Bone Tissue: Supportive Connective Tissue
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:14 PM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
What are 3 important cells of the bone tissue?
1. Osteoblast
2. Osteocyte
3. Osteoclast
2
New cards
What does an osteoblast do?
Builds bone tissue (immature cell)
3
New cards
What does an osteocyte do?
This is a **mature bone cell**; maintain bone tissue, matrix and mineral homeostasis
4
New cards
What does an osteoclast do?
Collapse/destroy bone matrix; macrophages
5
New cards
Proximal and Distal meanings?
* Proximal = close to middle
* Distal = away from middle (Ends of the bone)
* Distal = away from middle (Ends of the bone)
6
New cards
What are PTH and calcitonin?
Antagonists
7
New cards
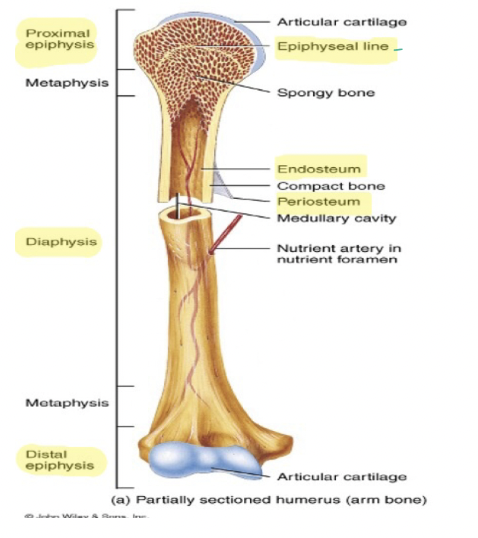
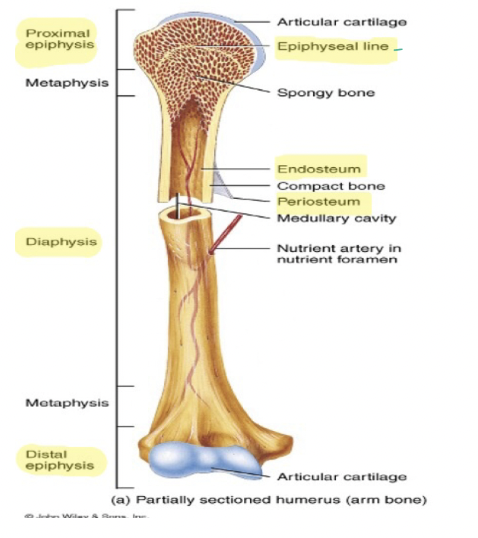
Know where these parts and structures are
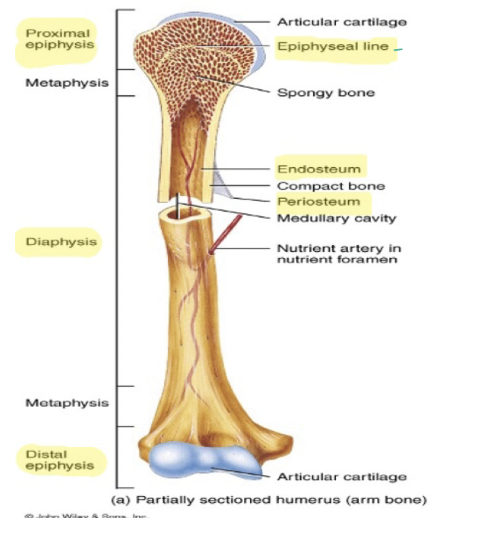
8
New cards
What does Diaphysis mean?
Shaft of any bone
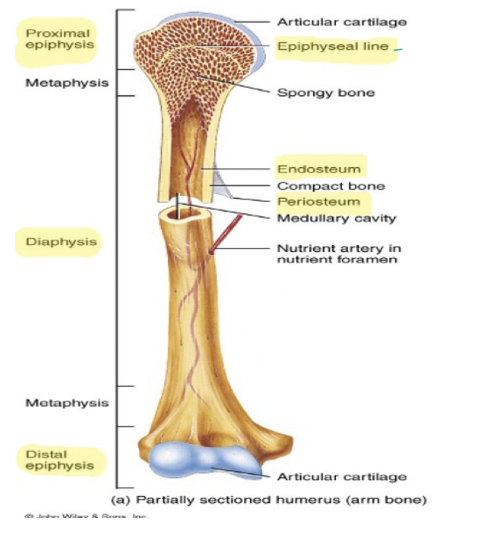
9
New cards
What does Epiphyseal line mean?
