RADIOLOGY - GI
1/212
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
213 Terms
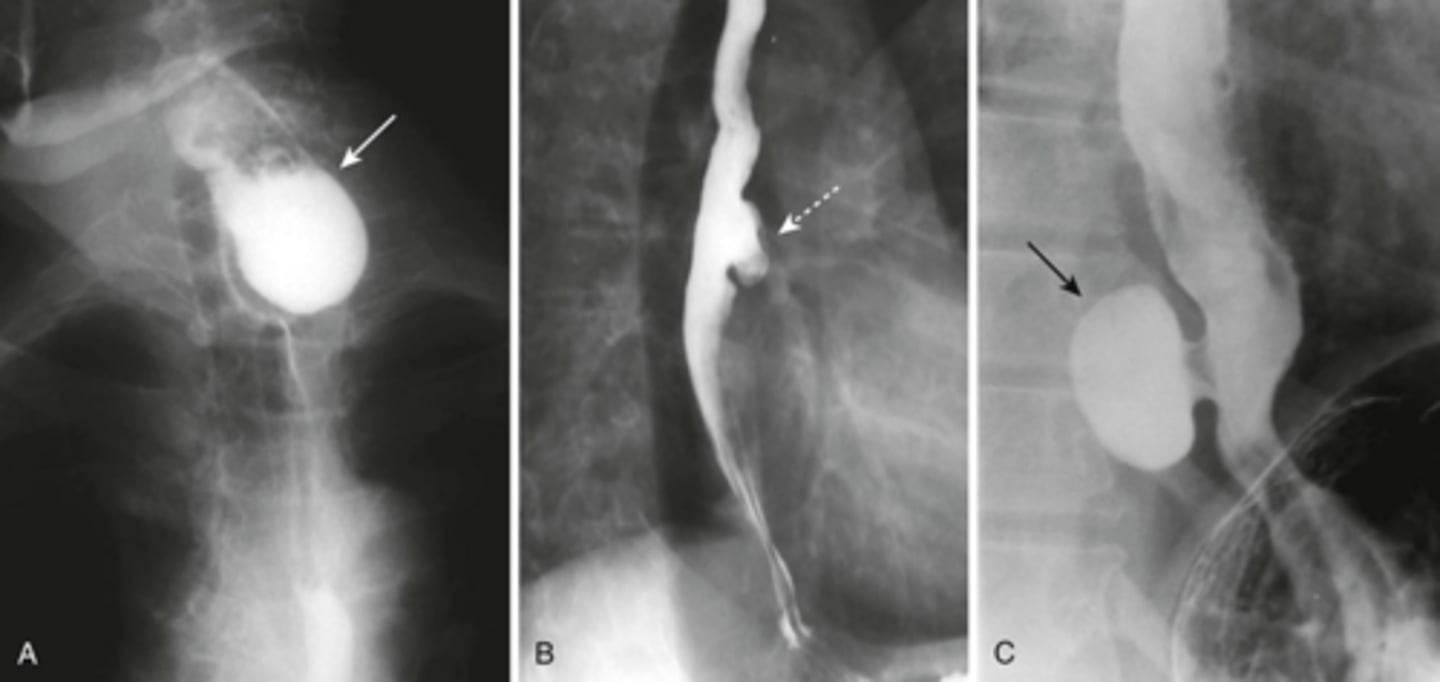
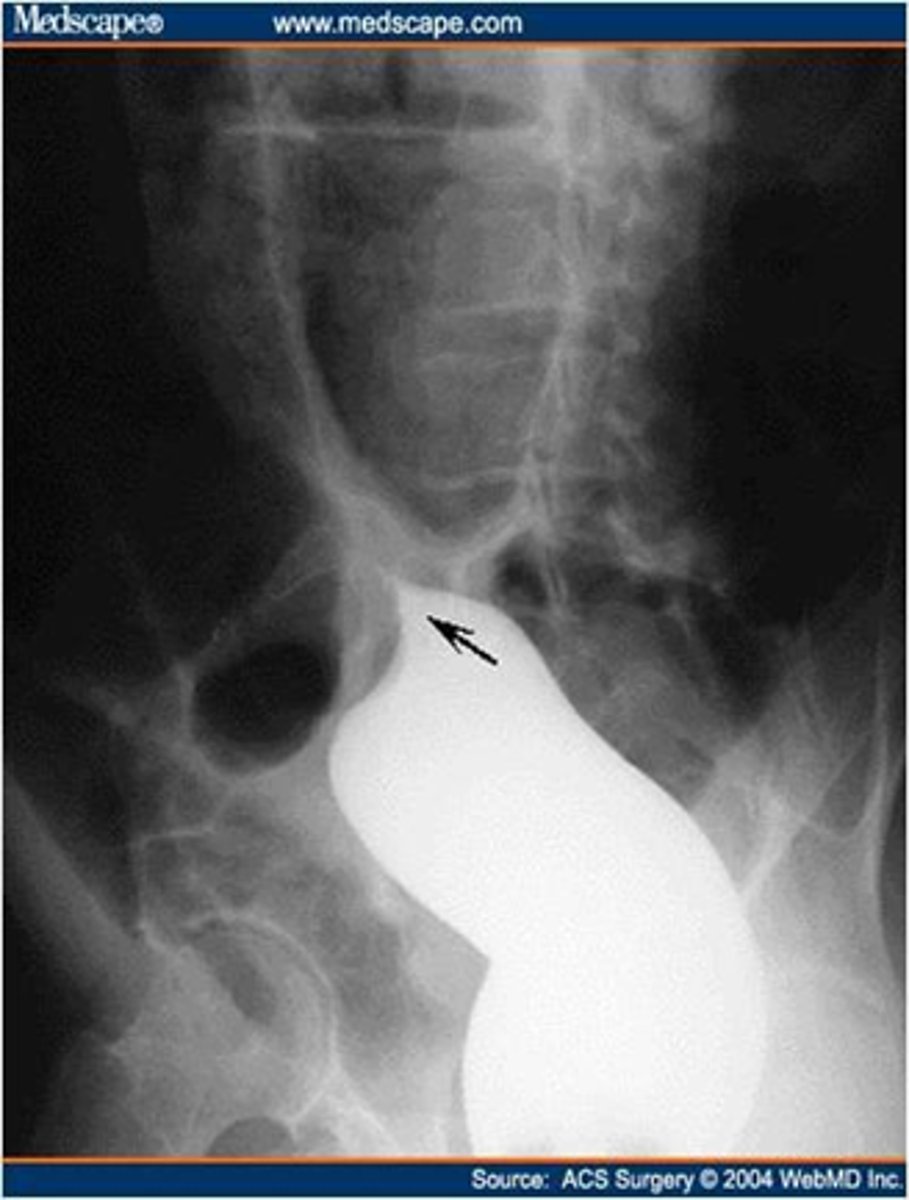
Esophageal diverticula.
(A)WHITE ARROW:
localized weakness in the posterior wall of the hypopharynx;
in the mid-esophagus from extrinsic disease such as tuberculosis that causes fibrosis, which pulls on the esophagus, forming a traction diverticulum (dotted white arrow)
DOTTED WHITE ARROW:
traction diverticulum. fibrosis pulling on the esophagus.
B: BLACK ARROW:
Epiphrenic diverticulum, just above the diaphgram in the distal esophagus.
(C). Only the traction diverticulum is a true diverticulum in that it has all layers of the esophagus involved; the Zenker and epiphrenic are false or pseudodiverticula because the mucosa and submucosa herniate through a defect in the muscular layer. The Zenker diverticulum is the only one of the three that typically produces symptoms.
Gas Pattern
Extraluminal air
Calcification
Soft tissue masses
What are four things to look for in a normal abdomen?
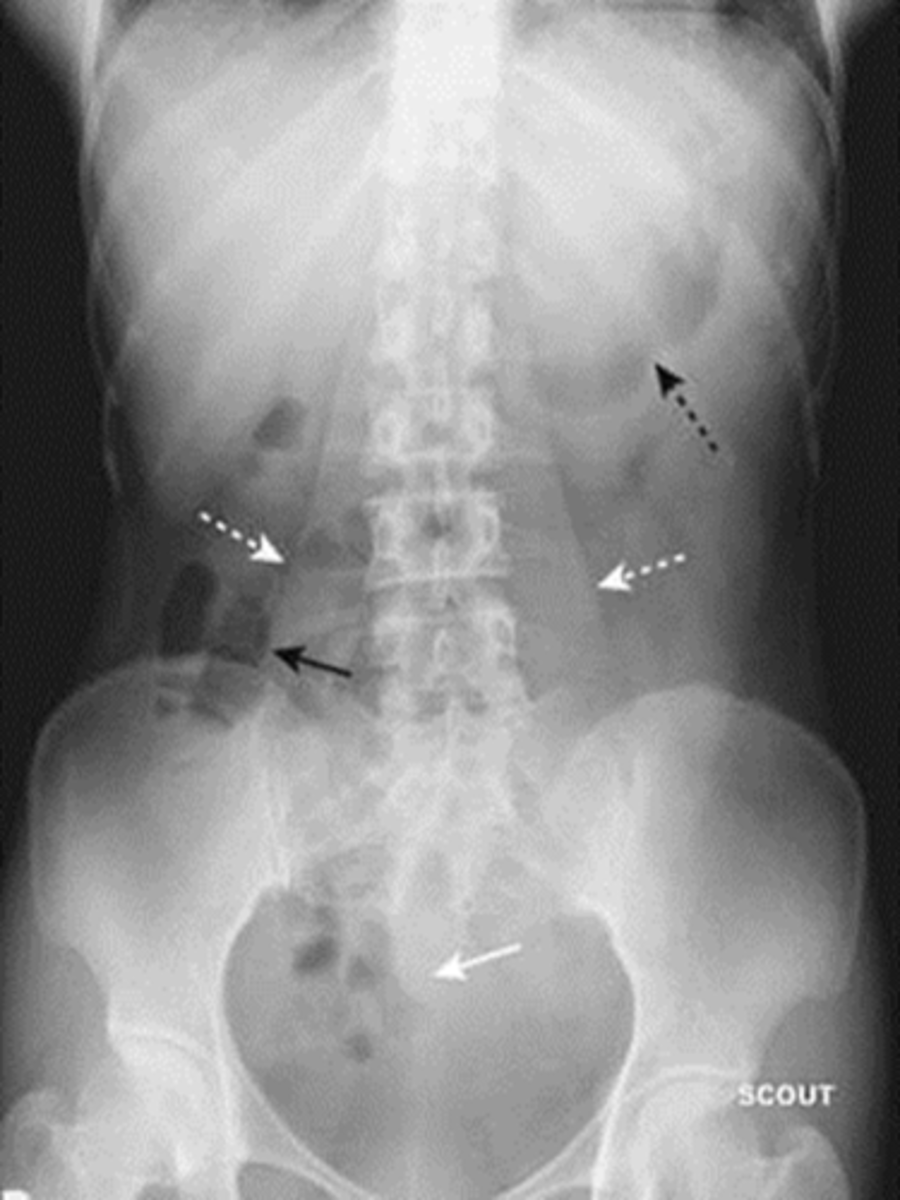
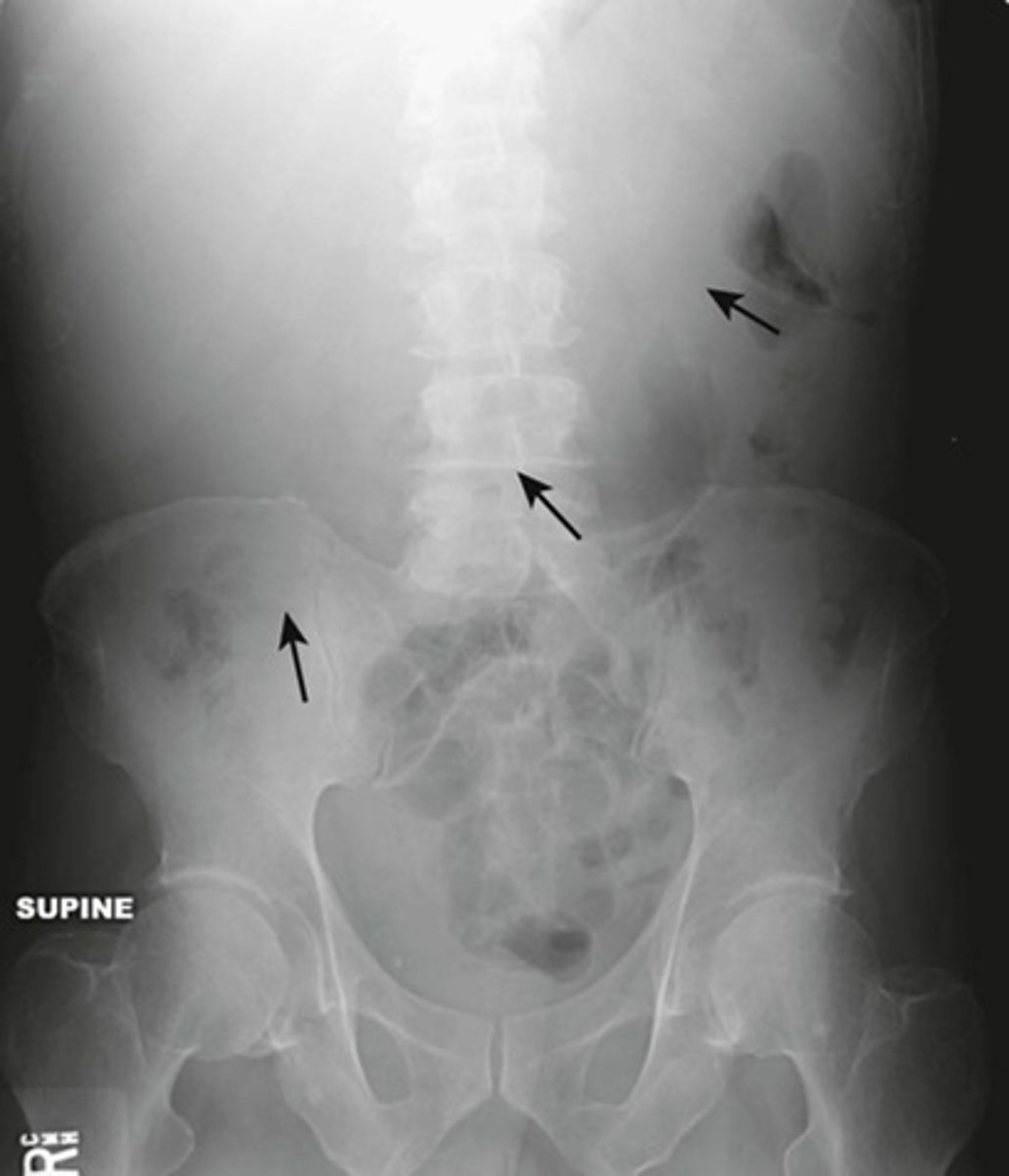
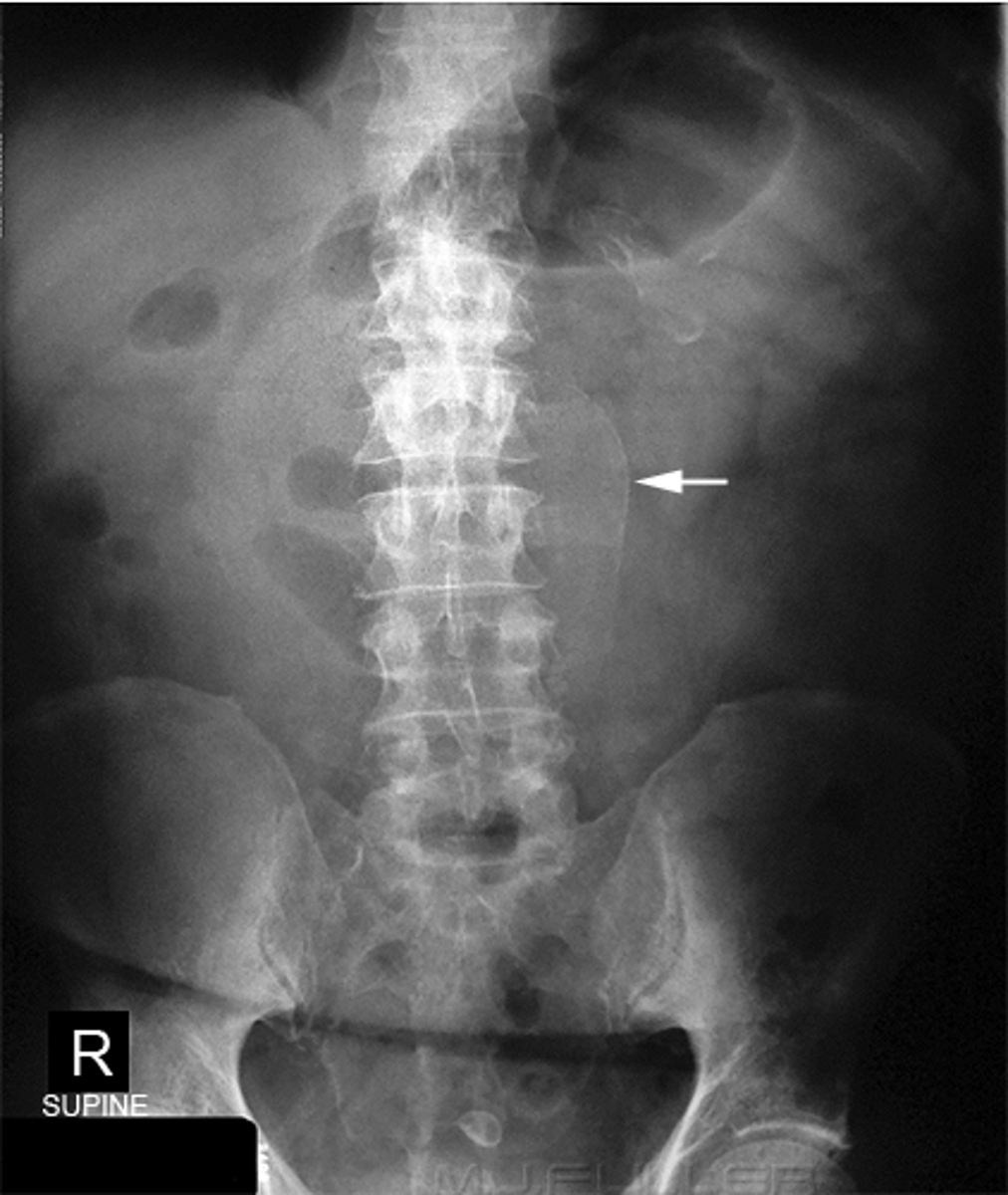
Normal supine abdomen
SOLID BLACK ARROW: small amount of air in about two or three loops of nondilated small bowel
DOTTED BLACK ARROW: air in stomach, always will have.
SOLID WHITE ARROW: air in the rectosigmoid colon.
DOTTED WHITE ARROWS: psoas muscles outlined by fat.
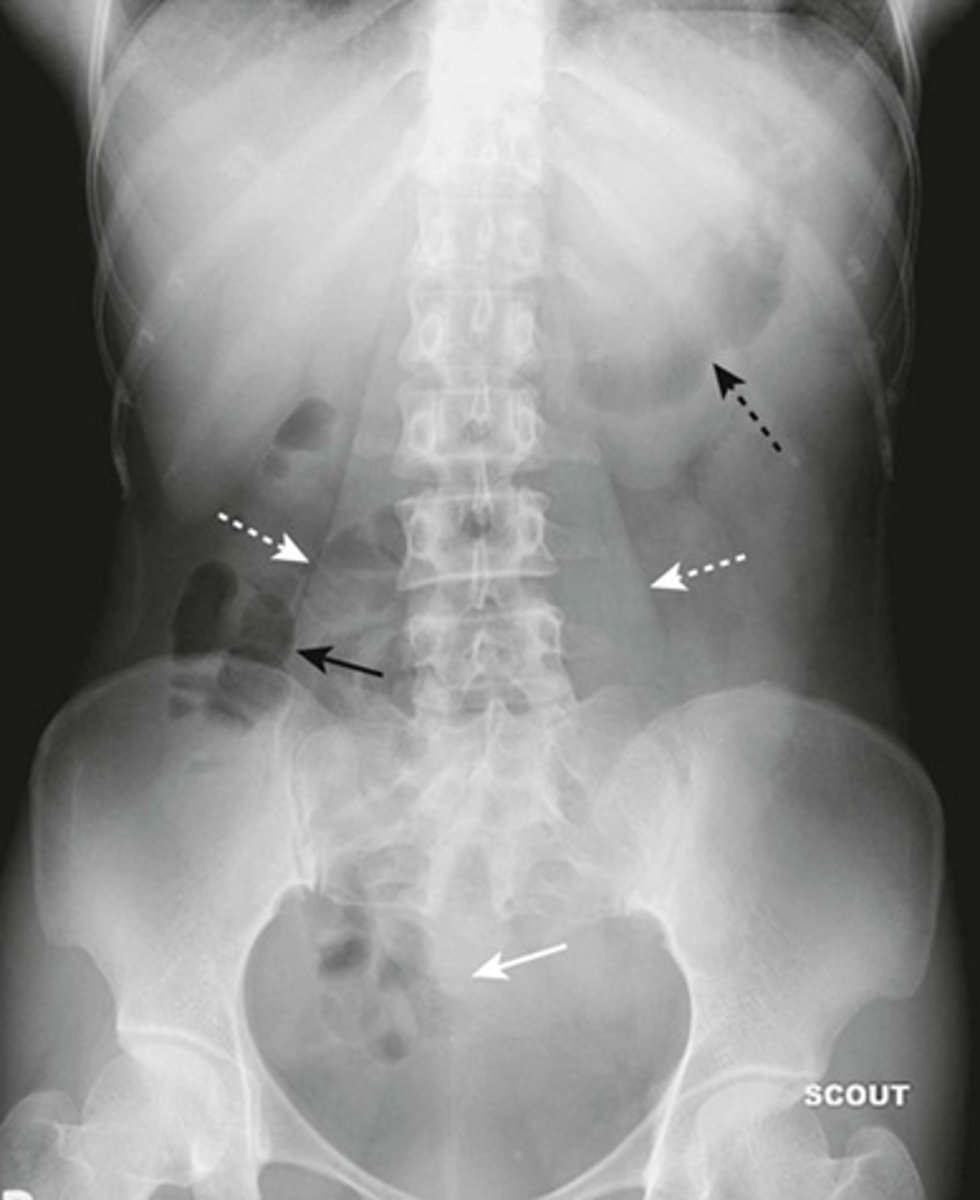
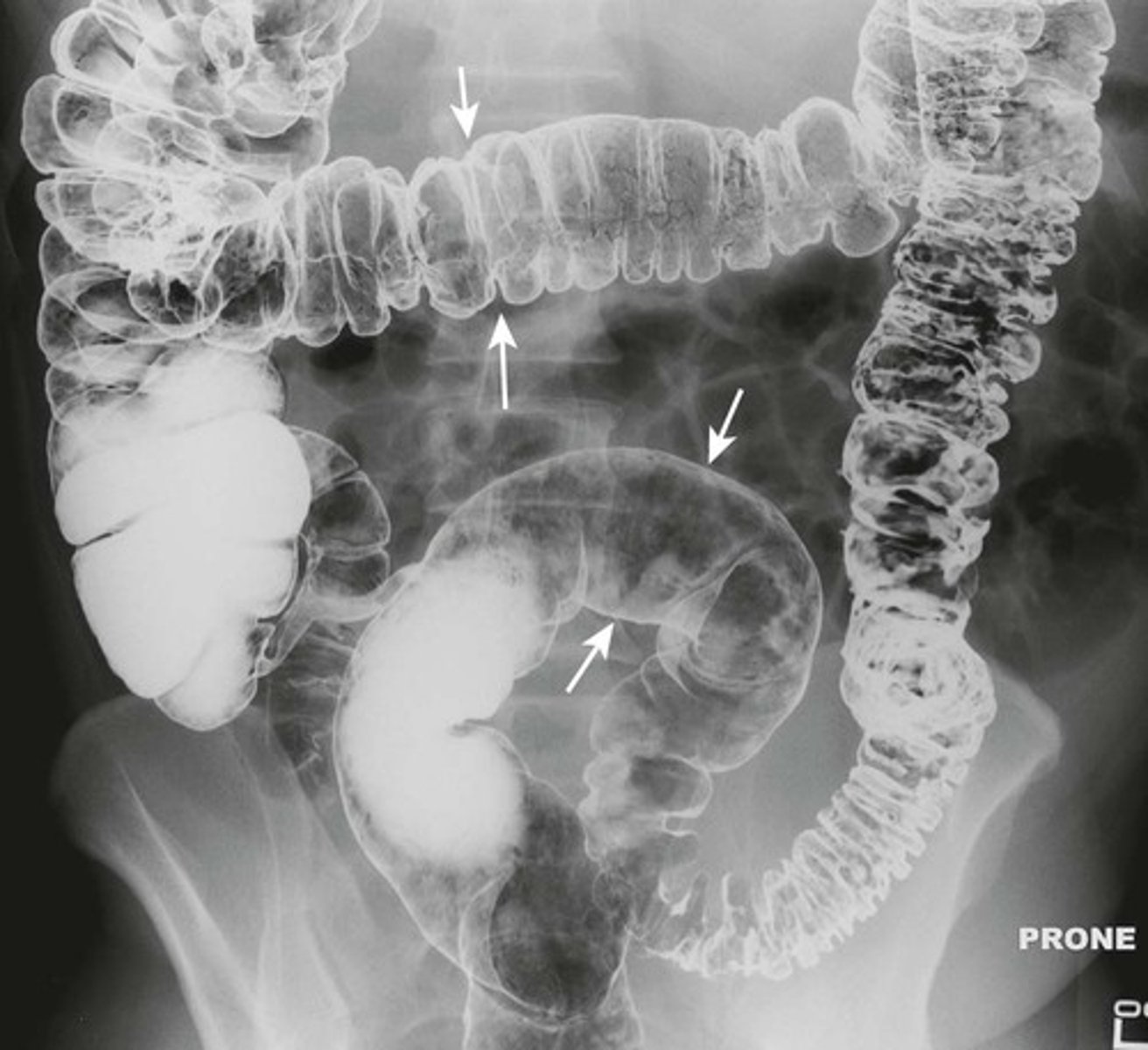
Normal prone abdomen
BLACK ARROW: S-shaped rectosigmoid colon.
WHITE ARROWS: air throughout the remainder of colon
In prone position, ascending, descending and rectosigmoid colon are the highest parts of the large bowl and will fill with air.
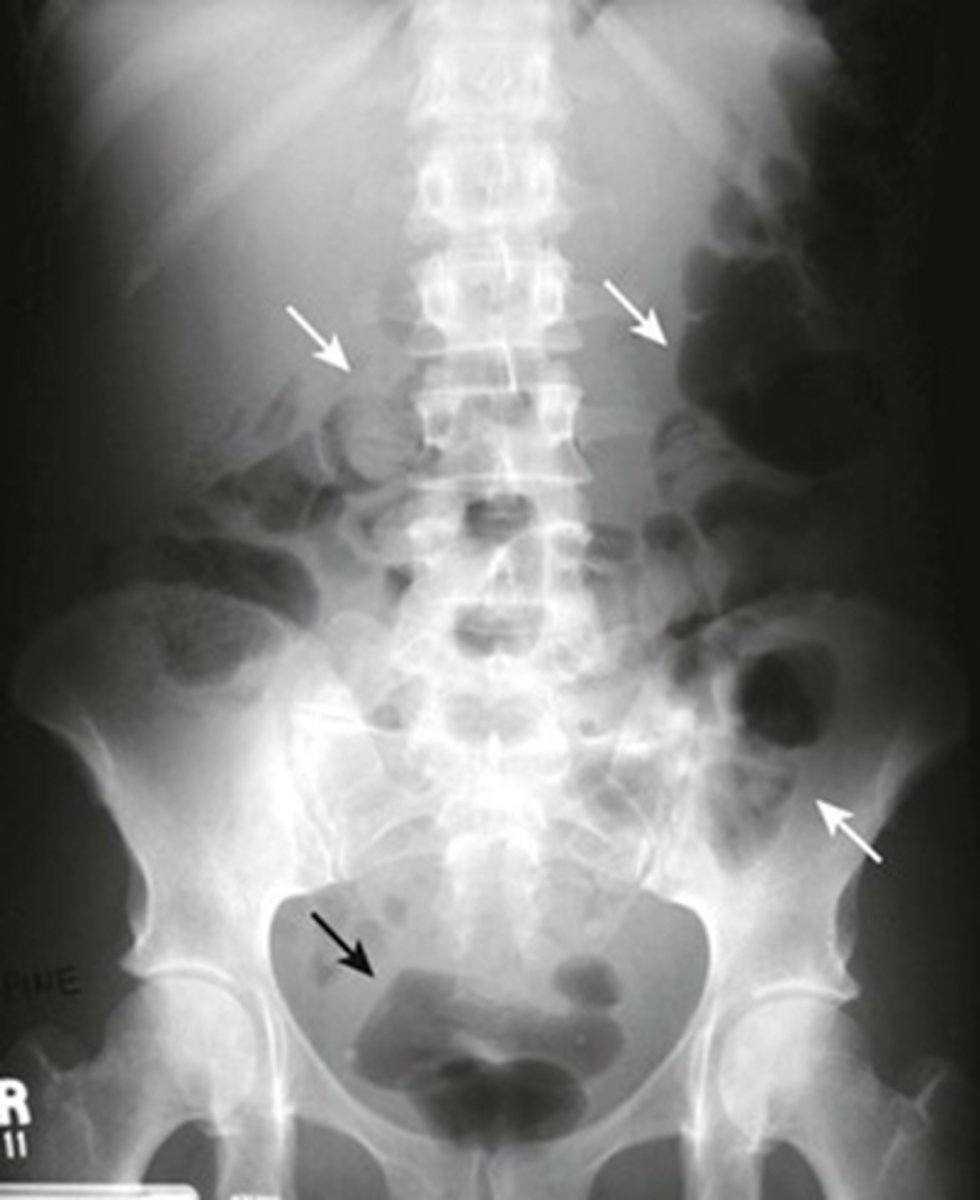
Normal colonic distension from barium study.
WHITE ARROW: normal distension of colon
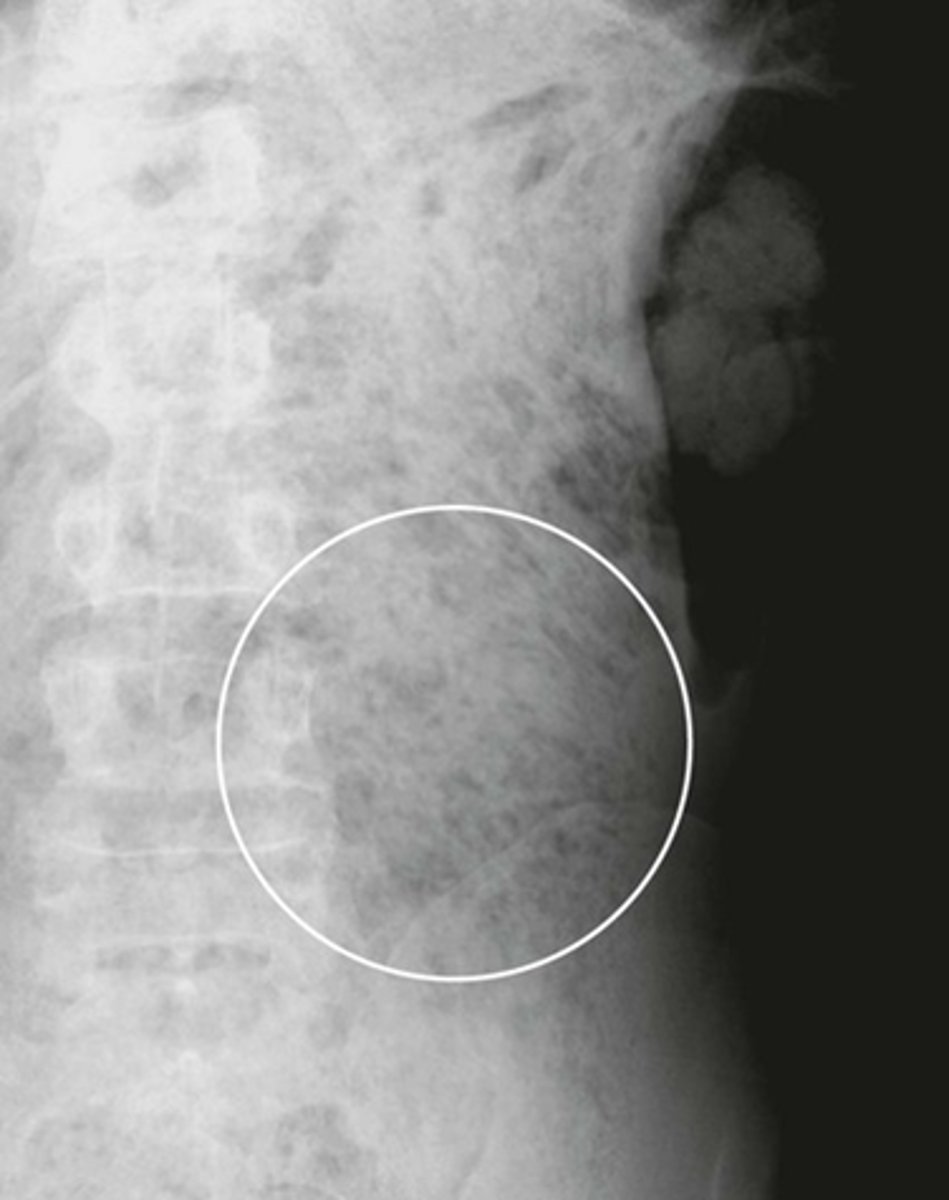
Stool patterns
WHITE CIRCLE: multiple, small bubbles of gas within semi-solid appearing soft tissue density.
helps mark location of large bowel and help identify individual loops of bowel
What can you see on this xray?
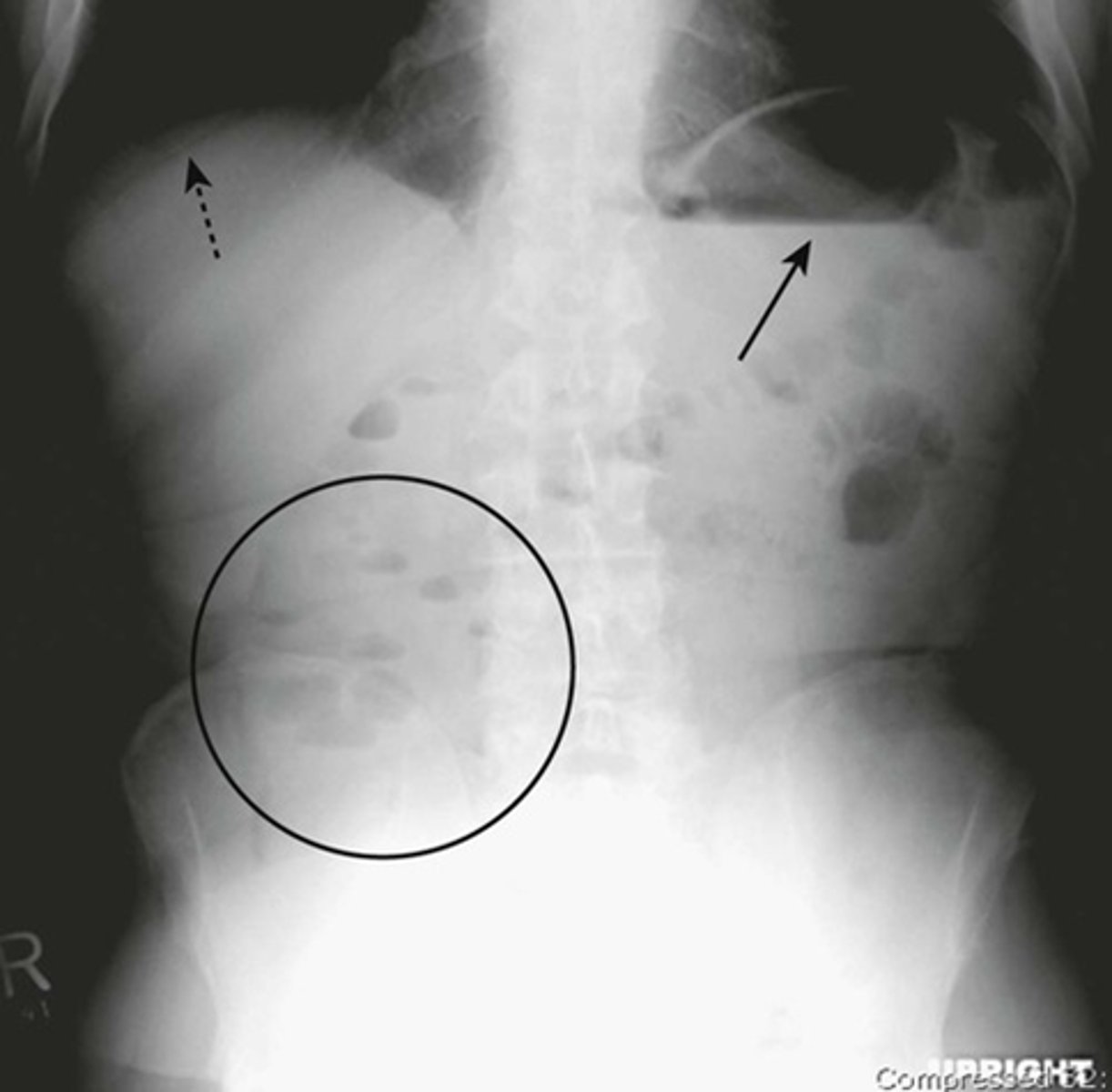
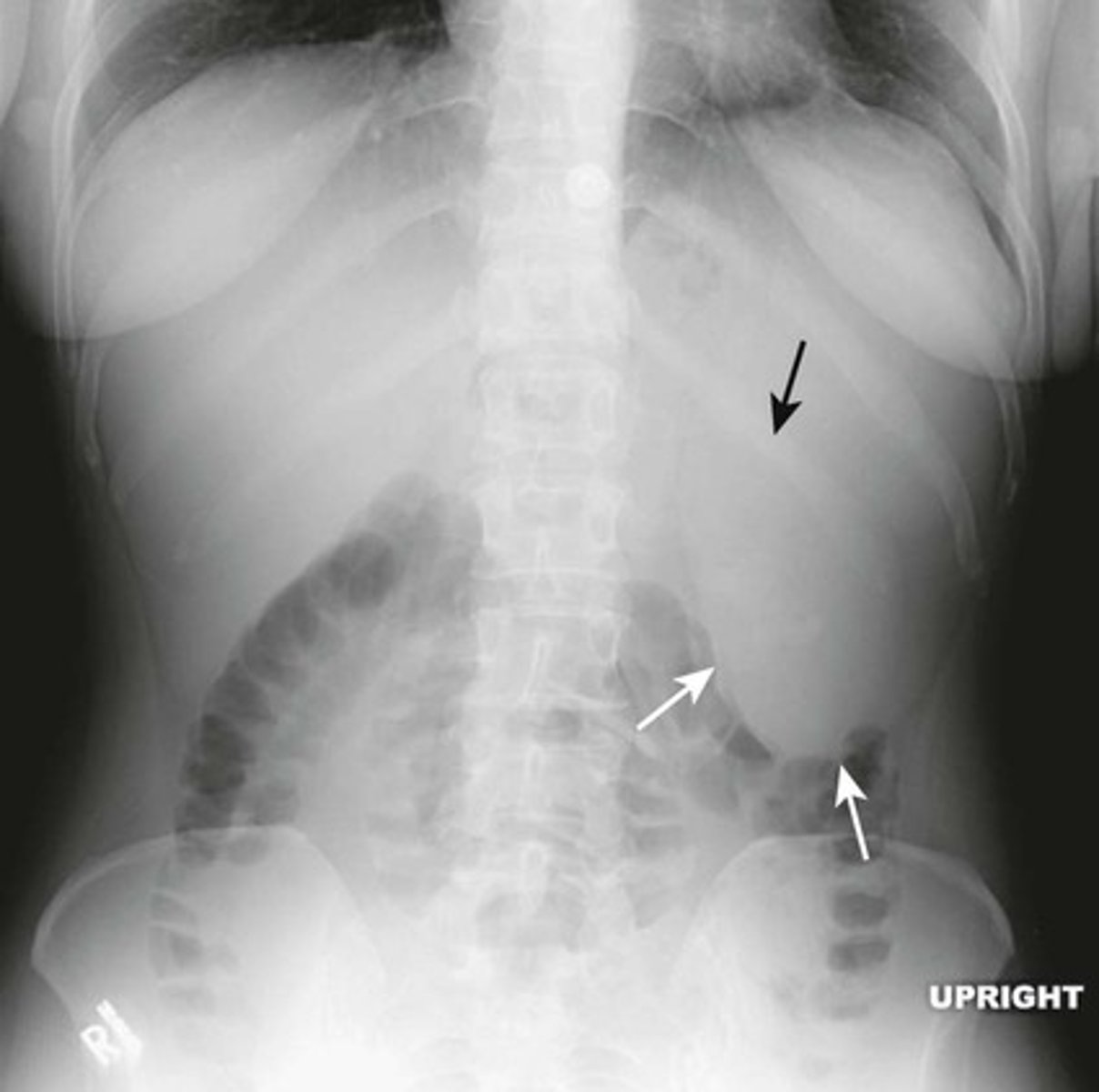
Normal upright abdomen
SOLID BLACK ARROW: normal air-fluid level in stomach
BLACK CIRCLE: short air-filled levels in a few non-dilated loops of small bowel.
