Private Pilot FAA Written
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
245 Terms
With respect to the certification of aircraft, which are
- categories of aircraft: normal, utility, acrobatic
- class of aircraft: airplane, rotorcraft, glider, balloon
With respect to the certification of airmen, which are
- categories of aircraft: airplane, rotorcraft, glider, lighter-than-air
- classes of aircraft: single-engine land and sea, multiengine land and sea
- types of cert: student pilot, recreational, PPL, commercial, airline transport pilot
- ratings: IFR, MEI, rotorcraft, glider, lighter-than-air
medical exam for PPL
3rd class valid
- <40yo: 60m
- >=40yo: 24m
BasicMed Rule
- max 6 seats (include pilot)
- <18k ft MSL
- max 250 kts
- not for hire/compensated
How to increase lift?
- increase speed
- increase wing's camper (shape or flap)
- increase angle of attack
note: Bernoulli and 3rd law of Newton
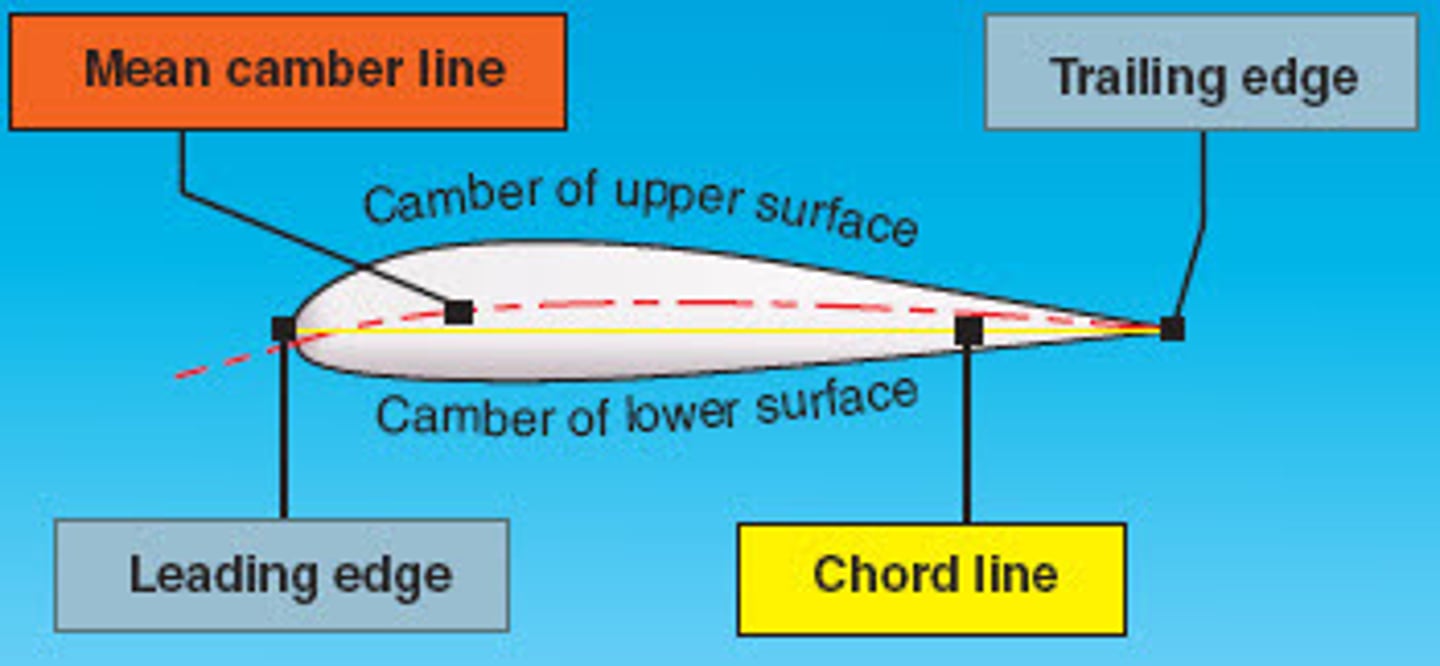
chord line
- An imaginary straight line from the leading edge to the trailing edge of an airfoil.
- flap down will increase angle of attack
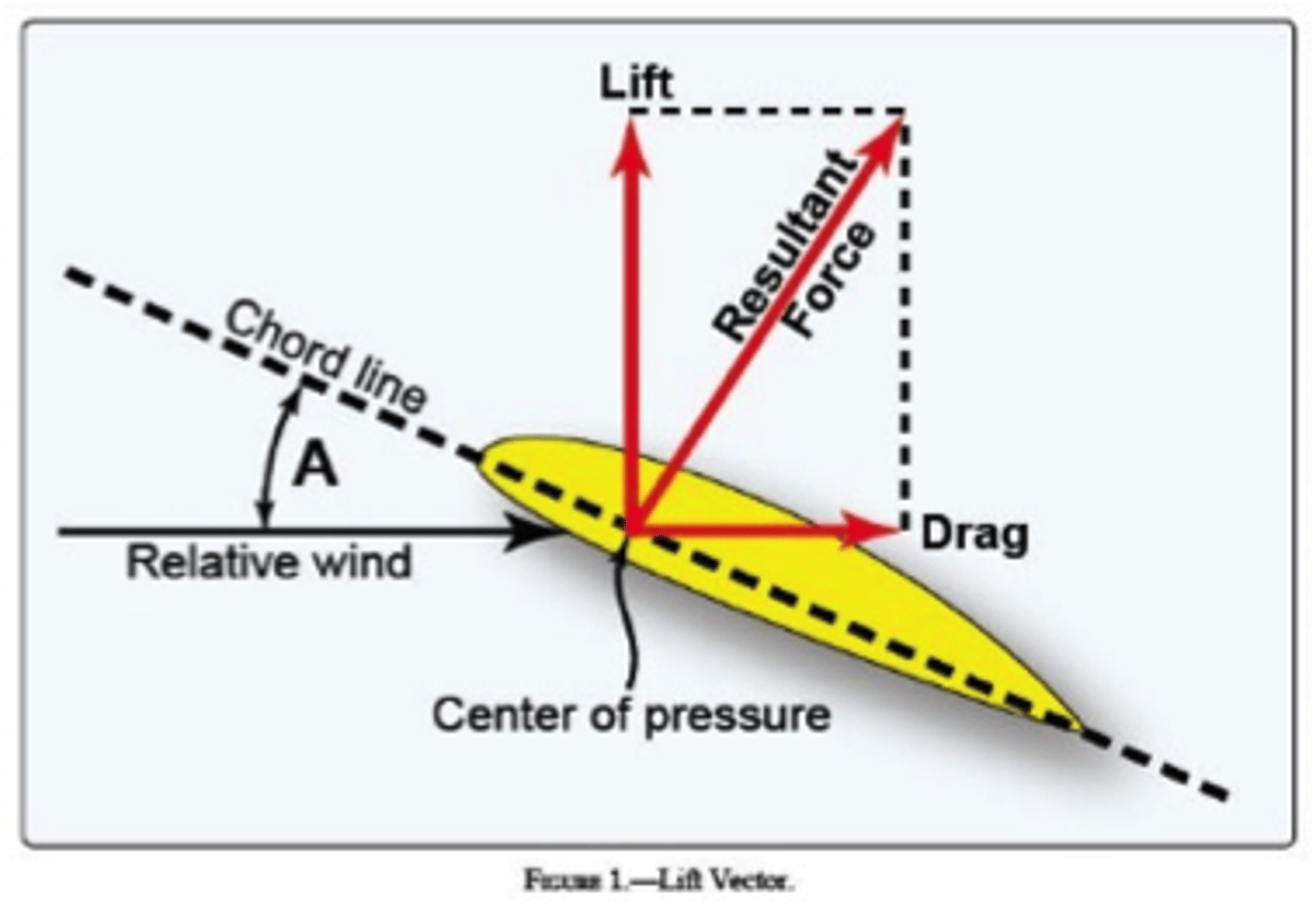
Angle of Attack
The angle formed by the wing chord line and the relative wind.