Growth Plate
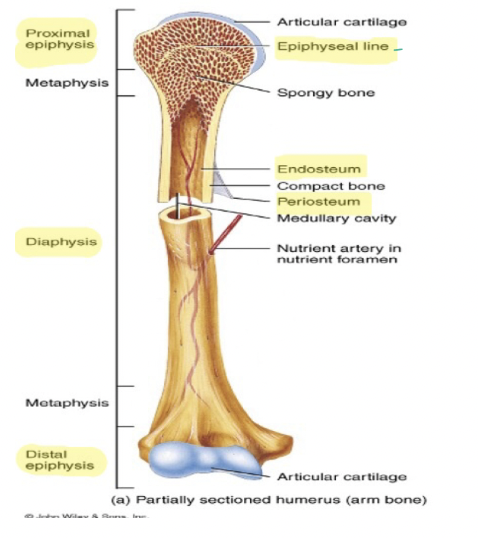
10
New cards
What is the inner most layer of the bone?
Endosteum
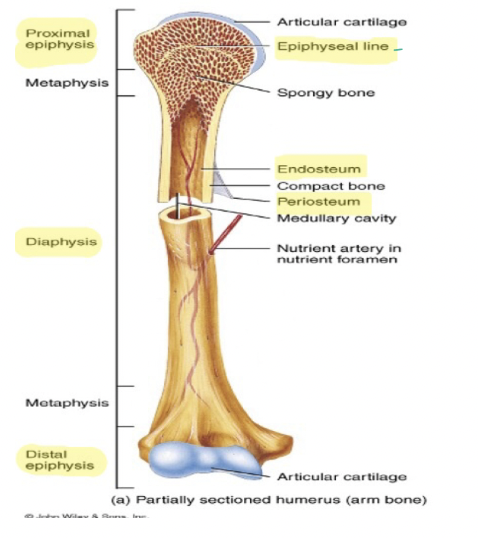
11
New cards
What is the outermost layer of the bone?
Periosteum
12
New cards
What does epiphysis mean?
Ends of bones
13
New cards
What are the two kinds of bone?
1. Compact bone
2. Spongy bone
14
New cards
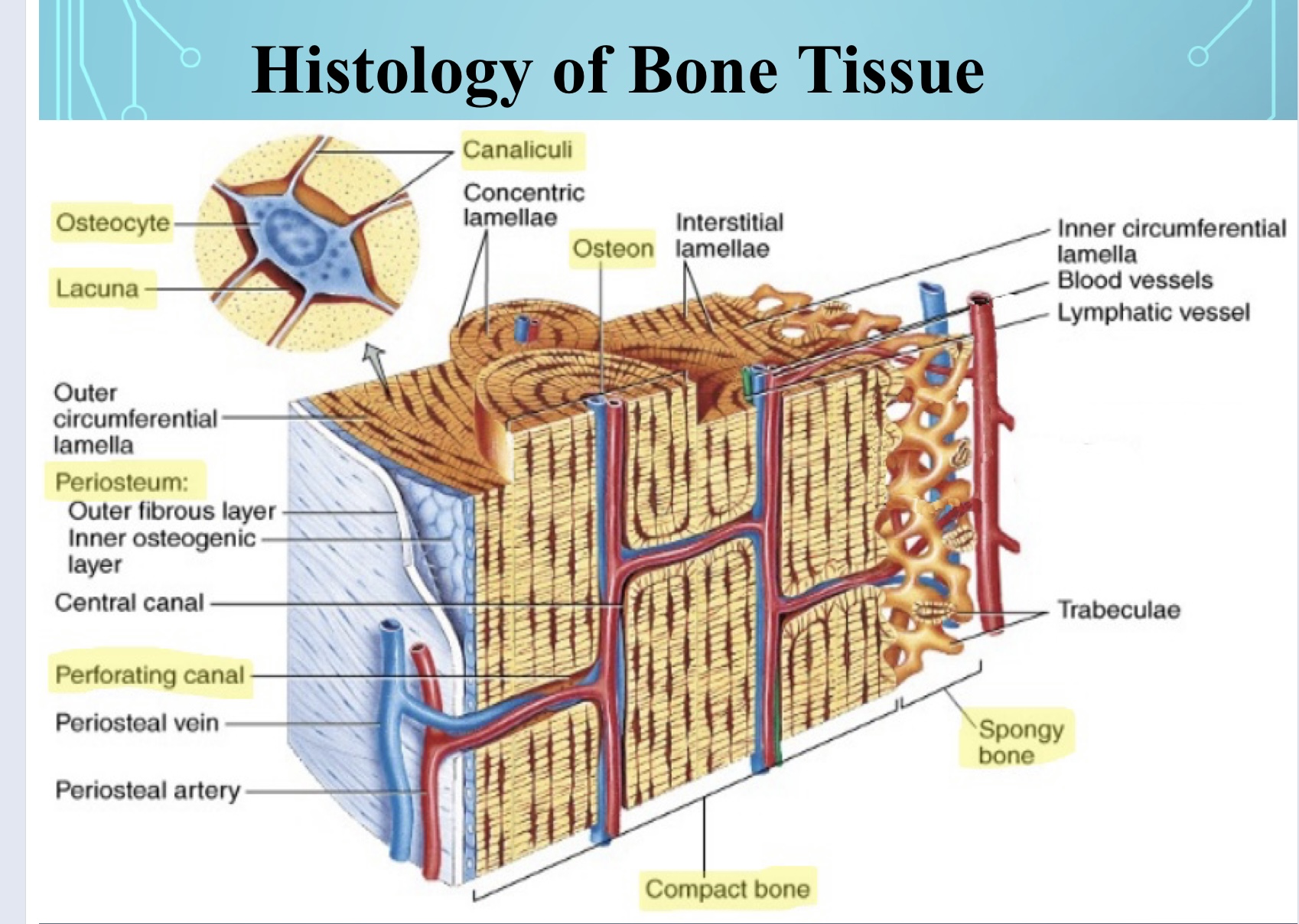
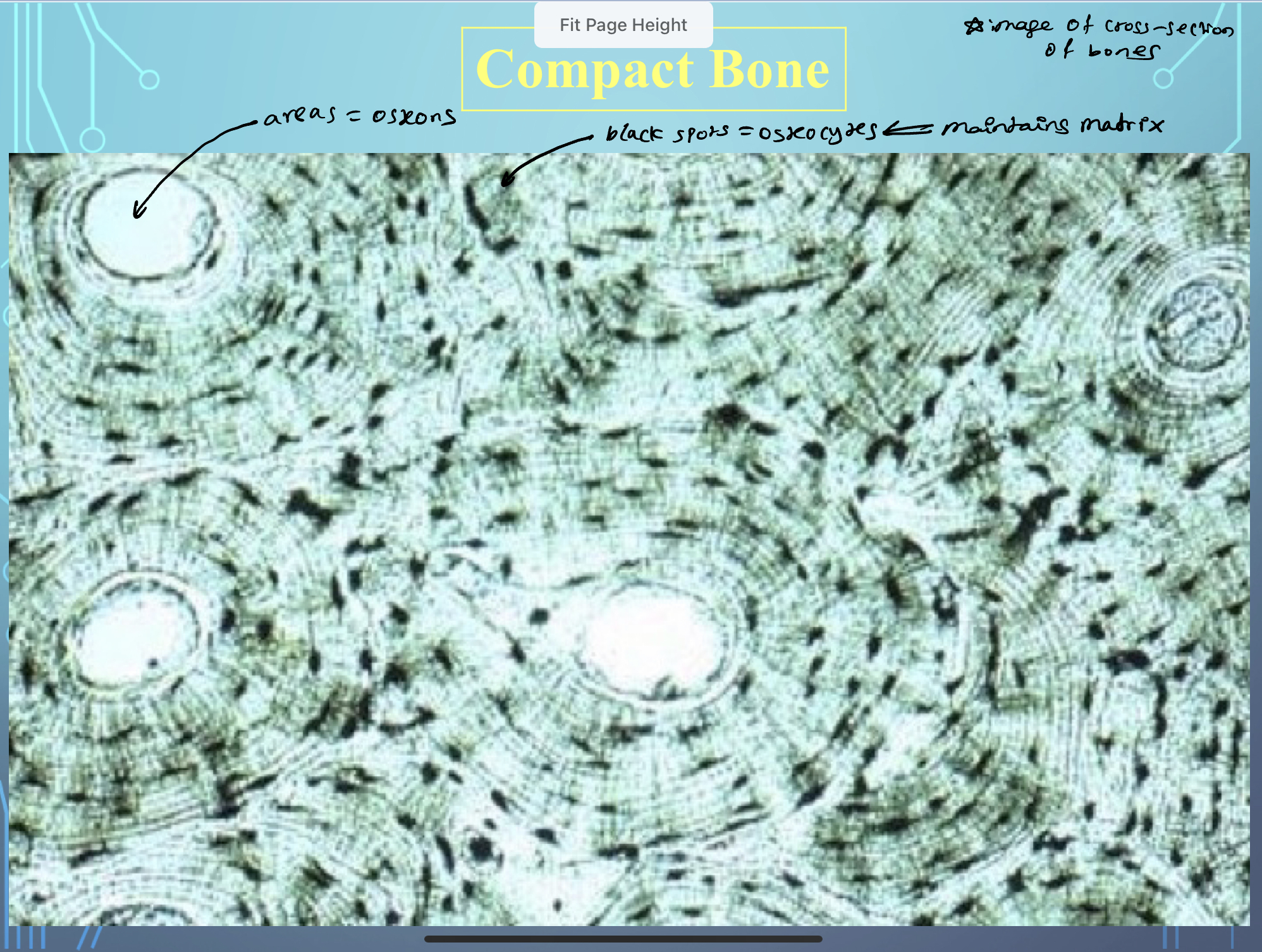
What are the units in which compact bone is arranged called?
Osteons or Haversian systems
15
New cards
What are Osteons?
White center parts in compact bones
16
New cards
What are osteocytes?
Black dots that communicate through **canaliculi** (lines) filled with fluid
17
New cards
