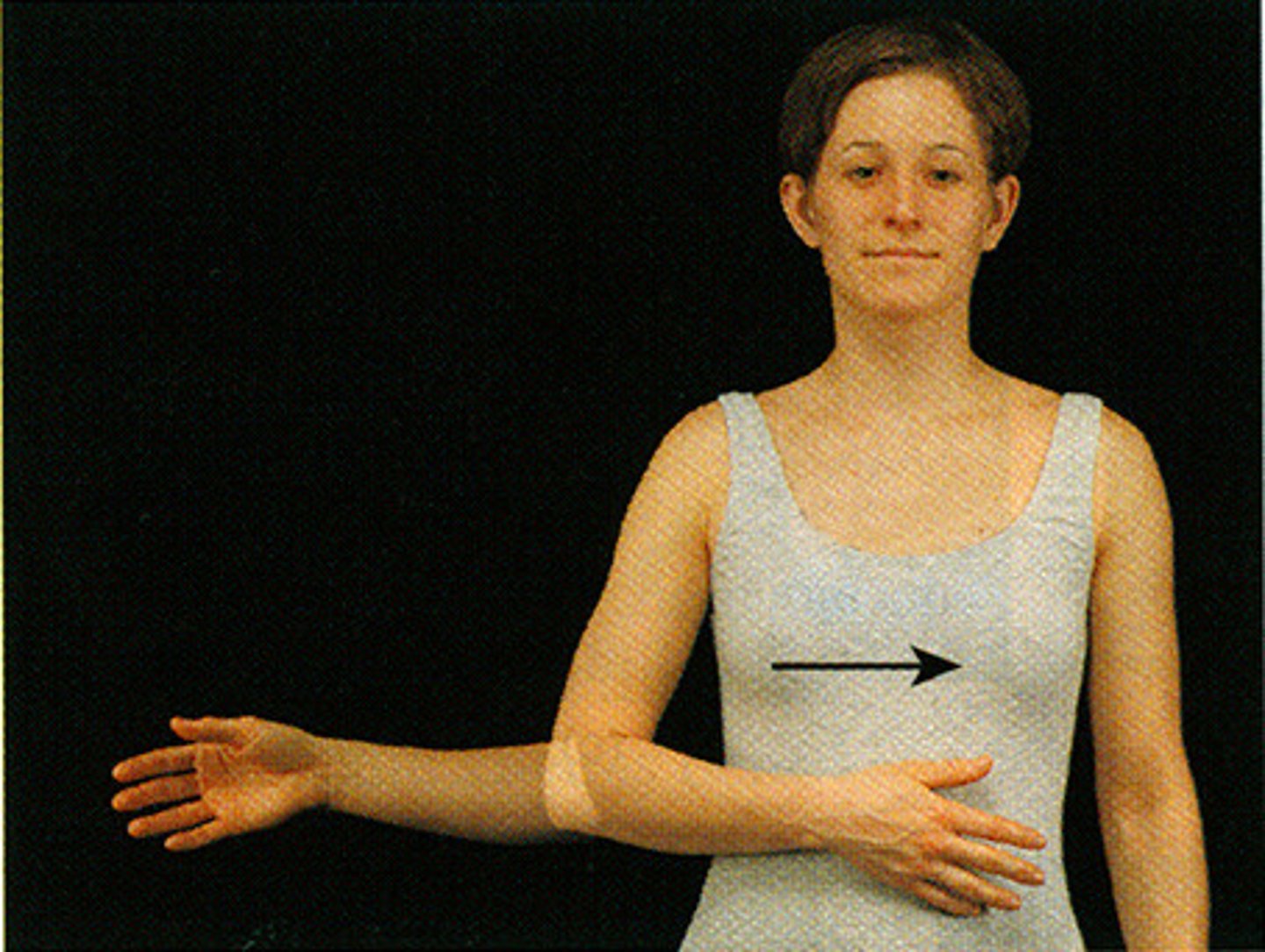
internal (medial) rotation
anterior surface of the arm or leg rotates medially toward midline
external (lateral) rotation
anterior surface of the arm or leg rotates laterally away from midline
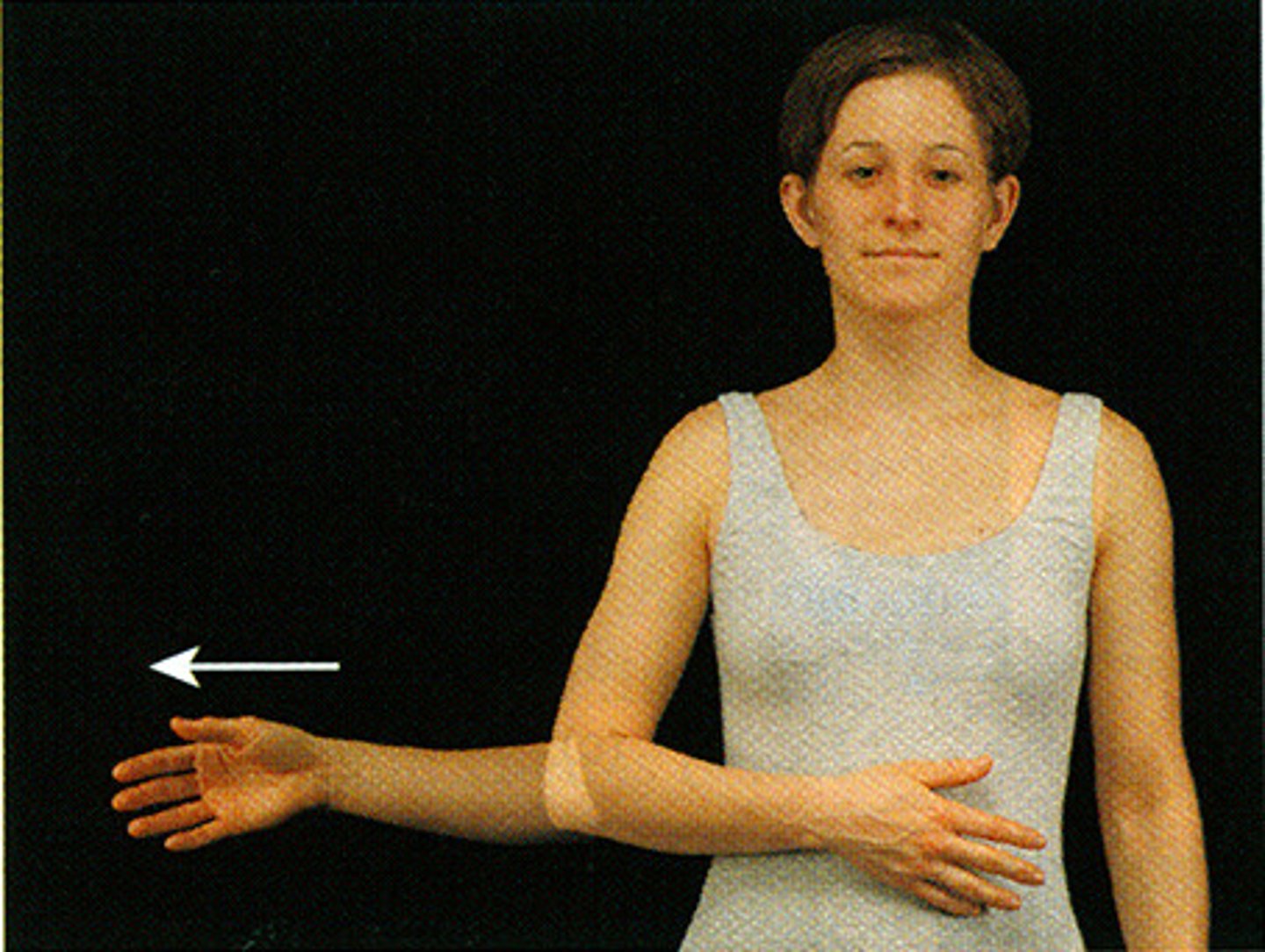
Circumduction
movement in 2 or 3 planes
