Anatomy and Physiology 101 Final Exam Ivy Tech
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
What is the difference between anatomy and physiology
anatomy- study of structure
physiology- study of function
what are the levels of organization
subatomic particle- protons, electrons, neutrons
atom
molecule
macromolecule
organelle
cell
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
what are the characteristics of life?
movement
responsiveness
respiration
absorption
secretion
digestion
assimilation- changing of absorbed substances into chemically different forms
circulation
reproduction
growth
what are the requirements of life?
water
food
heat
pressure
oxygen
define homeostasis
maintaining of a stable enviroment
what is a homeostatic mechanism
monitors aspects of internal environment and corrects as needed
*negative feedback mechanism
define matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
element
composed of chemically identical atoms
atom
smallest particle of atom, basic unit of matter
what are structure of an atom
nucleus
protons
neutron
electrons
define nucleus, proton, electron, neutron
nucleus- central part of atom
proton- positive charge
electron- negative charge
neutron- no electrical charge
ionic bond
formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another
what are covalent bonds
when two molecules share electron
hydrogen bond
formed between water molecule, attraction between positive end of polar molecule and negative end of another polar molecule
define synthesis, decomposition, and exchange reactions
Synthesis- A+B=AB
Decomposition- AB=A+B
exchange- AB+CD=AD+BC
define reactant
starting materials of reactions
product
ending material
define catalyst
a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction
what is an acid
dissociates with water
base
combines in water
what happens to salts when dissolved in water and what is produced?
