27 - Amino Acids as Precursors
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is the primary role of tyrosine in the synthesis of catecholamines?
Tyrosine is the precursor for the formation of catecholamines.
Describe the pathway for the synthesis of catecholamines.
The required coenzymes and cofactors include BH4 (tetrahydrobiopterin), vitamin B6 (pyridoxal phosphate), vitamin C (ascorbic acid), and copper.
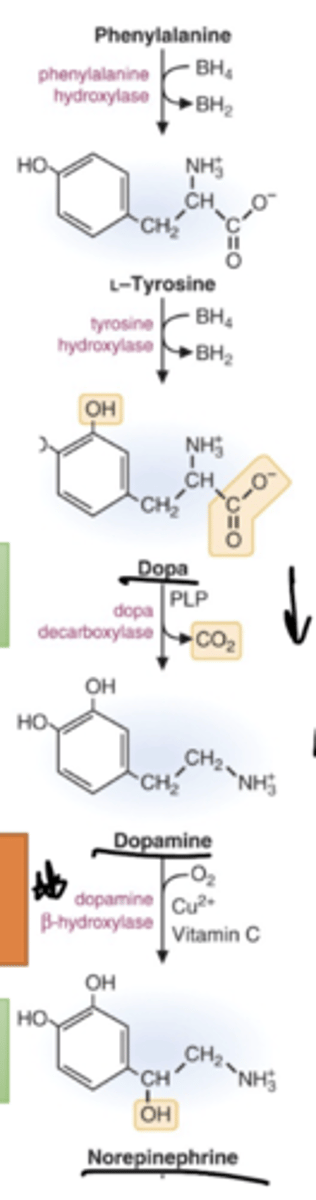
What are some of the products that tyrosine is able to synthesize?
Catecholamines, melanin, thyroid hormones
Describe some characteristics of thyroid hormones
They consist of 2 tyrosines linked upside down. They are the only hormones that exclusively use iodine. These hormones affect heart rate, metabolism, skin maintenance, growth, heat, fertility, and digestion
What does iodine deficiency cause?
Goiters. They can be reduced by supplementation of iodine. Usually, iodine is in the American diet in salt.

What are the different levels of thyroid hormone and how do they appear in people?
Euthyroid - normal levels; asymptomatic
Hyperthyroid - high levels; hyperactivity, thinness, Grave's Disease (protruding eyes)
Hypothyroid - low levels (obesity, high LDL, lethargy, coldness)
What is the role of PLP in the synthesis of catecholamines, serotonin, histamine and GABA
In catecholamines: DOPA is converted into dopamine using PLP by DOPA decarboxylase.
In melatonin: S-hydroxytryptophan is converted into serotonin using PLP by DOPA decarboxylase.
In histamine: Histidine is decarboxylated into histamine using PLP by histidine decarboxylase.
In GABA: Glutamate is converted into GABA using PLP is glutamate decarboxylase.
The moral of this story is that decarboxylase enzymes PROBABLY use PLP.
What the the purpose of tetrahydrobiopterin in the context of catecholamines and serotonin?
In catecholamines, BH4 is used in the reactions catalyzing the conversion of phenylalanine into tyrosine (phenylalanine hydroxylase). Also, tyrosine is converted to DOPA by tyrosine hydroxylase, requiring BH4.
In serotonin/melatonin, BH4 is used for the conversion of tryptophan into S-hydroxytryptophan by tryptophan hydroxylase.
This story also appears to have a moral at the end of its pages, for BH4 seems to be involved in hydroxylation reactions. Consider this.
What enzyme recycles BH4?
DHPR - dihydropteridine reducatase converts BH2 to BH4.
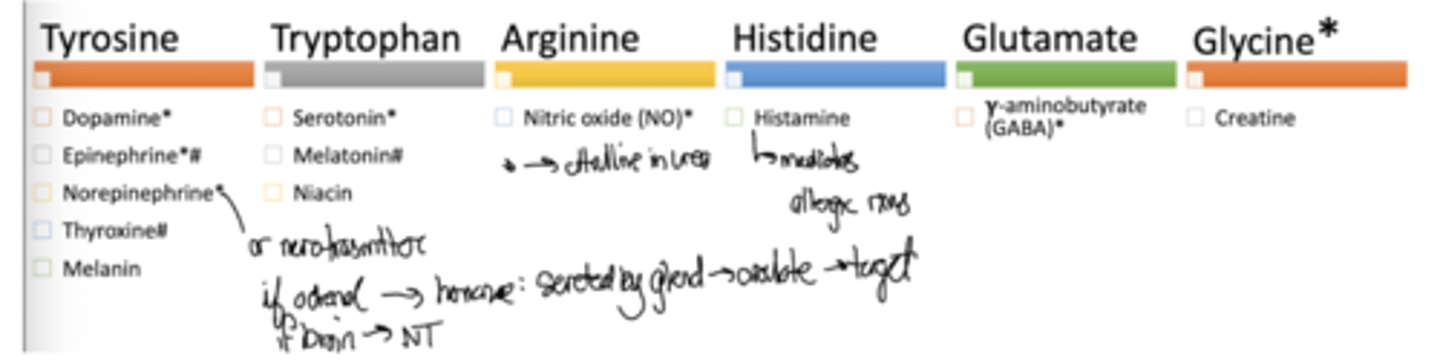
What are the hormonal, neurotransmitter, and signaling molecule products of tyr, trp, arg, his, glu, gly?
What is the major thyroid hormone? How does it become active?
The major one is T4 thyroxine, with 4 iodine atoms. It is converted into T3 triiodothyronine by the removal of an iodine to exert its effects.
What are the roles of the different catecholamines?
Dopamine controls movement, the reward center, pleasure, enjoyment, etc.
Norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter that functions in the sympathetic nervous system in fight or flight, but in the central nervous system for increased alertness and arousal. It also plays roles in learning and memory retrieval. As a hormone, it is secreted from the adrenal gland for fight or flight.
What can deficits in norepinephrine do? How is norepinephrine used in pharmacology?
