ap environmental science - unit 4: earth systems and resources
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:46 PM on 1/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
1
New cards
adiabatic cooling
the process by which the temperature of an air mass decreases as the air mass rises & expands
2
New cards
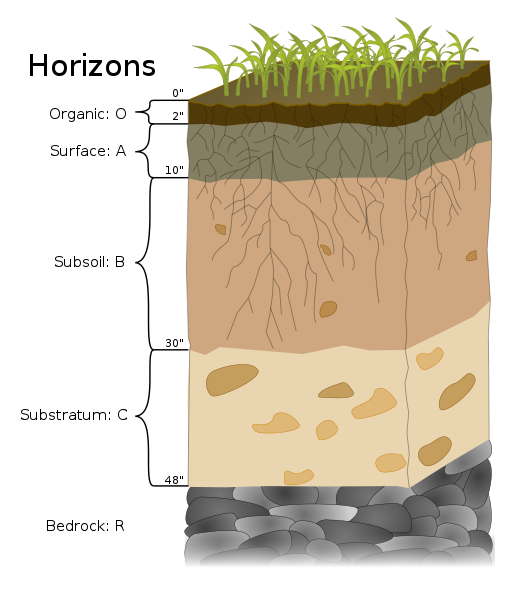
a-horizon
topsoil where bacteria, fungi, and small animals thrive
burrowing animals help to circulate air and water and mix materials
burrowing animals help to circulate air and water and mix materials
3
New cards
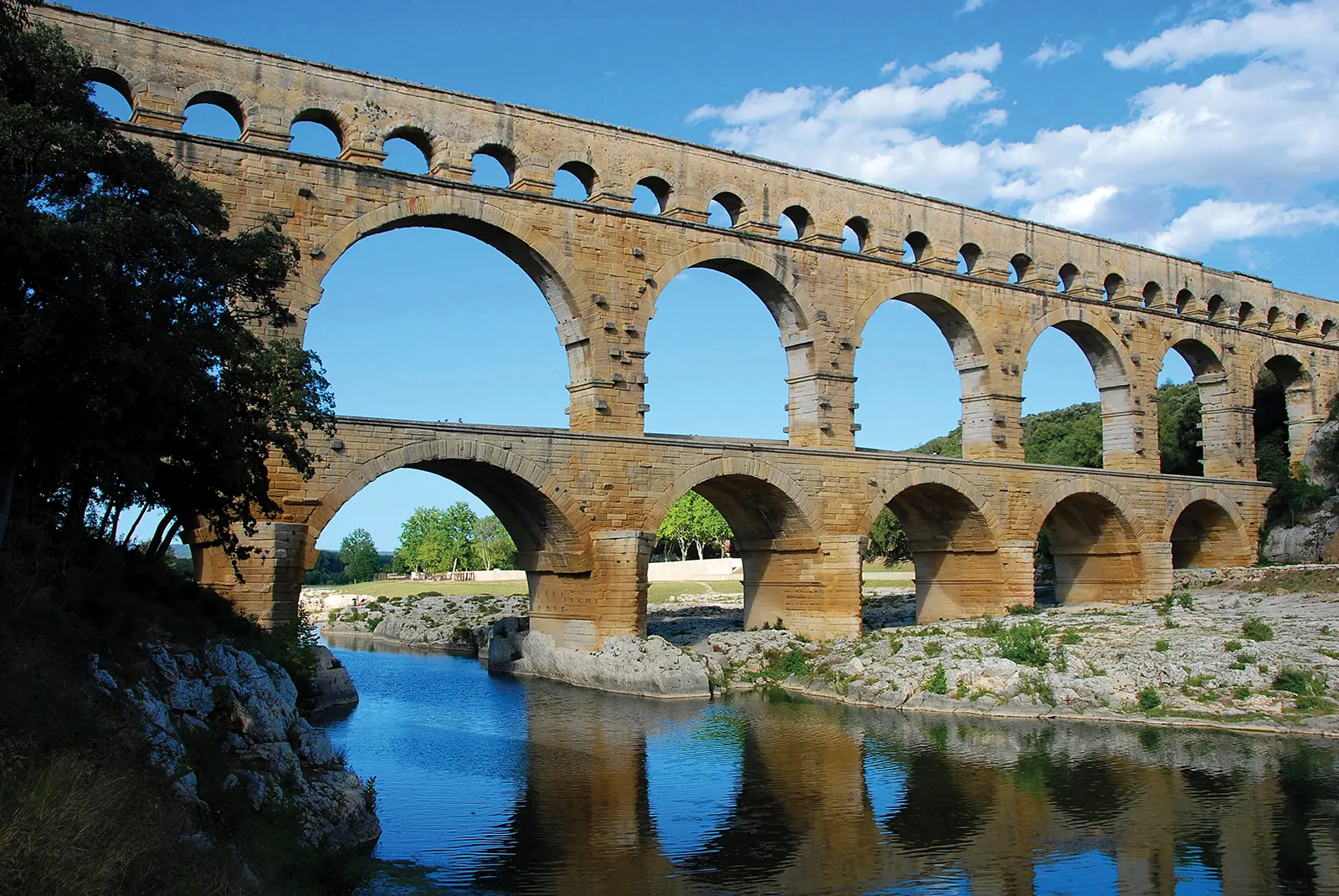

aqueducts
a pipe/passage for transporting water
can displace wastewater, but can be expensive and damage habitats
can displace wastewater, but can be expensive and damage habitats
4
New cards
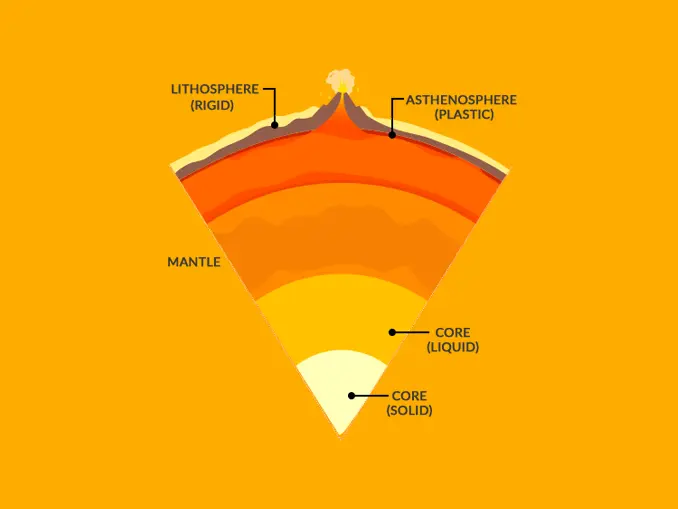
asthenosphere
outer mantle - semi-molten, ductile, flexible rock
5
New cards

basalt
dark-colored, fine-grained, igneous rock
6
New cards
bedrock
parent material from which soil horizons form
7
New cards
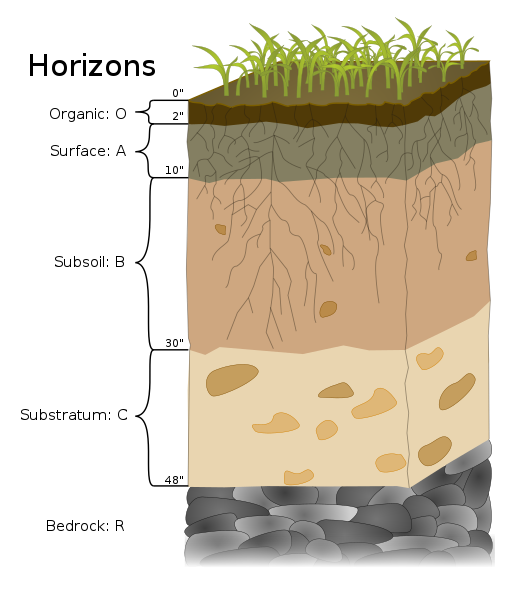
b-horizon
subsoil which contains minerals brought by groundwater or leeched from the a-horizon. high in iron, calcium, and aluminum; made of clay
8
New cards
biological soil properties
fungi, bacteria, & protozoan account for 80-90% of soil's productivity and can break down organic material
9
New cards
cation
positively charged ion
10
New cards
cation exchange
the ability of a particular soil to absorb and release cations
11
New cards
chemical soil properties
acidity which can be neutralized by ways of base material (i.e., calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium)
12
New cards
chemical weathering
the chemical process by which rock is broken down
13
New cards
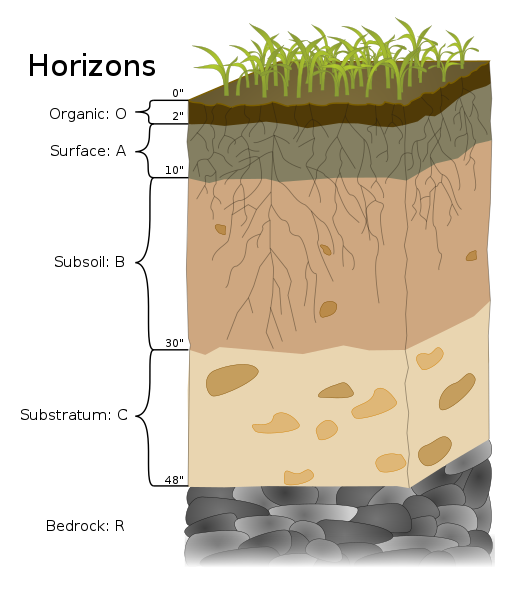
c-horizon
partially weathered bedrock - some is from the parent material and others from forms of past erosion
14
New cards

cinder cone volcano
steep, cone-shaped hill/small mountain made from ash, cinders, and bombs piled up around the opening of a volcano
15
New cards
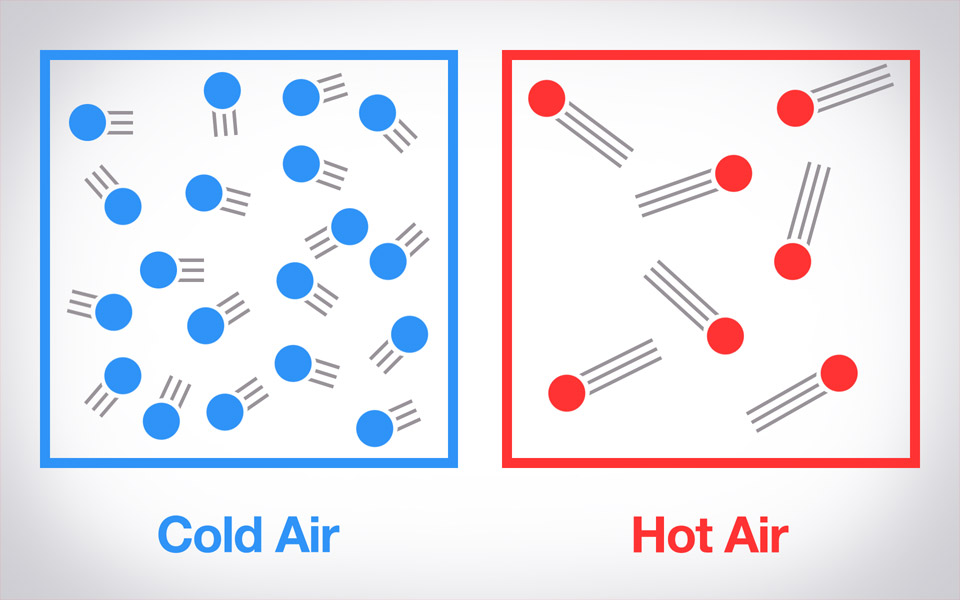
cold air vs. hot air
cold: falls due to its higher density
hot: rises due to its lower density
hot: rises due to its lower density
16
New cards

