Advanced Clinical Parasitology Practice Exam
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Humans, especially children, are occasional hosts of this cestode parasite of dogs, cats, and wild carnivora. Transmission results from accidental swallowing of infected fleas from dogs or cats. Finding the proglottids or eggs in the feces is diagnostic. This parasite is:
Dipylidium caninum
Echinococcus granulosus
Hymenolepis diminuta
Toxocara canis
None of the above
Dipylidium caninum
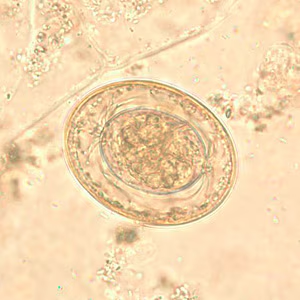
The egg shown below may cause infection by hand-to-mouth transfer or by internal autoinfection. This small worm most often infects children, and finding the egg in feces is diagnostic. Identify the parasite.
Ascaris lumbricoides
Enterobius vermicularis
Hookworm
Hymenolepis diminuta
Hymenolepis nana
hymenolepis nana
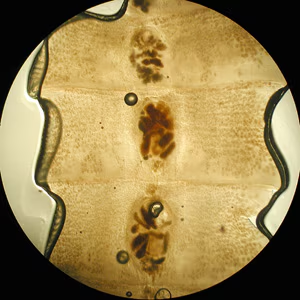
A tapeworm scolex is shown below. Select the best description of a gravid proglottid of this species.
Barrel shape with double genital pores
Longer than wide, with less than 14 main
uterine branches per side
Longer than wide, with more than 14 main
uterine branches per side
Wider than long with a rosette-shaped uterus
None of the above
Wider than long with a rosette-shaped uterus
The best direct diagnosis of Echinococcus granulosus infection in man is made by identification of:
Adult worms in the intestine
Adult worms in tissues
Eggs in feces
Hydatid cysts in tissues
Larvae in feces
Hydatid cysts in tissues
Which stage of Taenia saginata is usually infective for man?
Cysticercus larva
Embryonated egg
Filariform larva
Plerocercoid larva
Rhabditiform larva
Cysticercus larva
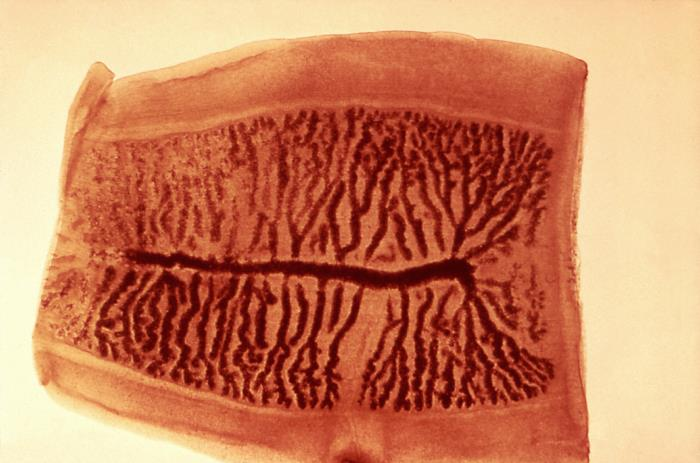
Important diagnostic information can be provided by correct identification of the gravid proglottid shown below. Which tapeworm species produces this type of proglottid?
Diplyllobothrium latum
Hymenolepis diminuta
Hymenolepis nana
Taenia saginata
Taenia solium
taenia saginata
Enterobius vermicularis infection is usually diagnosed by:
Finding adult worms in feces
Finding larvae in feces
Finding larvae in perianal specimens
Finding eggs in the feces
Finding eggs in perianal specimens
Finding eggs in perianal specimens
Visceral larval migrans is associated with which of the following organisms?
Ancylostoma duodenale
Dracunculus medinensis
Onchocerca volvulus
Toxocara canis
Trichinella spiralis
toxocara canis
Which of the following is frequently helpful in differentiating an immature cyst of Entamoeba histolytica from Entamoeba coli?