The salt molecules are "torn apart" by the water, and are reduced to sodium (Na+) and chlorine (Cl-) ions.
what is the pH scale? what ions are involved in the pH scale?
pH scale- indicated the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution, H+ and OH-
organic molecule
contains Carbon and hydrogen and dissolves in water.
inorganic molecule
does not contain C and H and dissociates with water
What is dehydration synthesis
taking water out (producing water) to form a new product. Uses energy
hydrolysis
separation of two macromolecules by adding water. Releases energy
what are carbohydrates
provide energy and cell structure
lipids
provide energy and cell structure
proteins
structural material, enzymes, energy, hormones,
nucleic acids
store information for protein synthesis, control cell activity
what are amino acids?
Protein building blocks which are help together by peptide bonds
what are enzymes?
a substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction.
DNA
Part of chromosomes and in nucleus. responsible for storing and transferring genetic information.
RNA
located in cytoplasm. directly codes for amino acids and as acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes to make proteins
describe cell membrane
controls what goes in and out of cell, phospholipid bilayer
nucleus
control center
cytoplasm
contains cytosol
cytosol
aqueous substance
organelles
organized/specialized structures in cell
Function of Ribosomes
synthesize protein
ER
transport system, ribosome attachment, synthesize lipids
Golgi apparatus
modify, package, deliver protein
mitochondria
generate energy
Function lysosome
digest worn out cell parts or unwanted substances
peroxisome
breakdown organic molecules
centrosome
produce cilia and flagella, distribute chromosomes during cell division
Function vesicle
store, transport or digest cellular products and cellular waste
cilia
propel substances across surfaces
flagella
