Lab 2 - Introduction to the Animals (Invertebrate classification)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Ecdysozoa (Larger Clade)
Molecular evidence rRNA
Have Ecdysis: shed their exoskeleton
Phylum:
Onycophora
Tardigrada
Nematoda
Arthropoda
What are the common names of Phylum: Onychophora?
Walking or velvet worm
Cambrian

What two groups was Phylum: Onychophora thought to be a link between?
Annelids and arthropods
Have in common with each group: segmented and have appendages
What group is Phylum: Onychophora most closely related to?
Arthropods
Cambrian

What temperature, pressures, radiation, can Tardigrada (Water Bears), withstand?
Temperature; just above absolute zero of water and boiling point of water
Pressures; 6 times greater than deepest ocean trenches
Radiation; hundreds times higher than lethal dose for humans
How long can Tardigrada go without food and water?
More than 10 years
What characteristic is responsible for the branching off of Phylum: Nematoda?
Pseudocoelomate; “false cavity” not fully lined with mesoderm
Precambrian
Phylum: Nematoda Digestive system
Alimentary canal (mouth and anus)
Extra and intracellular
Phylum: Nematoda Level of Organization and Tissue Layers
Organ System level of organization
Triploblastic
Phylum: Nematoda Strctures (CS)
Cuticle
Epidermis
Pseudocoel
Longitudinal muscle
Nerve cords
Intestines
What is the excretory system in Phylum Nematoda?
Waste exits excretory pores
What is the nervous system of Phylum: Nematoda?
Cerebral ganglia or nerve ring with anterior and posterior nerves
Sexual Reproduction in Phylum: Nematoda
Complicated life cycles
What is the mode of infection and hosts in Ascaris?
Phylum: Nematoda
Mode of infection: children playing in dirt ingest eggs
Hosts: parasites in small intestines

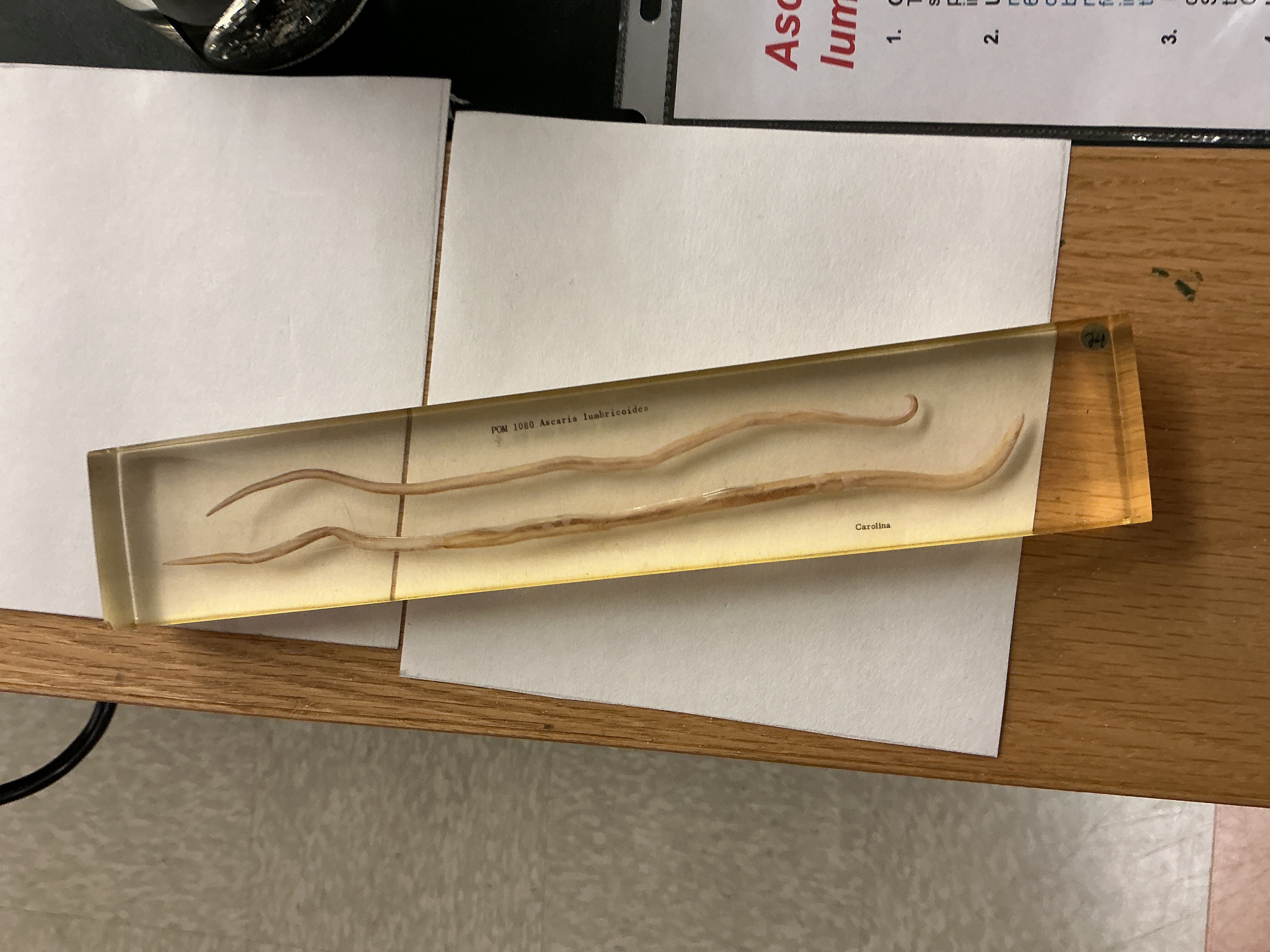
Difference between Male and Female Ascaris
Phylum: Nematoda
Male; curved end, thinner, slightly pointy ends
Female; hooked end, thicker, very pointy ends
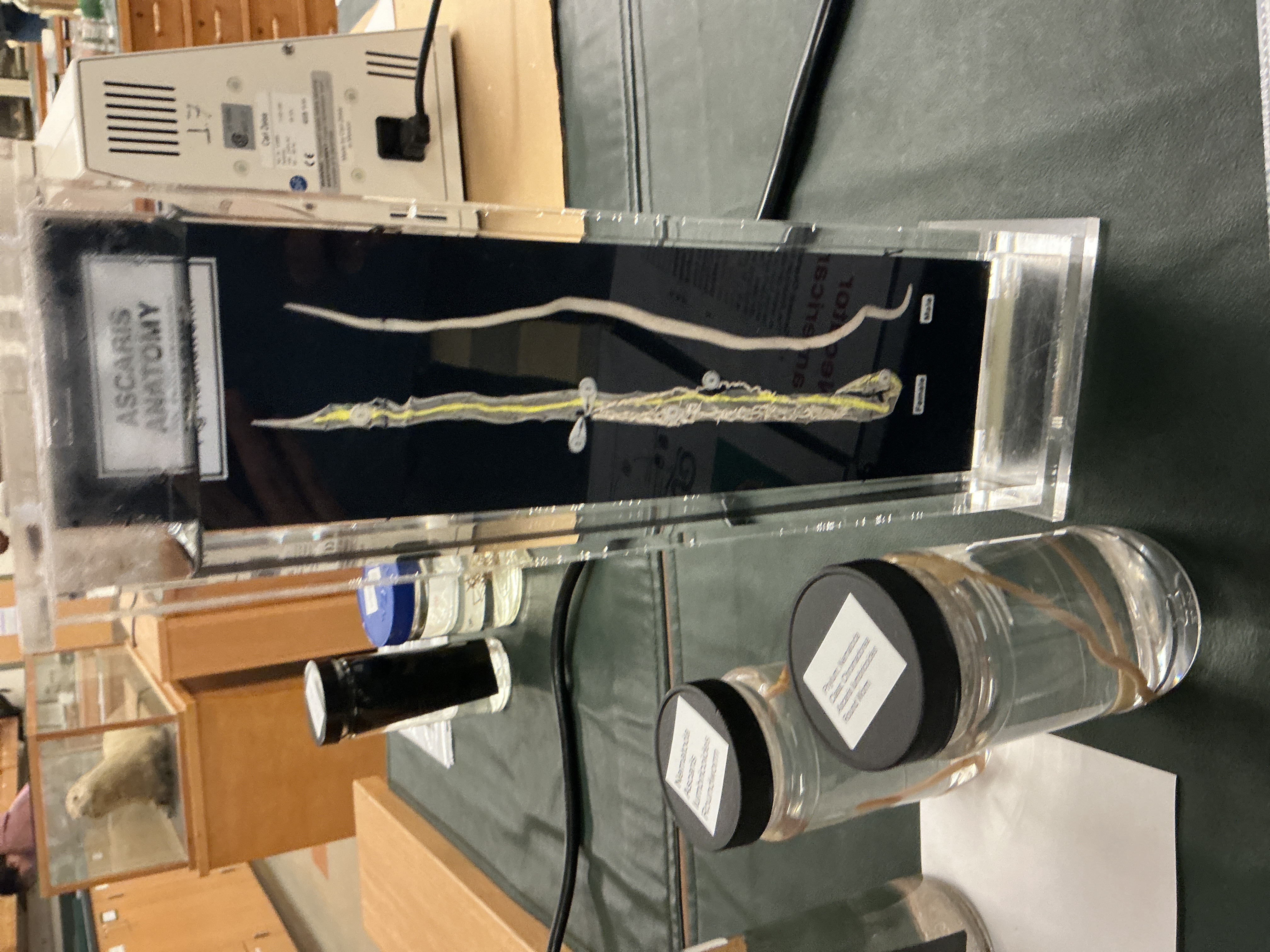

Biogeography of Ascaris
Phylum: Nematoda
Africa/southeast Asia and U.S.

What is the mode of infection and hosts of Necaetor?
Phylum: Nematoda
Mode of infection: eggs in feces/juveniles in soil burrow in skin and intestine
Hosts: humans
Biogeography of Necaetor
Phylum: Nematoda
New world
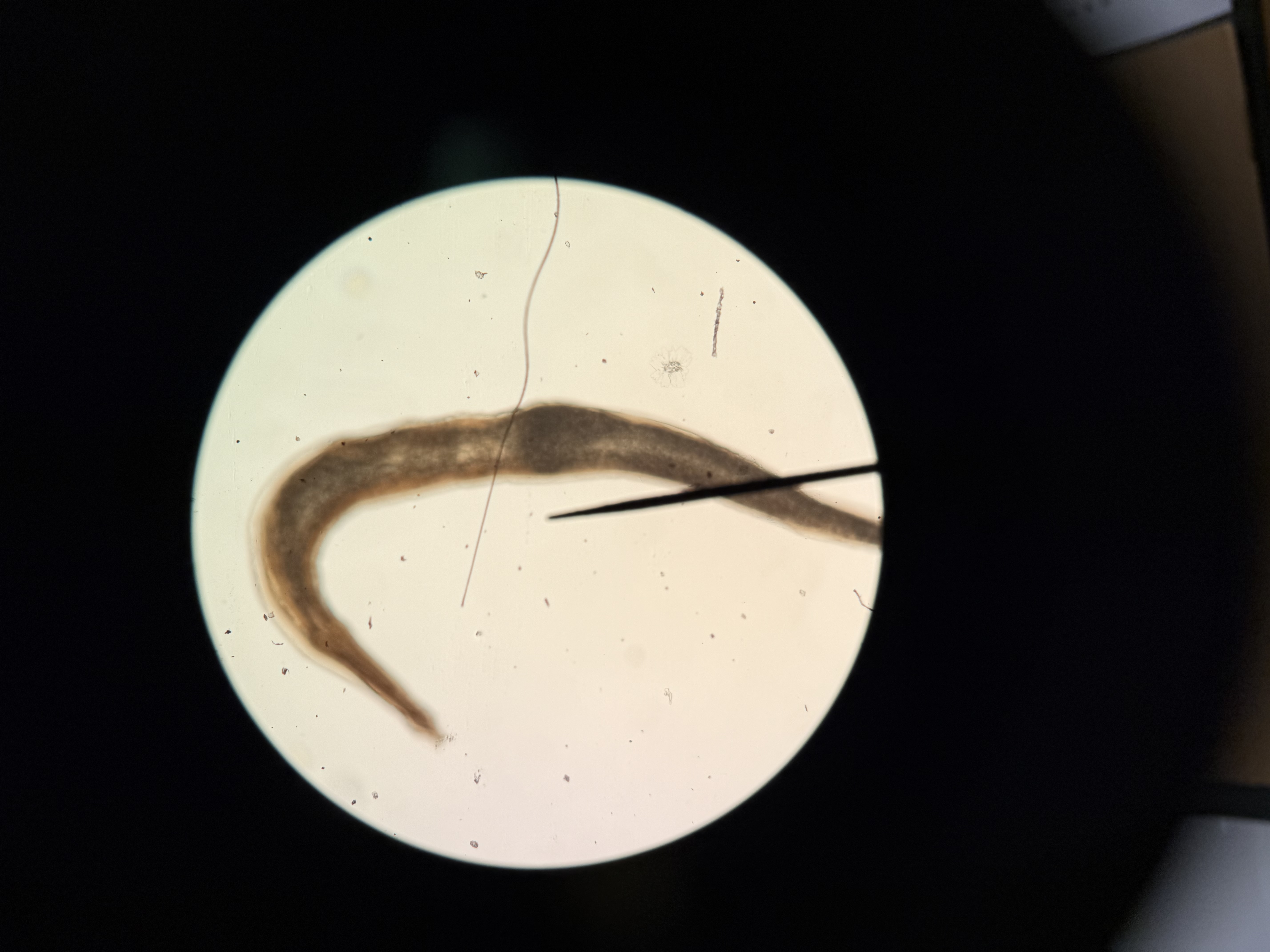
What is the mode of infection and hosts of Trichinella?
Phylum: Nematoda
Mode of infection: eating undercooked meat
Hosts: pigs, rats, humans