Deficits lead to low energy and depression. In pharmacology, it is used as a drug to prevent hypotension (it increases bp through vasopressor activity.
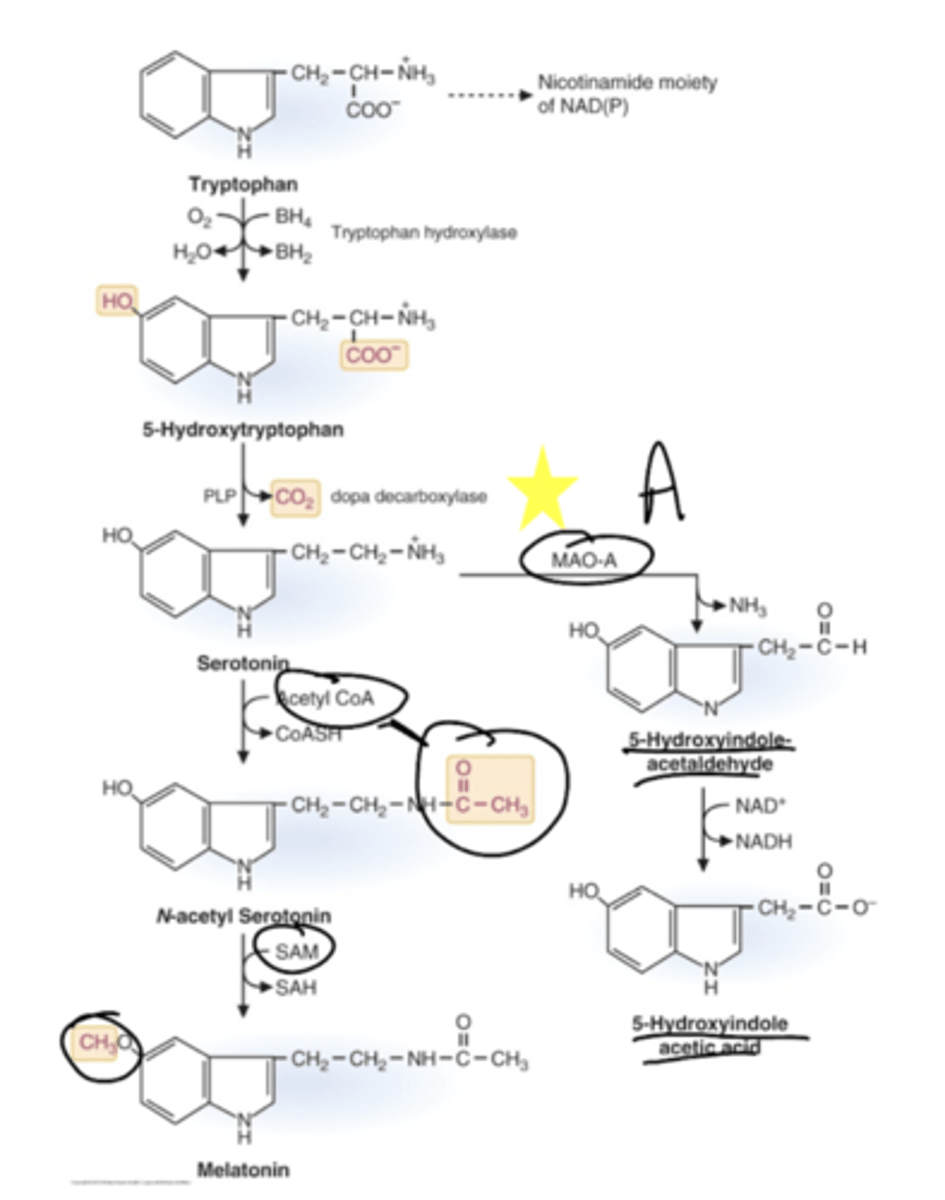
Why does serotonin exist? What are some characteristics?
Serotonin is stored in the intestinal mucosa, platelets, and in serotonin neurons of the CNS.
The physiological functions of serotonin are to regulate behavior (eating, sleeping, mood, body temperature, circadian rhythm, and neuroendocrine function).
It is also a precursor to melatonin.
What promotes melatonin synthesis?
Produced in response to darkness, helps with timing of circadian rhythm - being exposed to light blocks melatonin production
How does serotonin relate to depression?
Imbalances between serotonin and norepinephrine can lead to depression. It can be treated by SSRIs.
Some medications include Prozac, Zolofy, Paxil, Leuvox, Celexa, Lexapro
Describe the serotonin/melatonin pathway, with key cofactors and enzymes.