DOTTED BLACK ARROW: Free air just below the hemidiaphgram (Usually very few or no air-fluid levels in the colon)
Two things to look for on an upright view of the abdomen are:
1) Air-fluid levels
2) Free intraperitoneal air.
Large bowel.
Peripherally bounding the small bowels.
Also shows normal amount of air.
Liver occupies the RUQ and normall displaces all bowels from this area.
What are the black arrows pointing to?
NORMAL LARGE BOWEL HAUSTRAL MARKINGS
In comparison to Small bowel:
most haustral markings in the colon do not traverse the entire lumen. (vs. valvulae conniventes in small bowel that does appear to traverse the entire lumen)
Haustral markings are also spaced more widely apart than valvulae of the small abdomen.
What are the white arrows pointing to?
Normal SMALL BOWEL VALVULAE
Marking extends across the entire lumen. Spaced much closer together than haustral markings even when the small bowels are dilated.
What are the white arrows pointing to?
HEPATOMEGALY
BLACK ARROWS: displacement of all bowel loops from RUQ to iliac crest and across the midline.
Hepatomegaly is usually indicated by displacement of all bowel loops from RUQ to the iliac crest and across the midline, as in this pt with cirrhosis.
Sometimes the liver can be so enlarged that it will be obvious even on conventional radiographs
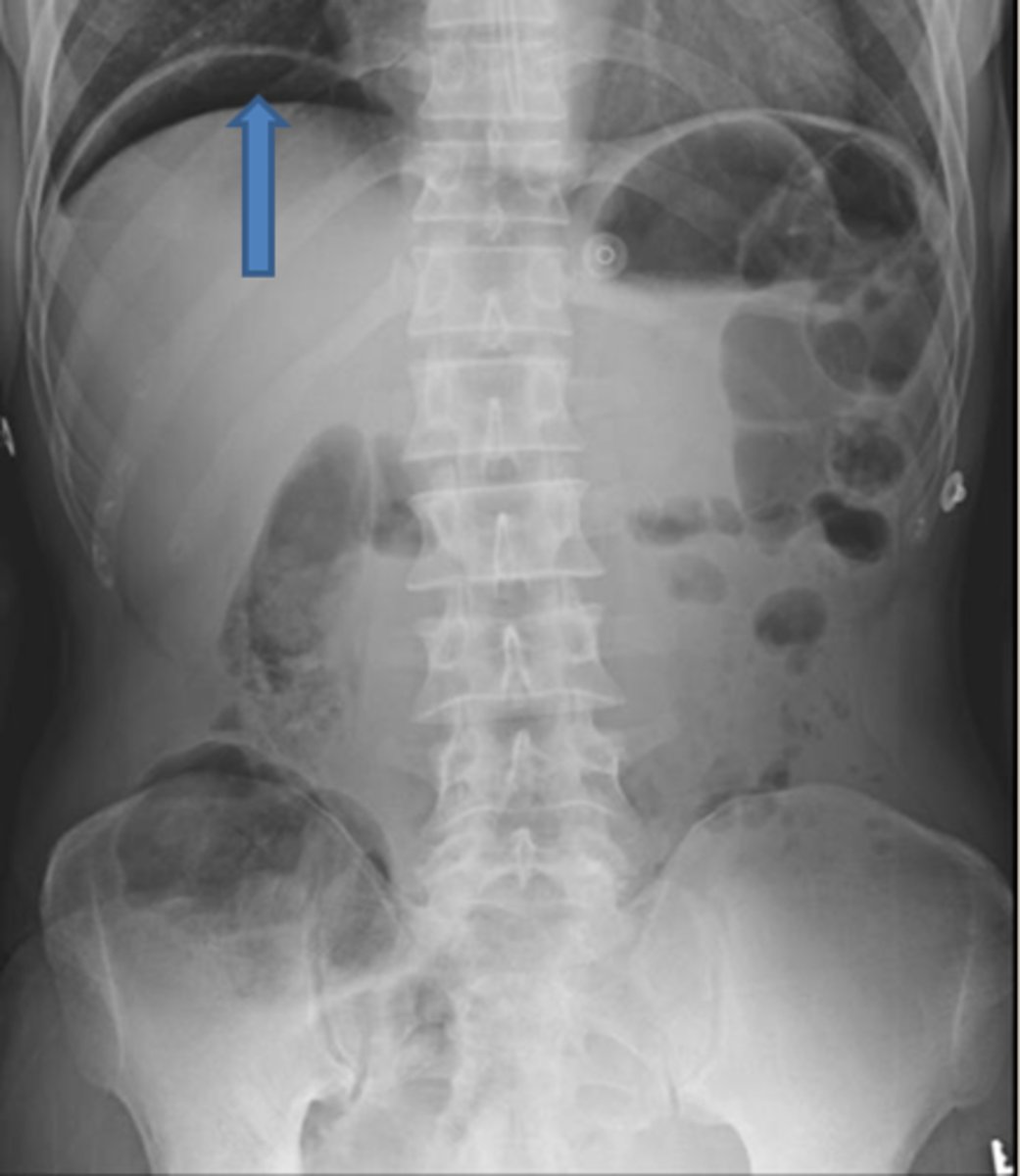
SPLENOMEGALY
WHITE ARROWS: spleen
BLACK ARROW: 12th posterior rib
Spleen is usually about 12 cm in length and DOES NOT project below the 12th posterior rib.
Splenomegaly can also displace the stomach bubble toward or across the midline.
SOLID WHITE ARROWS: kidneys
SOLID BLACK ARROWS: ureters
DOTTED BLACK ARROW: Urinary bladder
DOTTED WHITE ARROW: Liver (normally depresses the right kidney more inferior than the left)
Image: intravenous urogram / IV pyelogram.
What are the arrows pointing to?
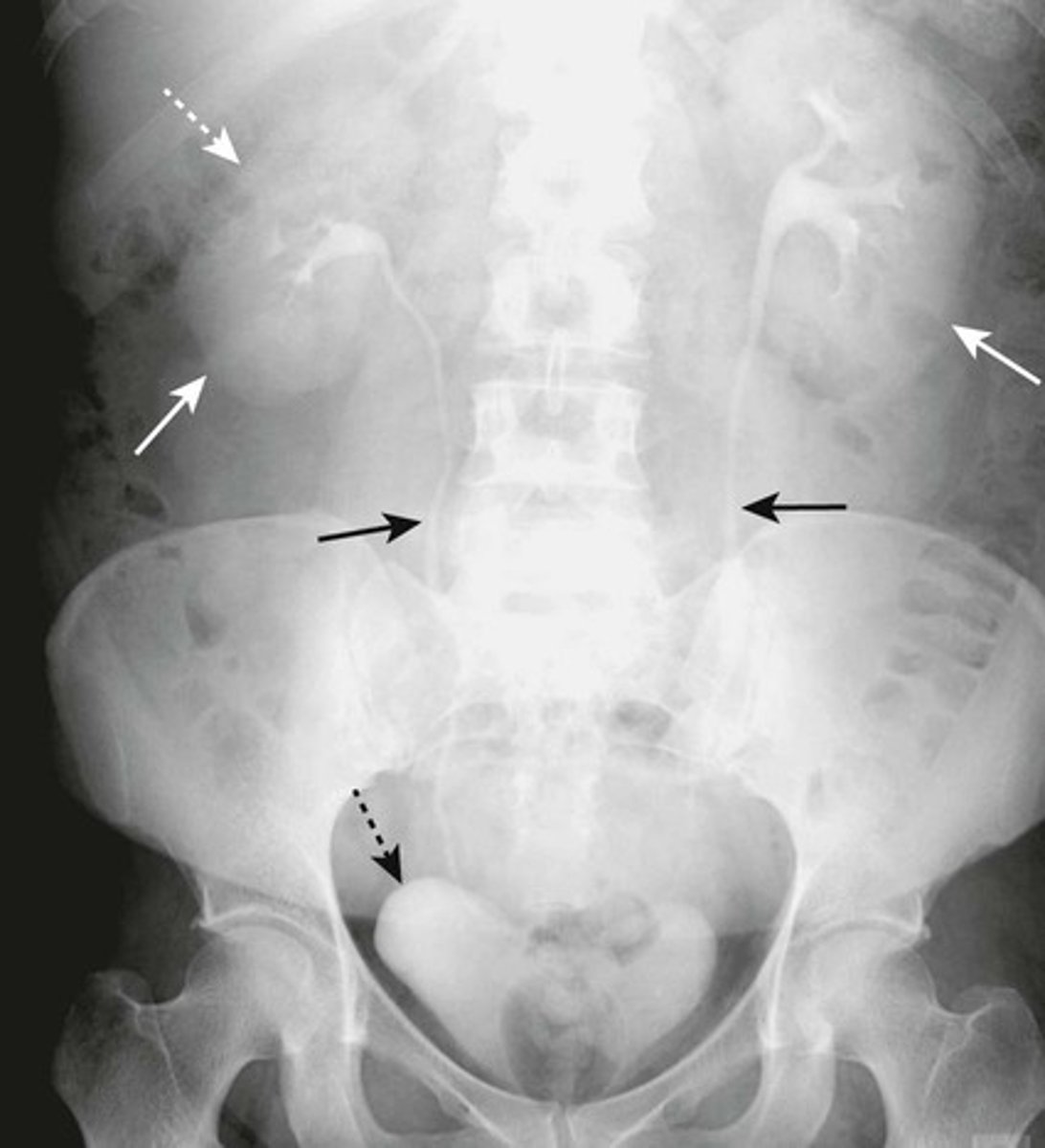
ENLARGED KIDNEY
Organomegaly or soft tissue masses - can be dx either by:
1) visualizing the edge of the mass if there is fat or air surrounding it
2) displacement of bowel
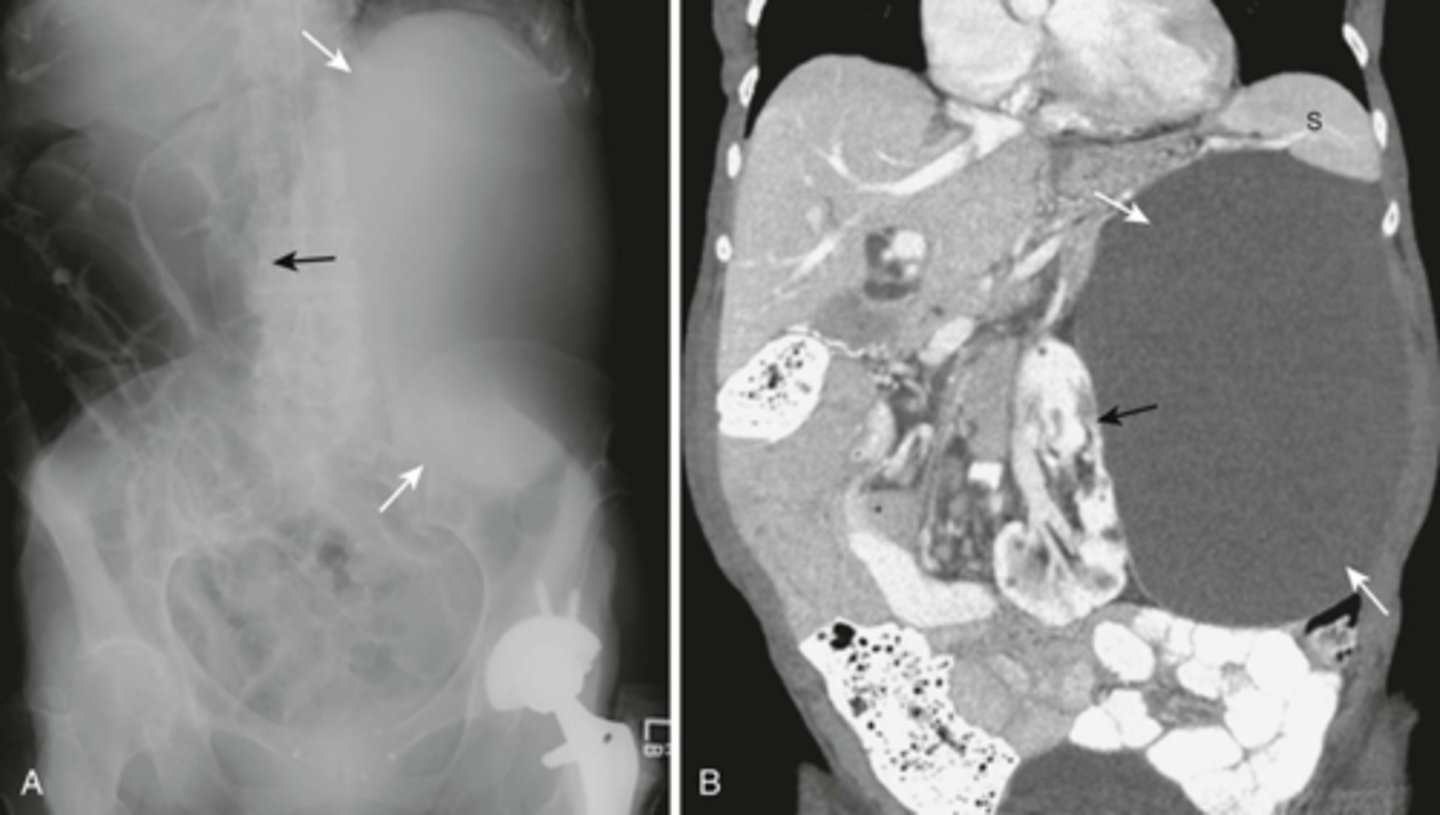
A:
WHITE ARROWS: soft tissue mass on LUQ
BLACK ARROW: displacement of bowels to the right
B: CT of the same patient
WHITE ARROW: large renal cyst arising from left kidney, displacing it and surrounding bowel.
BLACK ARROW: left kidney.
S: spleen, compressed by cyst.
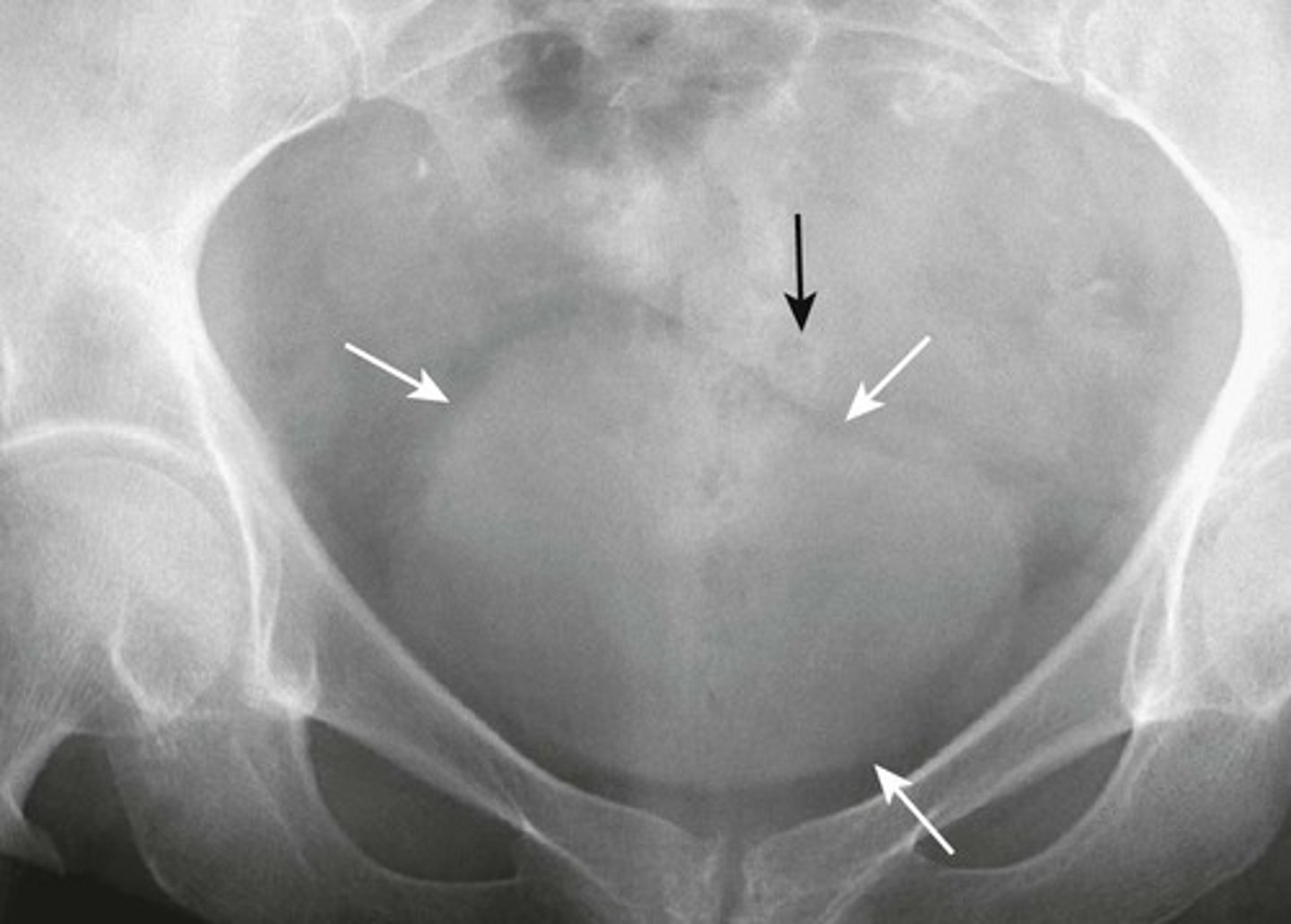
NORMAL BLADDER
WHITE ARROWS: outline of URINARY BLADDER visible by perivesical fat
BLACK ARROW: SIGMOID COLON occupying the space just above the bladder. (this is common in men; in women, soft tissue above bladder could be uterus or Sigmoid colon)
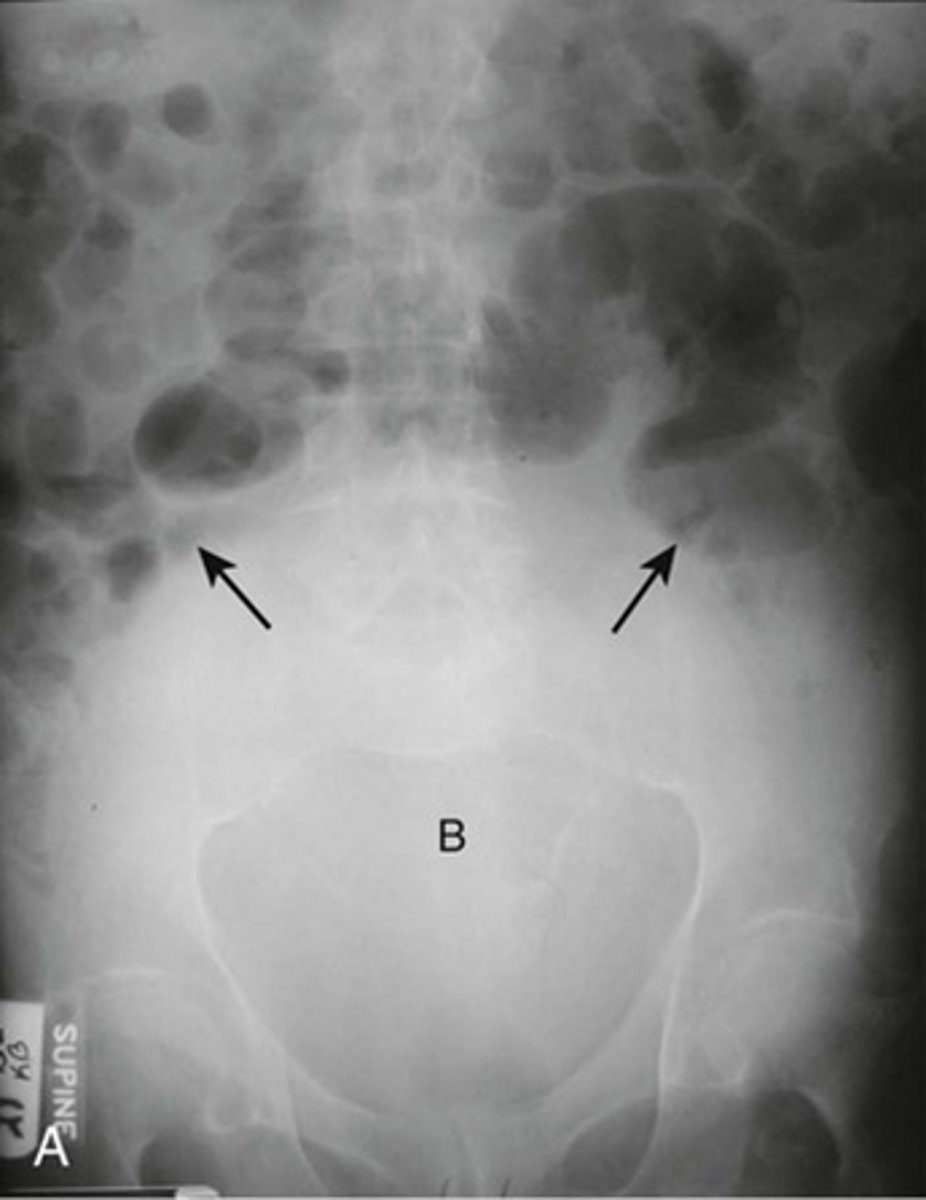
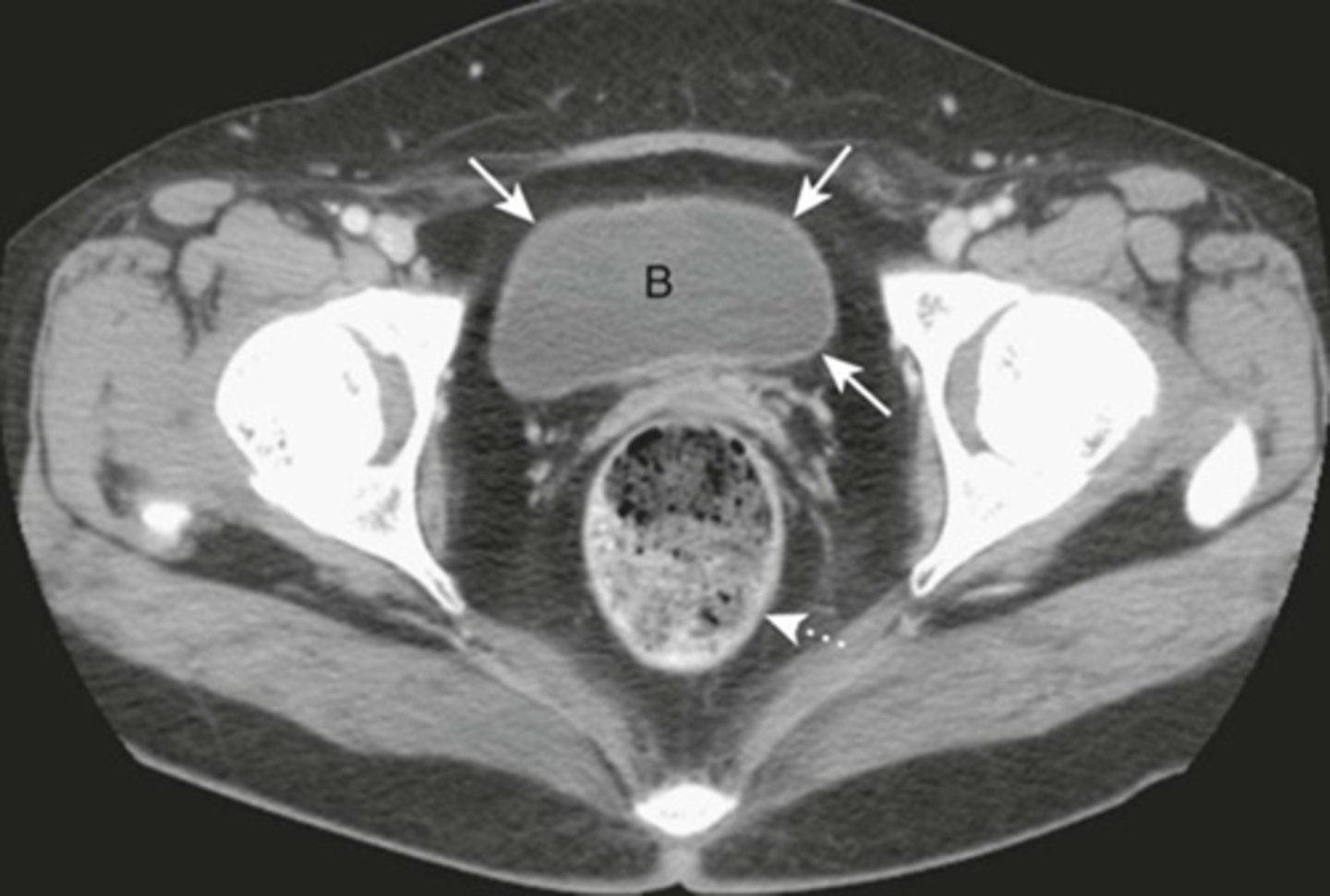
Distended bladder
Image A:
B: Distended bladder - soft tissue mass ascends from pelvis into lower abdomen, and displacing bowel.
BLACK ARROW: displacement of bowel into mid abdomen.
Image taken from 72y.o. male with bladder outlet obstruction due to BPH.
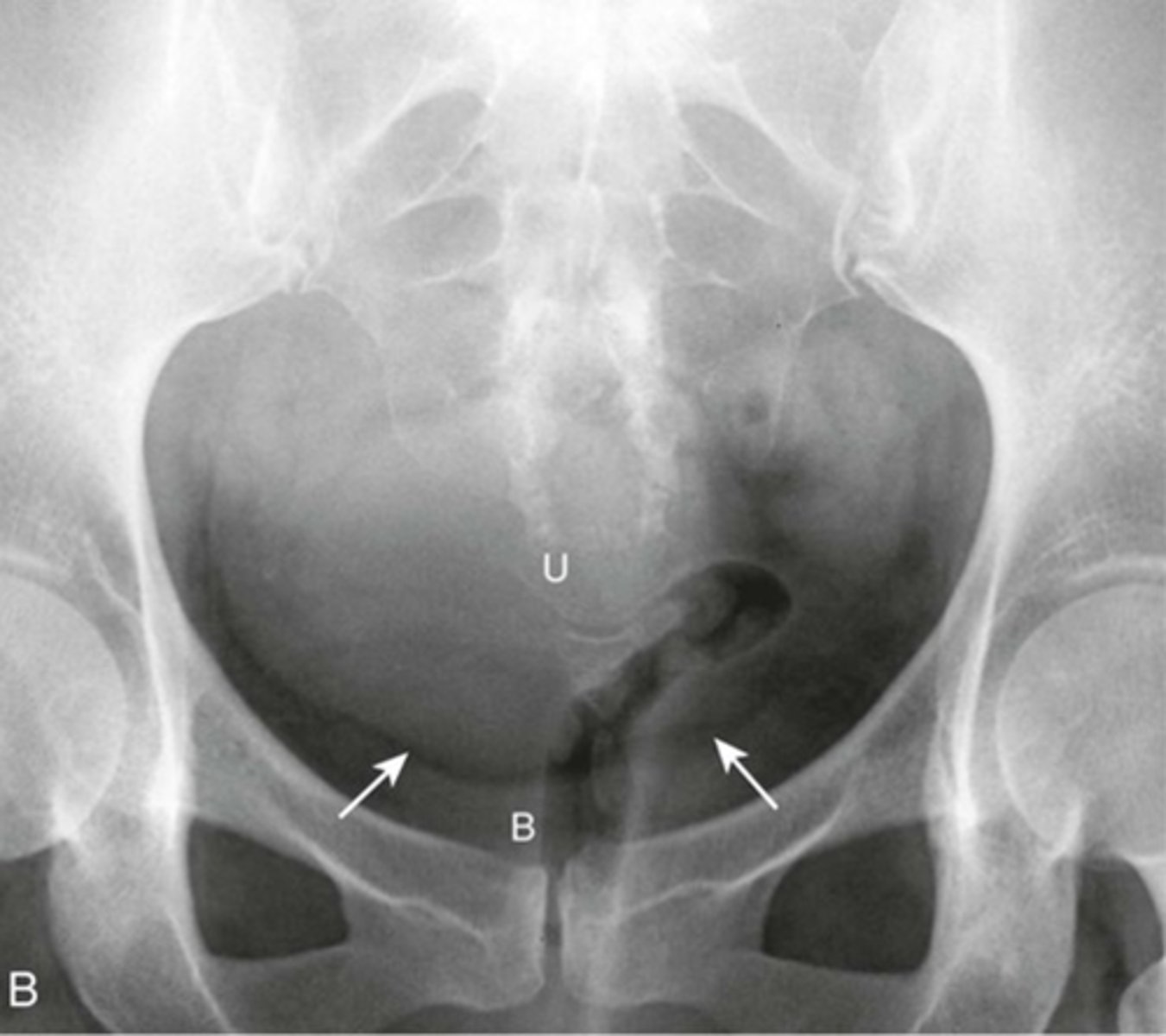
ENLARGED UTERUS
U: enlarged uterus
(can be distinguished from bladder because there is a FAT PLANE between it and urinary bladder)
WHITE ARROWS: fat plane
B: Urinary bladder
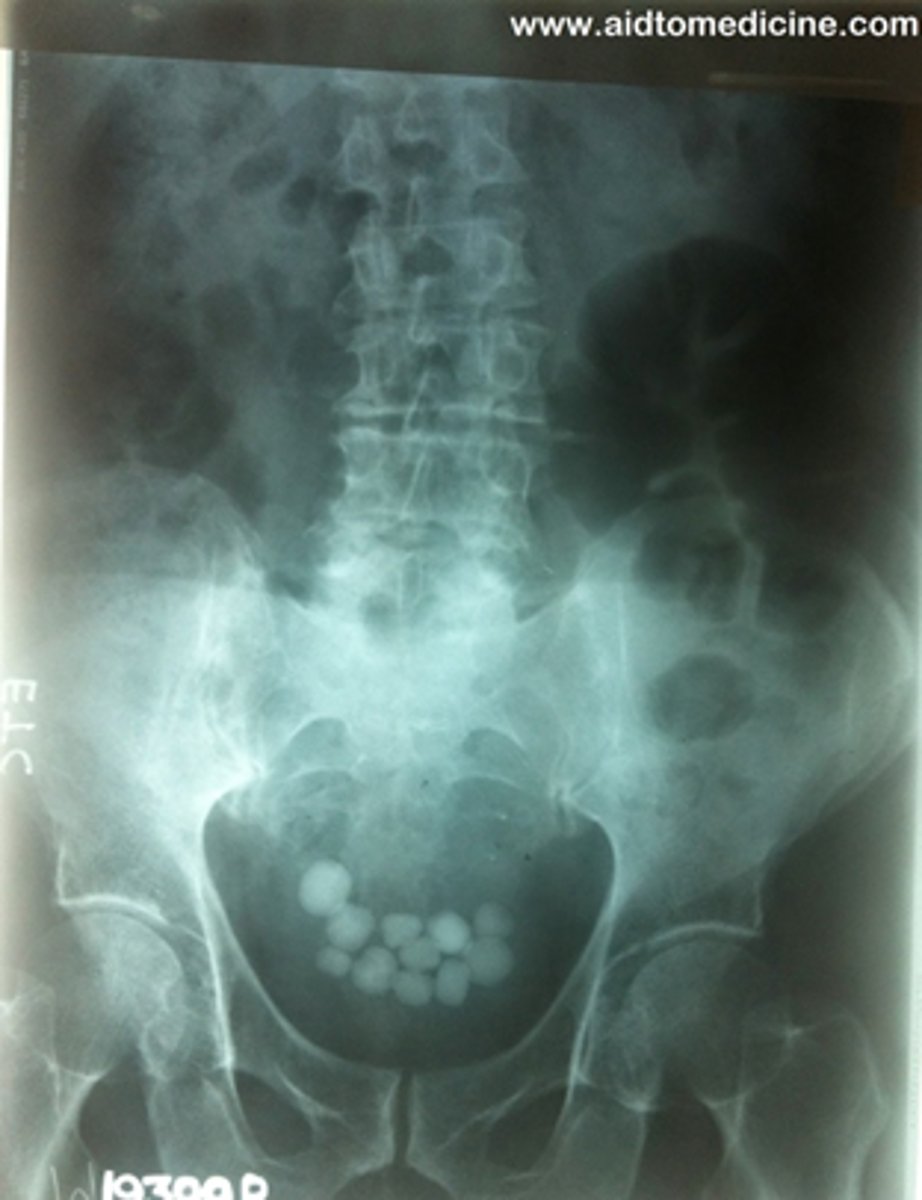
Bladder stones
Kidney stones
Gall stones
Fibroids
Fibroids
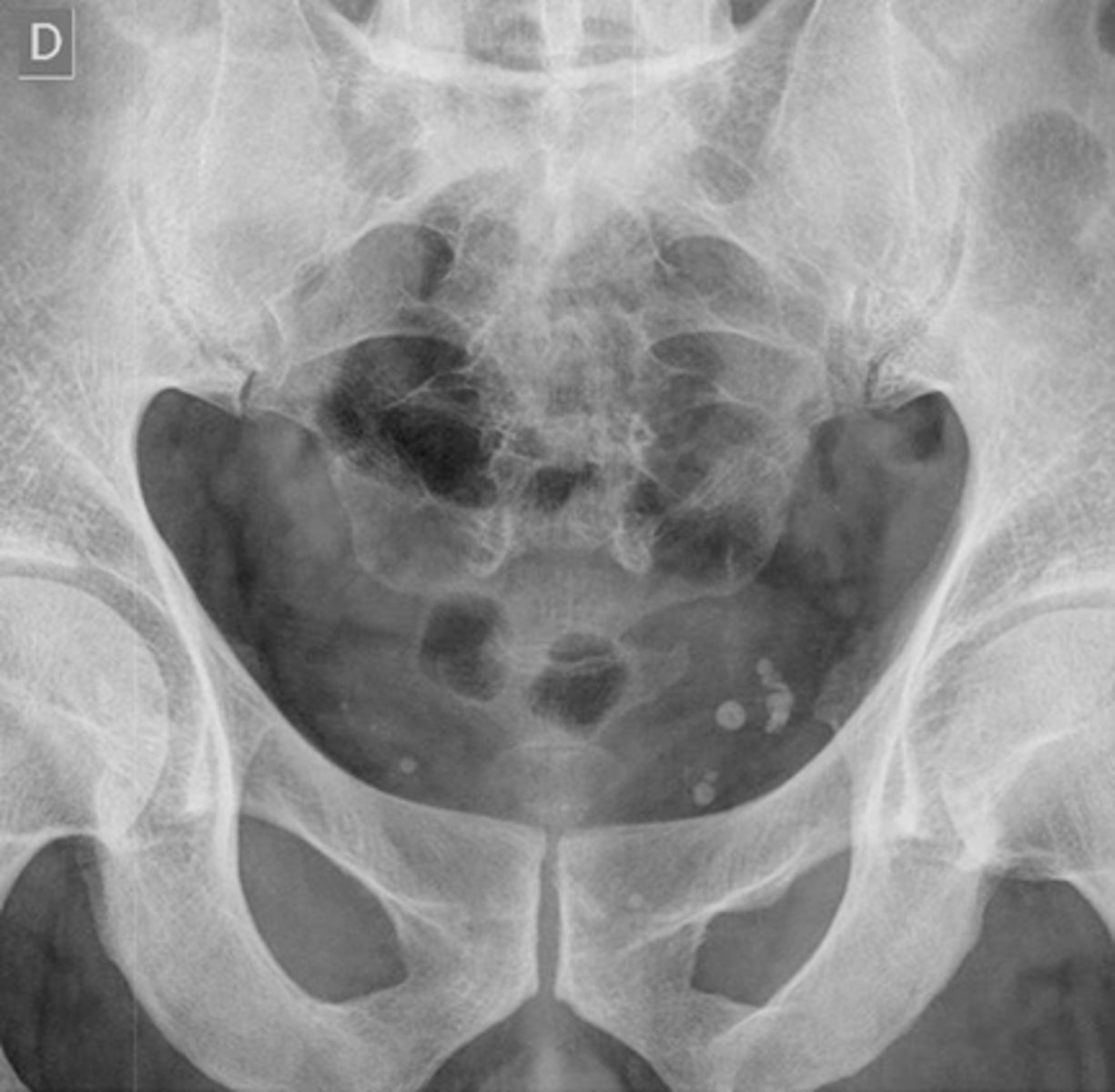
Phleboliths
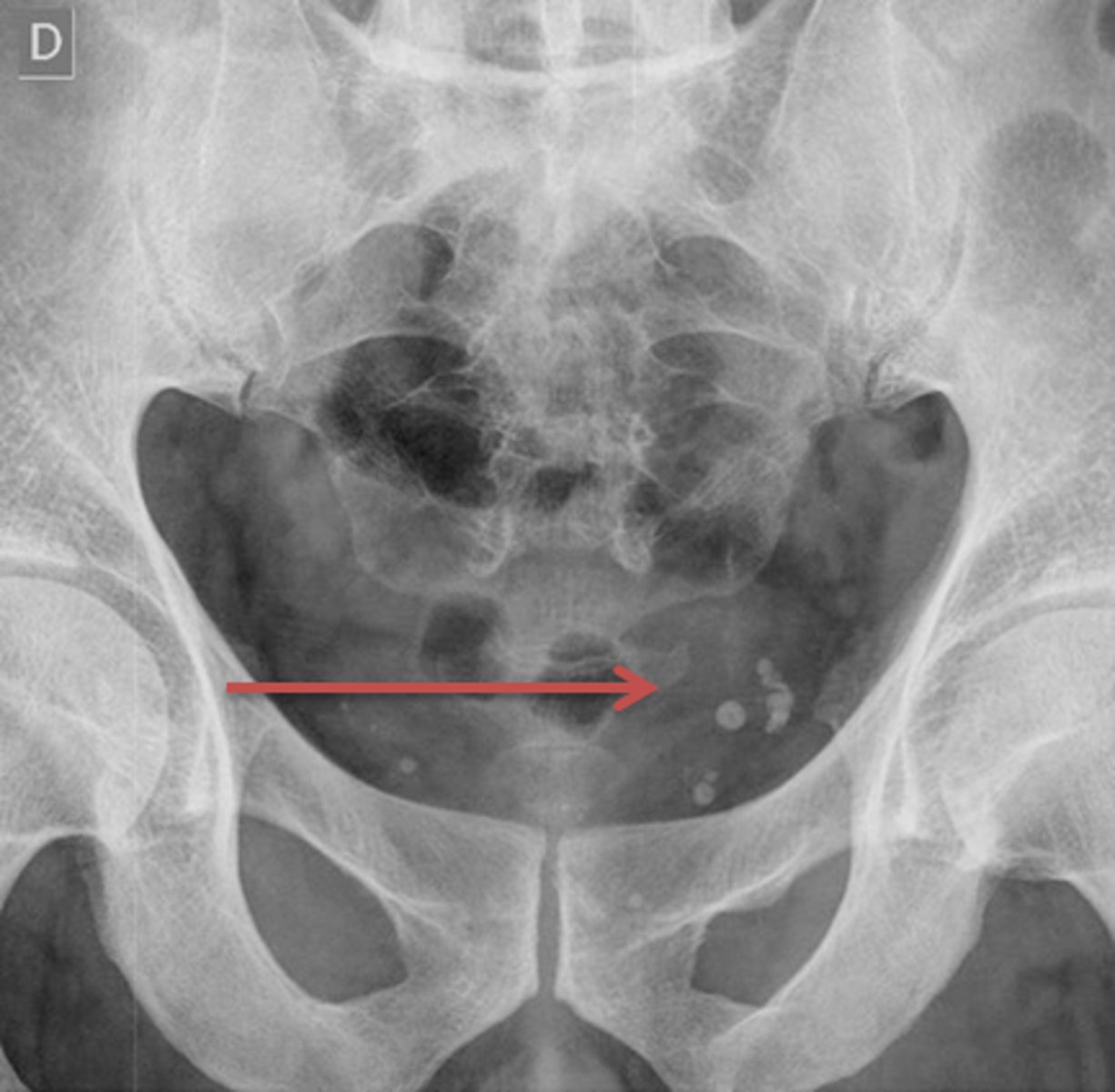
Phleboliths
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Free air upright abdomen
free air lateral decub

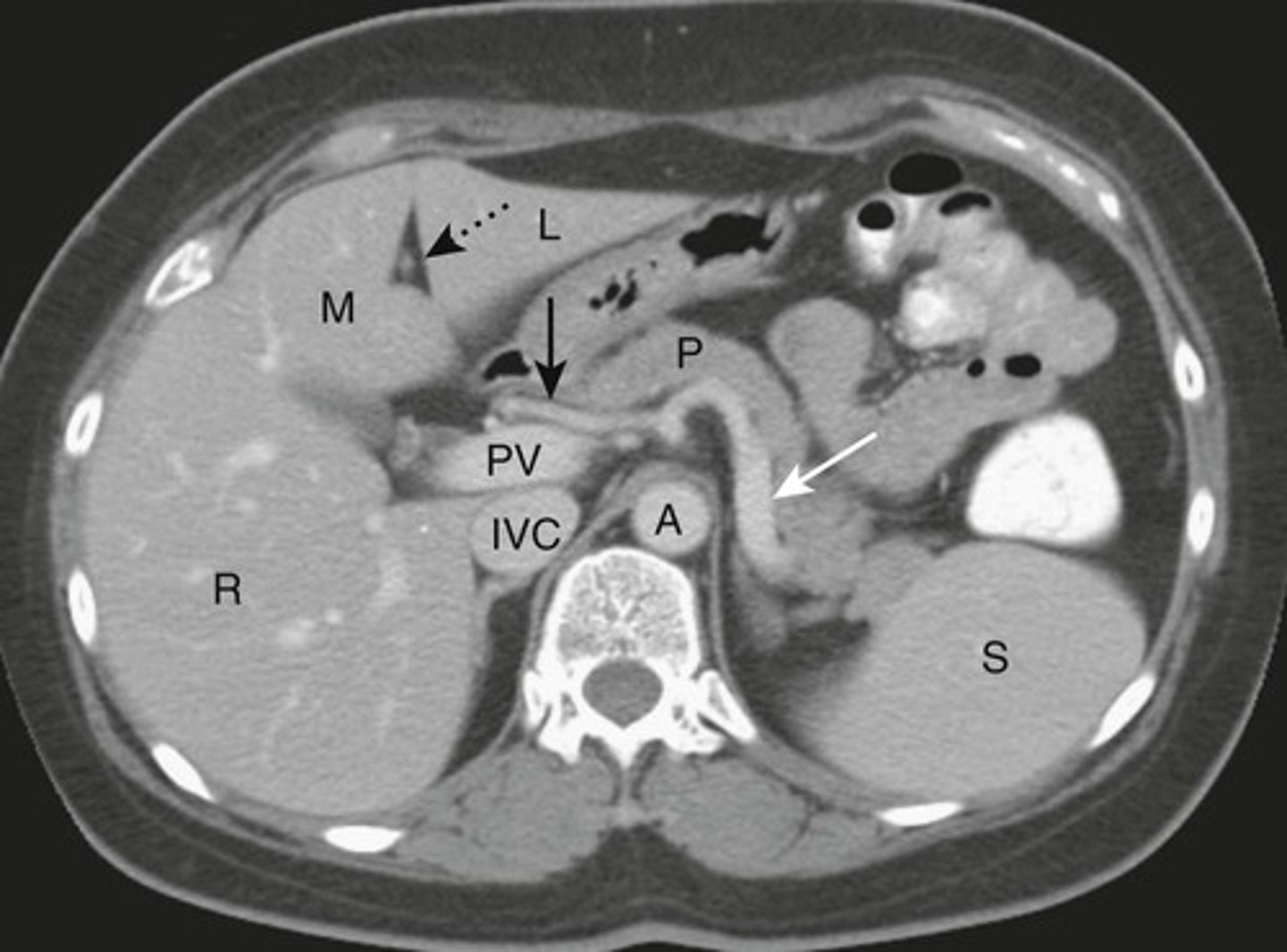
NORMAL LIVER ANATOMY
DOTTED BLACK ARROW:
Ligamentum teres - divides the left love of the liver into medial and latera segments, with larger right lobe more posterior.
