Review Lesson 2 Bio 2 Quarter 3
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Skeletal System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
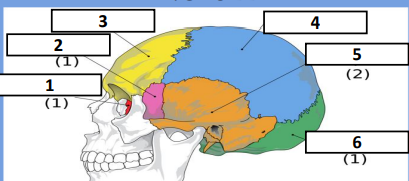
Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital
Identify the bones respectively
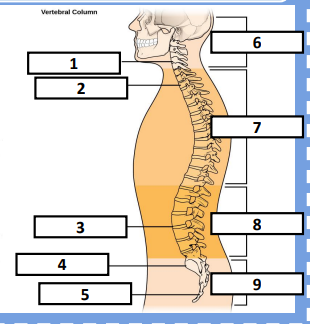
Cervical vertebrae, Thoracic vertebrae, Lumbar vertebrae, Sacrum, Coccygeal vertebrae, Cervical curve, Thoracic curve, Lumbar curve, Sacral curve
Identify the bones respectively
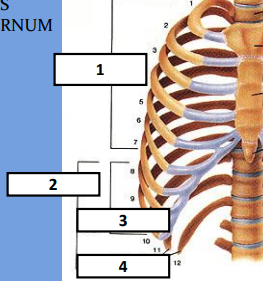
vertebrosternal, false ribs, vertebrochondral, vertebral
Identify the bones respectively
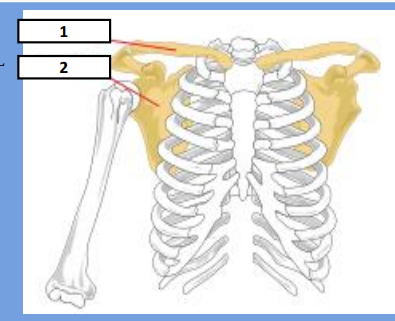
Clavicle and Scapula
Identify the bones respectively
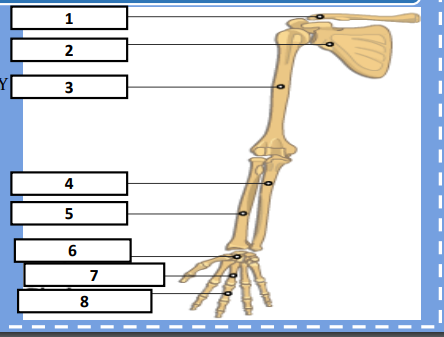
Clavicle, Scapula, Humerus, Ulna, Radius, Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges
Identify the bones respectively
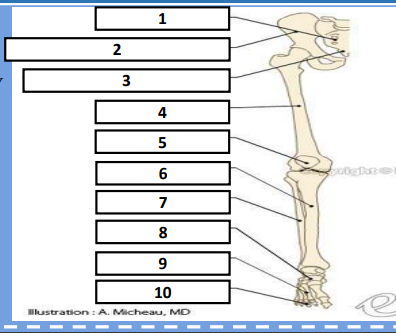
Sacrum, Pelvic bone, Coccyx, Femur, Patella, Tibia, Fibula, Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges
Identify the bones respectively
Long Bones
longer than they are wide
Short bones
can be approximately cube-shaped
Short bones
length is similar to width/depth/diameter
Flat bones
have a thin shape, in some case. it provides mechanical protection to soft tissues beneath or enclosed by flat bone
Irregular bones
have complicated shape that cannot be classified as long, short, or flat
Irregular bones
Their shape depends with their role
Sesamoid bones
Develop in some tendons in locations where there is considerable frictions, tension, and physical stress
Long bones
What classification of bones is femur
Long Bones
What classification of bones is tibia
Long Bones
What classification of bones is fibula
Long Bones
What classification of bones is humerus
Long Bones
What classification of bones is radius
Long Bones
What classification of bones is ulna
Short bones
What classification of bones is carpal bones
Short bones
What classification of bones is tarsal bones
Flat bones
What classification of bones is frontal
Flat bones
What classification of bones is parietal
Flat bones
What classification of bones is sternum
Flat bones
What classification of bones is ribs
Flat bones
What classification of bones is scapula
Irregular bones
What classification of bones is atlas
Irregular bones
What classification of bones is axis
Irregular bones
What classification of bones is vertebra
Irregular bones
What classification of bones is hyoid
Irregular bones
What classification of bones is zygomatic
Sesamoid bones
What classification of bones is patella
Skeletal system
It provides supporting frameworks of body
Skeletal system
It provides lever for muscle
calcium and phosphorus
Skeletal system has minerals like ?
Ossification or osteogenesis
It is the process of bone formation by osteoblast
Intramembranous ossification
fibrous membranes of some part of fetal skeleton are converted to bone
Endochondral ossification
conversion of cartilage into bone. All of the bones of the body, except for the flat bones of the skull, mandible, and clavicles, are formed through ?
Joints
this provide the means for movement
Joints
also known as an articulation or articular surface
Joints
a connection that occurs between bones in the skeletal system
fibrous joints
these are fixed joints
immovable joints
fibrous joints are also called ?
fibrous joints
these are found where bones are not flexible
Cartilaginous joints
These joints occur only in those regions where the connection between the articulating bones is made up of cartilage.
Synovial joints
the most common type of joint
Synovial joints
this joint helps us to perform a wide range of motion such as walking, running, typing and more
Pivotal Joints
In this type of joint, one bone has tapped into the other in such a way that full rotation is not possible.
Pivotal Joints
This joint aid in sideways and back-forth movement
Hinge Joints
only back and forth movement is possible
Saddle joints
the biaxial joint
Saddle joints
allows the movement on two planes– flexion/extension and abduction/adduction.
Plane joints/Gliding
This joint permit two or more round or flat bones to move freely together without any rubbing or crushing of bones.
Ball and Socket Joints
One bone is hooked into the hollow space of another bone
Ball and Socket Joints
This type of joint helps in rotatory movement.
Condyloid joints
the joints with two axes which permit up-down and side-toside motions
Condylar or ellipsoid joints
Condyloid joints are also known as ?
Pivotal Joints
What type of joint is neck
Hinge joints
What type of joint is ankle
Hinge joints
What type of joint is elbows
Hinge joints
What type of joint is knee joints
Saddle joints
What type of joint is thumb
Plane joints/Gliding
What type of joint is lower leg to ankle joint
Plane joints/Gliding
What type of joint is forearm to wrist joint
Ball and Socket Joints
What type of joint is shoulders
Condyloid Joints
What type of joint is the base of the finger
Condyloid Joints
What type of joint is carpals of the wrist
Condyloid Joints
What type of joint is the wrist joints
Skeletal system
provides support, movement, protection, blood cell production, and mineral storage.
8
How many cranial bones are there
7
How many cervical vertebrae are there
12
How many thoracic vertebrae are there
5
How many lumbar vertebrae are there
Axial Skeleton
This forms the core structure of the body
Skull
Protects the brain
Vertebral Column
Supports the body and protects the spinal cord
Ribs
Protects the heart and lungs
Appendicular Skeleton
This consists of the limbs and girdles, allowing movement.
Pectoral Girdle
Connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton
Pectoral Girdle
Allows a wide range of arm movement
Pelvic Girdle
Supports the weight of the upper body
Pelvic Girdle
Protects the reproductive and urinary organs