Chapter 10&11
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
general formula of alkanes
CnH2n+2
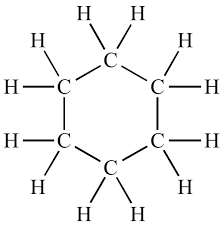
what is this called?
cyclohexane
general formula of alkenes
CnH2n
what is a test to check if a molecule is unsaturated?
add Br2 (which is brown) because it will be added across the double bond of an alkene and turn colourless
how to calculate the degree of saturation
(max number of H possible - actual number of H) / 2
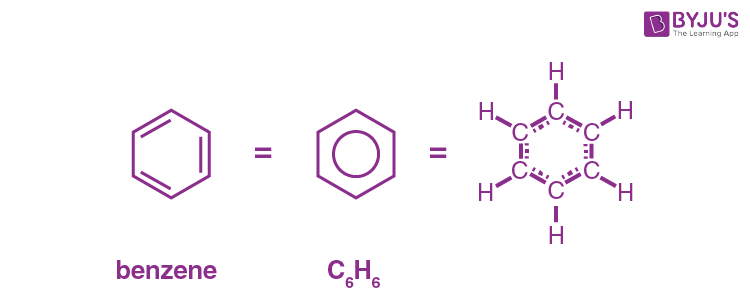
what is this called?
benzene
when a benzene ring is bonded to an alkyl group or a functional group, the ring structure is known as a _____ functional group
phenyl
how to identify an alcohol
OH
what is a primary alcohol?
OH attached carbon is bonded to 1 alkyl group
what is a secondary alcohol?
OH attached carbon is attached to 2 alkyl groups
What is a tertiary alcohol
OH attached carbon is attached to 3 alkyl groups
how to identify an amine
NH2
how to identify an aldehyde
CHO
how to identify a ketone
CO
how to identify a carboxylic acid
COOH
how to identify a primary amide
CONH2
how to identify an ester
COO
functional group priority scale (highest to lowest)
carboxylic acid, ester, aldehyde, ketone, alcohol, amine, alkyne and alkene, alkane
which homologous series have hydrogen bonding?
alcohols carboxylic acids, amines, amides
which homologous series have dipole-dipole attractions?
haloalkanes, aldehydes, ketones, esters
what is viscosity? And general info
viscosity is resistance to flow
increases as chain length increases because forces of an attraction increase
decreases as temperature increases because molecules gain enough energy to overcome the forces
what are dimers?
a molecule consisting of two identical molecules that are linked together
What are some properties of hydrocarbons?
most are nonpolar with dispersion forces
Insoluble in water but soluble in a nonpolar solvent
Melting point and boiling point increases as chain length increases because dispersion forces get stronger
What are some properties of halo alkanes?
contained bonds that are polar
Have a weak dispersion forces but the carbon-halogen bond allows for dipole dipole attraction
Substitution reactions of halo alkanes
reaction between an alkane and chlorine
Reaction conditions: UV light
Chlorine atom in molecule can be substituted by other functional groups
Addition reactions of alkenes
carbon carbon double bond becomes a single bond
Unsaturated compound become saturated
atoms added across the double bond
A test for unsaturated molecules is to add bromine or iodine which are brown because they will be added across the double bond and become colourless.
Hydrogenation (addition of hydrogen) in alkenes
solid nickel catalyst used
Alkene and hydrogen gas forms an alkane
Halogenation (addition of group 17 elements)
no catalysts used
A di-substituted halo alkanes produced (2 halogens)
Addition of a hydrogen halide in alkenes
alkene plus hydrogen halide produces haloalkane
Note: can have isomers depending on position of the double bond
Hydration (addition of water) in alkenes
catalyst is phosphoric acid (H2PO4)
Temperature of 300°C
Water is added across the double bonds of the alkene to form an alcohol
Combustion of alcohol
produces carbon dioxide and water
Highly exothermic
Redox reactions
Oxidation of alcohols
oxidised by KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7 in the presence of an acid (H+)
Three types of alcohols: primary, secondary, tertiary
Primary alcohols oxidise into aldehydes then carboxylic acid
Secondary alcohols oxidise into ketones
Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation
Alcohol oxidation test
Acidified dichromate is orange and when Cr2O7 2- ions are reduced to Cr 3+ they turn green
Acidified permanganate ions are deep purple and when MnO4 -1 ions are reduced to Mn 2+ they become colourless
Ionisation of Carboxylic acid with water (and what is the reversible reaction)
weak acid that ionise in water
CH3COOH (aq) + H2O (l) → CH3COO- (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
ethanoic acid (aq) + water (l) →
Reactions of Carboxylic acids with alcohols
they are condensation reactions (water is eliminated) and specifically Esterification reactions
But not all Condensation reactions are esterification reactions
H2SO4 (l) as catalyst
Reverse reaction is hydrolysis
Hydrolysis of Esters
hydrolysis is the breaking apart with the addition of water
Transesterification and the production of biodiesel
triglyceride breaks down into three fatty acid methyl esters (biodiesel) and glycerol
OH- catalyst
How to make an alcohol
alkene + h2o and H3PO4 (l) catalyst and 300 degrees
Alkene + HCl, then + OH-
How to make a carboxylic acid
alkane + Cl2 and UV light → chloroalkane
Chloroalkane + OH- → alcohol
Alcohol + Cr2O7 2-/H+ → carboxylic acid
How to produce a polyalkene from an alkene
catalyst and high pressures
Factors that can affect the yield of a reaction
equilibrium reactions
Losses when transferring between containers
Decomposition of products
Liquid lost due to evaporation
Formula for percentage yield
= actual yield / theoretical yield x 100
Formula for atom economy
= M(product) / M(all reactants) x100
OR
= m(product) / m(all products) x 100
Aims for the sustainable production of chemicals
minimal waste
replace fossil fuels with renewable resources
products that are biodegradable or recyclable
design processes are efficient and don’t harm the environment
Biopolymers
made from feedstocks derived from plants
Are biodegradable
Most POLYMERS are made from fractional distillation of crude oil
eg. biodegradable sutures
Advantages of biopolymers and bio solvents
Manufacturing does not require use of finite resources (Cold, oil, natural gas)
Can be obtained from plant sources which are renewable
Many are biodegradable and many can be recycled
What do catalysts do and what are their advantages?
Allow reactions to take place at a much lower temperature
reduces heating costs (saving energy resources)
Increases reaction rate (more product in shorter time)
Not consumed in the reaction so can be used continuously
alkane → haloalkane
reagent: Cl2 (g)
conditions: UV light
haloalkane → alcohol
reagent: OH- (aq) or NaOH (aq)
conditions: none
alcohol → carboxylic acid
reagent: Cr2O72- (aq)
conditions: acidic medium H+ (aq)
carboxylic acid → ester
reactant: primary alcohol (l)
conditions: H2SO4 (l)
alkene → chloroalkane
reagent: HCl (g)
conditions: none
alkene → alcohol
reagent: H2O (g)
conditions: H3PO4 (s)
carboxylic acid → amide
reagent: RNH2 (l)
conditions: none
alkenes → alkanes
reagent: H2 (g)
conditions: Ni (s)
secondary alchohol → ketone
reagent: H+ (aq) / Cr2O72- (aq)
conditions: heat
Advantages of high atom economy:
Produces less chemical waste → less environmental pollution.
More efficient use of raw materials → lower costs.
Less money spent on waste treatment and disposal.