at which joints is the movement possible? hip and shoulder
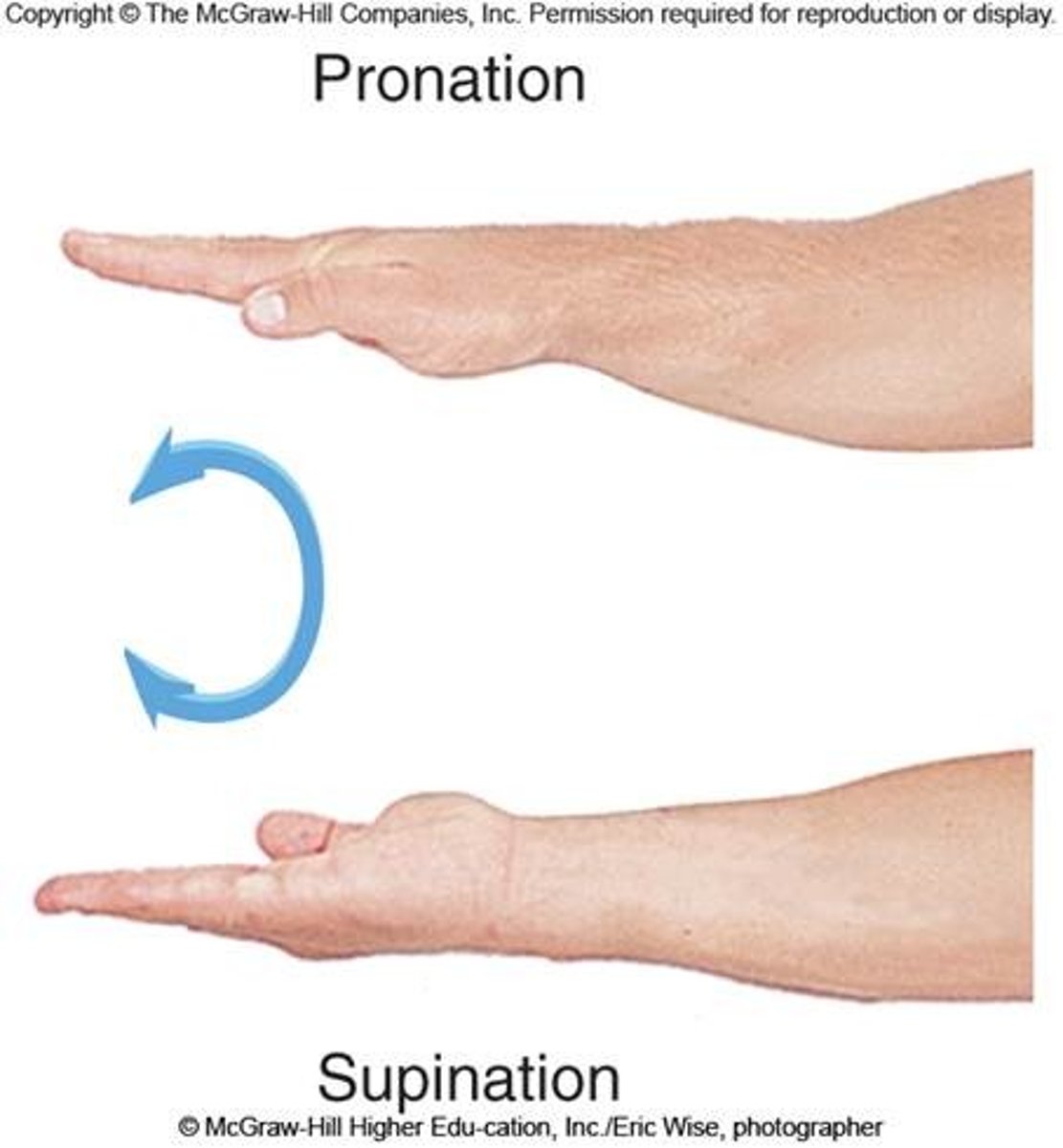
pronation
turning the forearm toward the body
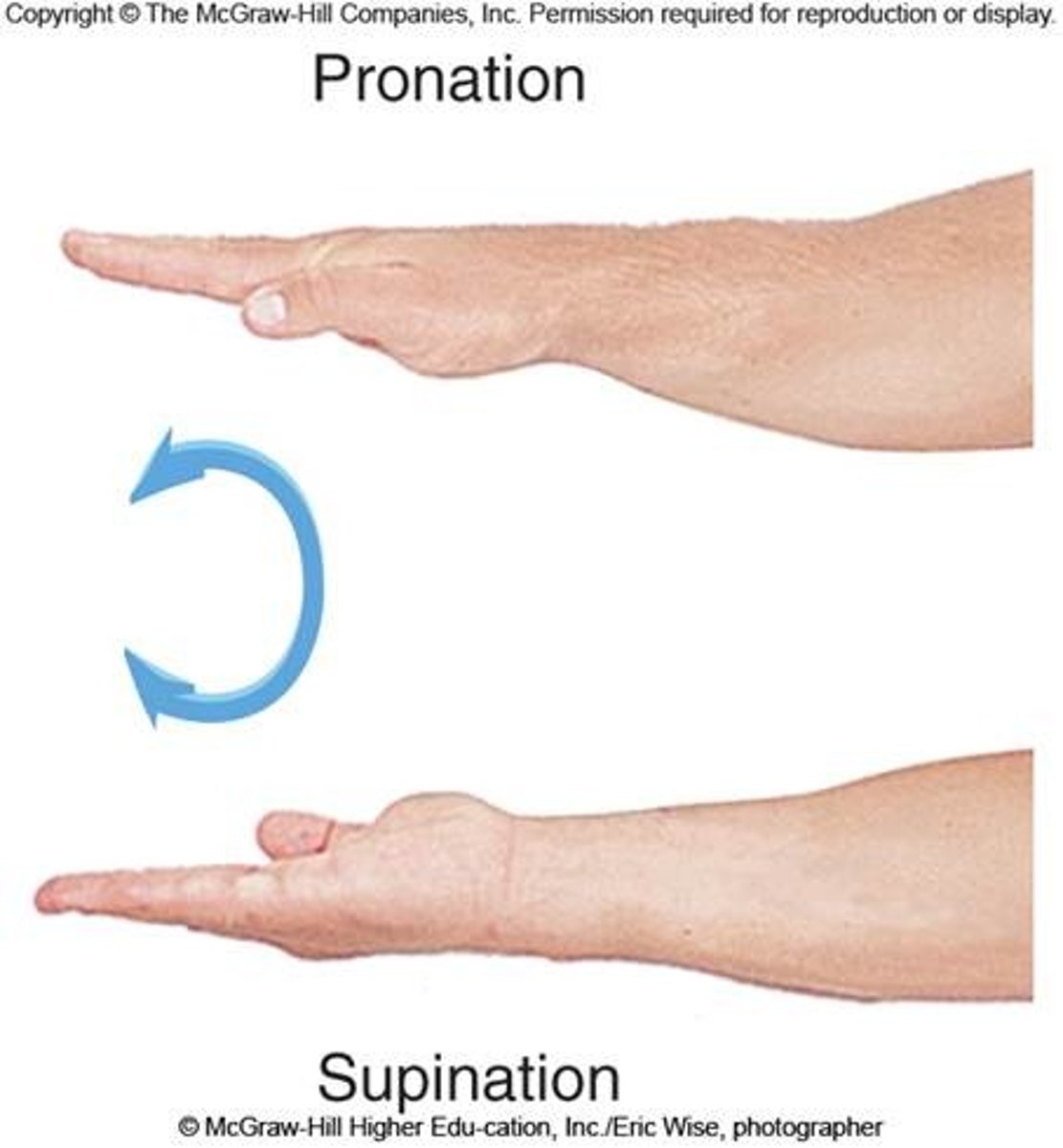
supination
turning the forearm outward from pronated position (holding cup of soup)
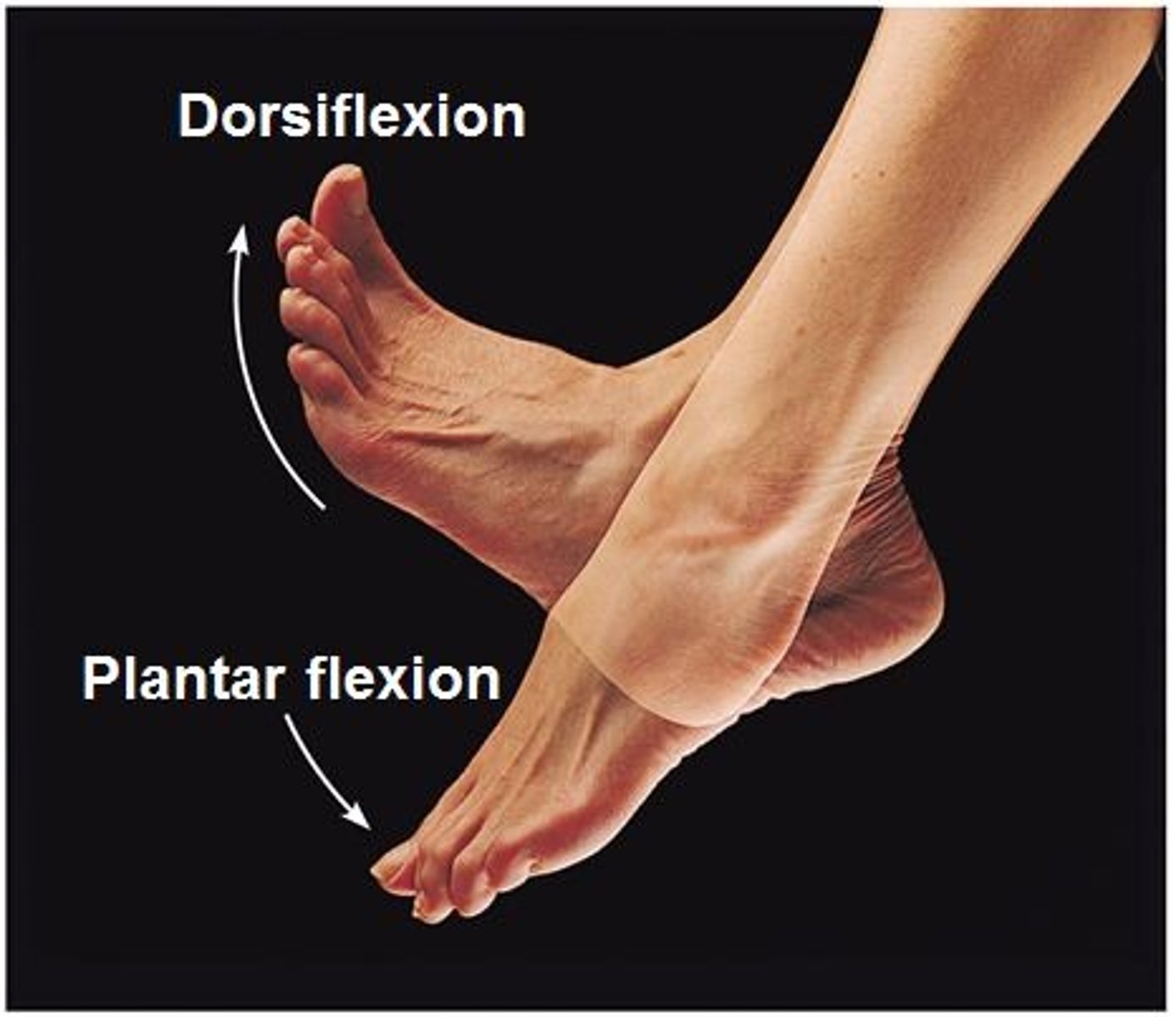
Dorsiflexion