Biogeography and Unique Characteristic of Trichinella
Phylum: Nematoda
Biogeography: all continent except antartica
Unique: causes trichinosis
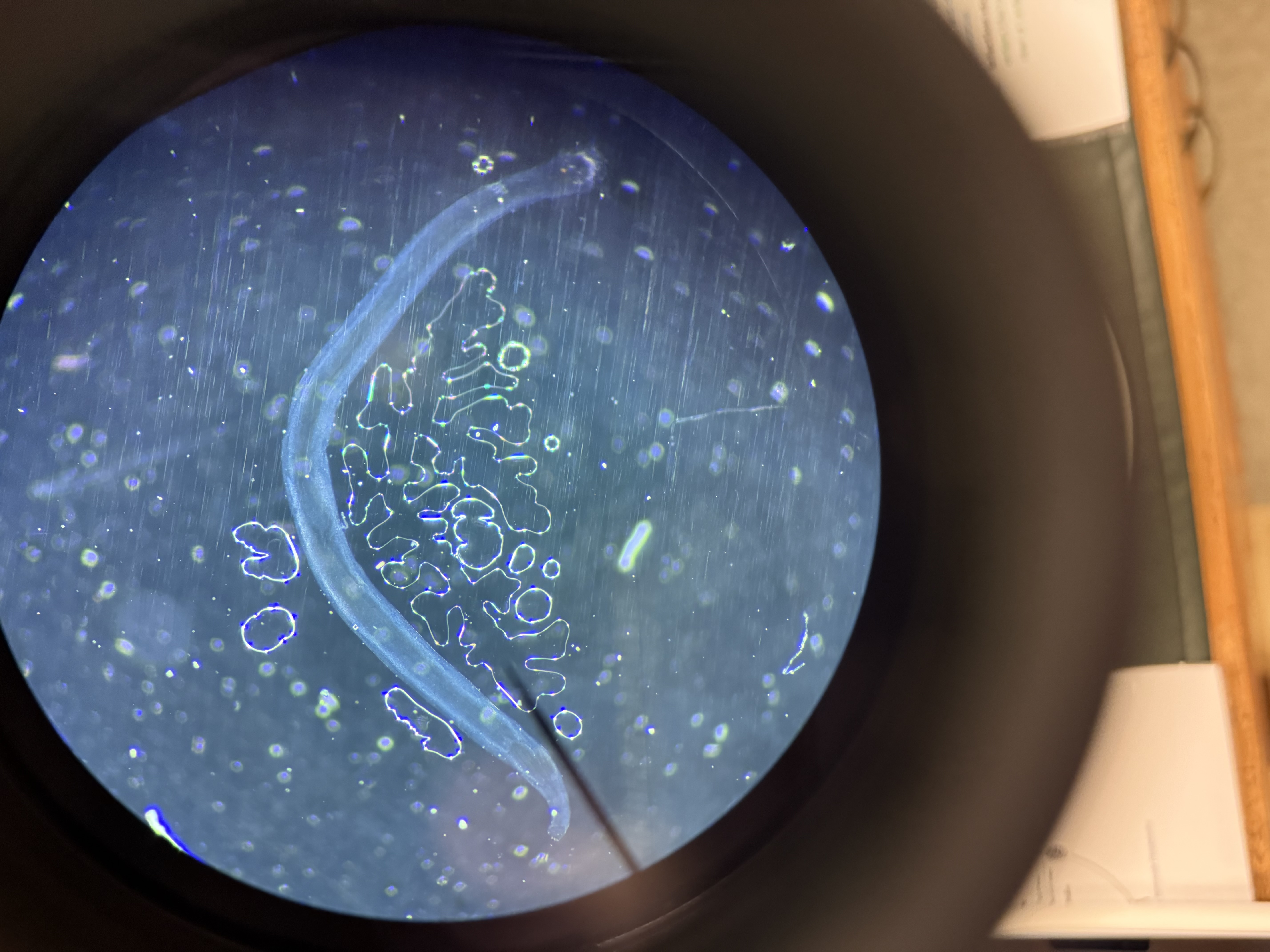
What is the mode of infection and hosts for Enterobius?
Phylum: Nematoda
Mode of infection: ingestion of eggs
Hosts: humans
Worldwide
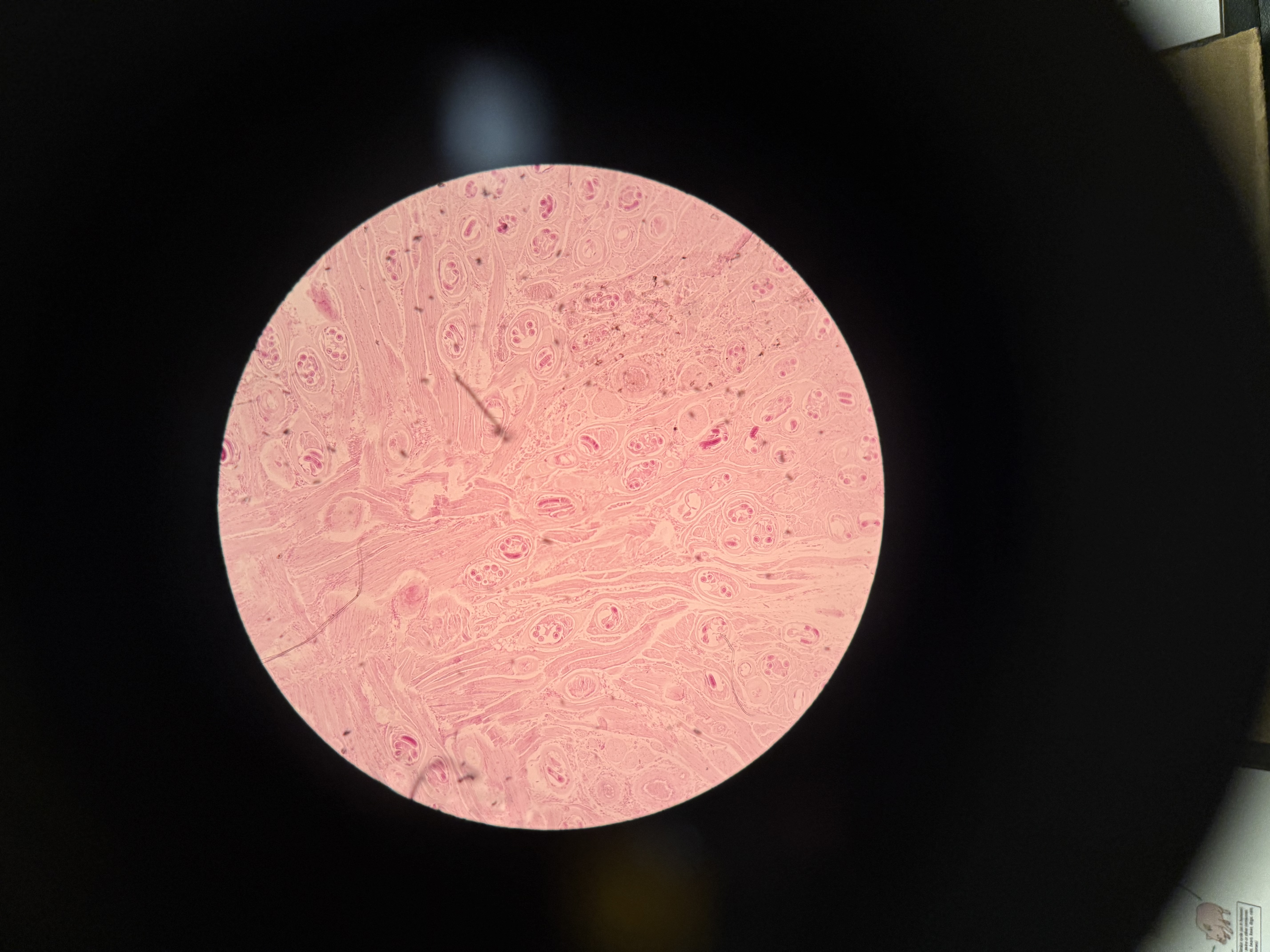
What is the mode of infection and hosts of Macracanthorynchus (spiny headed worm)?
Phylum: Nematoda
Mode of infection: larvae found in beetles is ingested
Hosts: pigs, humans
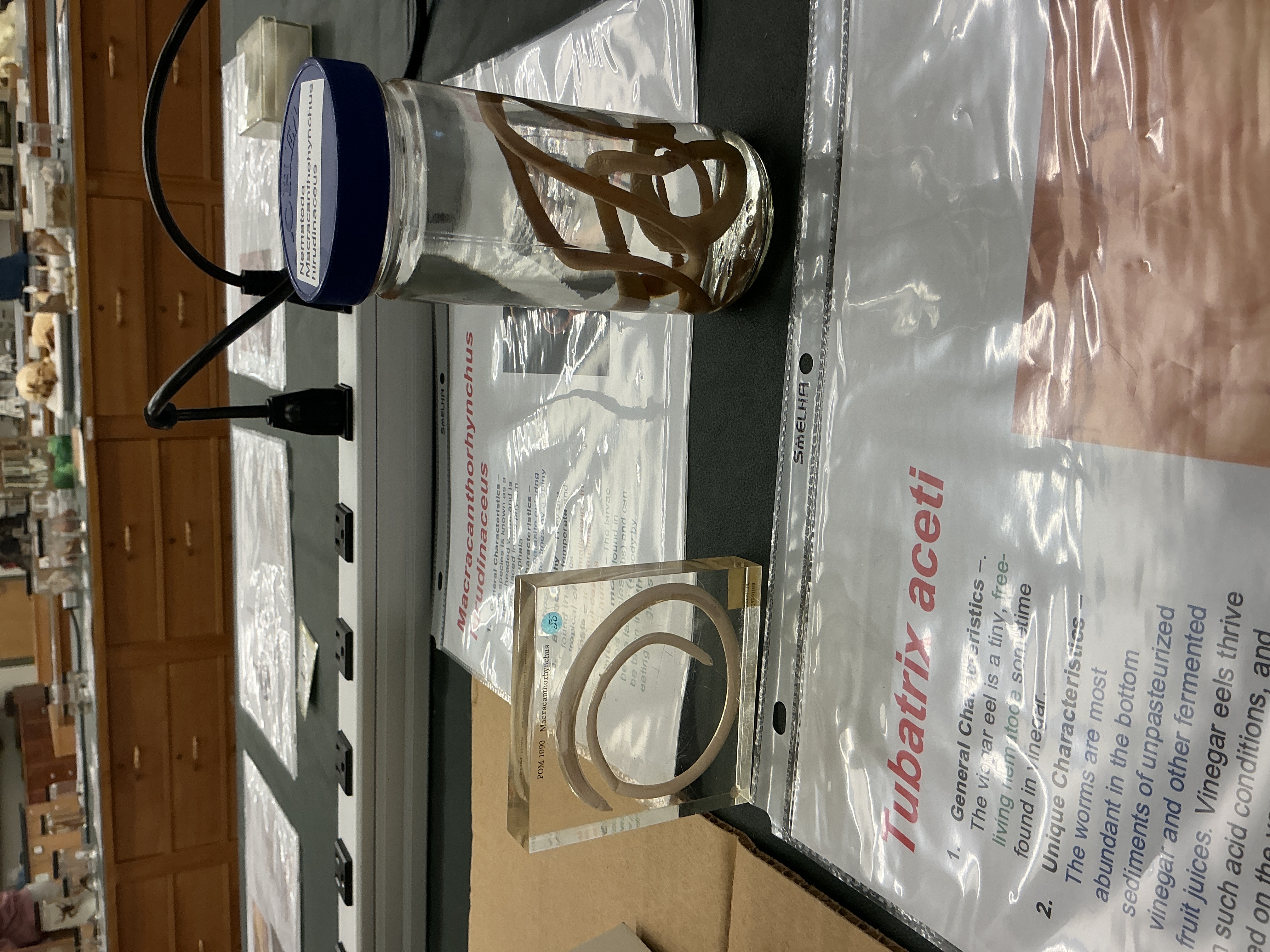

Biogeography of Macracanthorynchus (spiny headed worm)
Phylum: Nematoda
Tropical/temperate climates
Tubatrix (vinegar eel)
Phylum: Nematoda
None
Worldwide
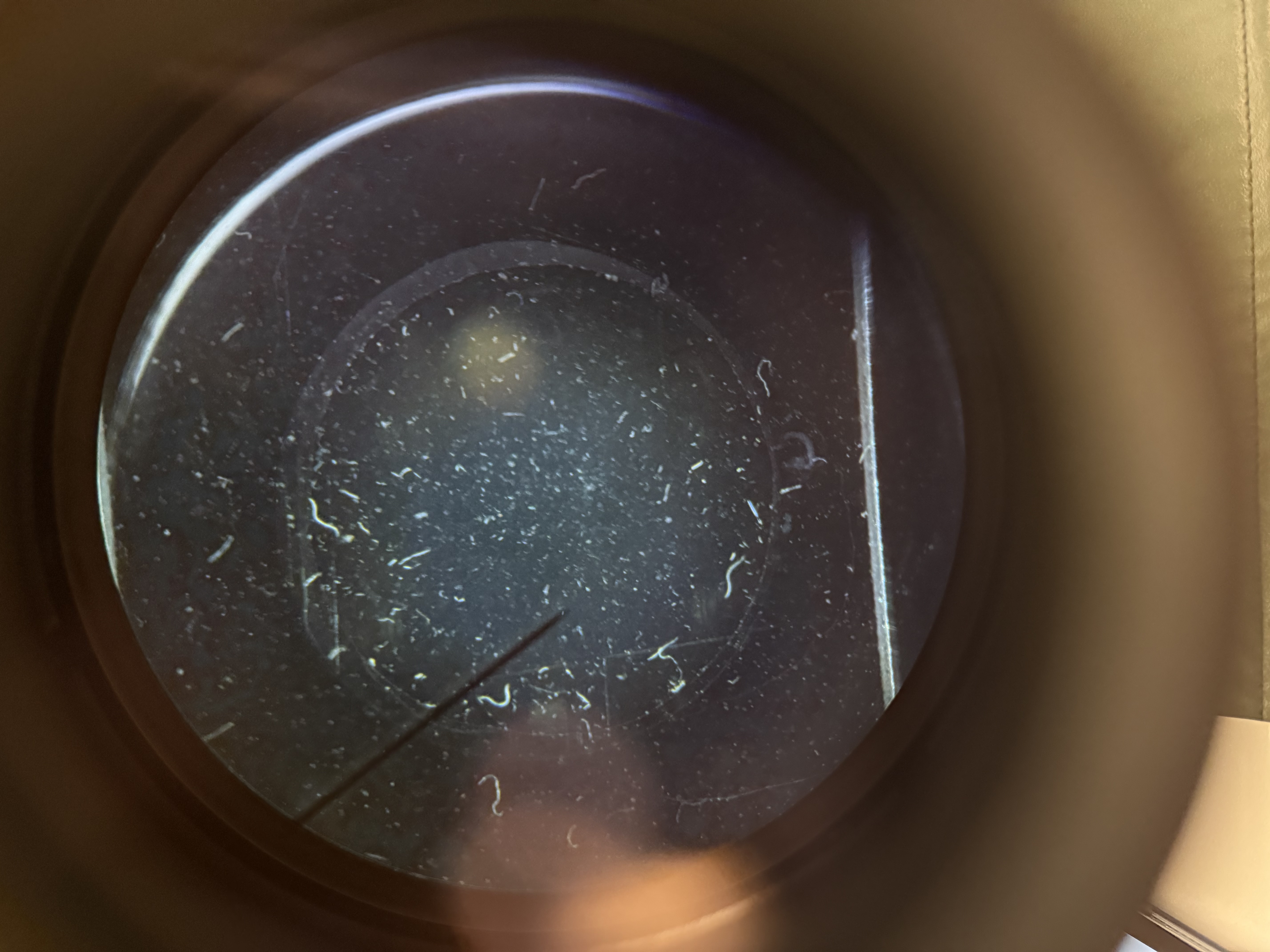
What is the mode of infection and hosts of Wucherieria (roundworm)?
Phylum: Nematoda
Mode of infection: Worms spread by mosquito
120 million people
Hosts: humans
Biogeography and Unique Characteristic of Wucherieria
Phylum: Nematoda
Bio: Africa, South America, Asia
Unique: causes chronic disease elephantisis
What is the mode of infection and hosts of Dracunculiasis?
Phylum: Nematoda
Mode of infection: drinking water with water fleas with larvae
Hosts: humans
Biogeography and Unique Characteristic of Dracunuculiasis?
Phylum: Nematoda
Bio: Asia and Africa
Unique: forms blister on skin, worm comes out, wrap it around stick
What characteristic is responsible for the branching off of Phylum: Arthropoda?
Eucoelomates
Hard, segmented body
Precambrian
What characteristic does all Phylum: Arthropoda have in common?
Cuticle: hard exoskeleton
Segmented body
Jointed appendages
Phylum: Arthropoda Level of Organization and Tissue Layers
Organ system
Triploblastic
5 Subphyla of Phylum: Arthropoda
Trilobita
Checlicerata
Crustaceae
Myriapoda
Hexapoda
Excretory System of Phylum: Arthropoda
Excretory glands
Circulatory system of Phylum: Arthropoda
Open circulatory system with true heart
Respiratory system of Phylum: Arthropoda
Body surfaces, skin, tracheae, book lungs
Nervous System of Phylum: Arthropoda
Dorsal ganglia connected by nerve ring
Body Cavity of Phylum: Arthropoda
Eucoelomates
Sexual Reproduction of Phylum: Arthropoda
Dioecious
How are appendages arranged in Subphylum: Checlicerata?
Phylum Arthropoda
6 appendages:
1 pair of pedipalps
1 pair of chelicerae
4 pairs of legs
Does Subphylum: Checlicerata have a mandible or antennae?
Phylum: Arthropoda
No mandible
No antennae
What does Subphylum: Trilobita have in common and differs from other arthropods?
Phylum: Arthropoda
In common; paired appendages
Differ; segmented without specialization
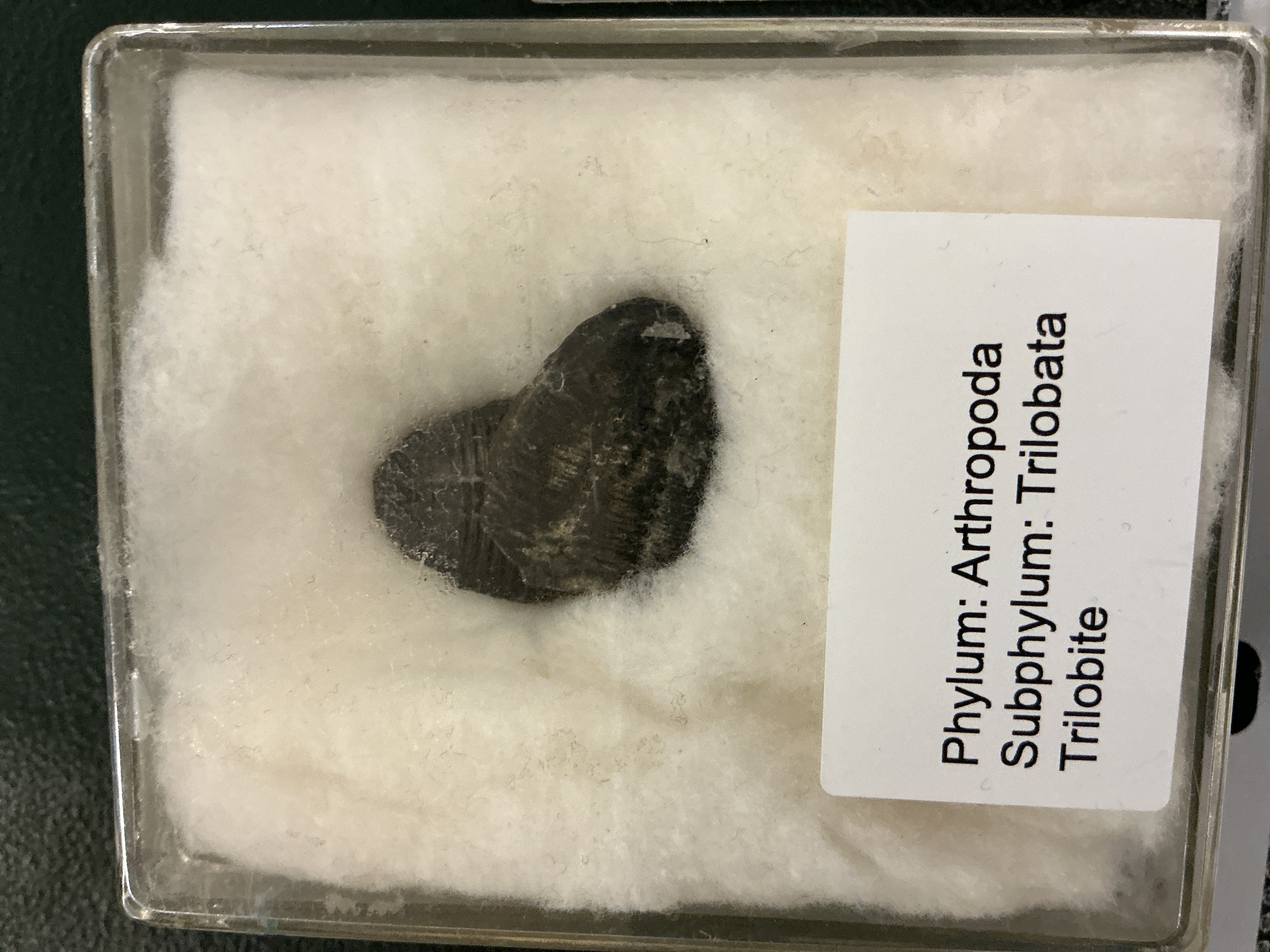