composite volcano
tall, cone-shaped mountain in which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash and other volcanic material
17
New cards
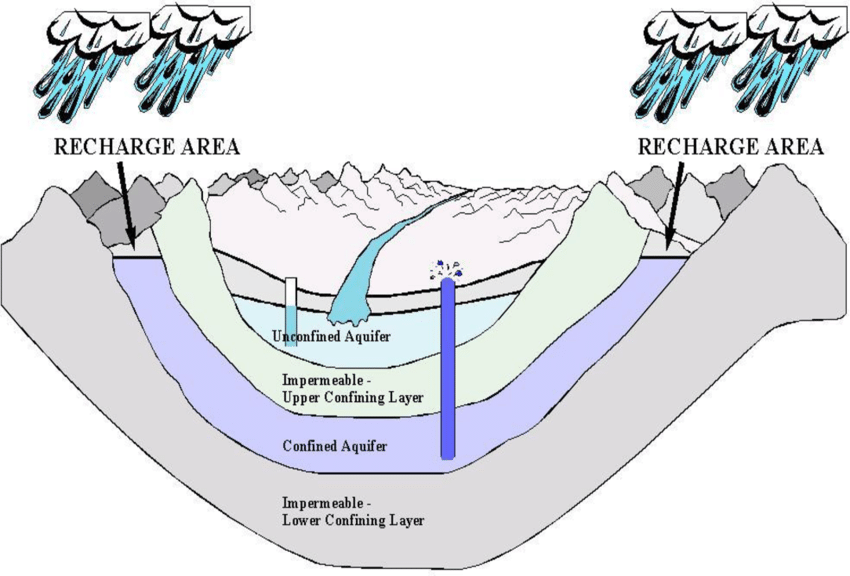
confined vs. unconfined aquifers
confined: surrounded by impermeable rock (clay) which impedes water flow
unconfined: made of porous rock covered by soil
unconfined: made of porous rock covered by soil
18
New cards
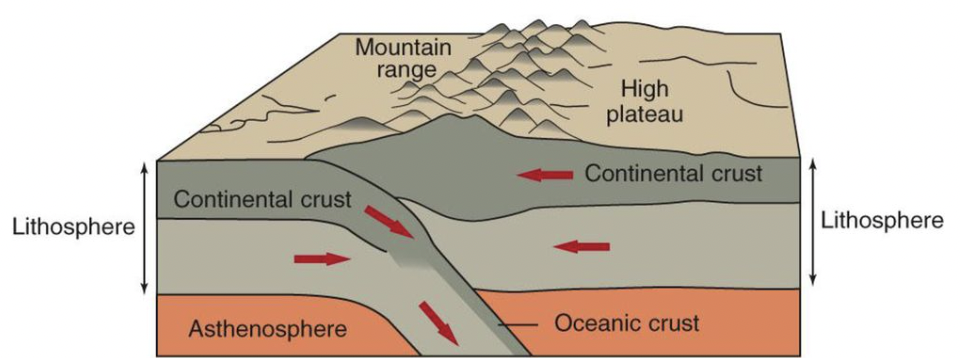
continental-continental convergent boundary
two continental plates collide, leading to mountain ranges being created as the colliding crust is compressed and thus pushed upward
19
New cards
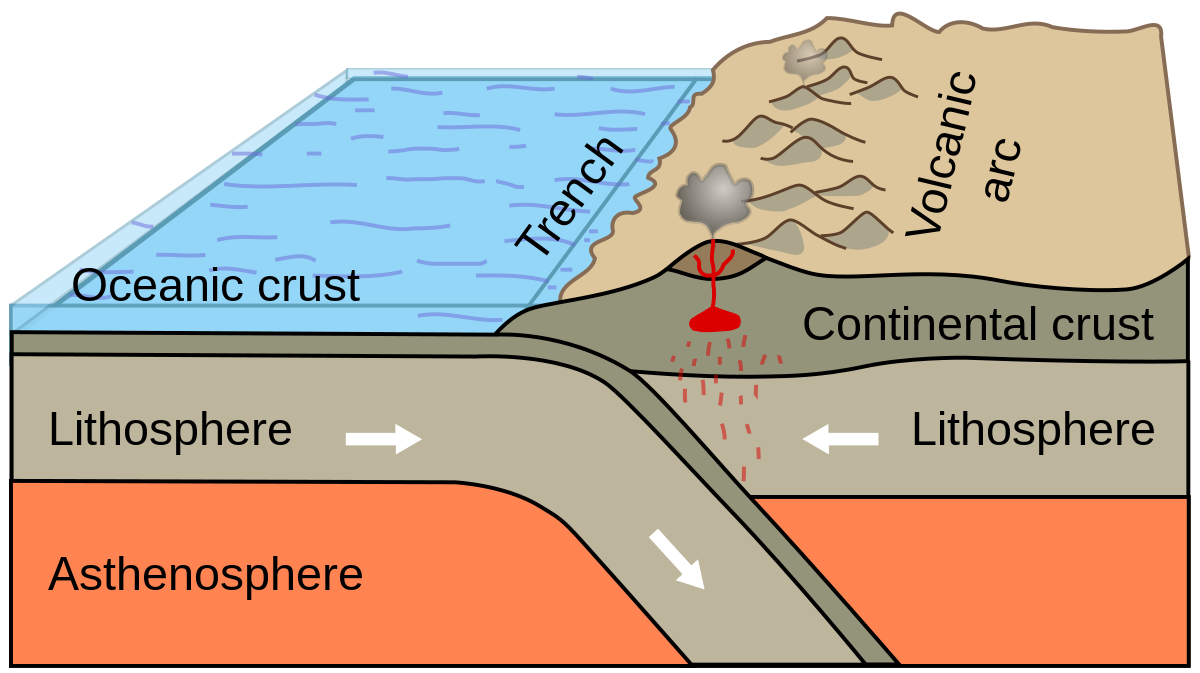
continental-oceanic convergent boundary
subduction occurs where the plates collide and the oceanic plate bends and slides into the mantle
20
New cards
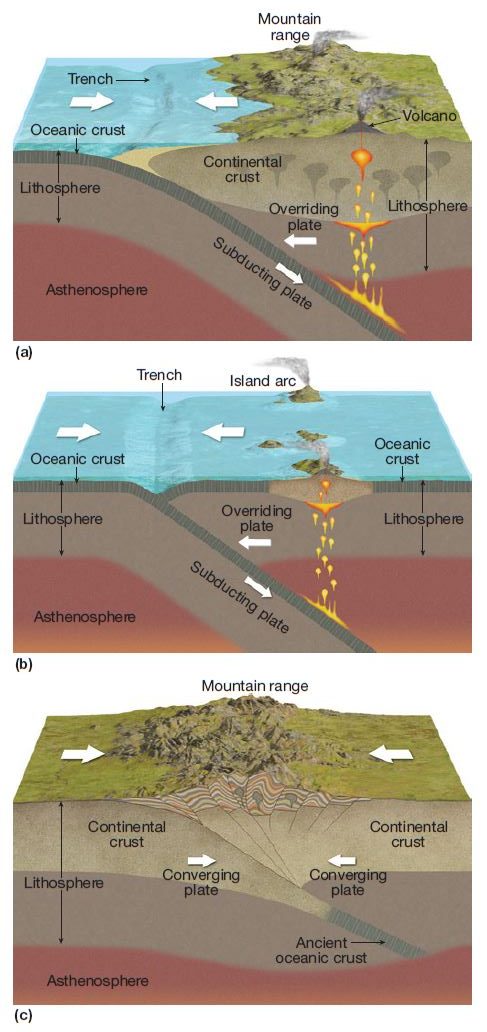
convergent plate boundary
tectonic plate boundary where 2 plates collide/crash into each other
21
New cards
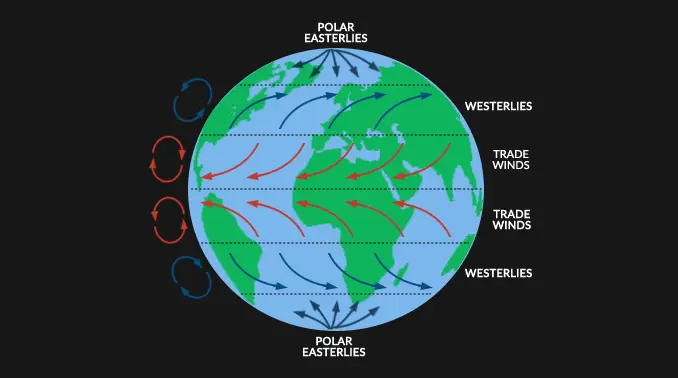
coriolis effect
the effect of earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents
22
New cards
crustal abundance
the average concentration of an element in earth's crust
23
New cards
dams - pros and cons
p: control the flow of water
c: possible overuse of hydroelectric power