bringing the toes up towards the body
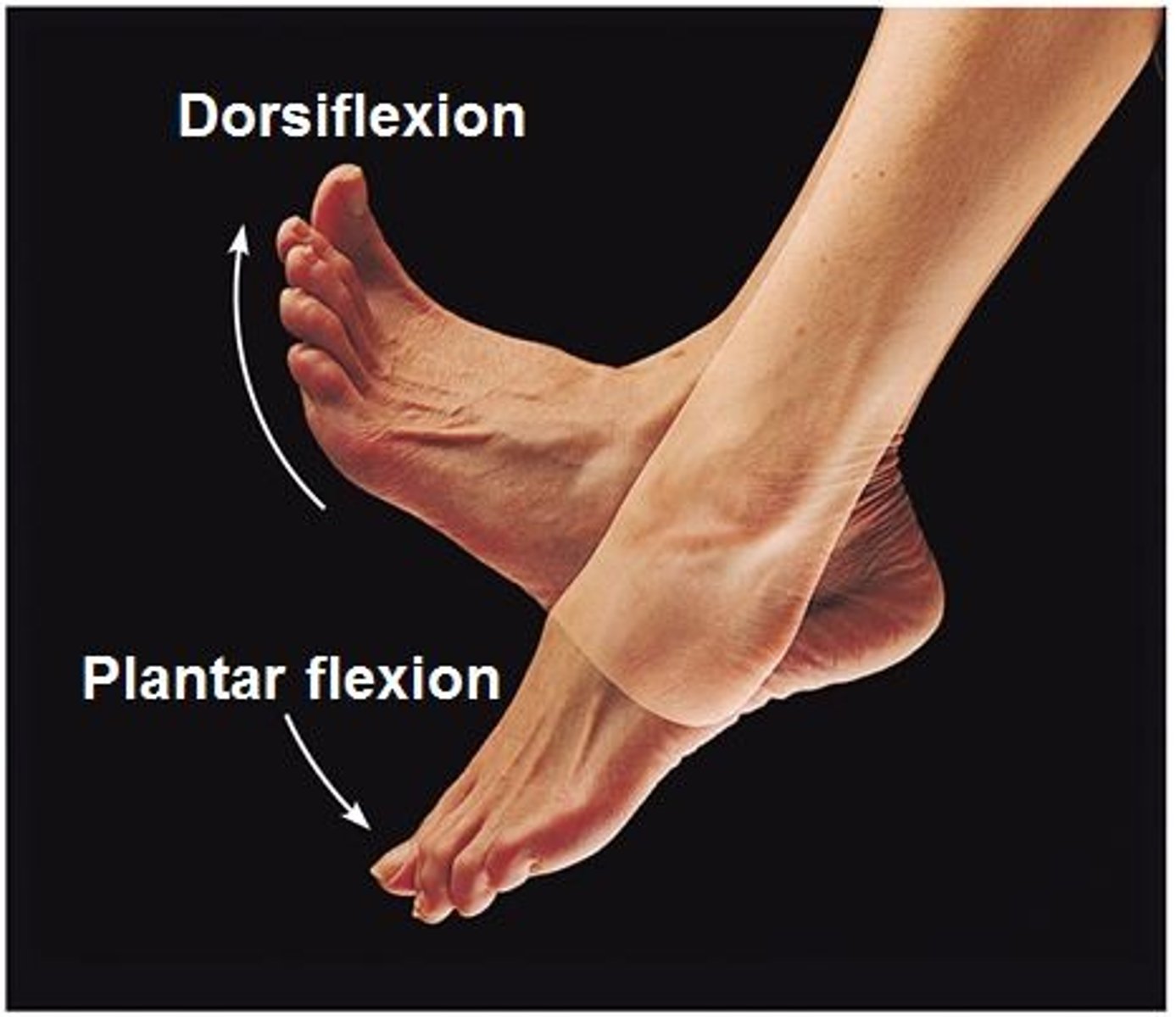
plantar flexion
pointing the toes down away from body
abrasion
skin surface scraped away
acute
recent or new injury; sudden onset
atrophy
wasting away of tissue or an organ
avulsion
tearing away of a part or a structure
bursa
fluid filled sac
