Clinical Medicine of the Hepatobiliary System
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Dentist have the most increased exposure risk to which hepatitis viruses?
-Hep B
-Hep C
True or False: Alcoholism is more prevalent amongst dentists than in the general population
False ==> rate of alcohol & drug use disorders in dentists is the same as the general population
True or False: Liver disease can have oral manifestations
True
Why is it important to evaluate coagulation factor levels in patients?
need to evaluate bleeding risk in patients
*pts w/ liver dysfunction are at high risk of bleeding
Name the tests that are used to evaluate liver function.
-total protein
-albumin
-total bilirubin --> unconjugated (indirect); conjugated (direct)
-alkaline phosphatase (AlkP)
-Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
-Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
-y-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
-prothrombin time/INR --> measure of coagulation
-ammonia
Can you make a diagnosis based solely abnormal liver function tests?
no ==> lab tests aren't specific to liver (can be abnormal with other systems)
*diagnosis in combo w/ patient history & physical + patterns of lab abnormalities
What is the breakdown product of hemoglobin?
bilirubin
what is unconjugated bilirubin?
bilirubin that is bound to albumin in blood as it travels to the liver
How is bilirubin processed in the liver?
conjugated & excreted
jaundice
yellow discoloration of the skin, sclera, & mucosa due to elevated blood levels & deposition of bilirubin
What is an associated symptom of jaundice?
pruritis (itchiness)
How is jaundice subdivided?
-pre-hepatic jaundice --> due to hemolysis
-hepatic jaundice --> due to liver disease
-post-hepatic jaundice --> due to biliary obstruction
pre-hepatic jaundice
jaundice due to increased hemolysis
hepatic jaundice
jaundice due to liver disease
post-hepatic jaundice
jaundice due to biliary obstruction
What percent of bilirubin in blood is unconjugated?
70%
What causes elevated unconjugated bilirubin?
-intravascular hemolysis --> RBC breakdown (pre-hepatic)
-Gilbert Syndrome --> impaired conjugation, genetic, benign, jaundice (hepatic)
Would you expect unconjugated or conjugated bilirubin levels to be elevated due to intravascular hemolysis?
unconjugated ==> pre-hepatic jaundice
Would you expect unconjugated or conjugated bilirubin levels to be elevated in Gilbert Syndrome?
unconjugated ==> hepatic jaundice
gilbert syndrome
hepatic jaundice due to impaired conjugation, genetic, benign, jaundice can be brought on by stress
Which conditions cause elevated conjugated bilirubin?
-hepatocellular disease--> cirrhosis, hepatitis, drugs (hepatic jaundice)
-cholestasis (hepatic)
-obstruction --> gallstones, cancer (post-hepatic)
Would you expect elevated unconjugated or conjugated bilirubin in patients with a hepatocellular disease?
conjugated ==> hepatic jaundice
ex: cirrhosis, hepatitis, drugs
Would you expect to see elevated unconjugated or conjugated bilirubin in patients with cholestasis?
conjugated ==> hepatic jaundice
Would you expect elevated unconjugated or conjugated bilirubin in patients with obstructions due to gallstones or cancer?
conjugated ==> post hepatic jaundice
What are the 2 sensitive indicators of hepatocyte injury?
-AST --> less specific b/c also present in cardiac & skeletal muscle, & kidney
-ALT
*these enzymes usually stay in hepatocyte--> increase in blood indicates hepatocyte injury
Of the 2 sensitive indicators of hepatocyte injury, which one more specific to the liver?
ALT
What does a spill of AST and ALT into the bloodstream indicate?
acute hepatocellular injury
True or False: Elevated AST and ALT indicates hepatocyte cell death.
False ==> elevated levels indicates injury not necessarily cell death
True or False: Elevated AST and ALT does not correlate with the degree of injury
True
Which conditions cause very high AST & ALT levels (> 1000)?
-drugs/toxic insult --> tylenol toxicity
-acute hepatitis infection
-ischemia/shock
Which conditions cause moderately elevated AST and ALT (250-1000)?
-viral infections such as EBV, HSV
-drugs (NSAIDs)
-autoimmune hepatitis
-wilson's disease
Which conditions cause mildly elevated AST and ALT (<250)?
