Organisation of an ecosystem .2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what are decomposers
bacteria and fungi, which break down dead organisms in a process called decomposition or rotting
how do bacteria and fungi, break down dead organisms
release enzymes onto dead matter and then consume the broken down substances
When organisms die and decompose plants….
absorb the broken down nutrients through their roots.
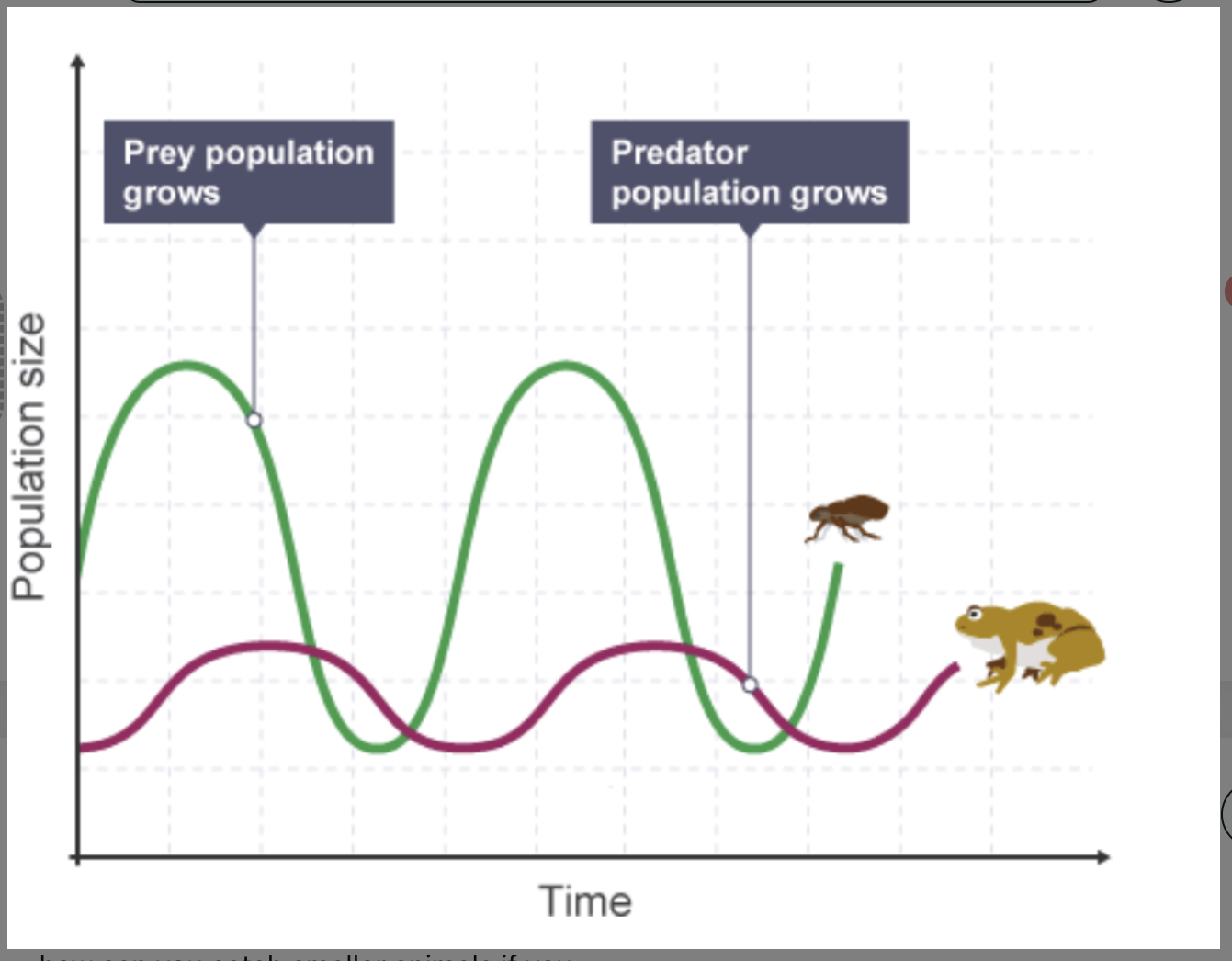
what 3 things does the graph show
the number of predators increases because there is more prey
the number of prey reduces because there are more predators
the number of predators reduces because there is less prey
how can you catch smaller animals if you want to do an investigation on how many mammals live in an area
Pitfall traps
are small traps dug into the ground, which often has food inside to attract small mammals.