**Patient Case:**
* around 5 years old
* Bone break from jumping on trampoline
* Arm was S - shape
* Doesn’t hurt
* Since the person is young, the bones will still have cartilage
\
What happened?
* around 5 years old
* Bone break from jumping on trampoline
* Arm was S - shape
* Doesn’t hurt
* Since the person is young, the bones will still have cartilage
\
What happened?
Green-stick fracture
* kinda breaks but still attached (one side of shaft broke)
* bones are more flexible on younger people
* kinda breaks but still attached (one side of shaft broke)
* bones are more flexible on younger people
18
New cards
Identify and remember **osteocyte, canliculi and most of the highlighted** items?
19
New cards
What are canaliculi?
The lines used for Osteocytes to communicate through; filled with fluid; connects cells
20
New cards
Identify and remember where Osteons and Osteocytes are located
21
New cards
Understand where the caniliculi are as well
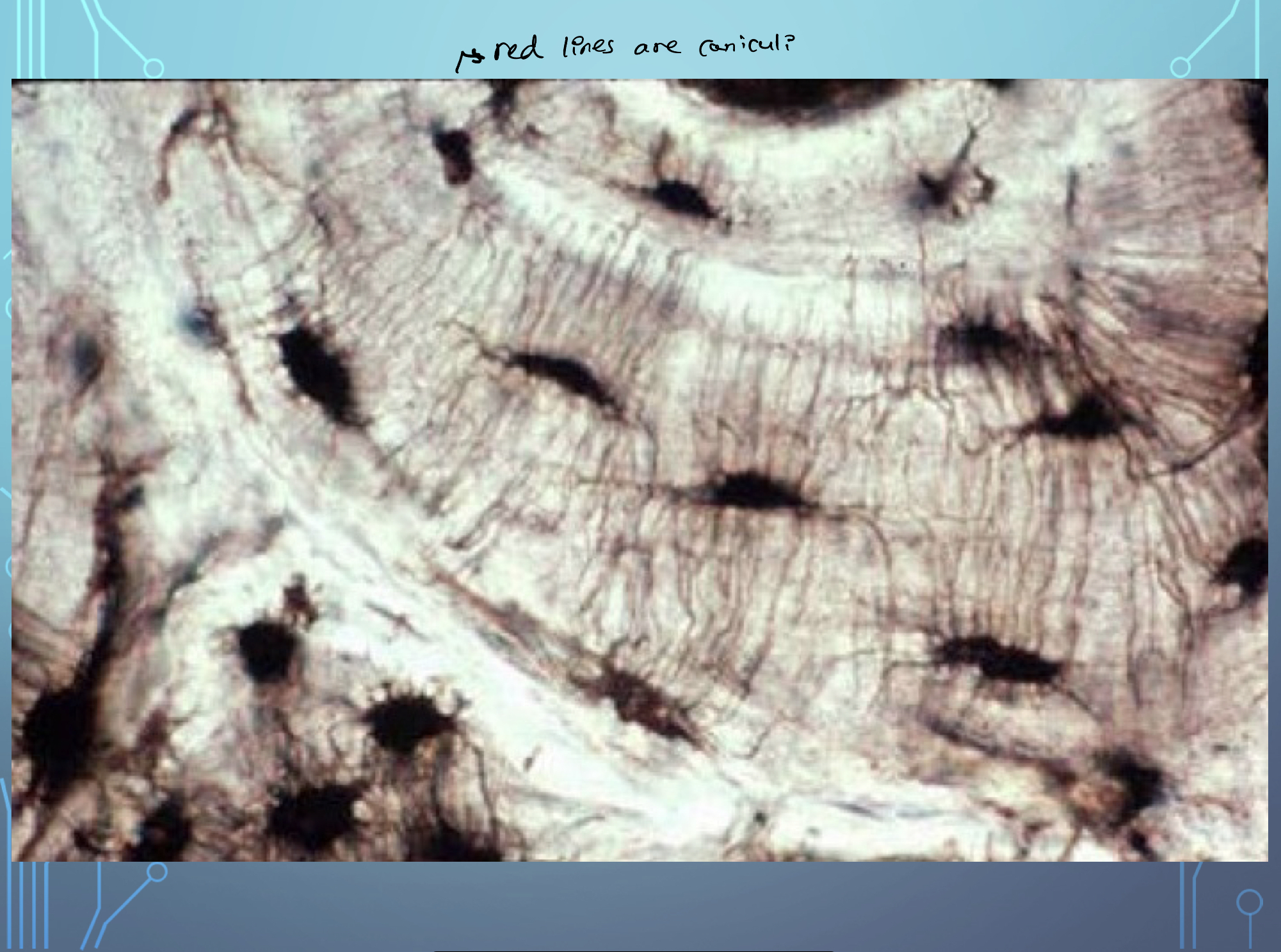
22
New cards
Spongy bone
* No Osteons
* vascular
* vascular
23
New cards
What is mesenchyme?
This is how all embryonic connective tissue begins as
24
New cards
What is bone formation termed as and what does it mean?
* Osteogenesis (creating bone)
* Ossification (cartilage becoming bone)
* Ossification (cartilage becoming bone)
25
New cards
What are the two types of ossification?
* Intramembranous ossification
* Endochondrial ossification
* Endochondrial ossification
26
New cards
What is Intramembranous ossification?
formation of bone **directly from or within fibrous connect tissue membranes**
27
New cards
What is Endochondrial ossification?\*
formation of bone from **hyaline cartilage models**
28
New cards
Where does intramembranous ossification occur?
* All roofing bones of the skull
* Frontal bone
* Parietal bones
* Occipital bone
* Temporal bones
* Mandible
* Clavicle
* Frontal bone
* Parietal bones
* Occipital bone
* Temporal bones
* Mandible
* Clavicle
29
New cards
What are the soft spots between skull bones?
Fontanelles
30
New cards
Where is a good area to diagnose meningitis in infants?
Anterior Fontanelle
31
New cards
Why do we have the centers of ossification?