calcification
deposits of calcium in an area
chronic
injury with long onset and long duration
contraindictate
to advise against
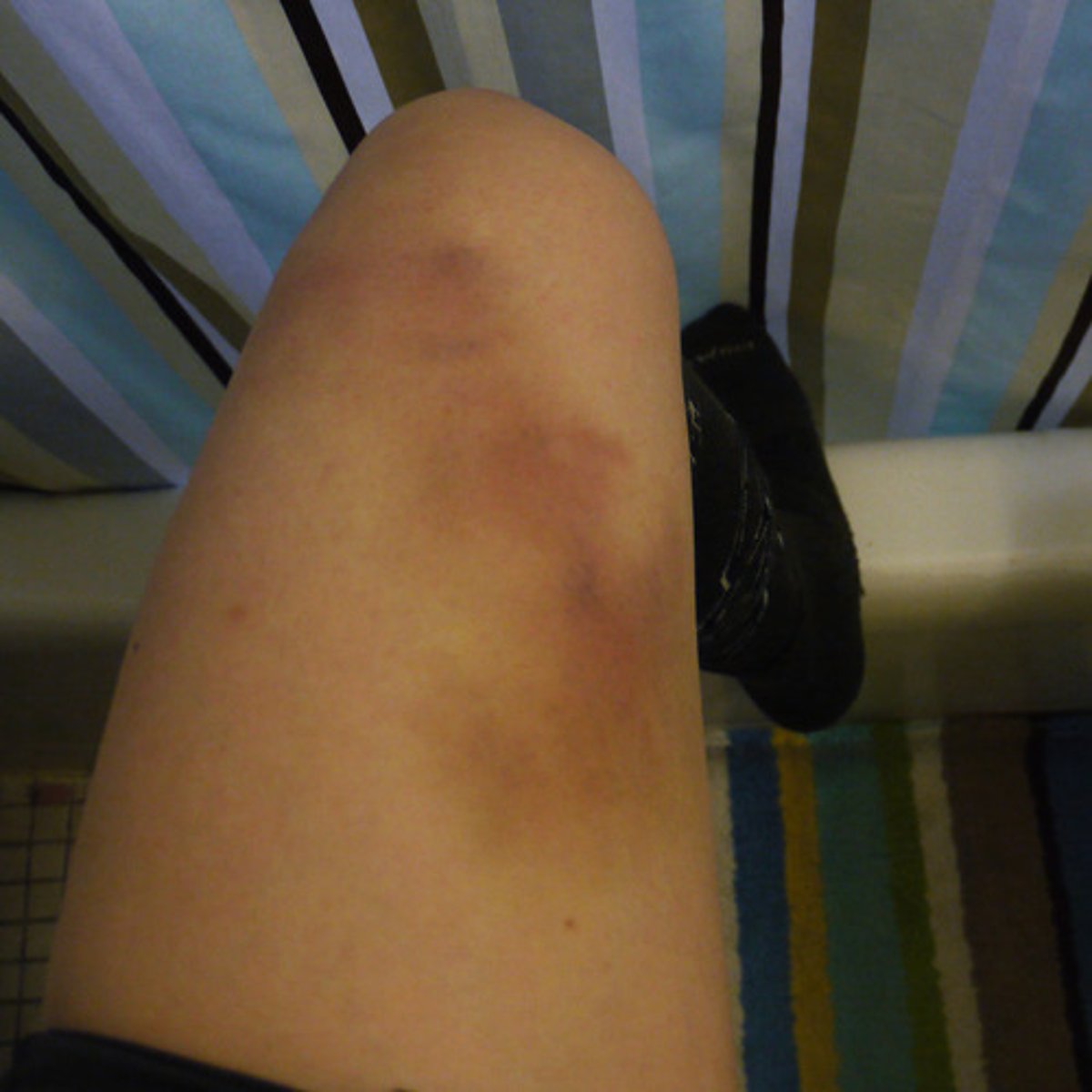
Contrusion
bruise
crepitus
crackling sound

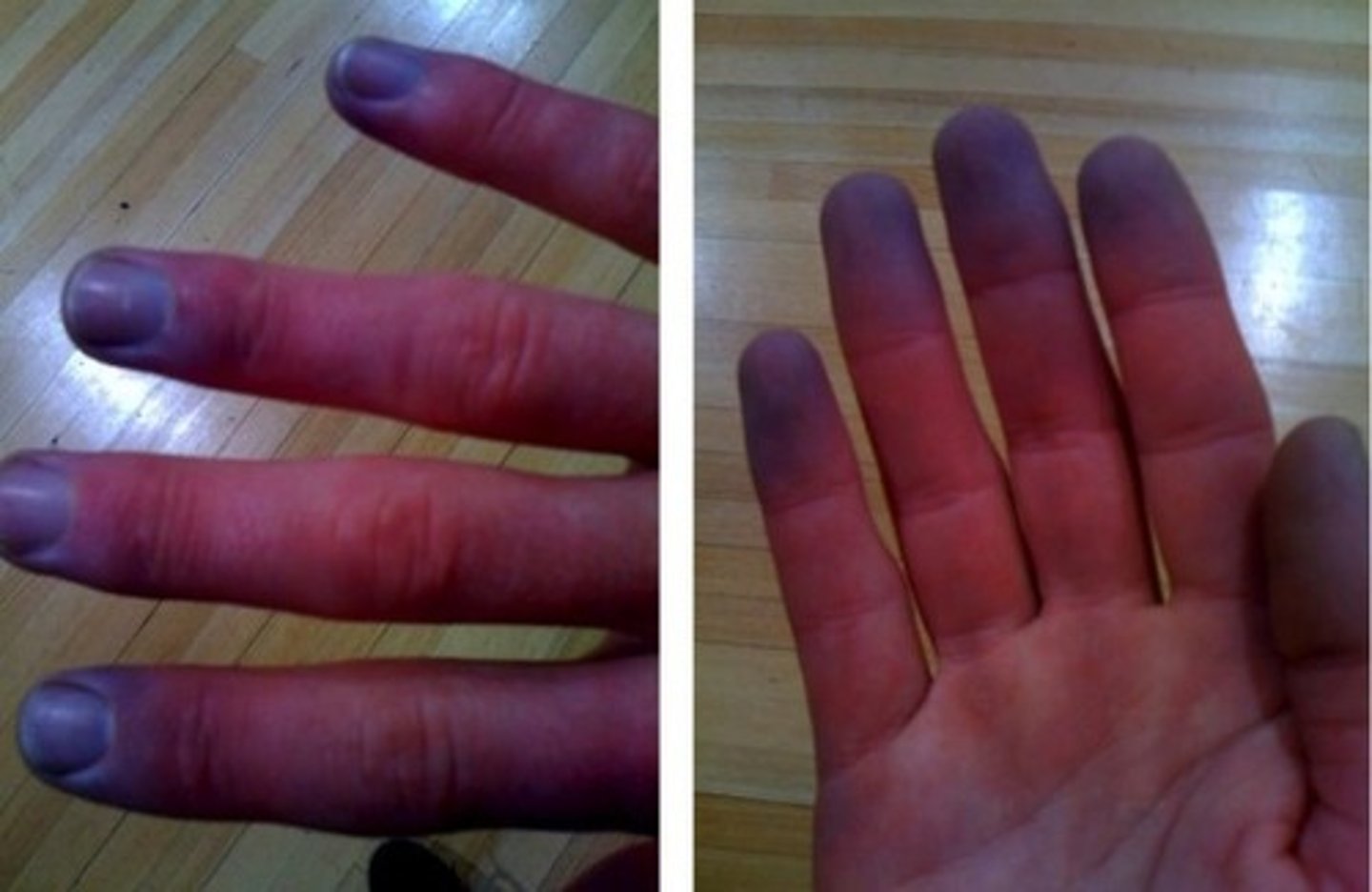
cyanosis
blue discoloration

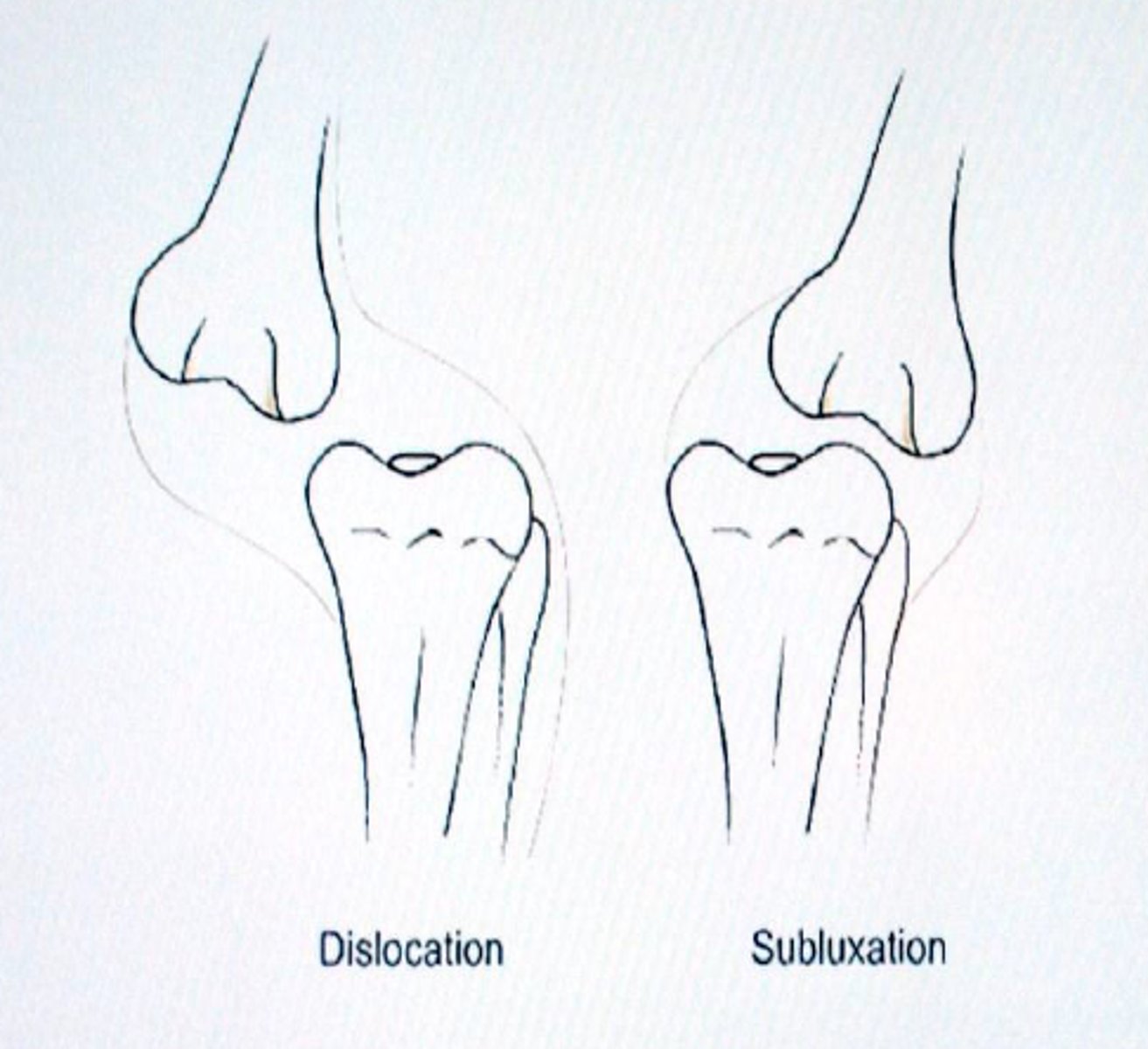
