Psych exam 3
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Superego
‘you can’t have it"‘, it is the counterbalance to the Id and is based on societies moral values and ideals
Self stigma
occurs when a person accepts and agrees with the negative stereotypes and prejudicial beliefs held against themselves.
social stigma
Social stigma is the disapproval of, or discrimination against, an individual or group based on perceived characteristics that serve to distinguish them from other members of a society
Behaviourism limitations
It’s not enough for complex mental health conditions
When treating certain disorder e.g. severe depression behavioural therapy often must be used in conjunction with other medical and therapeutic treatments
It can help manage certain aspects of these conditions but shouldn’t be used alone.
It may not account for underlying problems
Focus on current problems with functioning and may not address underly factors that contribute to a mental health problem
It may not address the whole picture
Centred on the individual working to change their behaviours.
Does not address how situations and interpersonal relationships might be contributing to a person’s problems.
Behaviourism strengths
Effective therapeutic techniques are rooted in behaviourism
Useful in changing maladaptive behaviours in both children and adults
Widely used in treating a wide array of conditions mainly anxiety and addiction
Improved communication
Coping strategies
Healthier thought patterns
Self-esteem
Efficacy depends on treatment and condition
Treatment in substance disorders depends on substance being misused
Cognitive behaviourism limitations
Unscientific because we can’t observe the forces under discussion
Other perspectives find the computer model to be cold and mechanical, however cognitive theorists state the mind engages in active processing unlike a computer, and humans possess creativity and individuality
Cognitive behaviourism strengths
Goes beyond behaviourism
teach’s knew thought patterns
is most widely used
An example of superego
A child who wants to take a toy from another child, but doesnt because sharing is important and the child knows it would be wrong.
Protective factors
are characteristics associated with a lower likelihood of negative outcomes or that reduce a risk factor's impact
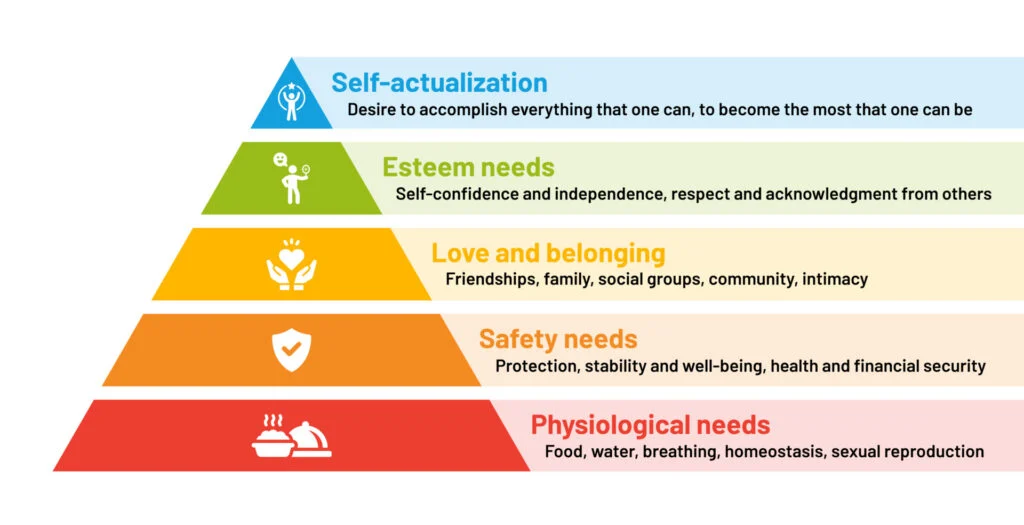
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
physiological
safety needs
love needs
esteem needs
Self-actualisation
CBT
helps individuals learn coping skills to change their thinking patterns, manage emotions, and improve their behavior.
Stress
A state of physiological and psychological arousal produced by internal or external stressors that are perceived by the individual as challenging or exceeding their ability or resources to cope.
Stressor
the stimulus that cause or produces stress internal or external
example of stressor
exams
distress
negative psychological response to a stressor eg anger, anxiety, tension
is short term or long term
Eustress
positive psychological response to a stressor eg enthusiastic, motivated
it provides energy and motivation
Stigma
refers to the negative attitudes and discrimination that people face based on certain characteristics that make them different from others in society
Anxiety disorders
When anxiety takes control and dominates a person’s life
Example of anxiety disorders
Generalised Anxiety Disorder
Phobia
PTSD
Panic disorder
OCD
Id
‘I want it’ Unconscious urges and desires that need immediate gratification to relieve tension from this state
an example of Id
Sally is thirsty rather than waiting for someone to refill her glass she drinks from Johns glass.
Mood disorders
A disturbance in the person’s emotions
Example of mood disorders
Major depressive Disorder
Bipolar disorder
Dysthymic disorder
Ego
‘lets talk it over’ mainly conscious thought that will postpone action designed to release tension until an appropriate solution is found. Results the conflict between the Id and the Superego.