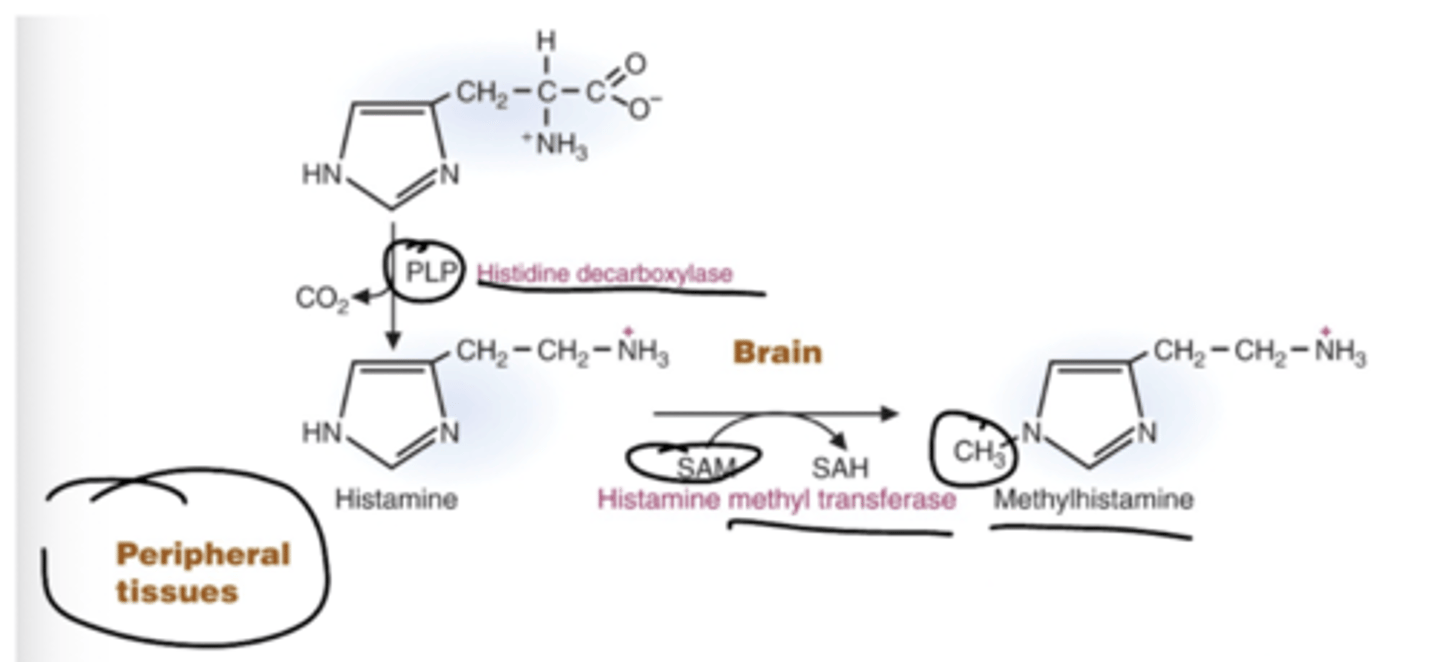
What on earth does histamine even do? What are some characteristics?
Histamine spawns from histidine by the PLP dependent enzyme histidine decarboxylase.
It is expressed in most cells (immune clels, gastric enterochromaffin-like cells)
Released in response to allergic reactions, acts on vascular smooth muscle, and endothelial cells leading to vasodilation and increased vascular permeability.
It INCREASES gastric secretion in stomach.
As a neurotransmitter, it regulates the circadian cycle, appretite, learning, memory,
What drugs act against histamines?
The archnemesis of histamines are antihistamines. They are used to relieve allergies (hay fever, hives, conjunctivitis, and reactions to insect bites), motion sickness, and insomnia.
Do NOT take benadryl and drive (you will be honk shooing onto the freeway). Doses over 25 mg will cause extreme drowsiness.
Briefly describe the synthesis pathway of histamine, with important things. How does it differ in synthesis between the brain and peripheral tissues?
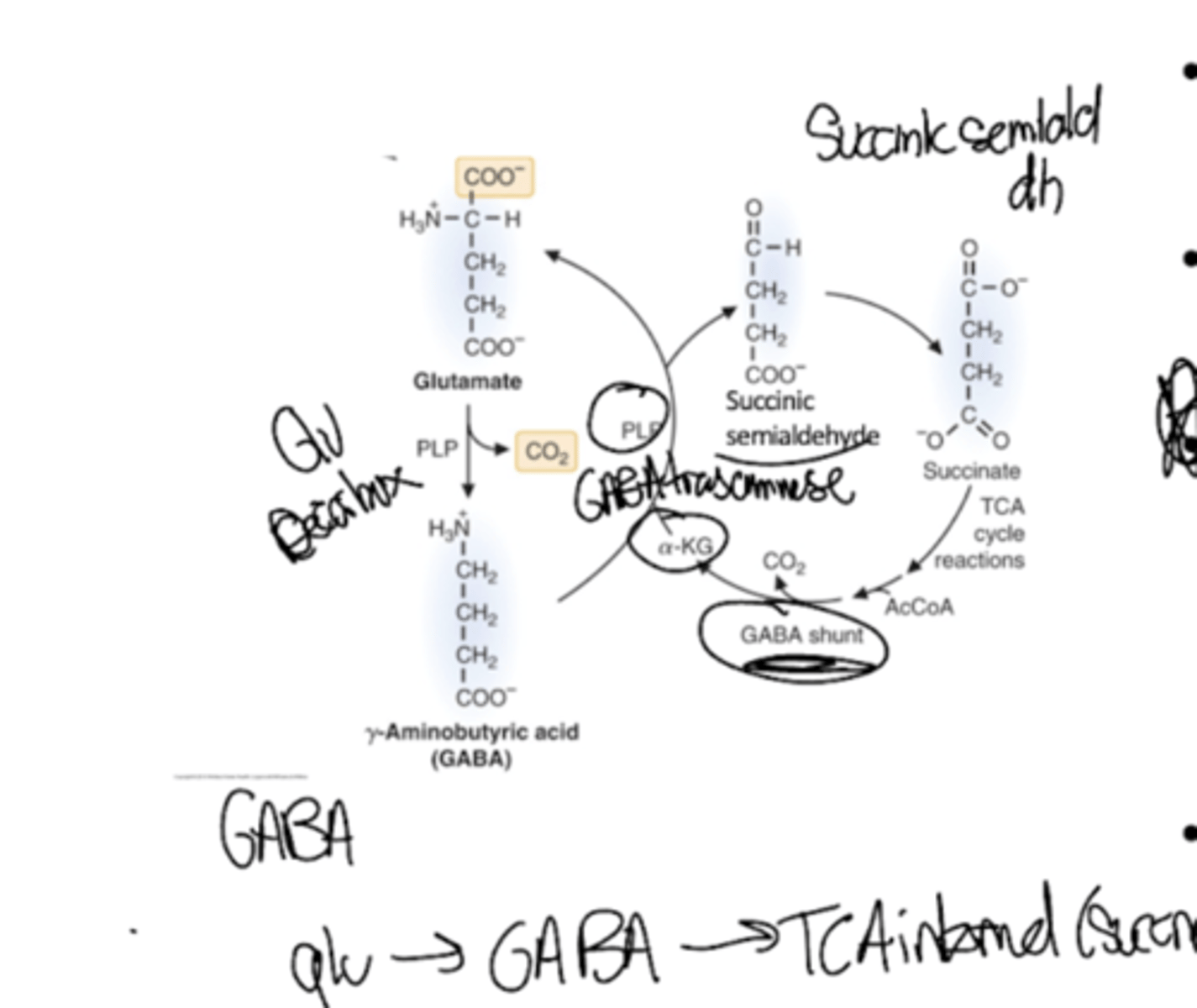
Why was GABA put upon this earth? What are some characteristics?