M: Medial segment of left lobe
L: Lateral segment of left lobe
R: larger right lobe of liver.
PV: Portal vein, lying just posterior to the hepatic artery
SOLID BLACK ARROW: hepatic artery
SOLID WHITE ARROW: Splenic artery, follows the path of the pancreas towards the spleen
P: PANCREAS
S: Spleen
IVC: Inferior vena cava, lying right of the aorta
A: Aorta
Normal
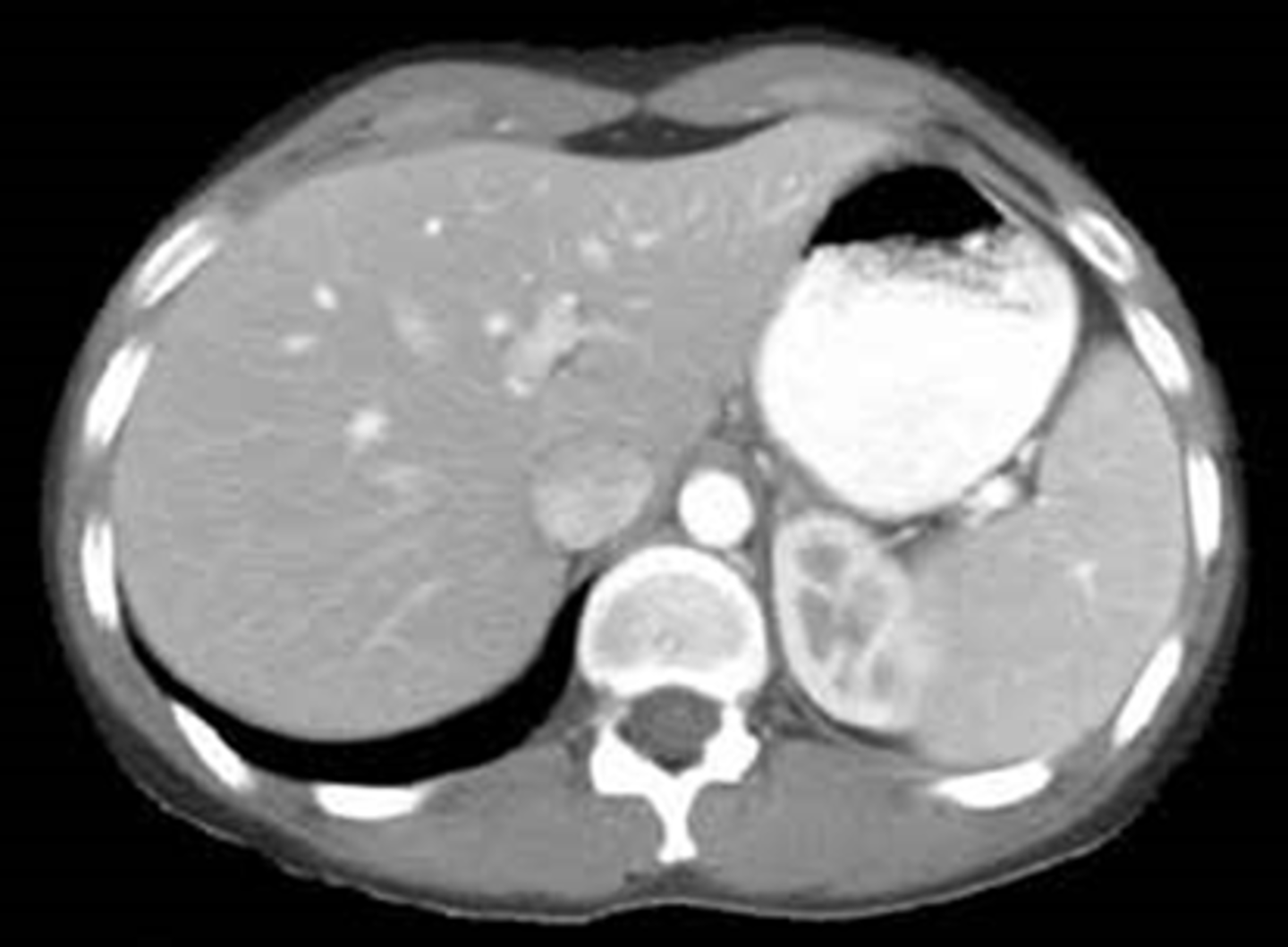
Normal
Normal
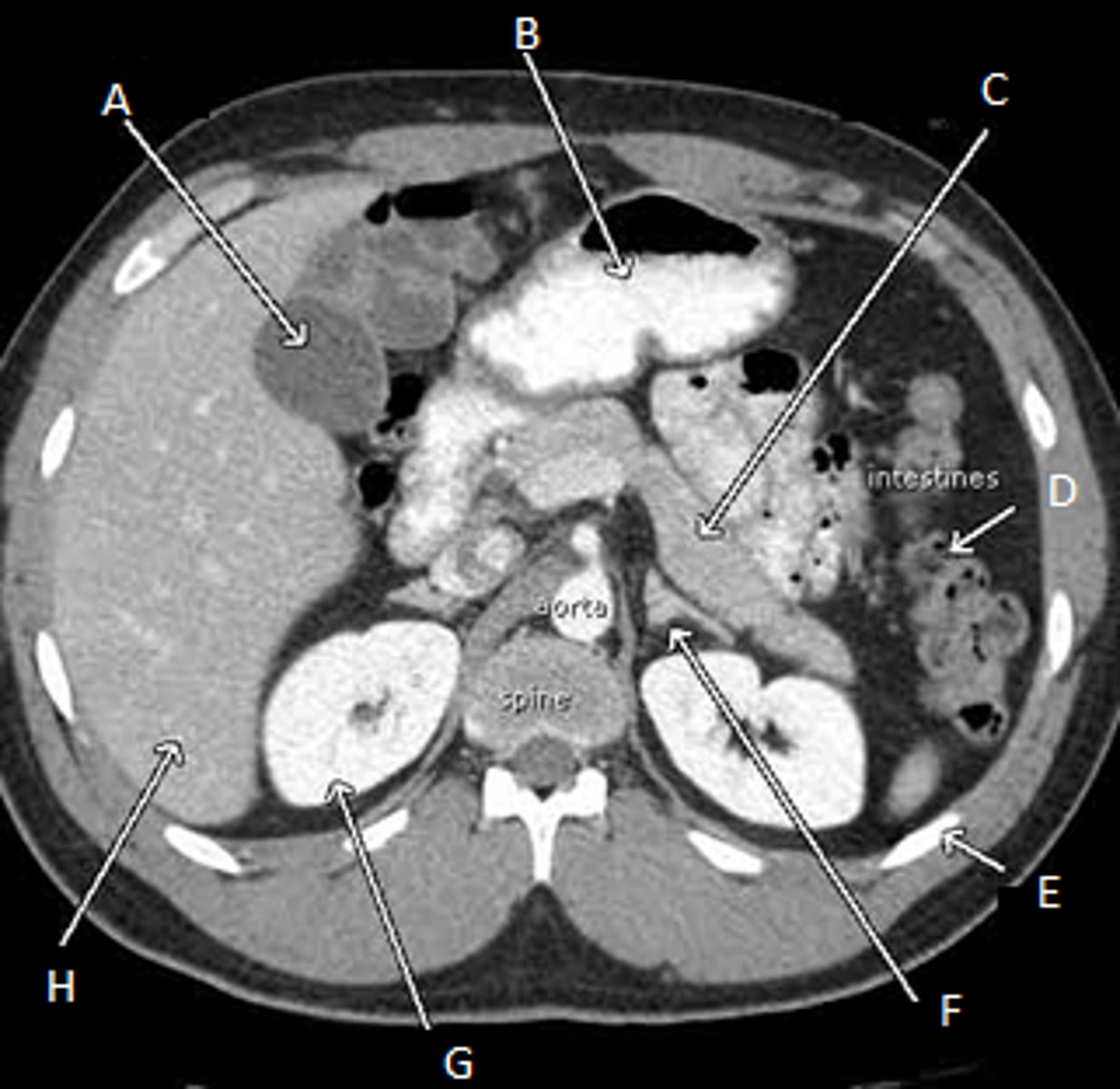
A: Gall bladder
B: Stomach
C: pancreas
D: Intestines
E: Ribs
F: Left Adrenal Glands
G: Right kidney
H: Liver
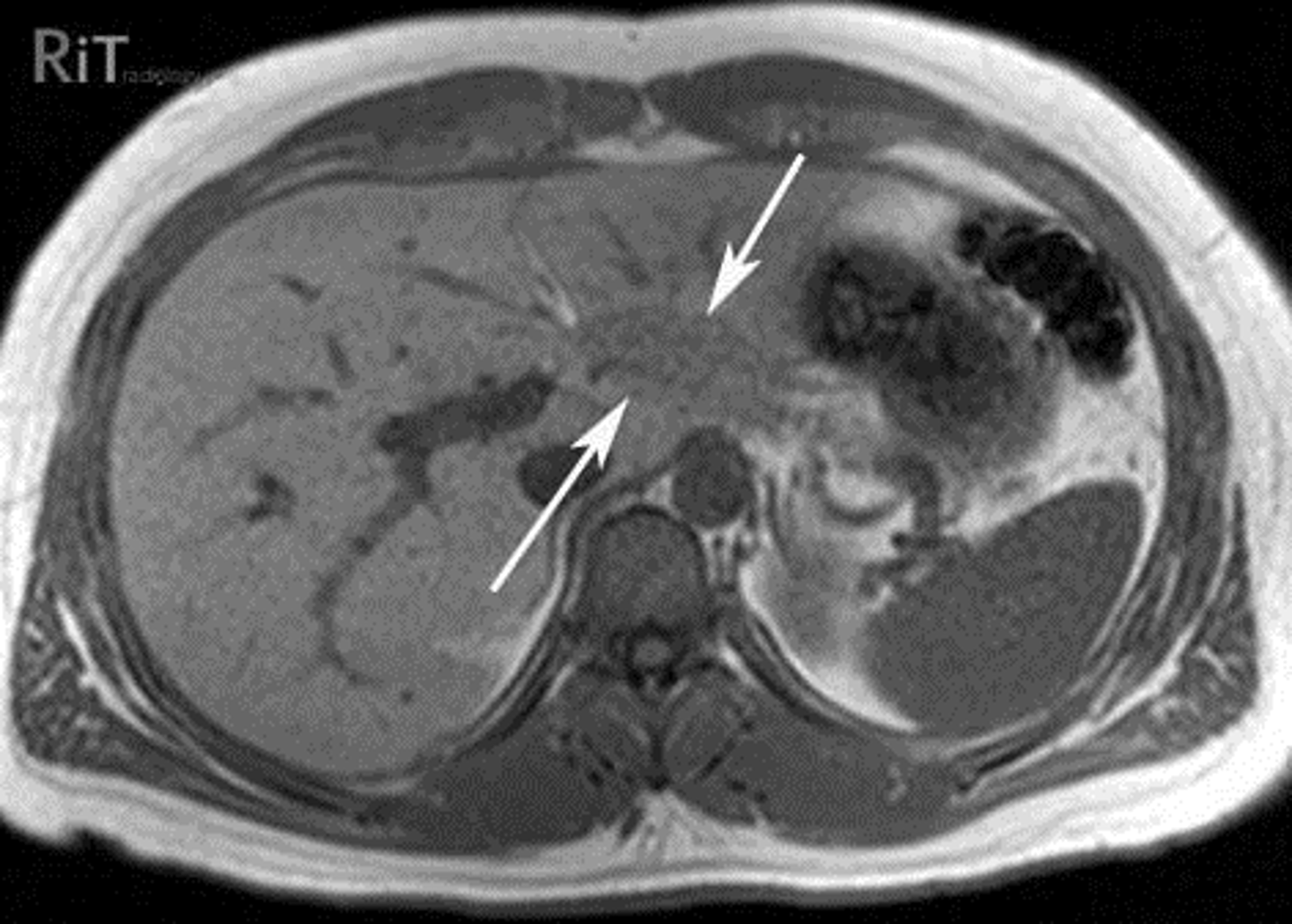
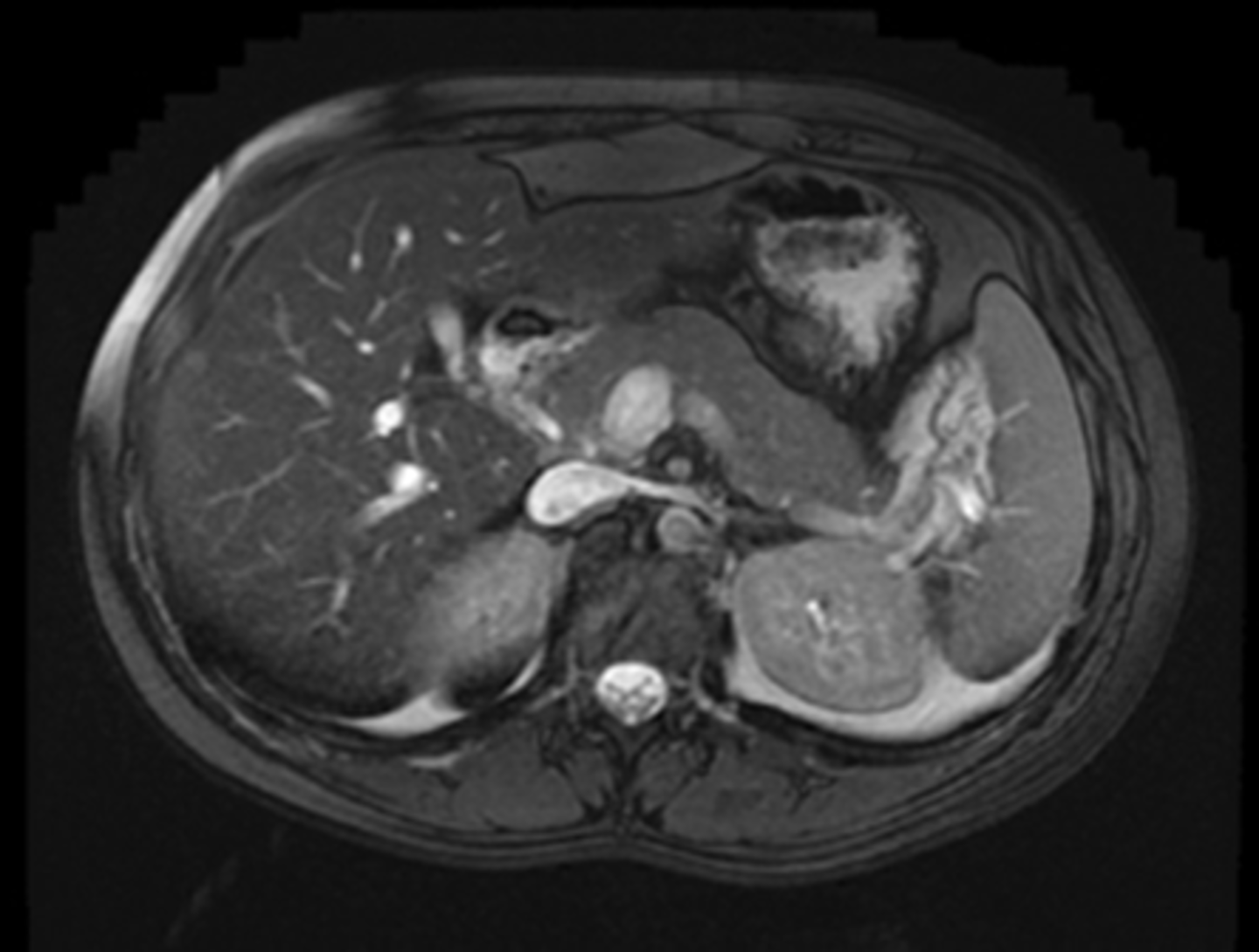
Normal pancreas
A:
THICK WHITE ARROW: Body of pancreas
THIN WHITE ARROW: splenic artery
DOTTED WHITE ARROWS: adrenal glands
BLACK ARROW: gall bladder
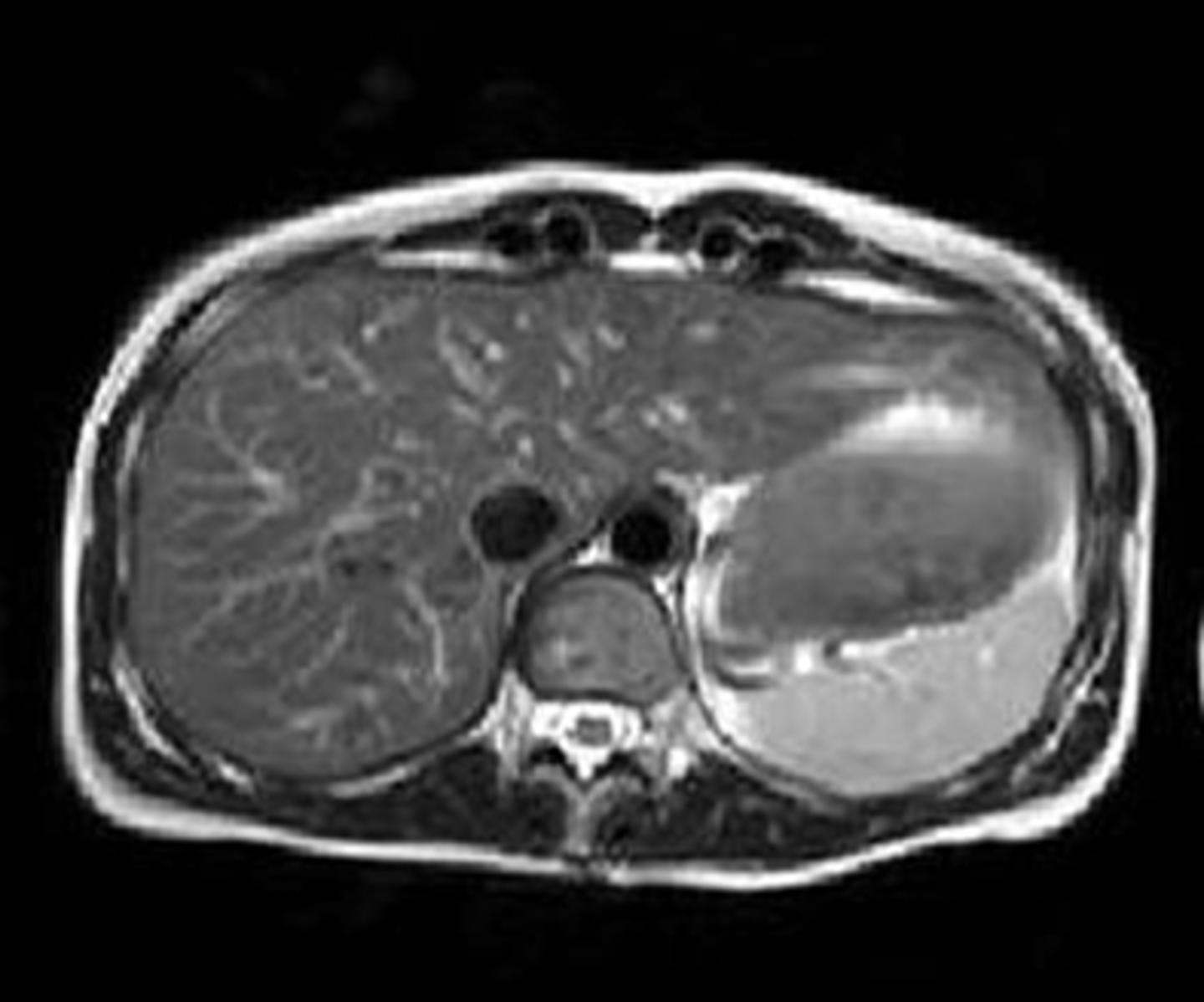
Normal pancreas
B:
SOLID WHITE ARROW: Normal head of pancreas.
Because pancreas is oriented obliquely, the organ is not seen on any one axial image of the upper abdomen. Tail - superior, body and head - inferior.
Normal pancreas
Normal Kidneys
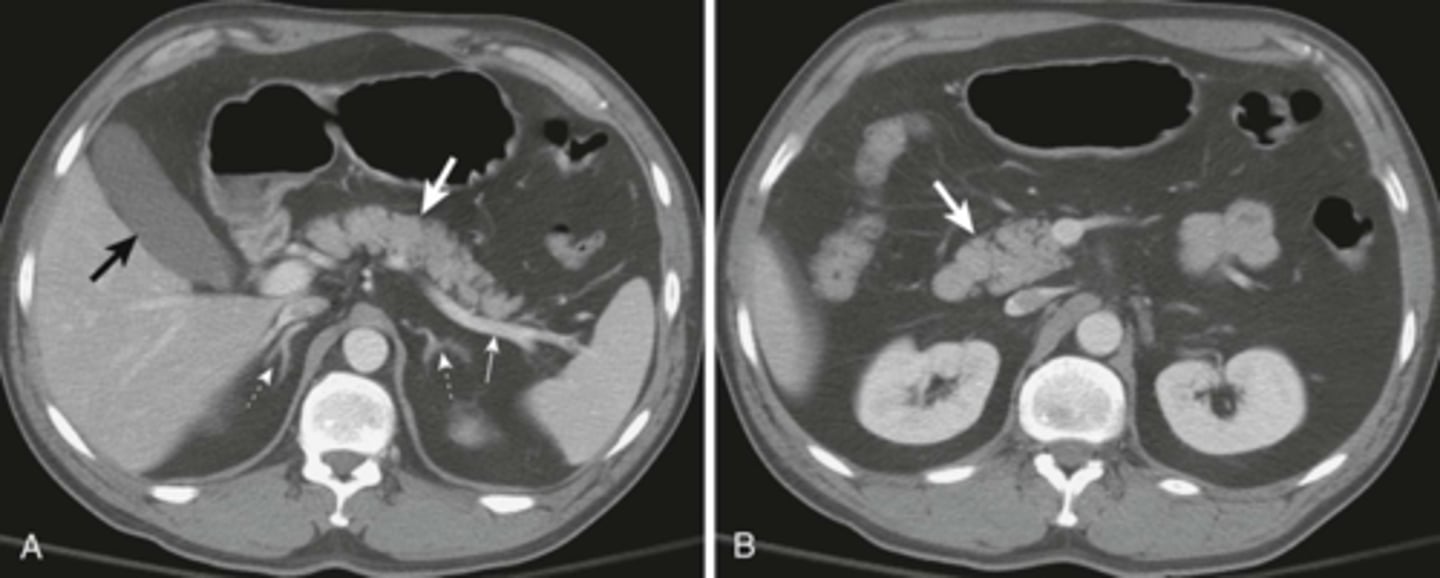
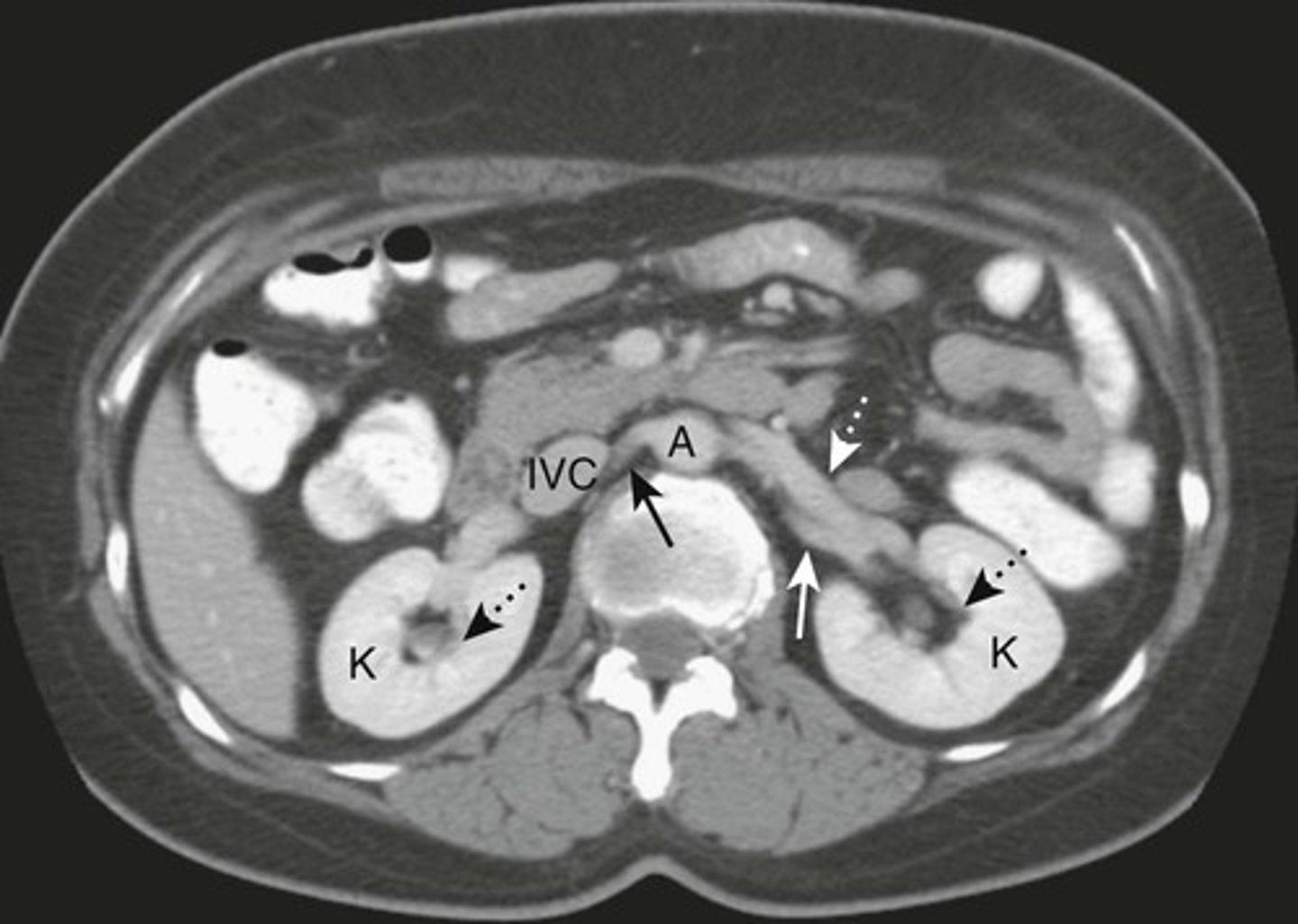
K: Kidneys, lie in the renal fossae
DOTTED BLACK ARROWS: Central portion of the kidneys, should contain fat in a normal renal pelviz.
SOLID BLACK ARROW: Right renal artery, running posterior to the IVC
DOTTED WHITE ARROW: Left renal vein, lies anterior to the left renal artery.
SOLID WHITE ARROW: left renal artery.
A: Abdominal Aorta
IVC: inferior vena cava
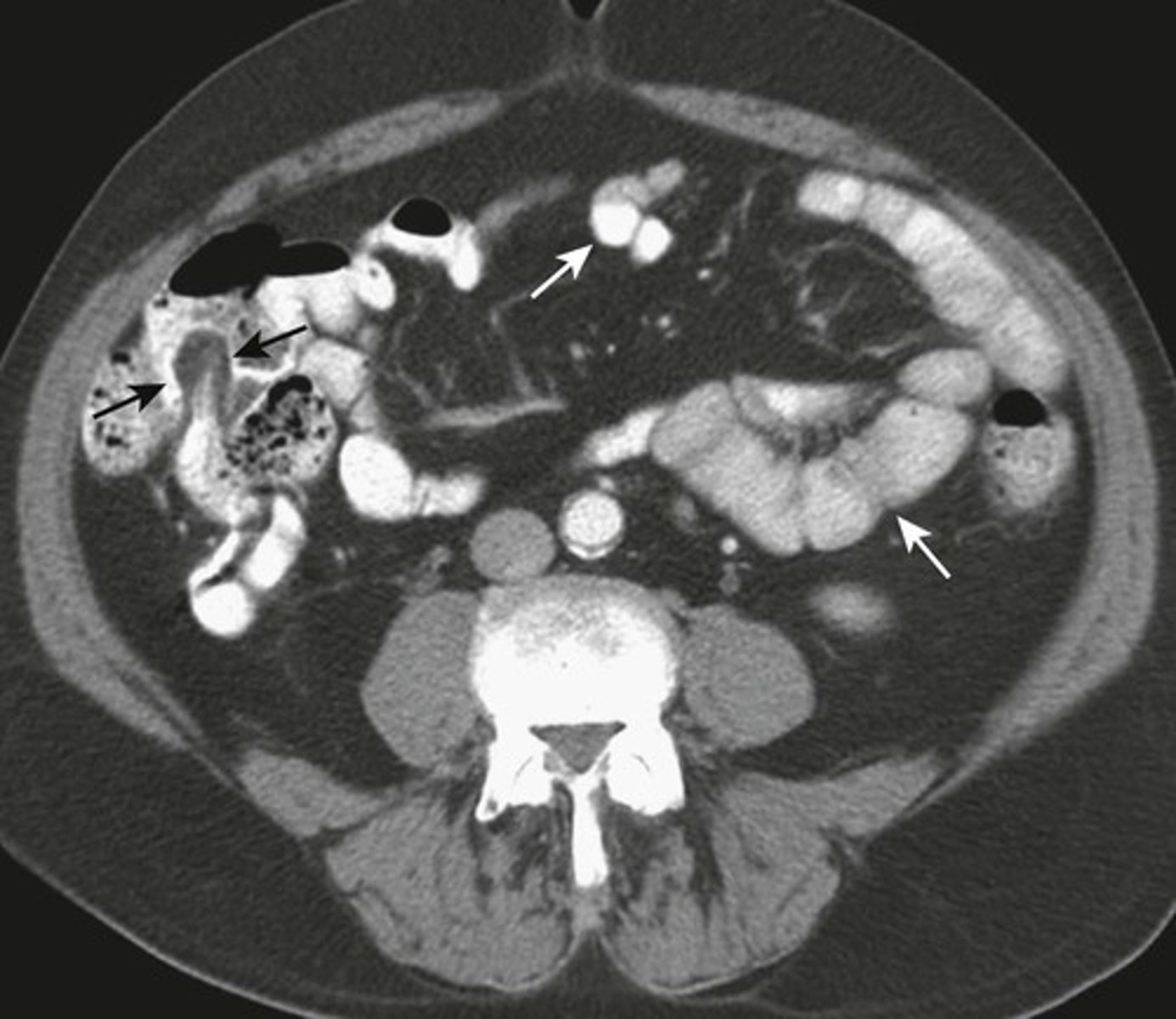
NORMAL Small bowel and large bowel.
WHITE ARROWS: small bowel
BLACK ARROW: Terminal ileum, recognized by fat-containing "lips" of the Ileocecal valve
Normal bladder
B: unopacified urine in CT with IC contrast.
SOLID WHITE ARROWS: bladder wall, thin and equal thickness around the circumference of the bladder.
DOTTED WHITE ARROW: Rectum, lies posterior to bladder
1) Air filled loops of large and small bowel
2) Large and small bowel equally distended
3) Equal air fluid levels
4) Bowels can be distended - look for air throughout large bowel and rectum.
What are xray findings of an ileus?
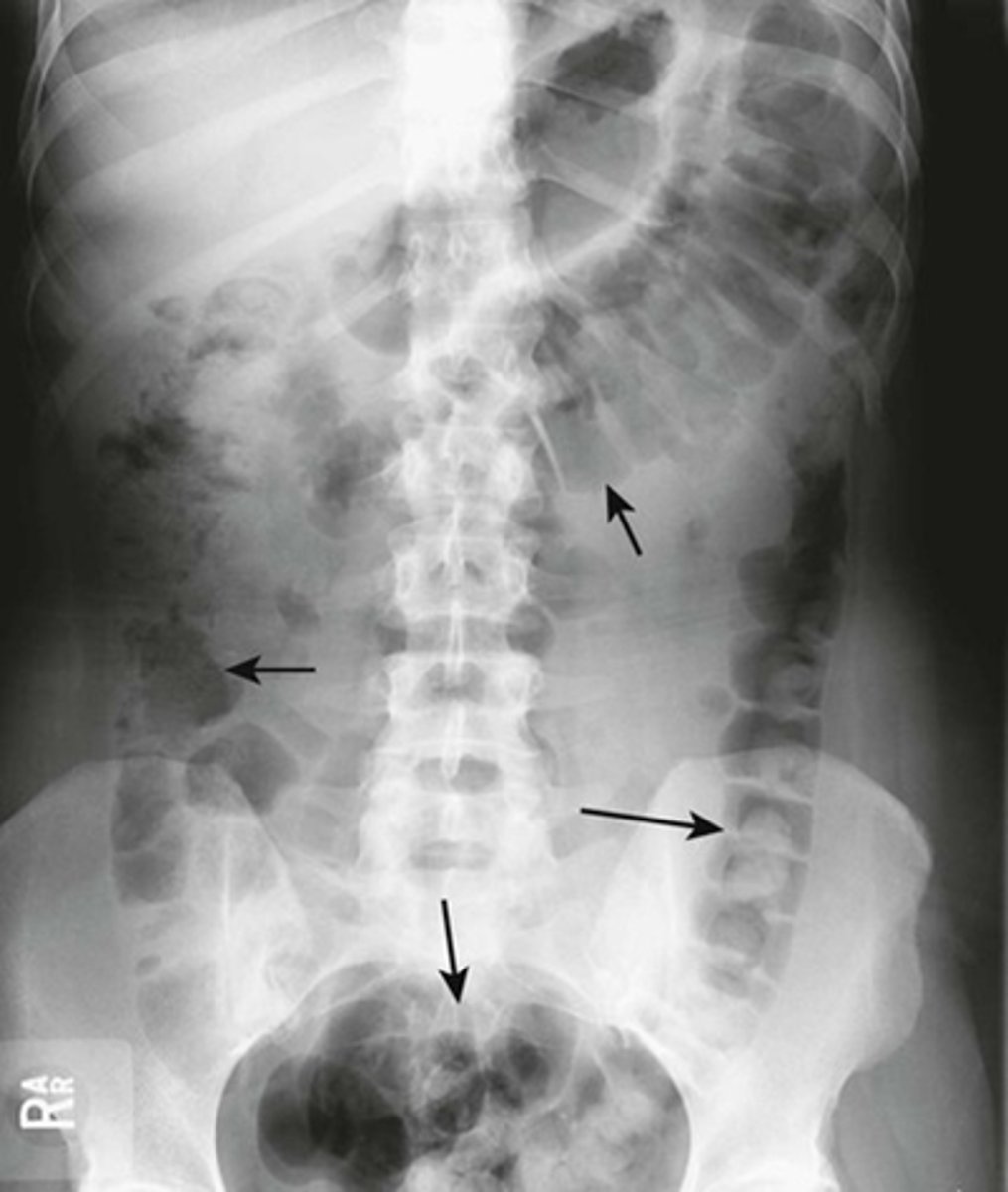
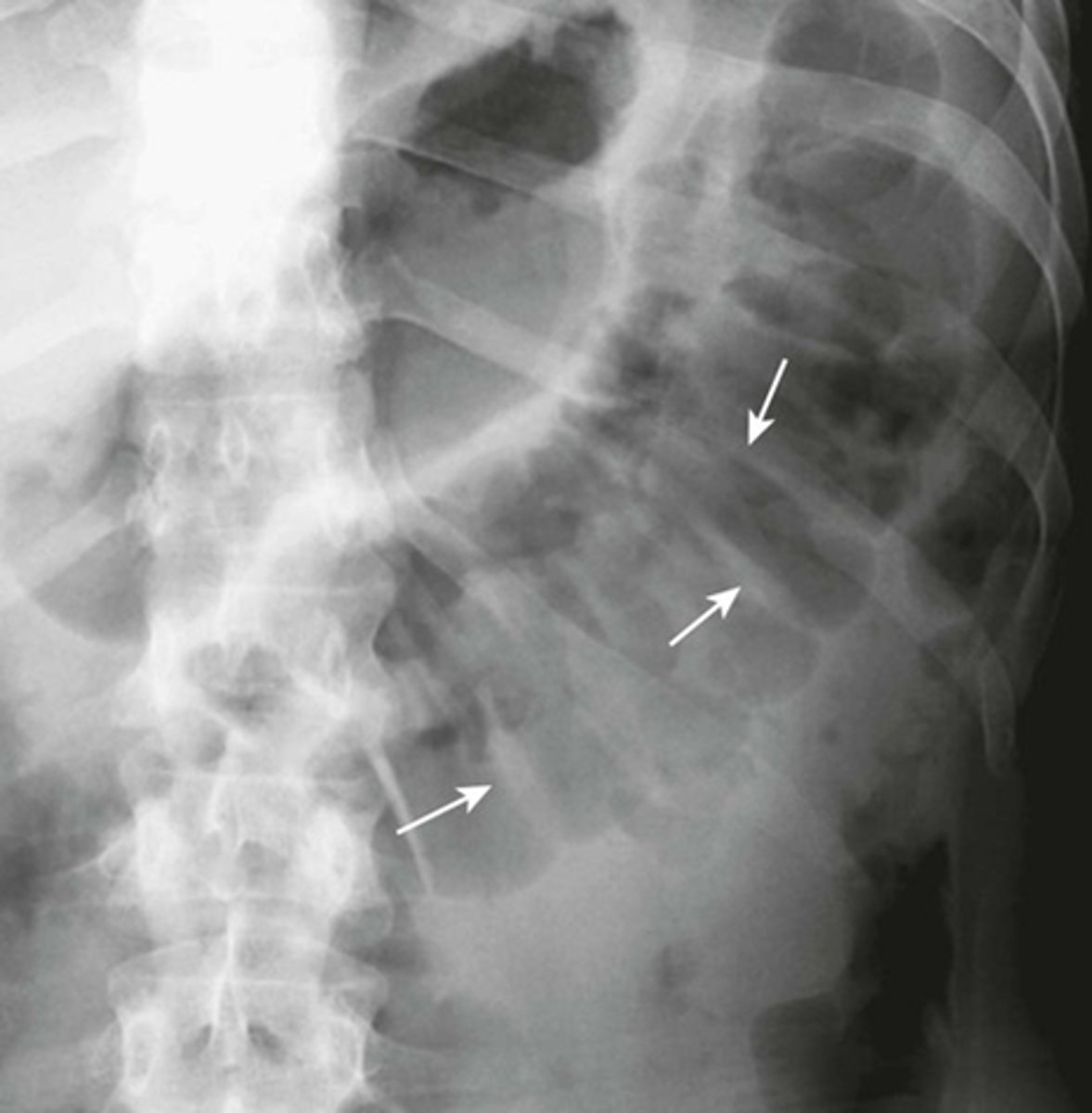
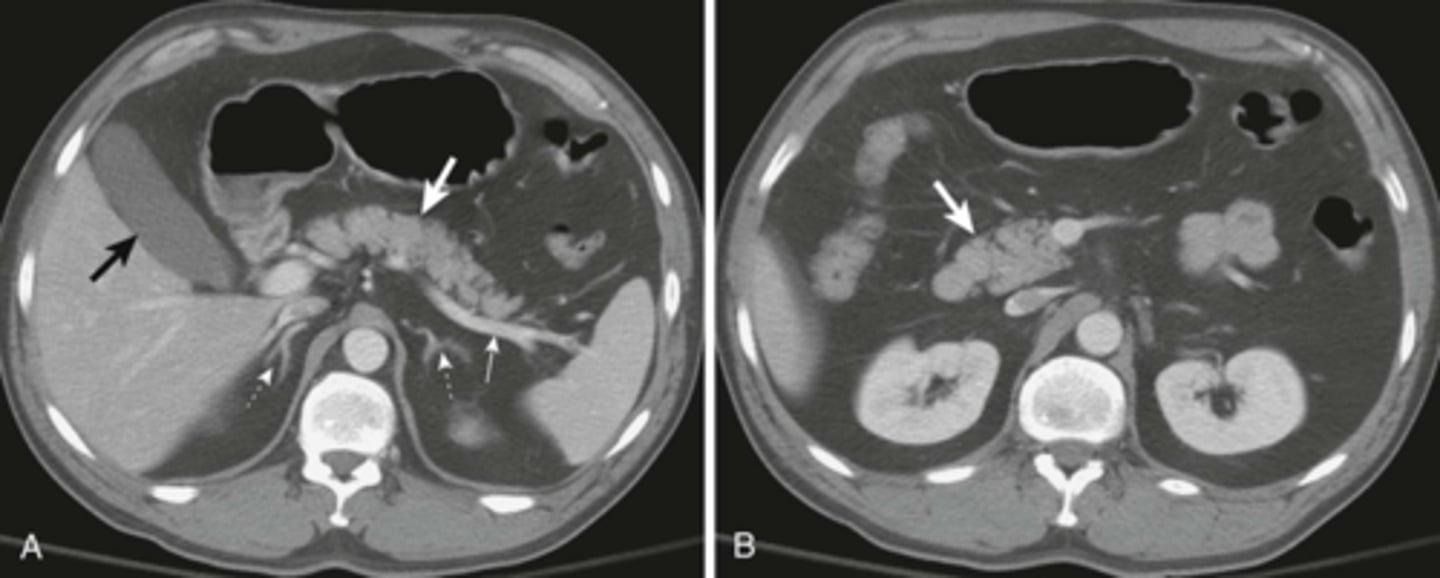
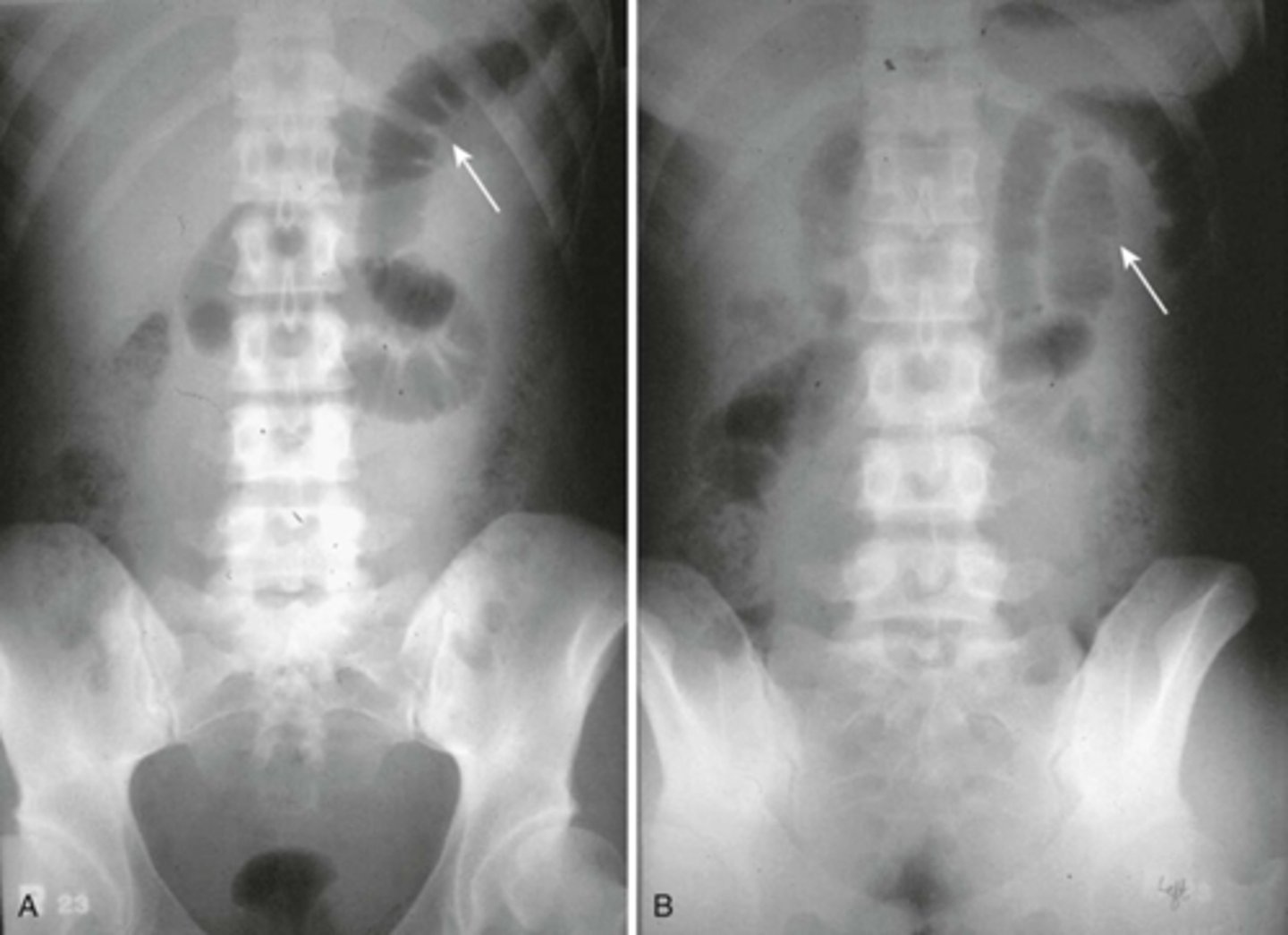
Localized ileus (sentinal loop) A: supine, B: prone
WHITE ARROWS: single, persistently dilated loop of Small Bowel in LUQ - representing a sentinel loop or localized ileus.