A well-defined glycogen mass
Ingested red blood cells
Ingested bacteria
Blunt chromatoidal bars
All of the above
blunt chromatoidal bars
Which of the following is the most important vector for Plasmodium vivax in Africa?
Fleas
Ticks
Sand flies
Mosquitoes
Tsetse flies
mosquitoes
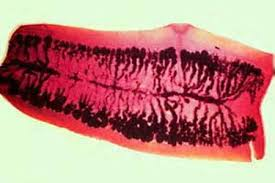
Important diagnostic information may be provided by the accurate identification of a tapeworm proglottid found in a stool specimen. The gravid proglottid shown below is typical of which of the following species?
Diphyllobothrium latum
Hymenolepis diminuta
Hymenolepis nana
Taenia saginata
Taenia solium
taenia solium
Which species of Plasmodium may readily be identified when crescent-shaped gametocytes are found in stained blood films?
P. vivax
P. falciparum
P. malariae
P. ovale
P. cynomolgi
P. falciparum
Rectal biopsy or sigmoidoscopy may be used to detect invasive parasitic infection. Which of the following is true of sigmoidoscopic material?
Helpful in diagnosing amebiasis
Can prepare permanent stains
Can detect motile trophozoites in direct mounts
Swabs should not be used to collect sample
All of the above
all of the above
Zinc sulfate flotation is not recommended for concentration of:
Oocysts of Cryptosporidium
Cysts of Giardia lamblia
Cysts of Entamoeba histolytica
Eggs of Hymenolepis nana
Eggs of Schistosoma mansoni
eggs of hymenolepis nana
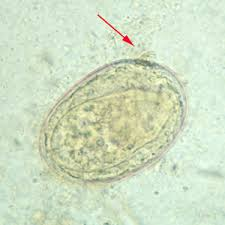
Identify the 90 x 70 µm egg shown below.
Diphyllobothrium latum
Fasciola hepatica
Hymenolepis diminuta
Paragonimus westermani
Schistosoma japonicum
schistosoma japonicum
Name the species of malaria parasite that usually produce(s) a mature schizont with 8 or 10 merozoites in a rosette, or irregular cluster, that practically fills a normal-sized erythrocyte.
Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium ovale
Plasmodium vivax
Plasmodium malariae
None of the above
Plasmodium malariae
The rhabditiform larva of Strongyloides stercoralis:
Is rarely passed in the feces
Has a prominent genital primordium
Has a notched tip of tail
Has a long buccal cavity
Is infective for man
has a prominent genital primordium
Babesia microti is an organism that has been recovered recently in a number of human infections in New England. In an examination of stained blood films, these organisms are likely to resemble:
Leishmania donovani
Plasmodium falciparum
Toxoplasma gondii
Trypanosoma cruzi
None of the above
plasmodium falciparum
On Sept. 9, 1981, a 72-year-old man from Edinburg, Texas, developed fever and weakness 16 days after being bitten by flies during a hunting trip in northwest Tanzania. Several days after the onset of fever, he noticed a raised, tender, erythematous nodule (6-8 cm in diameter) on the posterior aspect of his right arm. He was hospitalized in Africa and treated for 5 days with a cephalosporin for presumed cellulitis. After little improvement, he returned to Texas on Sept. 20. On arrival, the patient had a temperature of 38.9°C (102°F), a morbilliform rash of the trunk, and right-sided, anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) contained 12 red cells and 18 mononuclear cells/mm³, with a normal protein level (32 mg/dL). Laboratory tests revealed a hemoglobin level of 10.7 g/dL, a white cell count of 2400/mm³, and a platelet count of 75,000/mm³. The diagnosis was made by finding the extracellular flagellate parasite in a peripheral blood smear. Which of the following is the most probable etiologic agent of this infection?