dislocation
compete separation of two end joints
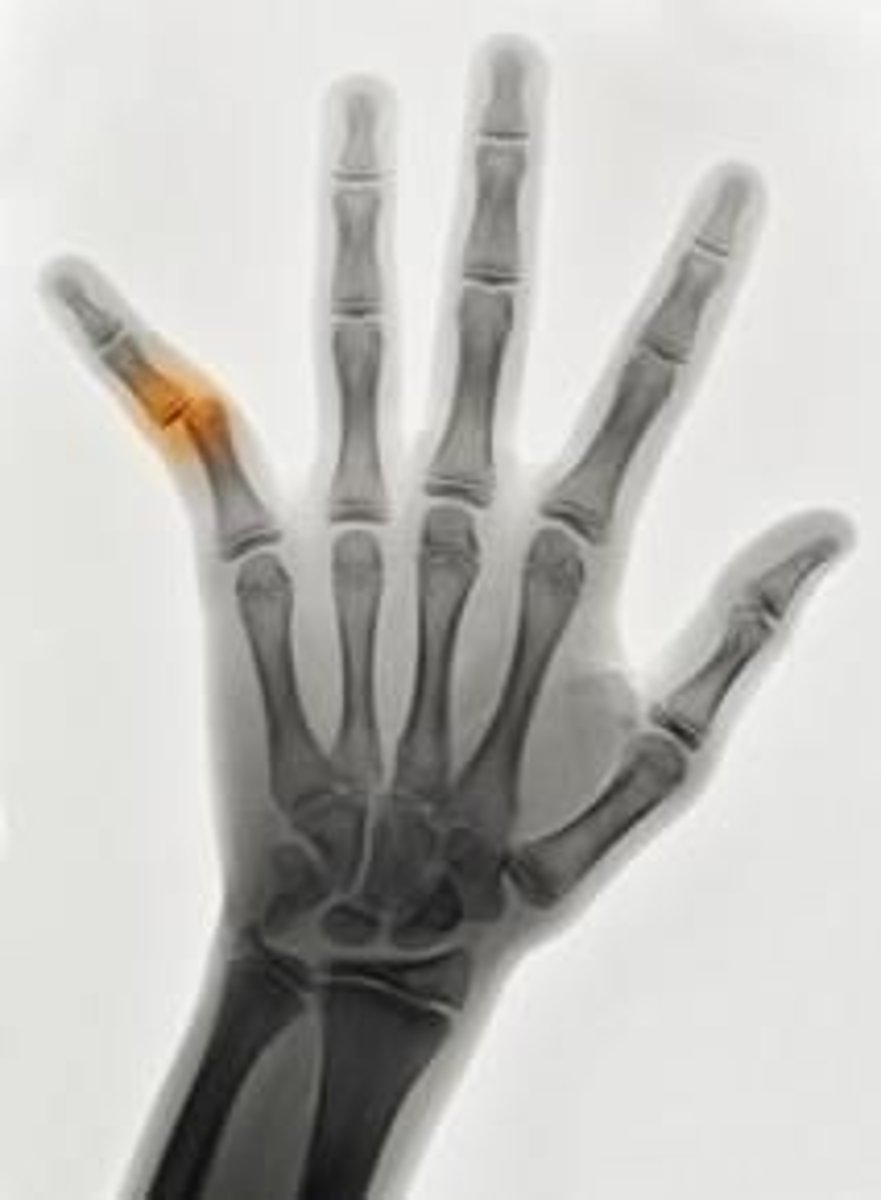
subluxation
partial or incomplete separation of a joint
ecchymosis
bruising, blue color
edema
swelling in tissue
effusion
swelling in joint
facture
break in the bone
hematoma
collection of or swelling that is blood, blood tumor
