Organization of skeletal muscles & physiology wish list
1/21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
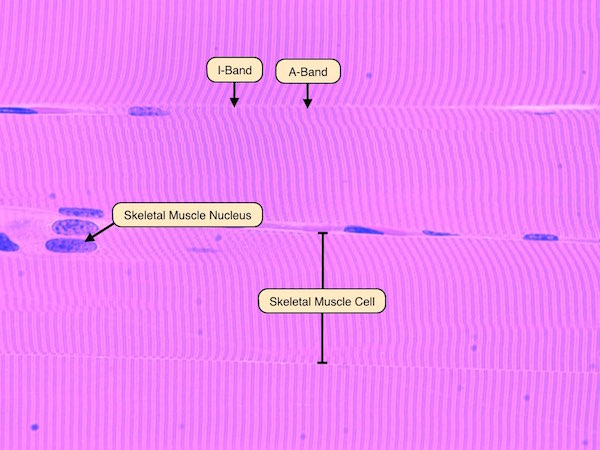
Nuclei
Dark spot on histology slide
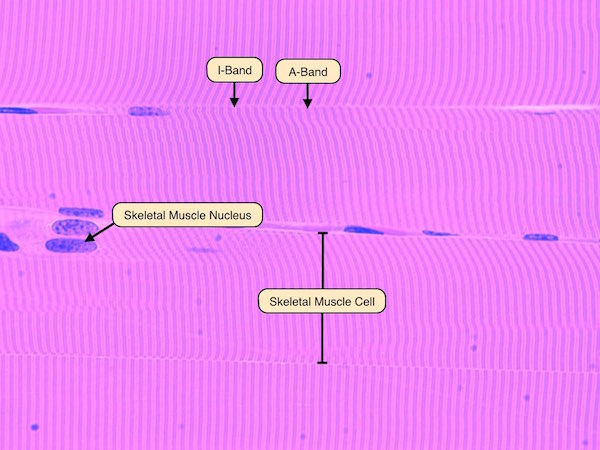
striations
‘lines’ that can be used to identify skeletal muscle histology
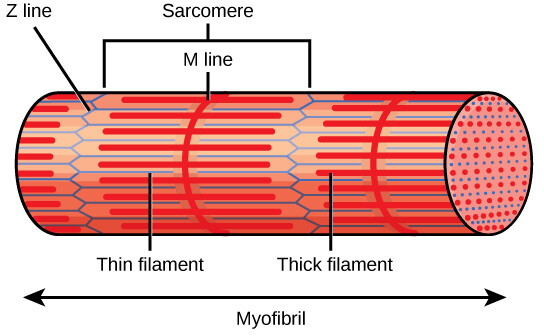
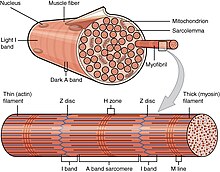
sarcomere
the basic repeating unit of muscle fibers, responsible for muscle contraction
I band
a light band found in skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers, primarily actin & contains z disk
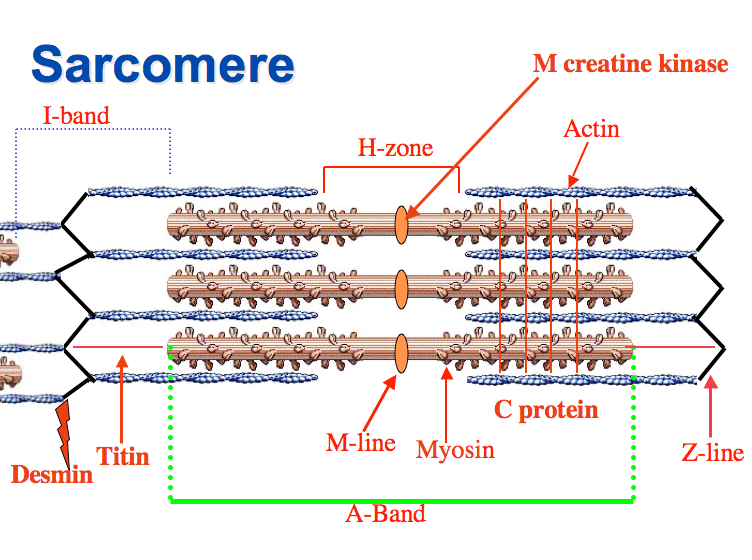
A band
the dark region within a sarcomere, containing the thick myosin filaments & overlapping portions of thin actin filaments