Leishmania donovani
Plasmodium falciparum
Toxoplasma gondii
Trypanosoma cruzi
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
Trypanosoma brucei rhodensiense
A free-living ameba that causes primary amebic meningoencephalitis is:
Amoeba proteus
Entamoeba gingivalis
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba polecki
Naegleria fowleri
Naegleria fowleri
The usual habitat of Trichinella spiralis adults in man is:
Blood
Intestine
Liver
Lymph
Muscle
intestine
For which of the following diseases do reduviid bugs serve as vectors?
African sleeping sickness
Chagas' disease
Kala-azar
Malaria
Oriental sore
Chagas’ disease. Also known as the kissing bug
An adult helminth parasite occasionally expelled by mouth, especially by children with fever, is:
Ascaris lumbriocoides
Echinococcus granulosus
Entamoeba gingivalis
Enterobius vermicularis
Trichomonas tenax
Ascaris lumbricoides
Decontamination of drinking water, fruits, and vegetables before consumption is necessary in countries without well-developed public sanitation. Which of the following diseases would probably be least affected by that kind of precaution?
Amebiasis
Ascariasis
Fasciolopsis infection
Giardiasis
Tapeworm infection
tapeworm infection
For which of the following diseases is close contact with an infected human host the most important mechanism of transmission?
Coenurosis
Schistosomiasis
Trichinosis
Trichomoniasis
Toxoplasmosis
Trichomoniasis. It is an STI caused by trichimonas vaginalis
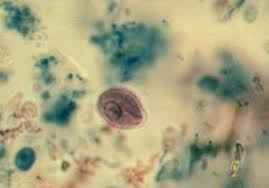
Identify this small protozoan cyst.
Chilomastix mesnili
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba hartmanni
Giardia lamblia
Trichomonas vaginalis
chilomastix mesnili
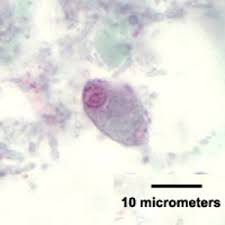
Identify this 12 µm parasite.
Balantidium coli
Chilomastix mesnili
Giardia lamblia
Trichomonas hominis
None of the above
Chilomastix mesnili
Filariform larvae
Rhabditiform larva
third infective stage of certain worms capable of penetrating the skin.
non-infective, free living stage. Nematodes
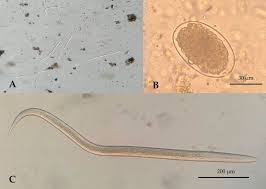
The egg shown below is the diagnostic stage of an intestinal parasite. What is the infective stage of this helminth?
egg as shown here
A fully embryonated egg
A filariform larva
A rhabditiform larva
None of the above
a filariform larva
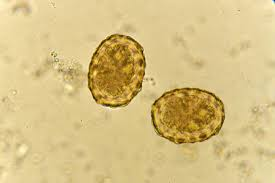
The egg shown below was detected in a preemployment stool specimen submitted by a kitchen worker who has never traveled outside the United States. He denied symptoms of gastrointestinal illness. Identify the parasite.
ylostoma duodenale
Ascaris lumbriocoides
Enterobius vermicularis
Fasciola hepatica
Paragonimus westermani
ascaris lumbricoides
The presence or absence of a sheath on a microfilaria seen in a peripheral blood smear is an important clue to species identity. In which of the following tissue nematodes are the microfilariae not sheathed?
Brugia malayi
Loa loa
Wuchereria bancrofti
Onchocerca volvulus
All of the above
Onchocera volvulus
Hydatid cyst in humans is due to ingestion of a tapeworm stage normally infective for herbivores. This stage is the:
Cercaria
Cercocystis
Cysticercus
Embryonated egg
Sparganum
embryonated egg
Which of the following is not a typical habitat of Trichomonas vaginalis?