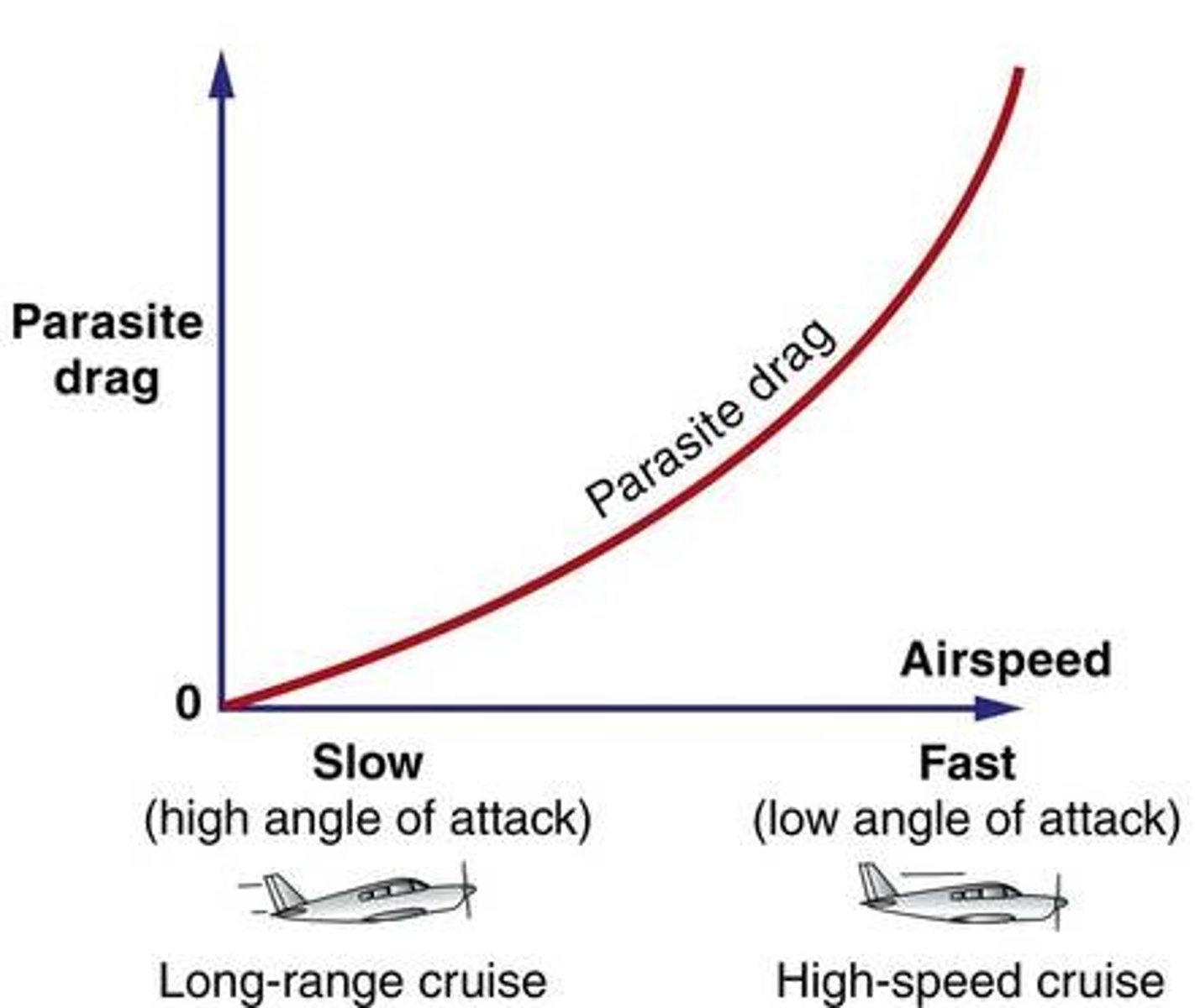
parasite drag
drag that does not contribute to lift generation; drag caused by landing gear struts, cooling intakes, antennas, rivet heads, etc.