c: possible overuse of hydroelectric power
24
New cards
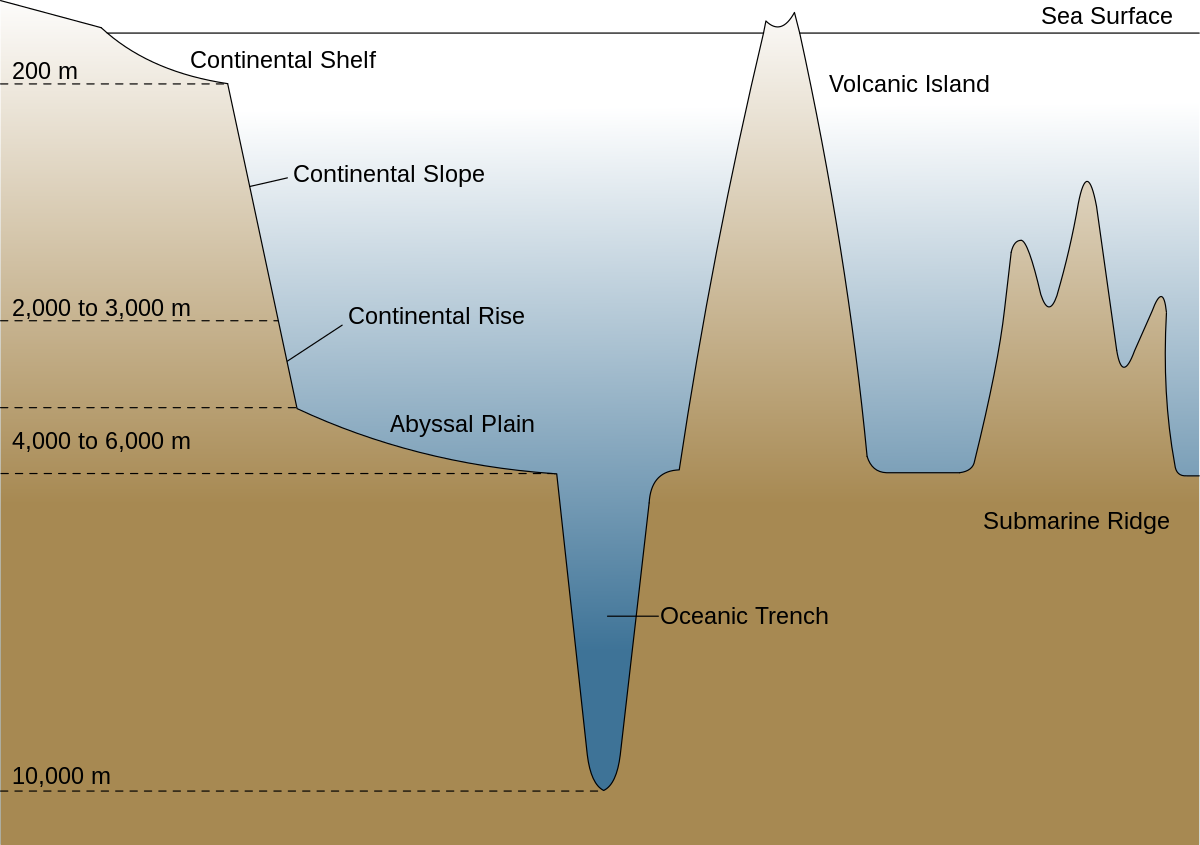
deep-ocean trench
indent in the ocean's surface floor - the deepest part of the ocean
25
New cards
desalination
obtaining freshwater by removing salt from saltwater
26
New cards
detritivores
organisms that eat dead/decaying organic matter
27
New cards
dikes
barrier used to prevent ocean water from flooding
28
New cards
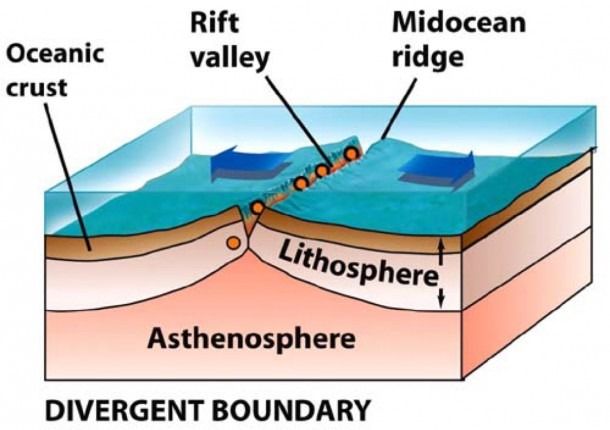
divergent plate boundary
boundary between 2 oceanic plates that are moving away from each other to form new ocean crust
29
New cards
drip irrigation
irrigates through a slowly-dripping hose
30
New cards
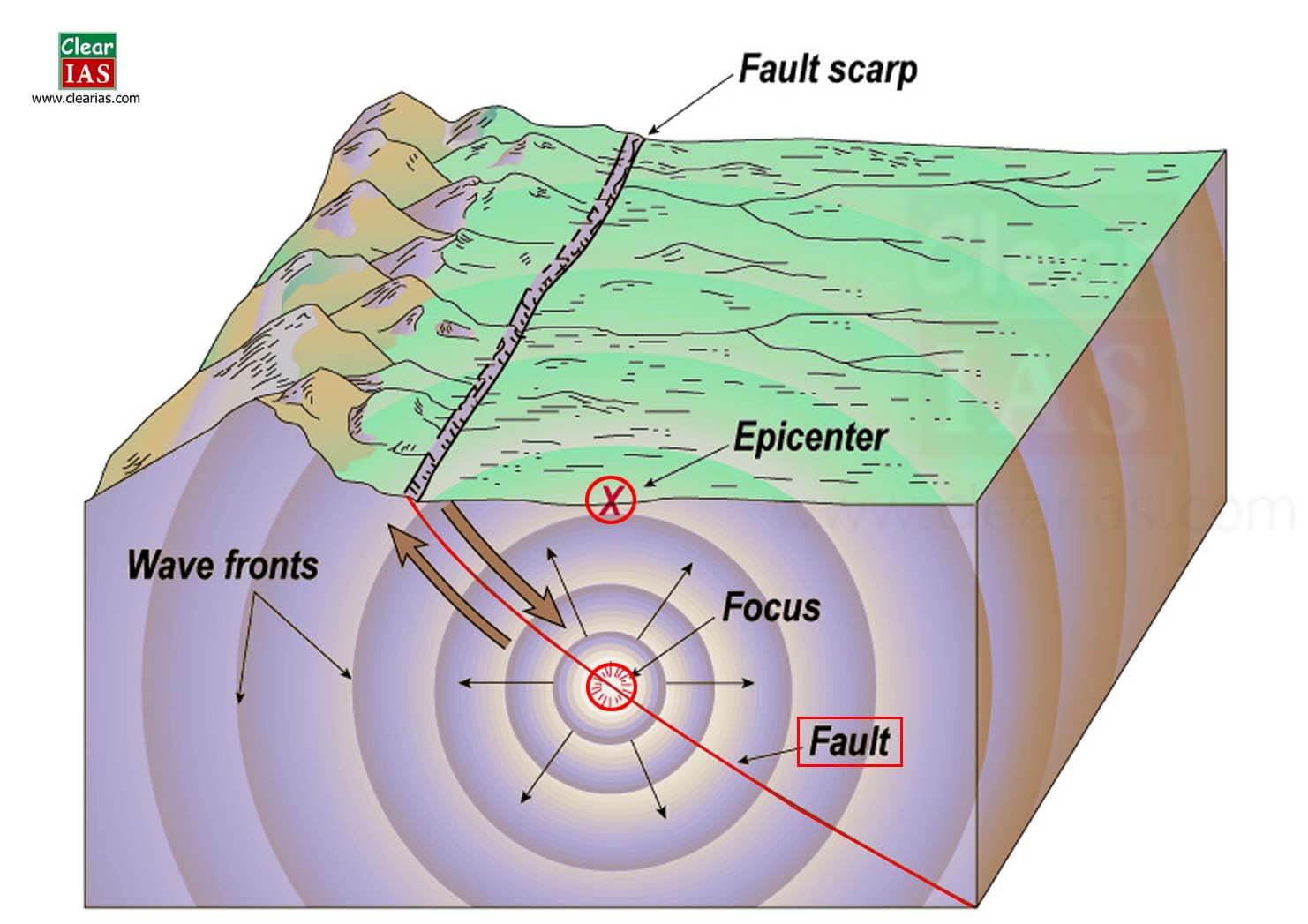
earthquake
sudden movement/vibration of earth's crust caused by a release of potential energy along a fault
31
New cards
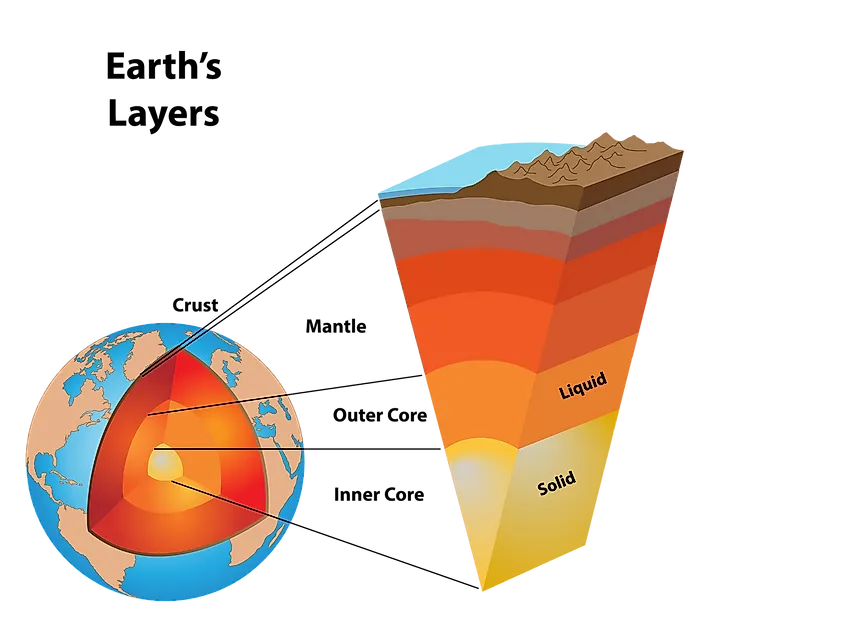
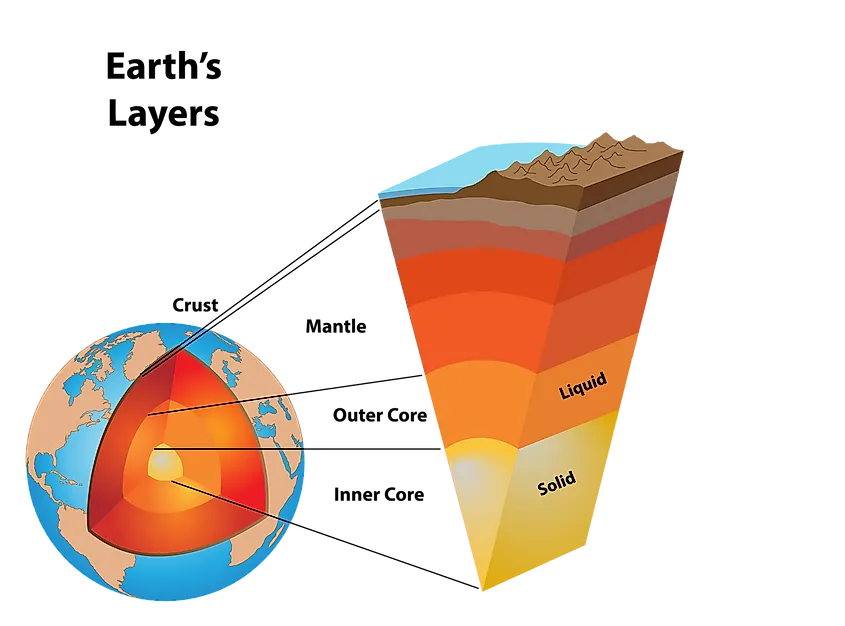
earth's layers
1 - crust
2 - mantle
3 - outer core
4 - inner core
2 - mantle
3 - outer core
4 - inner core
32
New cards
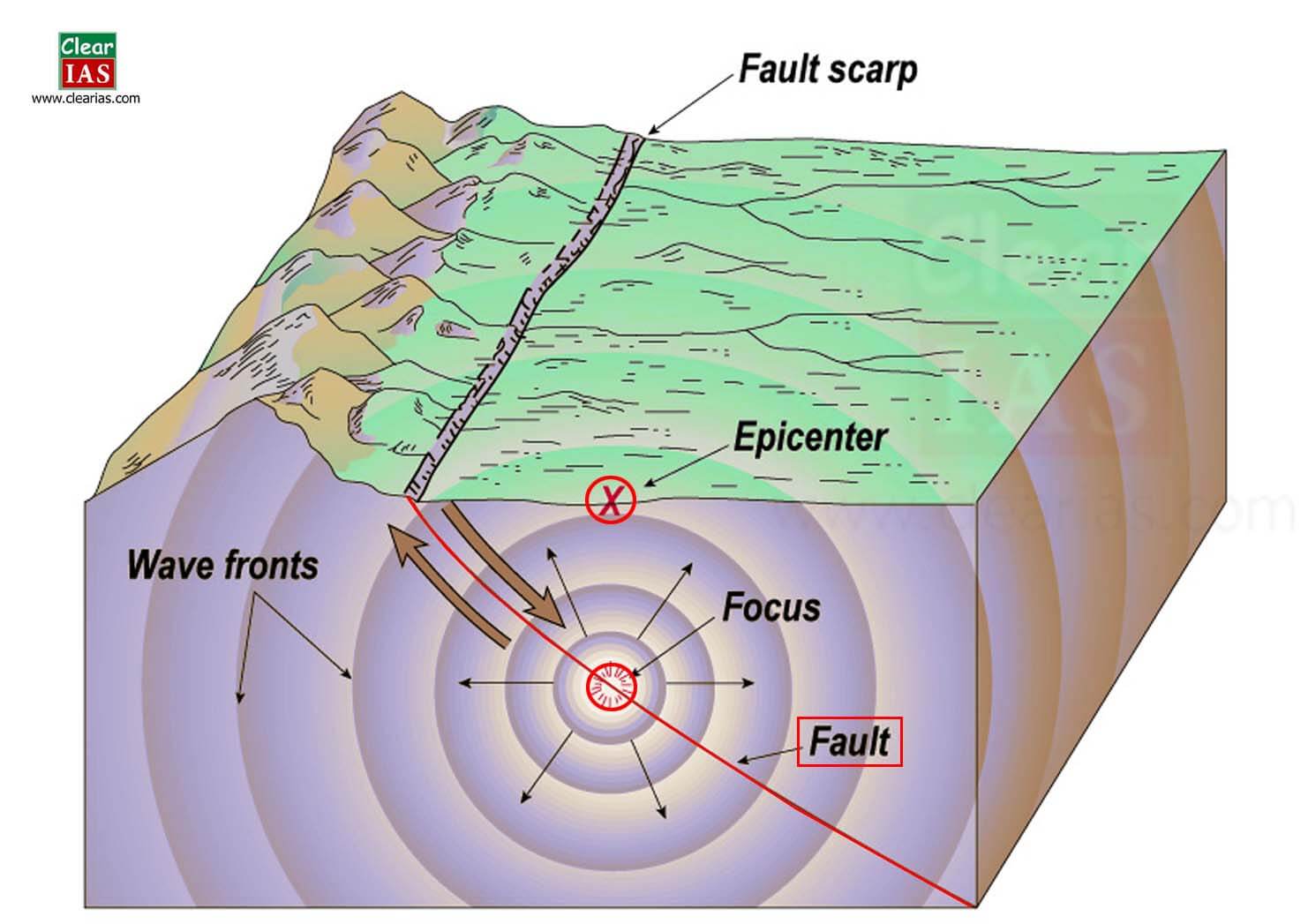
epicenter
the point on earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
33
New cards
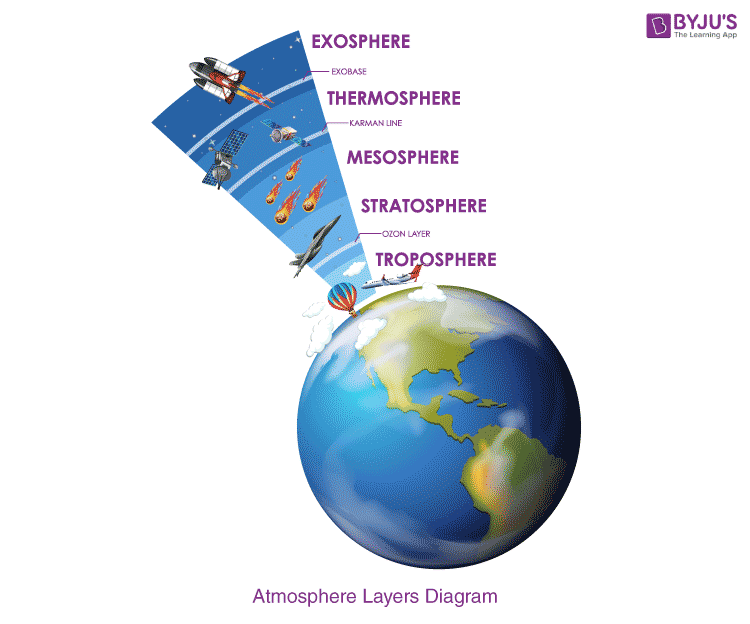
exosphere
uppermost region of earth's atmosphere
34
New cards
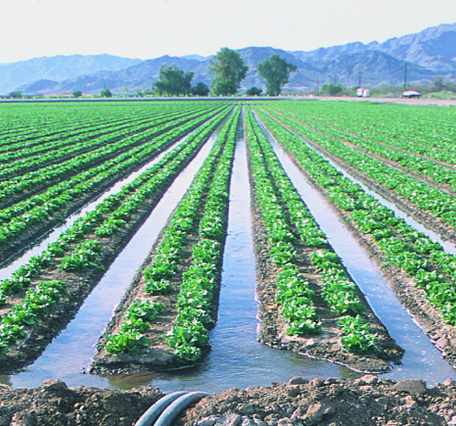