Prostatic secretions
Vaginal discharge
Urine
Urethral discharge
Feces
Feces
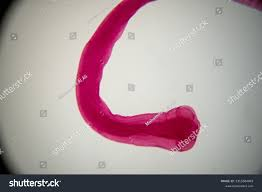
An elderly Russian woman who had recently immigrated to Israel visited her brother living in the United States. While in the United States the woman was found to have a severe anemia. The egg shown below, measuring 60 x 50 µm, was found in her stool specimen. Identify the parasite.
ascaris lumbricoides
Diphyllobothrium latum
Echinococcus granulosus
Fasciolopsis buski
Paragonimus westermani
Diphyllobothrium latum
A Giemsa-stained thick blood film showed many ring forms with no older stages, and a number of the rings had double chromatin dots. These findings are characteristic of:
Plasmodium cynomolgi
Plasmodium vivax
Plasmodium malariae
Plasmodium ovale
Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium falciparum
The formalin-ethyl acetate sedimentation concentration method is recommended for routine use primarily because it:
Preserves most parasites
Recovers protozoa
Recovers larvae
Is safer than formalin-ether sedimentation method
All of the above
All of the above
Which of the following helminths produces an elongate, barrel-shaped egg (50 x 22 µm) with a colorless polar plug at each end?
Ascaris lumbricoides
Dipylidium caninum
Hymenolepis nana
Necator americanus
Trichuris trichiura
Trichuris trichiura
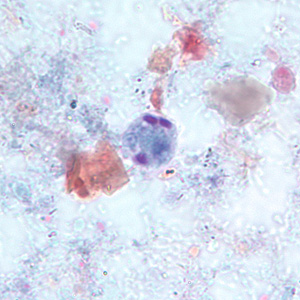
This amebic cyst has an average size of 6-8 µm and is usually spherical. When mature, it has four nuclei, but immature cysts with one or two nuclei are often seen. The nuclei have fine uniform granules of peripheral chromatin and small, discrete, usually central karyosomes. Chromatoidal bars with bluntly rounded ends are often present. Name the species.
olimax nana
Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba hartmanni
Entamoeba histolytica
Iodamoeba bütschlii
Entamoeba hartmanni

Identify this 20 µm amebic trophozoite.
Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba hartmanni
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba polecki
None of the above
Entamoeba coli
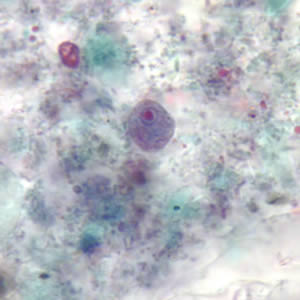
This ameba is more easily identified by its quadrinucleate cyst. Identify its 9 µm trophozoite shown below:
Dientamoeba fragilis
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba hartmanni
Entamoeba histolytica
Iodamoeba bütschlii
endolimax nana
Because of fecal contamination a urine specimen may contain the flagellate:
Balantidium coli
Entamoeba coli
Trichomonas hominis
Trichomonas tenax
Trichomonas vaginalis
Trichomonas hominis
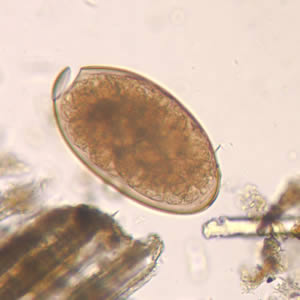
The large, operculate egg shown below is characteristic of:
Heterophyes heterophyes
Diphyllobothrium latum
Fasciola hepatica
Paragonimus westermani
Clonorchis sinensis
fasciola hepatica
A dog parasite that almost never develops to an adult in humans has been found in some persons as a cause of a subcutaneous nodule or a solitary peripheral nodule in the lung. This nematode is:
Ancylostoma braziliense
Dipylidium caninum
Dirofilaria inmitis
Echinococcus granulosus
Onchocerca volvulus
Dirofilaria inmitis
"River blindness" is a parasitic disease affecting many people in Africa, Central America, and northern South America who live within 5 miles of the rapidly flowing small streams where the black fly vectors of the causative parasite breed. The parasite causing river blindness is:
Leishmania tropica
Loa loa
Onchocerca volvulus
Toxocara canis
Trypanosoma brucei
Onchocerca volvulus
Which is the most dependable procedure for the accurate, specific diagnosis of an intestinal amebic infection?