GABA is produced by the PLP-requiring decarboxylation of glutamine. It is recycled through the GABA shunt.
It is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter counterbalancing neuronal excitation in the cerebral cortex. It is responsible for anxiety reduction, calming, and tension release (disturbance of this balance leads to seizures).
How does GABA function as a positive allosteric modulator?
It can cause sedation, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, and muscle relaxant>
Through benzodiazepines, barbiturates, ethanol, and induction anesthetics
Describe the GABA shunt
What does creatine do?
Creatine phosphate in the muscle serves as a high-energy molecule that can be used a substrate to rapidly synthesize ATP.
What is creatinine?
Formed from phosphocreatine by non-enzymatic hydrolysis in muscle and is urinated out.
How is creatinine linked to pathology?
Levels in urine used to estimate muscle mass and kidney damage.
If muscle mass decreases, levels in urine decreases.
Accumulation of creatinine is indication of renal damage.
Serum creatinine concentration for indicators of glomerular filtration rate - avg is 15mg/kg of body weight
Rise in serum creatinine is assumed to result from decreased excretion
Extent of rise in blood proportional to severity of pathology of glomerular units in kidneys
Kidney failure -- excretion of creatinine low
What are the levels of dopamine in Parkinson's Disease and Schizophrenia>
In Parkinson's Disease, dopamine levels are low - deficiency in dopamine synthesis
In Schizophrenia, dopamine levels are high - hyperactive dopamine transmission
What are the mechanisms of levodopa and carbidopa for Parkinson's?
Levodopa: Used for Parkinson's treatment; it is a precursor to dopamine. Decarboxylate in the brain. Side fx: nausea and vomiting (bc perphipheral conversion of levodopa to dopamine, activating peripheral dopamine receptors).
Carbidopa: Decarboxylase inhibitor. Keeps dopamine in circulation.
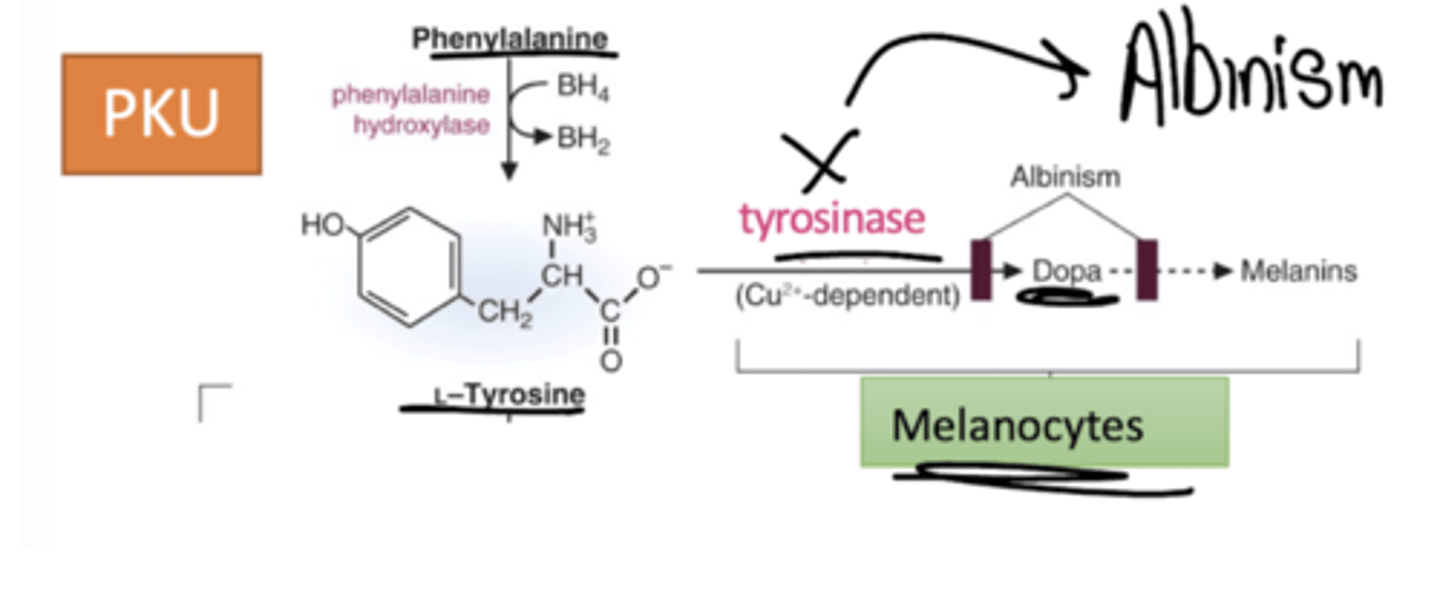
What is the role of tyrosinase in albinism?
