Pathology EXAM 1
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
corrugated
wavy or wrinkled surface
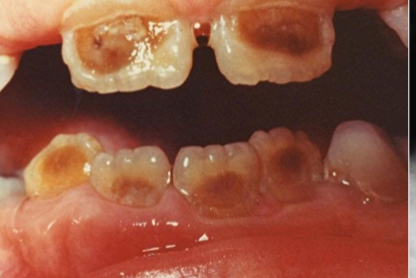
fissure
surface cleft/groove with prominent depth
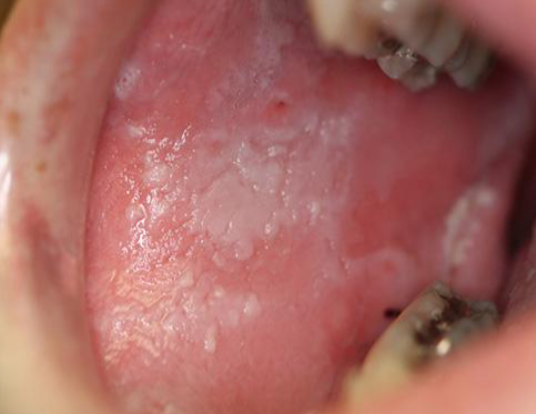
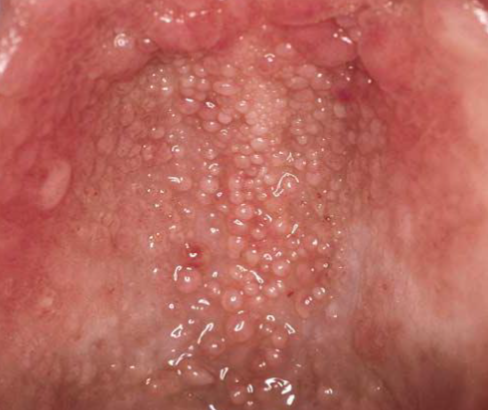
papillary
small solid surface projections/elevations found in clusters
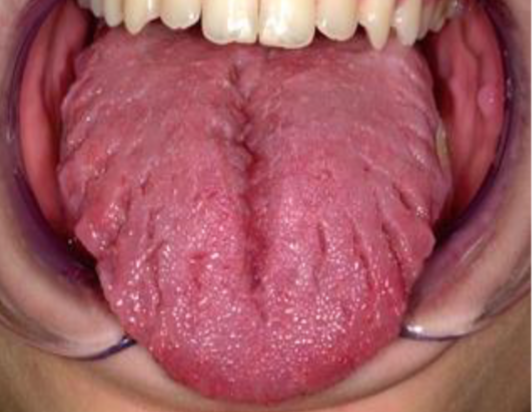
sessile
flat base
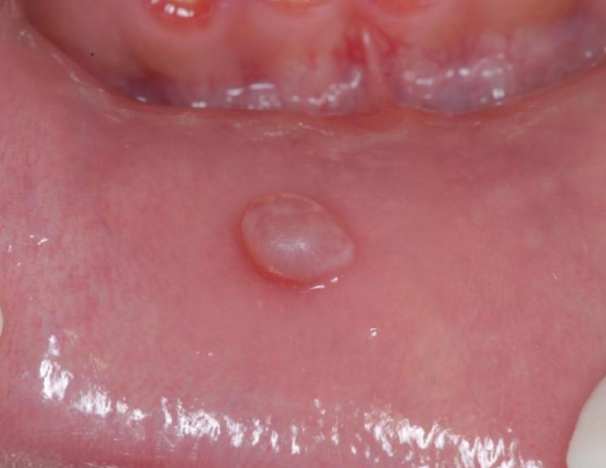
polypoid
base between sessile and pedunculated
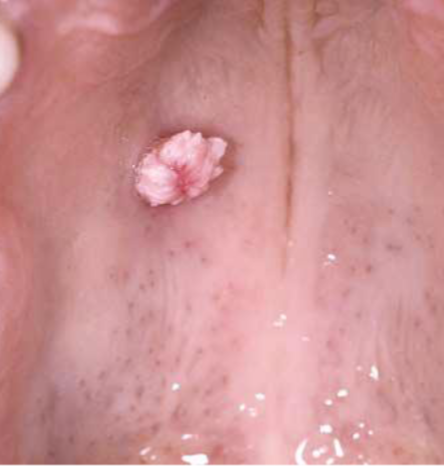
penduculated
stalk like base
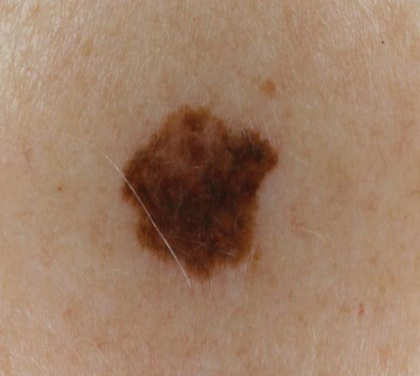
macule
a flat, discolored spot on the skin that is less than 1 centimeter in diameter.
papule
elevated, solid lesion on the skin that is less than 1 centimeter in diameter.