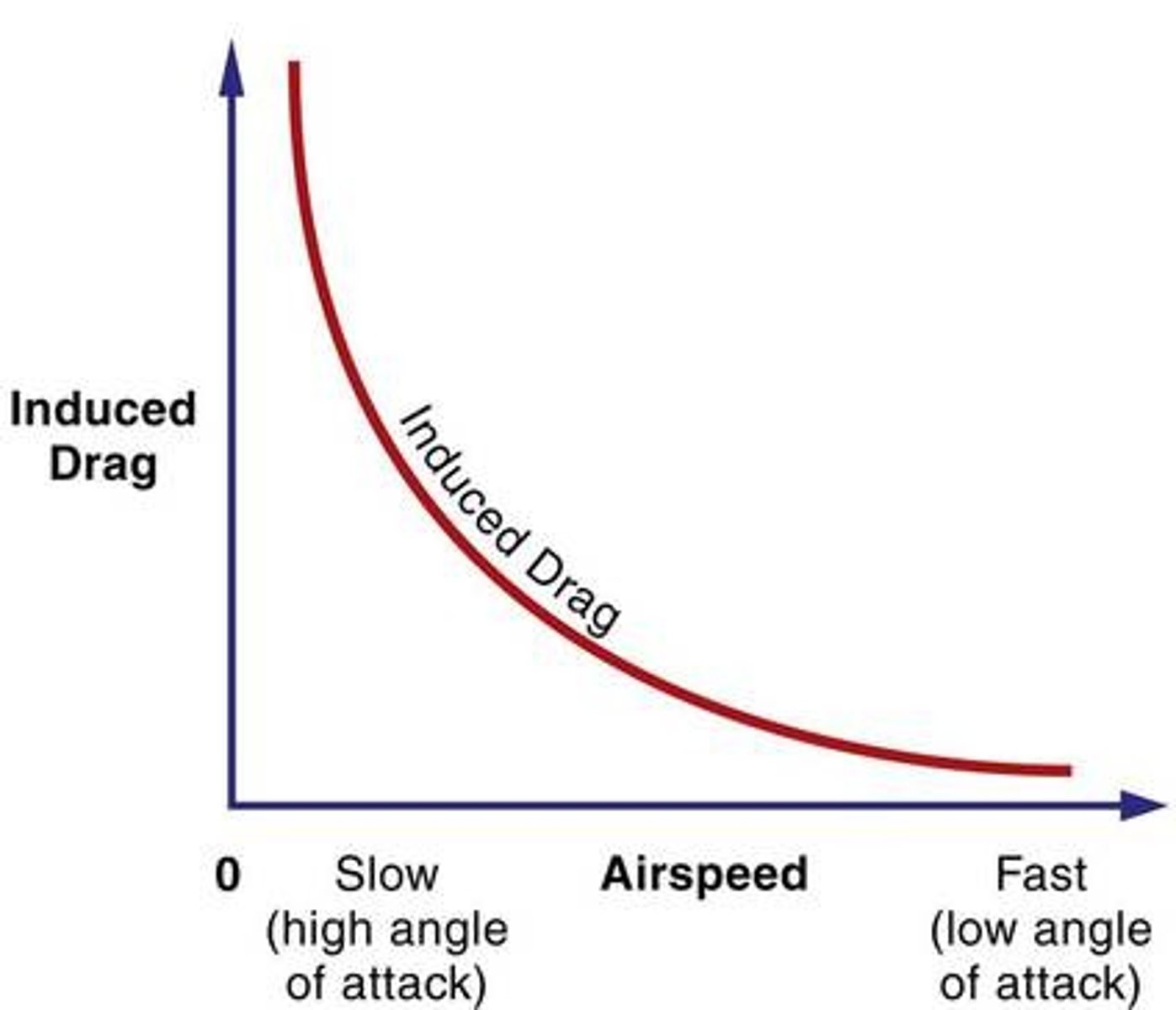
Induced Drag
Generated by the airflow circulation around the wing as it creates lift.
Drag and Speed Relationship
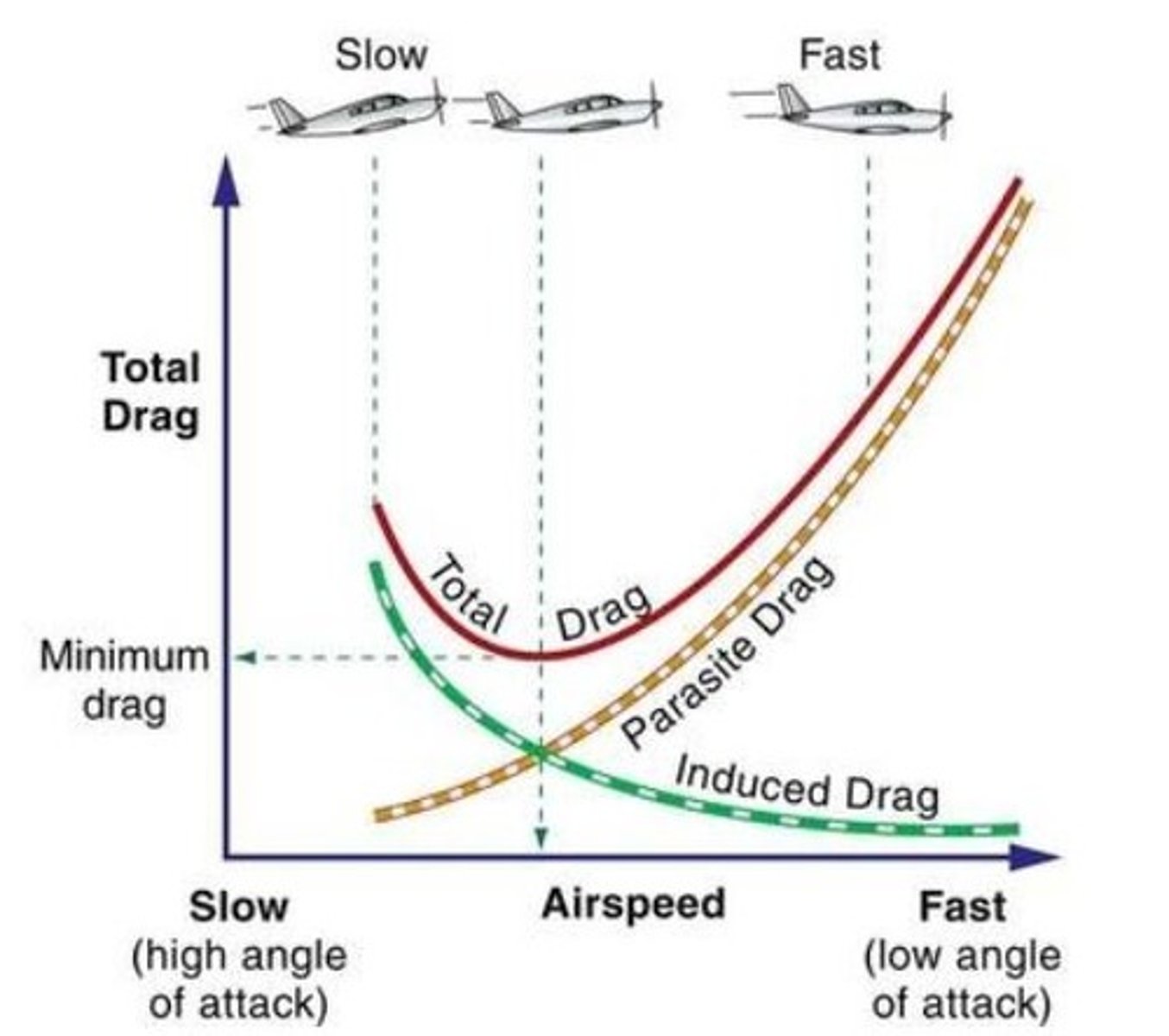
L/D max
The maximum ratio between total lift and total drag. This point provides the best glide speed. Any deviation from the best glide speed increase drag and reduces the distance you can glide
Critical angle of attack
The angle of attack at which an airfoil stalls (loses lift) regardless of the aircraft's airspeed, attitude, or weight.