* Because the brain is growing faster than skull, and these allow the skull to stretch
* Shaping of skull going through birth canal for baby to come out
* Shaping of skull going through birth canal for baby to come out
32
New cards
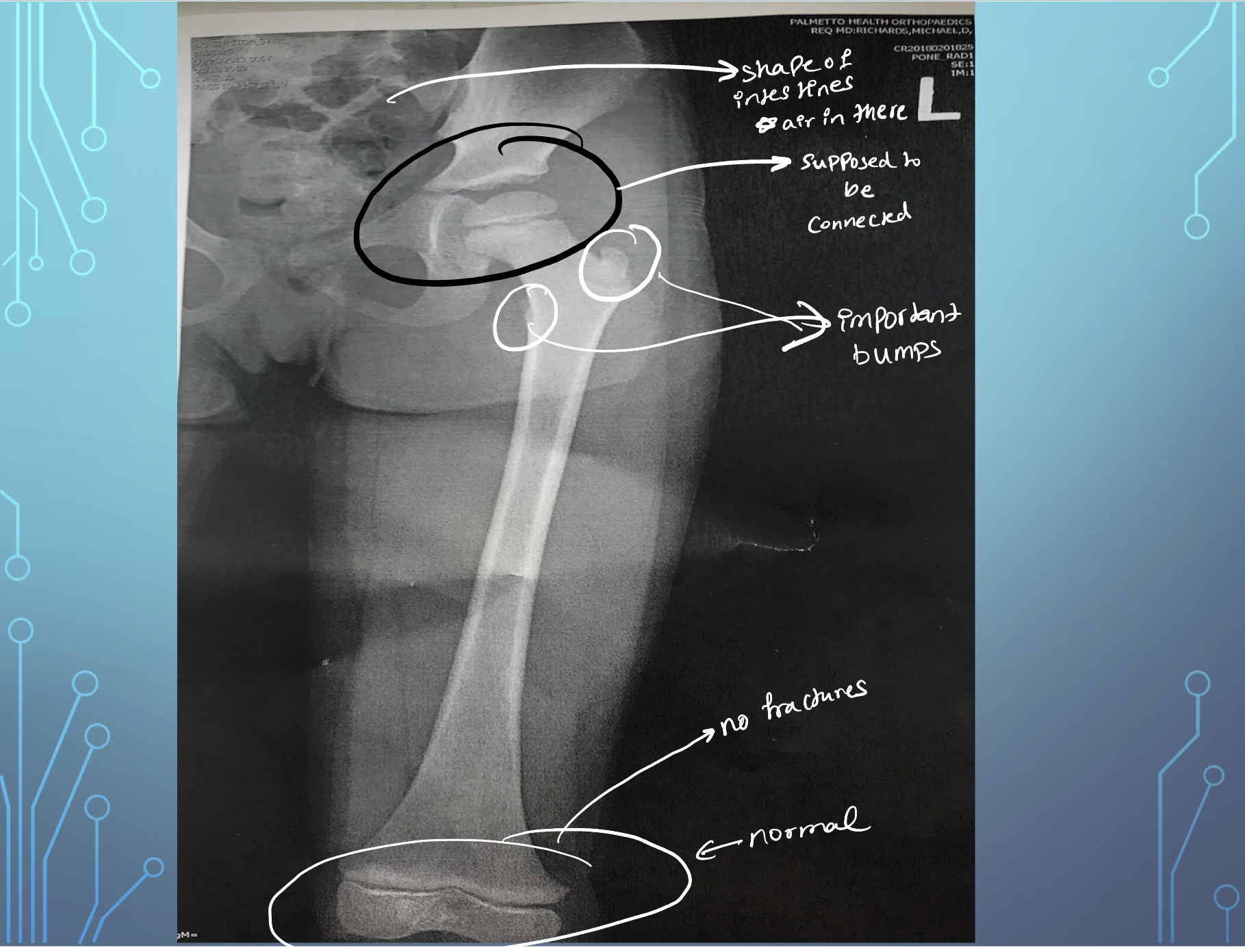
**Patient Case:**
* Know that the bones in xray are not broken, but are just developing
* They will eventually connect
* The two bumps circled are important
* Know that the bones in xray are not broken, but are just developing
* They will eventually connect
* The two bumps circled are important
33
New cards
What are the Zones of epiphyseal plates?
* Zone of Resting Cartilage
* Zone of Proliferating Cartilage
* Zone of Hypertrophic Cartilage
* Zone of Calcified Cartilage
* Zone of Proliferating Cartilage
* Zone of Hypertrophic Cartilage
* Zone of Calcified Cartilage
34
New cards
What is the function of the Zone of Resting Cartilage?
Anchors growth plate to bone
35
New cards
What is the function of the Zone of Proliferating Cartilage?
Rapid cell division **(stacked coins)**
36
New cards
What is the function of the Zone of Hypertrophic (enlargement) Cartilage?
Cells enlarged & remain in columns
37
New cards
What is the function of the Zone of Calcified Cartilage?
thin zone, cells mostly dead since matrix calcified
38
New cards
Which side of the body is the bone thicker on?
Dominant side/arm
39
New cards
How can bone grow in thickness or diameter?
Only by appositional growth
40
New cards
Steps of bone growth:
1. Periosteal cells differentiate into osteoblasts
2. Ridges fuse and the periosteum becomes the endosteum
3. New concentric lamellae are formed
41
New cards
What do periosteal cells differentiate into?