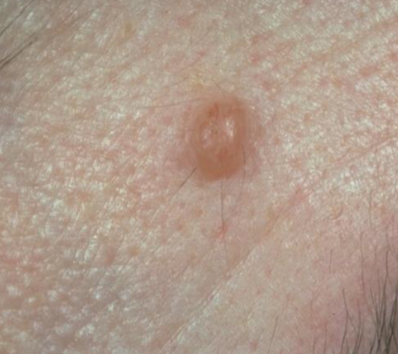
nodule
a solid, raised lesion on the skin that is more than 1 centimeter in diameter.
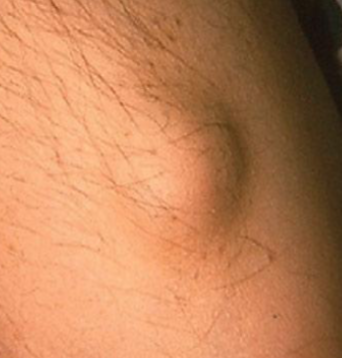
lobule
segment or lobe part of whole lesion, sometimes appear fused
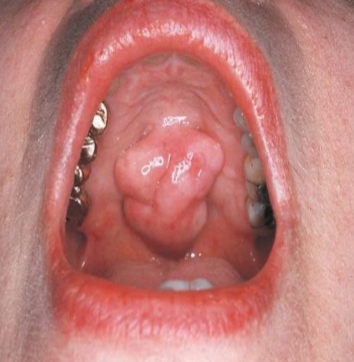
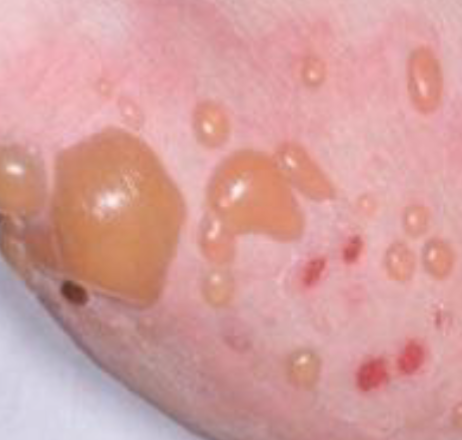
vesicle
small, elevated lesion that contains SEROUS fluid
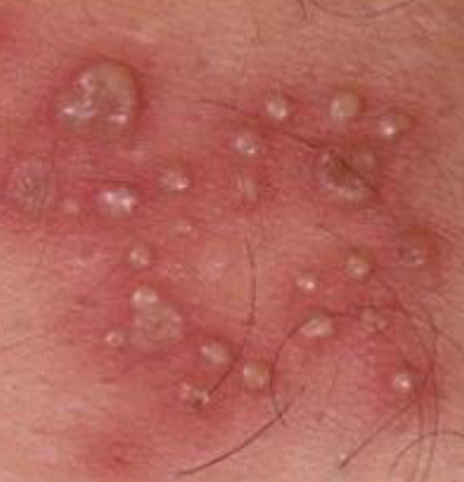
pustules
variously sized elevation containing PUS
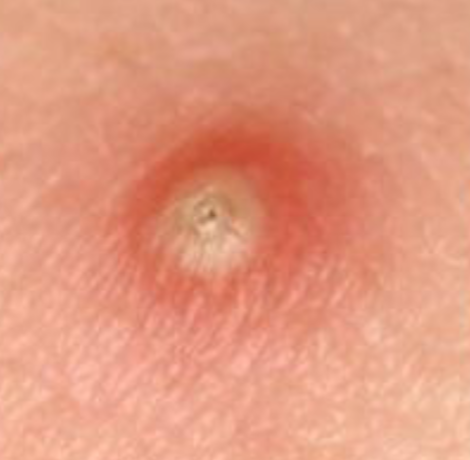
bulla
large (>5mm), blister-like elevation that contains fluid.
ill defined
how would you describe the BORDERs of this lesion
well-defined/circumscribed
how would you describe these borders
unilocular
describes a lesion that has a single compartment or cavity.
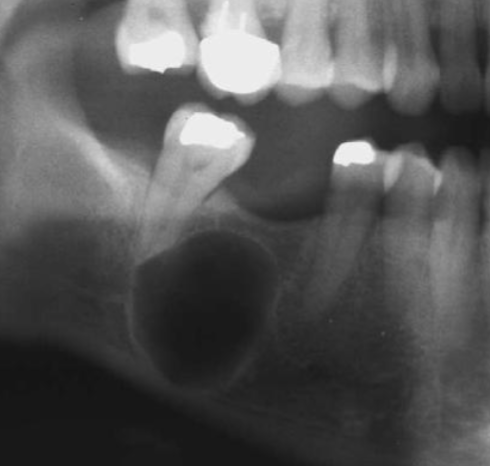
multilocular and well-defined
how would you describe this lesion?