Melanin:
Pigment that is syntheiszed from tyrosine in melanocytes of epidermis
Products underlying cells from sunlight
Defect in this results in albinism - common type due to defects in Cu-contaning tyrosinase
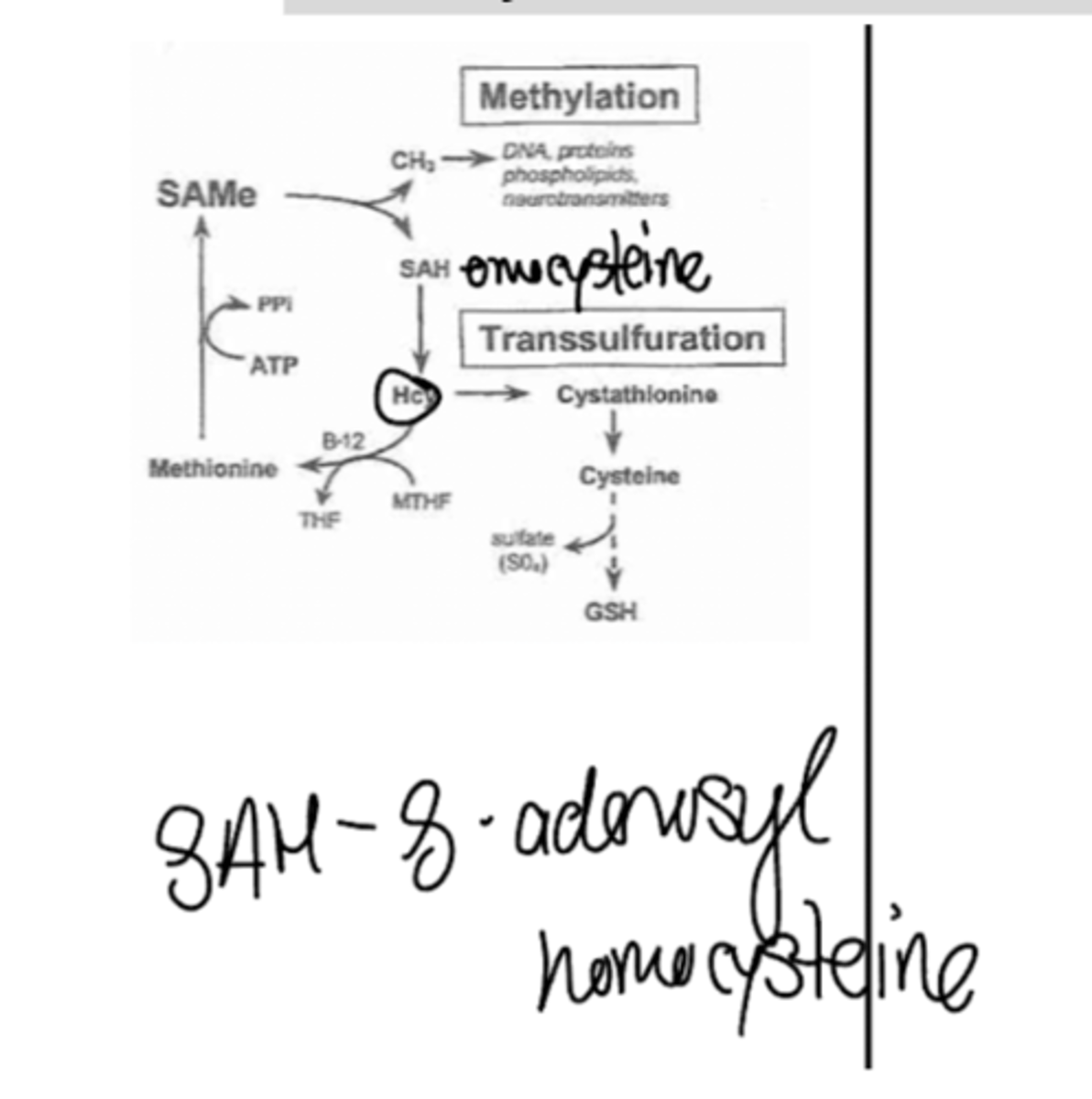
What is the role of SAM in catecholamines and serotonin/melatonin?
SAM acts as a methyl donor for the conversion of NE into E, and N-acetylserotonin into melatonin
What is the role of vitamin C in catecholamine synthesis?
Vitamin C in catecholamines:
Dopamine B-hydroxylase deficiency (needs vit C)
Regulates blood pressure, body temperature, and deficiency is caused by autosomal recessive disease
Deficiency results in low childhood blood pressure, vomiting, orthostatic hypotension (decrease in BP when standing), hypoglycemia, and drooping eyelids
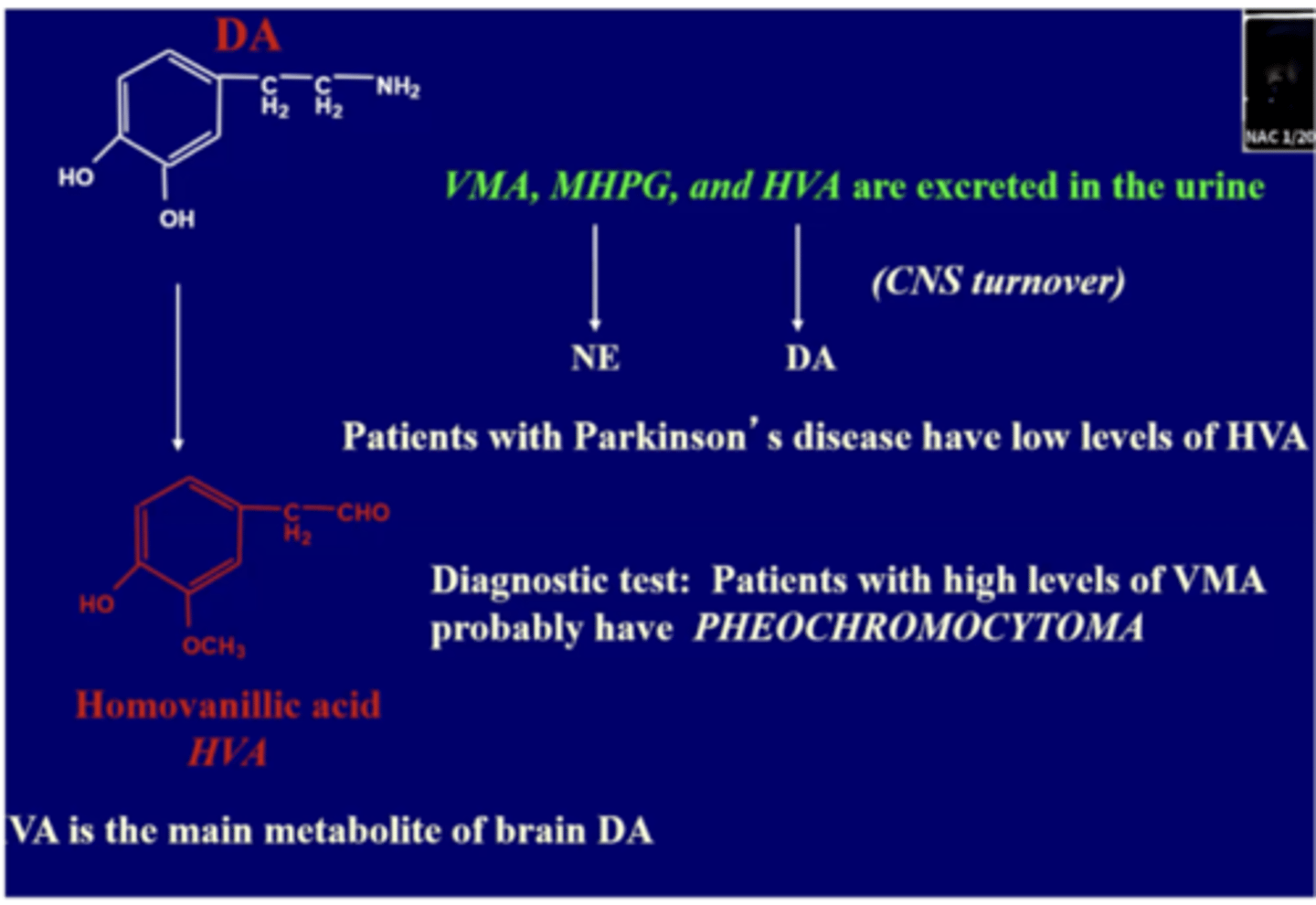
Detail the breakdown of norepinephrine and epinephrine. What does it produce? Where is each produced?