Osteoblasts
42
New cards
What do osteoblasts secrete?
Collagen fibers and organic molecules to form the matrix
43
New cards
What fuses and what becomes the endosteum during bone growth?
Ridges fuse and the periosteum becomes the endosteum
44
New cards
How does Calcium affect bone growth?
Makes bone matrix hard
45
New cards
What is hypocalcemia?
Low blood calcium levels
46
New cards
What are two ailments due to hypocalcemia?
Chvostek’s sign and Trousseau’s sign
47
New cards
What is hypercalcemia?
High blood calcium levels
48
New cards
How does Phosphorus affect bone growth?
Makes bone matrix hard
49
New cards
How does magnesium affect bone growth?
Deficiency in magnesium inhibits osteoblasts
50
New cards
How does Manganese affect bone growth?
Deficiency inhibits formation of new bone tissue
51
New cards
What does the lack of Vitamin C cause?
Scurvy Disorder
52
New cards
Why is Vitamin D important to Bone Growth?
Calcitriol helps build bone by increasing calcium absorption
53
New cards
What does Vitamin D deficiency result in?
Rickets in Children
54
New cards
**Patient Case:**
* dog tripped patient
* nothing is abnormal
* taking SSRIs -- anti depressants
\
How can SSRIs impact fractures and bone density?
* dog tripped patient
* nothing is abnormal
* taking SSRIs -- anti depressants
\
How can SSRIs impact fractures and bone density?
* SSRIs decrease bone density, especially in women
* Anti depressants can also lead to easier fractures
* Anti depressants can also lead to easier fractures
55
New cards
What is the function of Human growth hormone?
* Promotes general growth of all
* Body tissue and normal growth in children
* Body tissue and normal growth in children
56
New cards
Don’t need to know bone fractures, but this is the picture
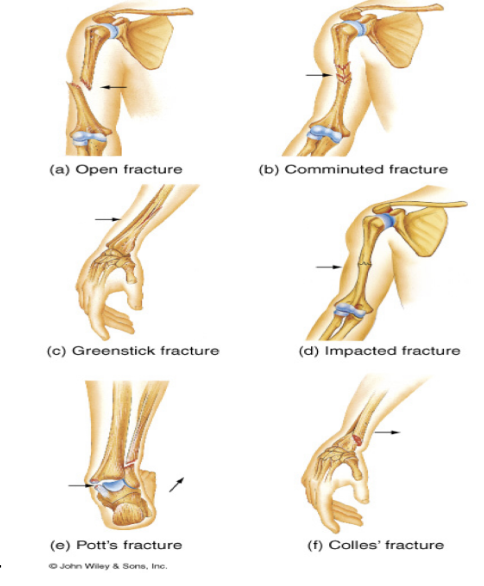
57
New cards
What are the steps in fracture repair?
1. Formation of a fracture hematoma; some swelling
2. Fibrocartilaginous callus formation
3. Bony callus formation -- makes it thicker
4. Bone remodeling -- around 5-6 months
58
New cards
What is a fracture hematoma?
Collection of blood where the bone first breaks
59
New cards
Is it true that it is easier to break the bone after it has already broken once?
No, this is not true. Happens if not formed/repaired properly
60
New cards
**Patient Case:**
* mainly child or elder abuse cases
* spinning arm around during abuse
\
What does this cause?
* mainly child or elder abuse cases
* spinning arm around during abuse
\
What does this cause?
Spiral fracture
61
New cards
What is the problem if there is blue on the whites of eyes?
Membrane disorder; not bone problem
62
New cards
What is the function of Synovial joints?
Allow for more or less free movement
63
New cards
What does synovial fluid help with?
Helps lubricate and protect the bones
64
New cards
What sacks contain Synovial fluid?
Bursa sacks
65
New cards
What are the two classifications of Joints/Articulations?
1. Functional
2. Structural
66
New cards
What are the 3 functional classifications of joints?
* Synarthroses
* Amphiarthroses
* Diarthroses
* Amphiarthroses
* Diarthroses
67
New cards
What are Synarthroses?
immovable joints
68
New cards
What are Amphiarthroses?
slightly movable joints
69
New cards
What are Diarthroses?
freely movable joints
70
New cards
What are Fibrous Joints?
Bones joined by dense fibrous connective tissue
71
New cards
What are the 3 types of Fibrous Joints?