Often signifies the presence of an adjacent irritative or inflammatory process. This pt had acute pancreatitis
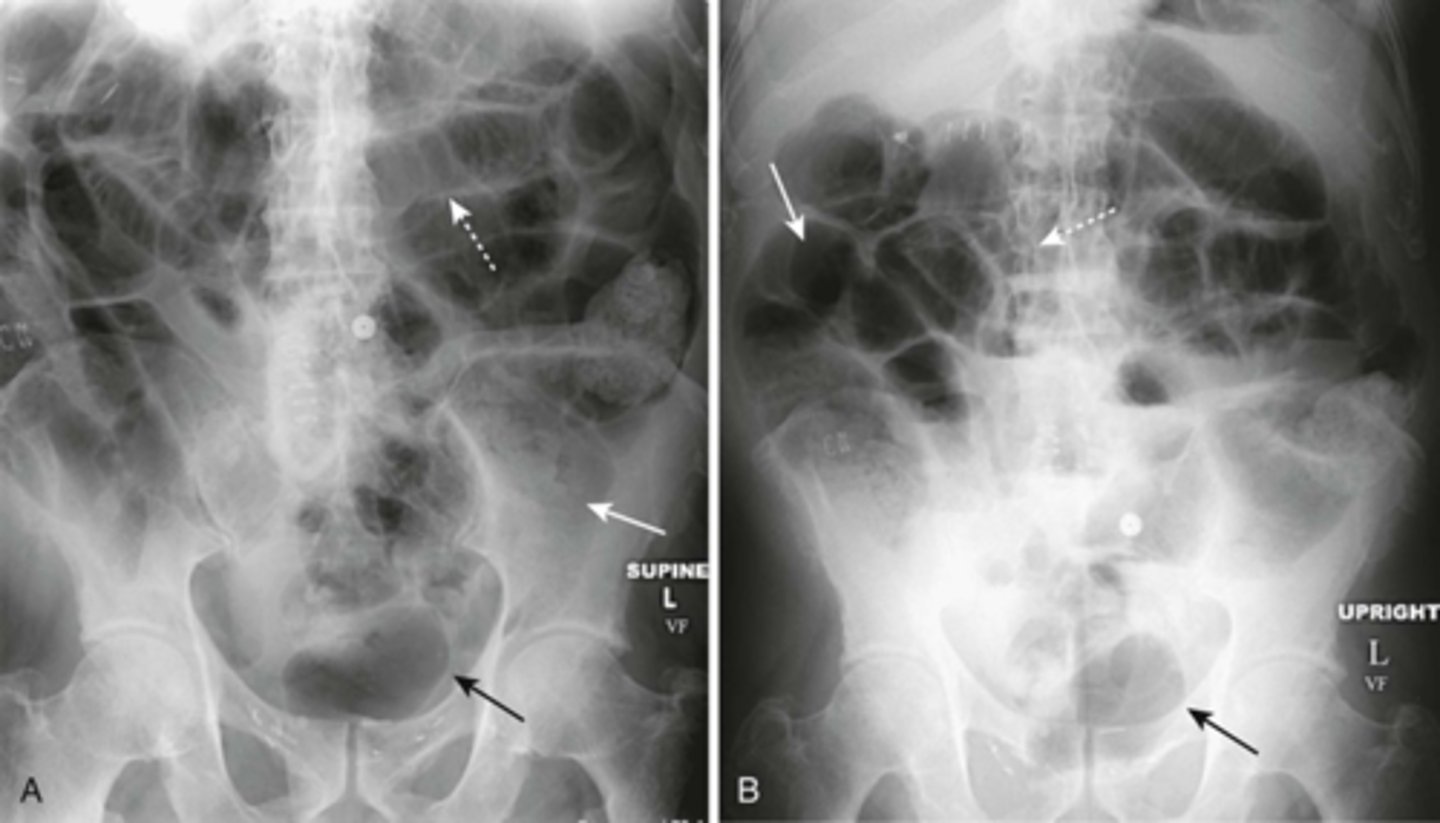
Generalized adynamic ileus, supine (A) and upright abdomen (B).
SOLID WHITE ARROWS: dilated loops of large bowel
DOTTED WHITE ARROWS: dilated loops of small bowel
SOLID BLACK ARROW: Rectum
Gas seen from small bowel to rectum. Patient had no bowel sound and had colon surgery the day before.
SBO - dilated loop of bowel proximal to point of obstruction, unequal air fluid levels in same loop
SBO - dilated loop of bowel proximal to point of obstruction, unequal air fluid levels in same loop
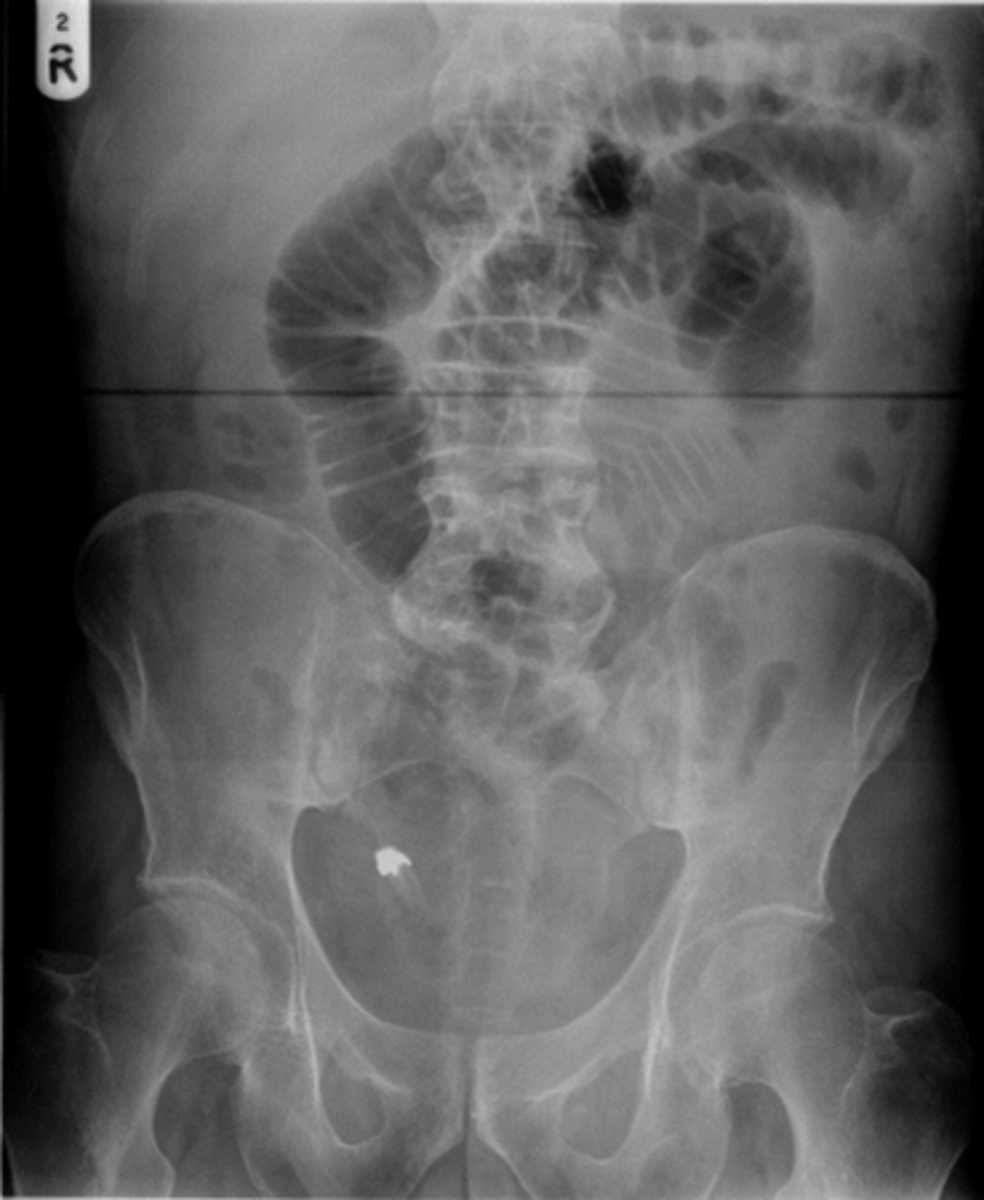
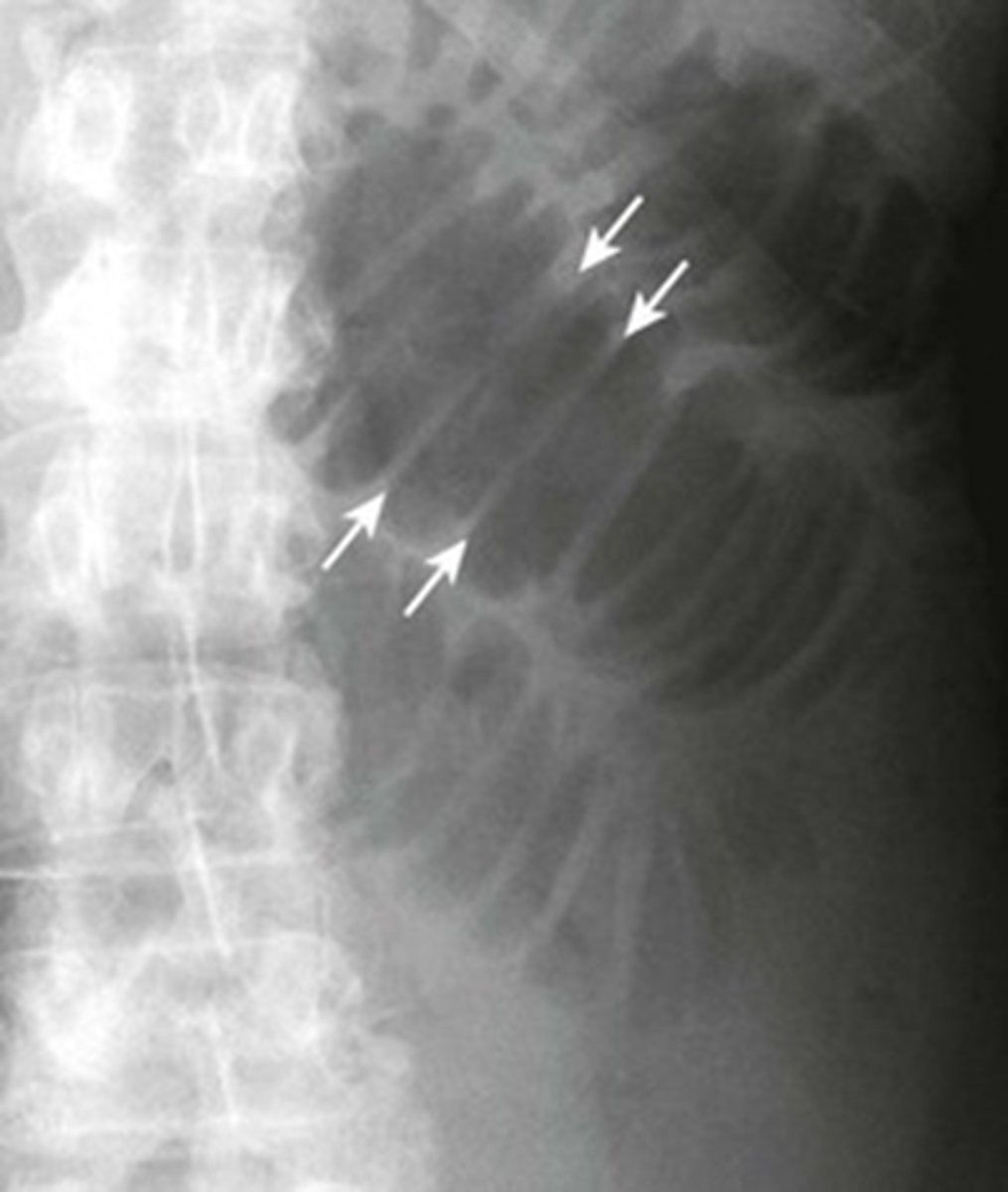
SBO - Step-ladder appearance of obstructed small bowel.
BLACK ARROWS: Dilation of small bowel loops --> stacking up, and form step-ladder appearance usually beginning in the LUQ and then to the RLQ.
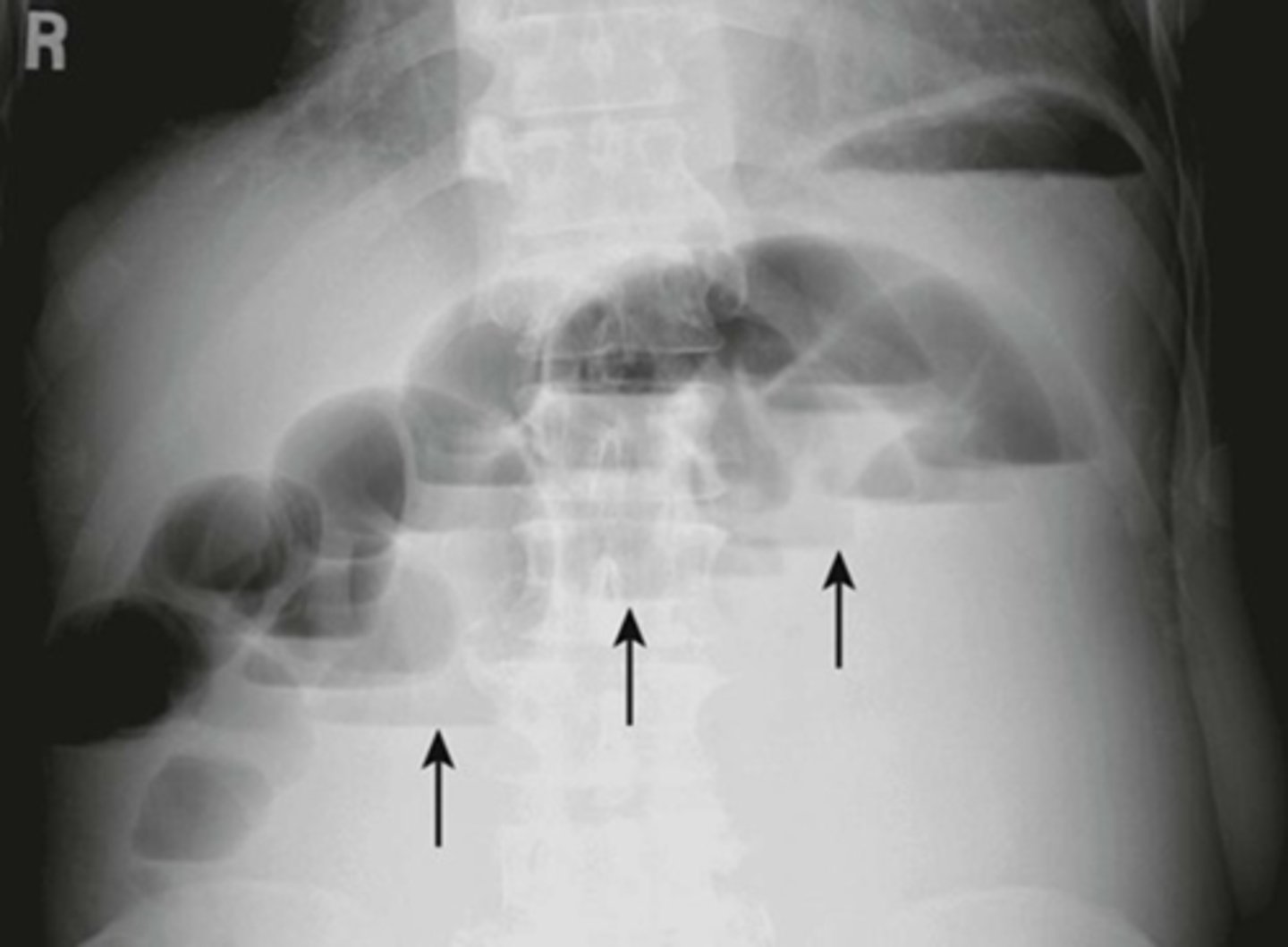
SBO
Mechanical SBO.
WHITE ARROW: small amount of air in the right colon, but overall gas pattern is disproportionate dilation of multiple loops of small bowels.
BLACK ARROWS: Small bowels.
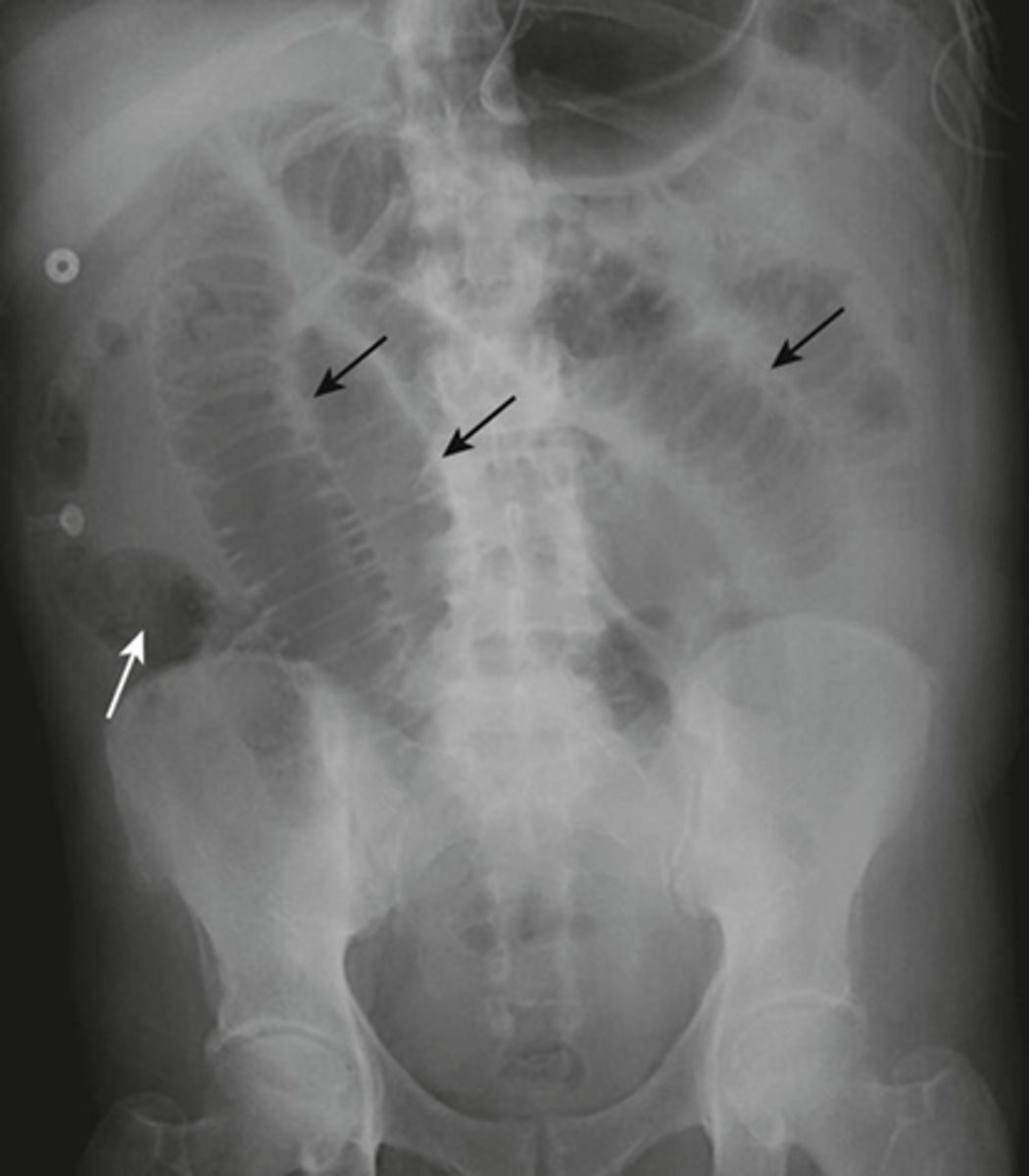
SBO
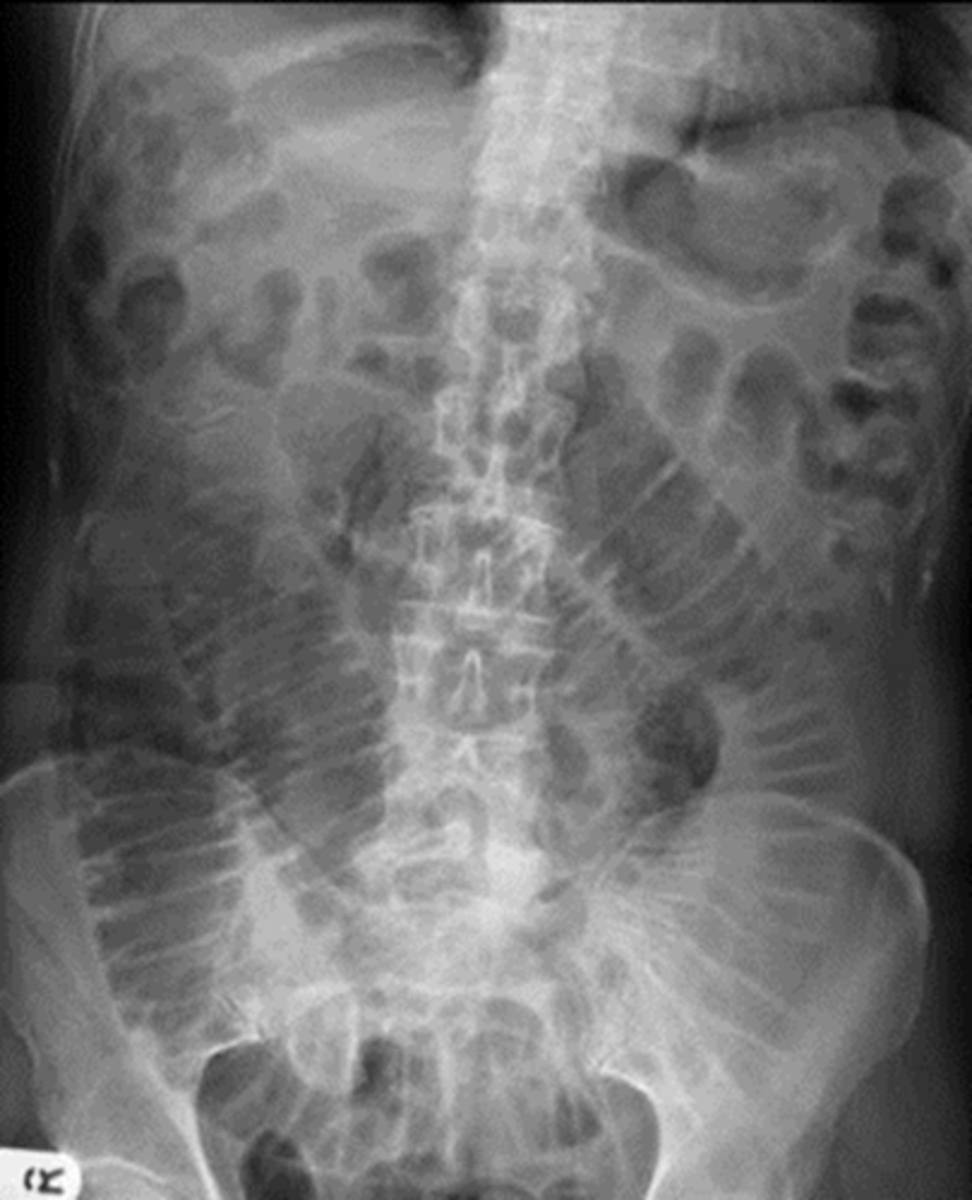
SBO
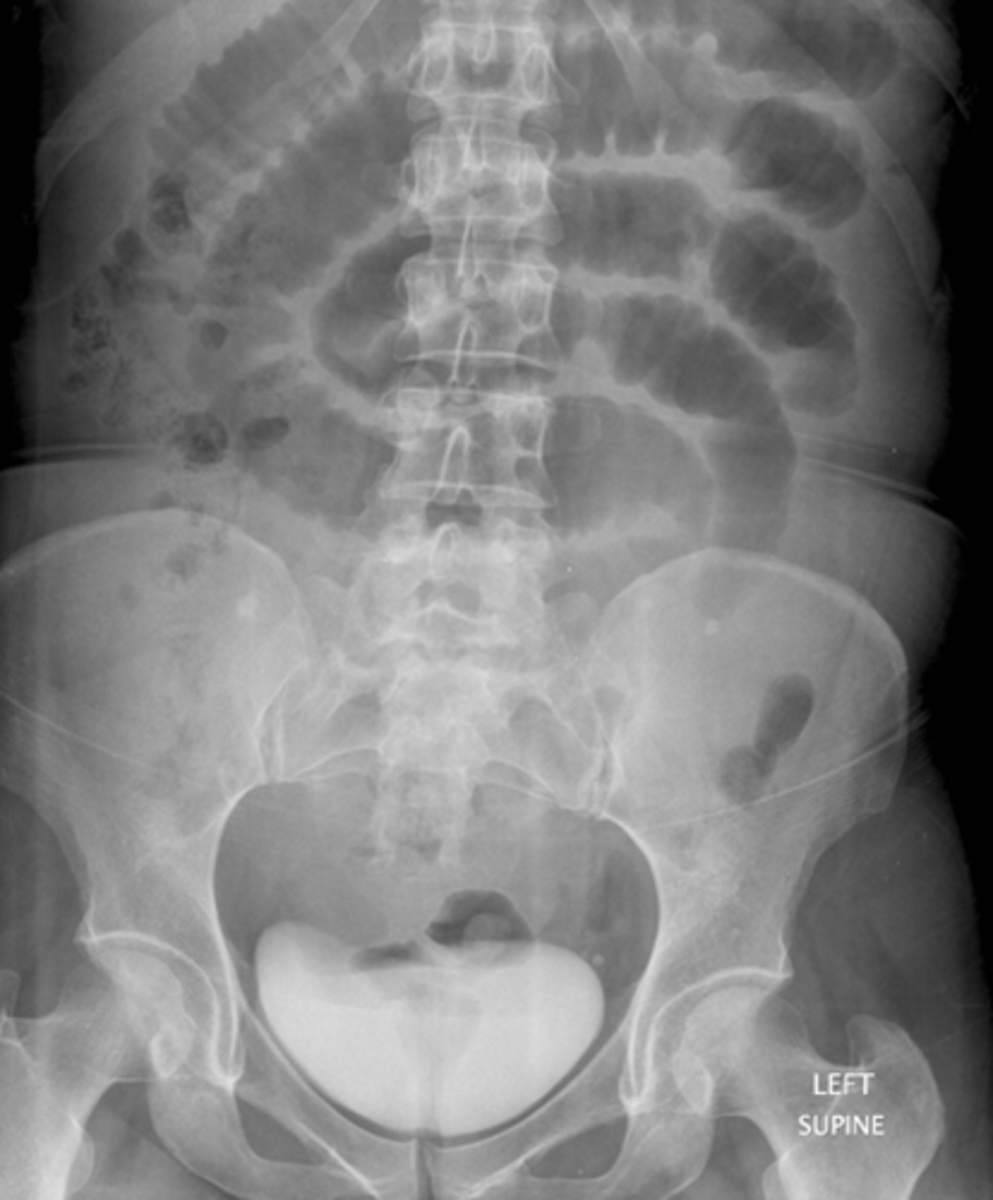
SBO from inguinal hernia.
A:
SOLID BLACK ARROW: dilated loops of small bowel, caused by left inguinal hernia
WHITE CIRCLE: left inguinal hernia.
Loops of bowel should not normally be in the scrotum.
B:
SOLID WHITE ARROWS: multiple fluid-filled and dilated loops of Small bowel, from inguinial hernia
WHITE CIRCLE: inguinal hernia
DOTTED WHITE ARROW: dilated loop of small bowel in inguinal hernia
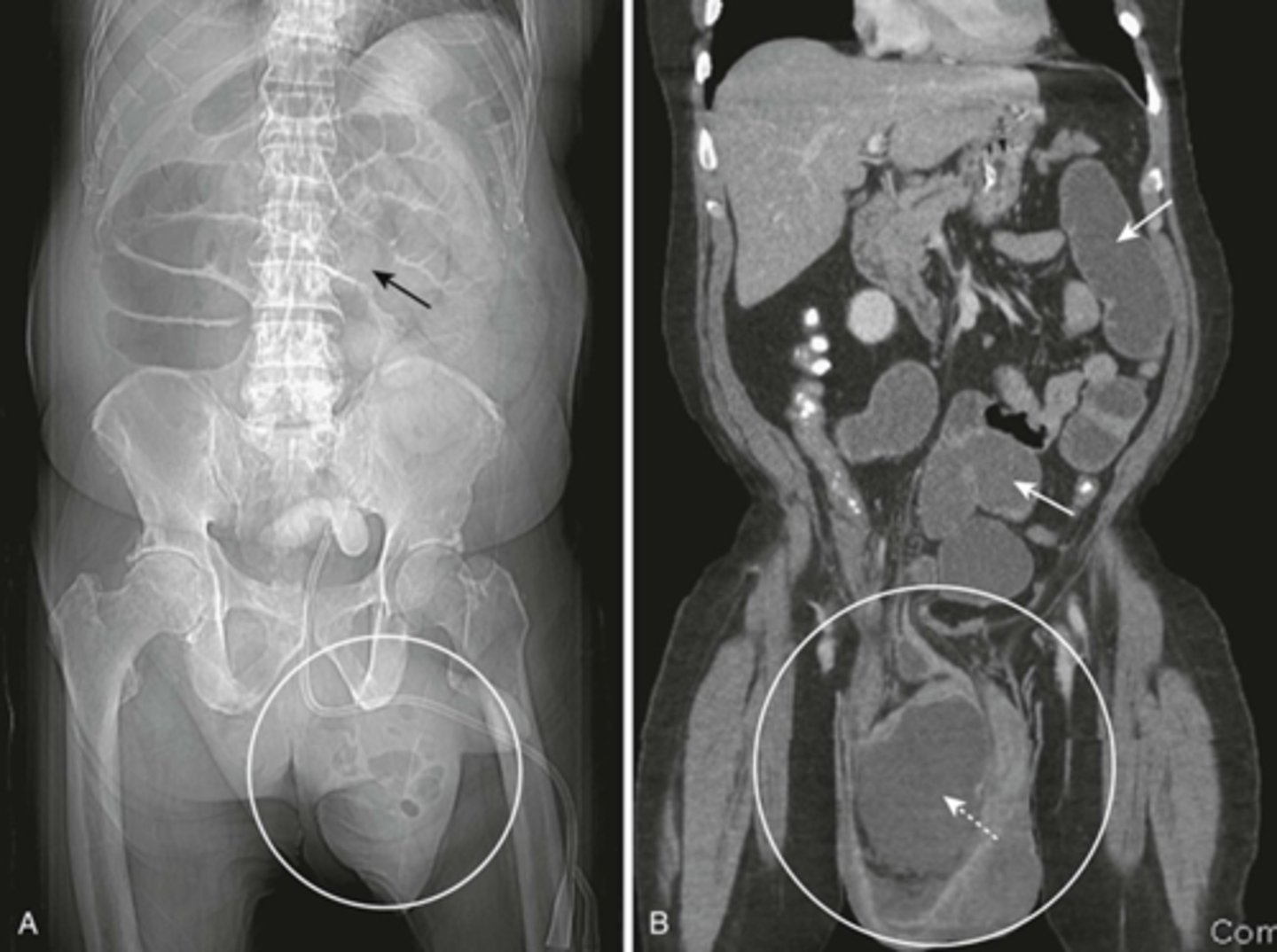
SBO caused by right inguinal hernia
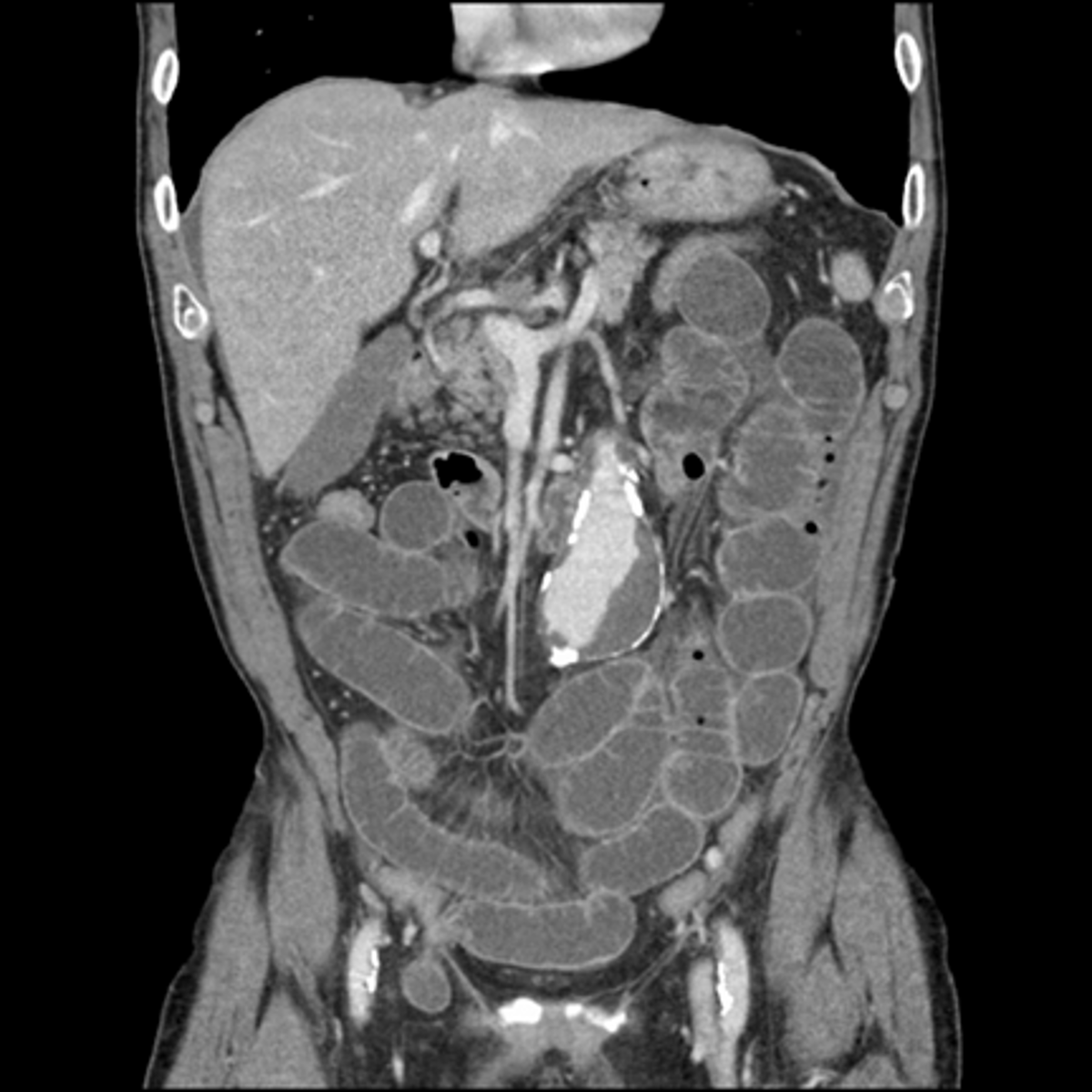
CT small bowel obstruction
, secondary to crohn's dz
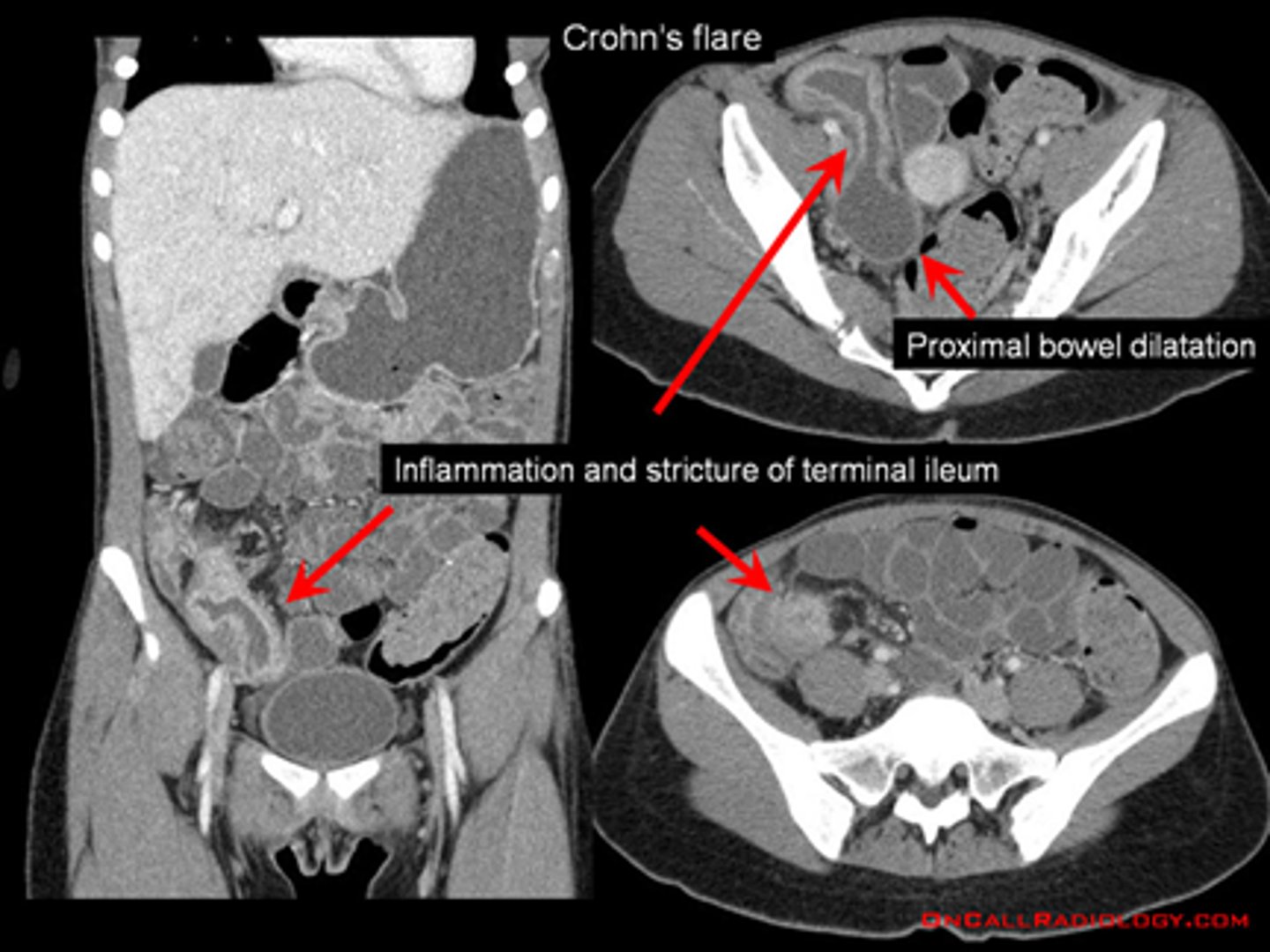
CT small bowel obstruction
Intussusception
CT small bowel obstruction
Abscess
CT small bowel obstruction
right adhesion / stricture

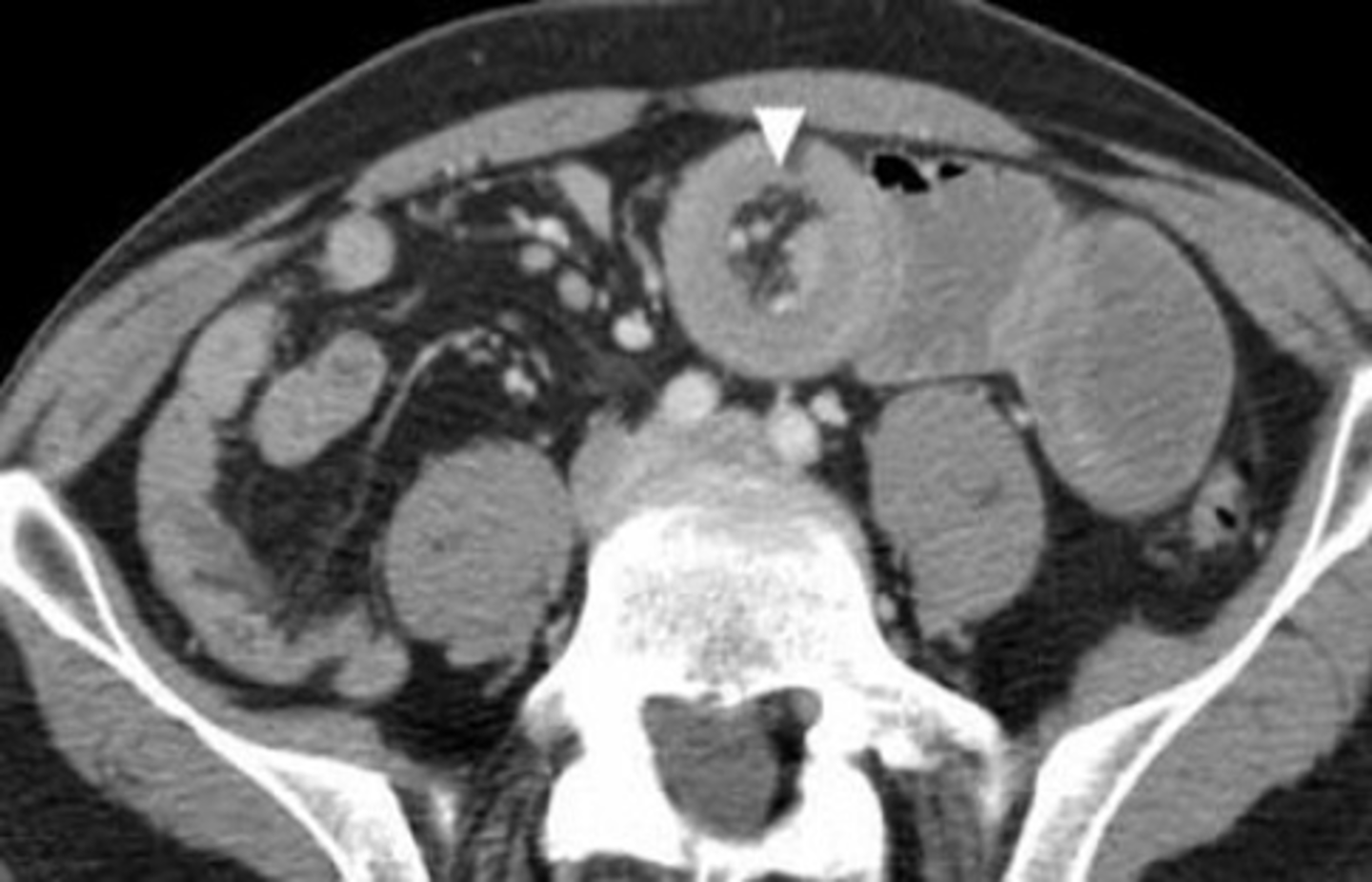
CT with IV contrast of SBO.