Stall Recovery Procedure
1. Lower the angle of attack (pitch
down)
2. Add full power and raise the nose after the stall is "broken"
3. Establish a full power climb
4. Flaps up incrementally (if applicable)
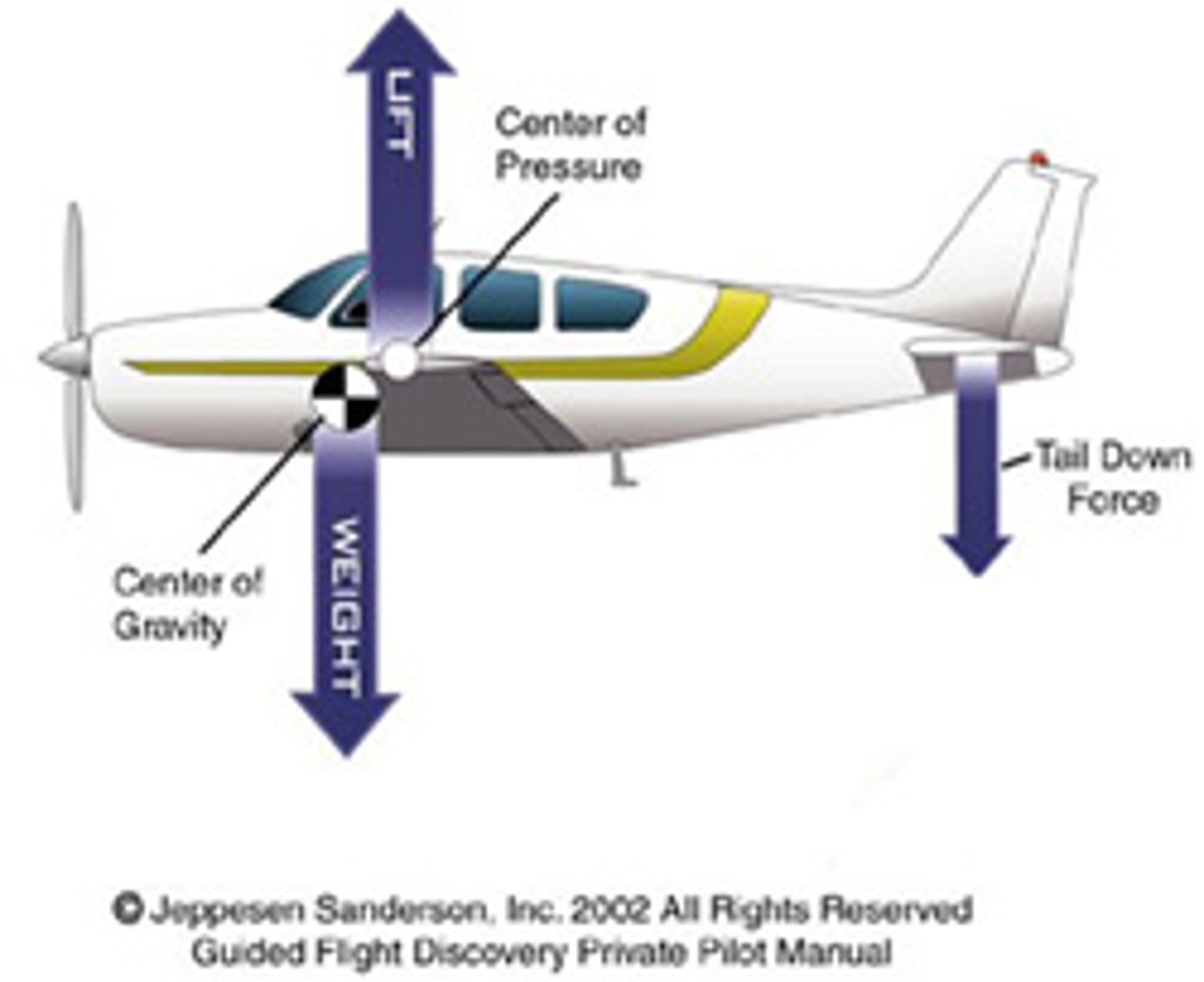
center of pressure (lift)
The point along the chord line of a wing at which all the aerodynamic forces are considered to be concentrated
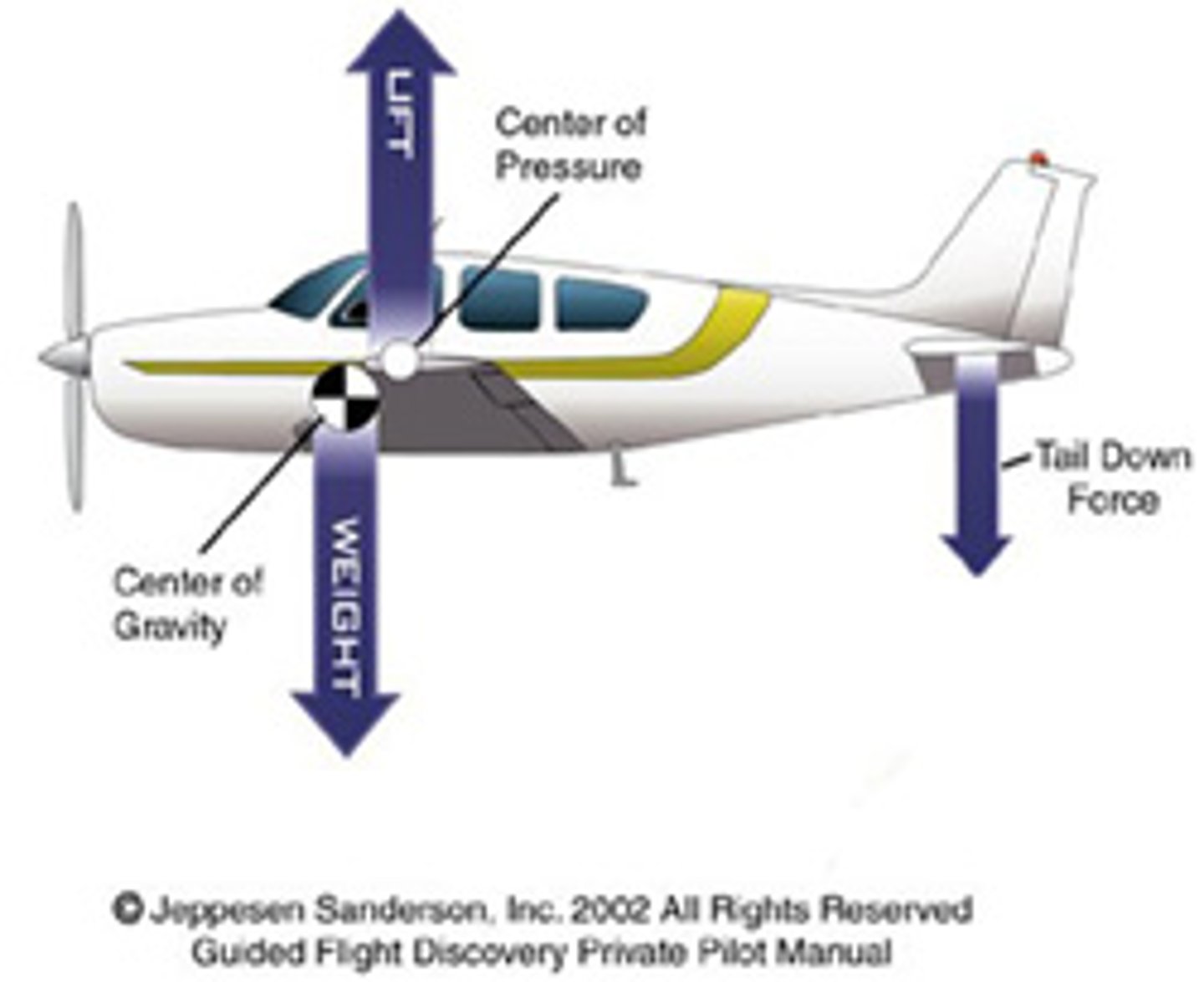
center of gravity (CG)
The center of gravity of the aircraft depending on weight and balance of the loads