incision
straight cut, surgical cut
indicate
advise the use of
inflammation
body's response to injury
joint laxity
looseness in the joint
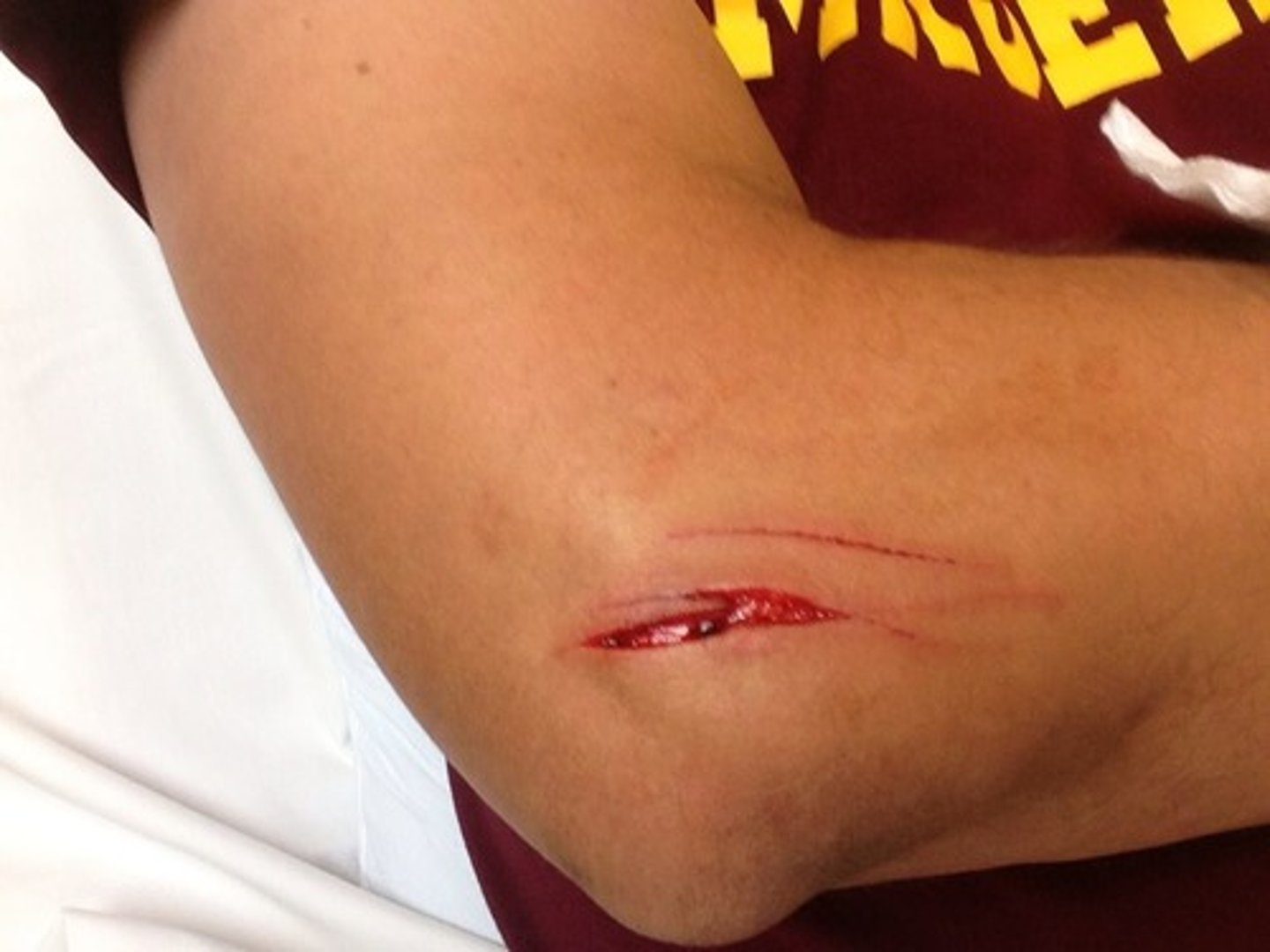
laceration
jagged tear of skin
ligament
structure that connects bone to bone
tendon
connect muscle to bone
modality
healing apparatus
Point tenderness