What is common name of Class: Eurypterids?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
Water Scorpions
Extinct

What is special about Class: Eurypterids?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
Largest known arthropod to ever live

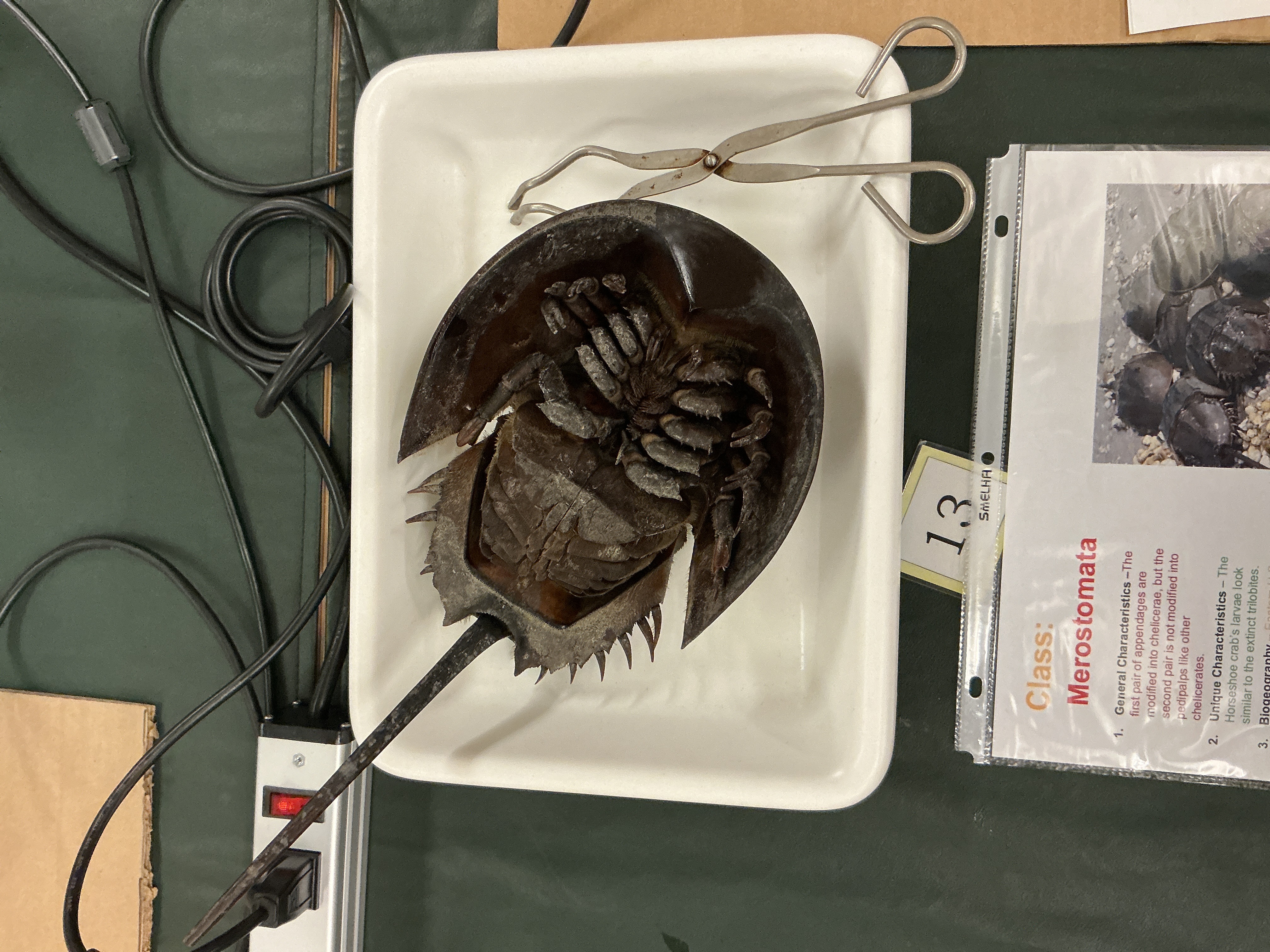
How are appendages of Class: Merostomata arranged?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
6 appendages
1 pair of chelicerae
5 pairs of legs
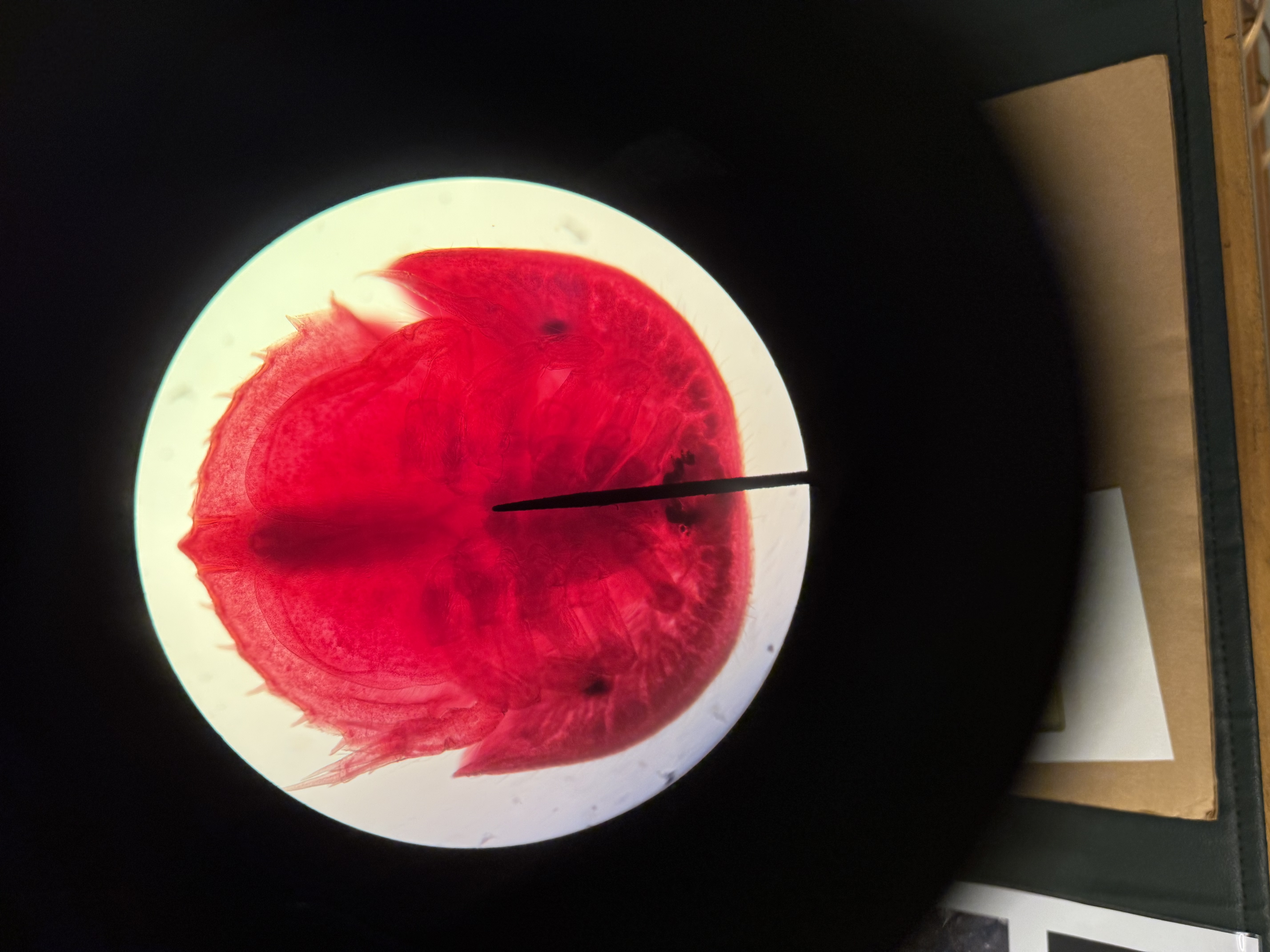
What do the larvae of Class Merostomata (Horseshoe crab) resemble?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
Resemble extinct trilobites

Where are horseshoe crabs found?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Checlierata
Class: Merostomata
Shallow coastal waters
How are appendages arranged in Class: Pycnogonida (Sea spiders)?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
Have 8 legs, but not a spider

How may the appendages in Class: Pycnogonida (Sea spiders) change?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
May have extra legs from duplicated segments

What does Class: Arachnida include?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
Spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites
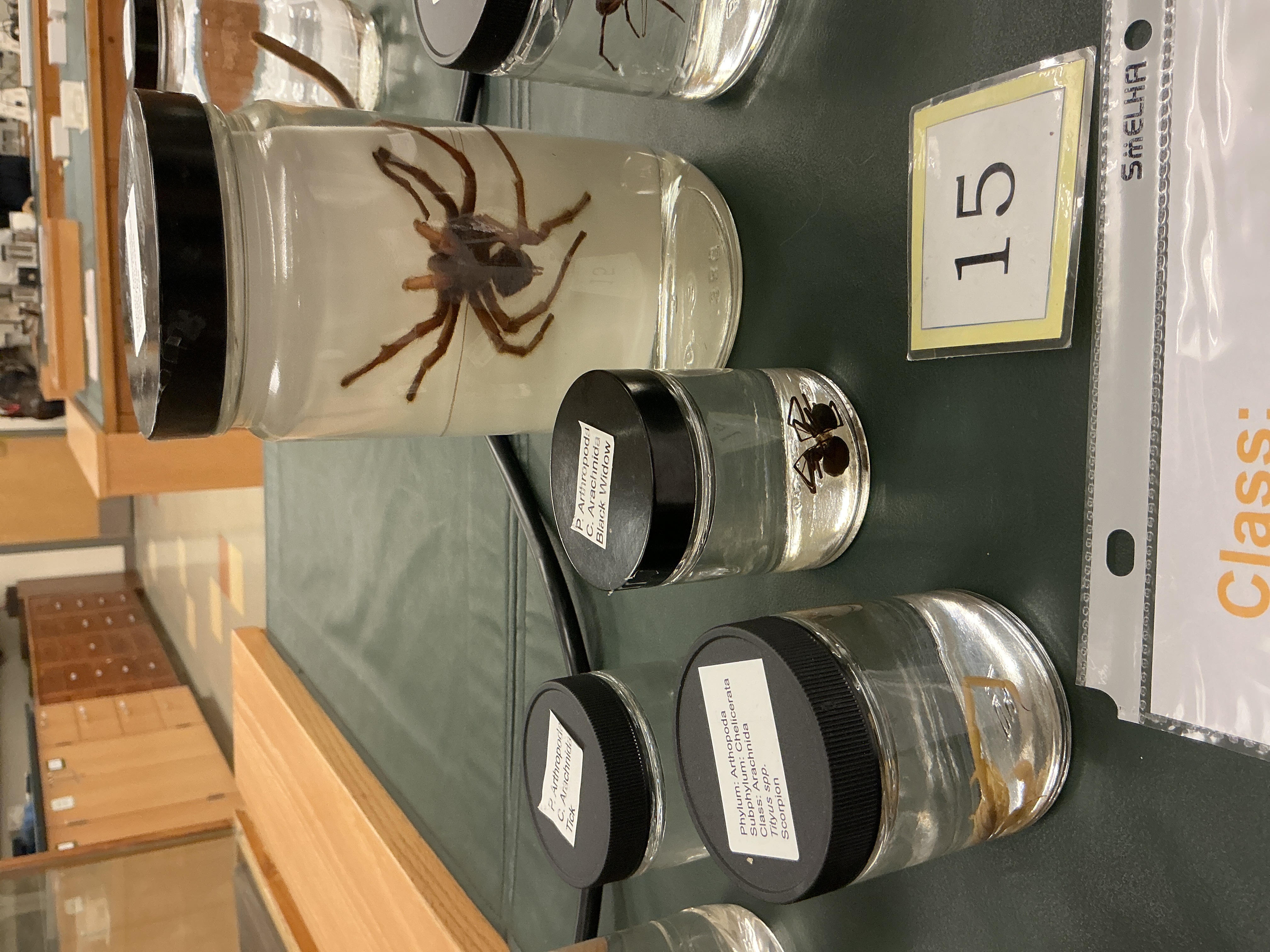