Aeronautical Sectional Chart
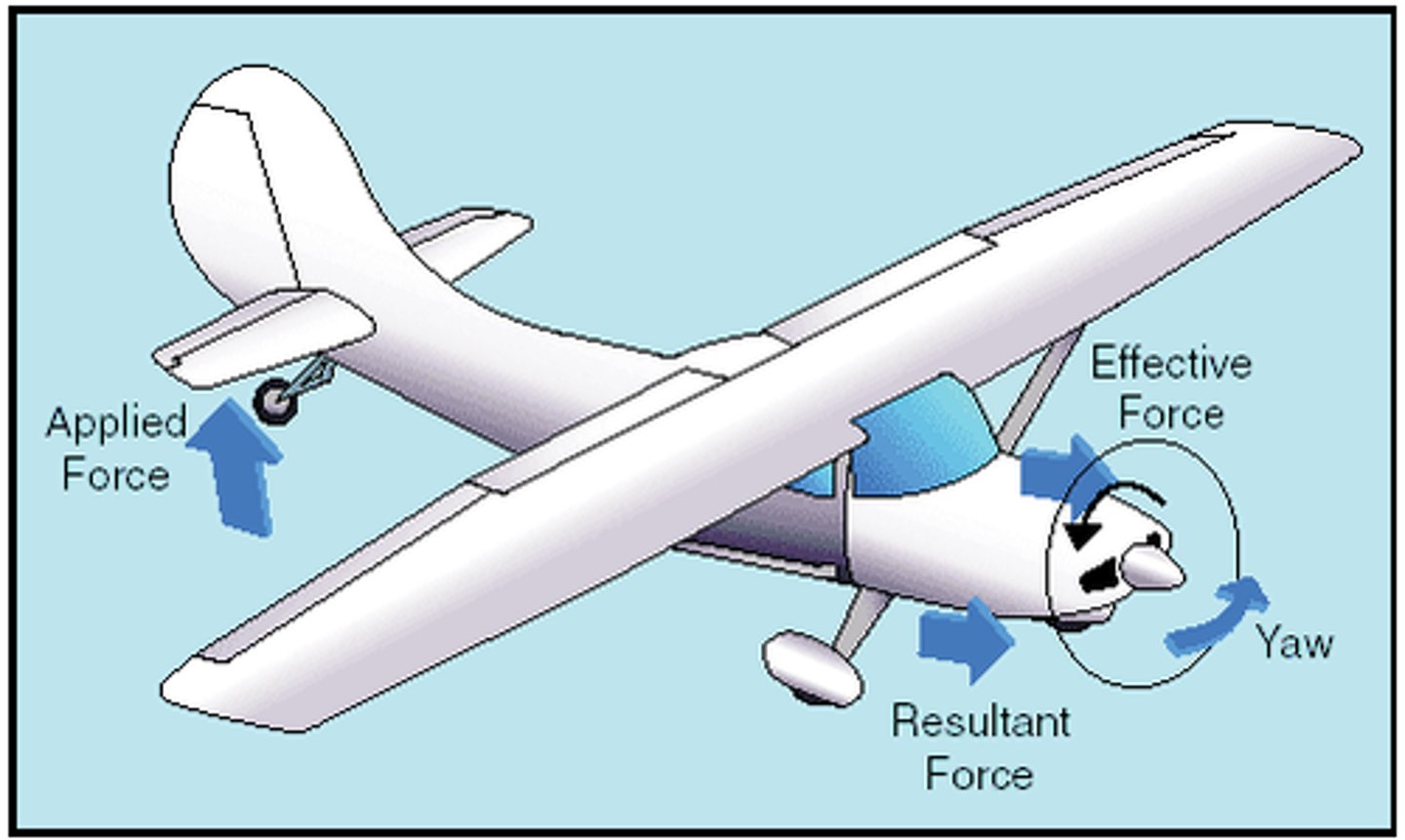
Gyroscopic Precession
When a force is applied to one side of a spinning object, the opposite happens to the other side.
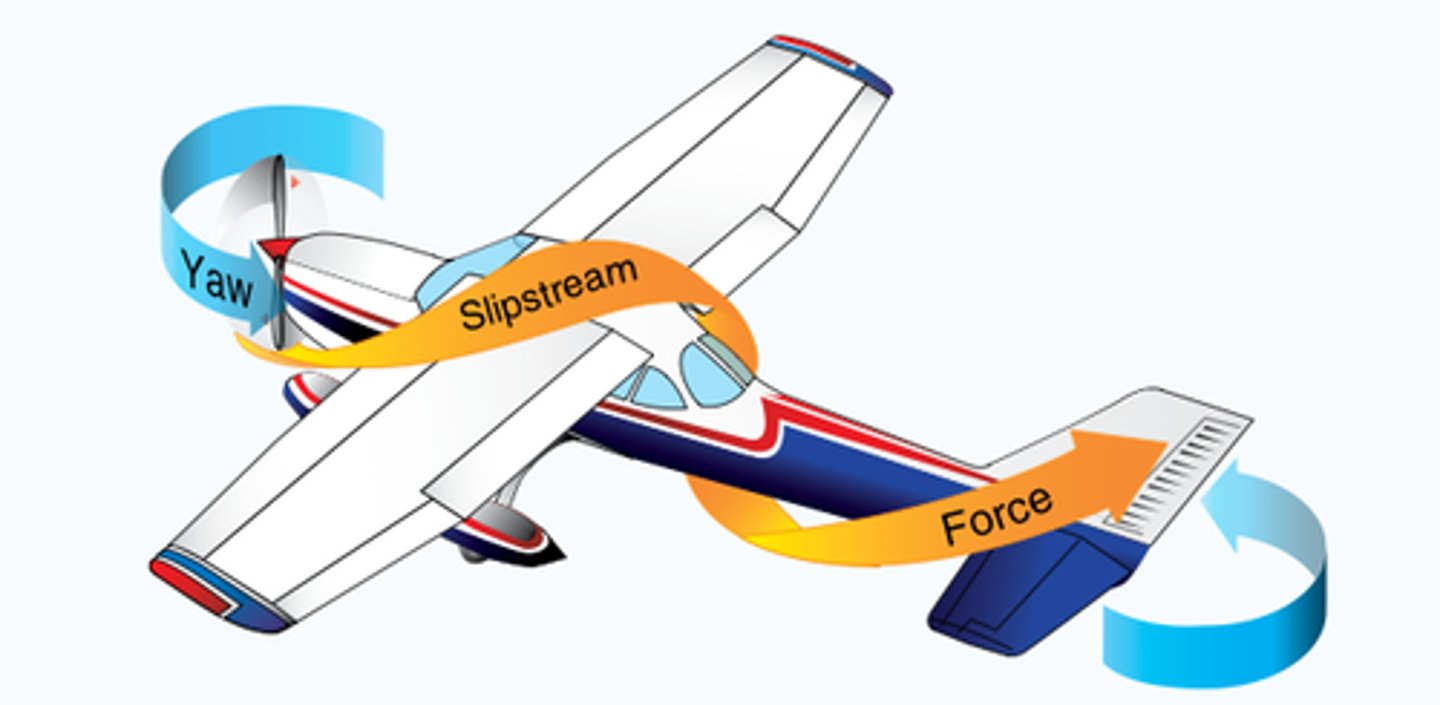
Spiraling Slipstream
The slipstream of a propeller-driven airplane rotates around the airplane. This slipstream strikes the left side of the vertical fin, causing the aircraft to yaw slightly. Rudder offset is sometimes used by aircraft designers to counteract this tendency.