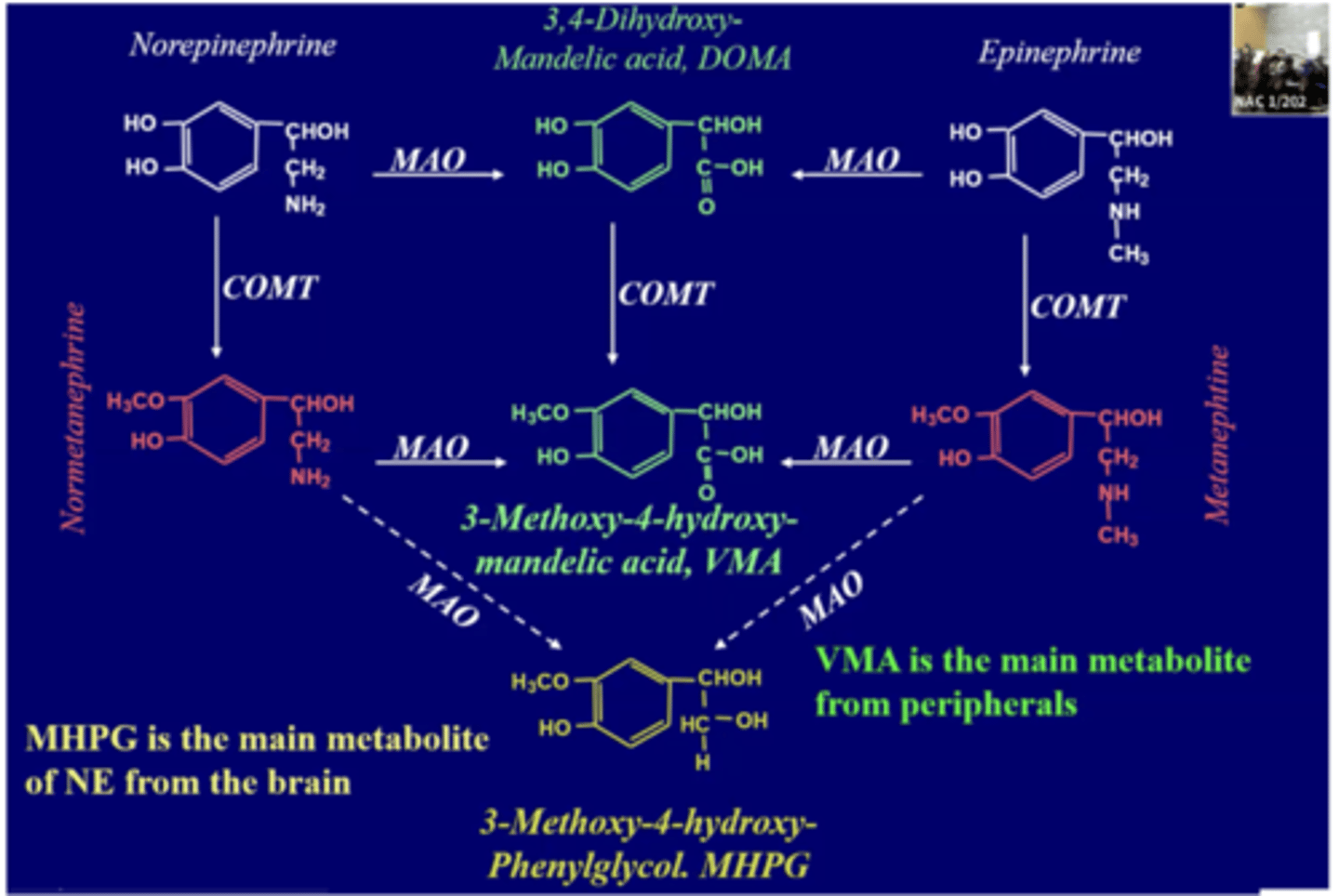
Detail the breakdown of dopamine? What is produced?