pain produced when structure is palpated
puncture wound
body part is pierced or stabbed by an object
range of motion
amount of movement allowed at joint
referred pain
pain felt somewhere other than its origin
sprain
stretching or tearing of ligaments
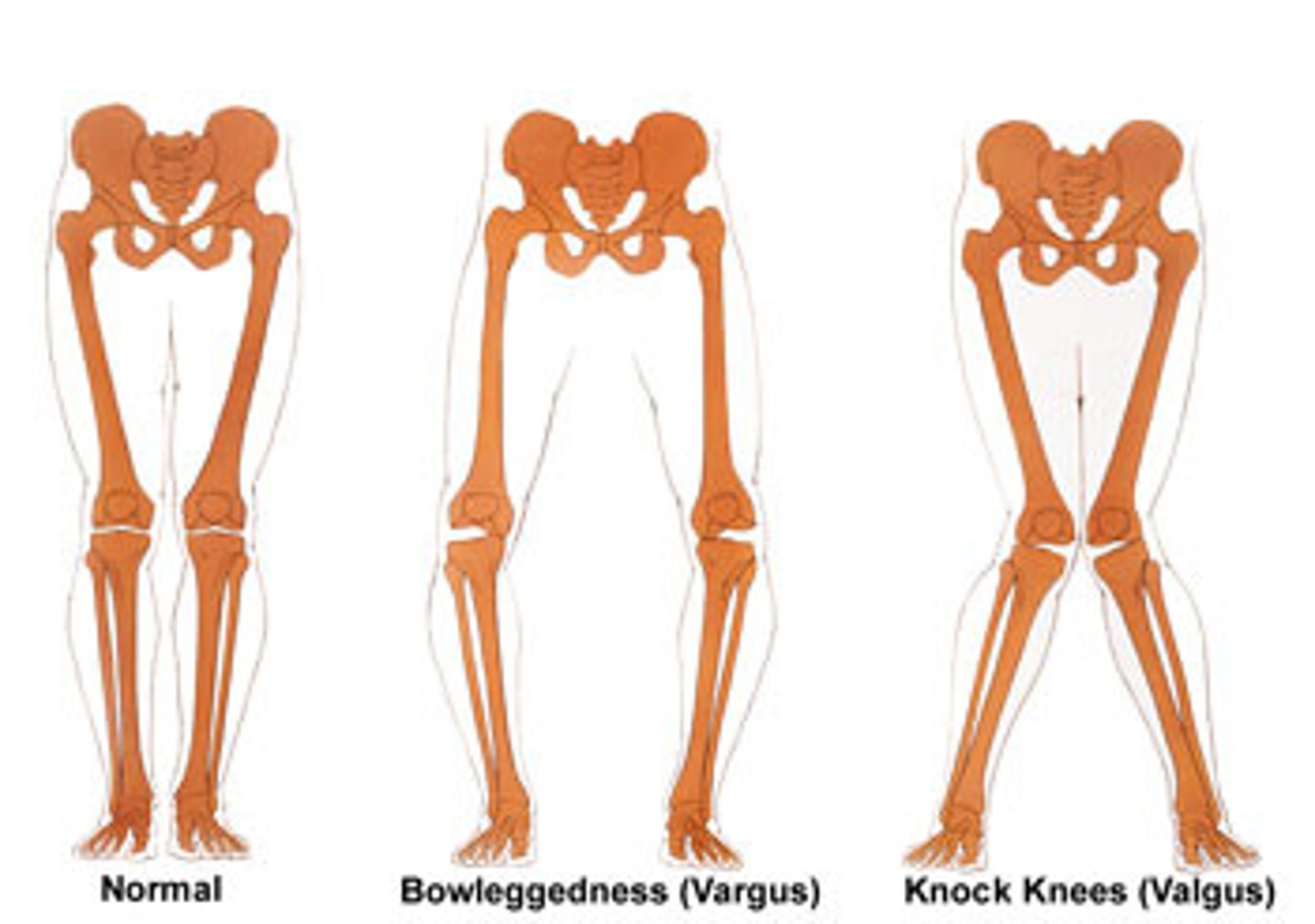
valgus