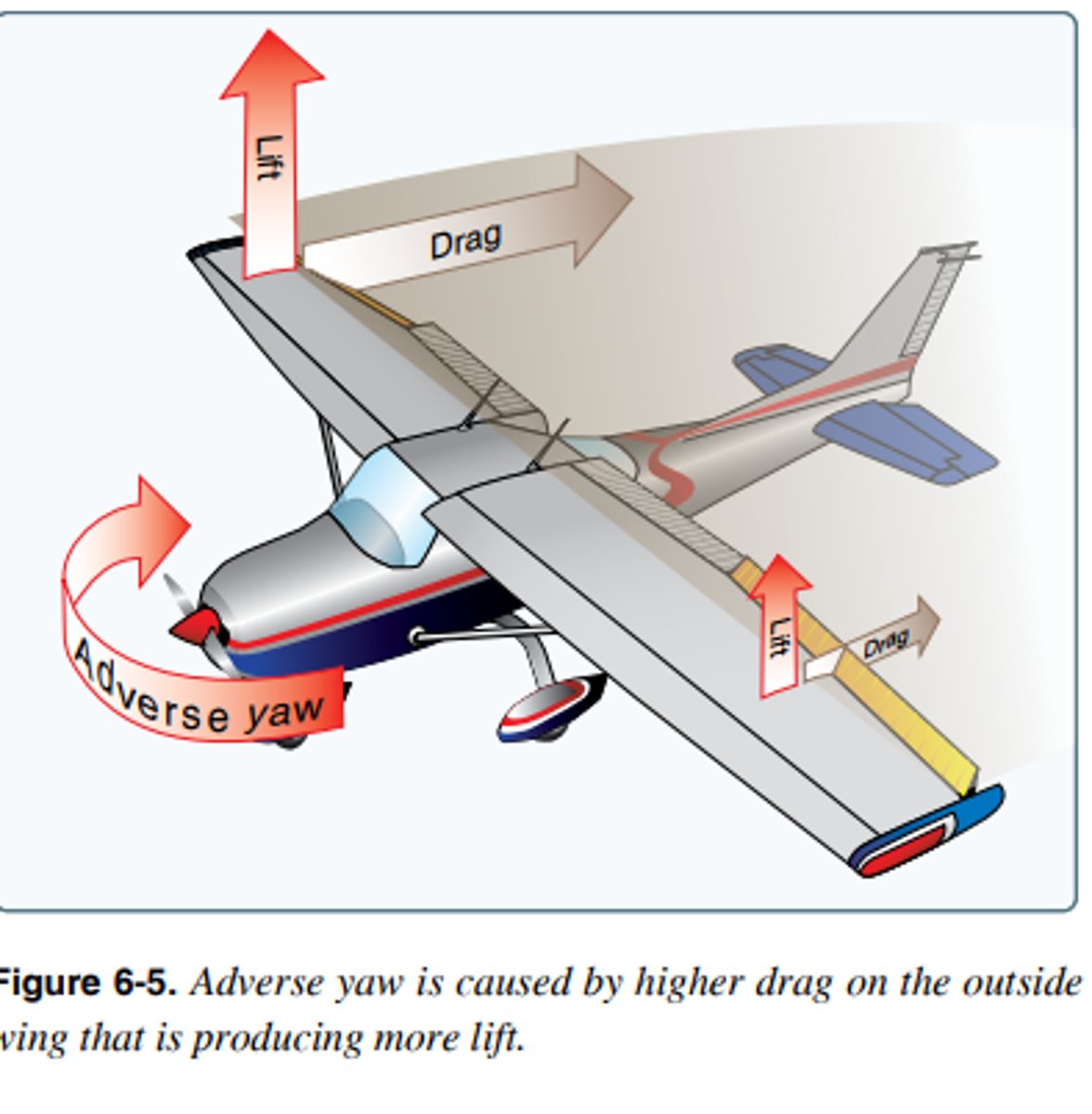
Adverse Yaw
Yawing tendency toward the outside of a turn.