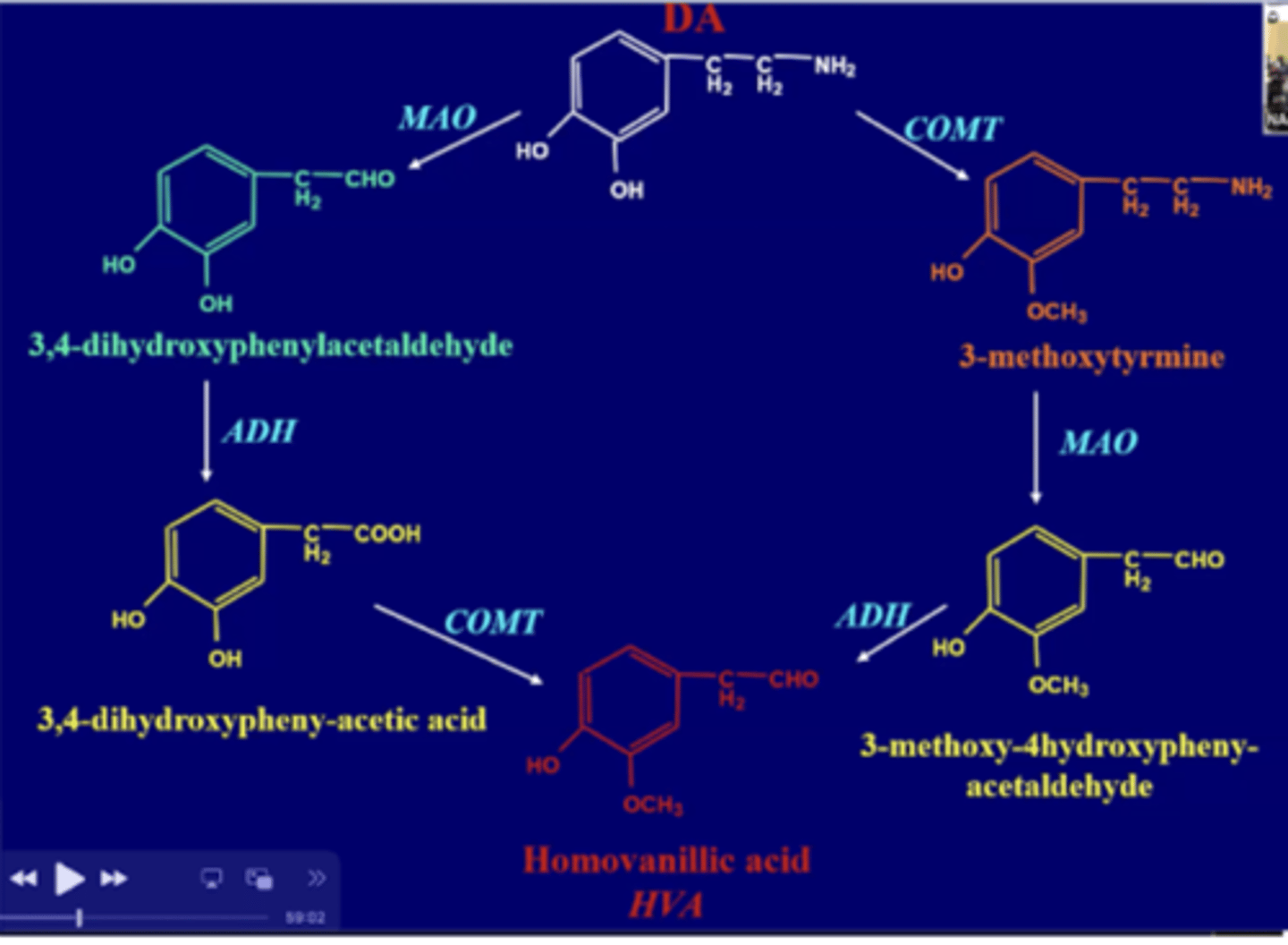
I truly have no idea how to form this information into a question so I'm just giving up and putting the slide in.
Sorry
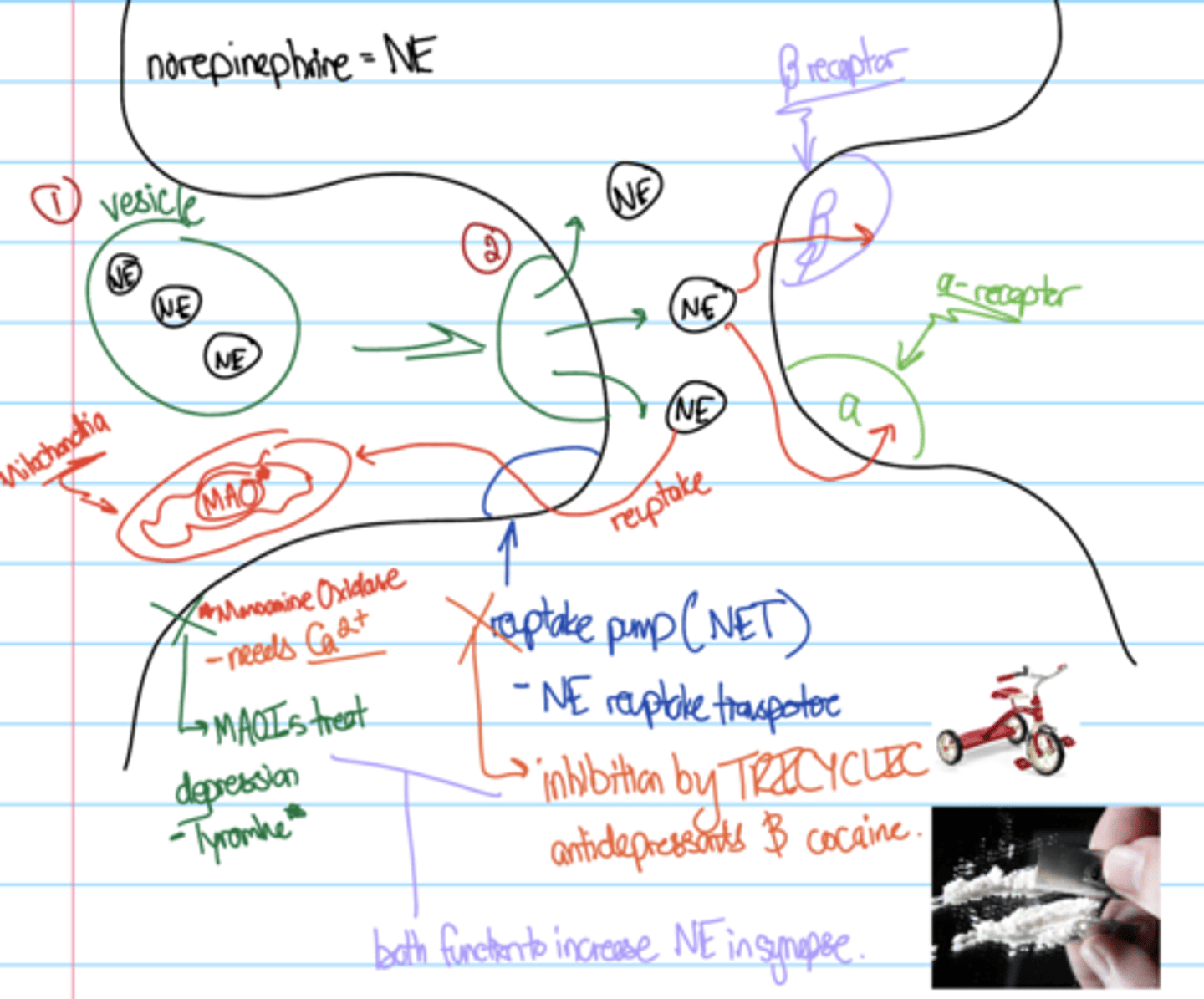
Describe the release of epinephrine in the neuronal synapse? What are the two ways its uptake are inhibited? What other fun facts are involved?