PTSD
An anxiety disorder triggered by a traumatic event. common symptoms include flashbacks, avoidance, negative thoughts and hyperarousal.
Bipolar disorder
a mood disorder and is characterised by extreme mood swings often resembling emotional highs known as mania and emotional lows or depression.
Risk factors
characteristics at the biological, psychological, family, community, or cultural level that precede and are associated with a higher likelihood of negative outcomes.
Systematic desensitisation
A reduction in fear, anxiety, or aversion brought about by planned exposure to aversive stimuli
4p model
A structured method used to describe assess and observe a patient’s narrative. It helps clinicians understand the progression and development of mental health disorders.
psychosexual stages
Oral
Anal
Phallic
Latency
Genital
What is the oral stage?
(0-1) It involves the mouth and the issues caused are smoking, gum chewing, and nail biting. Activities are tasting and suckling.
What is the anal stage?
(2-3) Involves Bowel and bladder can cause obsessiveness. Activities are toilet training.
What is the phallic stage?
(3-6) Involves genitals can cause pride, vanity, and exhibitionism. The complex is the Oedipus and Electra Complex ie wanting to sleep with someone like your respective parent. Activity is the excessive attachment to the parent of the opposite sex.
What is the latency stage?
(6-puberty) sexul feelings are inactive, the complex is penis envy. Most of the time is spent interacting with peers of the same sex.
What is the genital stage?
(puberty and beyond) Mature sexual interests, sexual attractions begin.
Free association
A therapy technique involving saying what comes to mind without caring.
Free association purpose
to lower the defences so that unconscious material can emerge.
transference
Transferring feelings of one onto another
resistance
Is interpreted as as revealing something important in unconscious thoughts.
Free-will
The ability to freely make choices that are controlled by genetics, learning, or unconscious forces. A person is responsible for their own choices.
e.g. commit crime or not
self-efficacy
Your belief in your ability to complete a task or achieve a goal.
self-actualisation
The process of becoming ‘everything you are capable of becoming’.
client-centred therapy
A non directive therapy, it emphasises accepting one’s true self. To achieve this the therapist creates a safe ‘atmosphere of growth’.
4 basic principles of therapy
Unconditional positive regard
Empathy
Authentic
Reflects
Humanistic
an approach that focuses on human experience, problems, potentials, and ideals
Behavioural
Assumes that people have learned to be the way they are - if they have learnt maladaptive behaviours, then they can change them by relearning more appropriate behaviours
Conditioning
Either a given stimulus becomes increasingly effective in evoking a response or a response occurs with increasing regularity in a well-specified and stable environment.
counterconditioning
unwanted responses are inhibited by activating an antagonistic response system
aversion therapy
Uses counterconditioning to treat unwanted habits or harmful behaviours.
An example of aversion therapy
Alcoholism patients are given an aversive drug, which causes vomiting-emetic drug. They start experiencing nausea; at this point, they are given a drink smelling strongly of alcohol, and they start vomiting almost immediately. The treatment is repeated with a higher dose of the drug.
maladaptive thinking
a belief that is false and rationally unsupported
Rational Emotive Behavioural Therapy
Helps recognise irrational beliefs an negative thinking patterns in order to overcome psychological problems and mental disorders
ABC’s
Activating event
Belief
Consequence
cognitive distortions
internal mental filters or biases that increase our misery, fuel our anxiety, and make us feel bad about ourselves.
4 criteria for abnormal behaviour
Maladaptive
Unjustifiable
disturbing
Atypical
strengths of classifying abnormal behaviour
Distinguish diseases
Offer best treatment
Common language among healthcare professionals
Explore causes
Limitations of classifying abnormal behaviour
Risk of misdiagnosis
Stigma
over diagnosis
outline the biopsychosocial model of health
A comprehensive approach to understanding health and well-being by considering three interconnected aspects of a patient’s biology, psychology, and sociology.
DSM-5
published by the APA, it serves as the handbook for clinicians and psychiatrists to diagnose psychiatric disorders
Dream analysis
Dreams reflect our working thoughts, emotions and fantasies. Freud believed dreams serve as wish fulfilment and originate from the id.
Rational Emotive Behavioural Therapy
Based on the principle that psychological problems are caused by irrational beliefs of the outside world. It helps recognise and alter those beliefs and negative thinking patterns in order to overcome problems.
Cognitive behaviourism
The assumption that our actions are a result of our thoughts
Unjustifiable
Behaviour that occurs without a rational basis
Disturbing
Behaviour that is troublesomes to other people
Atypical
Behaviour that is so different it violates the norm. there are two parts; unlike others behaviour and it violates a rule for accepted and expected behaviour in a particular culture
Example of Maslow’s hierarchy
If a person goes without food, they are motivated by hunger. Once that hunger is satisfied, the motivation for food decreases.