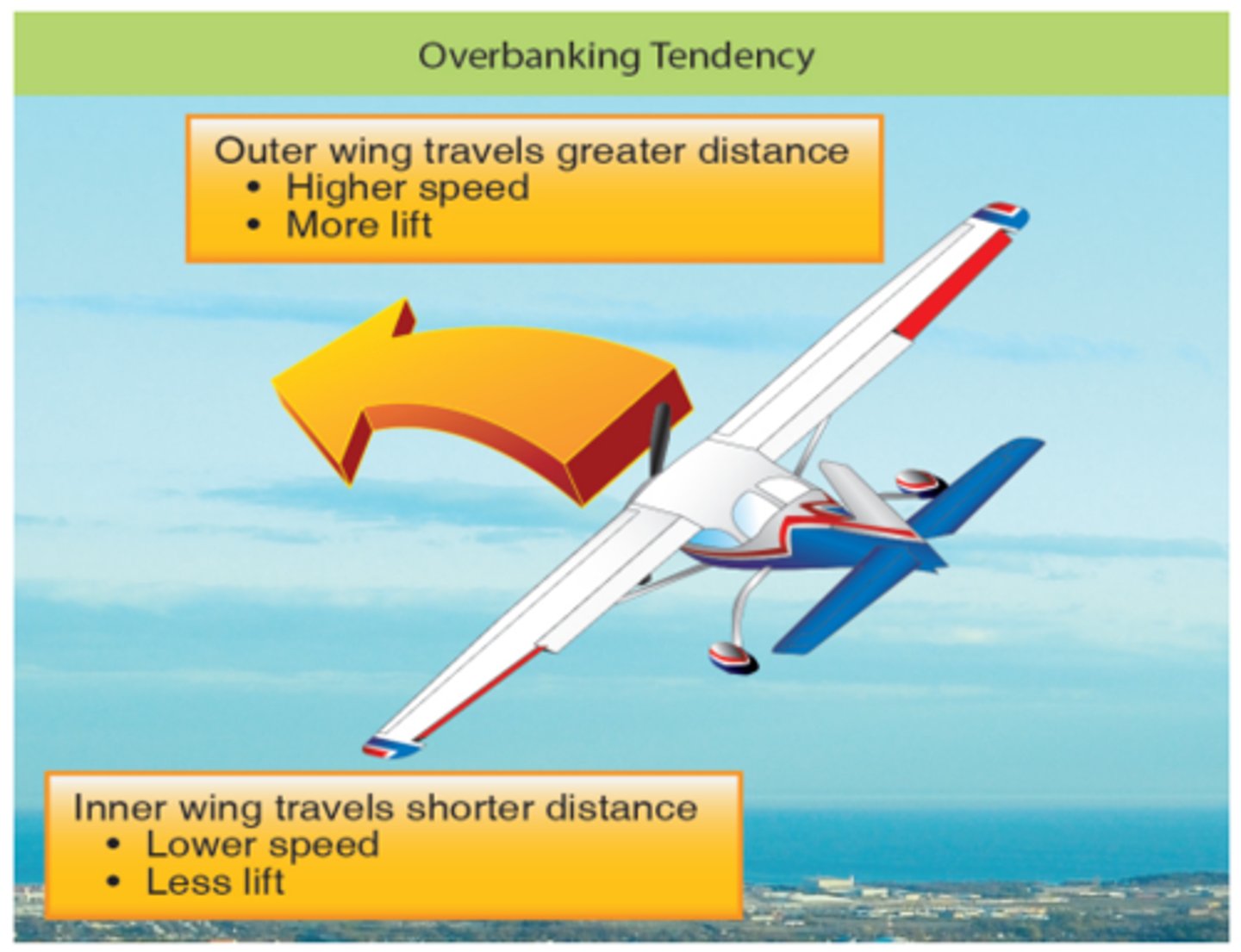
overbanking tendency
when entering a turn, the outside wing travel faster than inside wing, it produces more lift than inside wing, causes overbanking tendency
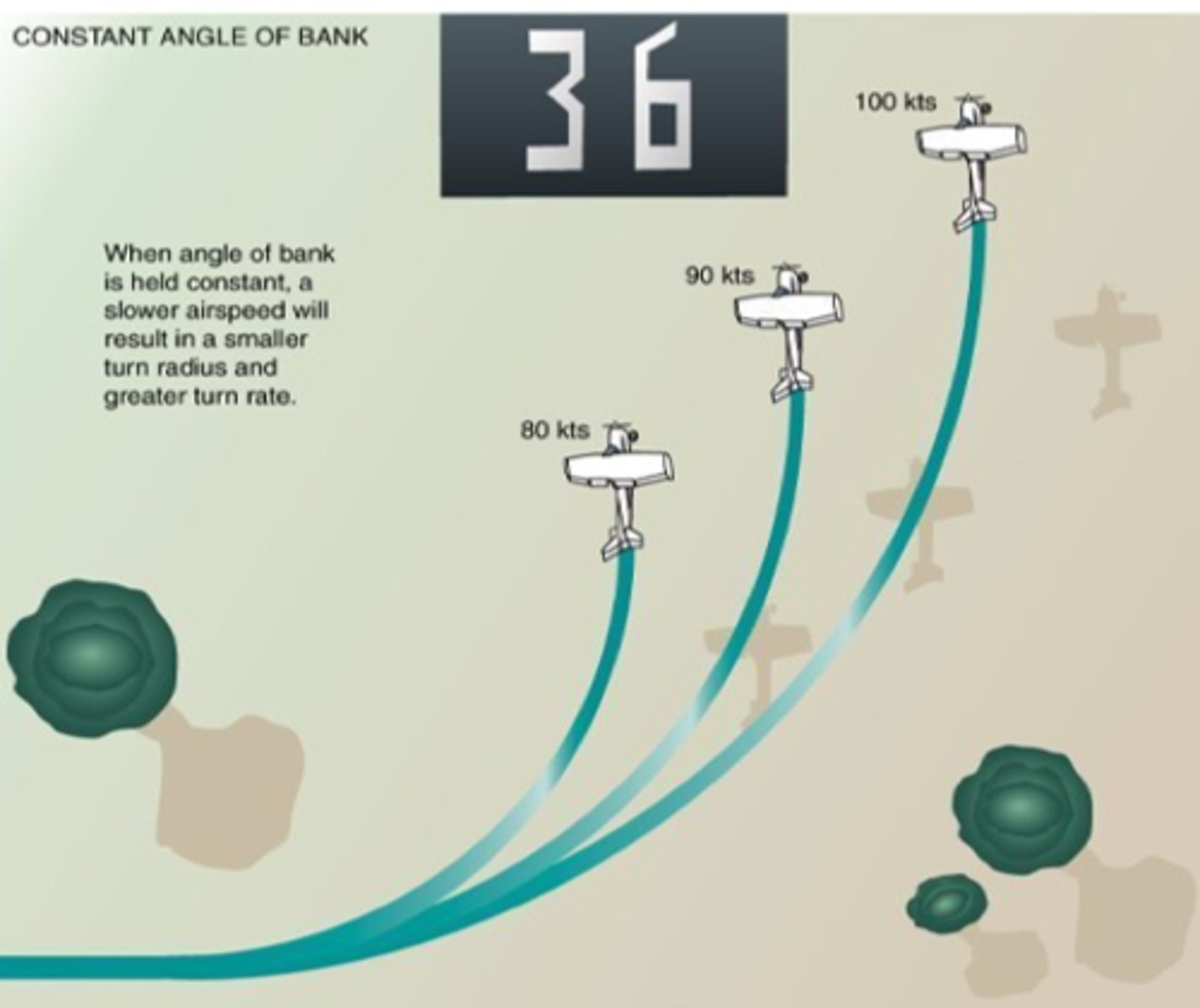
constant bank angle
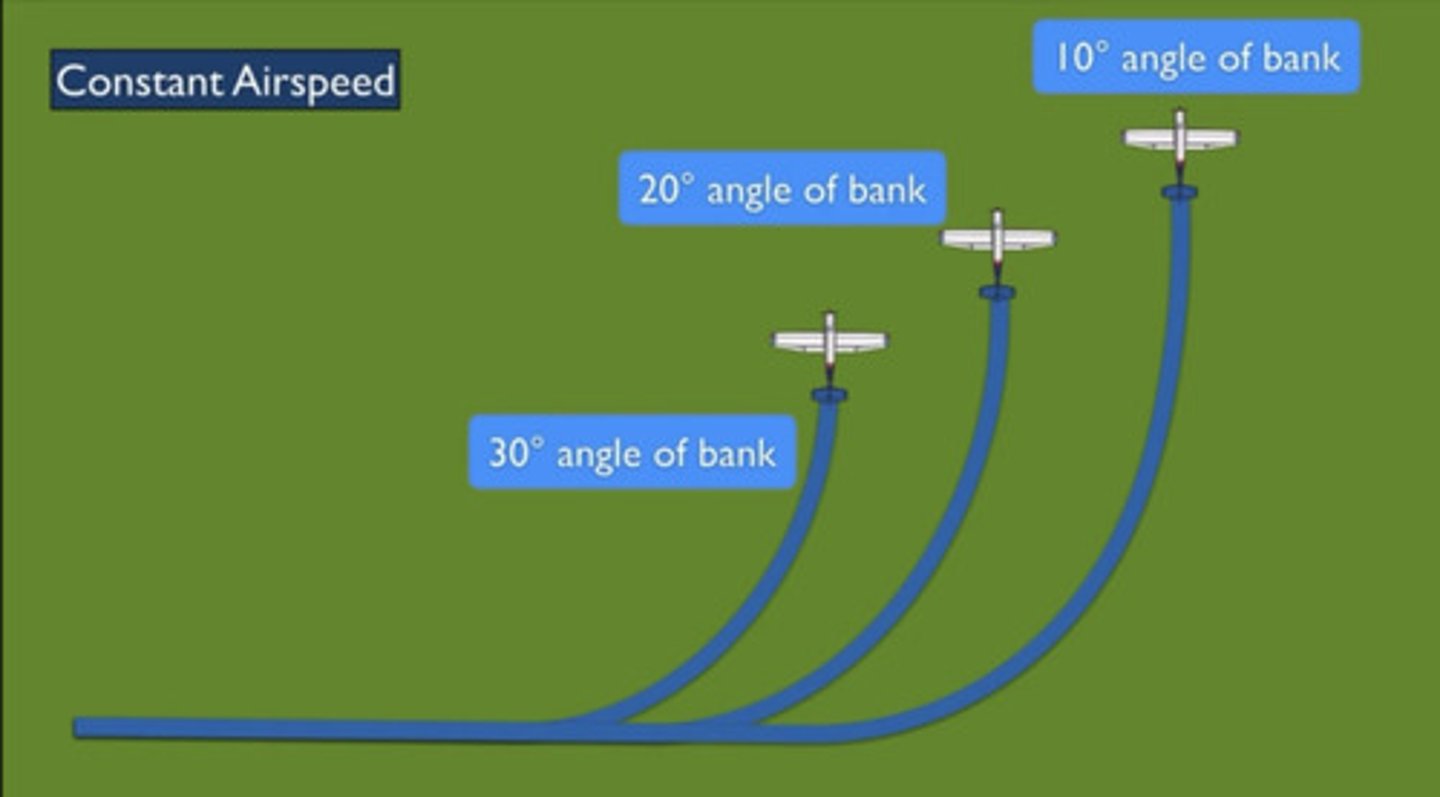