What is tyramine? How is it related to MAO?
Tyramine (in cheese amongst other things) is degraded by MAO.
MAOIs lead to accumulating tyramine levels, which are taken up into nerve terminals by NET and causes release of catecholamines.
This leads to hypertensive crises (headaches, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, high blood pressure.
MAO A deficiency: Low levels of VMA and HVA, Mild intellectual disability, behavioral difficulties (aggressive, violent).
What are som tryptophan derived molecules?
Serotonin, melatonin, niacin; also you can try to decipher those scrawlings that got screwed up by my dumb apple pencil but you can also give up like i am right now
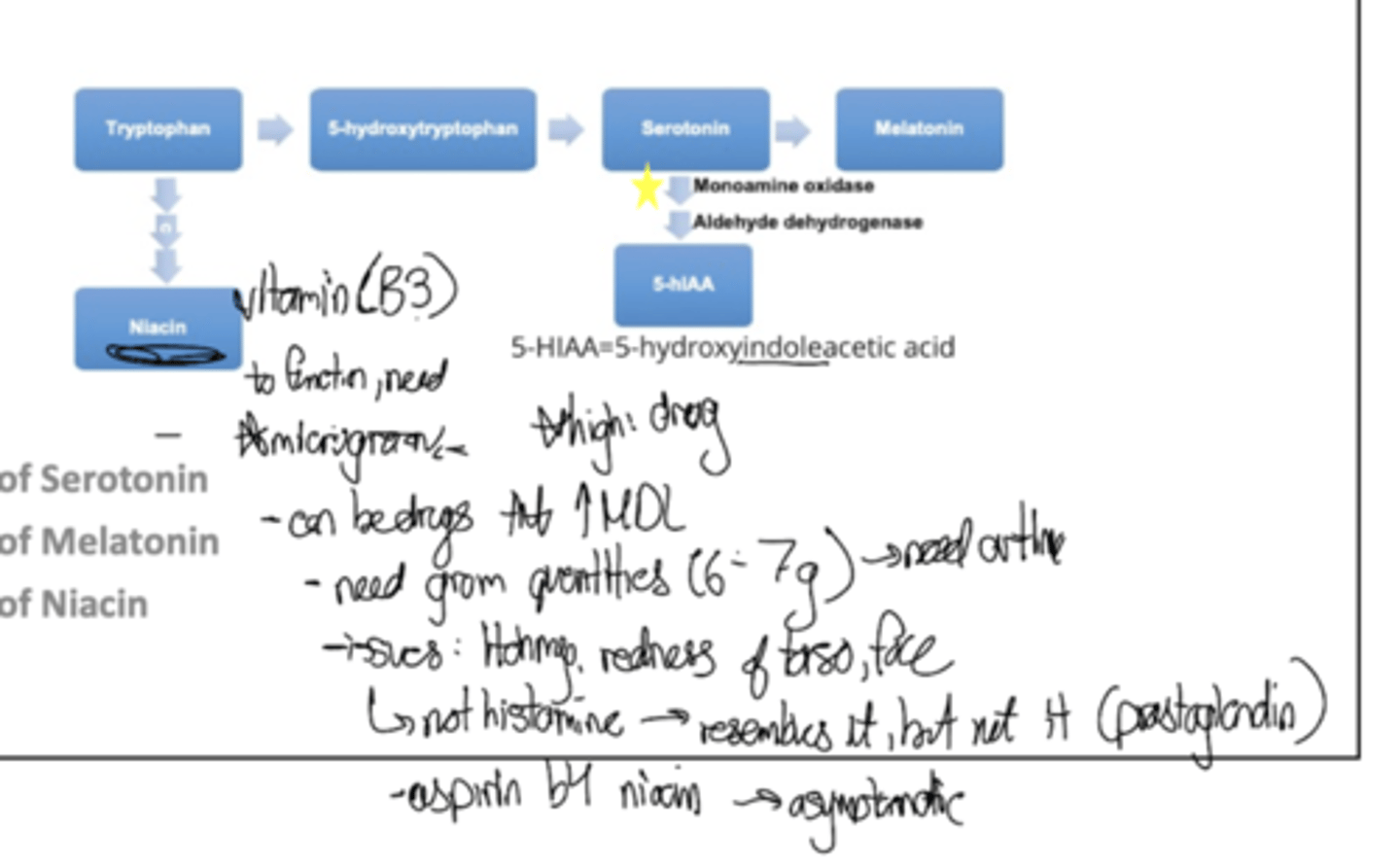
amino acid