root resorption
shortened/ irregularly shaped root apex
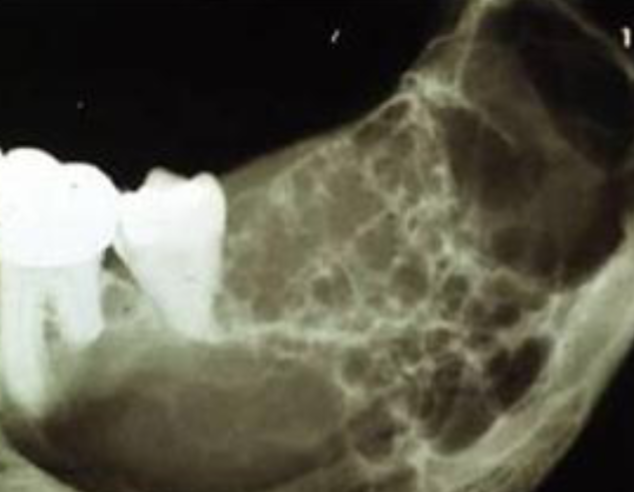
scalloping
radiolucent lesion that extends between the roots, seen in traumatic bone cyst (TBC)
fordyce granules
clusters of ECTOPIC SEBACEOUS glands
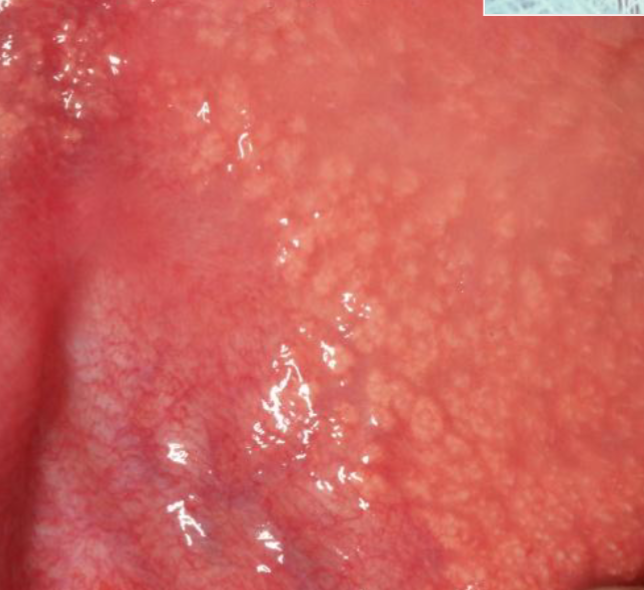
leukoedema
diffuse, gray-white, milky lesions on bilateral mucosa
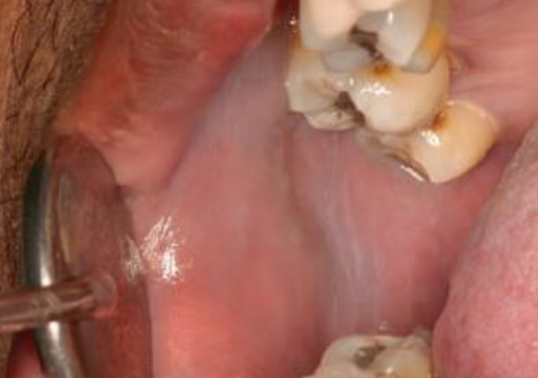
disappears when stretched
how is leukoedema diagnosed
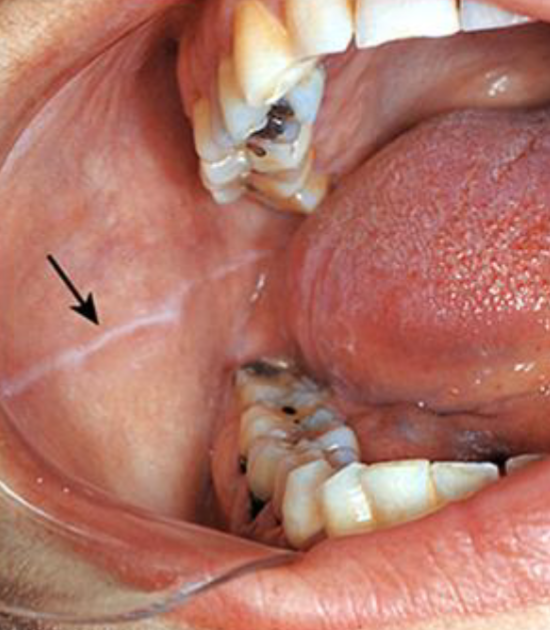
linea alba
prominent in CLENCHING/BRUXING pts
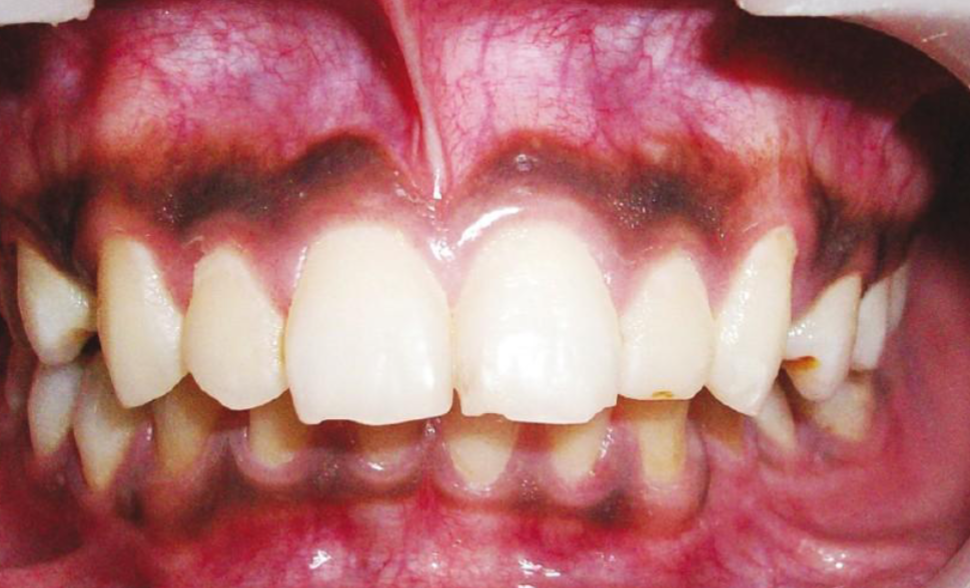
physiological pigmentation
melanin pigmentation of oral mucosa/gingiva
ligual varicosities
dilated veins located on the ventral/lateral surface of the tongue, most common over age 60
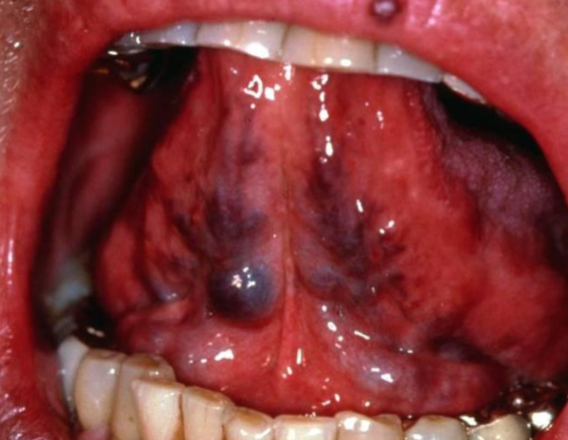
retrocuspid papillae
sessile nodule located on the lingual surface of the mandibular cuspids.
