Advanced sono exam 3 (fetal echo)
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
optimal time to image fetal echo
18-22 weeks
fetal echo can be performed as early as how many weeks?
10 weeks with TV and up to 16 weeks??
congenital malformations/ birth defects are caused by what
teratogens
most sensitive period for cardiac development in the 1st trimester?
3.5-6.5 weeks
which organ system is the first to reach a functional state?
cardiovascular
what weeks does circuclation begin?
3rd week
where does the vascular system begin?
in the wall of the yolk sac, connecting stalk and chorion
blank veins return blood from the embryo
cardinal
blank veins return blood from the yolk sac
vitelline
what is the caudal region of the primitive heart?
sinus venosus
what does the sinus venosus do?
receives all blood returning to the heart
the blank develops into the right ventricle
bulbus cordis
what dilates to form aortic sac from which the aortic arches arise?
truncus arteriosus
when does the division of the 4 heart chambers occur?
during the 4th and 5th week
the ductus arteriosus connects what?
between the aorta and the pulmonary artery
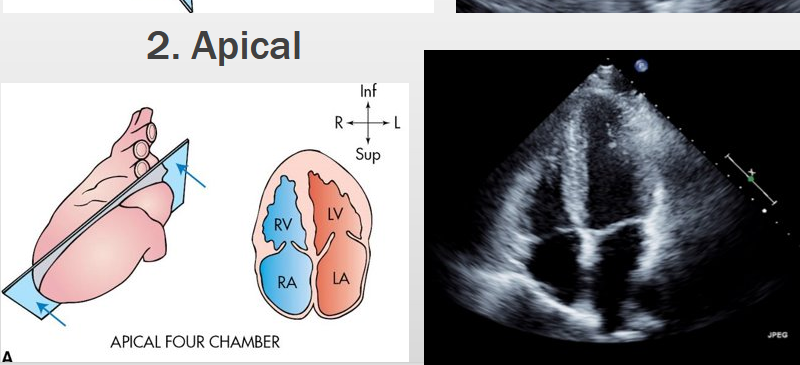
apical view of the heart
the primitive heart is a tubular structure that develops from blank cells
mesenchymal cells
paired endocardial heart tubes develop before the end of the blank week and begin to fuse, forming the primitive heart
third
what week does the heartbeat start
5th week
approx half of fetal blood passses through hepatic sinusoids; the rest bypasses the liver to go through the blank into the *blank
ductus venosus, IVC
after blood enters the SVC and IVC, where does it go?
right atrium
most of the blood from the IVC is directed by lower border of the blank through the foramen ovale into the left atrium
septum secumdum
small amount of oxygenated blood from the IVC is diverted by the blank and remains in RA to mix with deox blood from the DVC and coronary sinus
crista dividens
once blood moves into the LA where does it go?
it leaves the heart through the ascending aorta
three branches of the ascending aorta
innominate(brachiocephalic), left carotid and left subclavian
some of the blood in the RV goes through the blank
main pulmonary artery
pulmonary veins enter posterior of the blank
left atrium
cessation of placental circulation causes an immediate fall in BP in the newborns blanks
IVC and RA
Pressure in the LA becomes higher than in the RA after birth, causing blank to close
the foramen ovale
over time what causes complete closure of the foramen ovale?
adhesion of septum prmum to left margin of th eseptum secundum
what forms the floor of the fossa ovalis?
the septum primum
ductus arteriosus usually constricts blank hours after birth
24-48 hours
ductus arteriosus turns into the blank after birth
ligamentum arteriosum
normal fetal HR
120-160 bpm
in the 1st tri, HR begins arond blank
90 bpm, increasing to 170 before returning to normal
HR greater than blank is tachycardia
200 bpm
HR lower than blank is bradycardia
60 bpm
most common fetal risk factors for congenital heart disease
cardiac arrhythmias
what is associated with congenital heart disease?
presence of extracardiac abnormalities
other risk factors for CHD
IUGR, abnormal amniocentesis, amniotic fluid collections, HR and hydrops fetalis
maternal diseases affecting the fetus
diabetes, lupus and infection
if one parent has congenital heart defect, recurrance risk ranges from blank
2.5-4%
the apical 4 chamber view also contains what
the aorta
the parasternal view contains what
RV, LV, IVS, LA and Ao
the suprastenal view contains what
ascending Ao, right and left pulmonary artery, and SVC
cardiac window is found between what intercostal spaces
3rd and 5th
heart is displaced further toward the left chest
levoposition
heart is in the right chest with the apex pointed to the right thorax
dextrocardia
heart is in the right chest with apex pointed medially or to the left
dextroposition
heart is in atypical location with the apex pointing toward the midline
mesocardia
what is a disease of the myocardium, dialted chambers and thinning myocardial walls
cardiomyopathy
necrosis and destruction of myocardial cells and inflammatory infiltrate
myocarditis
failure of foramen ovale to close leads to what type of defect?
atrial septal- secundum type
what is the most common congenital lesion of the heart
ventricular septal defect
most common type of ventricular septal defect?
membranous (not muscular)
what is the failure of the endocardial cushion to fuse?
incomplete atriventricular septal defect
what is a single, undivided free floating leaflet stretching across both ventricles?
complete atrioventiruclar septal defect
what is an interruption of the growth of the tricuspid leaflet?
tricuspid atresia/stenosis
what is an abnormal displacement of the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve?
Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve
symptoms of Ebsteins anomaly
SOB, fatigue, palpitations and cyanosis
what is an underdeveloped right side of heart due to obstruction of the RVOT and pulmonary artery stenosis?
hypoplastic right heart
what happens due to hypoplastic right heart?
reduced oxygen pickup which causes cyanosis
most common form of cyanotic heart disease in children/infants
tetralogy of Fallot
4 defects in tetralogy of fallot
pulmonary stenosis, VSD, dextroposition of the aorta and RV hypertrophy
wwhat is a small hypertrophied left ventricle with aortic or mitral dysplasia
hypoplastic left heart syndrome
symptoms of hypoplastic left heart syndrome
CHF, effusion and hydrops
hypoplastic left heart syndrome is autosomal recessive or dominant?
recessive
what condition is when the Ao is connected to the RV and the pumonary artery is connected to the left ventricle?
transposition of the great arteries
what is a discrete shelflike lesion that presents in the isthmus of the arch or near the left subclav artery?
coarctation of the aorta
what are multiple septal benign masses
rhabdomyomas
rhabdomyomas are associated with what
tuberous sclerosis
what is a heart lesion that forms from an abnormal development of the primitive heart outside the embryonic disk?
ectopic cordis