SOLID BLACK ARROWS: multiple fluid- and contrast filled dilated loops of small bowels.
WHITE ARROWS: Collapsed colon
DOTTED BLACK ARROW: Right renal cyst
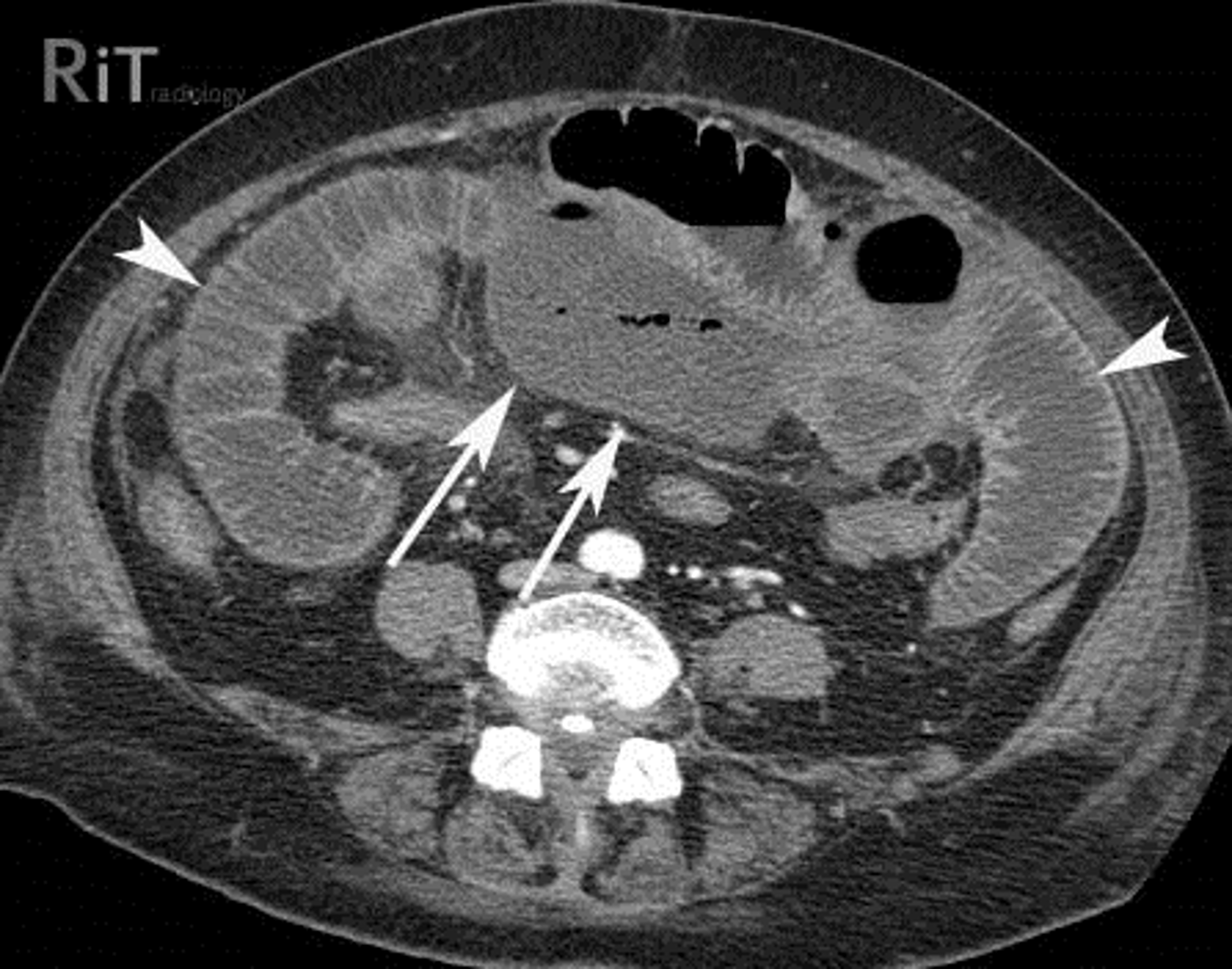
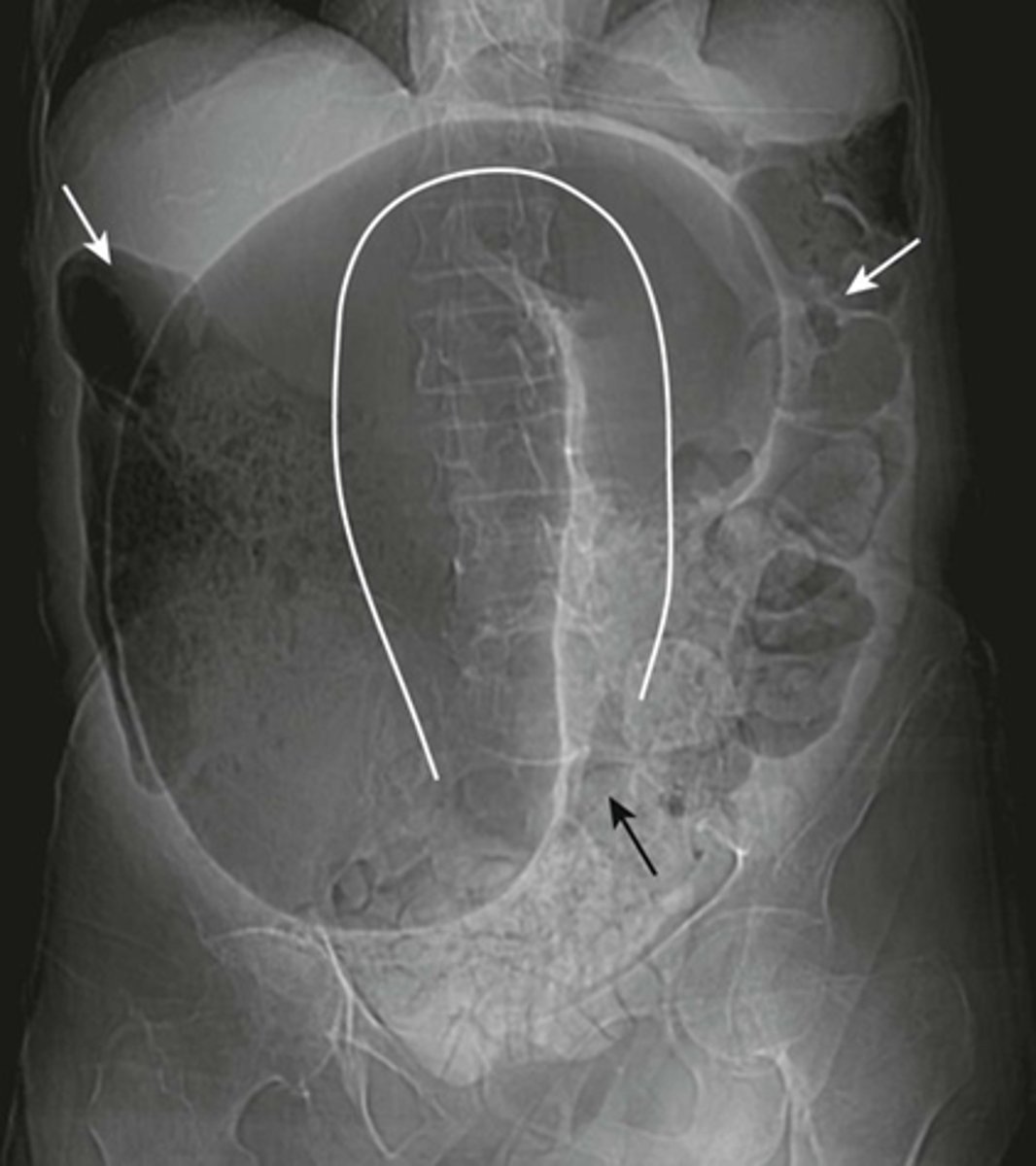
Partial SBO
SOLID BLACK ARROW (gas passing into colon)
DOTTED WHITE ARROW: small bowel is disproportionately dilated
SOLID WHITE ARROWS: Clips from prior surgery
A partial or incomplete mechanical SBO - allows some gas to pass the point of obstruction. Can be confusing as gas may pass into the colon and be visible long after the large bowel would be expected to be devoid of gas.
The important observation is that the small bowel is DISPROPORTIONATELY DILATED compared with the large bowel, a finding suggestive of SBO.
Partial or incomplete small bowel obstructions occur more often in patients in whom adhesions are the etiologic factors. Notice the clips (solid white arrows) attesting to prior surgery.
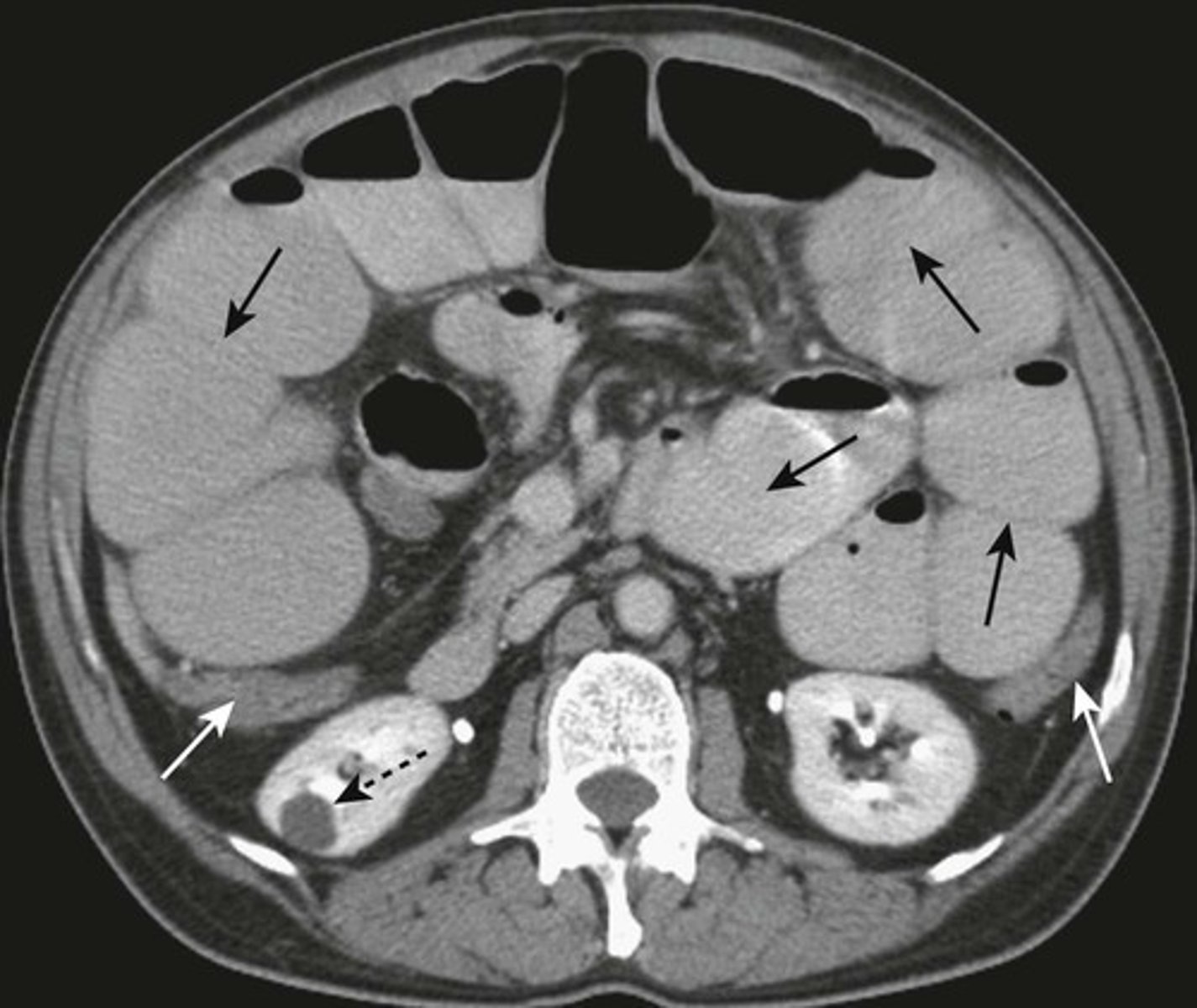
Partial SBO.
SOLID WHITE ARROWS: dilated and contrast containing loop of small bowel
DOTTED WHITE ARROWS: air in collapsed colon
Coronal-reformatted CT with oral contrast shows dilated and contrast-containing loops of small bowel. Although there is still air in the collapsed colon, the disproportionate dilatation of small bowel identifies this as a small bowel obstruction.
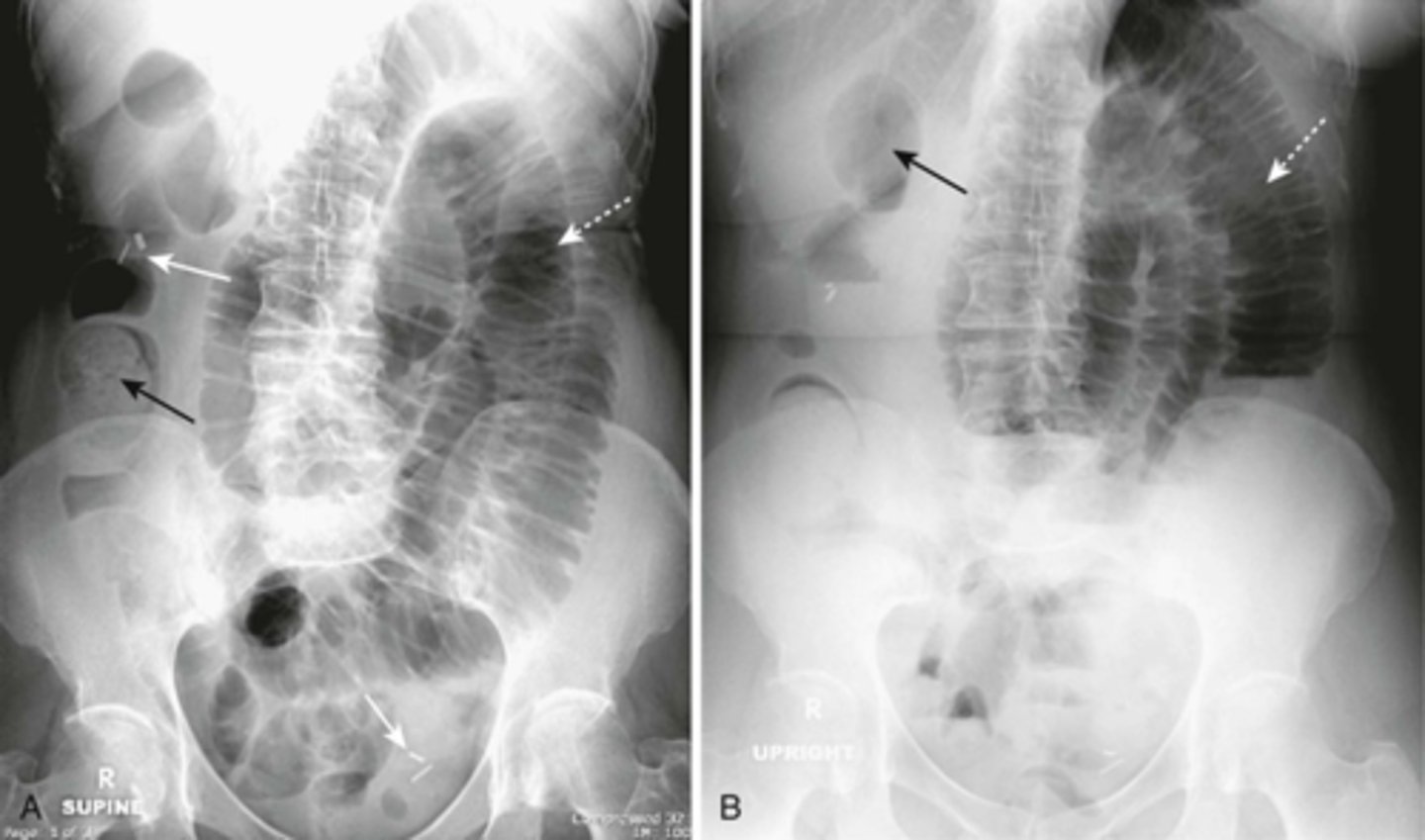
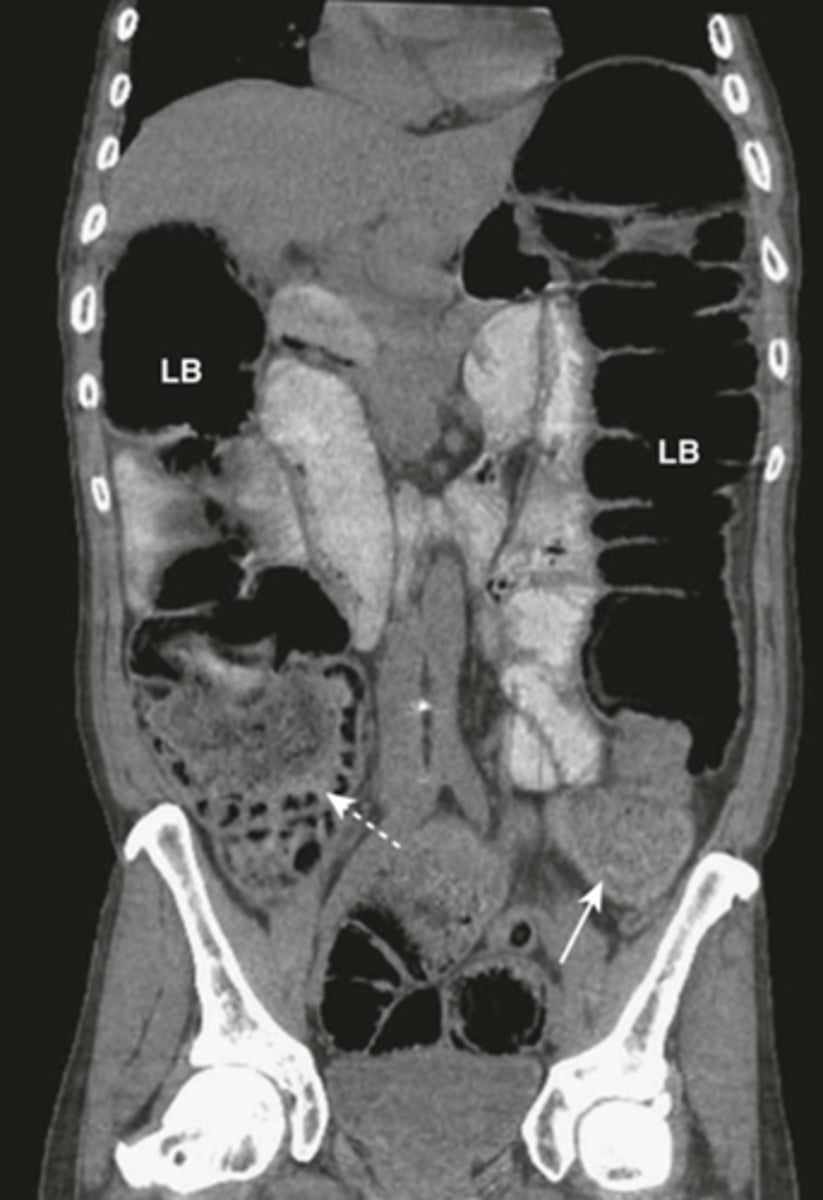
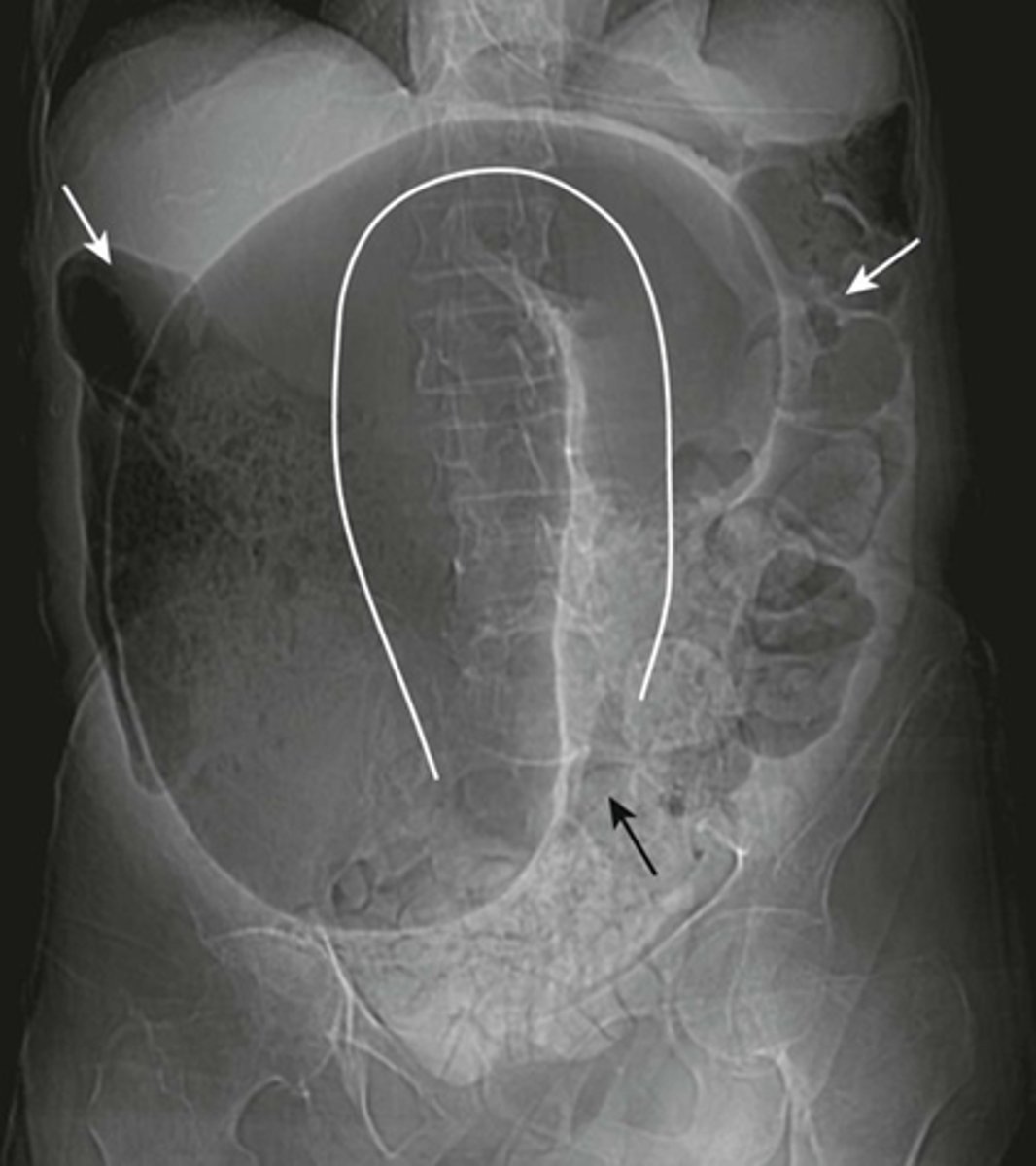
Mechanical LBO.
DOTTED WHITE ARROW:
entire colon that is dilated to a cut off point in the distal descending colon.
SOLID WHITE ARROW:
distal descending colon.
SOLID BLACK ARROW:
dilated ileum.
some gas passed backward through an incompetent ileocecal valve and outlines the ileum.
Note: large bowel is disproportionately dilated in comparison with the small bowel.
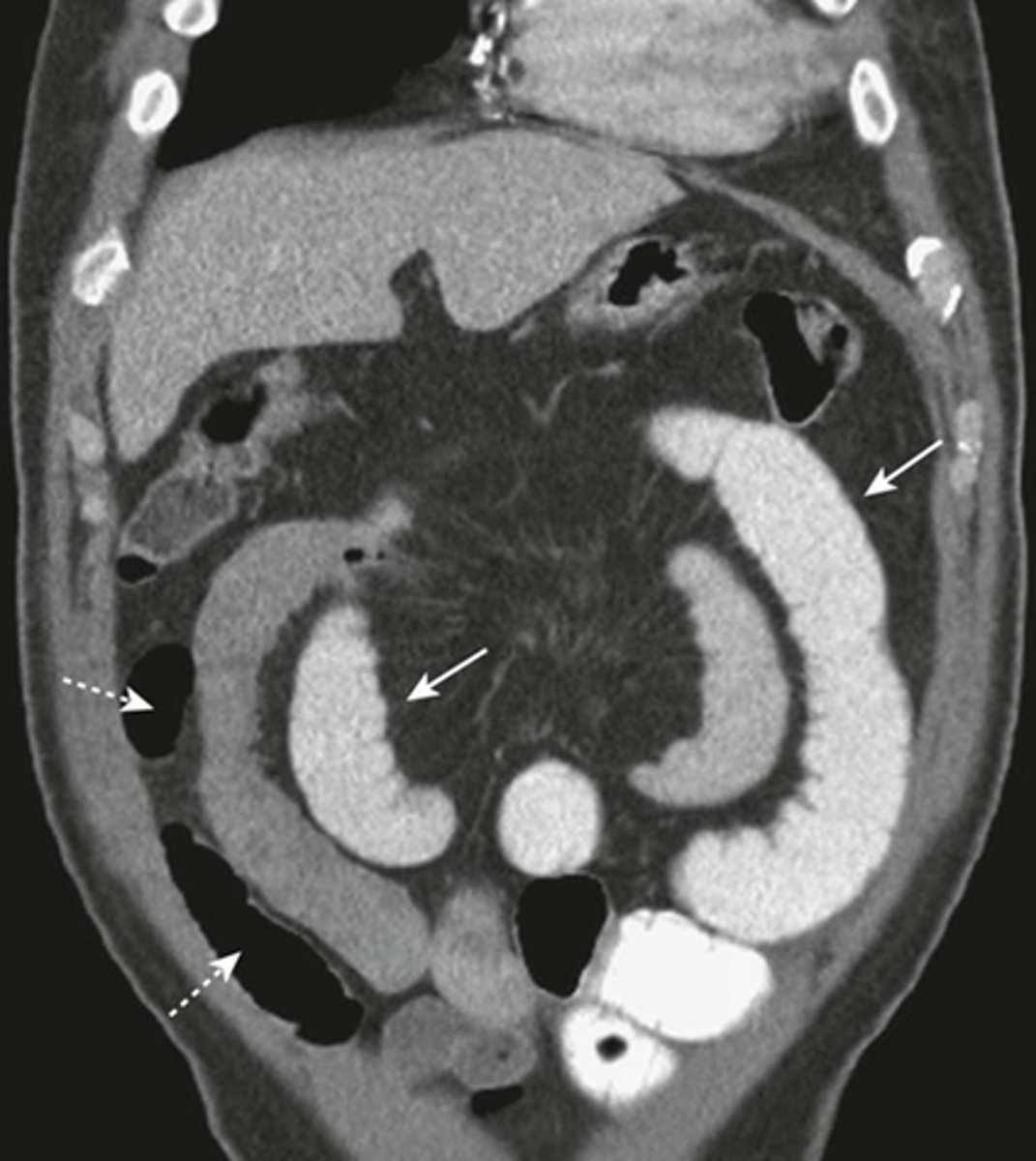
LBO (from carcinoma of colon)
DOTTED WHITE ARROW: dilated cecum containing stool
SOLID WHITE ARROW - where soft tissue mass was identified.
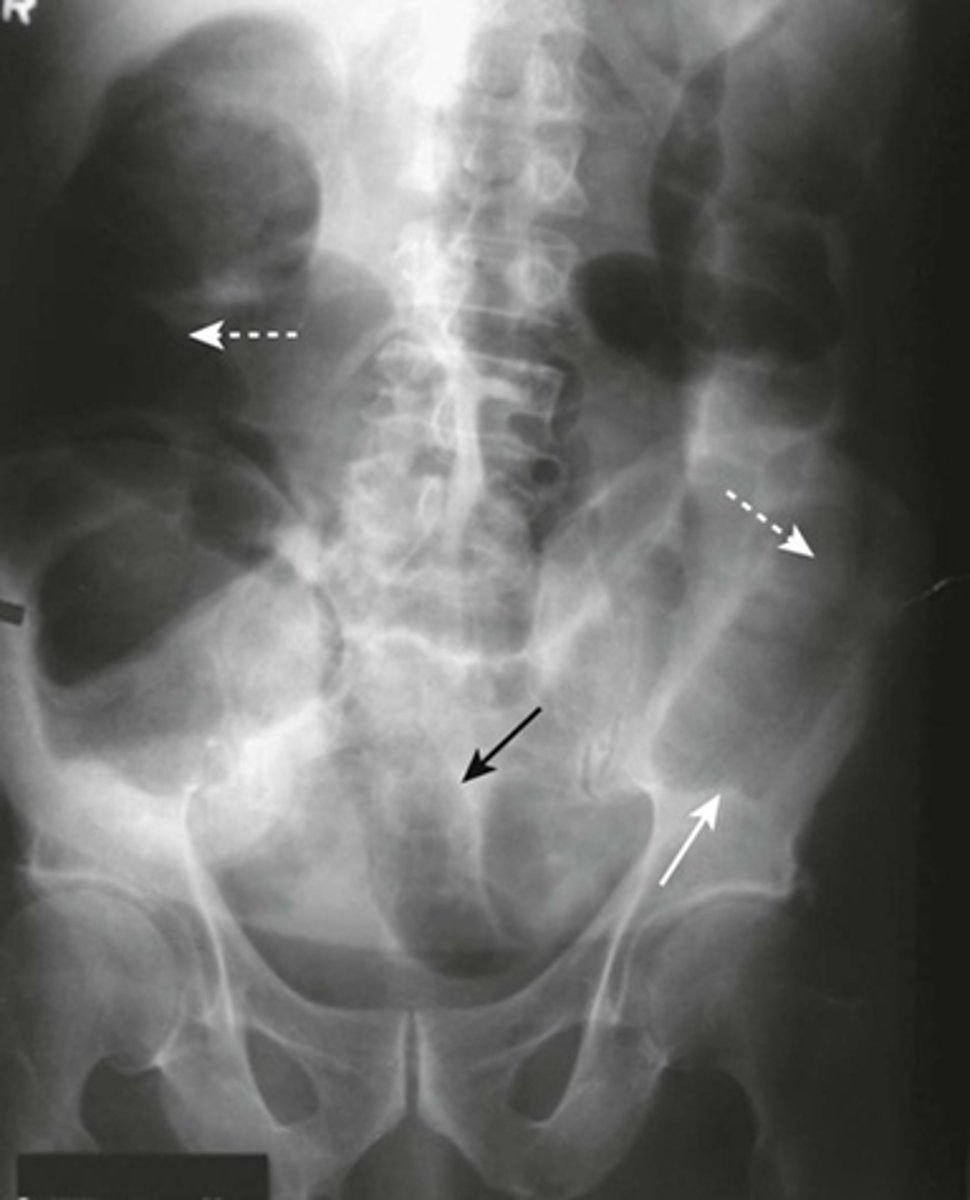
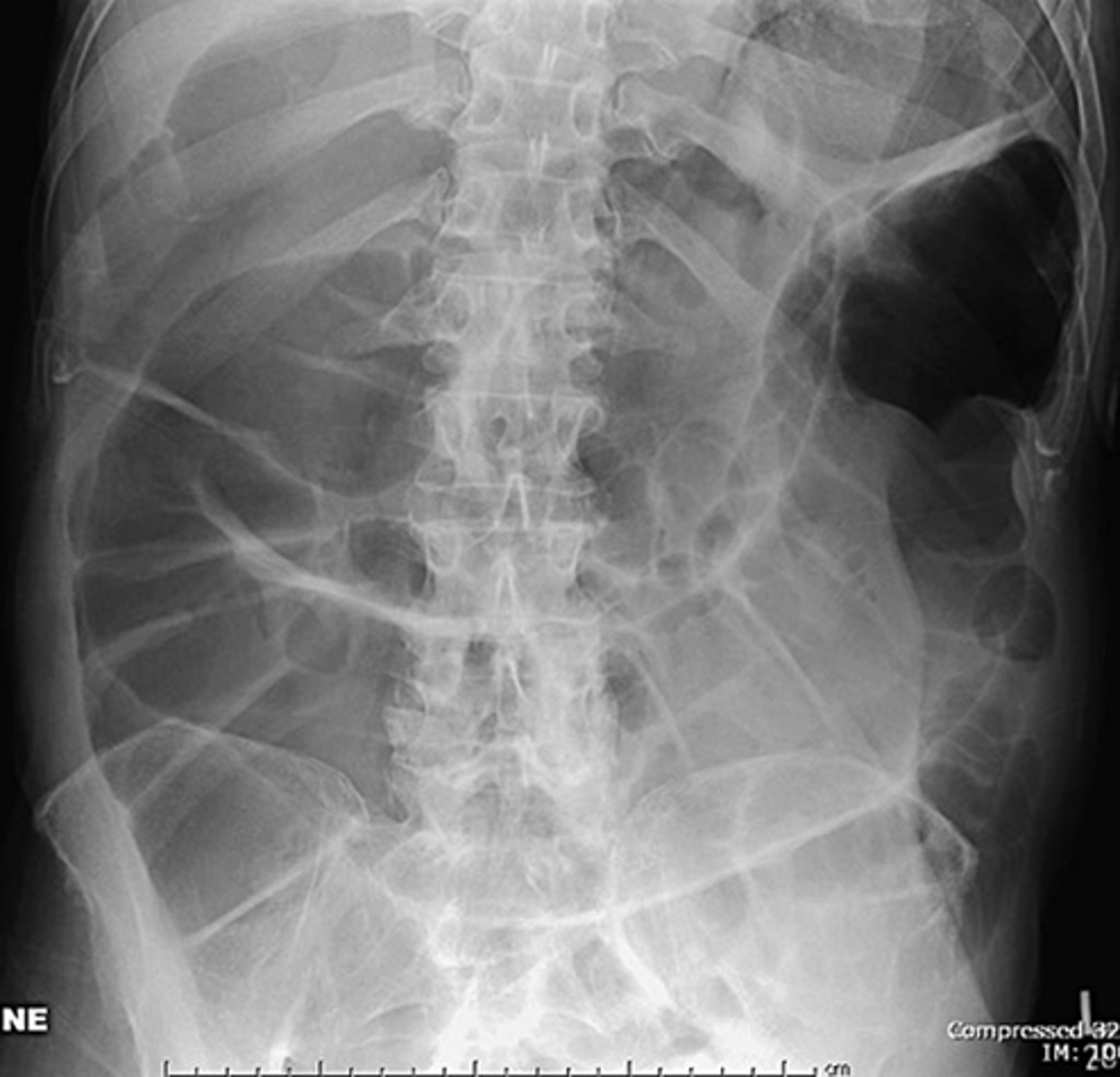
Sigmoid volvulus (coffee bean sign)
Sigmoid volvulus (coffee bean sign)

Sigmoid volvulus (coffee bean sign)
Condition in which the cecum or sigmoid can twist upon itself. Considered a LBO
What is volvulus?