position of a body part that is bent outward
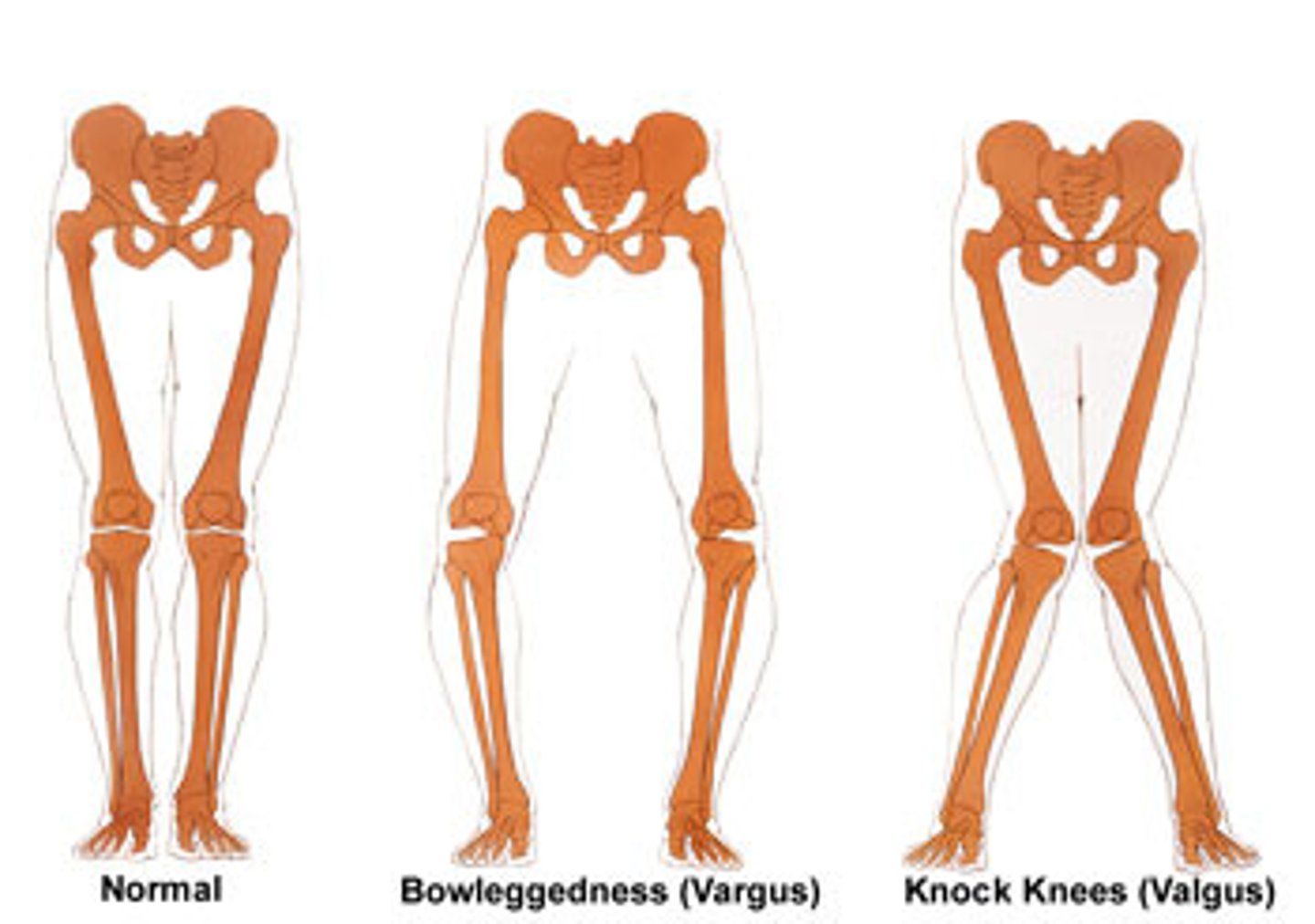
varus
position of a body part that in bent inward
skeletal system components
- hemopoietic tissue (responsible for forming blood cells)
- tendons
- ligaments
- bone
- cartilage
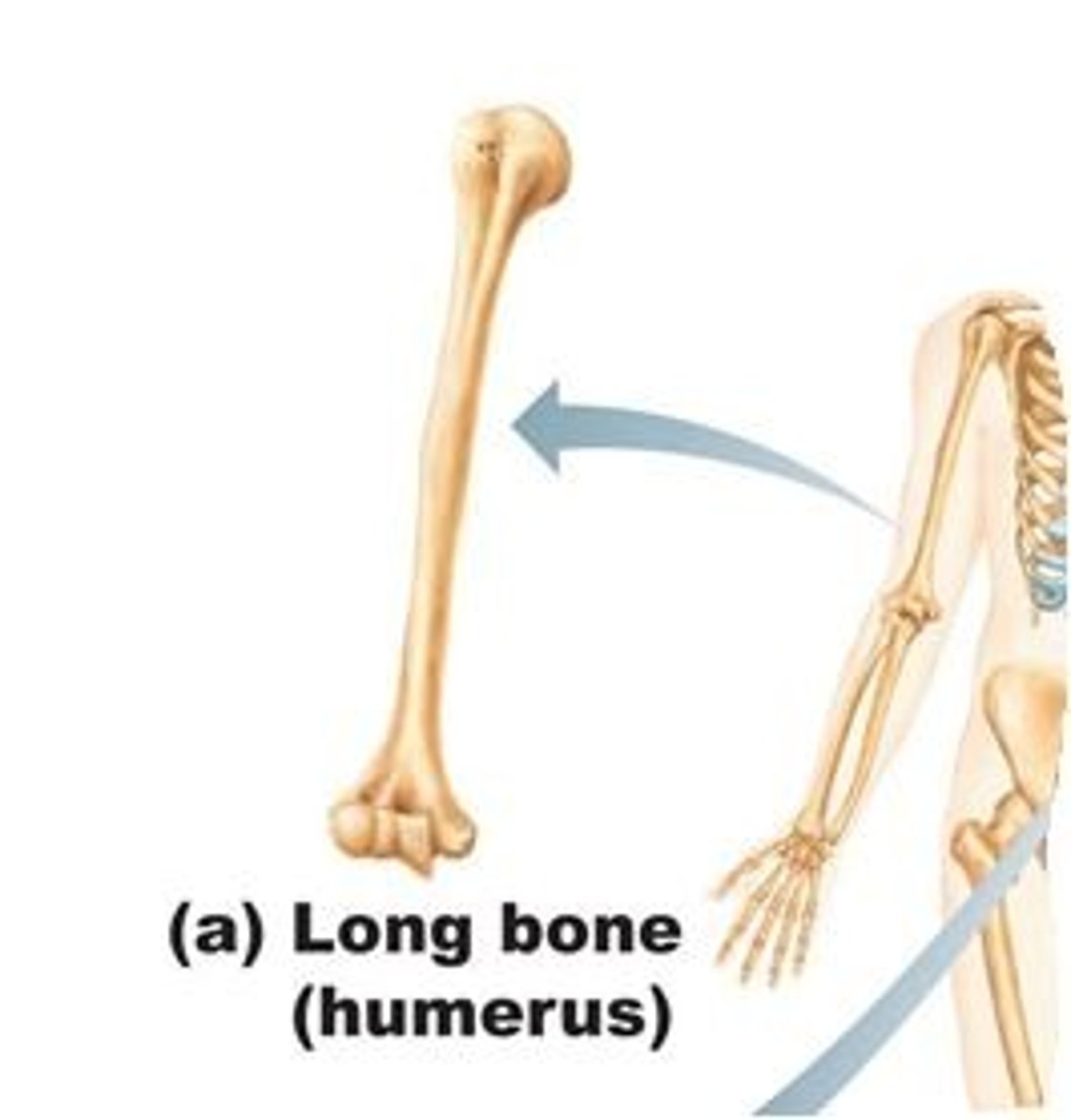
long bone
arms and legs, finger toes