flood irrigation
form of irrigation in which the entire field of crops is flodded
35
New cards
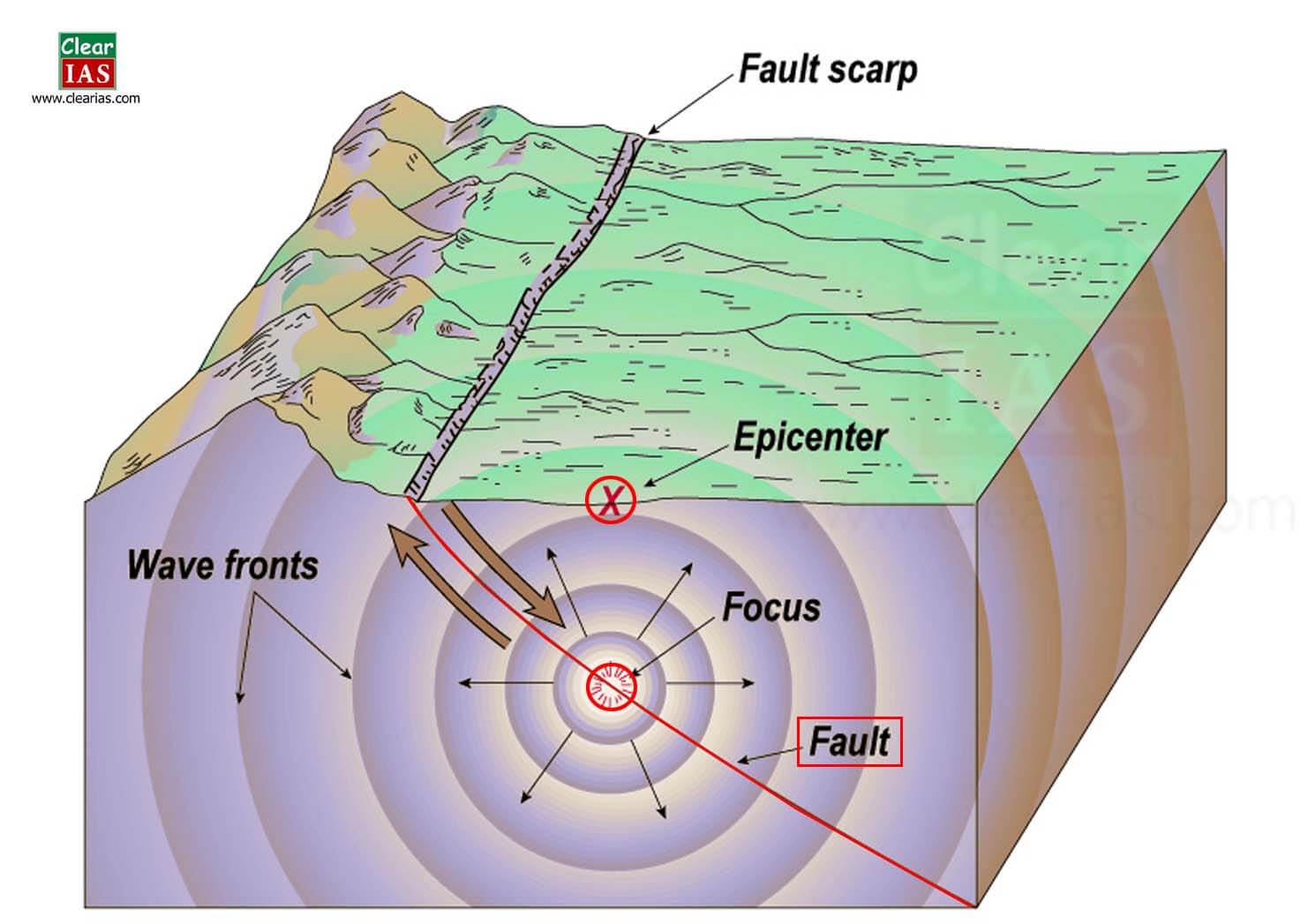
focus
location inside earth's crust where an earthquake originates
36
New cards
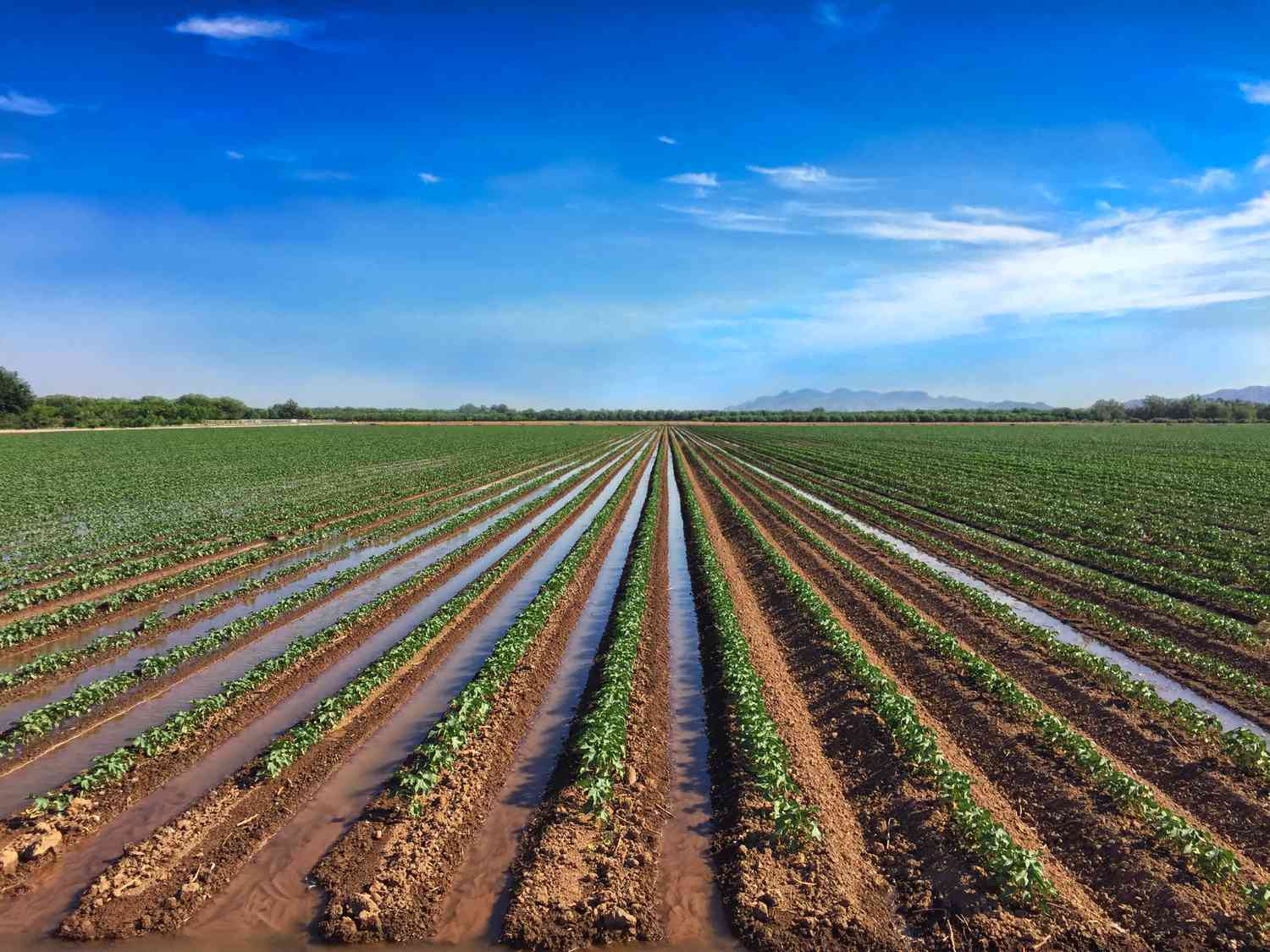

