GCSE AQA Chemistry - Chemical Changes
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Acids
Produce H+ ions in an aqueous solution.
Bases
Neutralise acids to form a salt and water.
Alkalis
Bases that are soluble in water and produce OH- ions in aqueous solutions.
pH probe
Determines pH electronically
Universal indicator
Changes colour depending on whether the solution is acid, alkaline or neutral.
Titration
Allows you to find exactly how much acid is required to neutralise a quantity of alkali.
What can a titration be used to work out?
The concentration of the acid or alkali.
Where is a pipette and pipette filler used in titration?
To add a set volume of acid or alkali to a conical flask.
How is a burette used in titration? (2)
Using a funnel, some acid/alkali of known concentration is added to the burette
Acid/alkali is added to the conical flask a bit at a time until there is a colour change.
What colour is phenolphthalein in alkalis?
Pink
What colour is phenolphthalein in acids or neutral solutions?
Colourless
Strong acids
Completely ionise in aqueous solutions.
Weak acids
Partially ionise in aqueous solutions.
pH
A measure of the concentration of H+ ions in the solution.
As pH decreases by one unit…
Hydrogen ion concentration of the solution increases by a factor of 10.
Concentration of an acid
The amount of acid in a certain volume of water.
Acid + Metal Oxide →
Salt + Water
Acid + Metal Hydroxide →
Salt + Water
Acid + Metal Carbonate →
Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
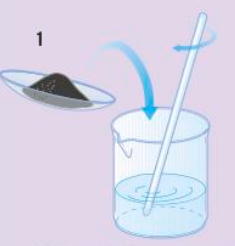
Making soluble salt/copper sulfate crystal - step 1
Neutralisation - insoluble copper oxide (base) is added in excess to gently warmed sulfuric acid and stirred until no more reacts.
Making soluble salt/copper sulfate crystal - step 2
Filtration - Excess copper oxide is filtered out

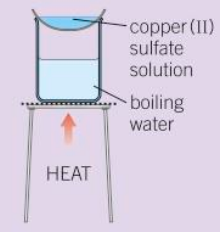
Making soluble salt/copper sulfate crystal - step 3
Evaporation - The solution is gently heated under a water bath to evaporate the water. Stop heating when the first crystals form at the edge of the solution.
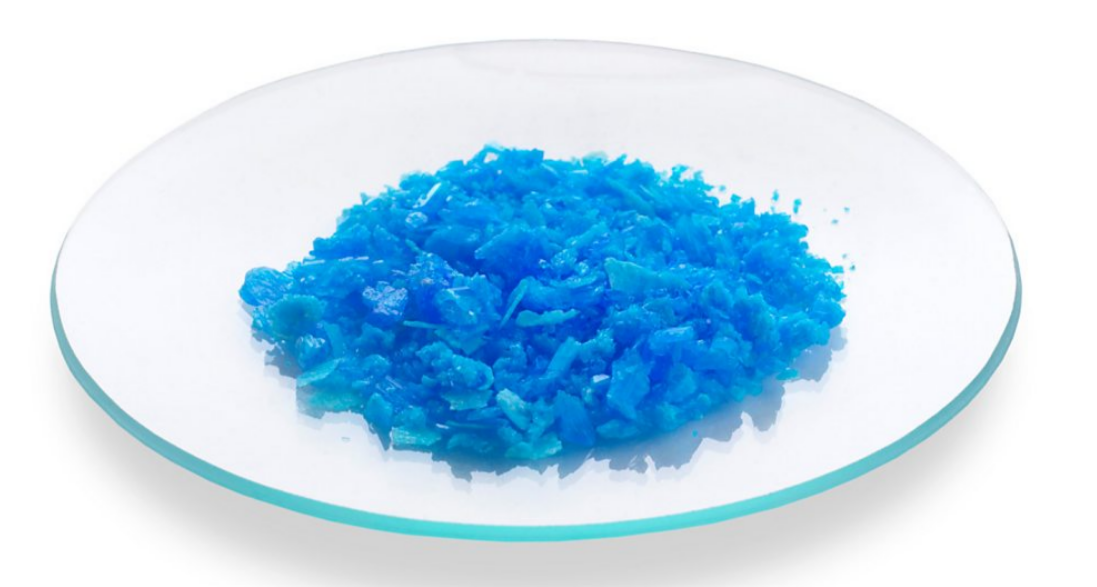
Making soluble salt/copper sulfate crystal - step 4
Crystallisation - The rest of the water evaporates off slowly, and then any excess of the solution can be removed by dabbing between filter paper.

The reactivity series (10)
Potassium
Sodium
Lithium
Calcium
Magnesium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Hydrogen
Copper
Metal + Acid →
Salt + Hydrogen
How can we measure the reactivity of a metal based on it’s reaction with an acid?
The speed of the reaction - rate at which bubbles of hydrogen are given off
The temperature change
Metal + Water →
Metal Hydroxide + Hydrogen
Oxidation (2)
Gain of oxygen
Loss of electrons
Reduction (2)
Removal of oxygen
Gain of electrons
How are metals less reactive than carbon extracted?
By reduction with carbon.
How are metals more reactive than carbon extracted?
By using electrolysis.
Redox reaction
A reaction in which one substance is reduced and another is oxidised.
Displacement
A more reactive metal displacing a less reactive metal from it’s compound.
Ionic equation
An equation that only shows the reactants that react and the products that form.
Spectator ions
Ions that are unchanged in a reaction.
Electrolysis
The process of breaking down a substance using an electric current.
Why is it that the ionic compound must be molten or aqueous to be electrolysed?
So that the ions can move freely and conduct electricity.
Cathode
Where positive metal ions are reduced to the element.
Anode
Where negative ions are reduced to the element.
Cryolite
Mixed with aluminium oxide to lower it’s melting point.
Describe electrolysis of aluminium oxide
Positive Al3+ ions are attracted to the negative electrode where they are reduced and sink to the bottom of the tank.
Negative O2- ions are attracted to the positive electrode where they are oxidised and combine to form O2 molecules.
What will be produced at the cathode in electrolysis of an aqueous solution?
If the metal ions are more reactive than hydrogen, hydrogen gas will be produced
If the metal ions are less reactive than hydrogen, the metal will be produced
What will be produced at the anode in electrolysis of an aqueous solution?
If halide ions are present, chlorine, bromine or iodine will be formed
If no halide ions are present, the OH- ions are discharged and oxygen will form.
Describe electrolysis of copper (III) sulfate
Copper metal is produced and coats the electrode
Oxygen is produced and can be seen as bubbles
Half equations
An equation that shows how electrons are transferred when a substance is oxidised or reduced.