What special characteristics does Class: Arachnida have?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
Special gland: produce silk for webs, eggs, escape, courtship
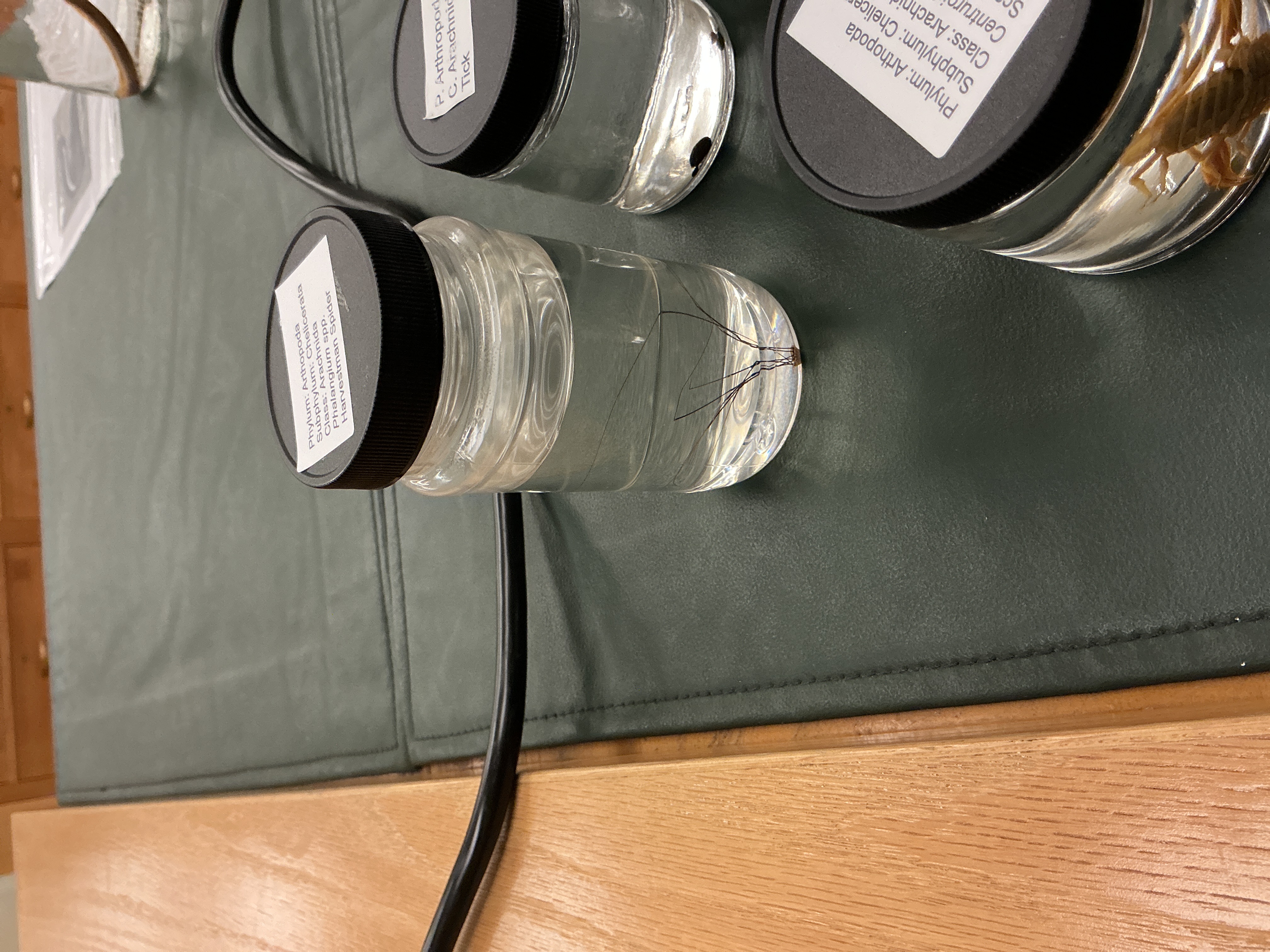

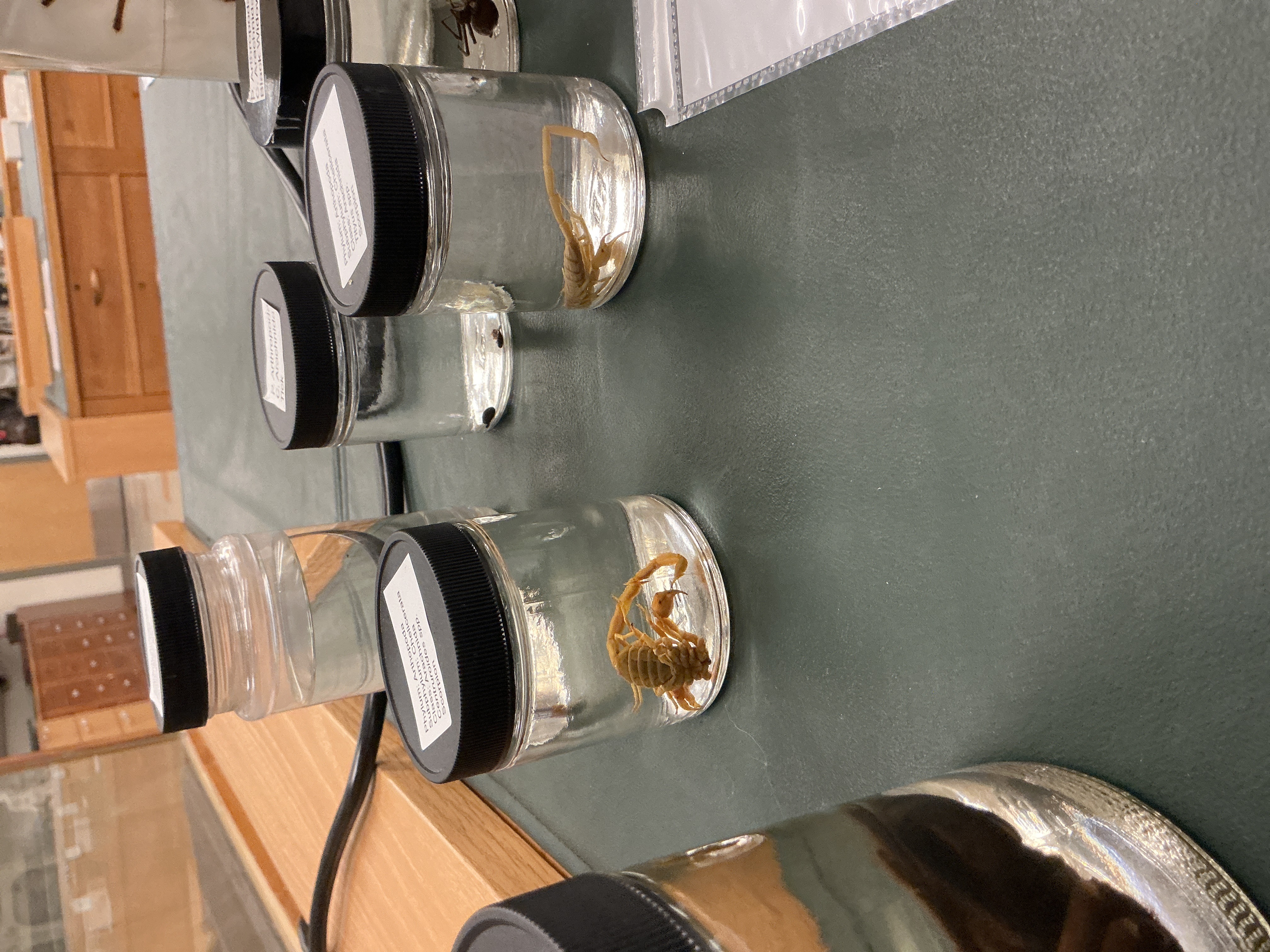
How are appendages modified in scorpions?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Checlicerata
Class: Arachnida
Pedipalps modified into pinchers
Tail modified into stinger
1st terrestrial invertebrates

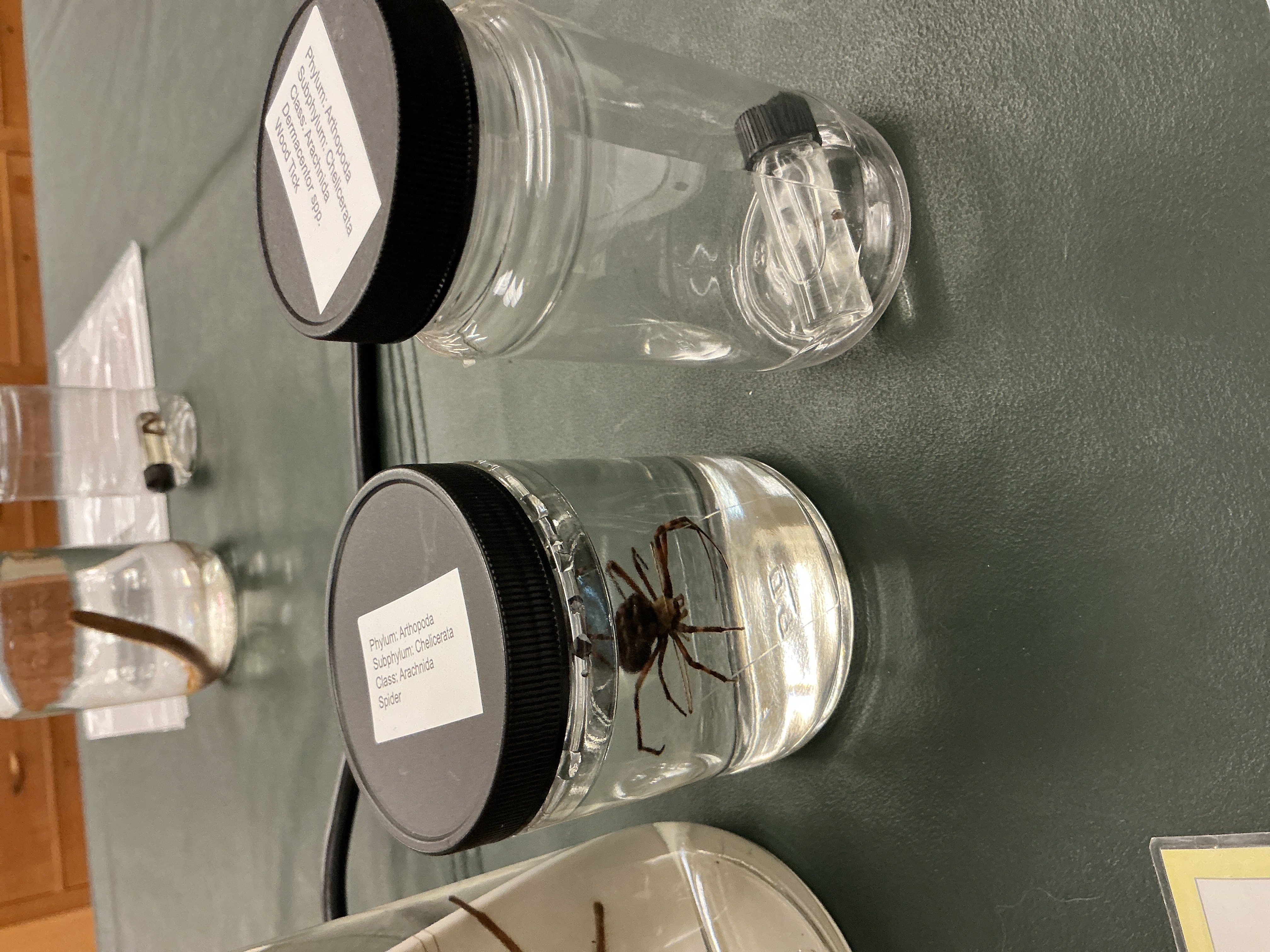
How are appendages modified in spiders?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Checlicerata
Class: Arachnida
Modified chelicerae used as fangs to inject poison

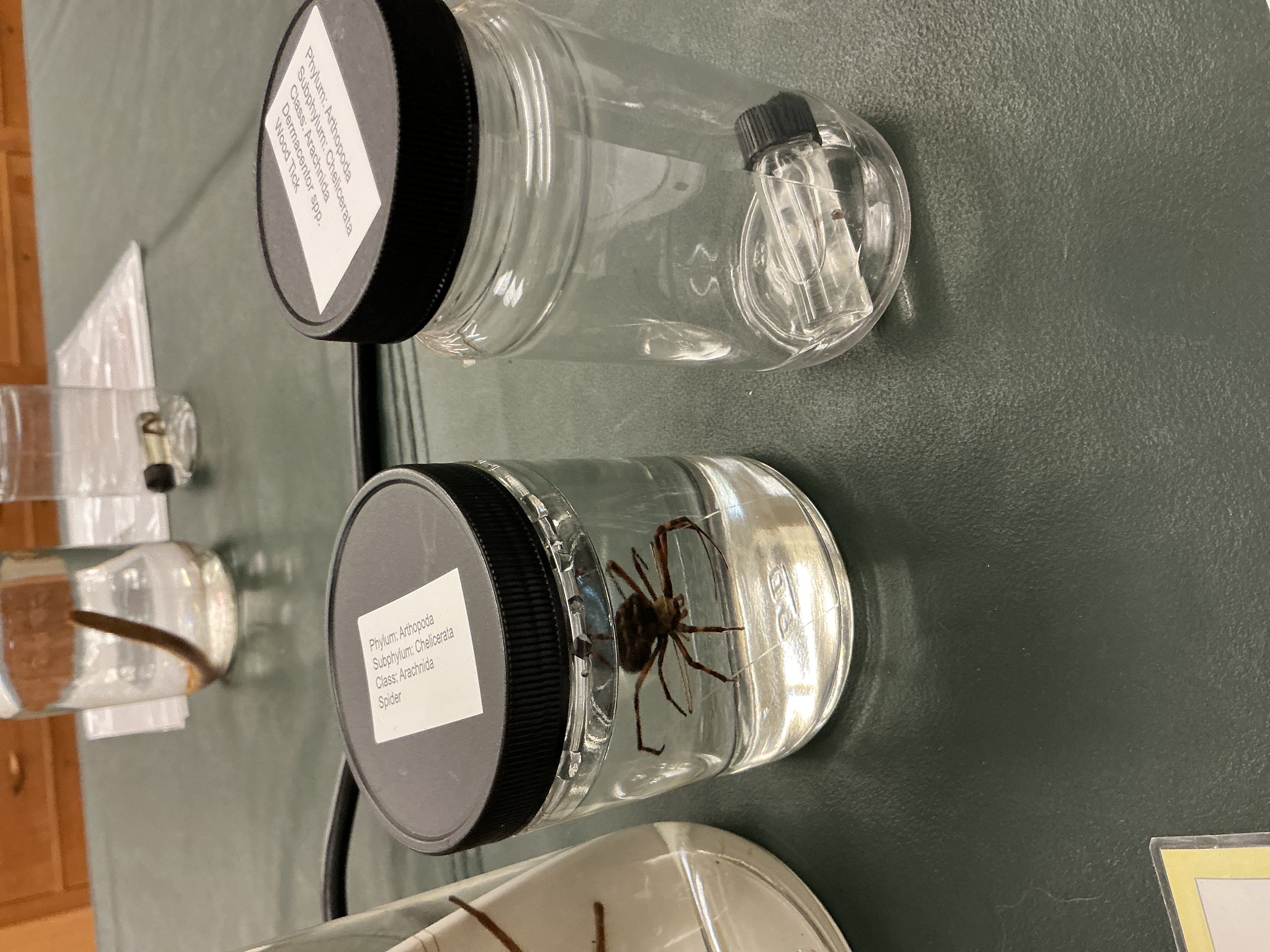
How are appendages modified in ticks/mites?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Checlicerata
Class: Arachnida
Parasites

How are appendages modified and bodies divided in Subphylum: Crustacea?
Two pair of antennae
2 pairs of appendages
Biramous: two main branches
2 or 3 body regions
Cephalothorx (head and thorax), abdomen
Does Subphylum: Crustacea have a mandible or anntenae?
Have mandible
Two pairs of antennae
What does Group: Isopoda eat?
Phylum: Athropoda
Subphylum: Crustacea
Dead plant/animal matter
Found: freshwater

What does Group: Decapoda eat?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Crustacea
Crayfish
Eat; scavengers
Have maxillipeds

What does Group: Copepoda eat?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Crustacea
Eat; Phytoplankton
Most numerous