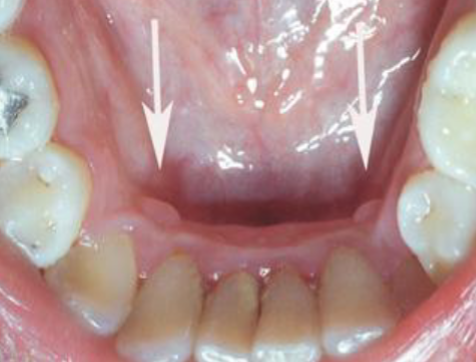
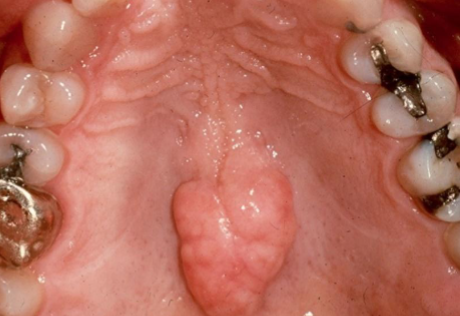
torus palatinus
exophytic growth of normal COMPACT bone on hard palate
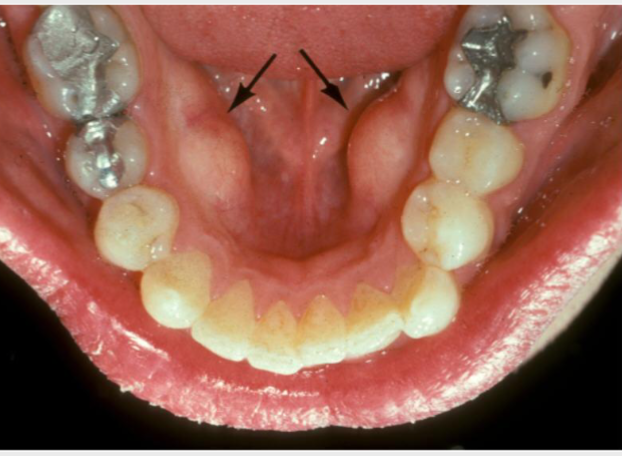
mandibular tori
outgrowths of normal dense bone on lingual of mandibular premolar area
diascopy
procedure to examine skin lesions by blanching with pressure
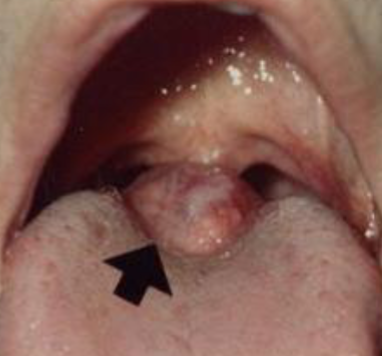
lingual thyroid
thyroid tissue is located on the tongue, often ONLY THYROID TISSUE (only remove if necessary), occurs in FEMALES more commonly
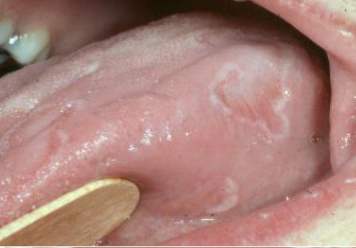
geographic tongue
a benign condition characterized by erythematous patches on the tongue
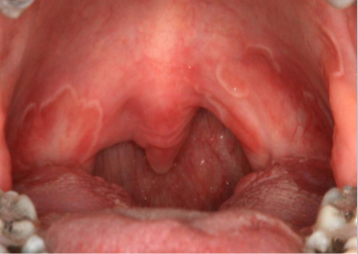
erythema migrans
erythematous patches on surfaces other than the tongue
hairy tongue
excess keratin on surface of filiform papillae
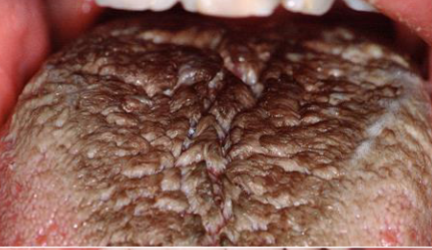
microglossia
abnormally small tongue, common with hypoplasia of mandible
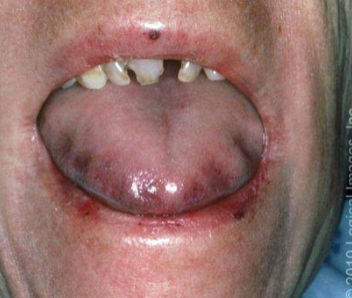
macroglossia
abnormally large tongue, often associated with conditions such as Down syndrome
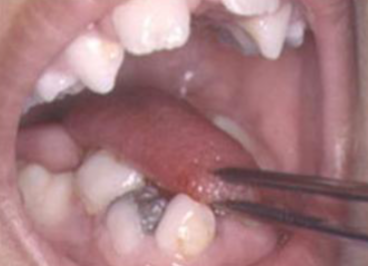
ankyloglossia
abnormally shot, thick lingual frenum that restricts tongue movement
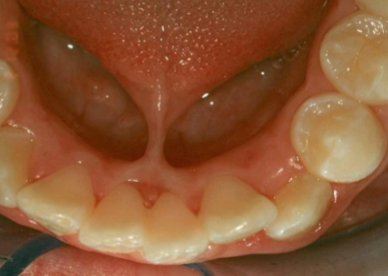
commissural lip pits
Mucosal invaginations that occur at the corners of the mouth on the vermilion border
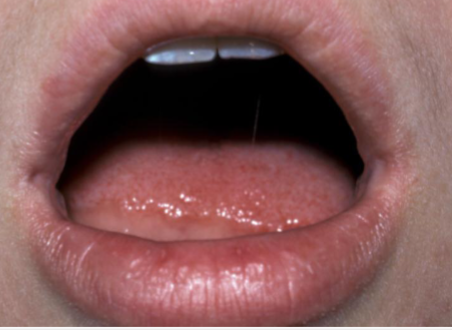