furrow irrigation
form of irrigation in which trenches are digged between rows of crops
37
New cards
impermeable surfaces
pavement/buildings that don't allow water penetration
38
New cards

levee
wall which blocks overflowing in rivers
39
New cards
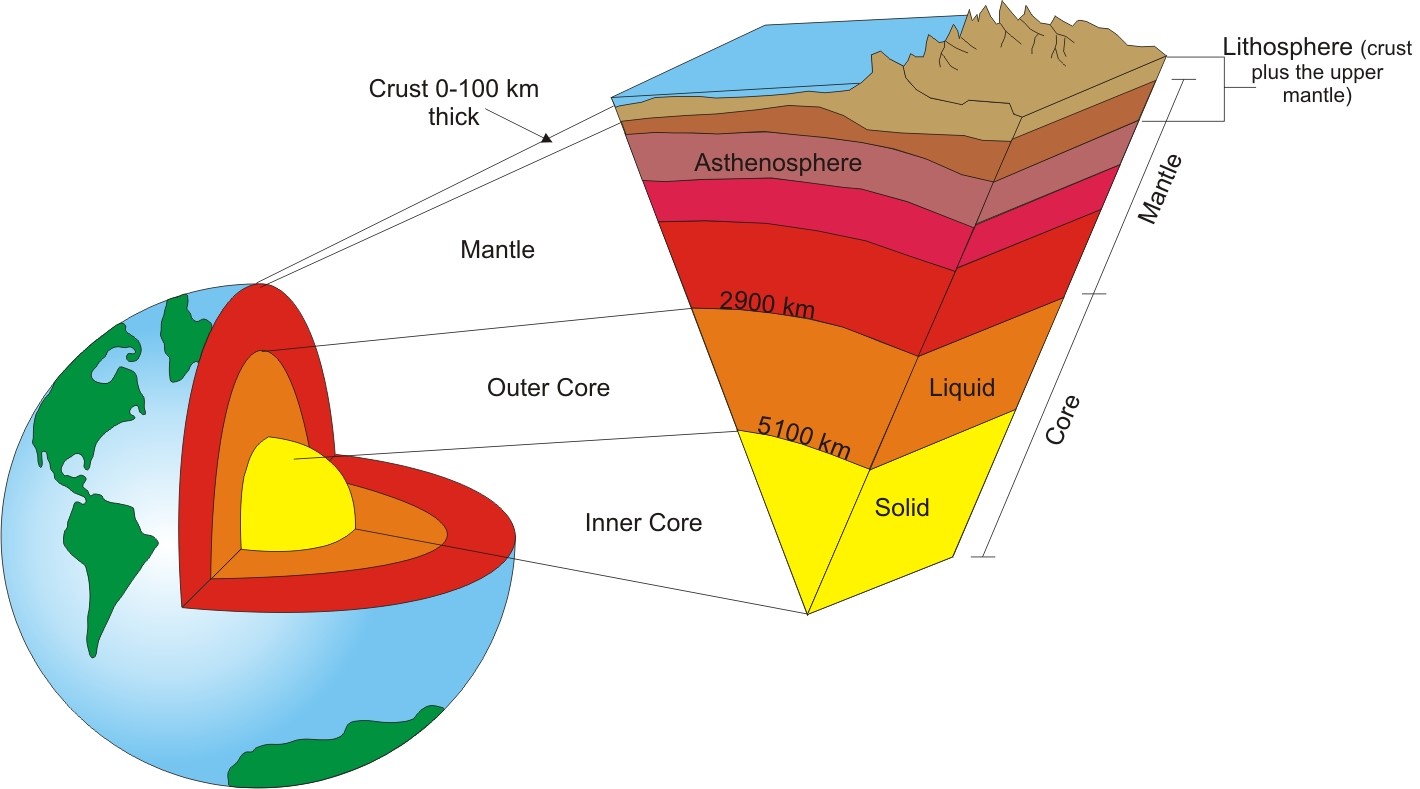
lithosphere
contains the crust & mantle
40
New cards
mantle
contains magma (molten rock)
41
New cards
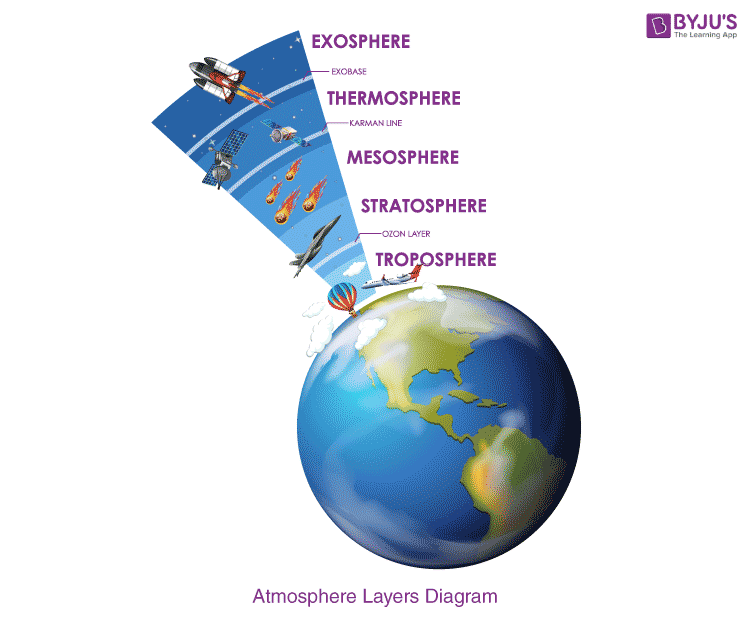
mesosphere
third layer of the atmosphere with little amounts of oxygen
42
New cards
metal
an element with properties that allow it to conduct electricity and heat energy and to perform other important functions
43
New cards
microorganisms
microscopic organisms which may exist in a single-celled form or in a colony of cells
44
New cards
mining legislation
1 - mining law of 1982: promoted the recovery of minerals and fuels from federal land
2 - surface mining control and reclamation act of 1977: promoted minimal disturbance of land during mining
2 - surface mining control and reclamation act of 1977: promoted minimal disturbance of land during mining
45
New cards
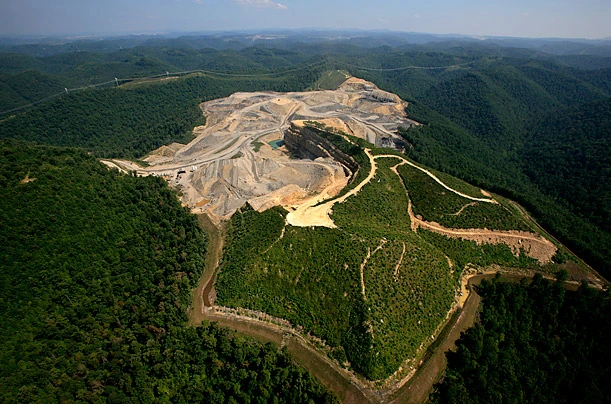

mountaintop removal
type of surface mining in which a mountaintop/ridgeline is destroyed through the use of explosives
46
New cards
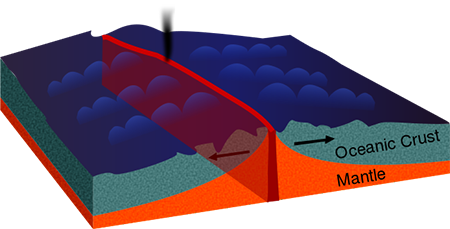
oceanic crust
thinner, more dense, younger crust made of basalt from shield volcanoes at the zone of divergence
47
New cards
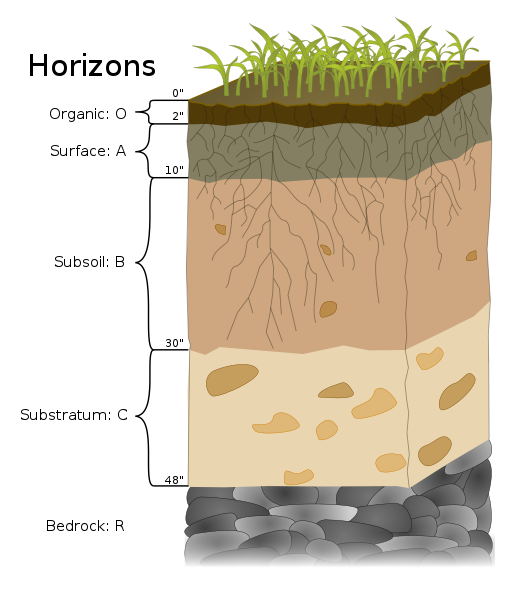
o-horizon
made mostly of leaves, litter, and humus
48
New cards
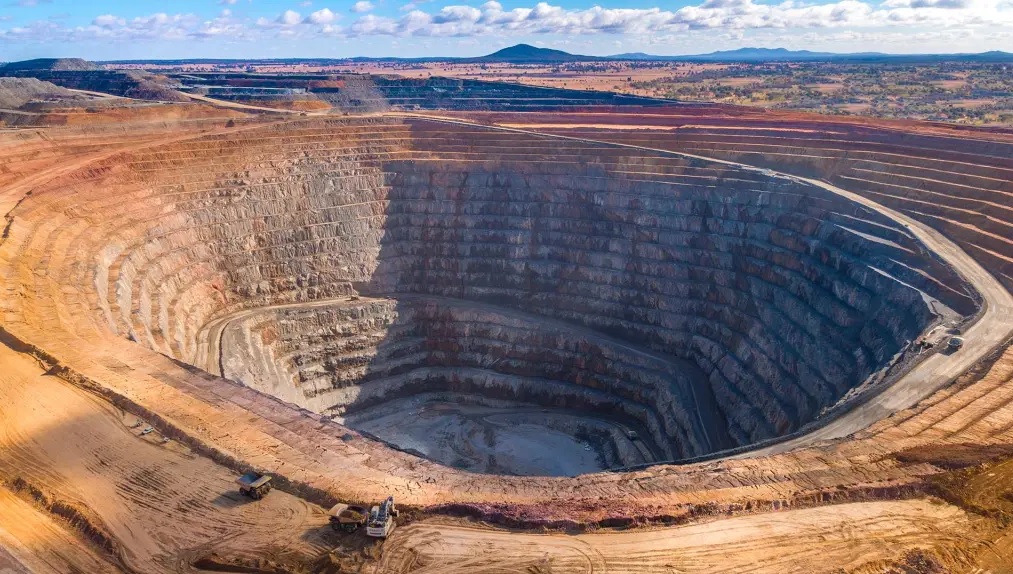