motility of sperm
function of nuclear envelope
control substance in and out of nucleus
nuclear pores
a large complex of proteins that allows small molecules and ions to freely pass, or diffuse, into or out of the nucleus
nucleolus
site of ribosome formation
chromatin
package DNA into a small volume to fit into the nucleus of a cell and protect the DNA structure and sequence
define pinocytosis
engulfs liquids from surrondings
define phagocytosis
engulfs solids from surroundings
exocytosis
vesicle fuses with membrane and releases contents outside of cell
transcytosis
ferries particles through cell
isotonic
neutral
hypertonic
cell shrinks
hypotonic
cell swells
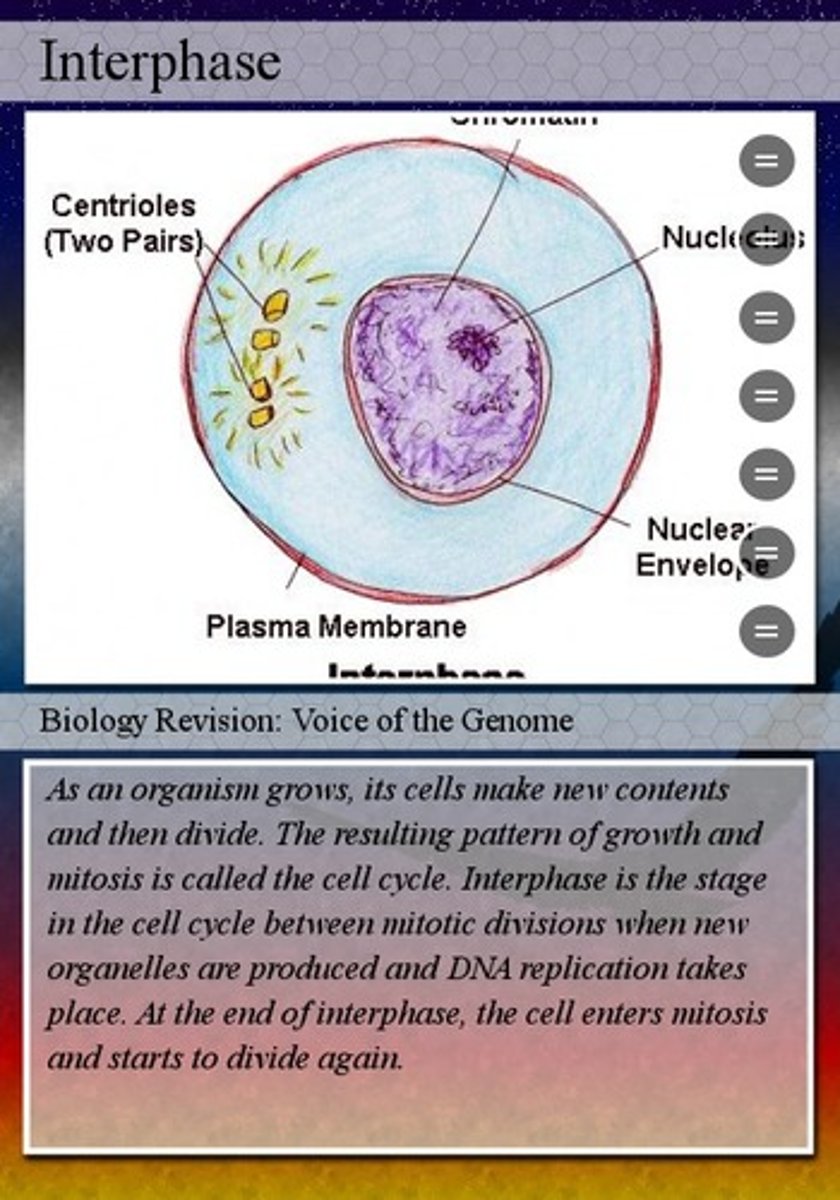
interphase
cell growth, replicates material to prepare for cell division, synthesize organelles for cell divisision
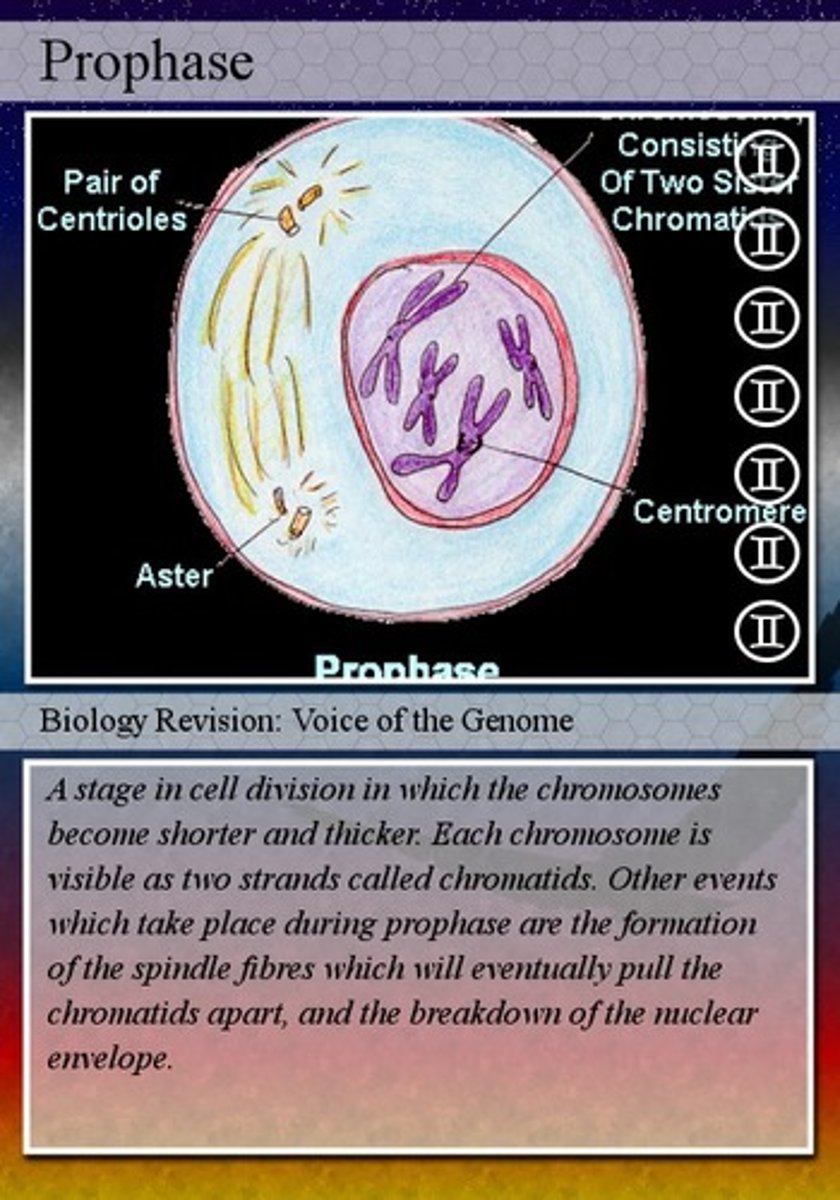
prophase
chromosomes form, nuclear envelop disappears
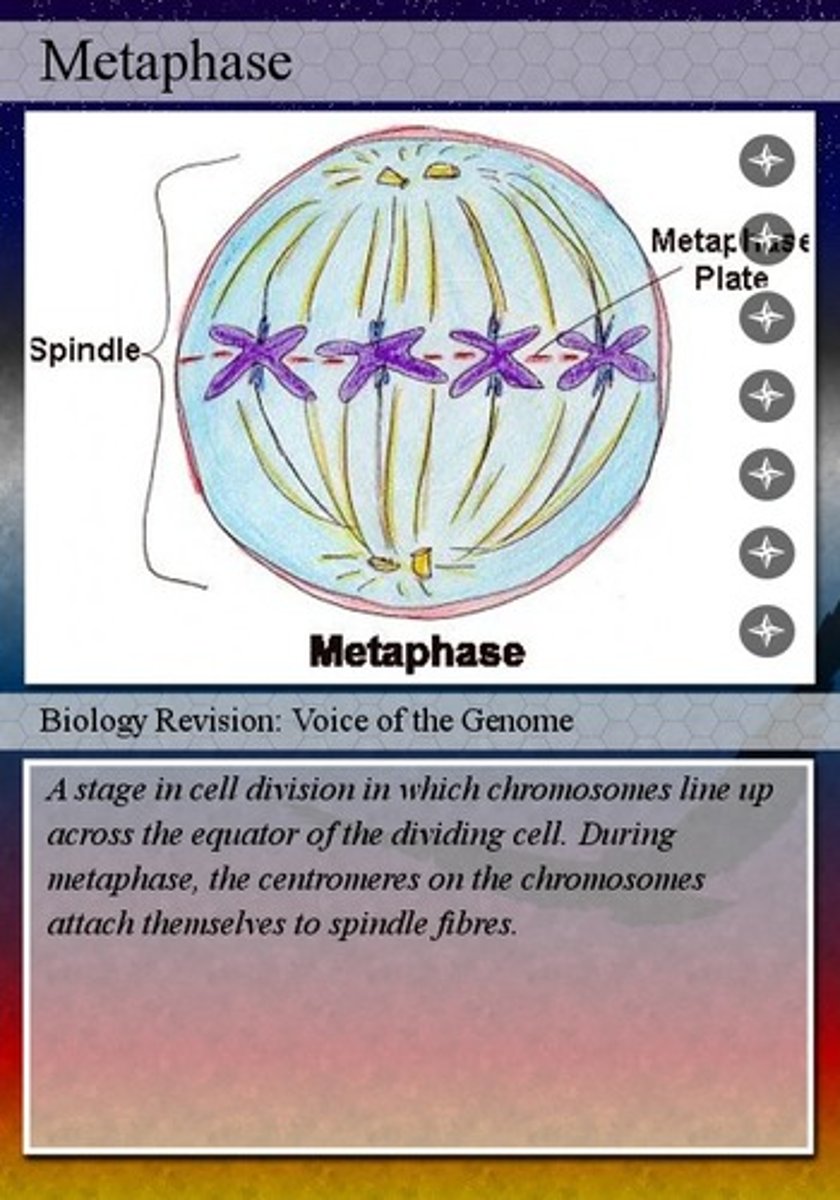
metaphase
chromosomes align midway between centrioles
anaphase
chromosomes separate and move to centrioles (opposite ends0

telophase
chromatin forms, nuclear envelope forms

anabolism
anabolism- provides the materials needed for cellular growth and repair
dehydration synthesis
catabolism
breaks down larger molecules into smaller molecules
hydrolosis
define denaturization
change the nature or natural qualities of a substance
How is ATP made?
glycolysis and cellular respiration
How is ATP broken down to release energy?
hydrolysis
what is a nucleotide
form the basic structural unit of nucleic acids such as DNA
what is transcription
process by which the genetic information encoded in a linear sequence of nucleotides in one strand of DNA is copied into an exactly complementary sequence of RNA
what is translation
genetic information present in an mRNA is converted into a corresponding sequence of amino acids in a protein
How is DNA replicated?