caliber persistent artery
upper lip vascular anomaly, BLEEDING RISK
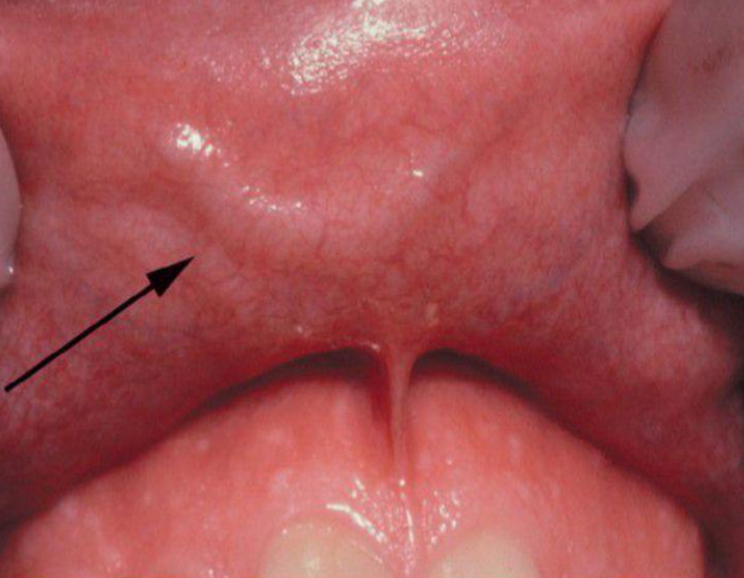
exostosis
a benign bony growth on the jawbone
condylar hypoplasia
underdeveloped condyle
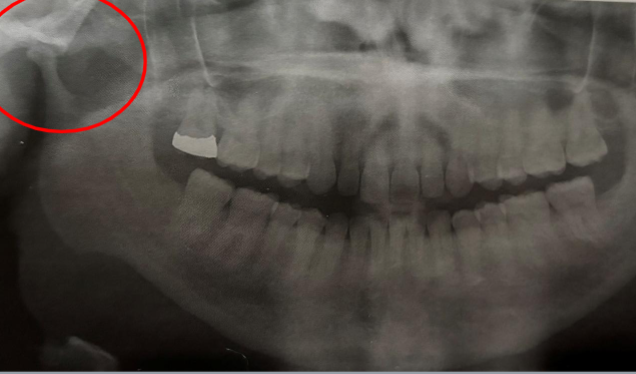
condylar hyperplasia
excessive growth of condyle due to NEOPLASM/ ENDOCRINE distubances
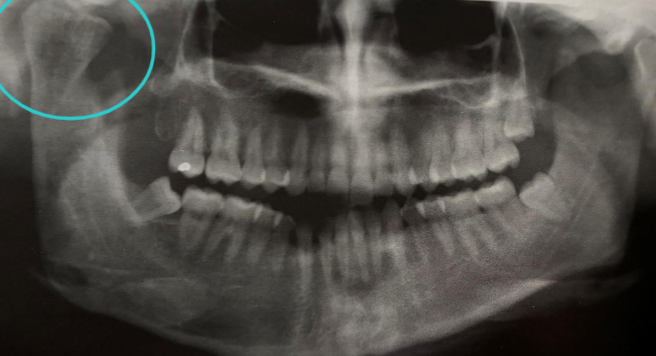
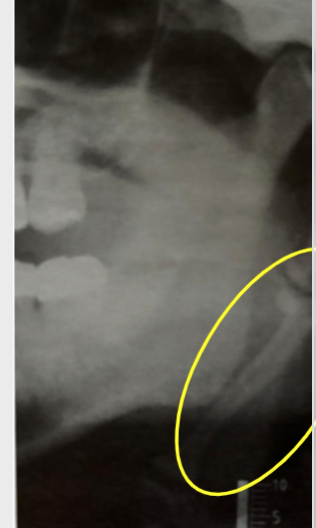
eagle syndrome
elongation of styloid process or mineralization of stylohyoid ligament
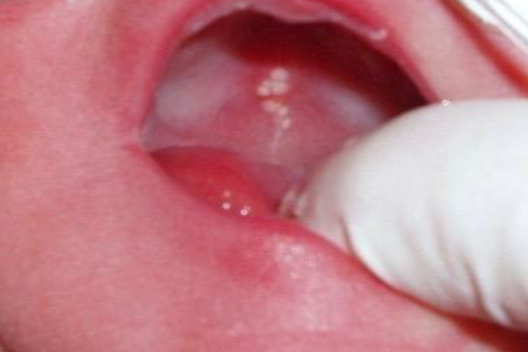
epstein’s pearls
small, white cysts along MEDIAN PALATAL raphe
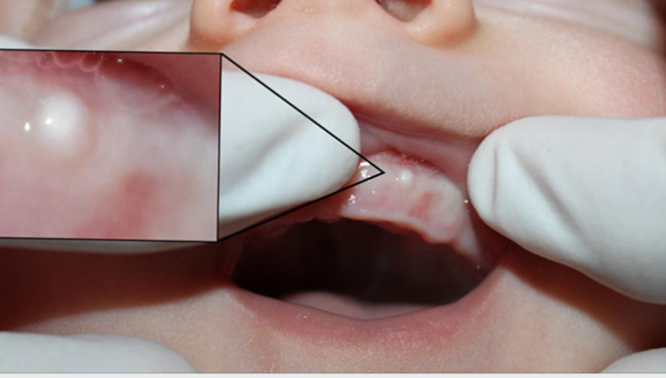
bohn’s nodule
small, painless cysts located along the alveolar ridges, common in newborn
median nasal process and maxillary process
what fails to fuse in cleft lip?
cleft palate
failure of fusion of PALATAL SHELVES
orofacial clefts
most common major congenital defects
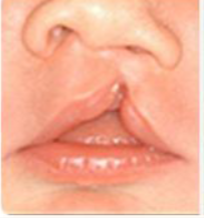
incomplete cleft lip
cleft lip that does not involve the nose
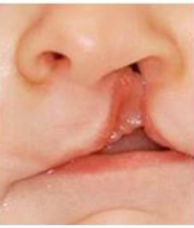
complete cleft lip
cleft lip that extends into the nose
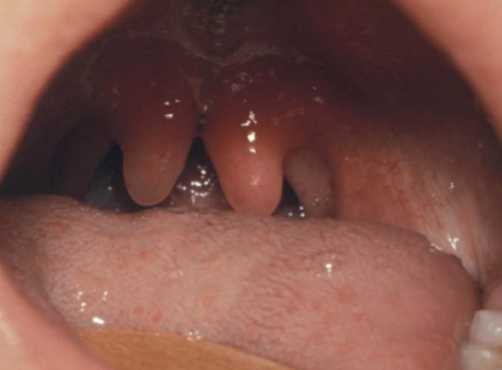
bifid uvula
minimal manifestation of cleft palate
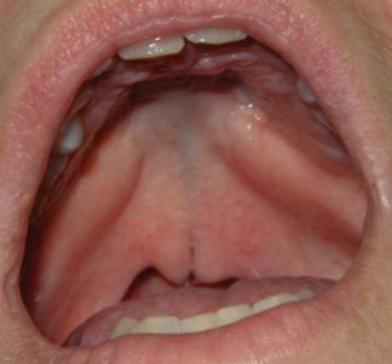
submucosa palatal cleft
surface intact but defect exists in underlying musculature of sooft palate
pierre robin syndrome
characterized by mandibular micrognathia, glossoptosis, and cleft palate