-fatty liver disease
-drugs
-cholestasis
-infection
-alcohol --> 2:3 AST:ALT ratio
-non-liver disorders --> celiac, muscle disease, intense exercise
Toxic insult to the liver has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
very high AST & ALT (>1000)
Acute hepatitis infection has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
very high AST & ALT (>1000)
Ischemia and shock has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
very high AST & ALT (>1000)
Viral infections such as EBV and HSV has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
moderate elevated AST & ALT (250-1000)
NSAIDs have what effect on AST & ALT levels?
moderate elevated AST & ALT (250-1000)
Autoimmune hepatitis has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
moderate elevated AST & ALT (250-1000)
Wilson's disease has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
moderate elevated AST & ALT (250-1000)
Fatty liver disease has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
mild elevation (<250)
Cholestasis has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
mild elevation (<250)
Infection has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
mild elevation (<250)
Alcohol has what effect on AST & ALT levels?
mild elevation (<250)
* 2 AST : 3 ALT
True or False: Celiac disease causes mild elevation of AST & ALT levels
True
True or False: Muscle disease causes mild elevation of AST & ALT levels
True
True or False: Intense exercise causes mild elevation of AST & ALT levels
True
What could elevation of alkaline phosphatase (AlkP) indicate?
biliary system
alkaline phosphatase (AlkP)
enzyme found in liver, biliary system, bone, placenta, kidney, placenta, intestines
Which hepatic conditions present with elevated AlkP?
-bile duct lesions
-primary biliary cirrhosis
-primary sclerosing cholangitis
-drug induced cholestasis--> anabolic steroid
-liver cancer
True or False: AlkP can be normally elevated in 3rd trimester of pregnancy
False
True or False: AlkP can be normally elevated in adolescence.
True ==> due to high bone growth
True or False: Patients who have diseases with high bone turnover have elevated AlkP
True
True or False: Metastasis to bone have elevated AlkP
True
True or False: TB causes elevated AlkP
True
Where is albumin synthesized?
liver
What is the half-life of albumin?
20 days
what do you expect the albumin levels to be in acute liver disease?
normal (even if low synthesis)
What do you expect the albumin levels to be in chronic liver disease
low
What is a major consequence of low albumin levels in the blood?
decreased oncotic pressure --> lead to ascites and/or edema
What can cause decreased albumin levels?
-liver disease
-malnutrition
-protein losing enteropathy
-nephrotic disease (kidneys)
-chronic infection
Why is INR used over prothrombin time to analyze coagulation?
b/c PT measurements vary in labs
Which clotting factors are synthesized in the liver?
-II
-V
-VII
-X
*the vitamin K dependent factors
Elevated INR = ?
longer clotting time
What effect does factor deficiencies and/or liver disease have on PT and INR?
-prolong PT
-elevated INR
Would you expect INR to be elevated or decreased in patients taking warfarin?
elevated
What is the most commonly overdosed medication?
acetaminophen
What is the maximum daily dose of tylenol in healthy patients?
4 grams (8 extra-strength tabs)
What is the maximum daily dose of tylenol in patients with liver disease or regular alcohol use?
2 grams (4 extra-strength tabs)
What are the symptoms of acetaminophen overdose?
-1st 30 min --> asymptomatic or vomiting
-18-72 hrs --> vomiting, Right upper quad pain
-73-96 hrs --> jaundice, significant liver dysfunction, renal failure, coagulopathies, acidosis, encephalopathy, death
What is the antidote for acetaminophen overdose?
N-acetylcysteine
What is the treatment for acetaminophen overdose?
-antidote = N-acetylcysteine
-supportive care at liver transplant site if evidence of failure
-most common reason for emergency liver transplantation in US
Why do GI doctors still recommend acetaminophen over NSAIDs for patients with liver disease?
-less risk of GI bleed
-safer in patients with coagulopathy
-less interaction with medications
-less toxic to kidneys --> liver failure can lead to kidney failure
Hepatocellular necrosis is found in which zone of the liver acinus in acetaminophen toxicity?
zone 3
Describe the lab work of patients with fulminant liver failure due to acetaminophen overdose
-multiple lab abnormalities
-multiple organ findings
What is the 7th leading cause of death worldwide?
viral hepatitis
what are the symptoms of acute hepatitis?
-nausea
-abdominal pain
-fatigue
-malaise
-jaundice
*symptoms of range in severity
which types of hepatitis are usually symptomatic?
-Hep A
-Hep B
True or False: Hep C is always symptomatic
False ==> can be asymptomatic (subclinical)
True or False: Acute hepatitis can resolve over days to months
True
Which hepatitis viruses can cause chronic infections?
-Hep B
-Hep C
*higher risk for cirrhosis & hepatocellular carcinoma
What are the risks of HBV & HBC?
can become chronic hepatitis & :
-increase risk for cirrhosis & hepatocellular carcinoma
-remain asymptomatic carriers & transmit the disease
What other viruses can cause hepatitis?
-cytomegalovirus
-epstein-barr
-herpes simplex
Describe the labs of patients with acute hepatitis.
-very high AST & ALT (>1000)
-elevated bilirubin
What will you start to see in labs if acute hepatitis progresses to acute liver failure?
elevated PT & INR
What is characteristic of fulminant liver failure die to acute hepatitis A or B?
hepatic encephalopathy ==> can be fatal
What is the incubation period of Hep A?
15-45 days
What is the route of infection of Hep A?