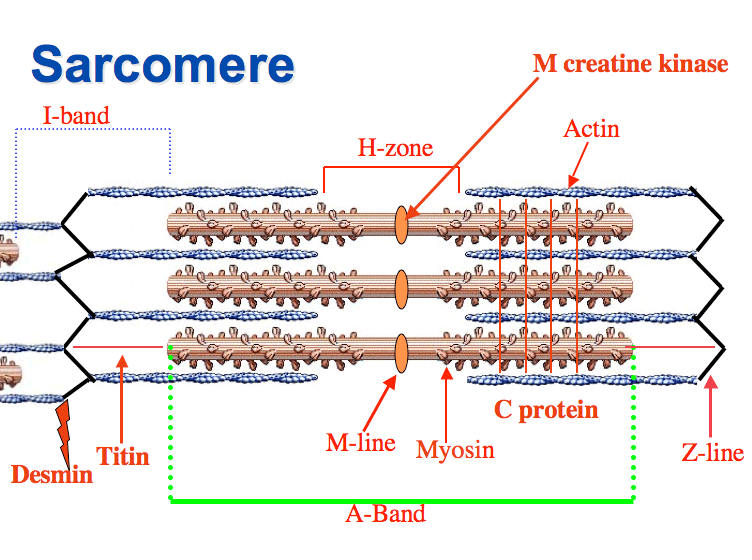
H band
a lighter region within the a-band of a sarcomere in skeletal muscle, consists solely of thick/myosin filaments and is bisected by m-line
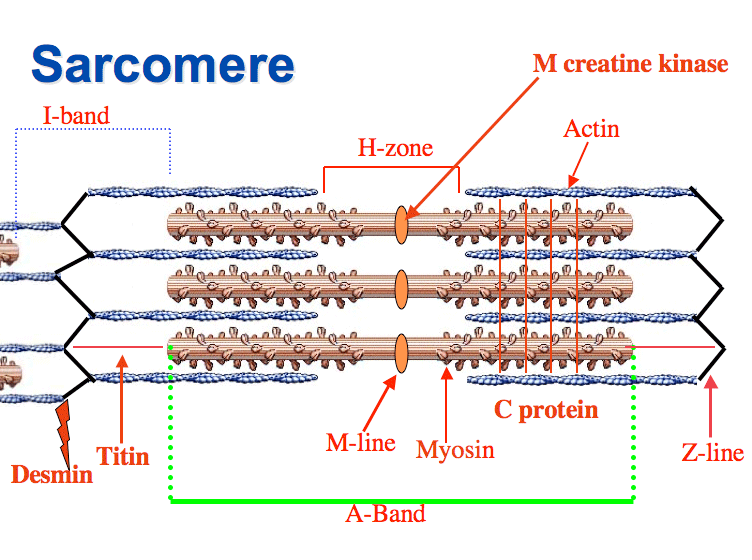
Z line/disc
protein structures that play a crucial role in the structure and function of muscles, attachment points for actin that makes up a sarcomere
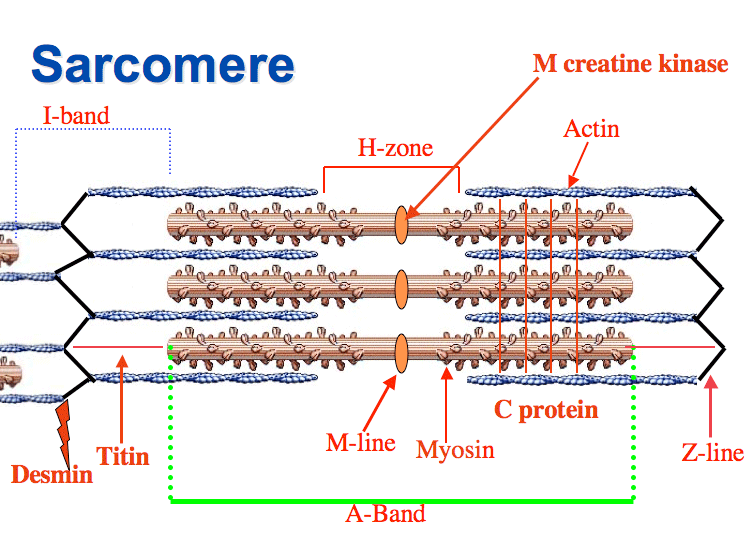
M line
a dark, vertical line located in the center of the sarcomere, anchoring myosin filaments and playing a crucial role in muscle contraction and maintaining structural integrity
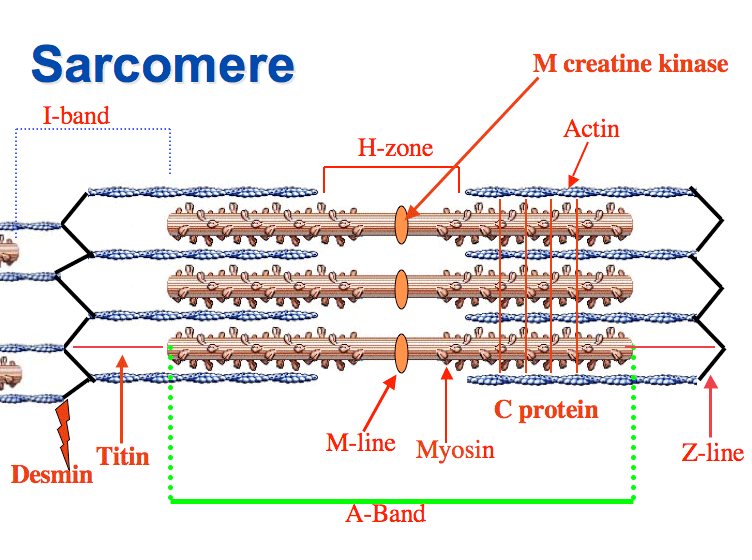
actin
a globular protein that polymerizes to form long thin filaments called microfilaments