The sides of these traps are smooth to stop the mammals escaping.
example of another method
use large nets to sweep through grasses or leaves of trees in a process called sweep netting
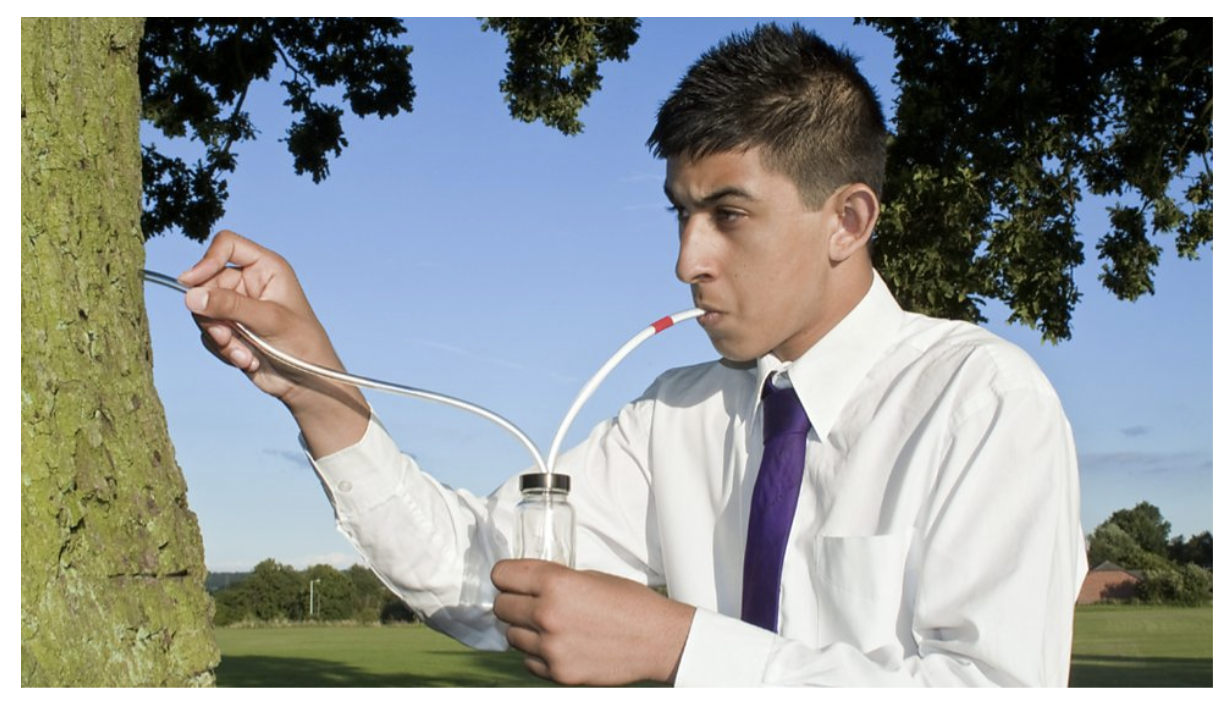
what can you use when sampling
pooters which are small devicies used to suck up small insects safetly without them going to your mouth

example of method for catching aquatic organism
nets are often held downstream of an area of river bed
The small animals float into the net.
This is called kick-sampling.
what are quadrants + size
placed on ground to look at plants / animals in them
sqaure frames of wire usually 0.25 m2
When looking at plants in a quadrant the following sampling can be used:
Number of an individual species
Species richness
Percentage cover
Required practical - measuring population size in a habitat - method
choose a starting point on the school field in an area where the grass is often cut
use random numbers to generate a set of coordinates to place your first quadrat
count the number of different plant species within this quadrat (the species richness)
return to your starting position and repeat steps two and three a further 14 times using different random numbers
repeat steps one to four for a part of the school field which the grass is infrequently cut
compare your results by calculating a mean for each location
How materials are cycled in an ecosystem (4)
rocks can cycle between igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic
carbon and water can exist in different forms at different times.
humans eat meat which is broken down in body for growth + repair + when we die these building blocks are returned to environment and used for other living organism
Decomposing bacteria and fungi help dead organisms break down and rot. They help recycle minerals and nutrients to the environment, which can then be used by other organisms
what does the carbon cycle show
how atoms of this element (carbon) can exist within different compounds at different times
the 4 carbon cycle stages
stage 1 : carbon enters atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration + combustion
stage 2 : co2 is absorbed by producers to make carbohydrates in photosynthesis
stage 3 : Animals feed on plants, passing the carbon compounds along the food chain. Most carbon they consume is exhaled as carbon dioxide during respiration. The animals and plants eventually die.