Volvulus
SOLID WHITE LINE:
massively dilated sigmoid colon, twisted upon itself in the pelvis
BLACK ARROW:
pelvis
WHITE ARROW:
more proximal portion of the colon filled with air and stool.
Ogilvie syndrome
- loss of peristalsis, resulting in sometimes massive dilatation of the entire colon, resembling a large bowel obstruction, as in this patient.
Ogilvie syndrome (acute intestinal pseudoobstruction) may occur in older adults who are usually already hospitalized or on chronic bed rest. Drugs with anticholinergic effects may cause or exacerbate the condition.
1. Intraperitoneal (free air) = most common
2. Retroperitoneal air
3. Air in the bowel wall (pneumatosis)
4. Air in the biliary system (pneumobilia)
4 most common locations of extraluminal gas
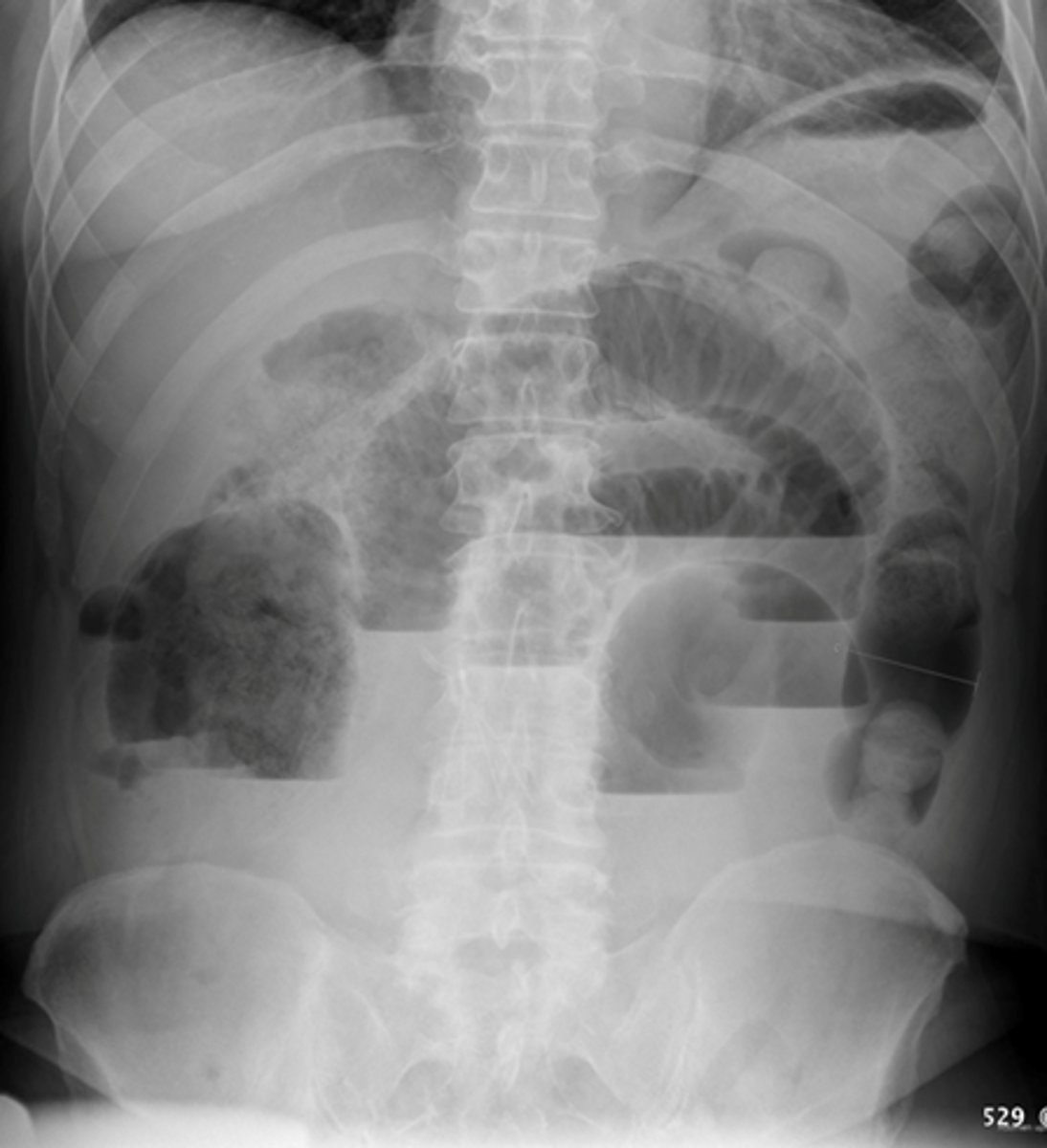
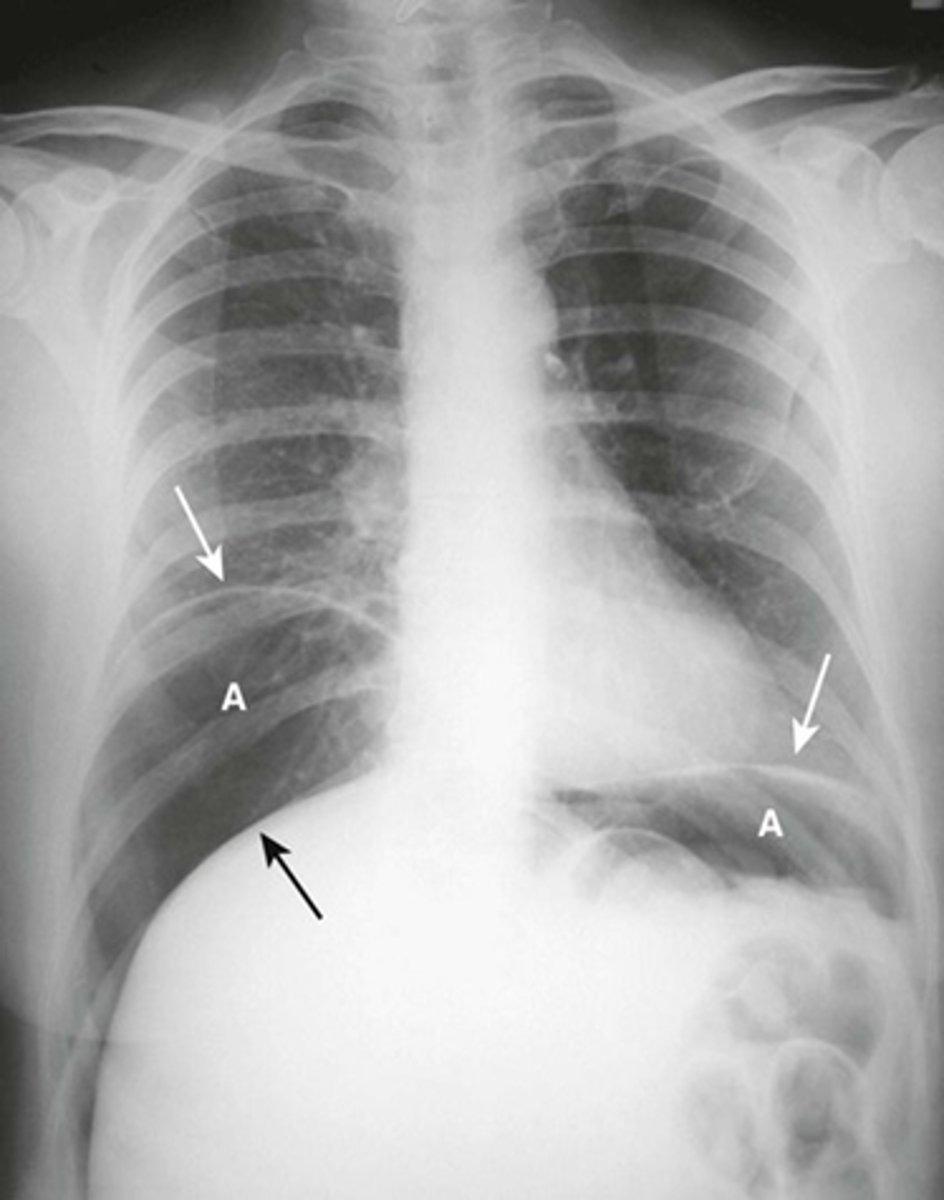
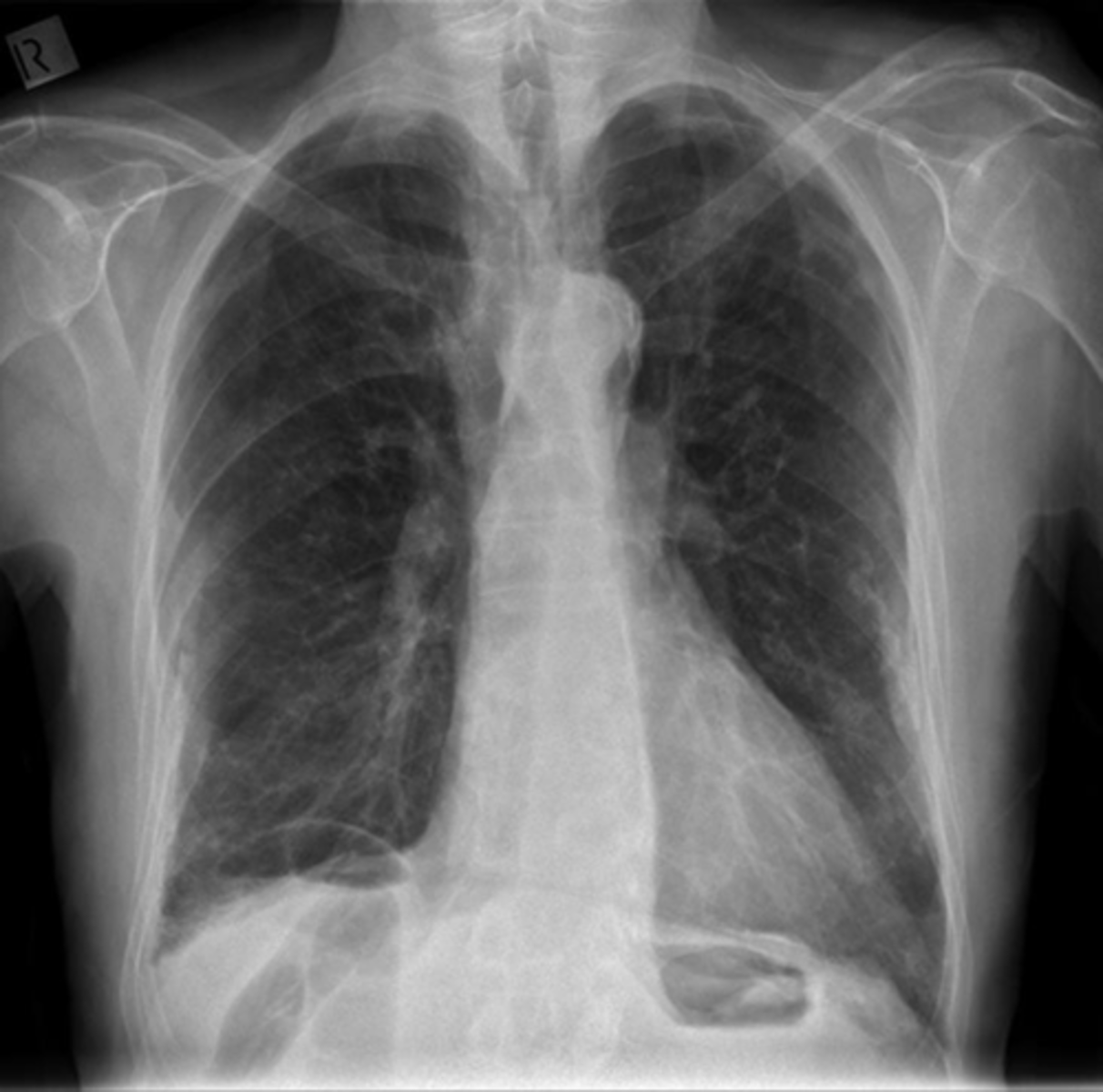
Free air beneath diaphragm
Free intraperitoneal air beneath hemidiaphragm
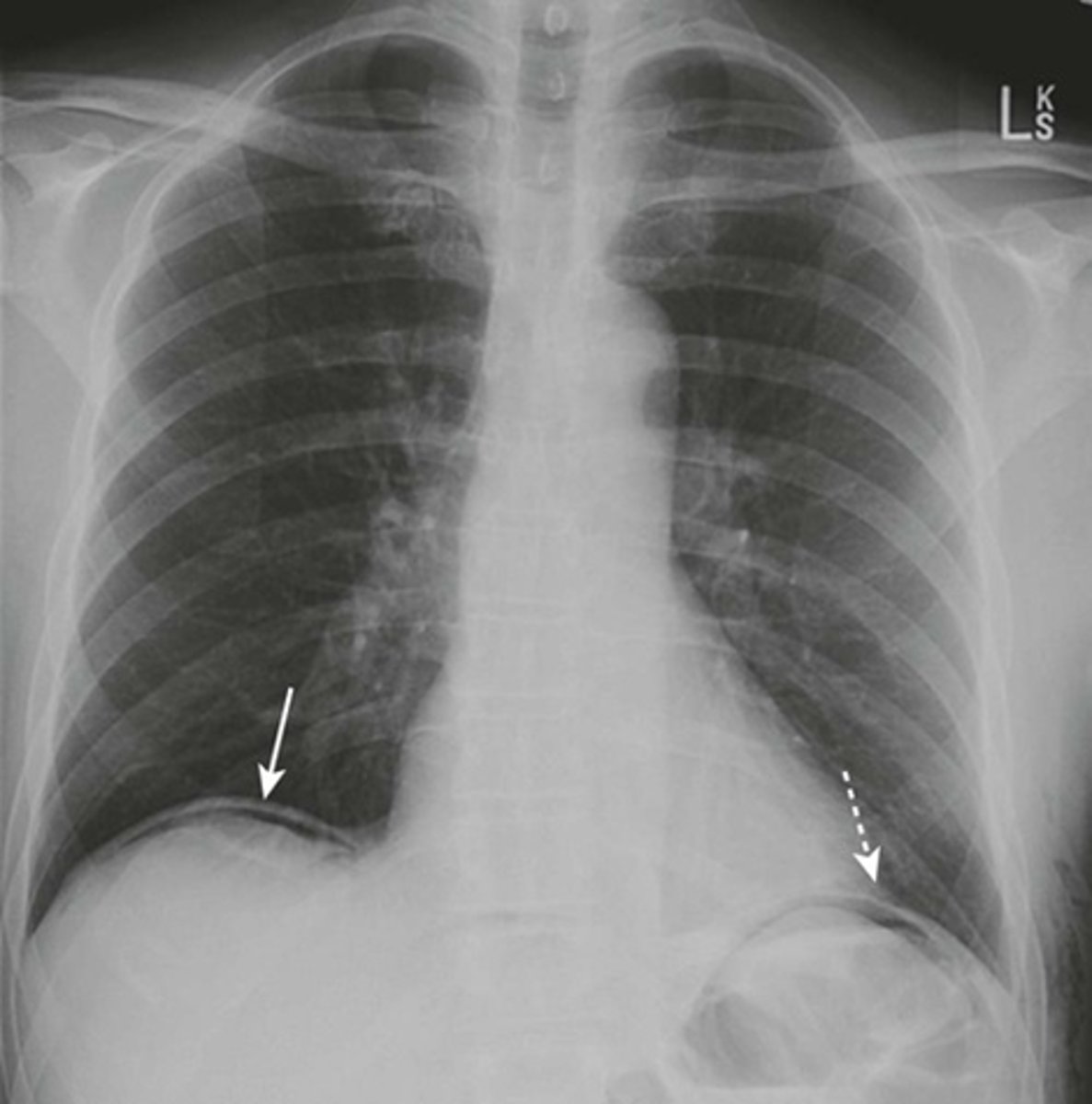
Large amount of free air
A: air
WHITE ARROW:
Hemidiaphragm
BLACK ARROW: Top of the liver made visible by air above it.
Pt has perforated gastric ulcer
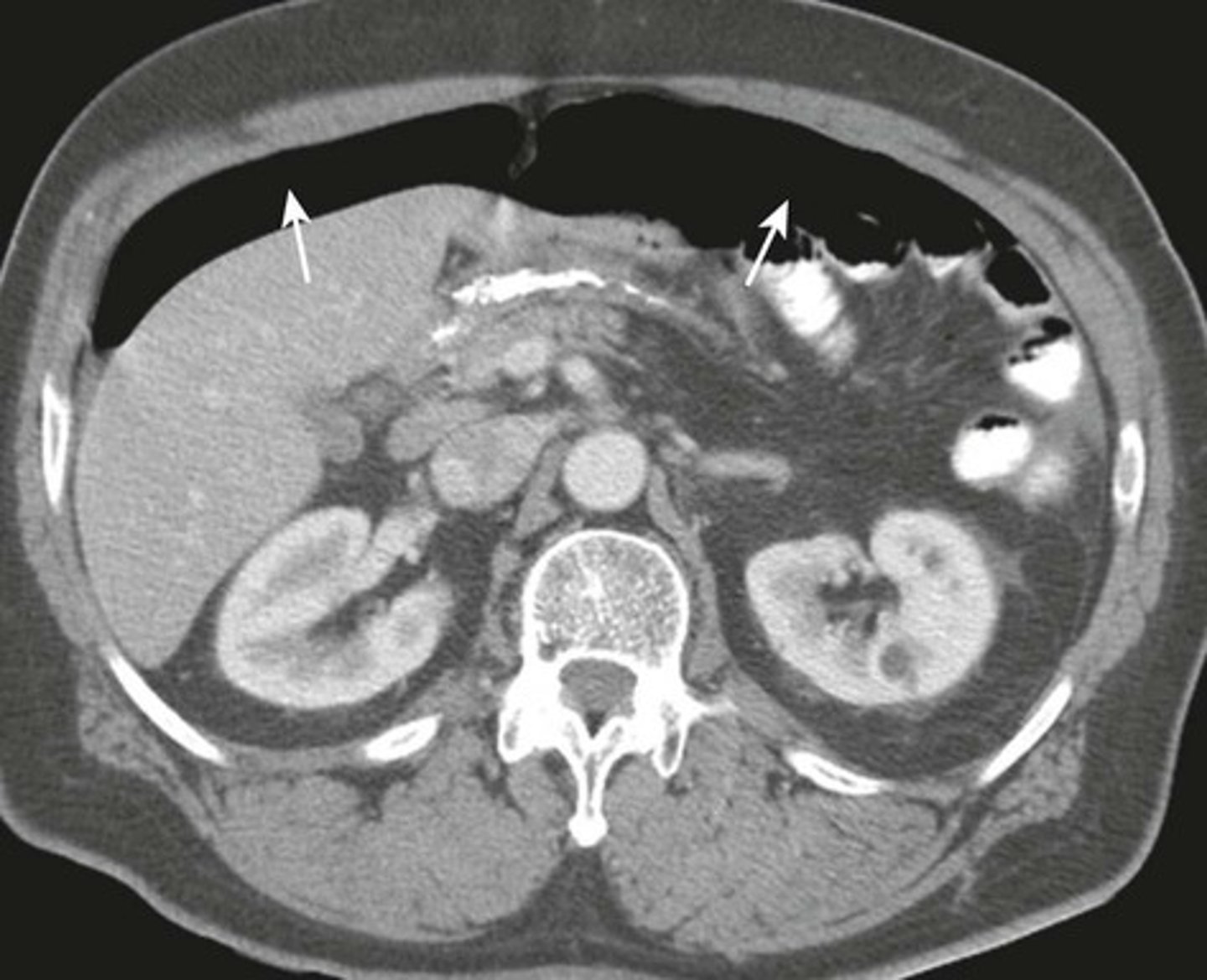
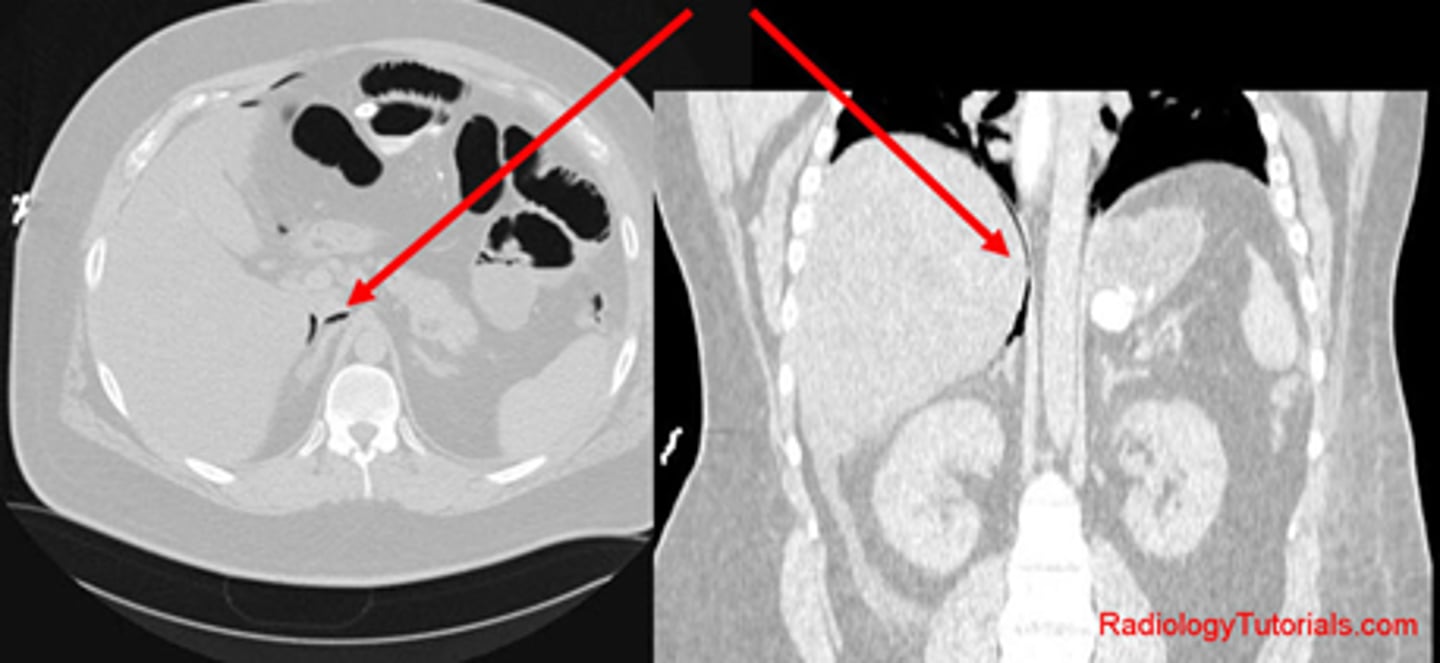
Free air seen on CT of upper abdomen.
WHITE ARROW:
Free air
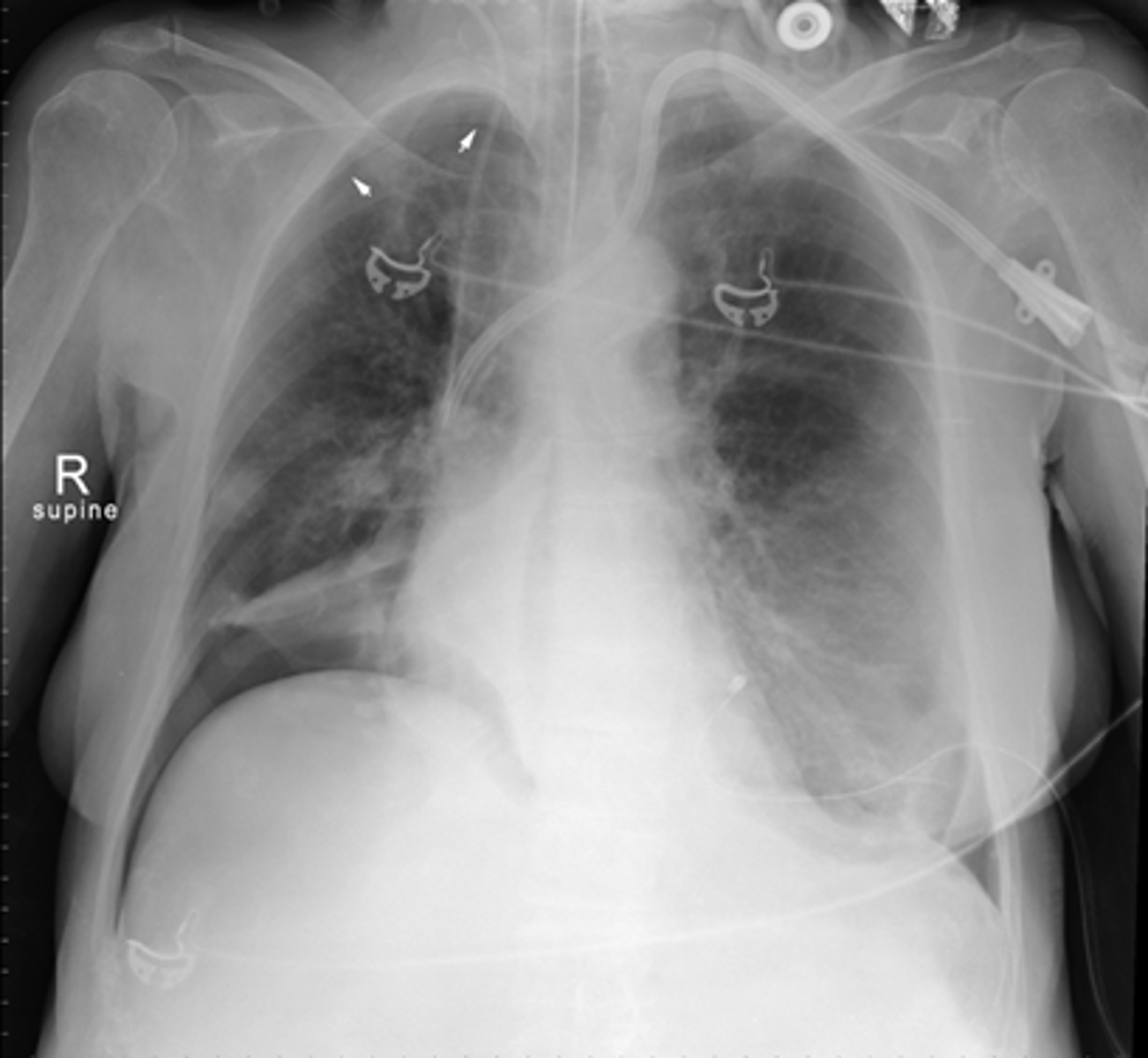
Free air

Free air
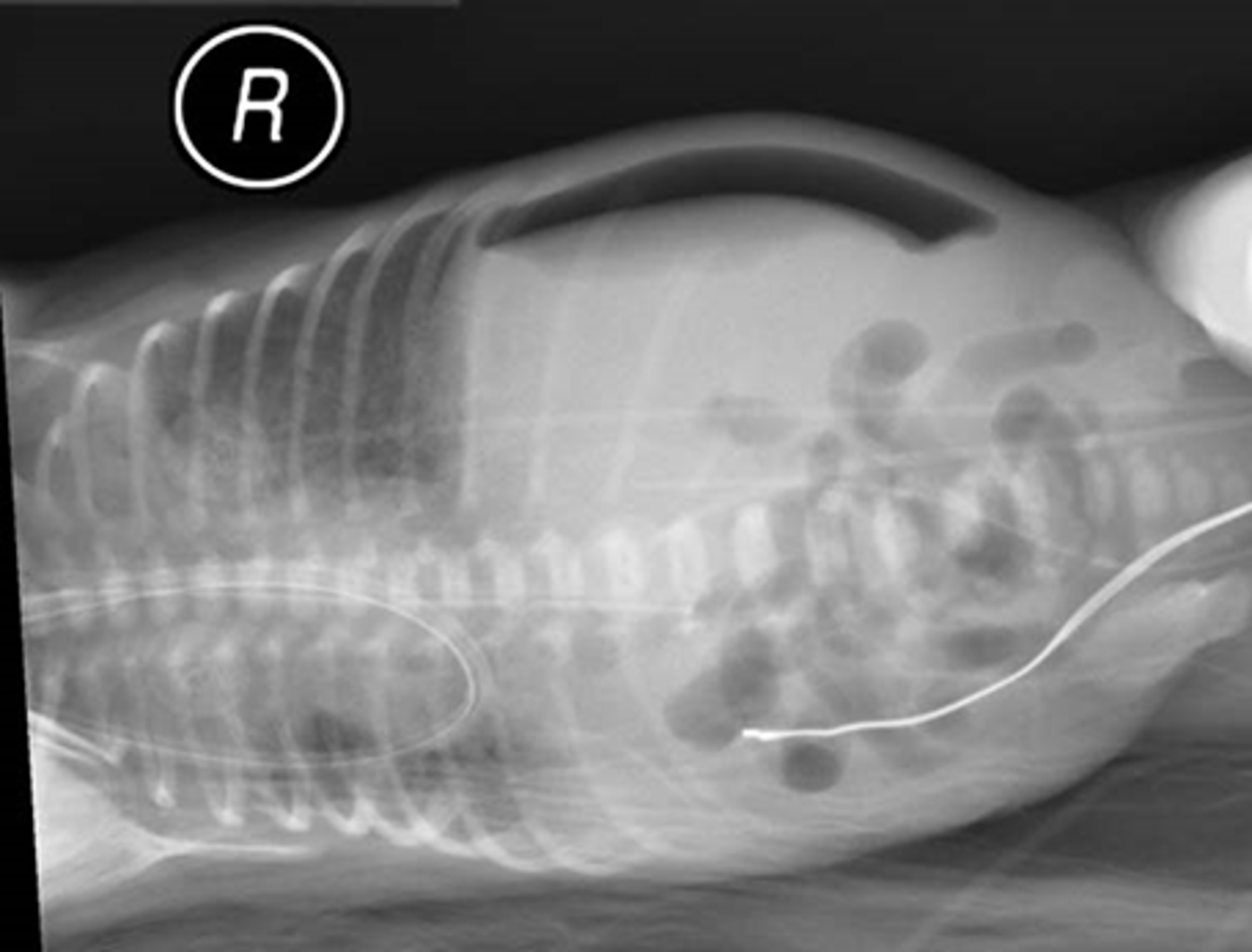
Free air
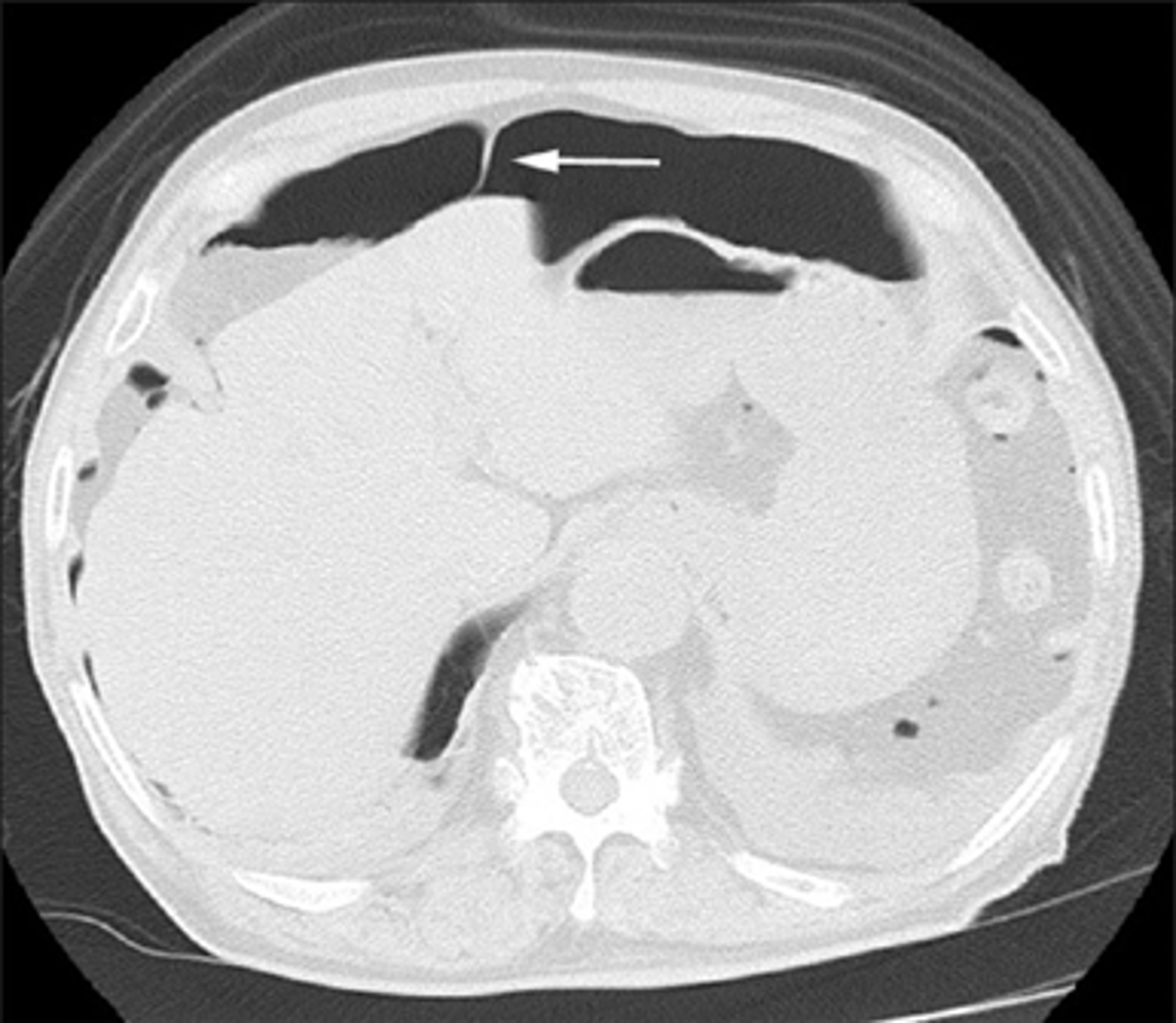
Not free air, but small bowel between liver and diaphragm
This has folds, and free air should not have folds.
Free air CT

Free air CT
Free air CT
Free air CT
Free air CT
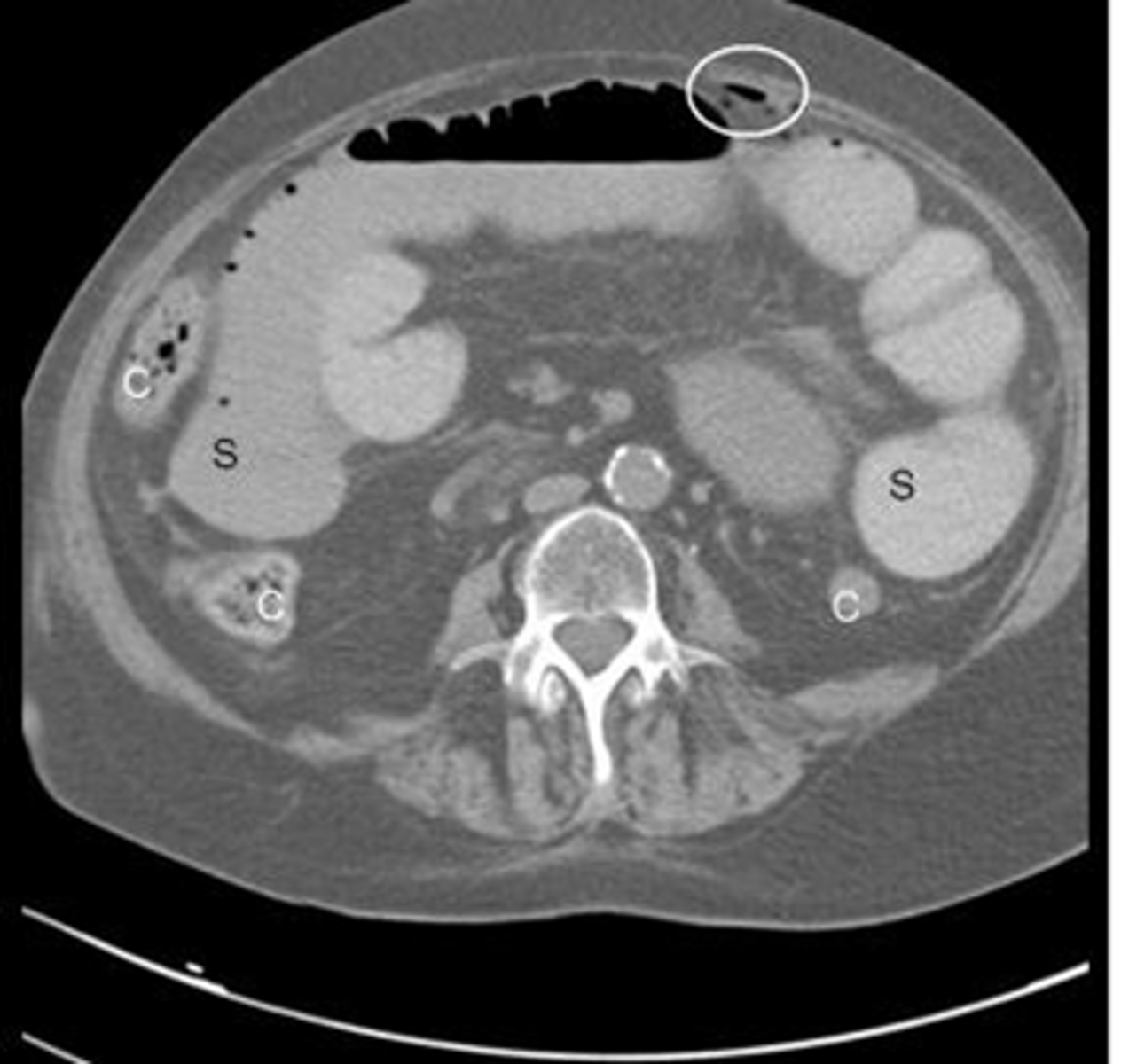
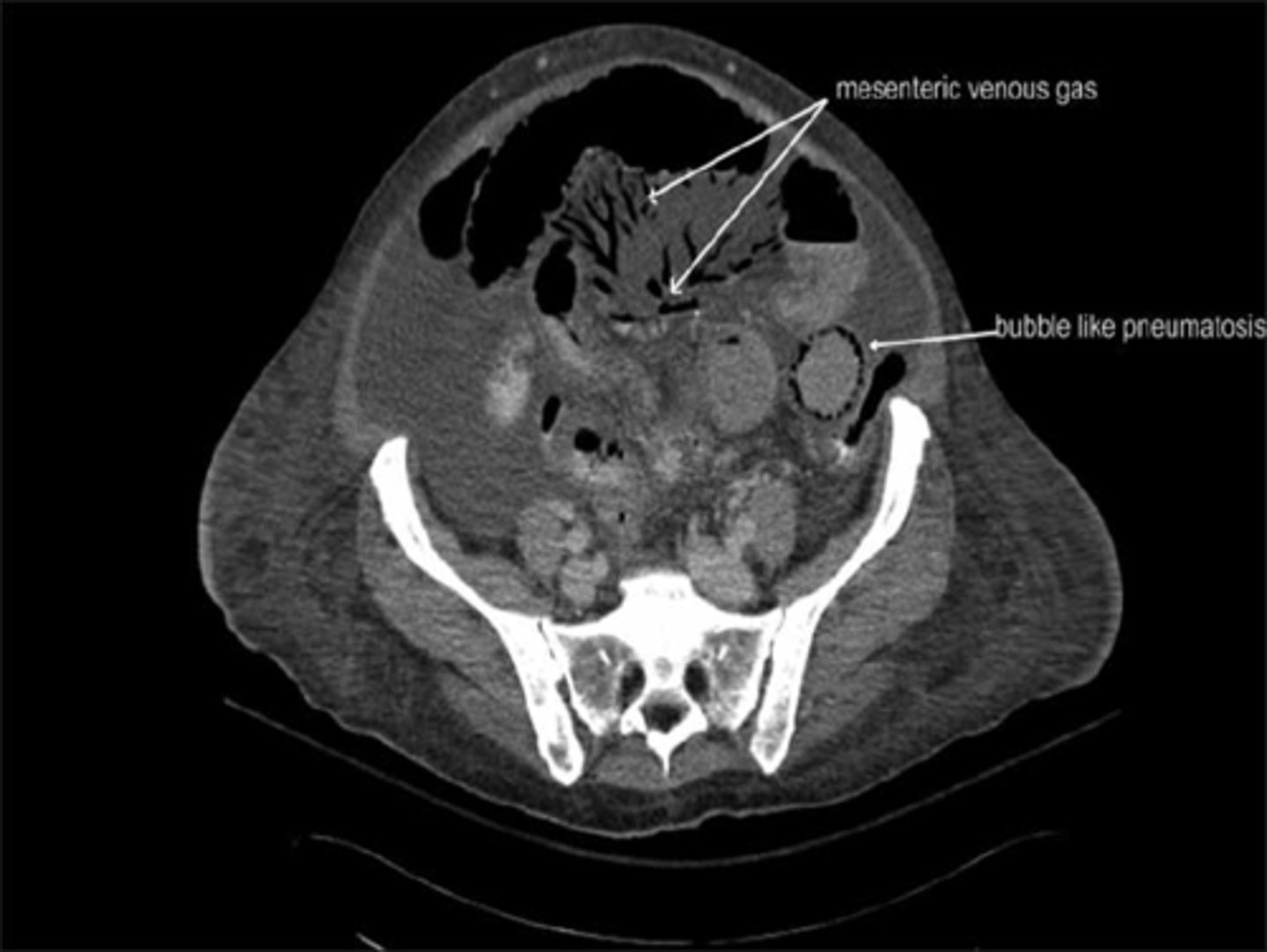
Pneumatosis - air in the abdominal wall.