open-pit mining
type of surface mining in which minerals are extracted from an open pit in the ground
49
New cards
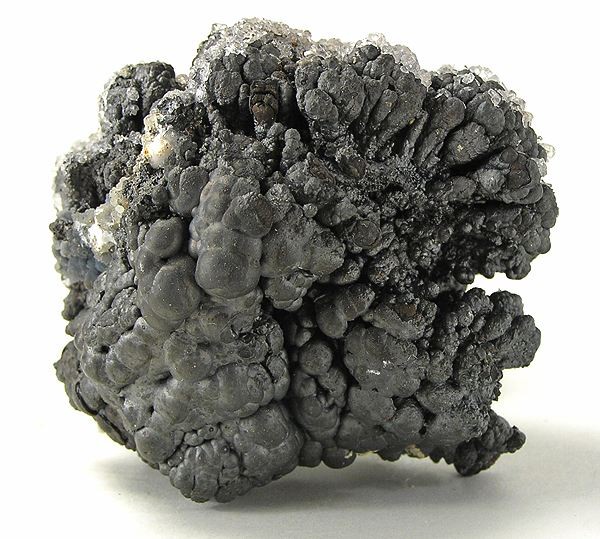

ore
a concentrated accumulation of minerals from which economically valuable materials can be extracted
50
New cards
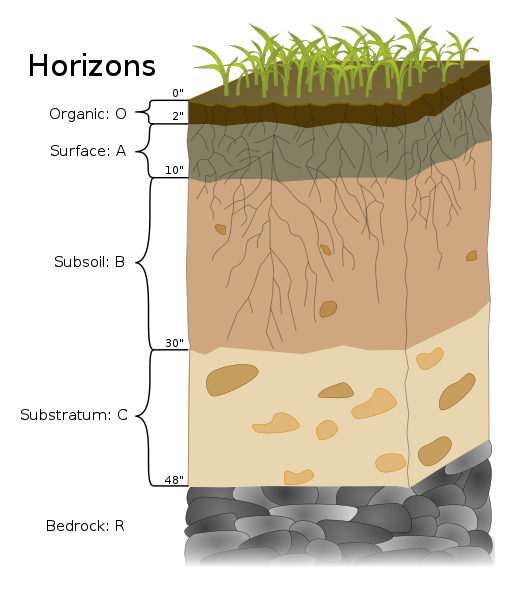
parent material
the rock material from which the inorganic components of soil are derived
51
New cards
permeability
the allowing of water and roots to move between particles in soil
52
New cards
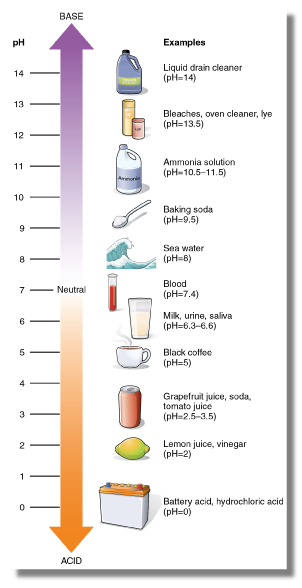
pH level
measure of how acidic/basic water is - the potential of hydrogen
53
New cards
physical weathering
the breaking down of rocks through physical processes (e.g., freezing, thawing)
54
New cards

placer mining
a type of surface mining in which water is used to separate ore from surrounding sediment
55
New cards
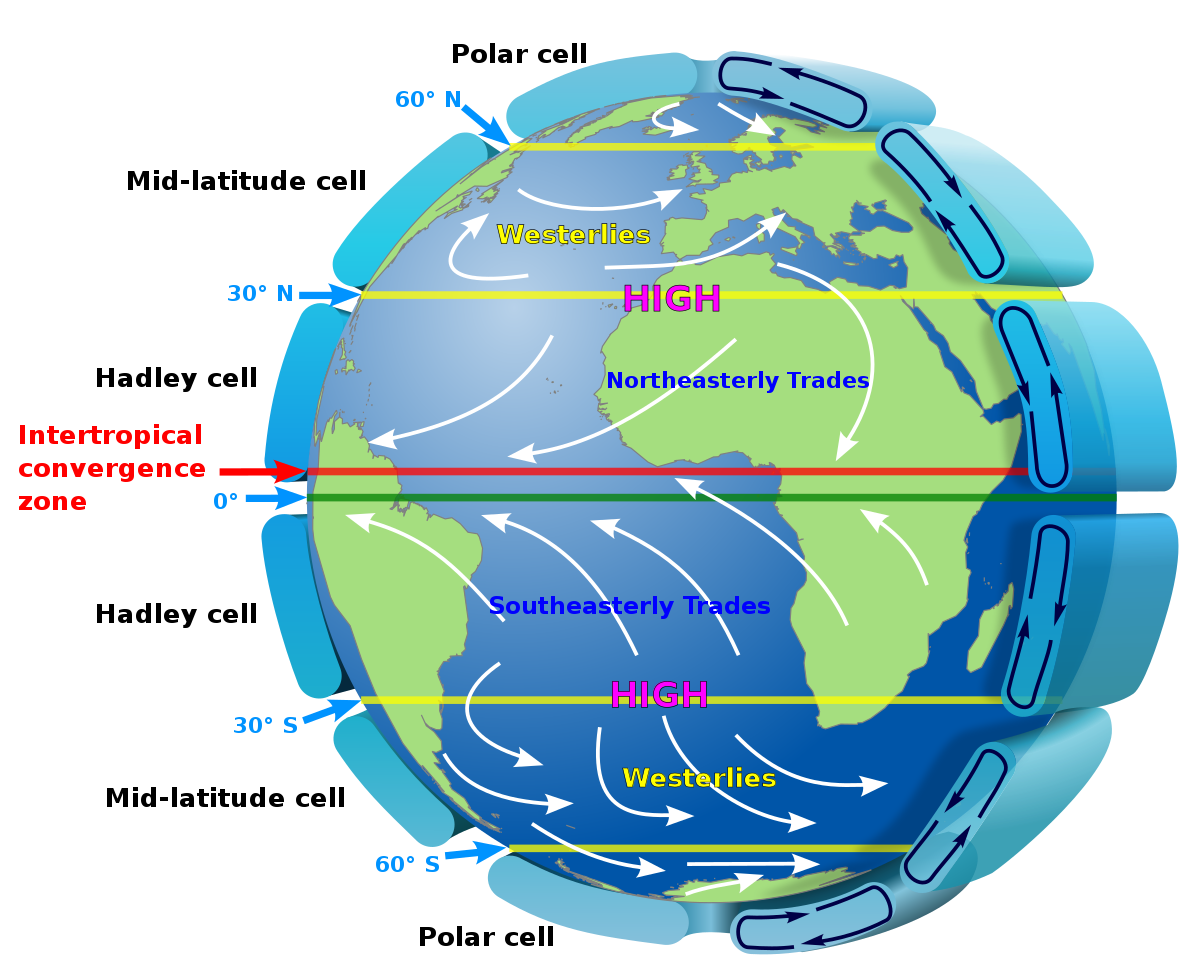
prevailing winds
winds that blow in specific directions over specific areas of the earth
56
New cards
reserve
the known quantity of a resource that can be economically recovered
57
New cards
richter scale
a logarithmic scale ranging from 1-10 used to express the energy released by an earthquake
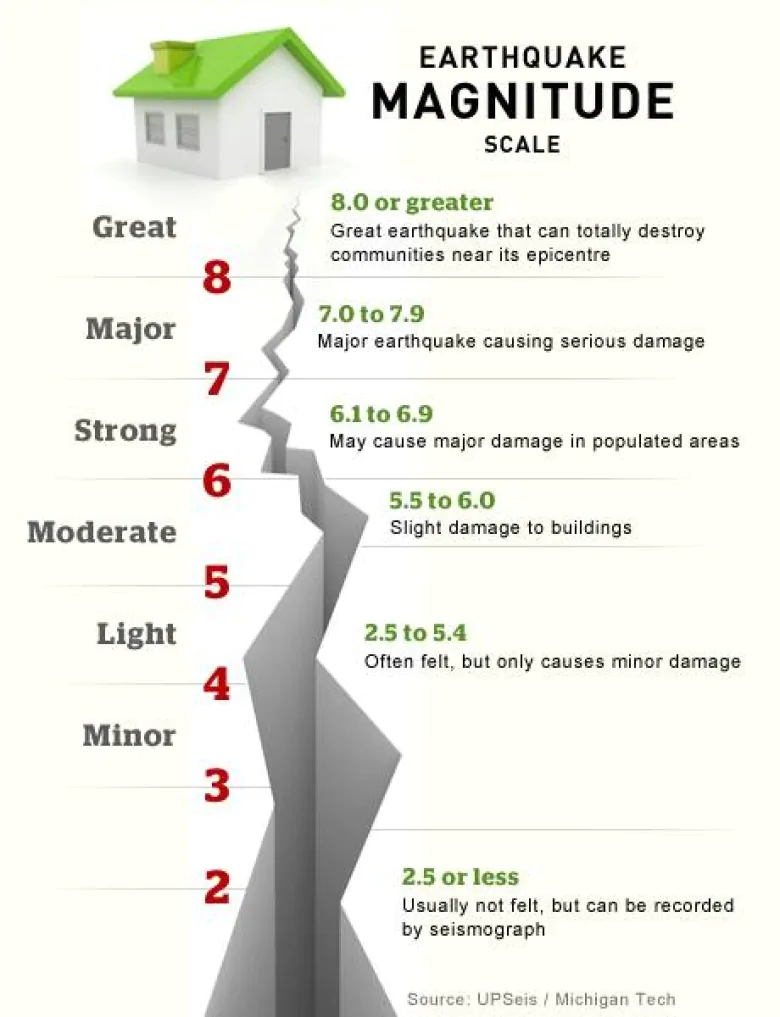
58
New cards
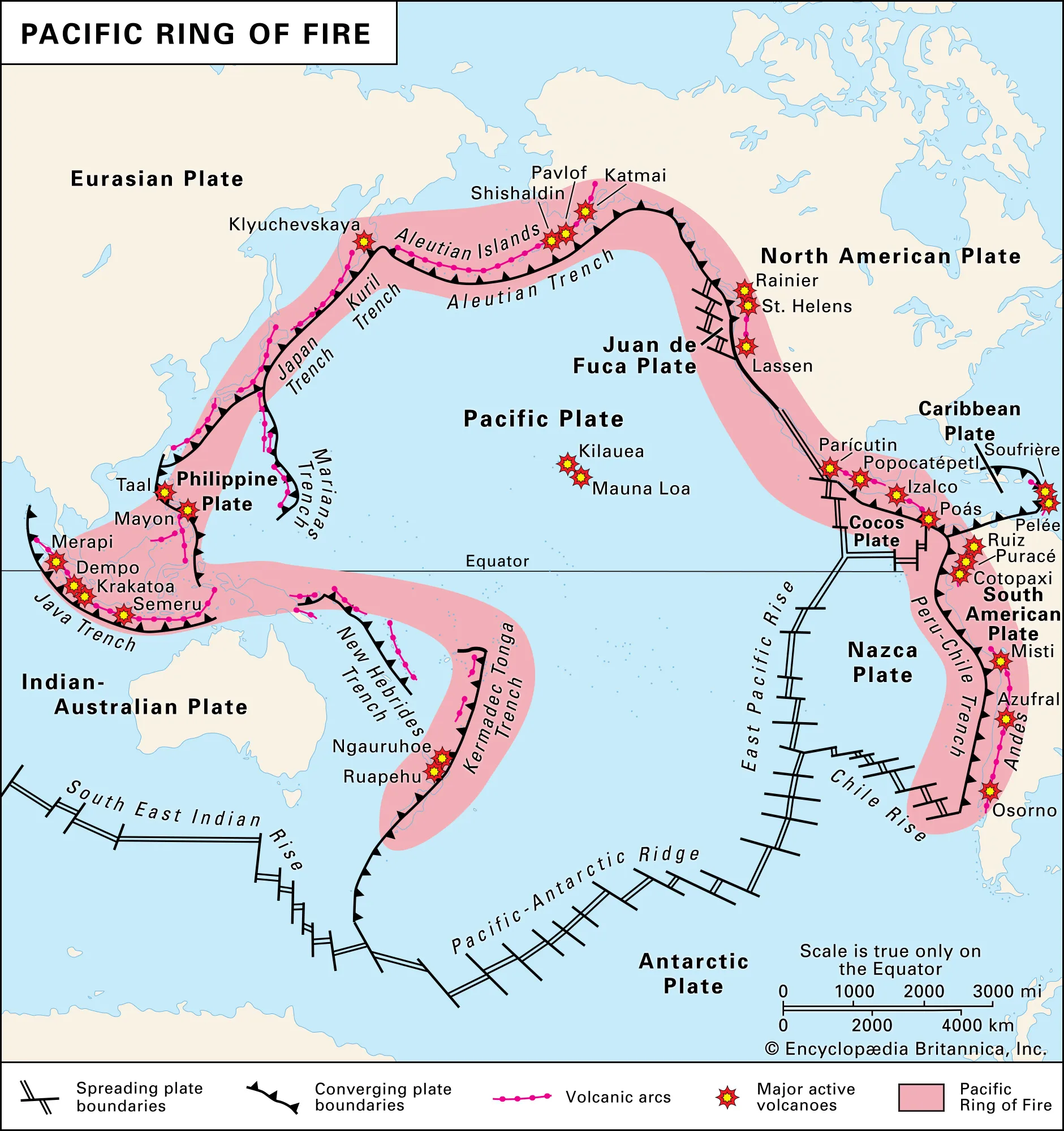
ring of fire
a major belt of volcanic activity that rims the pacific ocean caused by oceanic-continental plates at convergent boundaries overlapping
59
New cards
saltwater intrusion
rapid pumping that draws down the water table and leads to lessening pressure and saltwater infiltration
60
New cards
seafloor spreading
the formation of new oceanic crust as a result of magma pushing upward and outward from earth's mantle to the surface
61
New cards