van der woude syndrome
genetic disorder characterized by LIP PITS, and cleft lip and/or palate
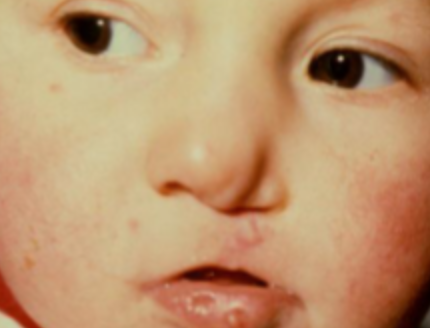
ascher syndrome
double lip, blepharochalasis (eyelid edema), and sometimes nontoxic thyroid enlargement
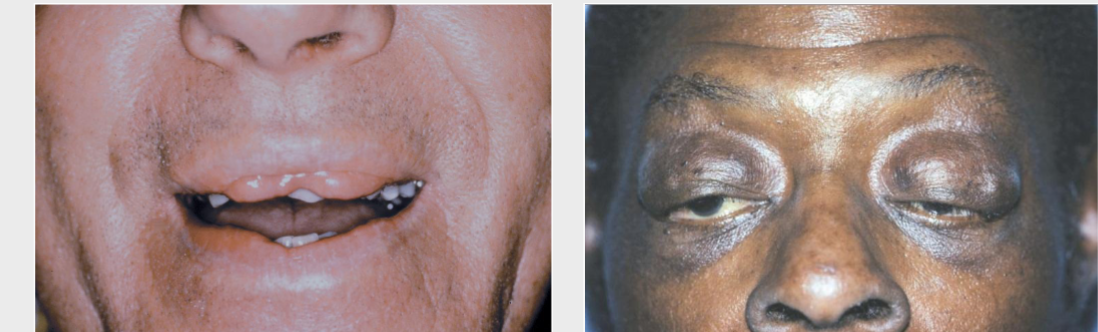
crouzon syndrome
craniosynostosis (premature cranial suture closure), ocular proptosis (bulging eyes), and clover leaf skull shape
apert syndrome
FUSED DIGITS, craniosynostosis, ocular proptosis, abnormal skull shape, maxillary hypoplasia
treacher collins syndrome
coloboma (notched lower eyelid), hypoplastic zygoma (depressed face), ear defect
anodontia
total lack of tooth development
ankylosis
cessation of eruption after emergence
concrescence
union of teeth by cementum alone
dens in dente
enamel organ invaginates into crown of the tooth before mineralization
dentinogenesis
formation of dentin
dilaceration
abnormal bend or curve in root of tooth
fusion
two adjacent teeth unite in the development stage, count reveals MISSING tooth
gemination
single enlarged tooh in which one tooth bud tried to divide, tooth count NORMAL
hypodontia
few teeth missing, 6 or less
impacted teeth
teeth that cant erupt due to physical obstruction
macrodontia
abnormally large teeth
microdontia
abnormally small teeth
oligodontia
type of hypodontia with 6 or more missing teeth
supernumerary
teeth that are extra beyond the normal set of teeth