WHITE ARROWS - RLQ demonstrating thin curvilinear lucency that parallels with the lumen of the adjacent bowel.
Appearance characteristic of gas in the bowel wall.
In infants the MC cause for this finding is necrotizing enterocolitis - a disease found mostly in premature infants in which the terminal ileum is most affected.
Pneumatosis intestinalis is pathognomonic for necrotizing enterocolitis in infants.
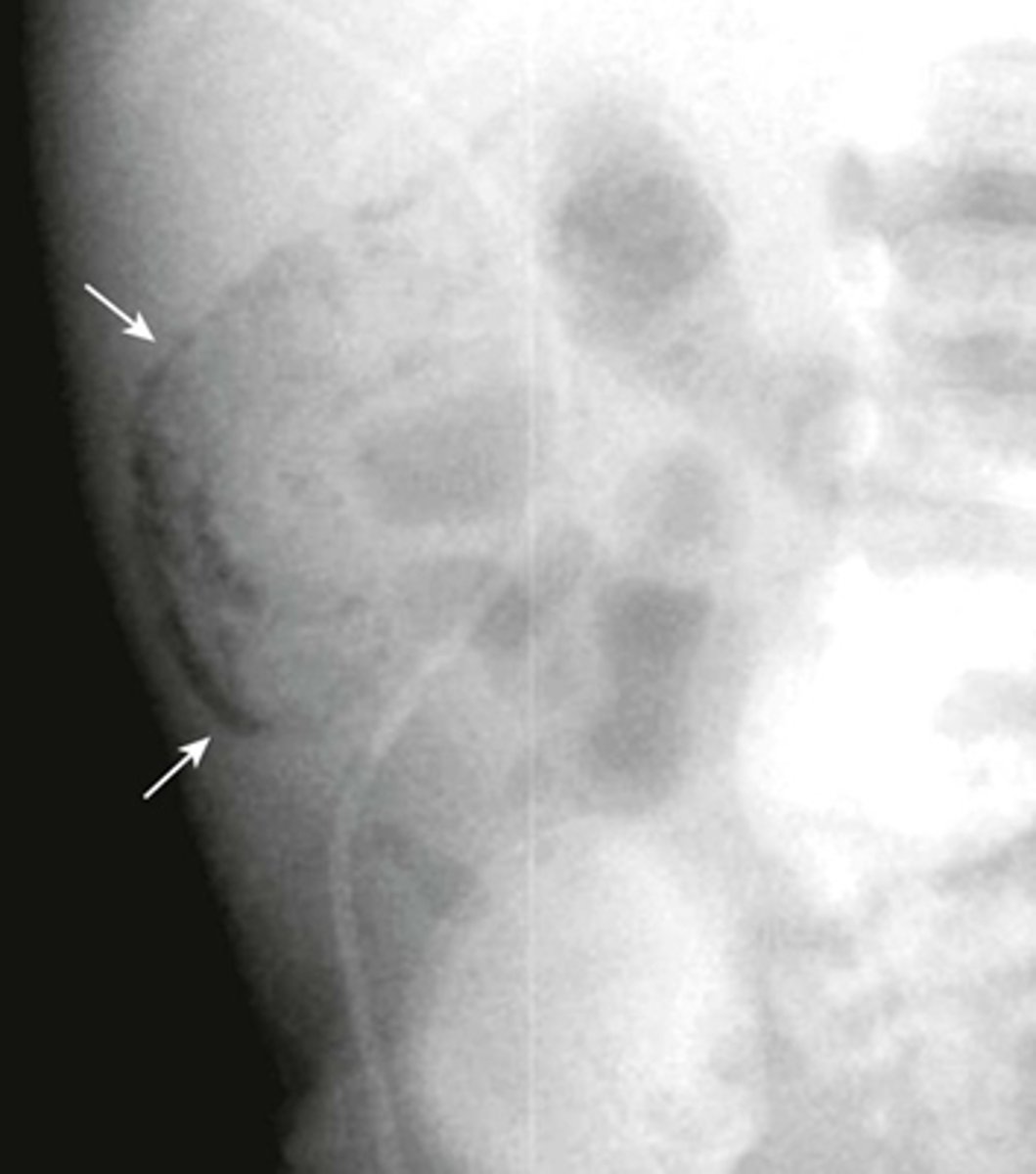
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis.
SOLID WHITE ARROWS:
Clusters of air-containing CYSTs associated with the left colon.
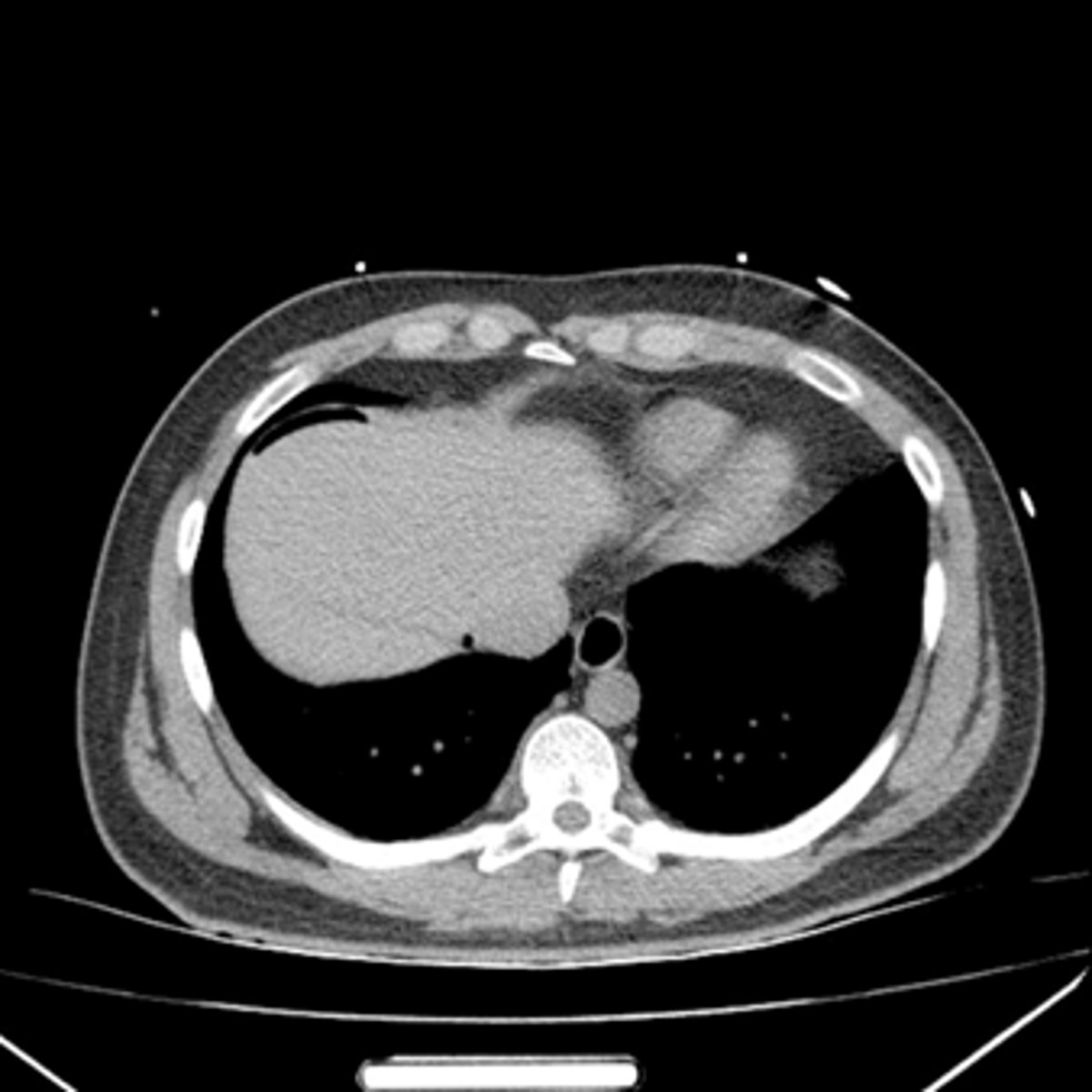
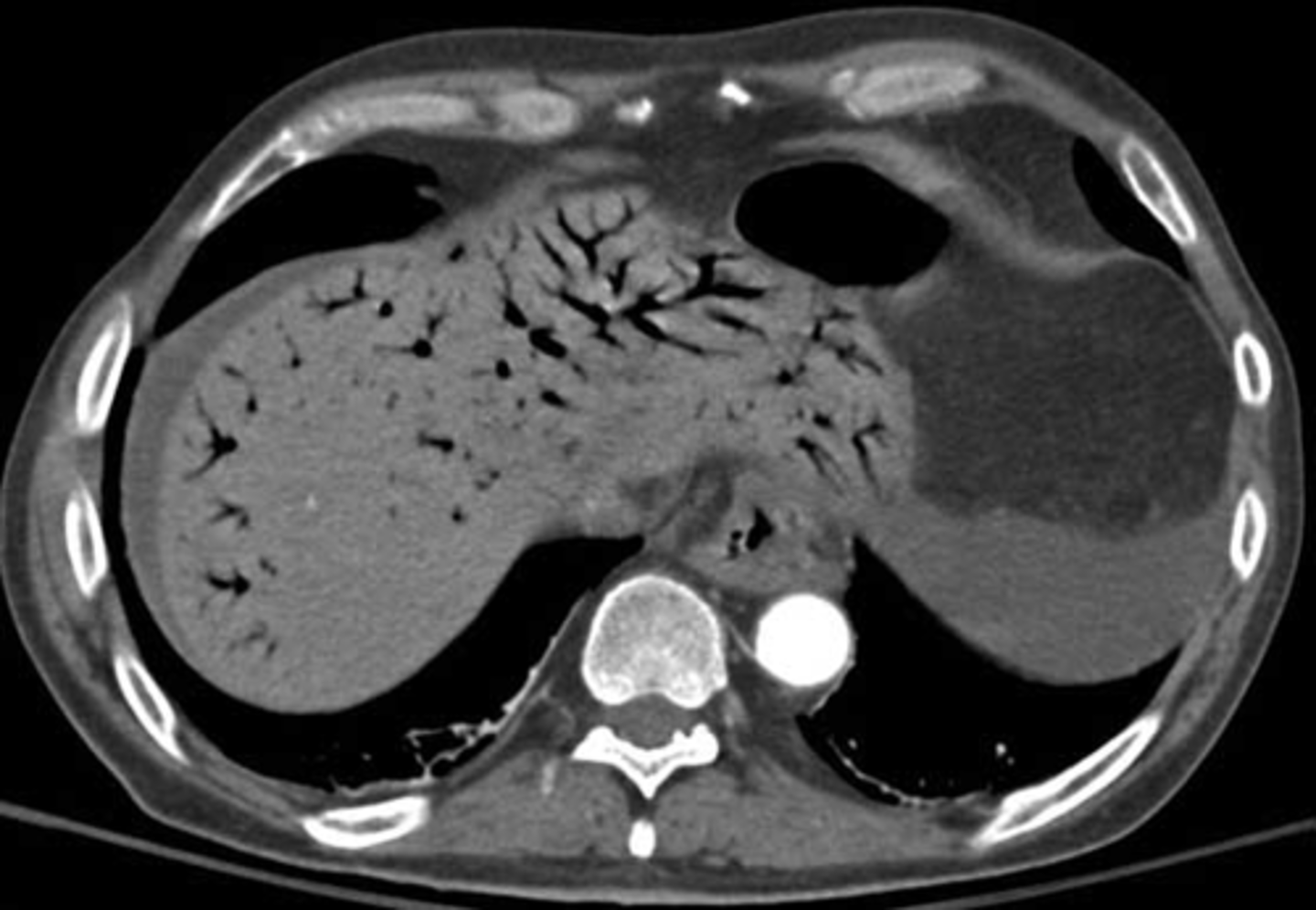
Portal air in liver secondary to pneumatosis
1. Rimlike
2. Linear
3. Lamellar
4. Cloudlike
What are the patterns of calcification?
Aortic Aneurysm Calcification
WHITE ARROWS: aorta demonstrating rim-like calcification.
The opposite wall is also calcified, but overlaps the spine, which is why calcifications in the aorta are usually easier to identify on lateral abdominal radiographs.
When the diameter of the abdominal aorta exceeds its normal diameter by more than 50%, an aneurysm is present.

Calcified gallbladder wall.
WHITE ARROW: rimlike calcification on wall of a cyst or saccular organ.
This is a porcelain gallbladder - occurs with chronic inflammation and stasis.
associated with gallstones in over 90% of cases and an increased incidence of carcinoma of the gallbladder in about 20% of cases.
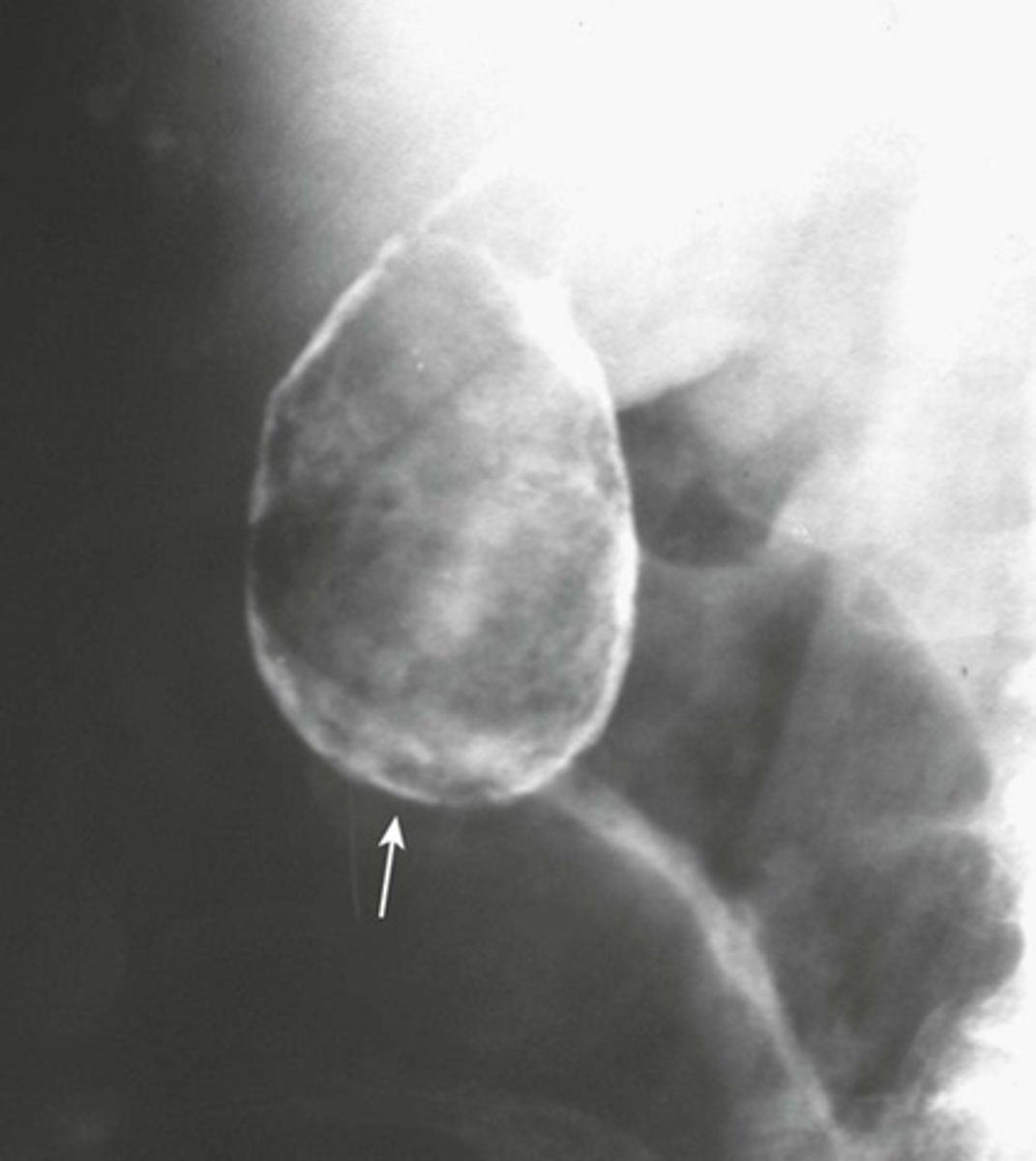
Renal calculi
BLACK ARROW: calcification
WHITE ARROW: shadow of left kidney
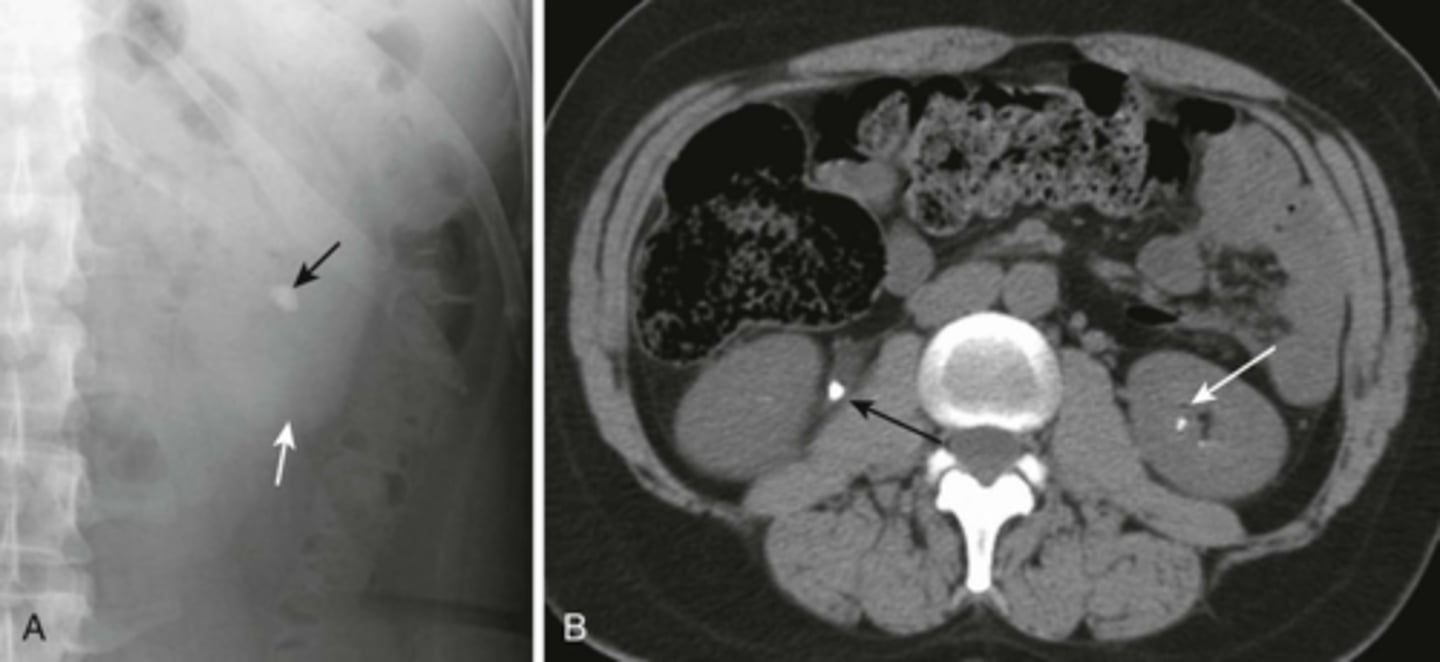
B:
BLACK ARROW: large calcification in the proximal right ureter
WHITE ARROW: smaller calcification in the left intrarenal collecting system.
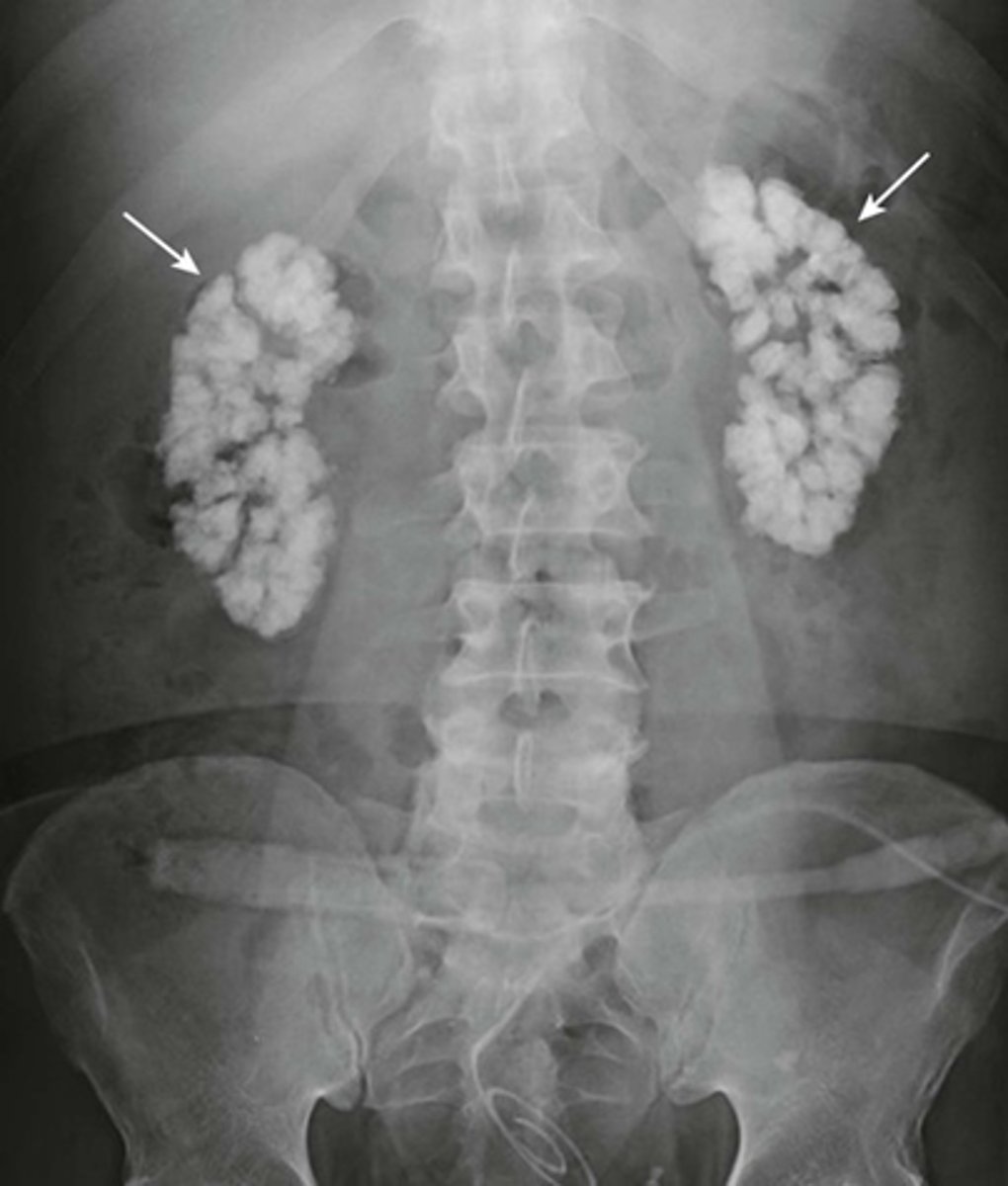
Medullary nephrocalcinosis.
WHITE ARROWS: cloudlike calcifications seen bilaterally.
suggests that these calcifications have formed within a solid organ or tumor.
The calcifications conform to the distribution of the renal collecting systems.
This is medullary nephrocalcinosis, a condition not synonymous with renal calculi because nephrocalcinosis signifies a metabolic derangement. This patient had primary hyperparathyroidism.
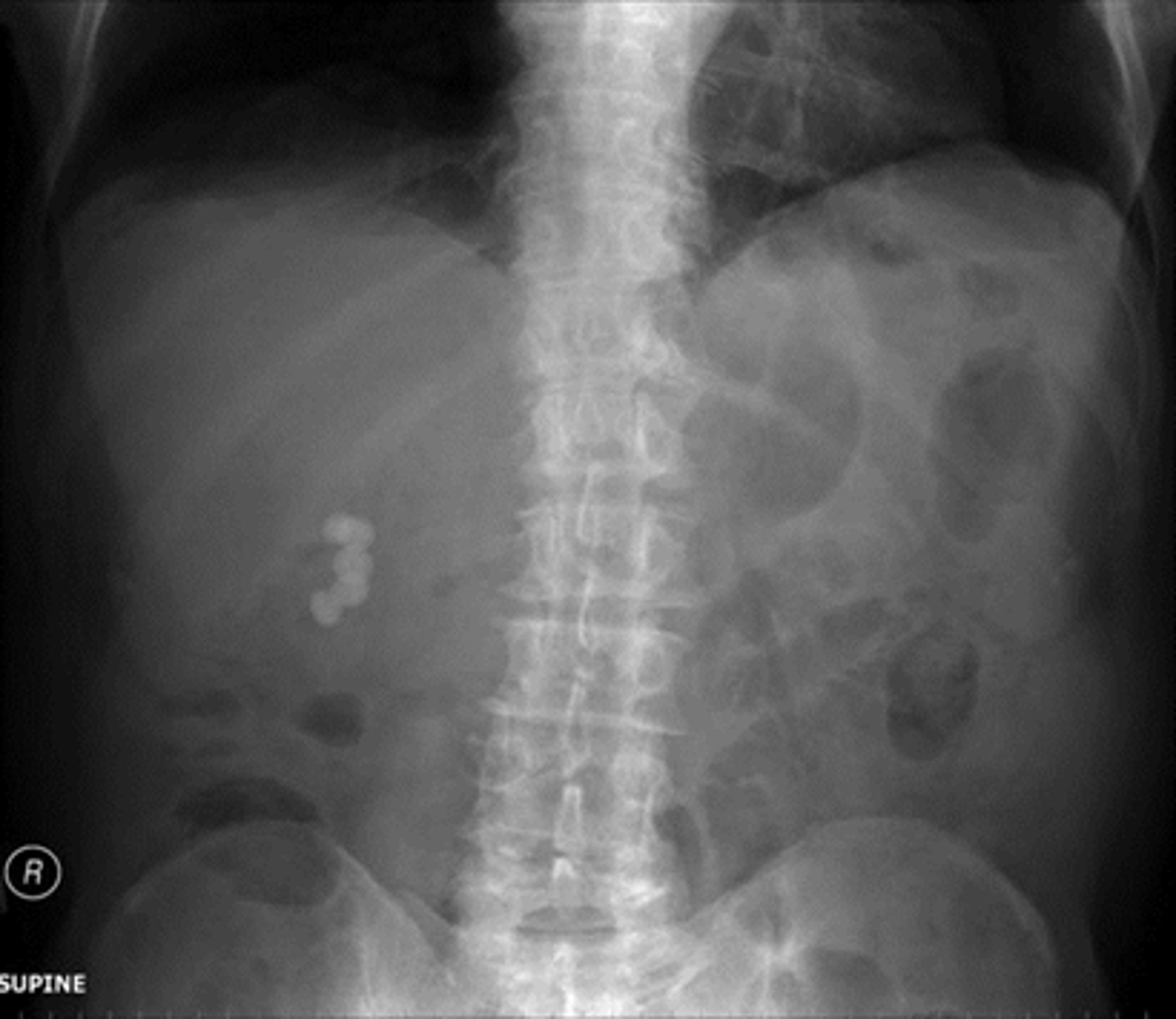
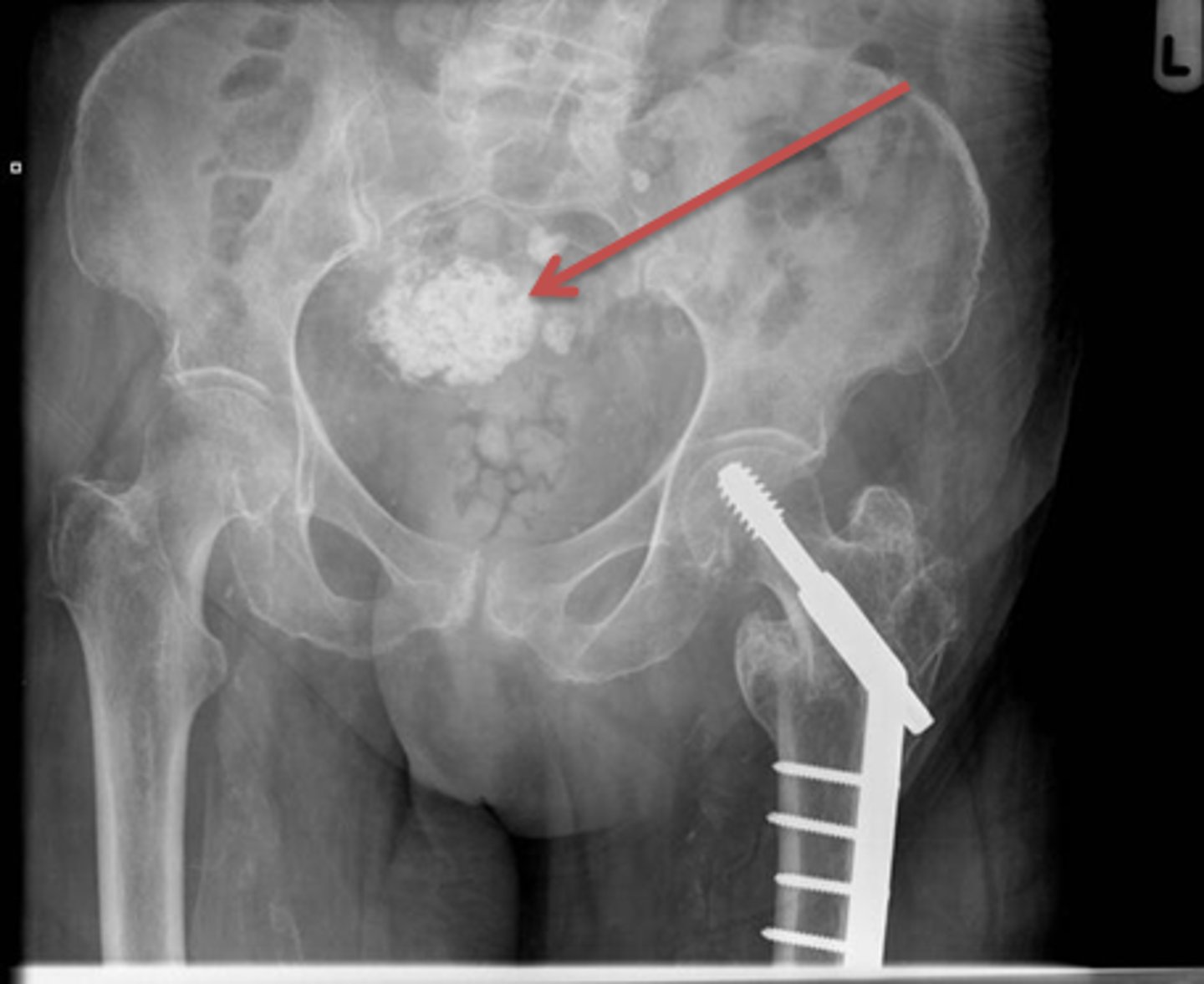
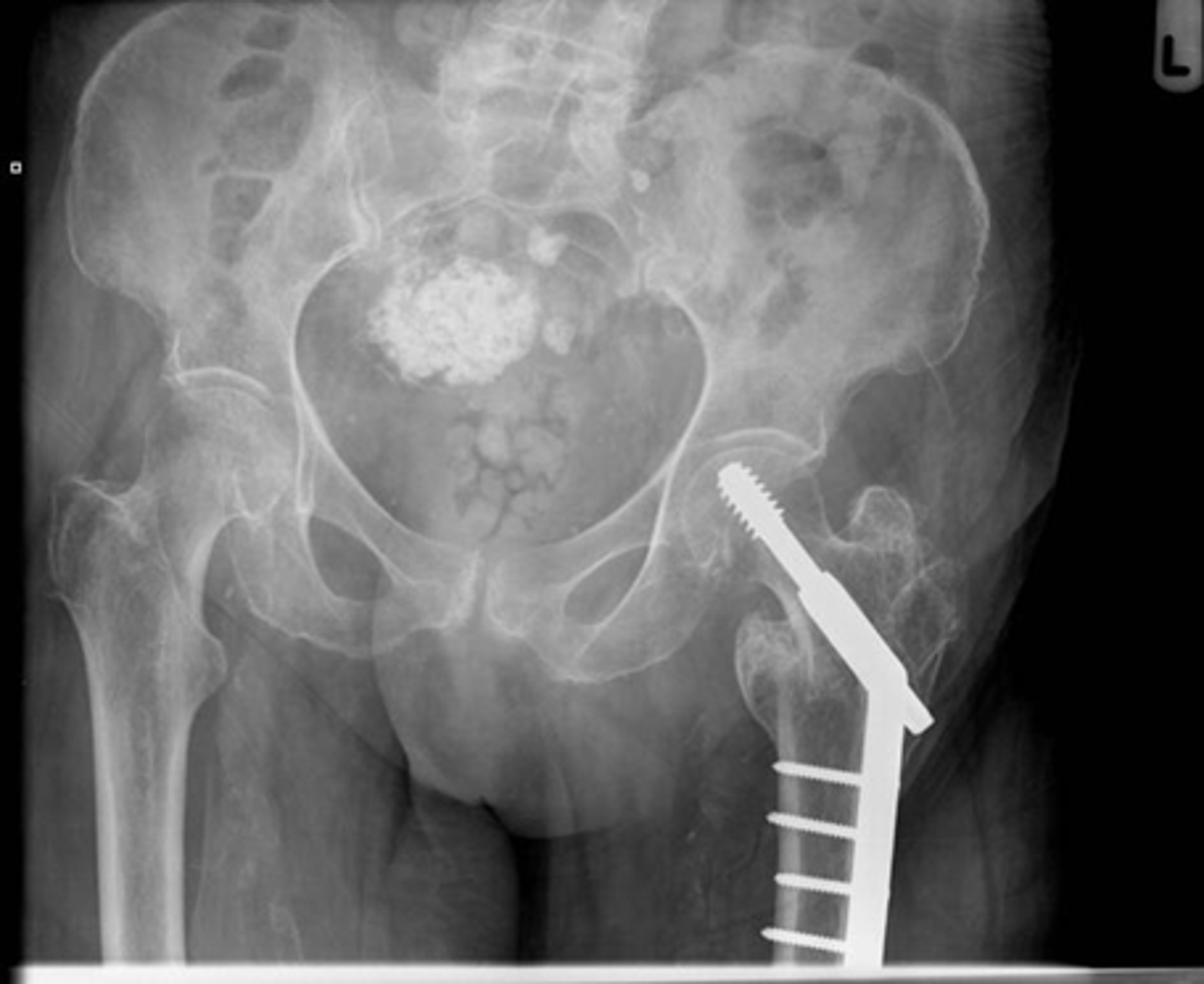
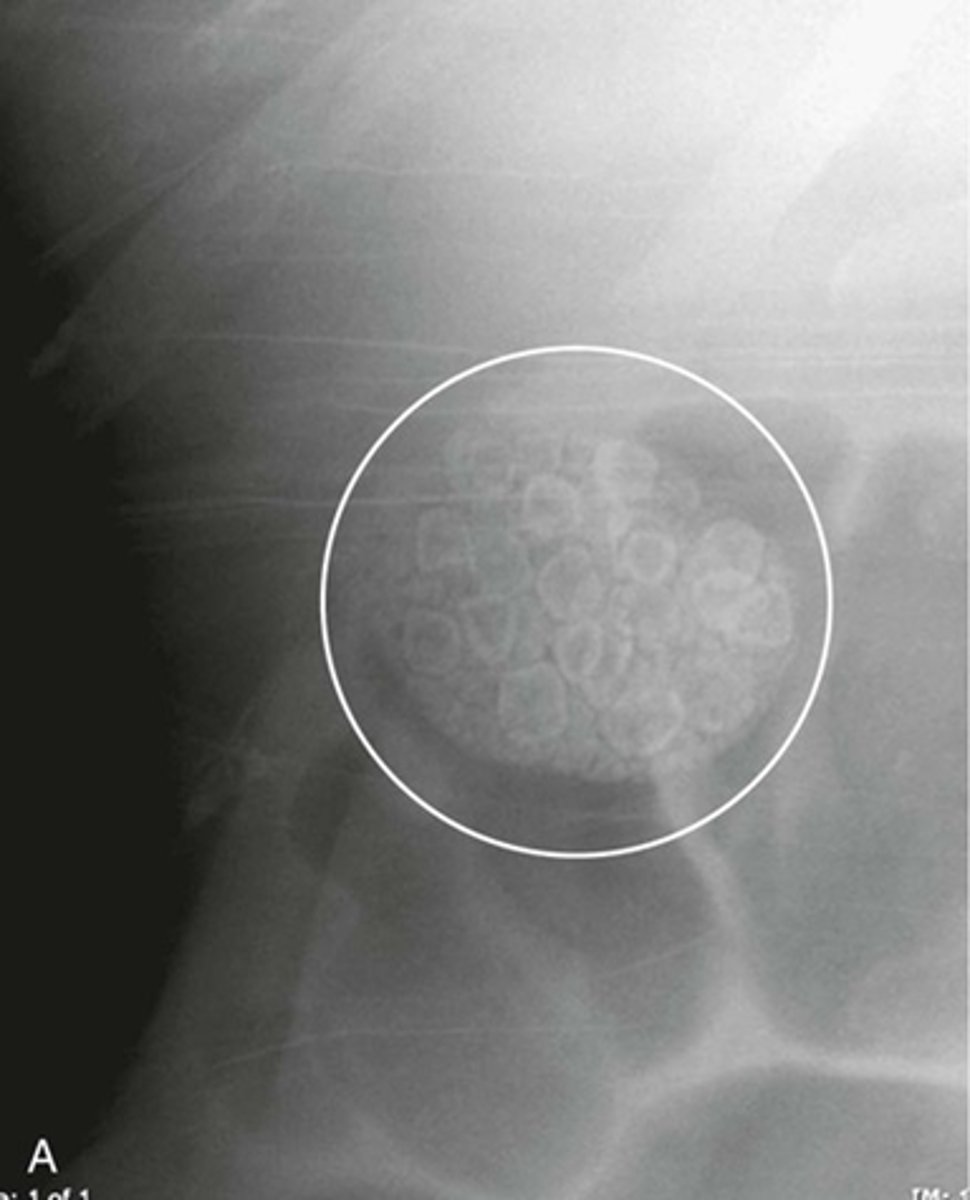
Gallstones
WHITE CIRCLE: multiple lamellar calcification, with interlocking edges that suggest that they all formed in a hollow viscus in proximity to each other.
Gallstones
WHITE ARROW:
gall stones in RUQ, two have central nidus surrounded by laminated concnetric rings of noncalcified and calcified material.
BLACK ARROW:
gall bladder containing bile fats and less dense than adjacent liver.