shield volcano
a wide, gently sloping mountain made of layers of lava and formed by quiet eruptions in rift valleys and erupt basalt
62
New cards
soil
a mixture of mineral particles and organic material that covers the land, and in which terrestrial plants grow
63
New cards
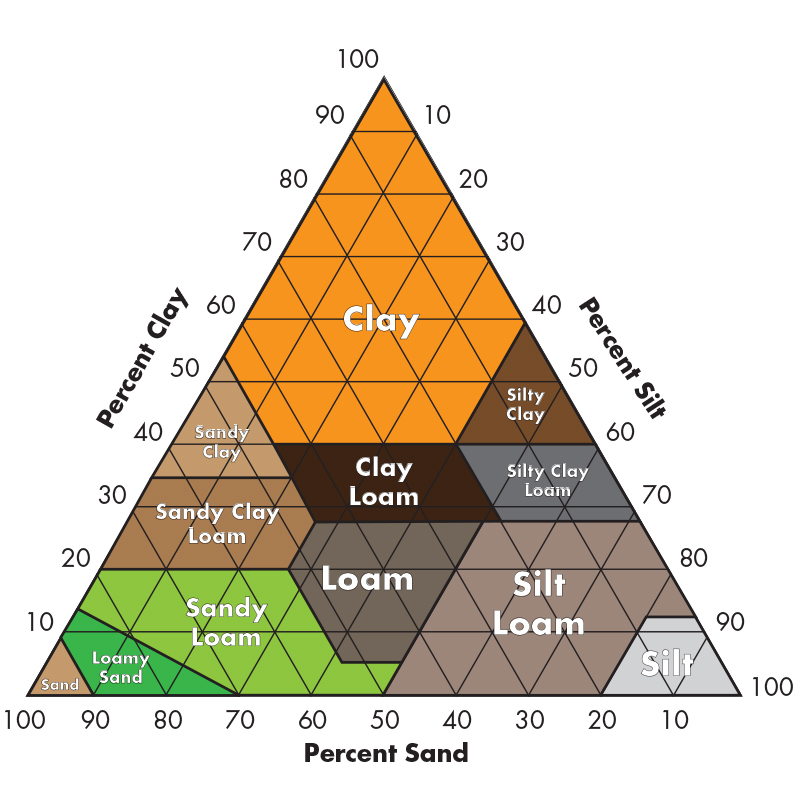
soil triangle
a graphic explanation of the proportions of sand, silt, and clay in soil
sizes from biggest to smallest:
1 - sand
2 - silt
3 - clay
sizes from biggest to smallest:
1 - sand
2 - silt
3 - clay
64
New cards
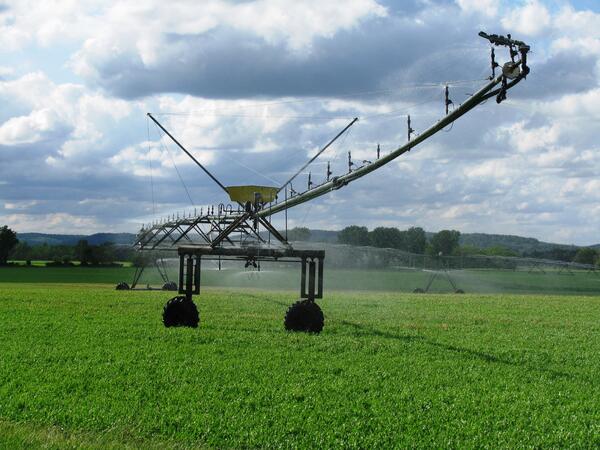

spray irrigation
form of irrigation in which a field of crops is sprayed
65
New cards
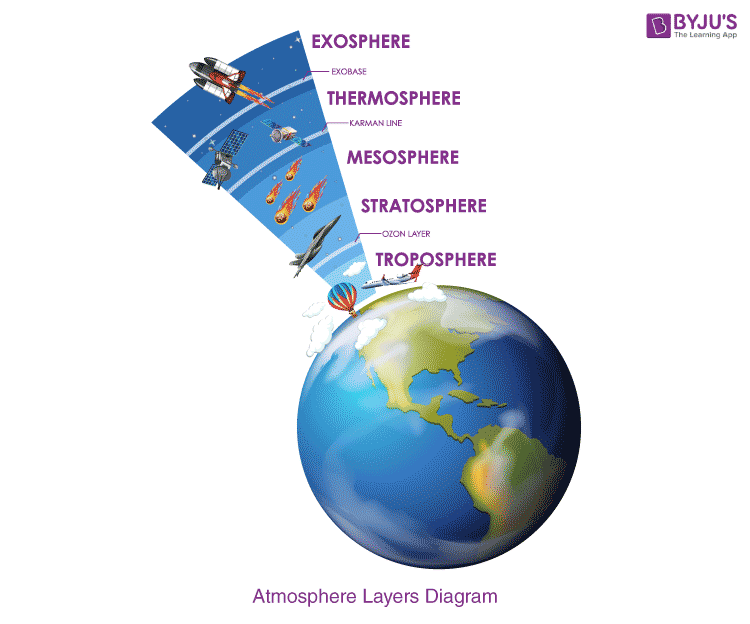
stratosphere
second layer of earth's atmosphere, also known as the ozone layer
66
New cards
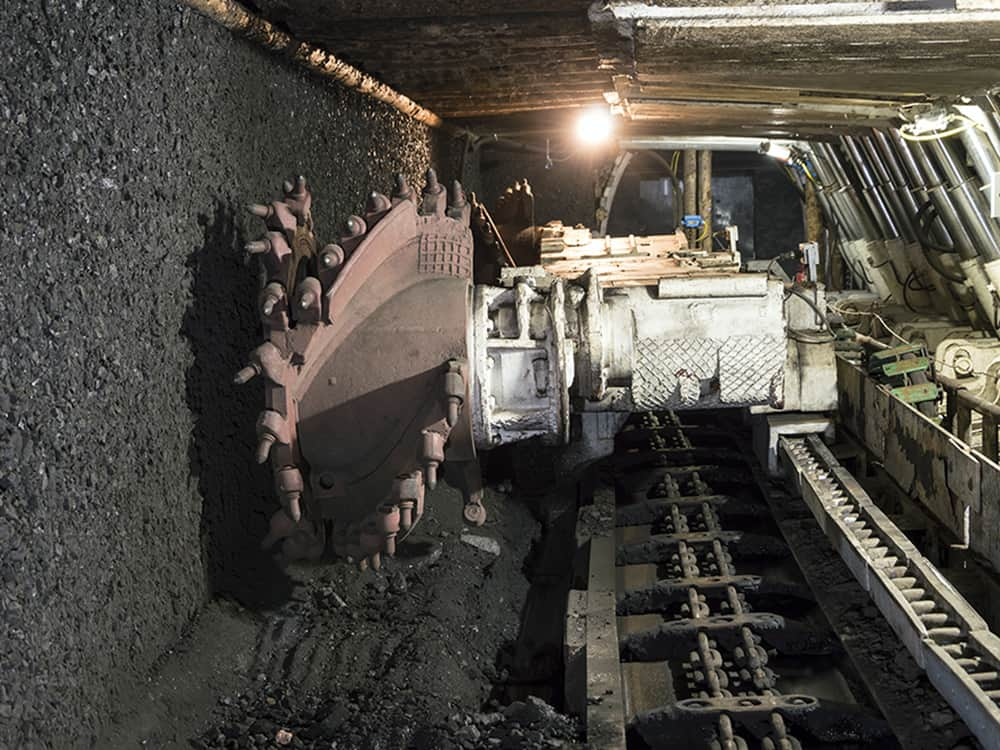