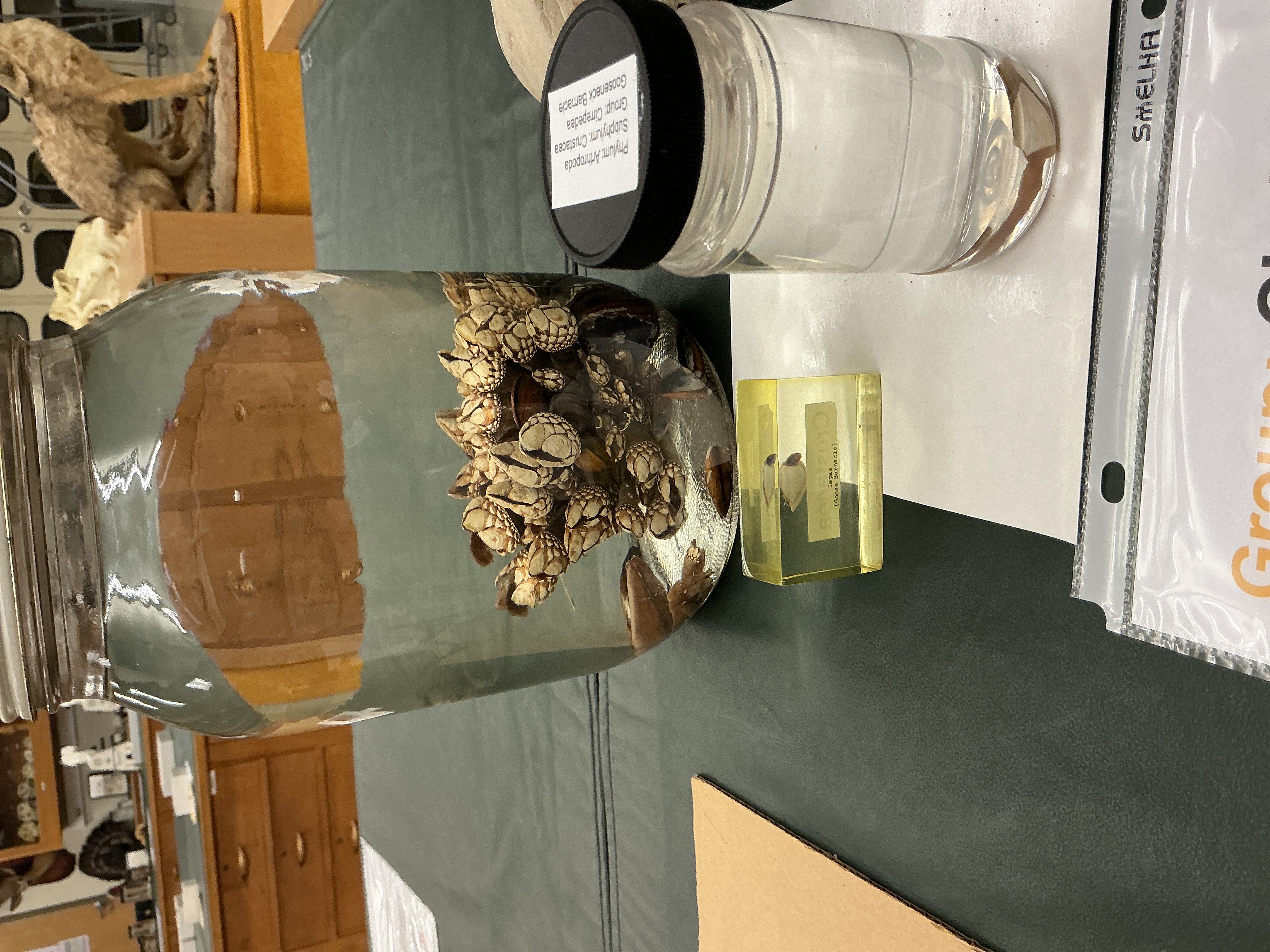
What does Group: Cirripedia eat and where are they found?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Crustacea
Gooseneck barnacles
Eat; suspension feeders
Found;
Encrusters attached to rocks
Inside carapace

How are appendages in Subphylum: Myriapoda modified and bodies divided?
Appendages uniramous: one main branch
Body is long with a head
Does Subphylum: Myriapoda have a mandible or anntenae?
Have mandible
One pair of antennae
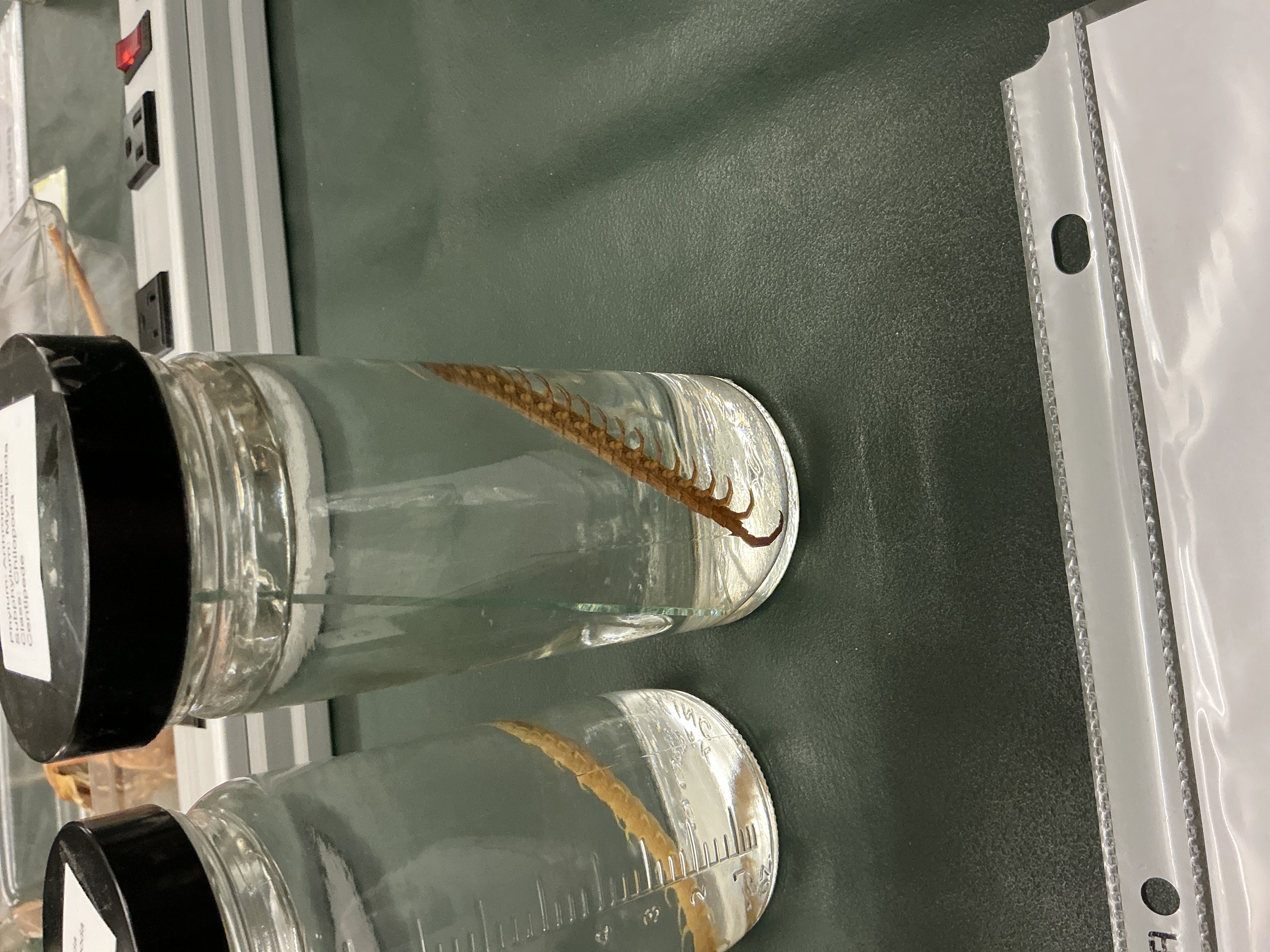
How many jointed legs per segment in Class: Chilopoda (centipedes)?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Myriapoda
One pair of jointed legs
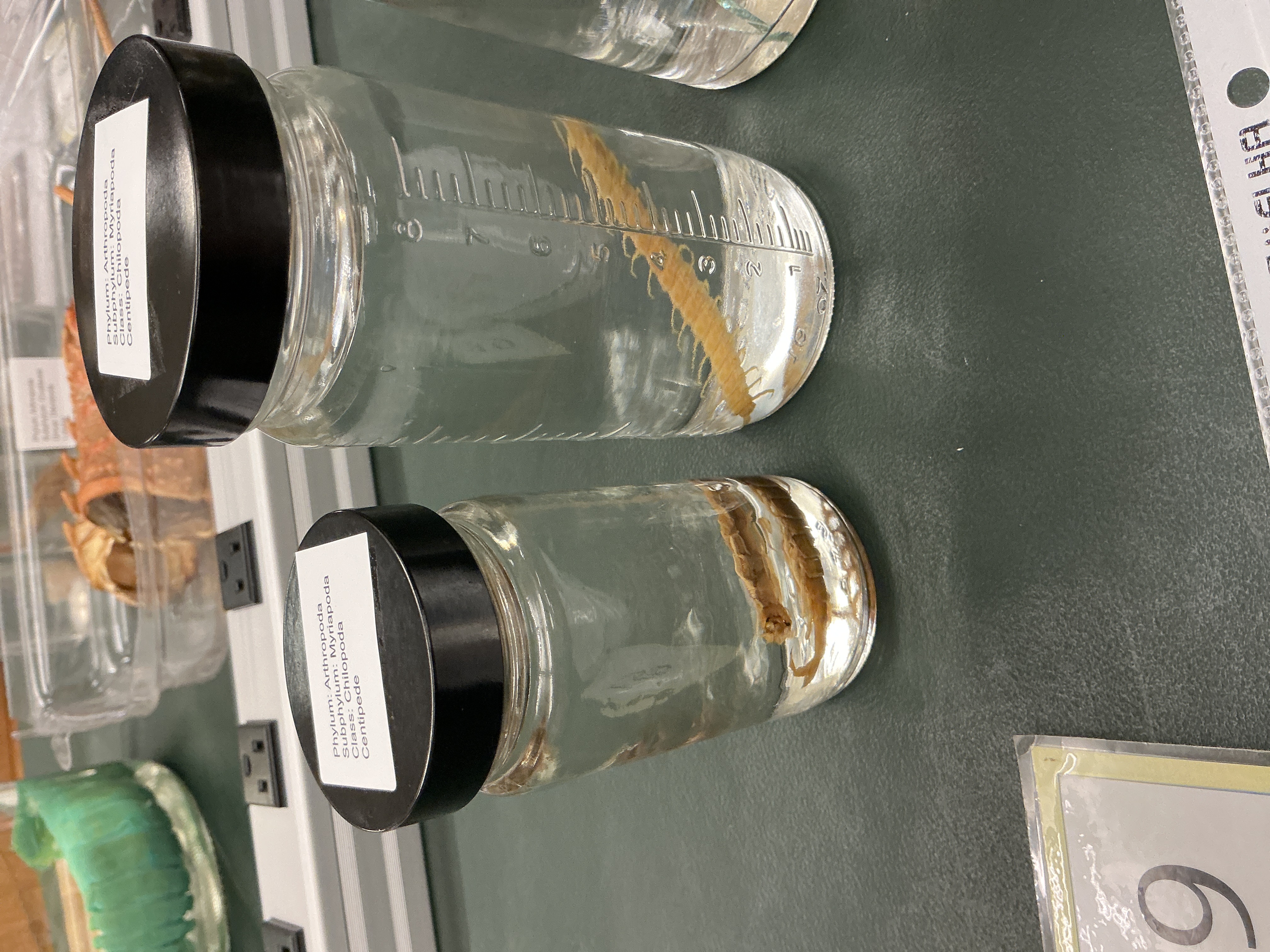

Diet Lifestyle of Class: Chilopoda
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Myriapoda
Predators, poison claws
Worldwide, forests

How many legs per segment in Class: Diplopoda (milipedes)?
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Myriapoda
2 pair of jointed legs per segment
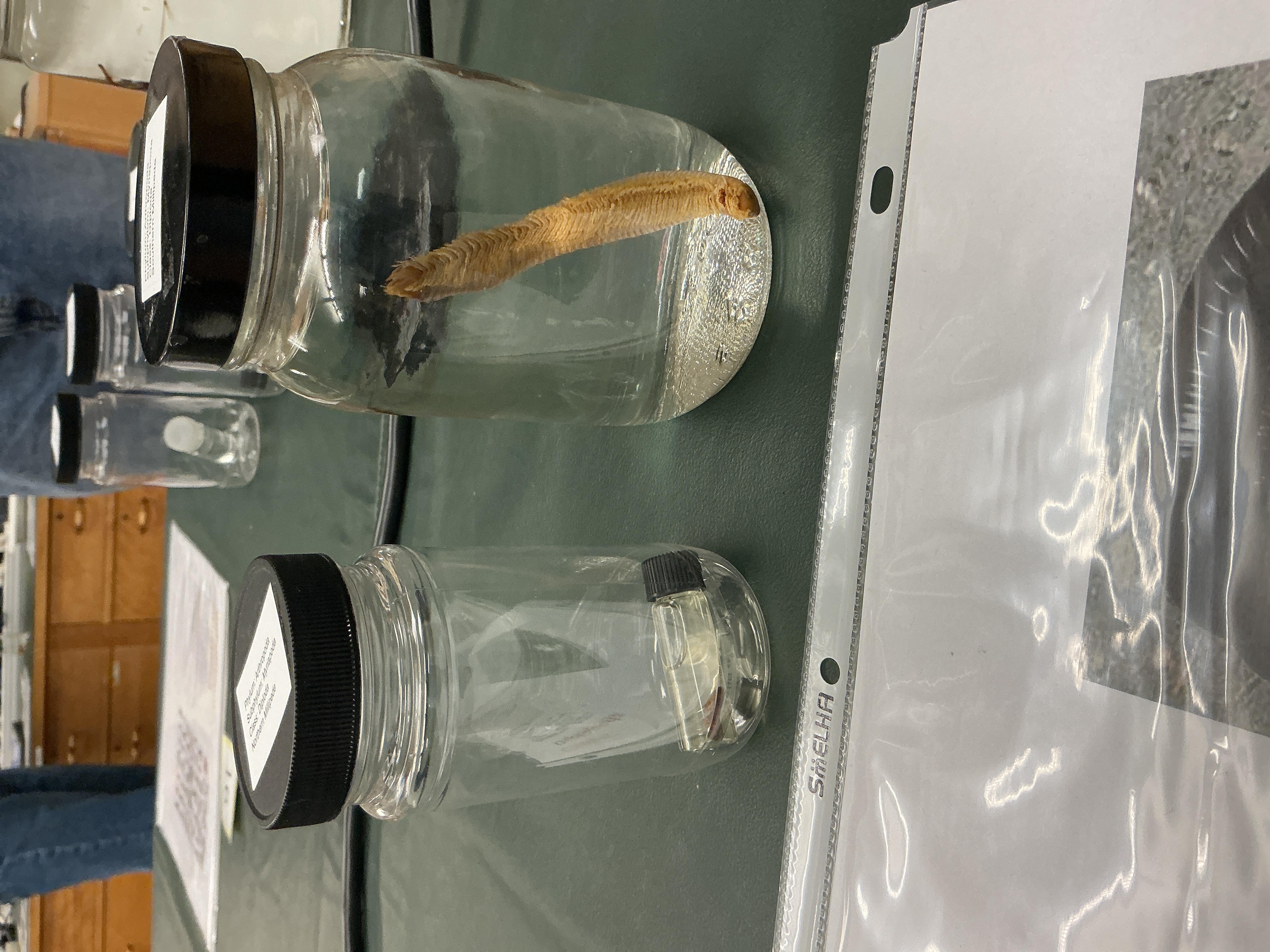