-contaminated water or food (shellfish)
-can spread quickly in families & institutions
-can be sexually transmitted
True or False: Hep A has high transmission in healthcare workers
False==> has low transmission
What are the symptoms of Acute Hep A?
-nausea
-ab pain
-fatigue
-malaise
-jaundice
-may have cholestatic hepatic failure
-may have relapsing course over a year
True or False: Hep A does not lead to chronic hepatitis
True ==> doesn't have carrier state
Describe the treatment of Hep A
supportive
Is a vaccine for Hep A available?
yes ==> for at risk populations --> travel, drug users, occupational risks, cirrhosis
Labs in Acute Hepatitis A
-very high AST & ALT (>1000)
-elevated bilirubin
-elevated Alkaline Phosphatase
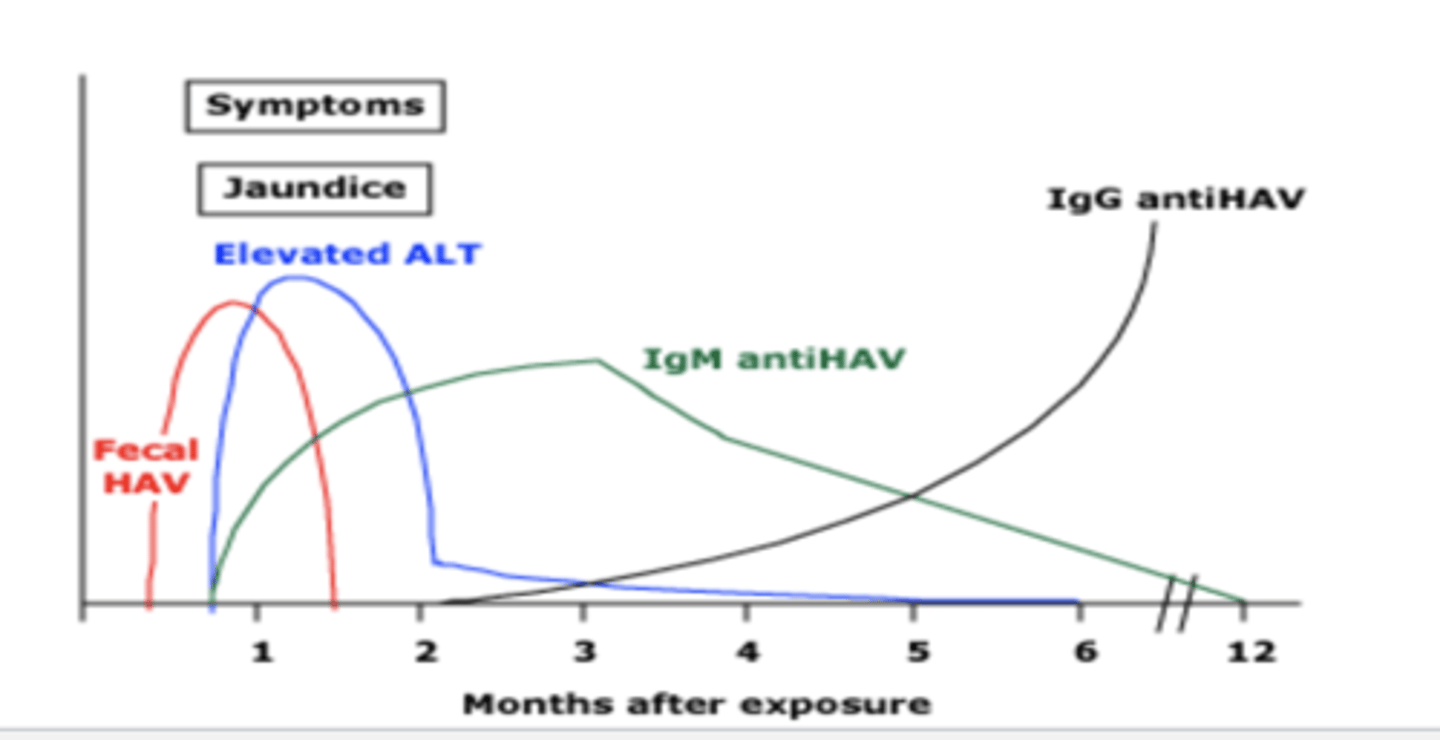
Describe the Serology of Hep A Infection
-IgM & HAV --> acute state
-IgG anti-HAV --> immune state (lifelong)
How is Hep B transmitted?
-sexual contact
-IV drug use
-blood
-vertical transmission
Which dental professional is at the greatest risk of Hep B infection?
oral surgeons
Which healthcare worker is at the greatest risk for Hep B infections?
dentists (3-4x)
How do dentists typically contract Hep B?
-puncture wounds with infected instruments
-absorption thru mucosa (oral or eyes)
What is the incubation period for Hep B?
30 - 180 days
Does viral shedding of Hep B start before or after symptoms of infection?
starts before symptoms