subsurface mining
mining below the surface
67
New cards
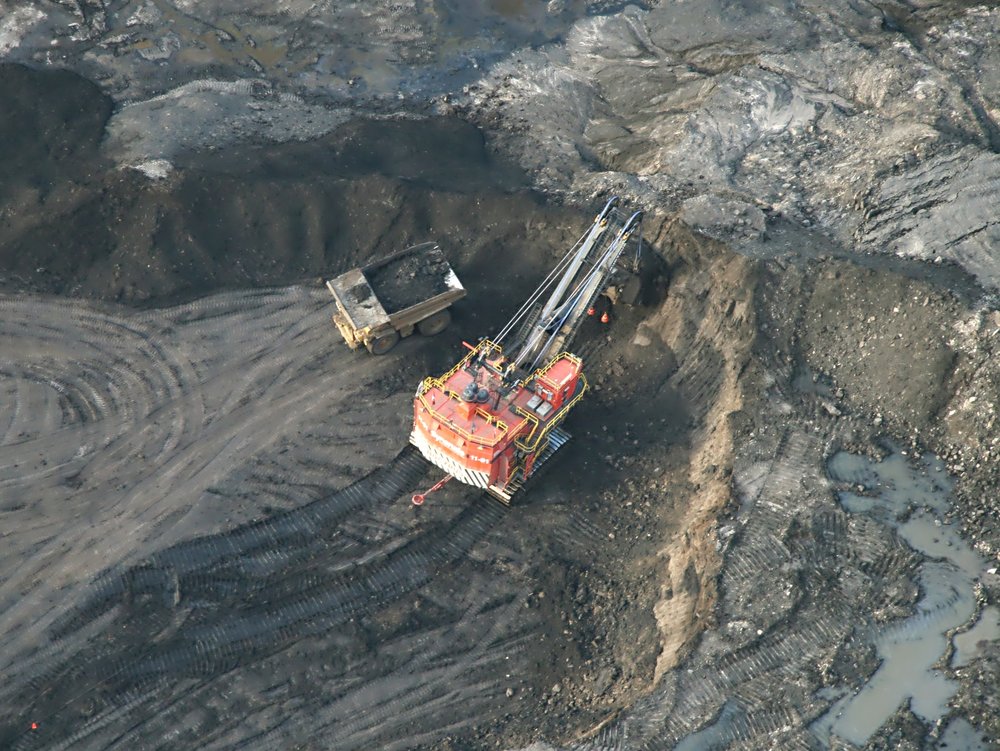

surface mining
mining above or on the surface
68
New cards
symbiosis
interactions between different species
types:
* mutualism: both benefit (+, +)
* commensalism: 1 benefits, the other is unaffected (+, o)
* parasitism: 1 benefits, the other is harmed (+, -)
types:
* mutualism: both benefit (+, +)
* commensalism: 1 benefits, the other is unaffected (+, o)
* parasitism: 1 benefits, the other is harmed (+, -)
69
New cards
tailings
waste material from mining ore. also known as mining spoils
70
New cards
texture
the amount of rock, sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample
71
New cards
theory of hotspots
some areas with hotspots are randomly more active than others
72
New cards
theory of plate tectonics
earth's lithosphere is broken up into huge, moving slabs of rock driven by motions in the mantle, causing geological events
73
New cards
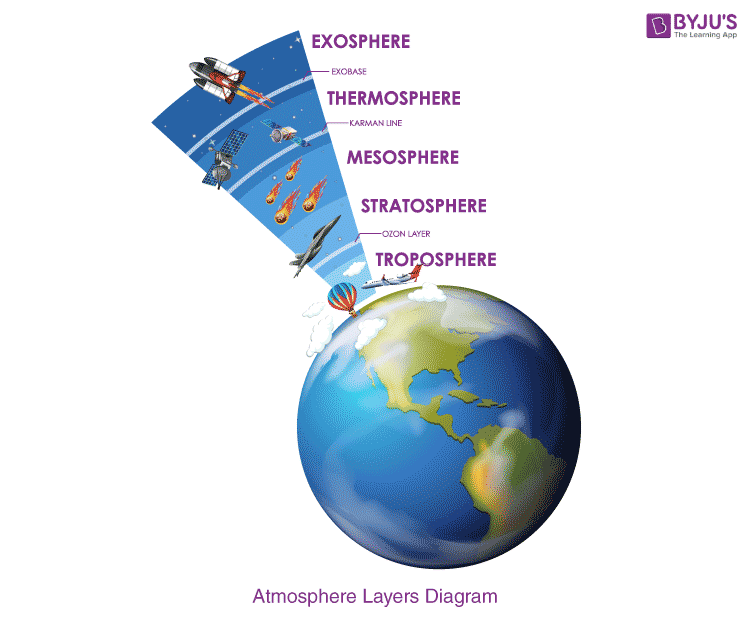
thermosphere
fourth layer of the earth's atmosphere where the sun's radiation is absorbed and puts on the auroras
74
New cards
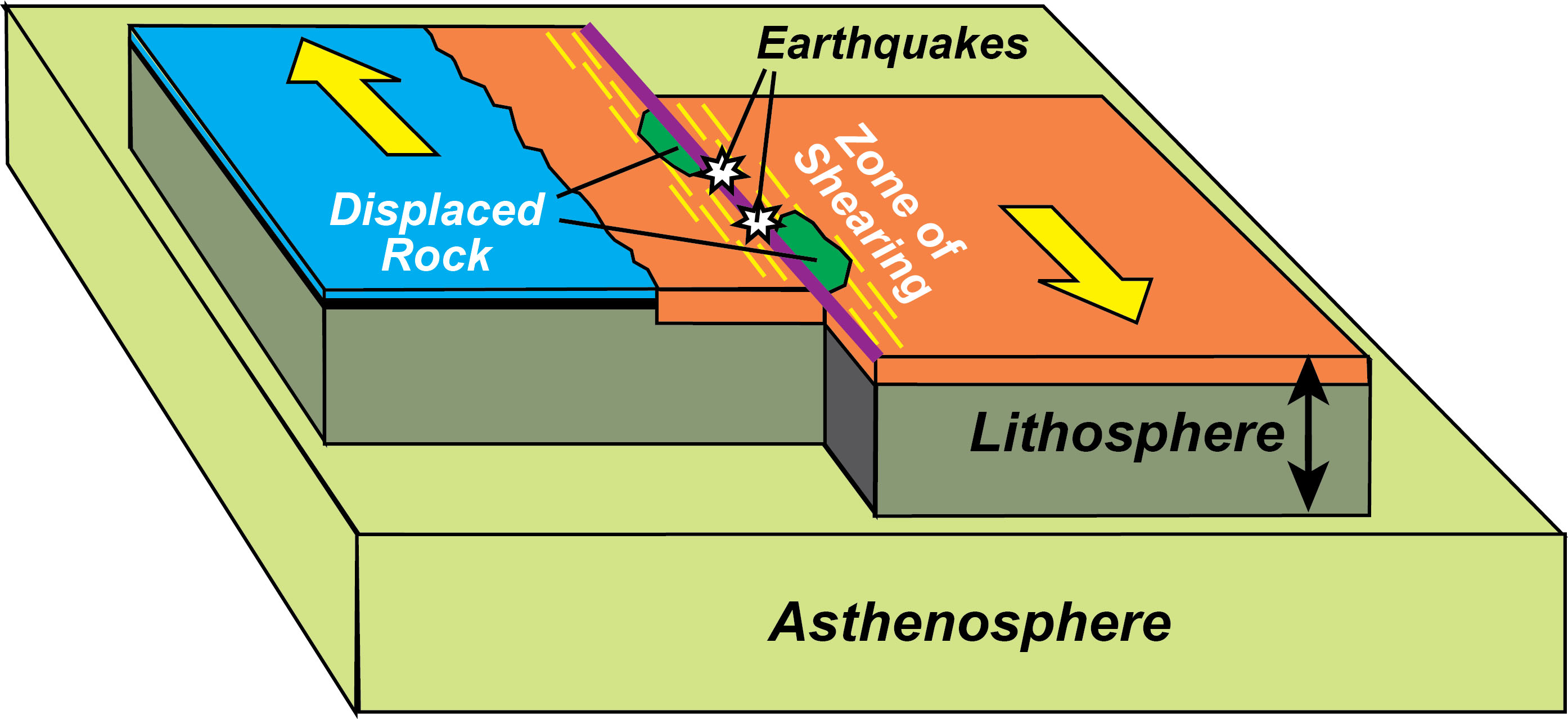
transform plate boundary
boundary between 2 plates that are sliding past one another
75
New cards
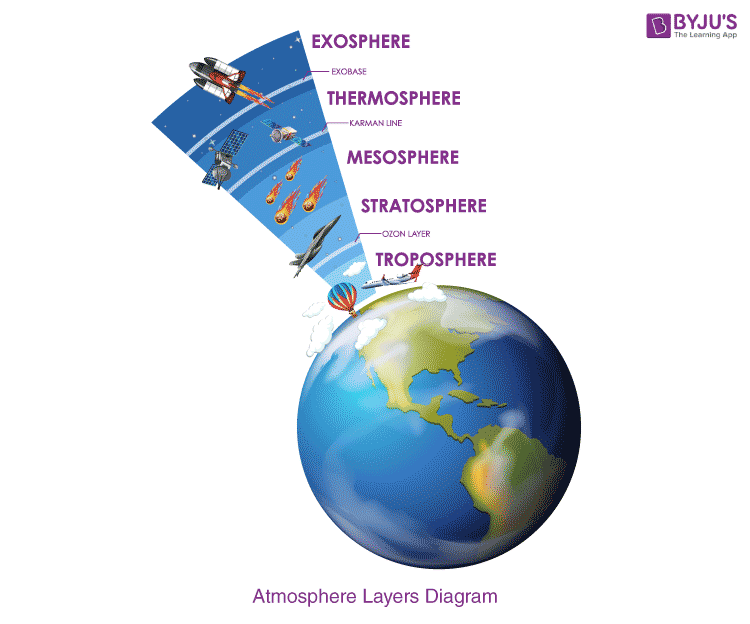
troposphere
first layer of the earth's atmosphere where weather, climate, and life form, as well as biogeochemical cycles
76
New cards
water table
the uppermost at which groundwater fully saturates rock/soil
77
New cards
weathering
the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces
can be physical (wind, rain, freezing/thawing of ice), biological (roots of trees cracking rocks), or chemical (acid rain, acids from moss/lichen)
can be physical (wind, rain, freezing/thawing of ice), biological (roots of trees cracking rocks), or chemical (acid rain, acids from moss/lichen)