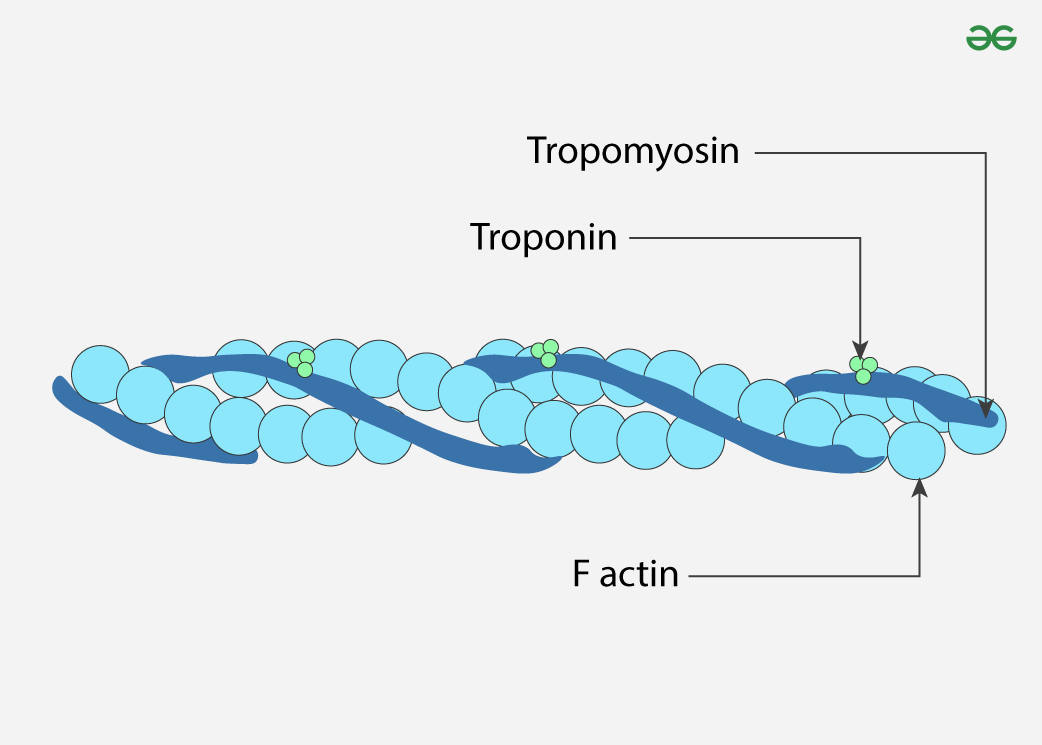
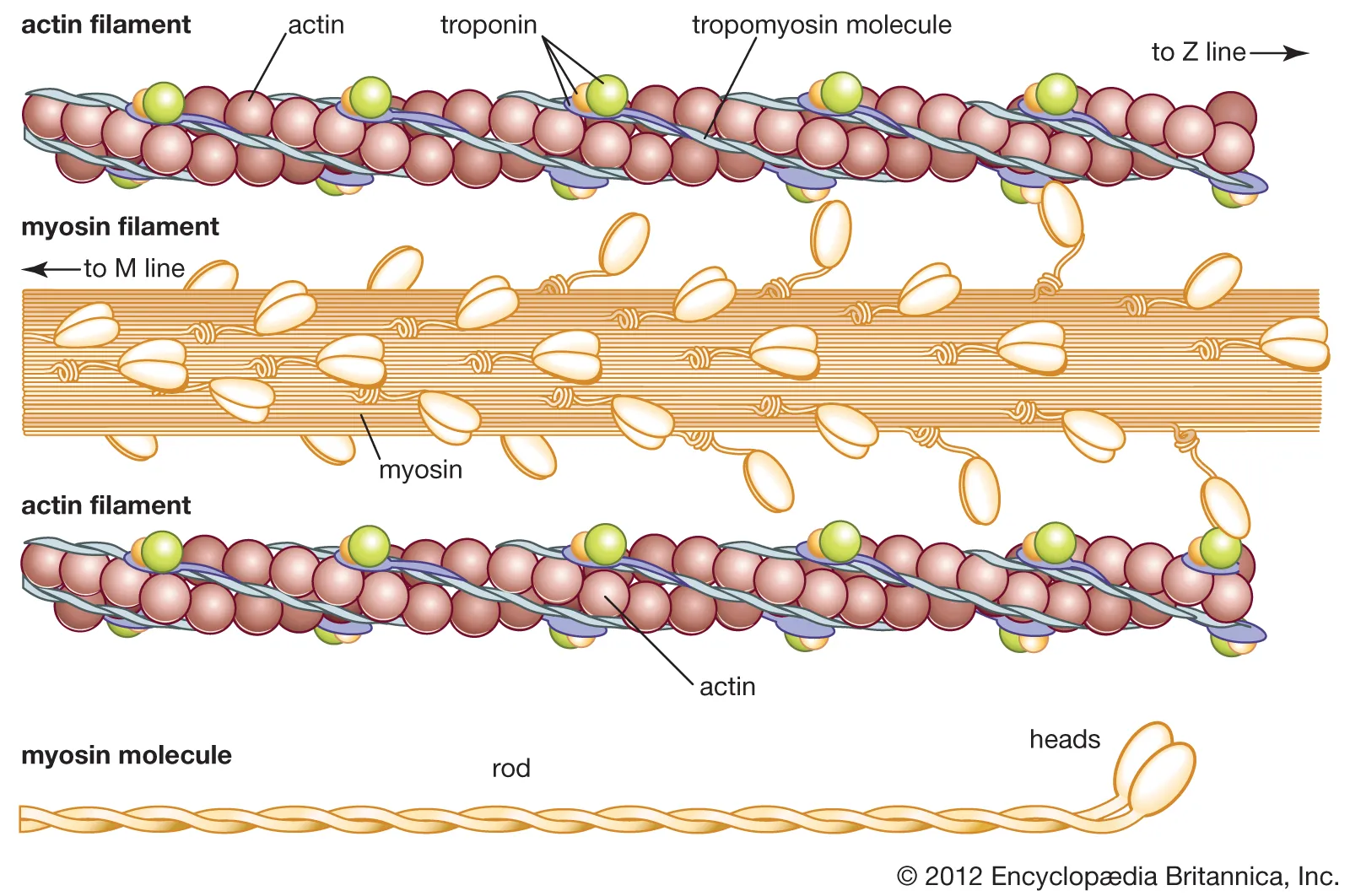
myosin
a long, rod shaped tail and a globular head like domain, assembles into thick filaments
T-tubules
invaginations of the plasma membrane (sarcolemma) in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, part of the ‘triad’
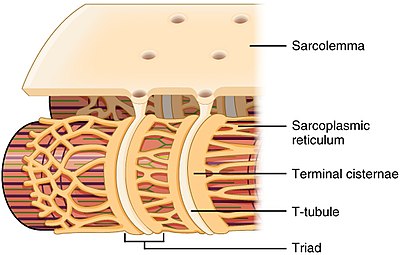
terminal cisternae
enlarged portions of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells, specifically located at the A-band-I-band junctions, that store and release calcium ions, initiating muscle contraction when an action potential travels down the t-tubules
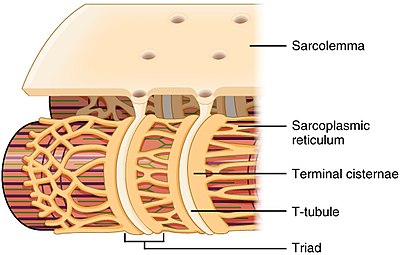
sarcoplasmic reticulum