Diet Lifestyle of Class: Diplopoda
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Myriapoda
Milipedes
Detritivores
Worldwide, forests
How are appendages in Subphylum: Hexapoda modified and bodies divided?
6 appendages, each pair attached to a segment of thorax
Body; head, thorax, abdomen
Does Subphylum: Hexapoda have a mandible or antennae?
Have mandible
One pair of antennae
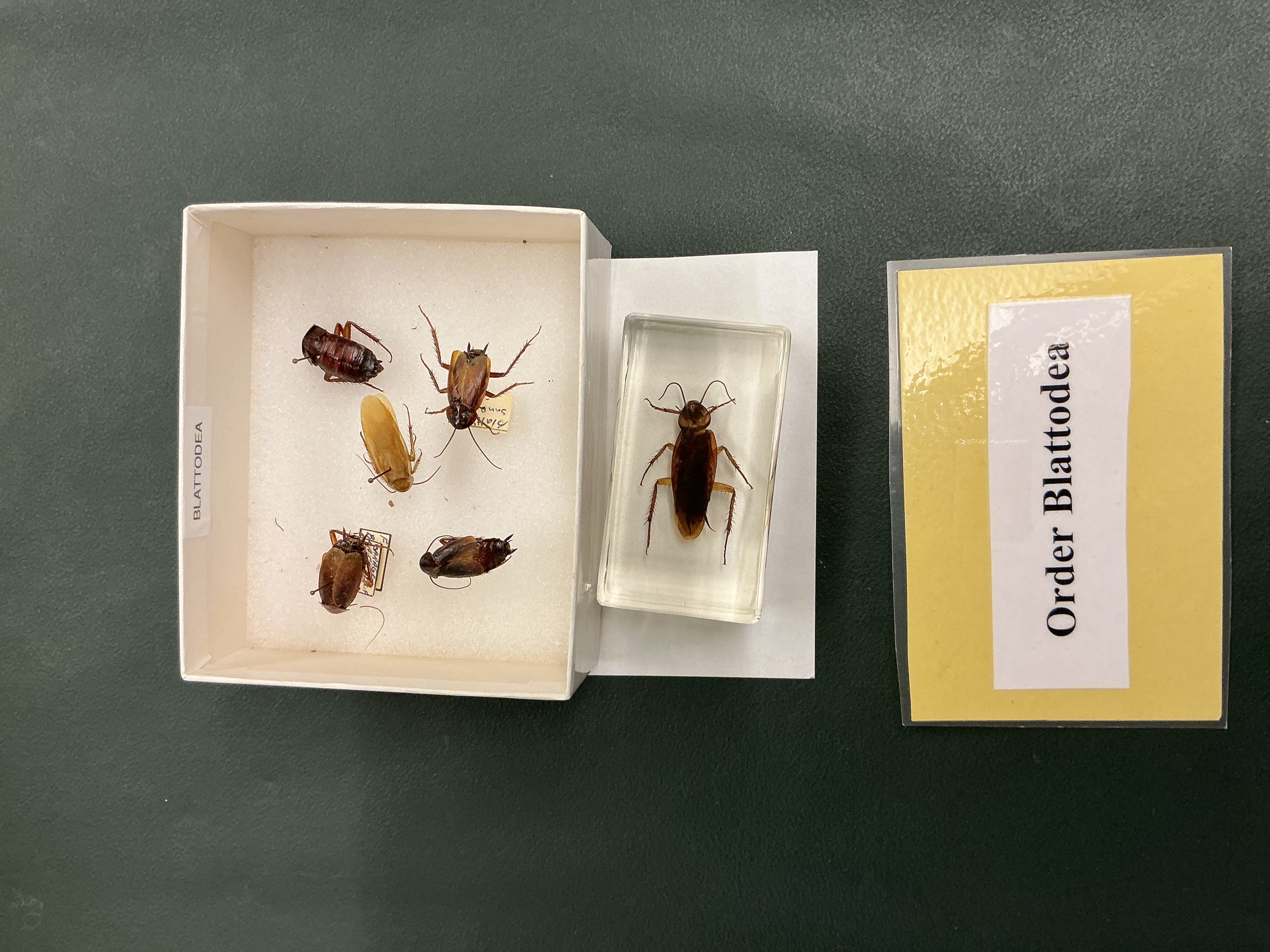
Order: Blattodea
Subphylum: Hexapoda
Class: Insecta
Cockroaches

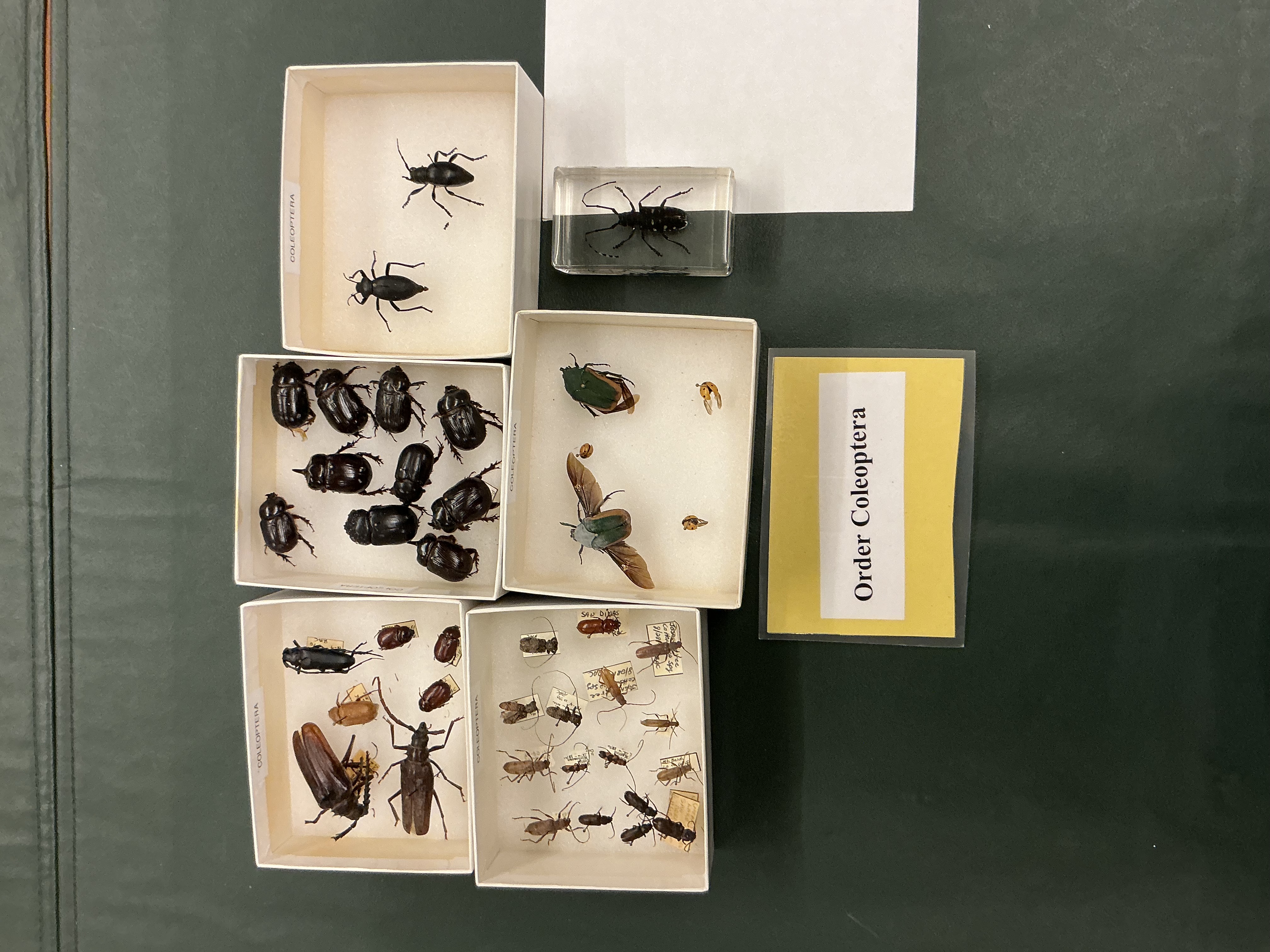
Order: Coleoptera
Subphylum: Hexapoda
Class: Insecta
Beetles

Order: Dermaptera
Subphylum: Hexapoda
Class: Insecta
Earwigs

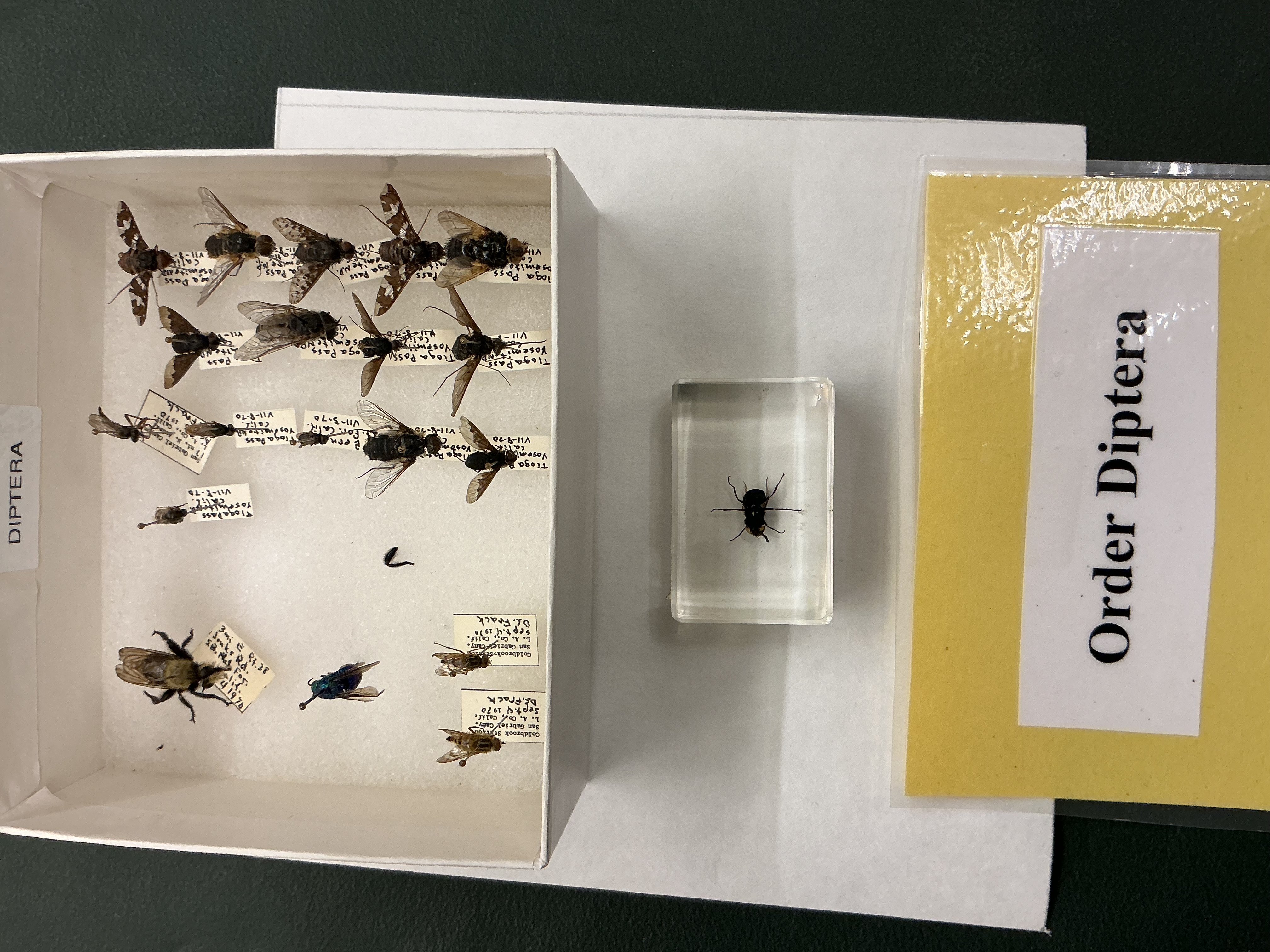
Order: Diptera
Subphylum: Hexapoda
Class: Insecta
Flies