Direct saline wet mount
Iodine-saline wet mount
Formalin-ether sedimentation technique
Permanently stained smear
Quensel's vital stain
Permanently stained smear
Elephantiasis is a complication associated with which of the following?
Cysticercosis
Guinea worm
Hydatid cyst disease
Filariae
Ascariasis
Filariae
Which Plasmodium species often causes "malignant tertian malaria" as a fulminating, fatal infection?
P. ovale
P. vivax
P. malariae
P. falciparum
P. knowlesi
P. falciparum
Which of the following pairs of helminths cannot be reliably differentiated by appearance of their eggs?
Trichuris trichiura and Trichinella spiralis
Hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta
Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale
Diphyllobothrium latum and Dipylidium caninum
Ascaris lumbricoides and N. americanus
Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale
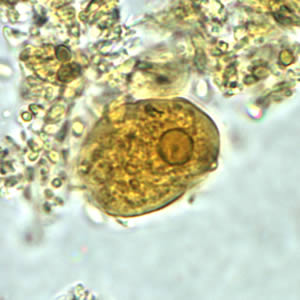
Identify this 17 µm ameoba.
Dientamoeba fragilis
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba hartmanni
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica
Sanitary disposal of human feces is the most important factor in decreasing the incidence of most infections with intestinal parasites. Which of the following diseases would not be affected by that kind of sanitation?
Ascariasis
Hookworm infection
Schistosomiasis
Taeniasis
Trichinosis
Trichinosis, acquired by eating raw or under cooked meat
Knowledge of its nocturnal periodicity is especially important in the diagnosis of infection with which of the following tissue roundworms?
Dracunculus medinensis
Loa loa
Onchocerca volvulus
Wuchereria bancrofti
Mansonella ozzardi
Wuchereria bancrofti
Chagas' disease is caused by:
Trypanosoma rhodesiense
Trypanosoma cruzi
Leishmania braziliensis
Mansonella perstans
Brugia malayi
Trypanosoma cruzi
Hematuria is one typical sign of human infection caused by:
Onchocerca volvulus
Trichinella spiralis
Trichomonas vaginalis
Schistosoma haematobium
Trypanosoma cruzii
Schistosoma haematobium
Because of the possibility of drug resistance or the persistence of extra erythrocytic (EE) parasites, identification of the causative species can be important in the choice of treatment for malaria. Which species of Plasmodium may have extraerythrocytic stages capable of causing relapses up to 3 or more years after initial infection?
P. falciparum
P. ovale
P. malariae
P. cyomolgi
P. knowlesi
P. ovale
Various species of the sandflies (genus Phlebotomus or Lutzomyia) serve as vectors for:
African trypanosomiasis
Chagas' disease (American trypanosomiasis)
Filariasis
Leishmaniasis
Toxoplasmosis
Leishmaniasis
What is the recommended test for diagnosing congenital toxoplasmosis?
PCR
Hemagglutination inhibition (HI)
IgM capture enzyme immunoassay (EIA)
IgG indirect immunofluoresence assay (IIF)
Immunoblot (IB)
PCR
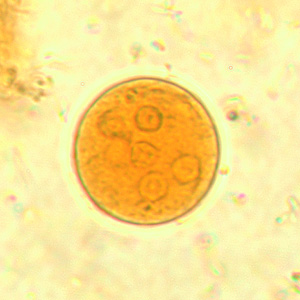
Identify the 20 µm cyst shown below.
Balantidium coli
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba polecki
entamoeba coli
Which of the following findings in a peripheral blood smear is especially associated with tissue-invading helminths but may also be found in a variety of allergic conditions and other diseases?
Anemia
Leukopenia
Neutropenia
Eosinophilia
Lymphocytosis
Eosinophilia
A 15 µm, pear-shaped flagellate with a visible parabasal body and "falling leaf" motility in a direct saline mount of a diarrheal stool specimen is most probably:
Chilomastix mesnili
Enteromonas hominis
Giardia lamblia
Retortamonas intestinalis
Trichomonas hominis
Giardia lamblia
Which of the following nematode (round-worm) parasites is acquired from eating inadequately cooked, infected pork?