a specialized form of the endoplasmic reticulum found in muscle cells, crucial for storing and releasing calcium ions that are essential for muscle contraction and relaxation
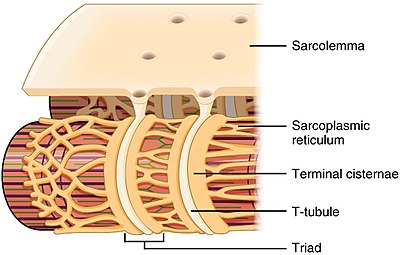
myofibril
bundles of protein filaments that contain the contractile elements of contraction, long strand of protein that makes up a muscle fiber
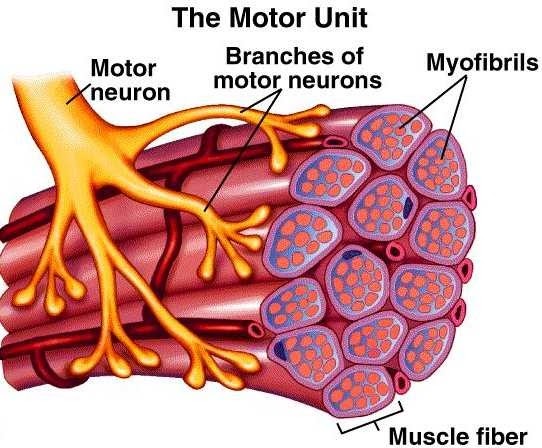
motor unit
the fundamental functional unit of skeletal muscle, consisting of a single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates, working together to produce movement
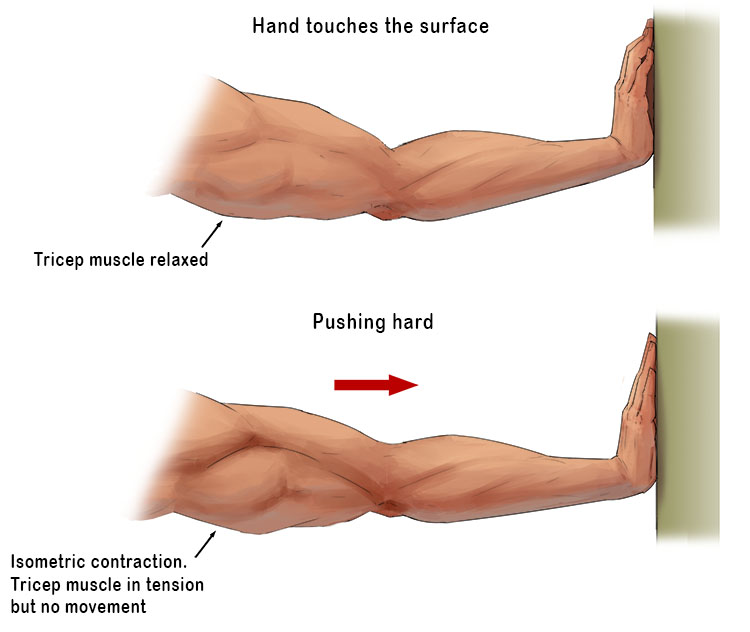
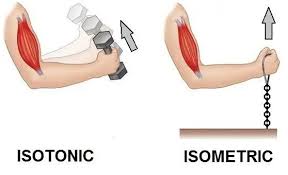
isometric muscle contraction
occurs when a muscle generates force without changing its length
isotonic muscle contraction
occurs when a muscle generates force without changing its length
agonist muscle
a prime mover muscle that contracts to produce a specific muscle. Primarily muscle responsible for generating force and initiating a movement
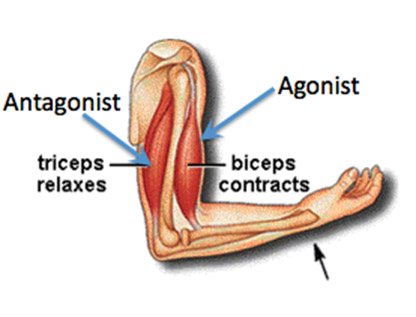
antagonist muscle
a muscle that opposes the action of the agonist muscle. Helps to control and stabilize movements by providing resistance
Electromyography
a diagnostic test that measures the electrical activity of muscles and the nerves that control them
muscle fatigue
a temporary decline in muscle strength and endurance, resulting in a feeling of weakness, tiredness & difficulty performing physical activities
muscular contraction
the process by which muscles generate force and movement