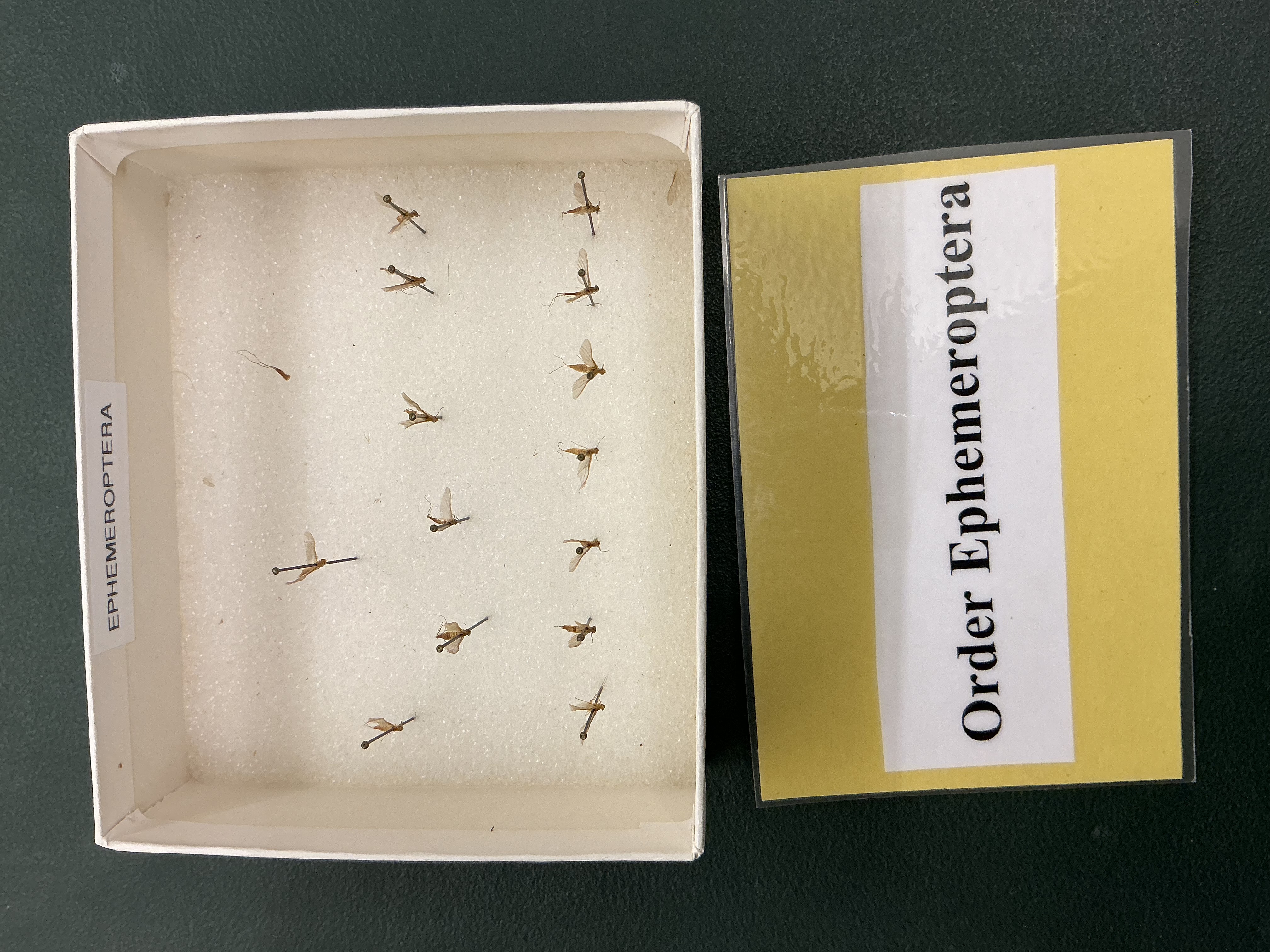
Order: Ephemeroptera
May flies

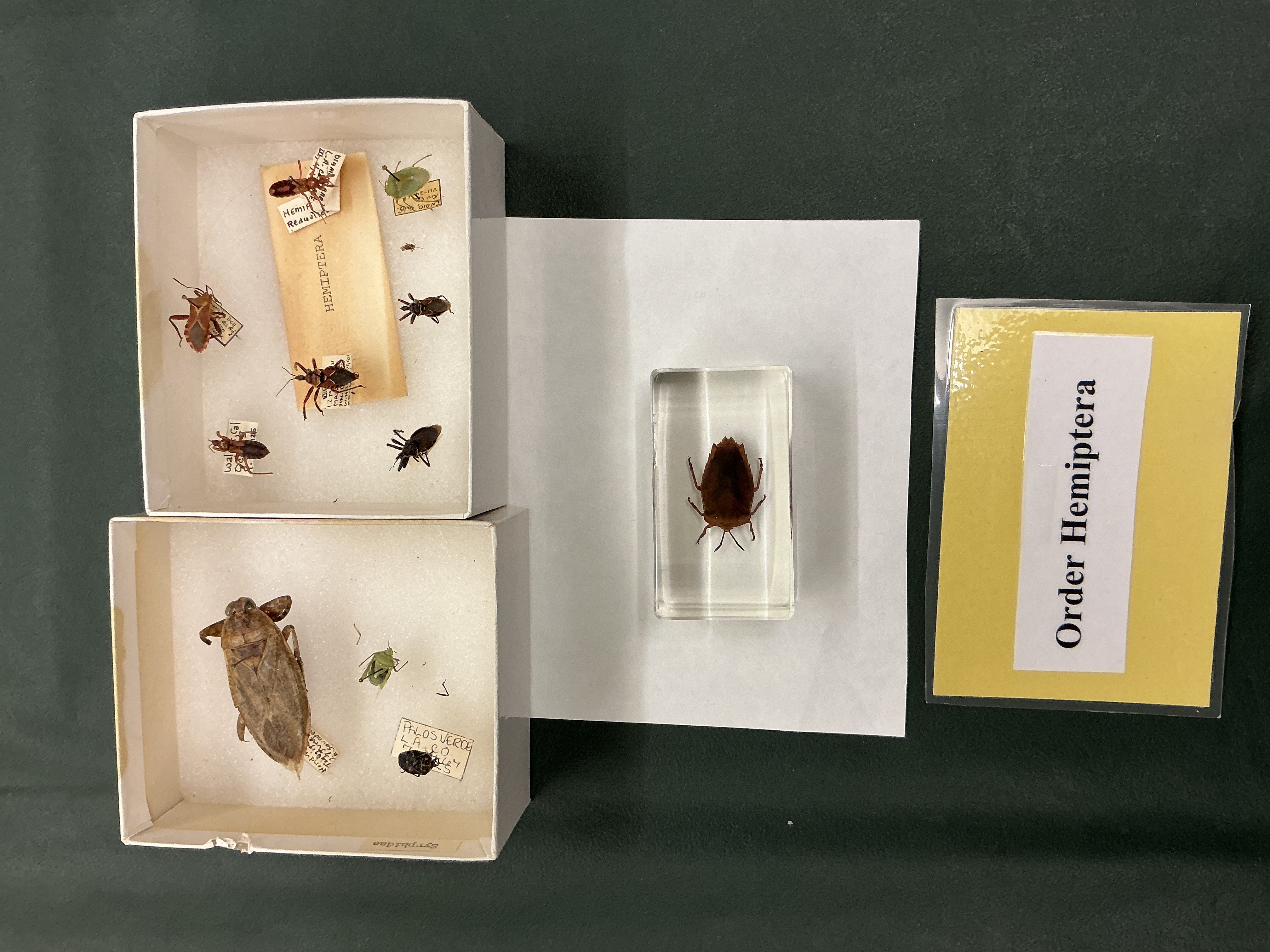
Order: Hemiptera
True bugs

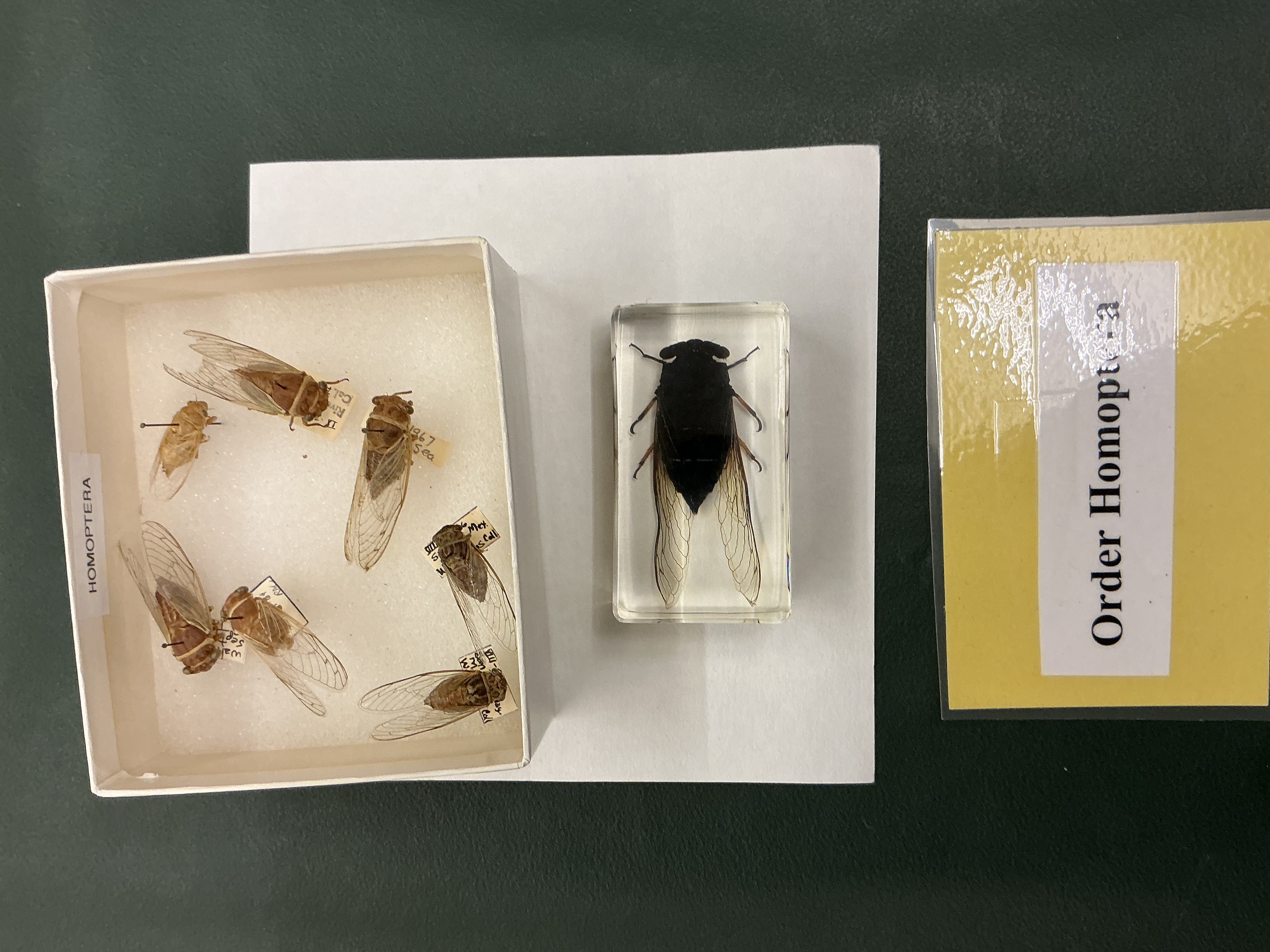
Order: Homoptera
Cicadas, Aphids, scale insects

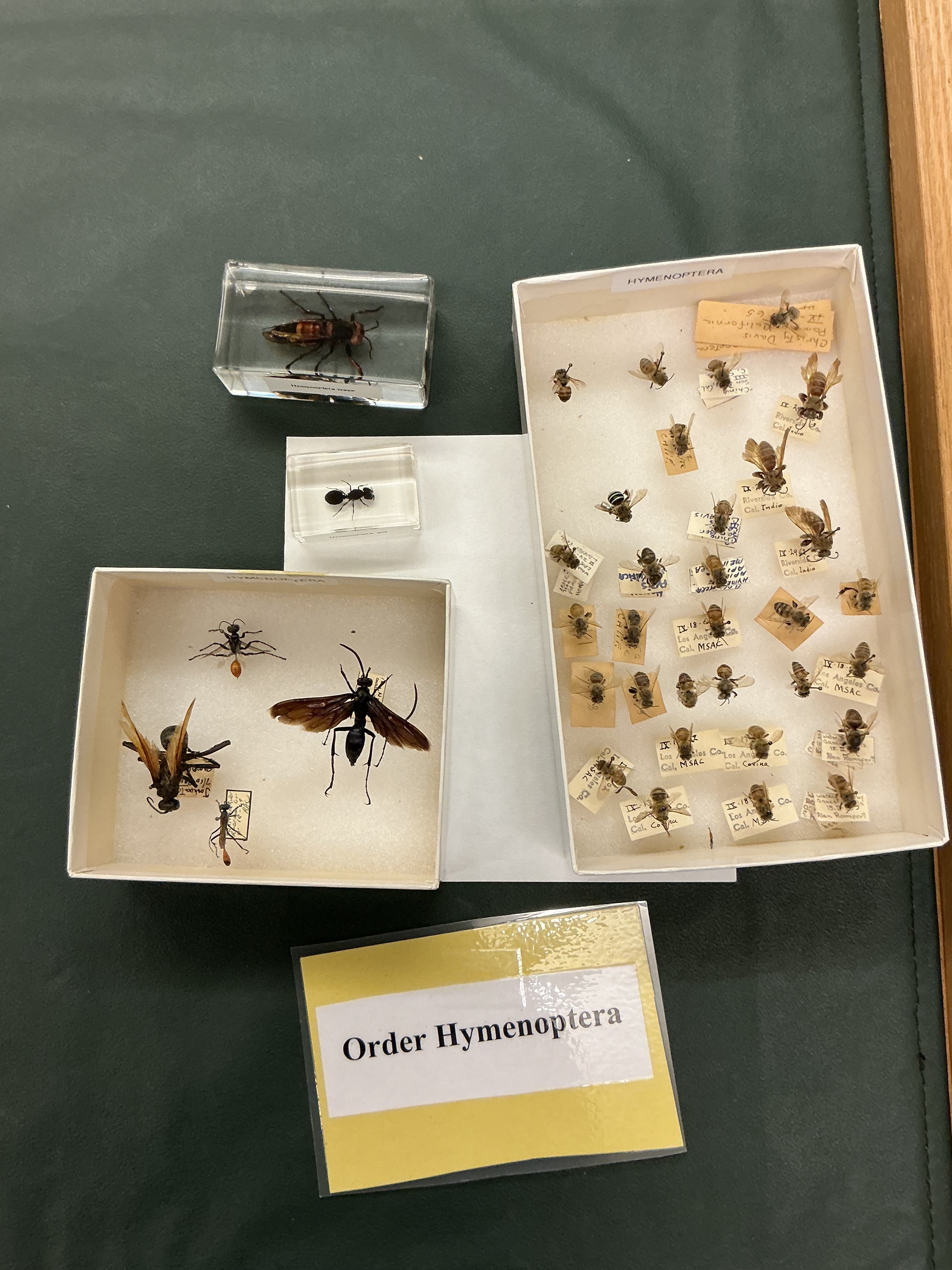
Order: Hymenoptera
Ants bees, wasps

Order: Isoptera
Termites

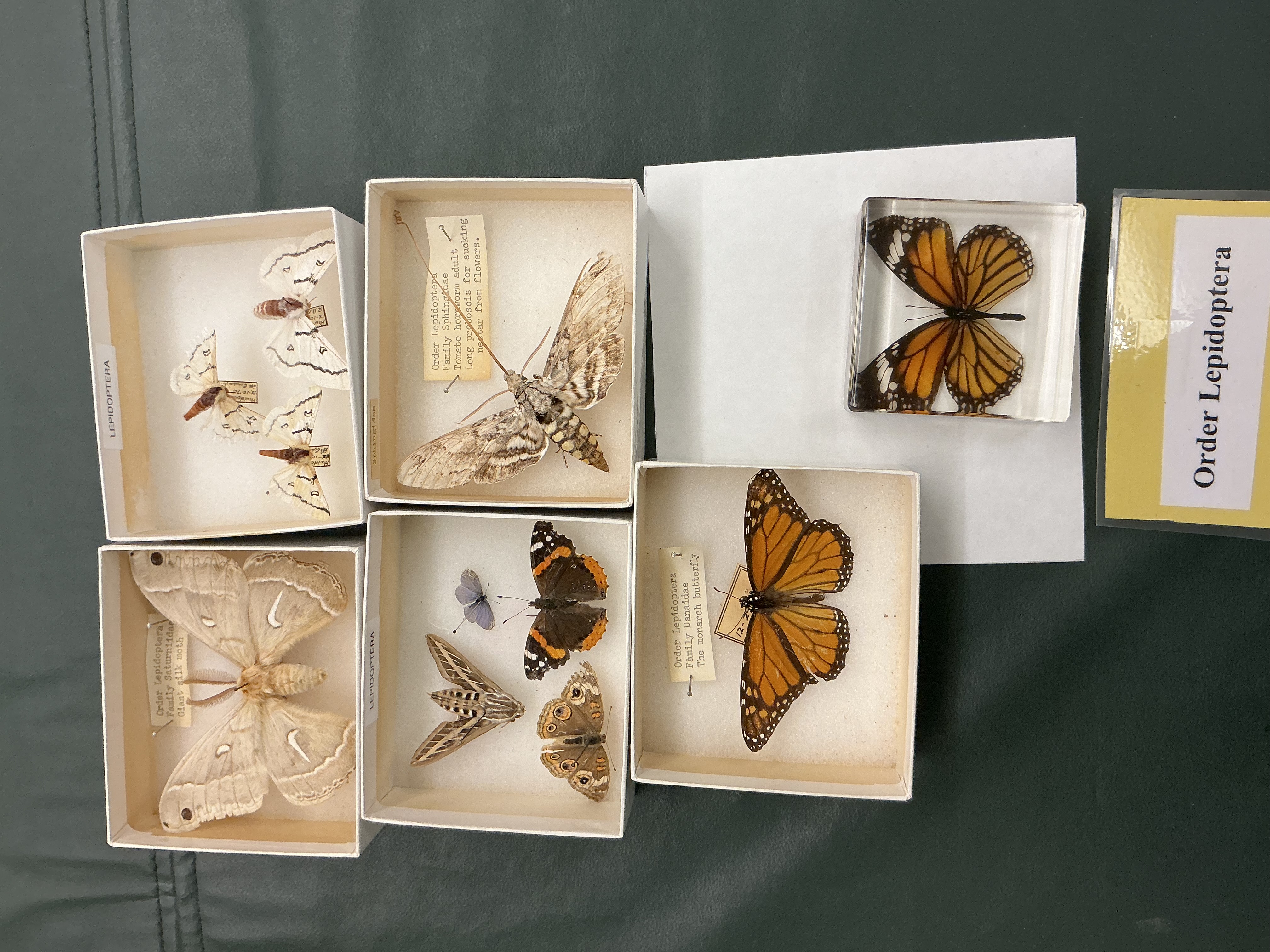
Order: Lepidoptera
Butterflies and moths