The double helix is unwound and each strand acts as a template for the next strand. Bases are matched to synthesize the new partner strands
what is a mutation
change in genetic information
how is RNA made?
DNA transcription
Where do you find simple squamous tissue?
lines air sacs, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
Where do you find simple cuboidal tissue?
line kidney tubules, ovaries, and ducts
where do you find simple columnar tissue
line uterus, stomach, intestines
where do you find pseudo-stratified columnar tissue
line respiratory pathways
where do you find stratified squamous tissue
line oral cavity, vagina, and anal canal
where do you find stratified cuboidal tissue
line ducts of mammary glands, sweat glands,salivary glands, and pancreas
where do you find stratified columnar tissue
line male urethra and part of pharnyx
where do you find transitional tissue
line urinary bladder, ureters, and part of urethra
loose CT
bind sin to structures
mainly fibroblasts, elastic and collagenous fibers
Adipose Tissue
cushion, insulate, store fat
adipocytes
reticular CT
reticular fibers
support internal organ walls
dense CT
bind body parts together
elastic and collegenous fibers, few fibroblasts
tendons, ligaments, dermis
elastic CT
elastic fibers, fibroblasts
attachment between bones
Bone
supports, protects, forms blood cells, attachment for muscles, skeleton
cartilage
hyaline- nose, ends of bone
elastic- ear
fibrocartilage- intervertebral discs
blood
transports, defends, clotting, throughout body
skeletal muscle
attached to bone, striated, voluntary, many nuclei
smooth muscle
walls of organs and blood vessels, skin, involuntary, striated, single nuclei
cardiac muscle
heart wall, involuntary, striated, intercalated discs, single nuclei
chondrocyte
cells of cartilage
lacunae
hole for chondrocyte
osteocyte
cells of bone
lamellae
thin calcified layer of bone
canaliculi
canal or duct