stage 4 : Dead organisms are eaten by decomposers and carbon in their bodies is returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. In some conditions decomposition is blocked. The plant and animal material may then be available as fossil fuel in the future for combustion.
if the process is photosynthesis:
what does carbon start as
what does carbon end as
carbon dioxide
glucose
if the process is respiration:
what does carbon start as
what does carbon end as
glucose
carbon dioixde
if the process is combustion (burning):
what does carbon start as
what does carbon end as
fuel (eg. methane/wood)
carbon dioxide
water cycle process
evaporation
condensation
transportation
precipitation
surface runoff
infiltration
transpiration
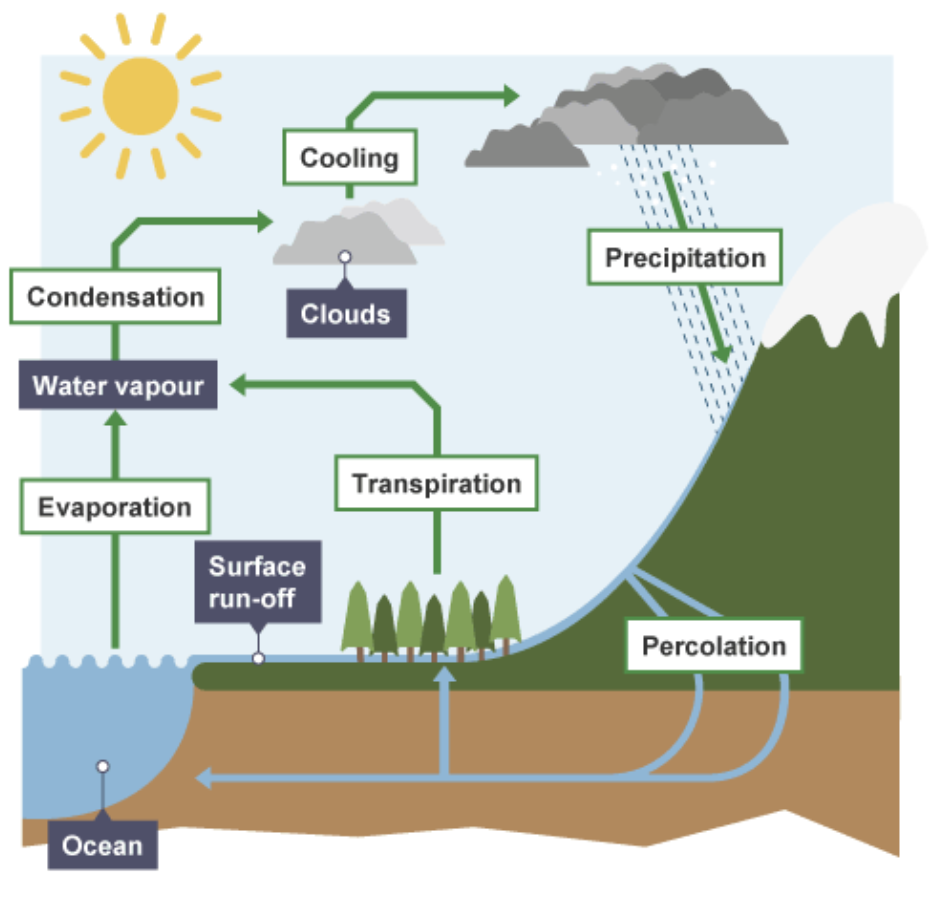
evaporation
water goes from liquid → gas when it evaporates
energy from sun can make this happen to places like puddles, ponds, lakes and oceans
condensation
after evaporation water cools + converts from gas → liquid
forms cloud often
transport
water in clouds is blown + transported to other areas by wind
precipitation
occurs when rain, snow ,hail and sleet falls from sky
surface runoff
water absorbed into group after precipitation
if lots falls + ground is wet, water runs along surface of ground
infiltration
occurs when water fallen as precipitation is absorbed into ground
can be stored within underground rocks called aquifers
transpiration
plants need constant stream of water to leaves for transport + support
so they allow some water to evaporate as water vapour from their leaves to mean that more is continually ‘pulled’ to their leaves from the soil.