Order: Megaloptera
Alder and Dobson flies
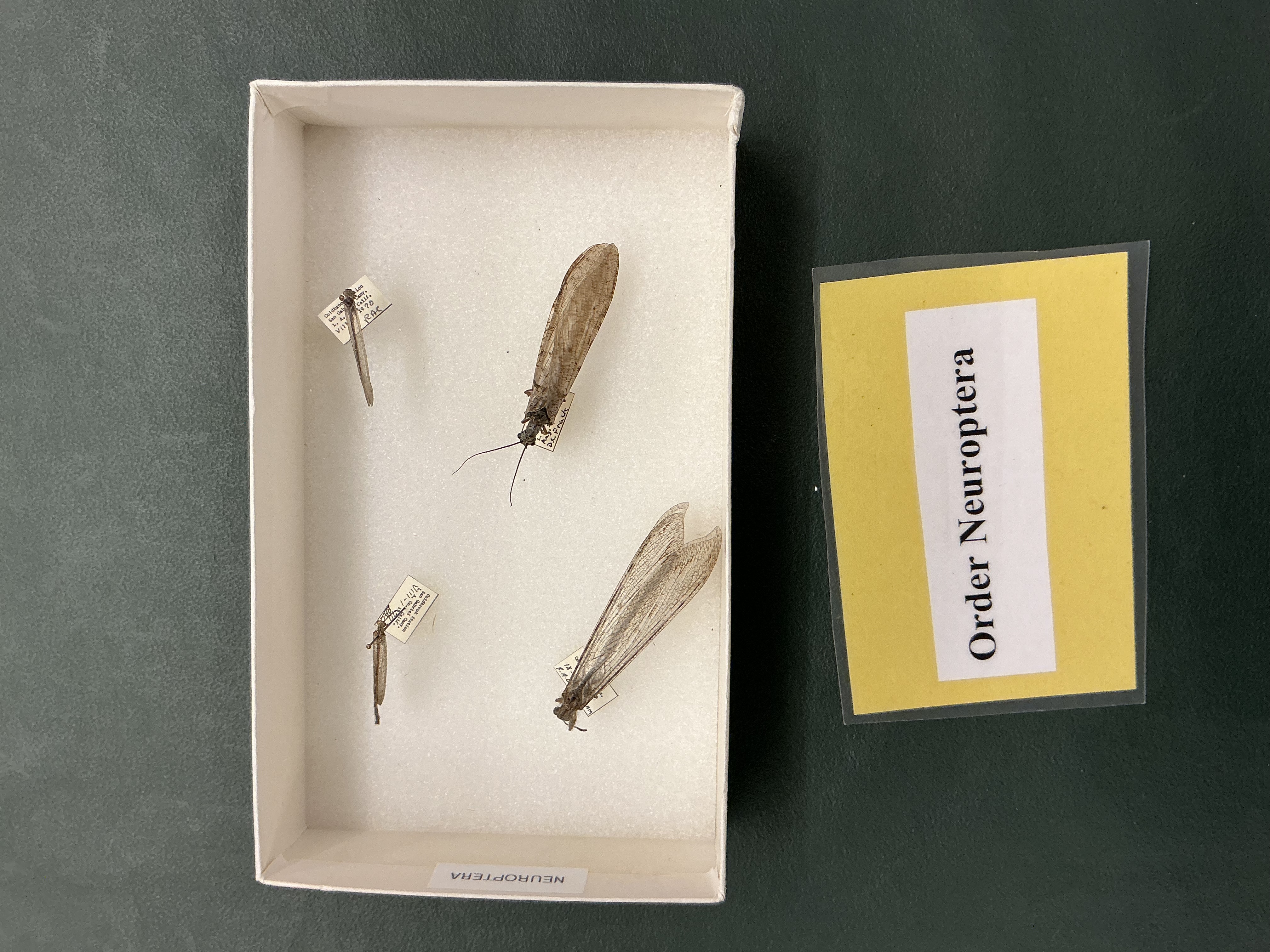
Order: Neuroptera
Antlions, lacewings

Order: Odonata
Dragonflies, damselflies

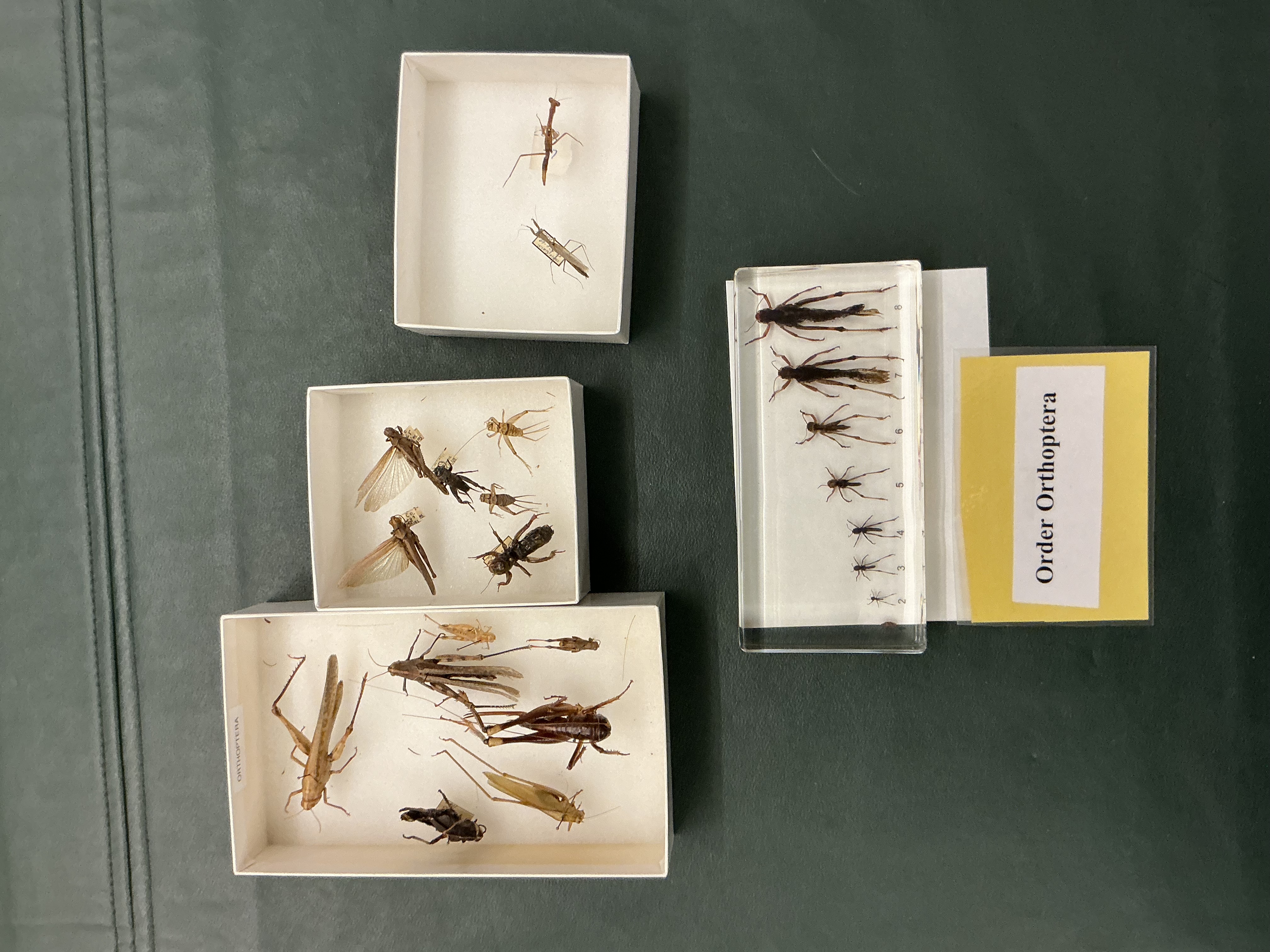
Order: Orthoptera
Grasshoppers

Order: Phasmatoidea
Stick insects
Order: Siphonaptera
Fleas

Thysanura
Silverfish
Order: Trichoptera
Caddisflies
Head Structures of Crayfish
Antenna/Antennules: taste, touch
Mandible/palp: crushing food
Maxilla: food handling
Maxillaped: food grasping
Thorax structures of Crayfish
Maxilliped/Gill: touch, taste, food handling
Cheliped: grasping food, offense
Walking leg: walking
Abdomen structures of Crayfish
Swimmerets
Males: assist with transfer of sperm
Females: carry eggs
Uropod: swimming, egg protection
What phyla belong to Deuterostommia and what morphological character do they share?
Phyla: Echinodermata
Blastopore becomes the anus (deuterstomes)
Precambrian
What is unique to Phylum: Echinodermata?
Water vascular system
Type of Symmetry and Name meaning of Phylum: Echinodermata
Type of symmetry: secondary radial symmetry
Name meaning: spiny skin
What type of development does Phylum: Echinodermata have?
Deuterostome development
Precambrian
Circulatory and Respiratory System of Phylum: Echinodermata
Circulatory: reduced
Respiratory: dermal brachiae
Nervous System and Body Cavity of Phylum: Echinodermata
Nervous system: ring and radial nerves
Eucoelomates
Reproduction of Phylum: Echinodermata
Asexual: regeneration
Sexual: dioecious
Echinodermata Terms
Oral side: mouth
Aboral: opposite of mouth
Madreporite: opening into water vascular system
Ambulacral grooves: contain tube feet
What are the pincher like organs found in Phylum: Echinodermata?
Pedicellariae
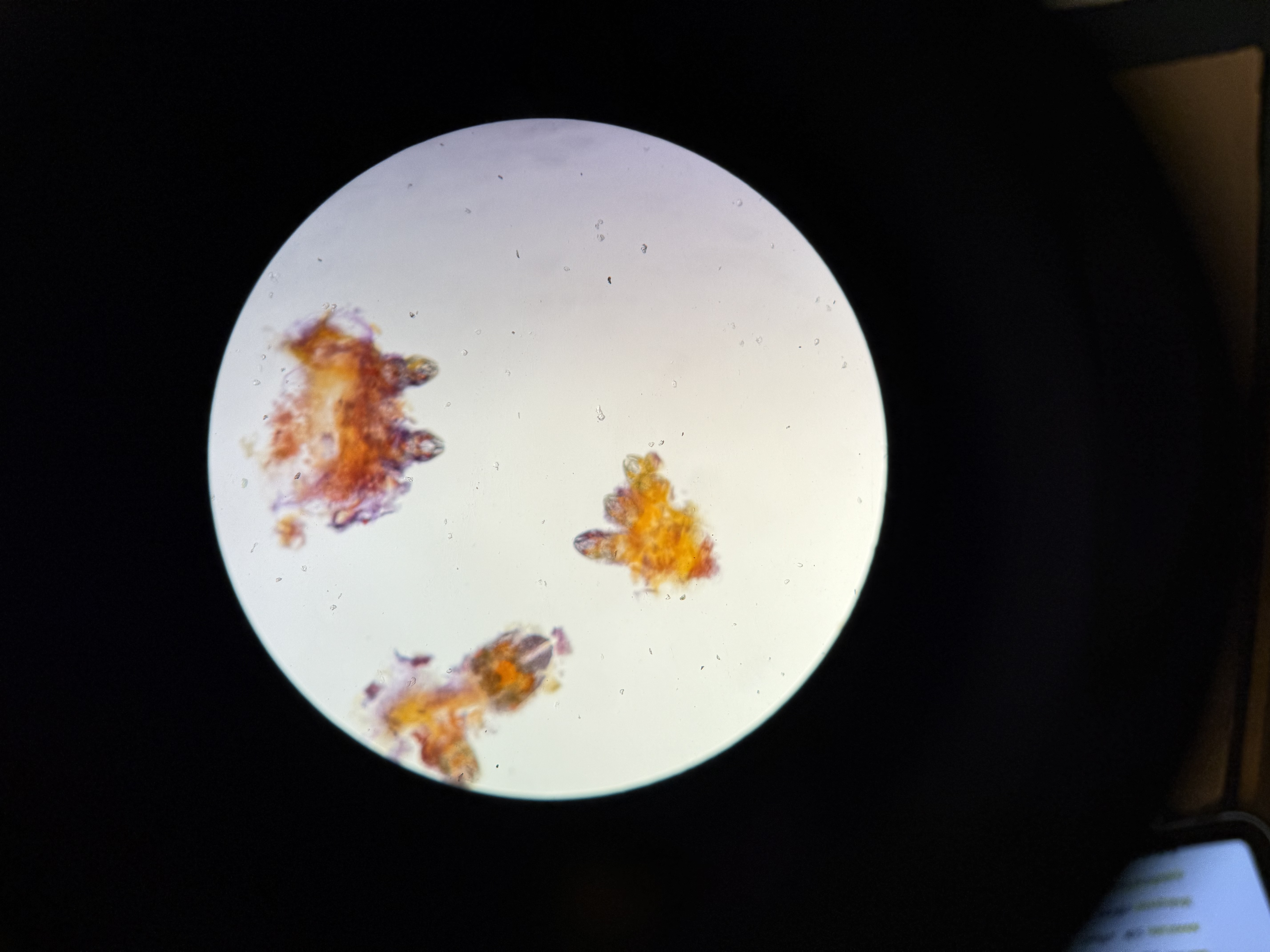
What is the bipinnaria larvae in Phylum: Echinodermata?
Function: dispersal
Evolved radial symmetry from a bilateral ancestor
What characteristic do sea stars have?
Phylum: Echinodermata
Class: Asteroidea
5 arms radiating from central disk
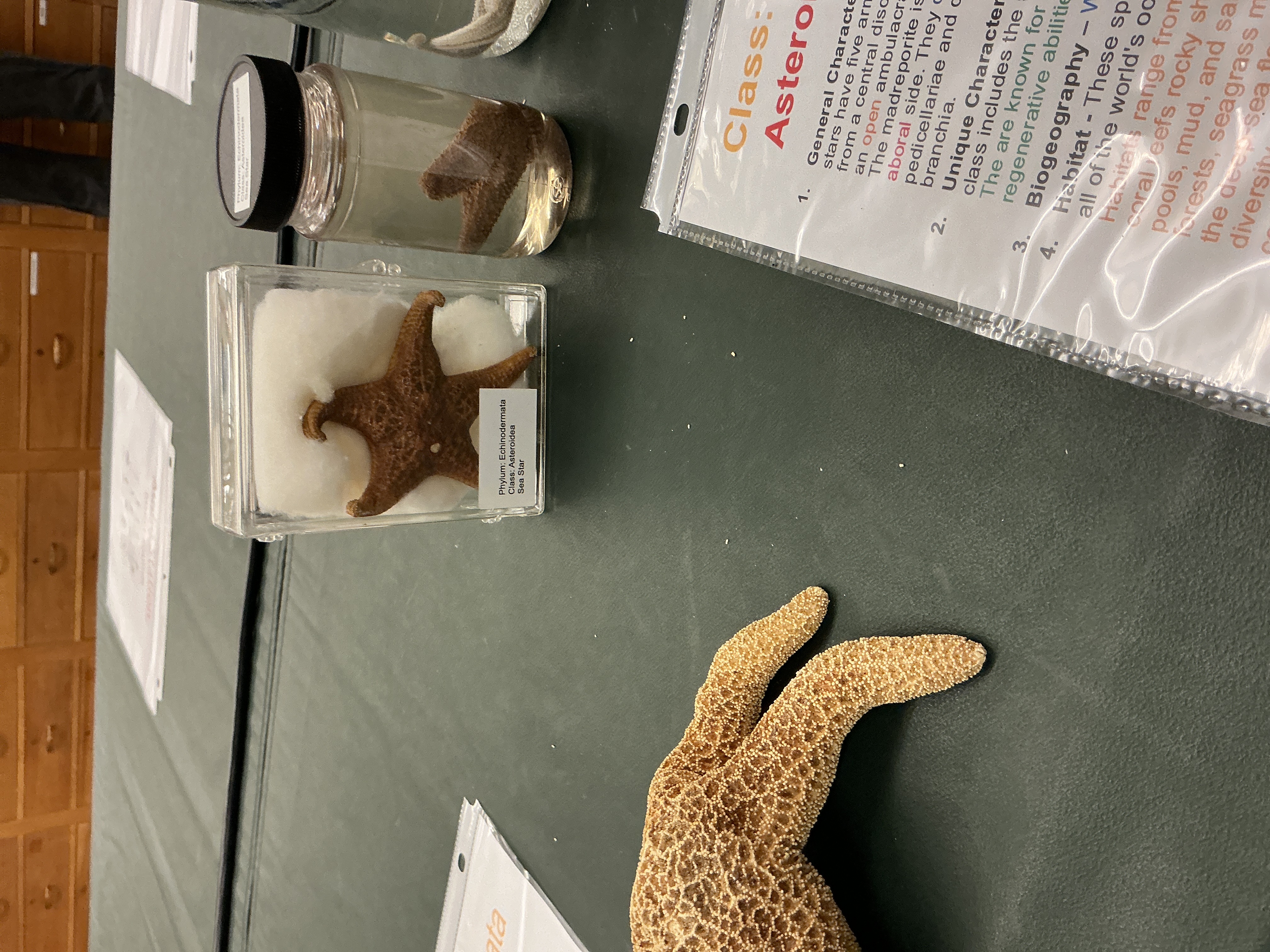
What does the ambulacral groove and madreporite look like on sea stars?
Phylum: Echinodermata
Class: Asteroidea
Madreporite on aboral side
Open ambulacral grooves