gardners and cleidocranial dysplasia
syndromes associated with hyperdontia
hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
HYPODONTIA, X-linked, reduced or absent sweating, heat intolerance, sparse hair
mesiodens
a type of supernumerary tooth that typically occurs between the MAX CENTRAL incisors
distomolar/distodens
a type of supernumerary tooth located distal to the THIRD MOLAR, often resulting in dental crowding or impaction.
paramolar
a type of supernumerary tooth located BUCCAL or LINGUAL to a MOLAR, often associated with dental anomalies.
neonatal teeth
teeth that are present with first 30 days after birth, often being primary incisors that appear earlier than usual.
natal teeth
teeth that are present AT BIRTH, typically primary incisors, which can cause feeding difficulties or dental issues.
cleidocranial dysplasia
dental hyperdontia, clavicle abnormalities, AD inheritance, and delayed/failure eruption of permanent teeth
gardner syndrome
multiple osteoma, RISK of COLORECTAL CANCER, hyperdontia, pigmented ocular fundus, epidermal cysts
isolated
most common type of macrodontia
peg lateral
type of microdontia with small lateral incisor
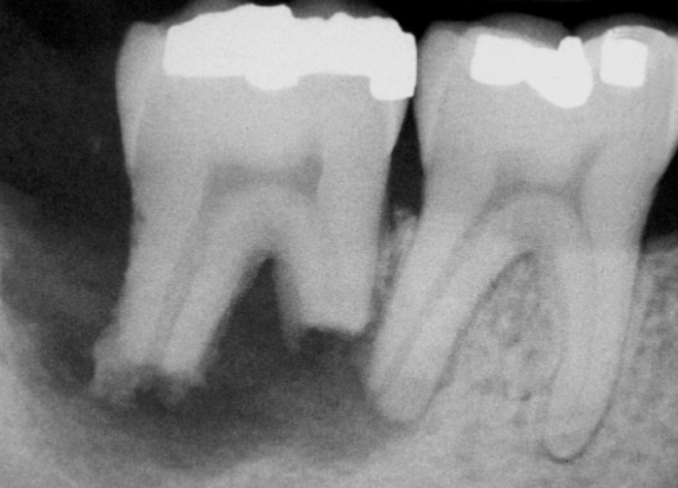
fusion
what dental abnormality is shown here?
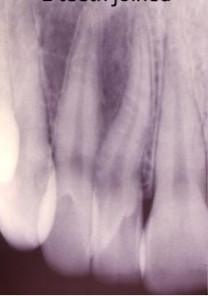
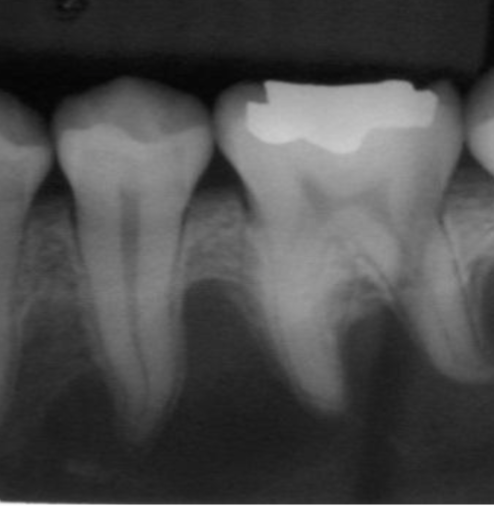
gemintation
what dental abnormality is shown here?