* Sutures
* Syndesmoses
* Gomphoses
* Syndesmoses
* Gomphoses
72
New cards
Sutures and fontanelles have same functions
73
New cards
What are gomphoses?
Peg-in-socket joints of teeth
74
New cards
What is the fibrous connection of gomphoses?
Periodontal ligament
75
New cards
What are the two types of Cartilaginous Joints?
* Synchondroses
* Symphyses
* Symphyses
76
New cards
What are synchondroses joints?
Bar/plate of hyaline cartilages unites bones
\
\-- Hyaline are more structural/supportive
\
\-- Hyaline are more structural/supportive
77
New cards
What are Symphyses Joints?
Fibrocartilage unites bone
78
New cards
What are the two layers of the articular joint capsule in synovial joints?
* External **fibrous layer**
* Inner **synovial membrane**
* Inner **synovial membrane**
79
New cards
What is the external fibrous layer?
Dense irregular connective tissue
80
New cards
What is the inner synovial membrane?
Makes synovial fluid drawn from plasma; mostly sterile
81
New cards
**Patient Case:**
* round bumps on finger
* Synovial fluid leaks out
* round bumps on finger
* Synovial fluid leaks out
Osteoarthritis; pushes fluid out
82
New cards
**Patient Case:**
* Track athlete
* joint pains
* Can cause bull’s eye rash; though most patients with this disease do not have this
\
What was the problem?
* Track athlete
* joint pains
* Can cause bull’s eye rash; though most patients with this disease do not have this
\
What was the problem?
Lyme disease
83
New cards
**Patient Case:**
* girl running
* pain and fatigue
* there is a tick, but is rarely outdoors
* was in a field one time
\
What is the problem?
* girl running
* pain and fatigue
* there is a tick, but is rarely outdoors
* was in a field one time
\
What is the problem?
Lyme disease
84
New cards
What can age do to synovial fluid? What does this do to bones?
Age can cause synovial fluid to calcify, and this pokes at bone like needles causing pain
85
New cards
What are hinge joints?
allows extension and retraction (Elbow & Knee)
86
New cards
What are ball and socket joints?
Radial movement in almost any direction (Hip & Shoulder)
87
New cards
What is bursitis?
* inflammation of bursa, usually cause by blow or friction
* Treated with rest and ice and, if severe, anti-inflammatory drugs
* Treated with rest and ice and, if severe, anti-inflammatory drugs
88
New cards
What is tendonitis?
* inflammation of tendon sheaths, typically caused by overuse
* symptoms and treatment similar to those of bursitis
* symptoms and treatment similar to those of bursitis
89
New cards
What is Osteopenia?
Bone mineral density is lower than normal peak BMD but not low enough to be osteoporosis
90
New cards
What is osteoporosis?
* loss of both bone salts and collagen fibers
* increased osteoclast activity and decreased osteoblast activity
* increased osteoclast activity and decreased osteoblast activity
91
New cards
Is Osteoporosis more common in males or females? Why?
* common in females because calcitonin and BTH are needed and work better in sex hormones
* while testosterone is common, women have menopause which affects hormones
* while testosterone is common, women have menopause which affects hormones
92
New cards
What is Osteomalacia?
loss of bone salts but NOT collagen
93
New cards
What is an example of a disorder due to osteomalacia?
Rickets in young children
94
New cards
What is Rickets?
* softening and weakening of bones in children
* usually due to extreme and prolonged vitamin-D deficiency
* usually due to extreme and prolonged vitamin-D deficiency
95
New cards
What is Paget’s disease?
* Abnormal bone remodeling
* Very high ratio of spongy to compact bone and reduced mineralization = bone made fast and poorly causing something called pagetic bone
* Very high ratio of spongy to compact bone and reduced mineralization = bone made fast and poorly causing something called pagetic bone
96
New cards
What is Osteomyelitis?
Infection of bone most commonly due to Staphylococcus Aureus
97
New cards
Where can you find Staphylococcus Aureus and what does it commonly cause?
It is literally everywhere and lives off on us. It most commonly causes Osteomyelitis
98
New cards
What is Osteogenic Sarcoma?
Bone cancer that affect osteoblasts
99
New cards
What is Arthritis?
Inflammatory joint disease
100
New cards
How is Arthritis pain characterized?
* unilateral, one side
* pain 1st thing in morning
* less pain with movement
* pain 1st thing in morning
* less pain with movement