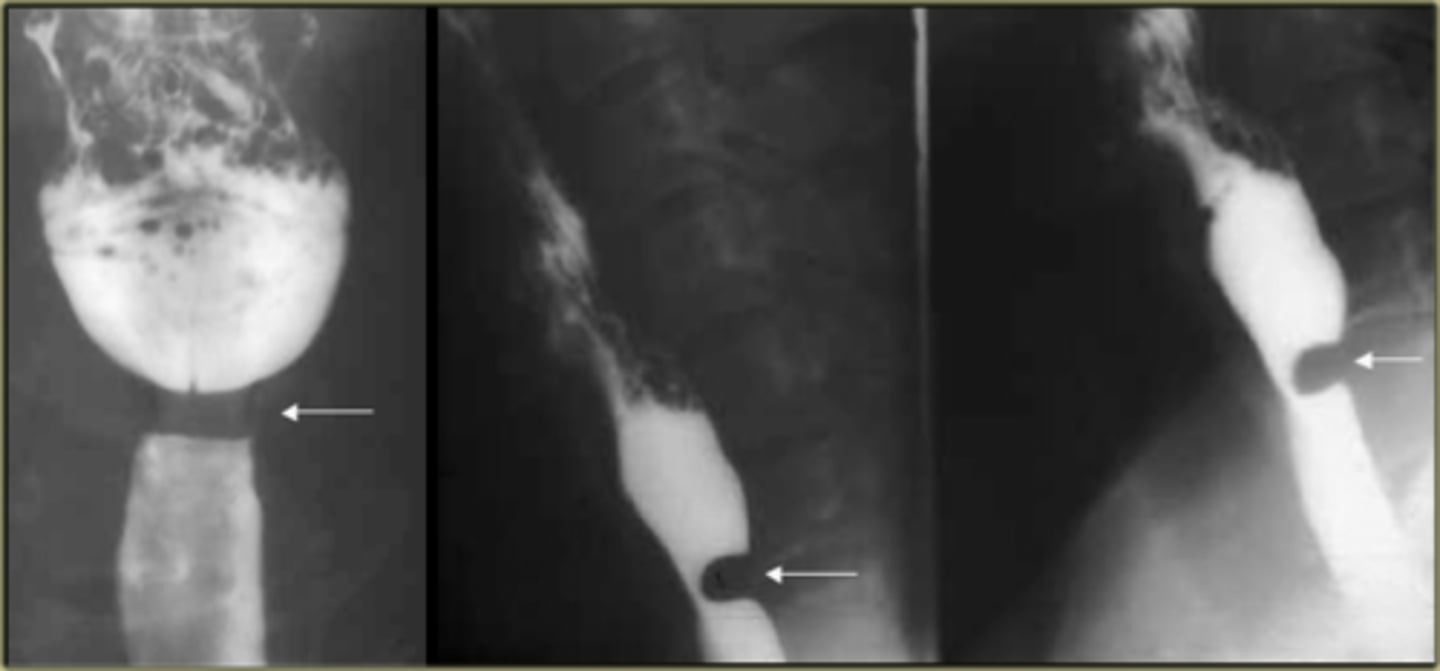
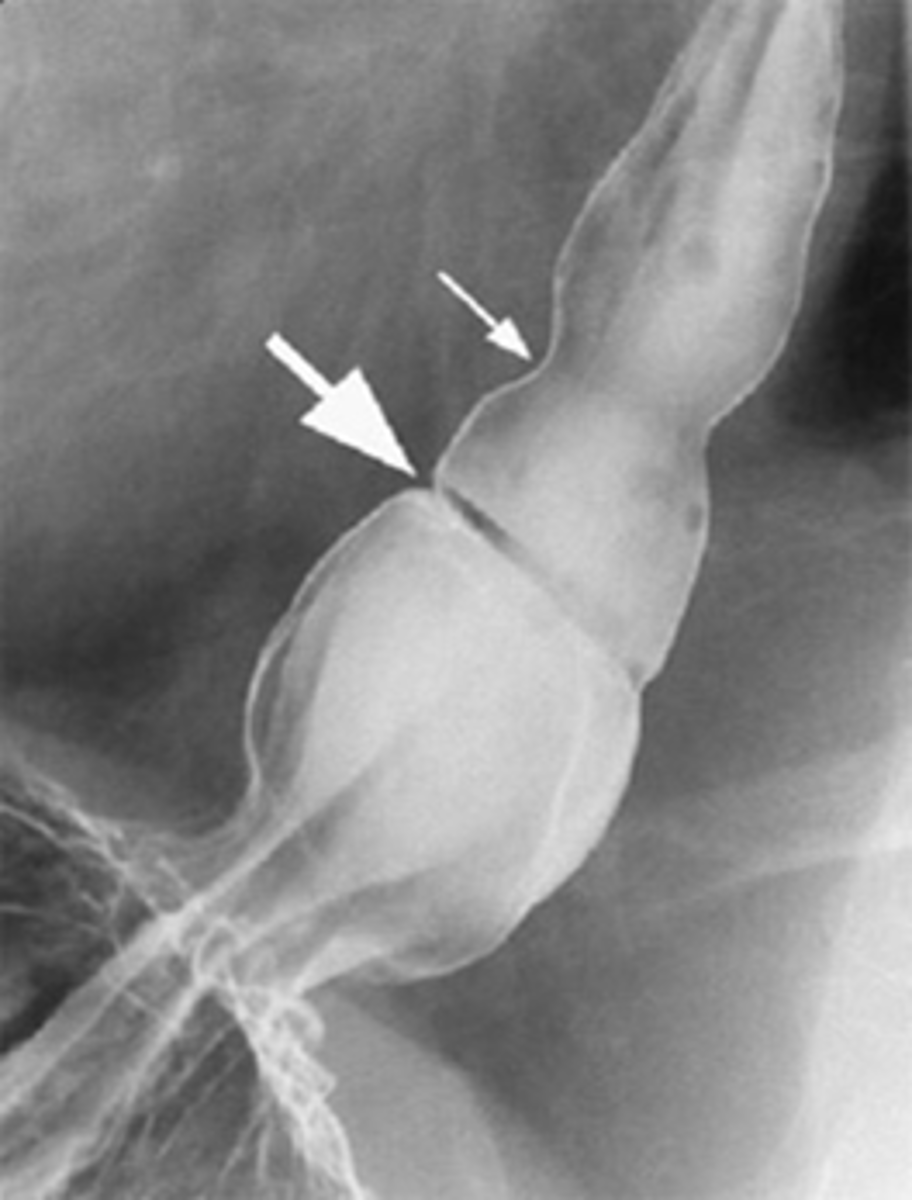
Cricopharyngeal achalasia/Zenker's diverticulum
rare clinical entity in which upper esophageal sphincter (cricopharyngeus) does not open adequately during swallowing leading to dysphagia.
Diverticulum of the mucosa of the pharynx just above the cricopharyngeal muscle.
What is it
Cricopharyngeal achalasia/Zenker's diverticulum
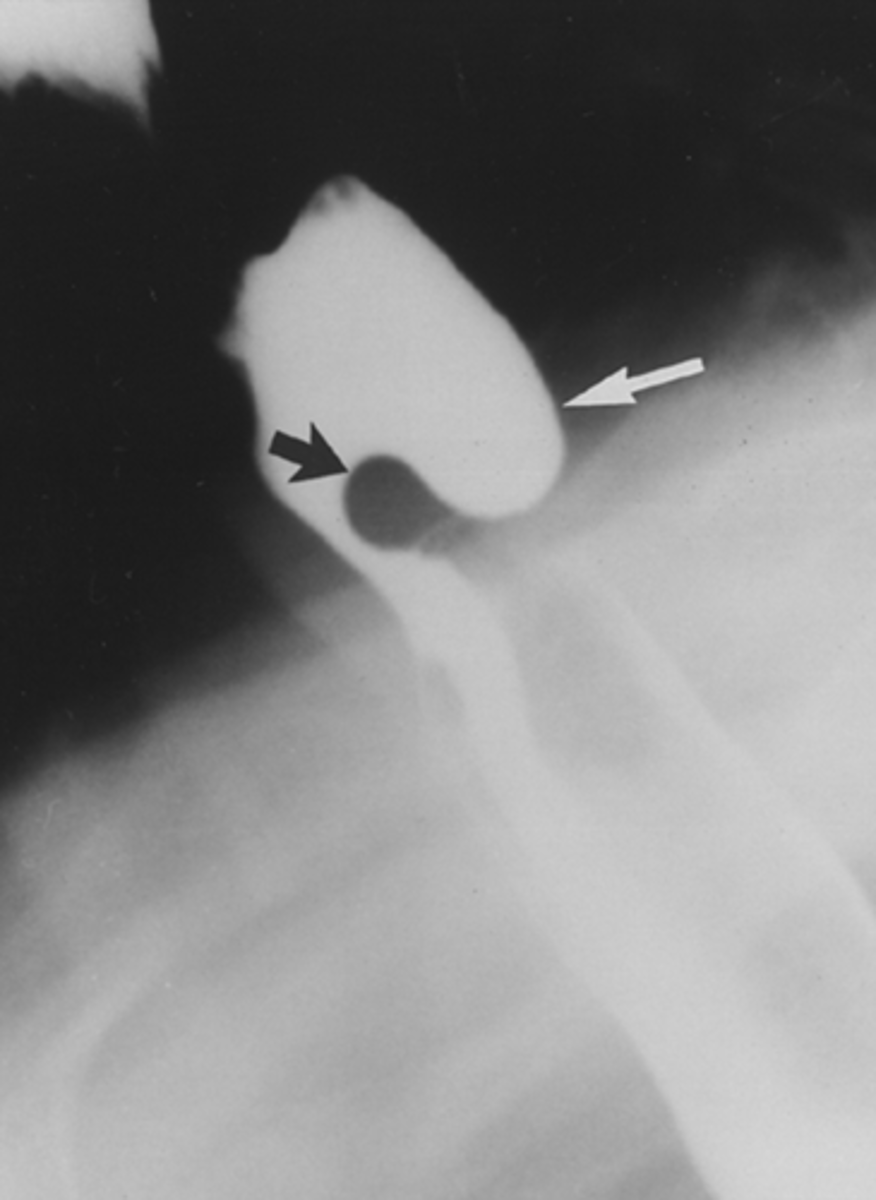
Zenker's diverticulum

Zenker's diverticulum
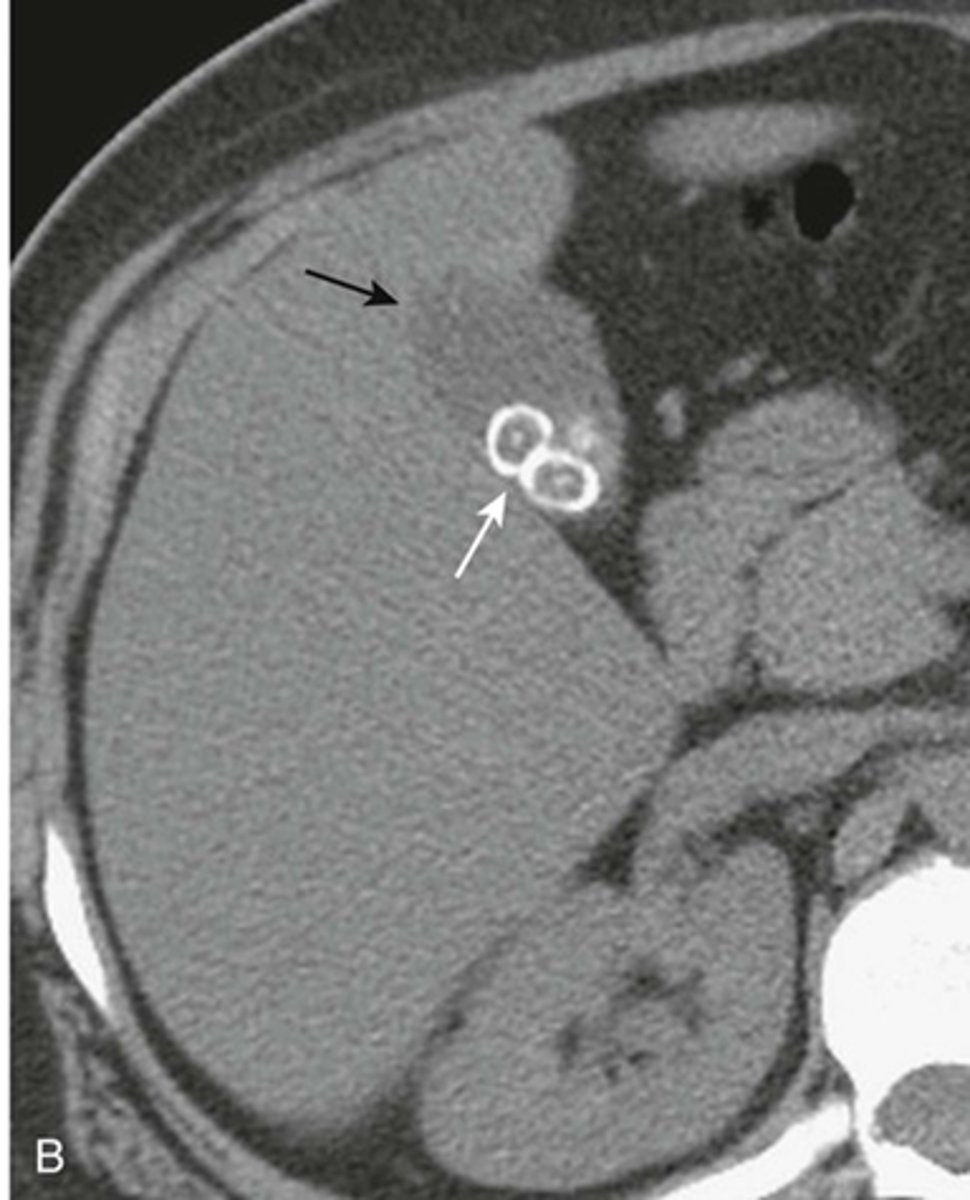
Upper left esophageal carcinoma
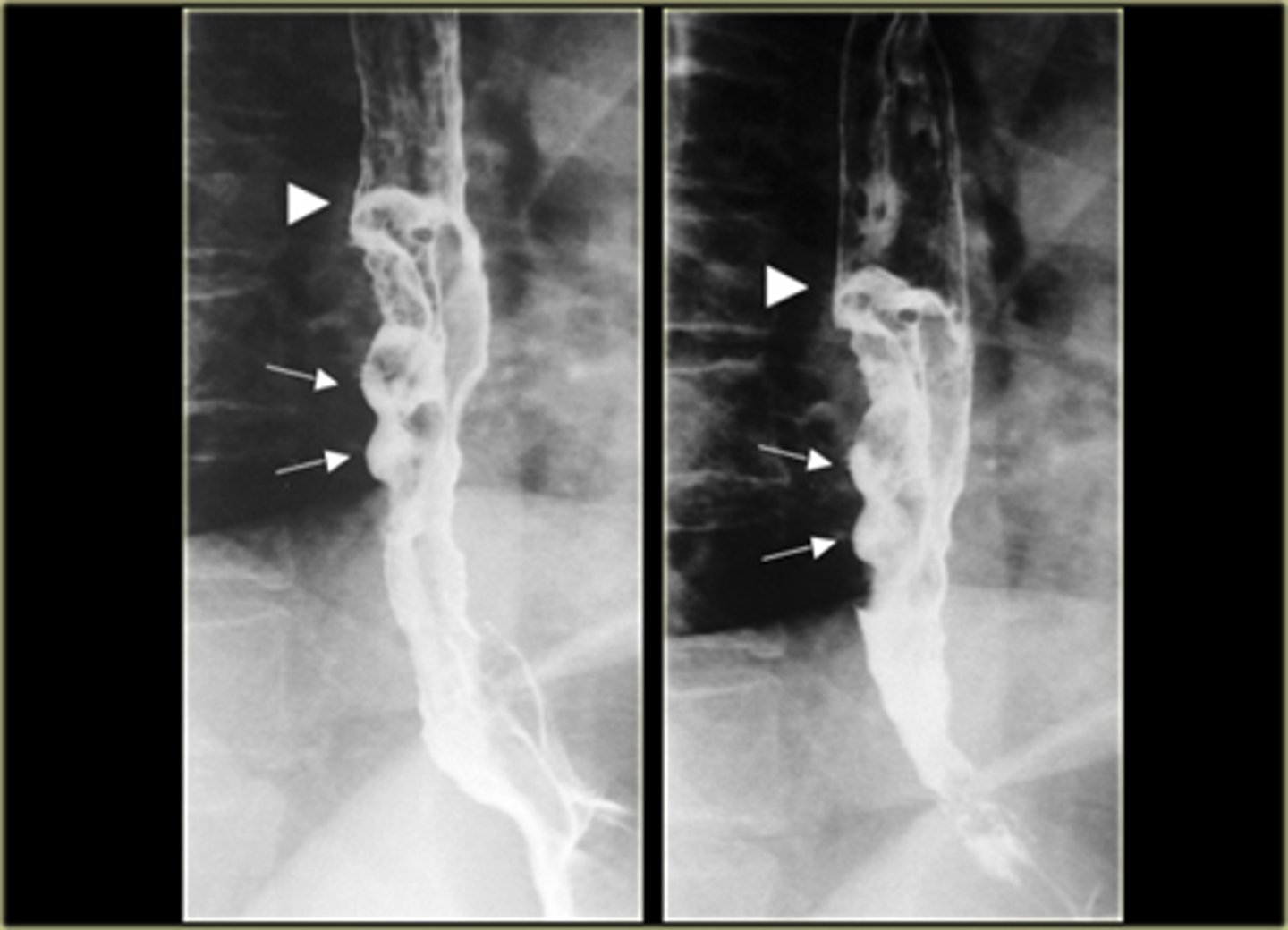
Lower left barrett's esophagus
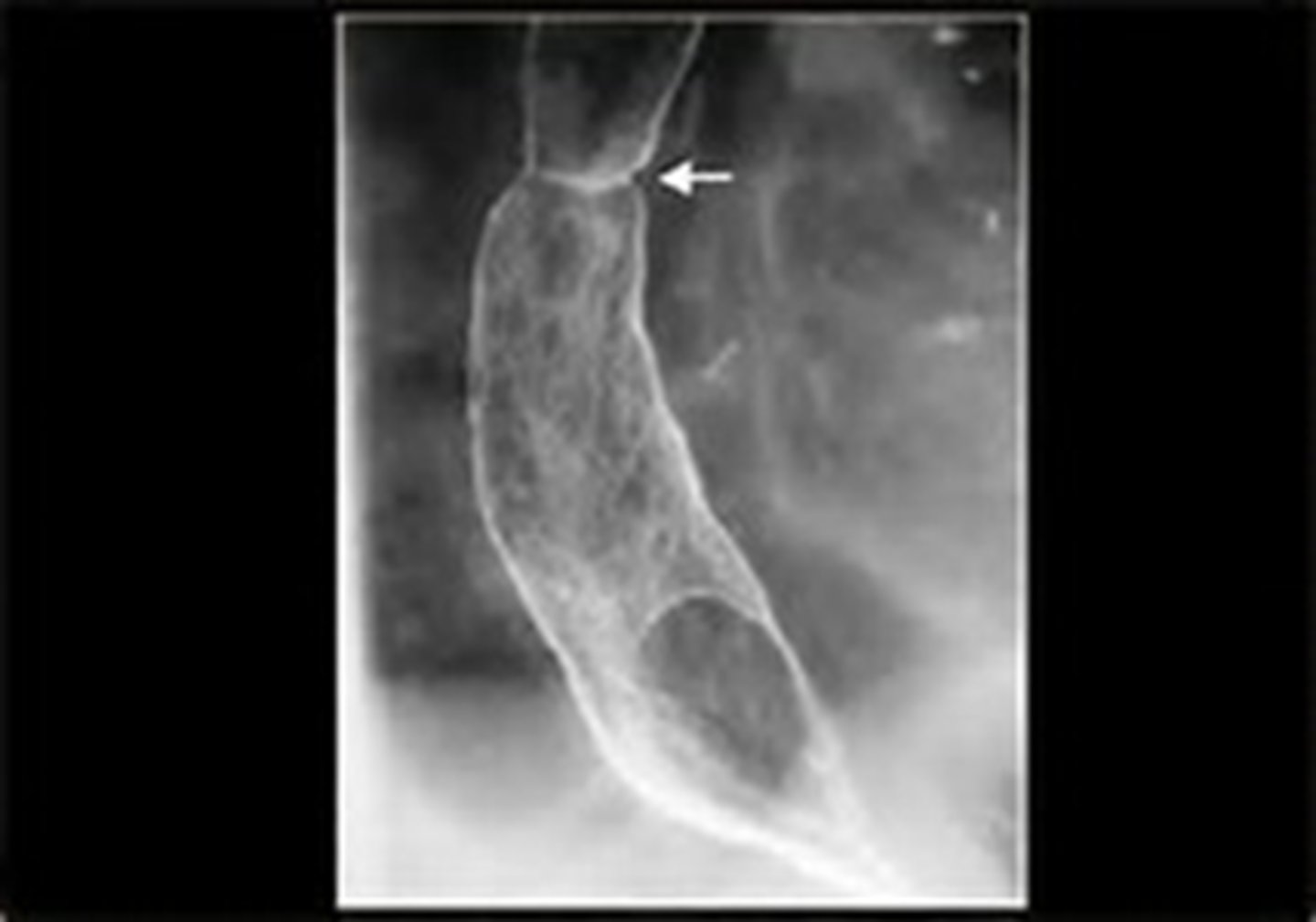
Upper right hiatal hernia with schatzki's ring
THICK WHITE ARROW: Schatzki's ring
THING WHITE ARROW: stricture
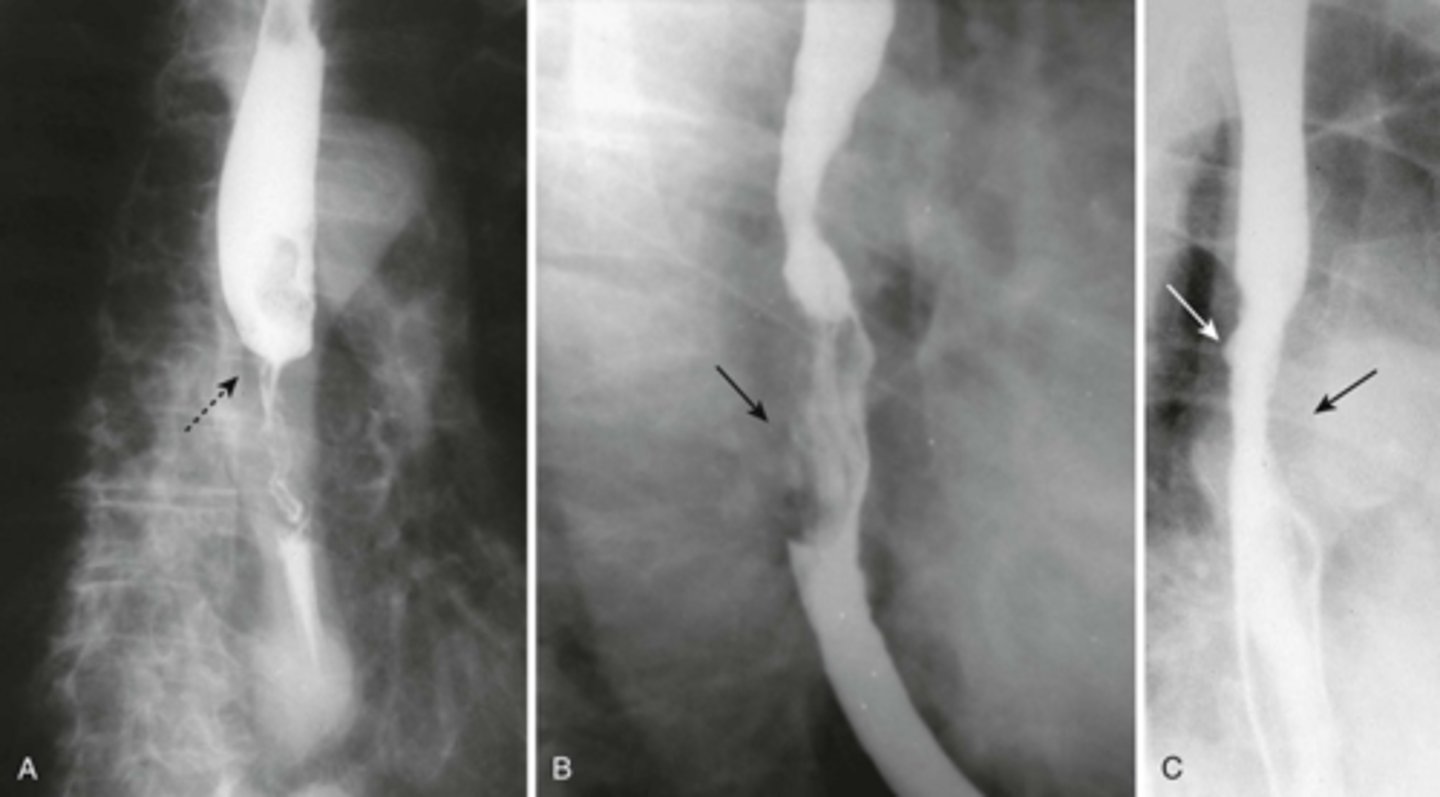
Esophageal carcinomas.
(A)
DOTTED BLACK ARROW:
annular constricting lesion of the midesophagus.
The tumor encircles the normal lumen and obstructs it in this case.
(B)
BLACK ARROW: Polypoid mass that arises from the right lateral wall of the esophagus and displaces the barium around it.
(C)
BLACK ARROW - wall, irregular and rigid
WHITE ARROW: a small ulceration (white arrow).
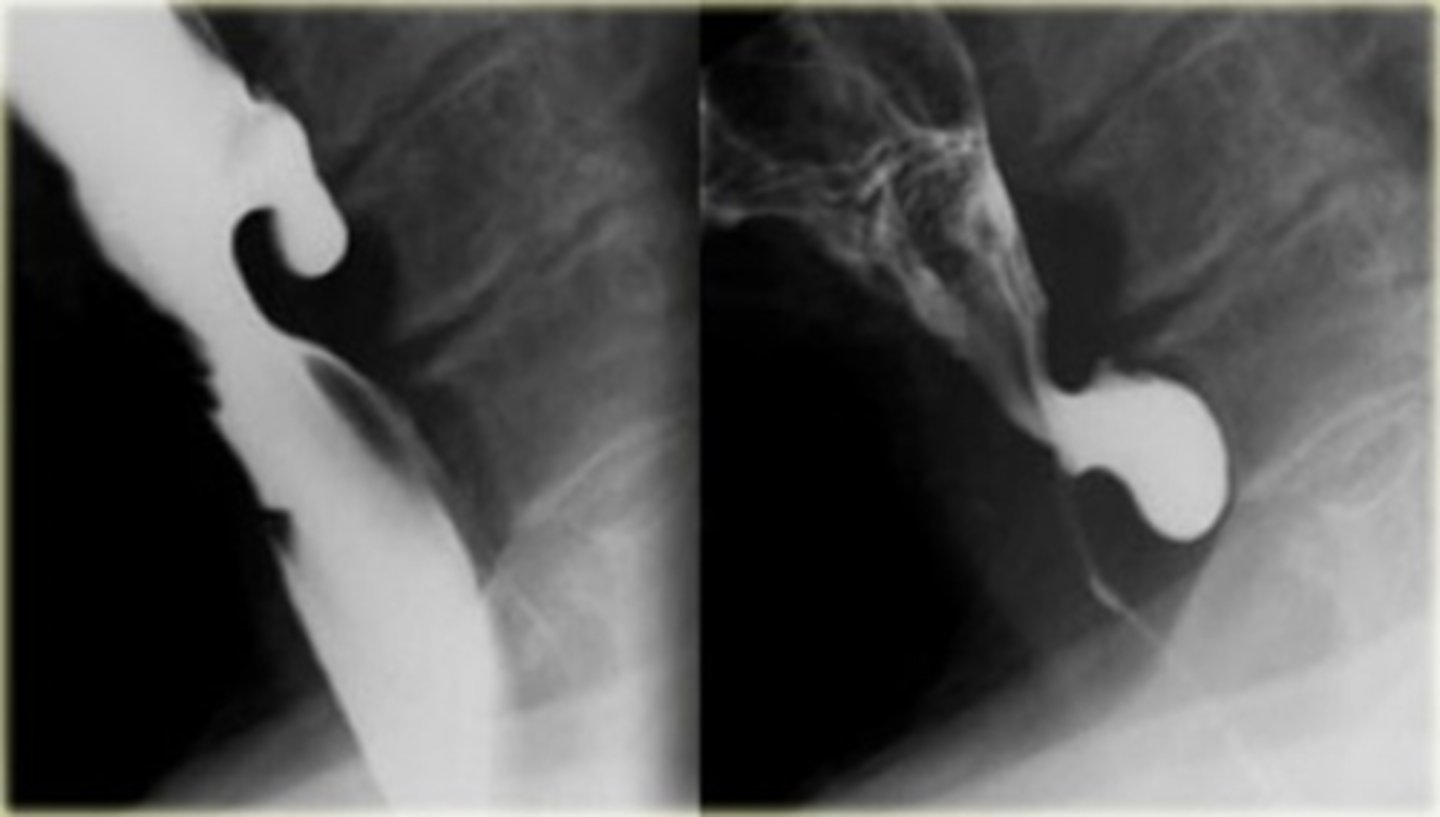
Achalasia - classic finding on barium studies is the bird's beak
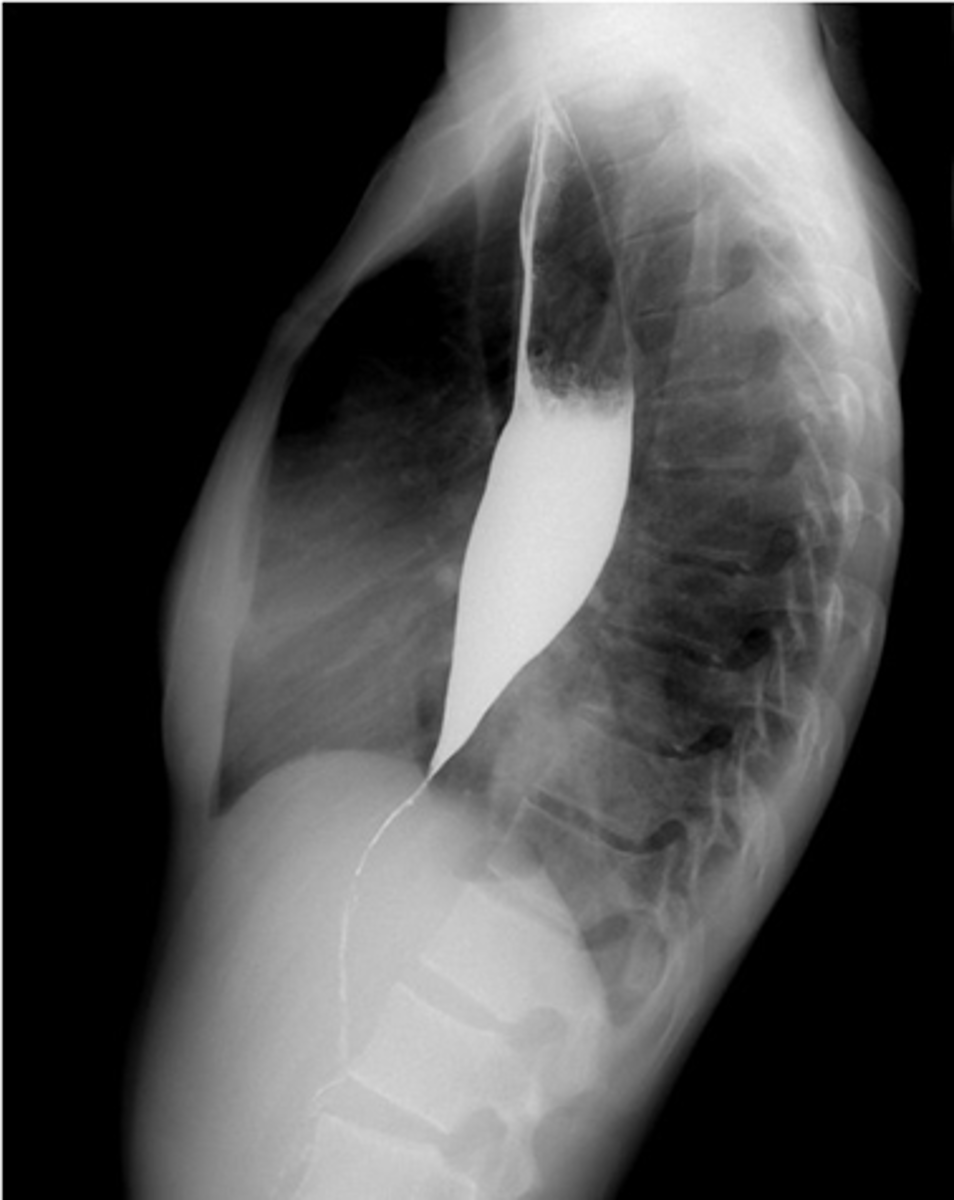
Achalasia
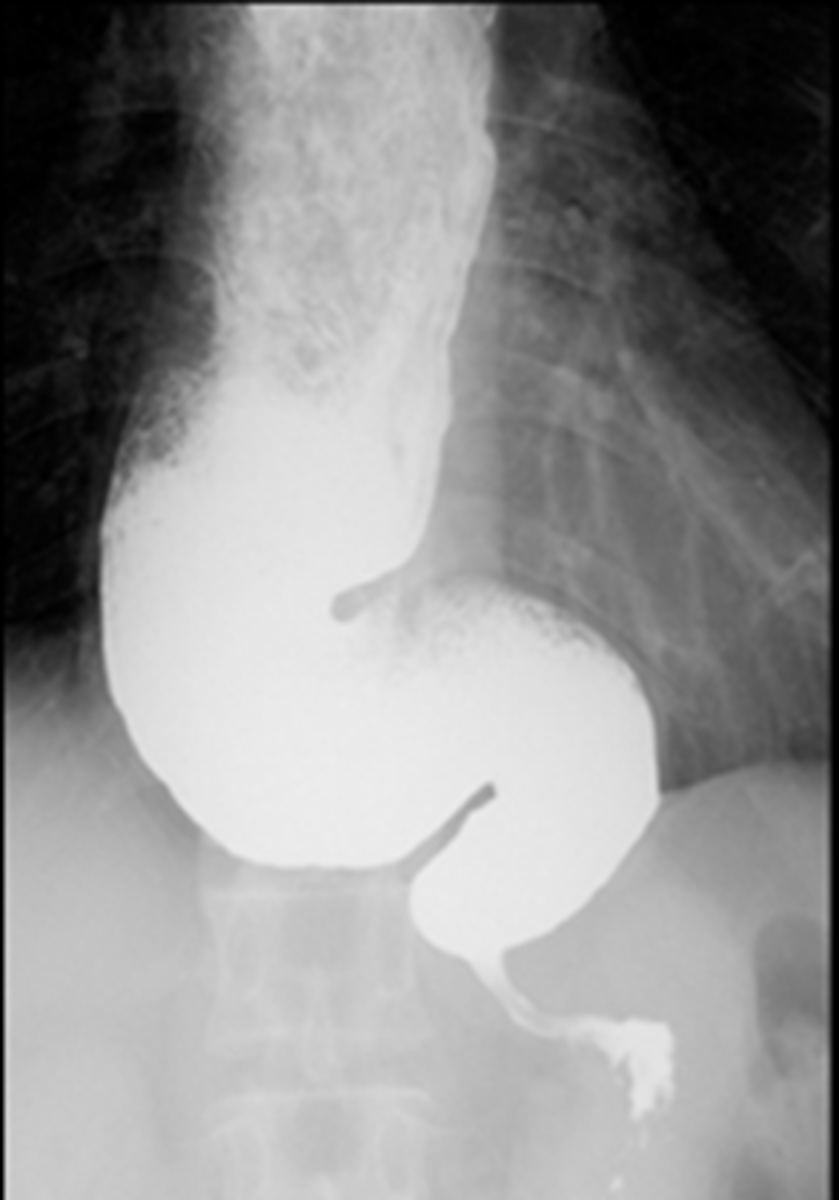
Normal
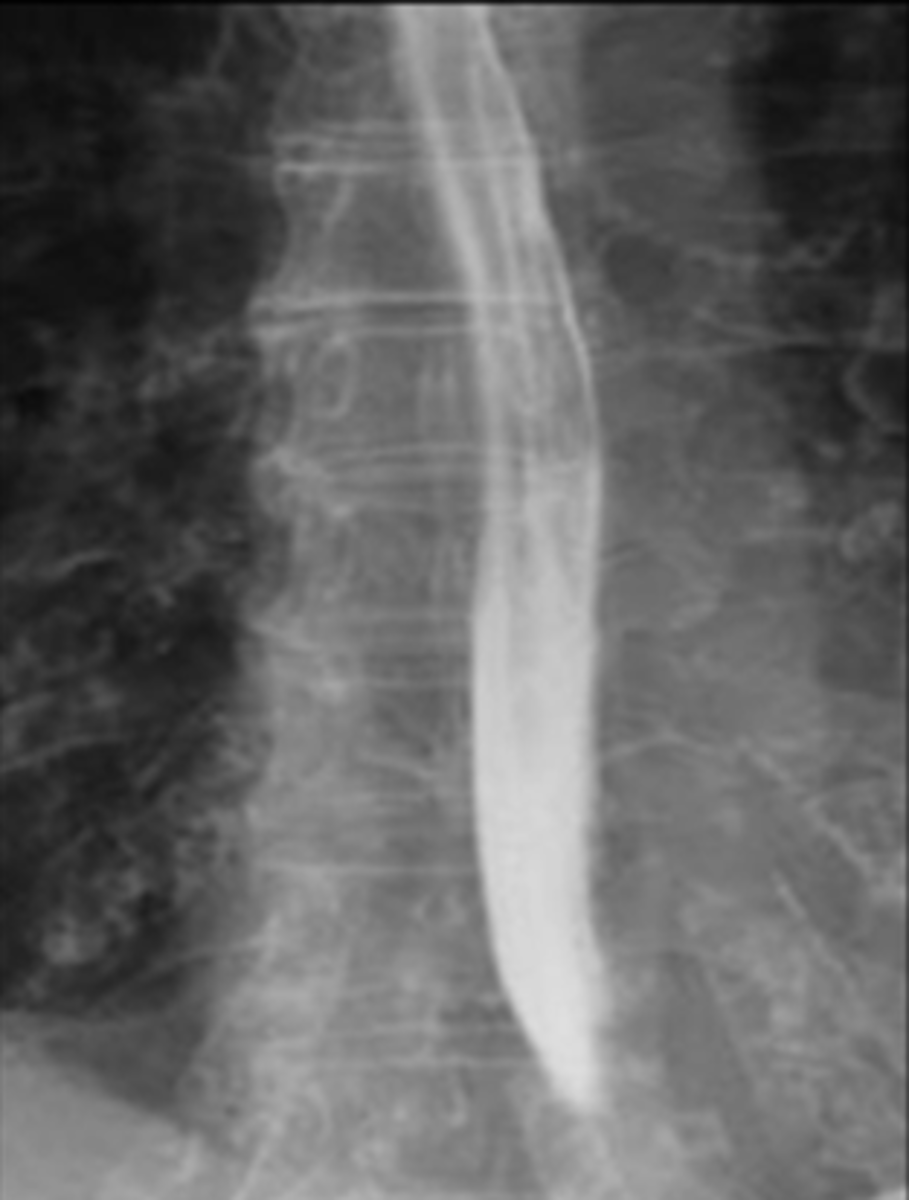
Achalasia barium swallow
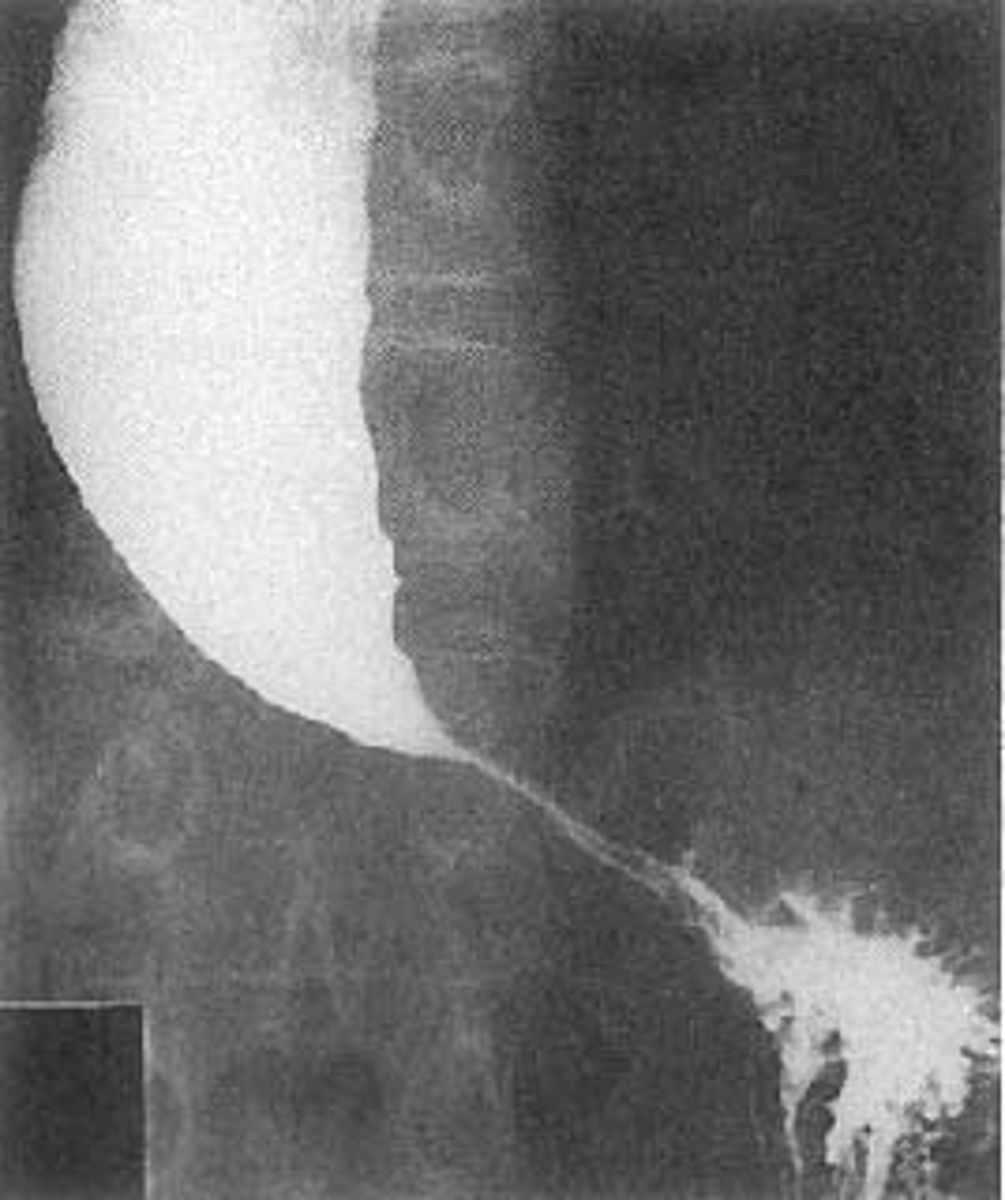
Achalasia barium swallow