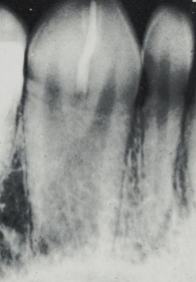
ML cusp of maxillary molar
location of cusp of carabelli
talon cusp
what is shown here?
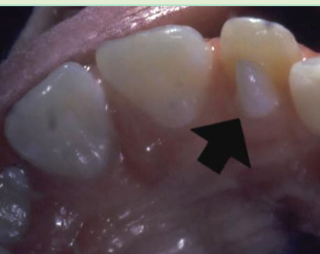
talon cusp
accessory cusp on lingual of incisor, usually MAX LATERAL
dens evaginitus/ occlusal pearl
what is shown here?
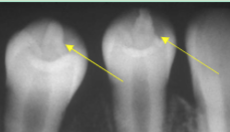
mandibular premolar
most common site for dens evaginatus/occlusal pearl
dens invaginitis/dens in dente
what is the diagnosis?
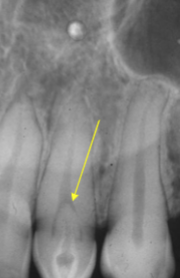
type I
dens in dente in which invagination is CONFINED TO CROWN
type II
dens in dente in which invagination extends BLEOW CEJ
type III
dens in dente with invagination extending through the ROOT
shovel shaped teeth
promienent marginal ridges associated with dens evaginatus
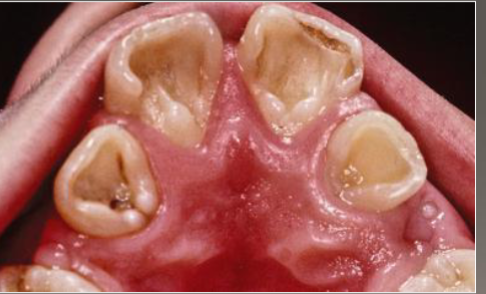
enamel pearl
nodules at furcation of multi-rooted teeth, most common on MAX MOLAR
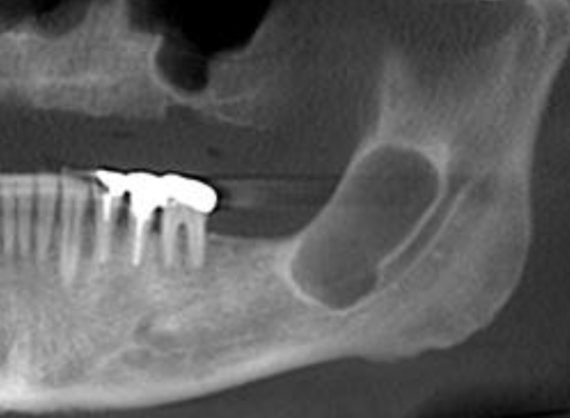
taurodontism
what is shown here?
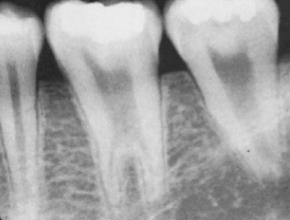
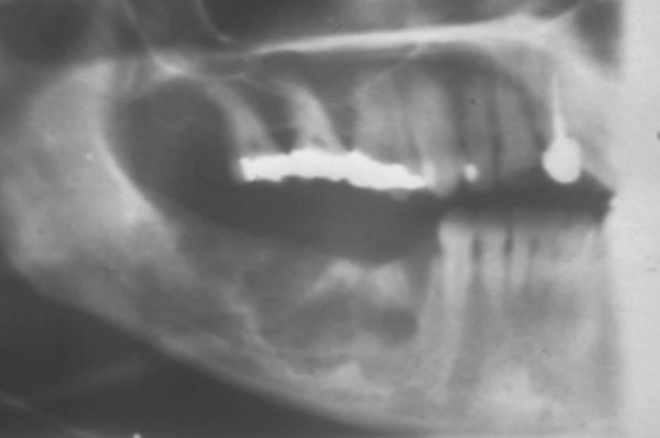
dilaceration
what is shown here?
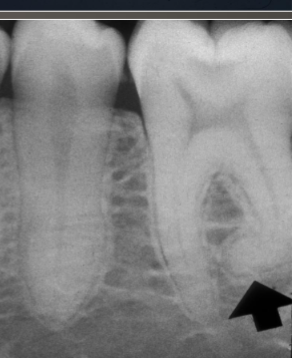
hypercementosis
a condition characterized by excessive deposition of cementum on root surfaces, associated with GARDNER and PAGET disease
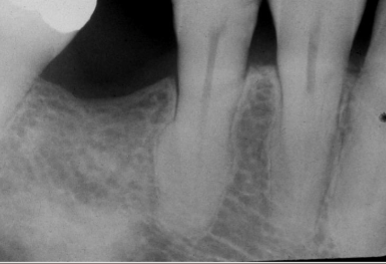
supernumerary root
increased number of roots
amelogenesis imperfecta
affects enamel, resulting in defective enamel formation and varying degrees of translucency and thickness