Strongyloides stercoralis
Taenia solium
Taenia saginata
Trichinella spiralis
Necator americanus
trichinella spiralis
Which of the following is the most important vector for Toxoplasma gondii?
Fleas
Ticks
Flies
Mosquitoes
None of the above
None of the above. Transmission through ingesting contaminated food or water.
In December 1990 a resident of Staunton, Virginia, presented to his physician with fever, muscle pain, periorbital edema, and eosinophilia. The case history revealed the patient had consumed pork sausage about 10 days previously. From what disease is this patient most likely suffering?
Chaga's disease
Cryptosporidiosis
Trichinosis
Taeniasis
Giardiasis
trichinosis
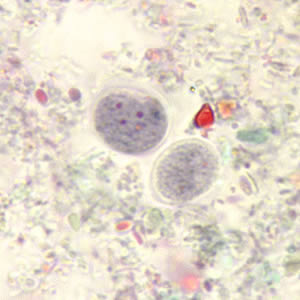
Identify the 7 µm cyst shown below.
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba hartmanni
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba polecki
Iodamoeba bütschlii
Endolimax nana
In which specimen is the 85 x 53 µm egg shown below most likely to be found?

Anal swab
Duodenal aspirate
Rectal biopsy
Sputum
Urine
sputum
The World Health Organization currently has a campaign to eliminate step wells to prevent transmission of the nematode parasite that is thought to have been the "fiery serpent" of the ancient Israelites. This parasite, which has various species of Cyclops as its intermediate host, is:
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
Dipetalonema perstans
Diphyllobothrium latum
Dipylidium caninum
Dracunculus medinensis
Dracunculus medinensis
Which of the following would be most helpful in controlling Necator americanus infections?
Good personal hygiene
Immunization
Thoroughly cooking food
Use of insecticides
Sanitary sewage disposal
sanitary sewage disposal
Which of the following is the most important vector for Babesia sp?
Reduviid bugs
Ticks
Lice
Mosquitoes
Rats
ticks
Cutaneous larva migrans, or "creeping eruption," is characterized by intracutaneous serpiginous lesions caused by certain nemotode larvae. The most common cause of this dermatitis is:
Ancylostoma braziliense
Ancylostoma duodenale
Necator americanus
Toxocara canis
Toxocara cati
Ancylostoma braziliense
Which of the following is typical in cysts of Iodamoeba bütschlii?
A glycogen mass
Blunt chromatoidal bars
Four nuclei with large karyosomes
Many ingested bacteria
Red blood cells
A glycogen mass
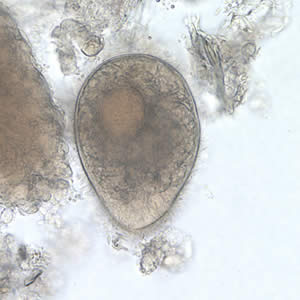
This ciliated intestinal parasite measures 50 µm. What is its identity?
Cercaria of Fasciolopsis buski
Coracidium of Diphyllobothrium latum
Trophozoite of Balantidium coli
Miracidium of Schistosoma japonicum
None of the above
Trophozoite of balantidium coli
Which stage of Trichuris trichiura is infective for man?
Egg in freshly passed feces
Filariform larva
Fully embryonated egg
Rhabditiform larva
None of the above
fully embryonated egg
Which species of malaria parasite usually has growing trophozoites with ameboid cytoplasm and produces small reddish dots in the red blood cell cytoplasm?
Plasmodium ovale
Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium malariae
Plasmodium vivax
None of the above
Plasmodium vivax
Species identification of an immature amebic cyst can be very difficult. This parasite stage would not, however, be found in infections caused by:
Dientamoeba fragilis
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba histolytica
Iodamoeba bütschlii
dientamoeba fragilis
Which of the following is the most important vector for Loa loa?
Fleas
Lice
Mango flies
Mosquitoes
Rats
mango flies
Cysticercosis is caused by the disseminated larvae of:
Echinococcus granulosus
Hymenolepis nana
Necator americanus
Taenia solium
Toxocara canis
taenia solium
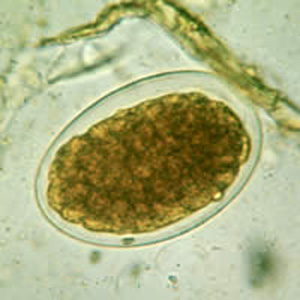
The egg shown below is the diagnostic state of an important parasite found in Puerto Rico and some other islands in the West Indies and in parts of northern South America and Africa. This helminth infects humans by:
Ingestion of the embryonated egg
Ingestion of the encysted larvae
Larval penetration of the skin
Vector injection of infective larvae
None of the above
larval penetration of the skin
With which species of malarial parasite are Schüffner's dots found in the infected erythrocytes?
Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium knowlesi
Plasmodium malariae
Plasmodium vivax
None of the above
Plasmodium vivax
Immunocompromised hosts have been found to have increased susceptibility to certain parasitic diseases. This has been found to be true for infections caused by:
Babesia
Cryptosporidium
Isospora
Strongyloides
All of the above
all of the above
The observation of embryonic flame cell activity is recommended to demonstrate the viability of eggs of:
Clonorchis
Fasciola
Necator
Schistosoma
Taenia
schistosoma
A recently recognized parasitic disease of humans is caused by ingestion of viable, third-stage larval nemotodes in the flesh of some saltwater fish such as herring. When the ingested larvae attempt to migrate through the wall of the gastrointestinal tract, a severe inflammatory reaction is produced at the site of penetration. These larvae have been found during gastroscopies and during surgery for intestinal obstruction or perforation. The name of the human zoonosis is:
Anisakiasis
Ascariasis
Dracunculosis
Filariasis
Toxocariasis
anisakiasis
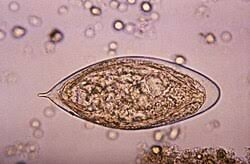
In which specimen is the large egg shown below most likely to be found?
Feces
Perianal swab
Sputum
Urine
None of the above
urine
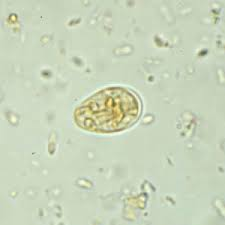
Identify this 15 µm protozoan cyst.
Balantidium coli
Chilomastix mesnili
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba histolytica
Giardia lamblia (duodenalis)
giardia lamblia (duodenalis)
Which of the following is a stage of Toxoplasma gondii infective for man?
Cercocyst
Gonad
Leptomonad
Oocyst
Plasmodium
oocyst
Which of the following forms of Toxoplasma gondii are produced in infected humans?
Bradyzoites
Merozoites
Sporoblasts
Oocysts
Macrogamete
bradyzoites
Eggs or larvae that are recovered in the stool are routinely used to diagnose infections caused by all of the following helminths, except:
Ascaris lumbriocoides
Necator americanus
Strongyloides stercoralis
Trichinella spiralis
Trichostronglylus colubriformis
trichinella spiralis
The string test (Entero-Test) for obtaining a small specimen of duodenal contents for parasitic infection would be most appropriate with:
Chilomastix mesnili
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba histolytica
Giardia lamblia
Iodamoeba bütschlii
giardia lamblia
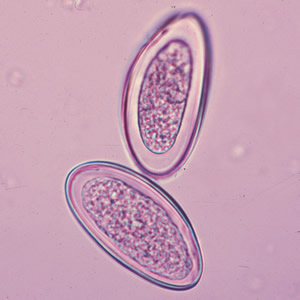
Identify the 55 x 26 µm egg shown below.
Ancylostoma duodenale
Ascaris lumbricoides
Enterobius vermicularis
Necator americanus
Trichuris trichiura
enterobius vermicularis
Which of the following would be most helpful in controlling infection due to Enterobius vermicularis?
Good personal hygiene
Immunization
Thoroughly cooking food
Preventive medication
Providing safe drinking water
good personal hygiene