constant bank speed
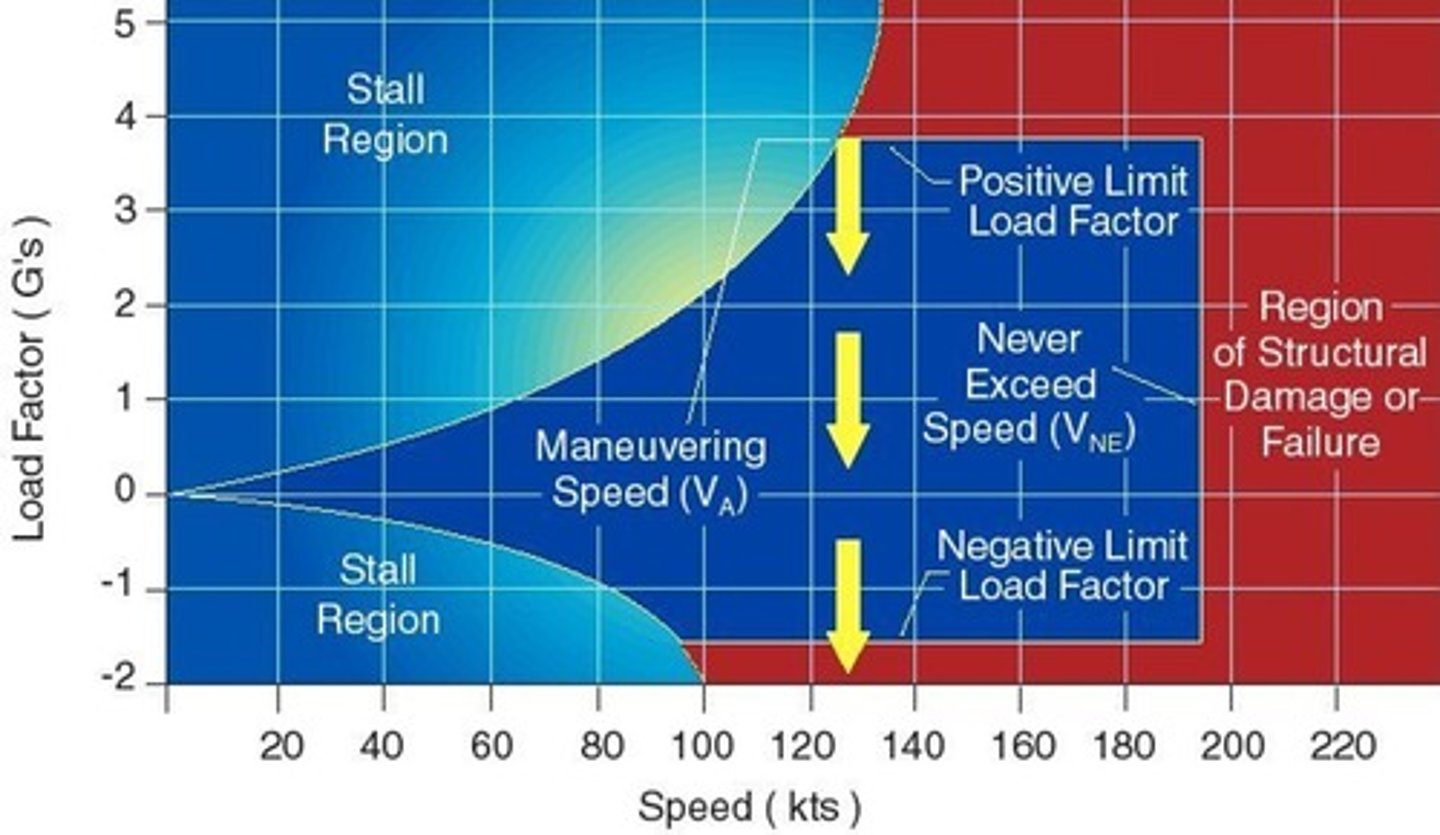
maneuver speed (Va)
stall speed increase during maneuver
Overtaking
Head-on
Converging

right of way
first to last
- mayday
- balloon
- glider
- aircraft refueling
- airship
- rotorcraft/aircraft
taxi aircraft
- head wind: turning into
- tail wind: diving away
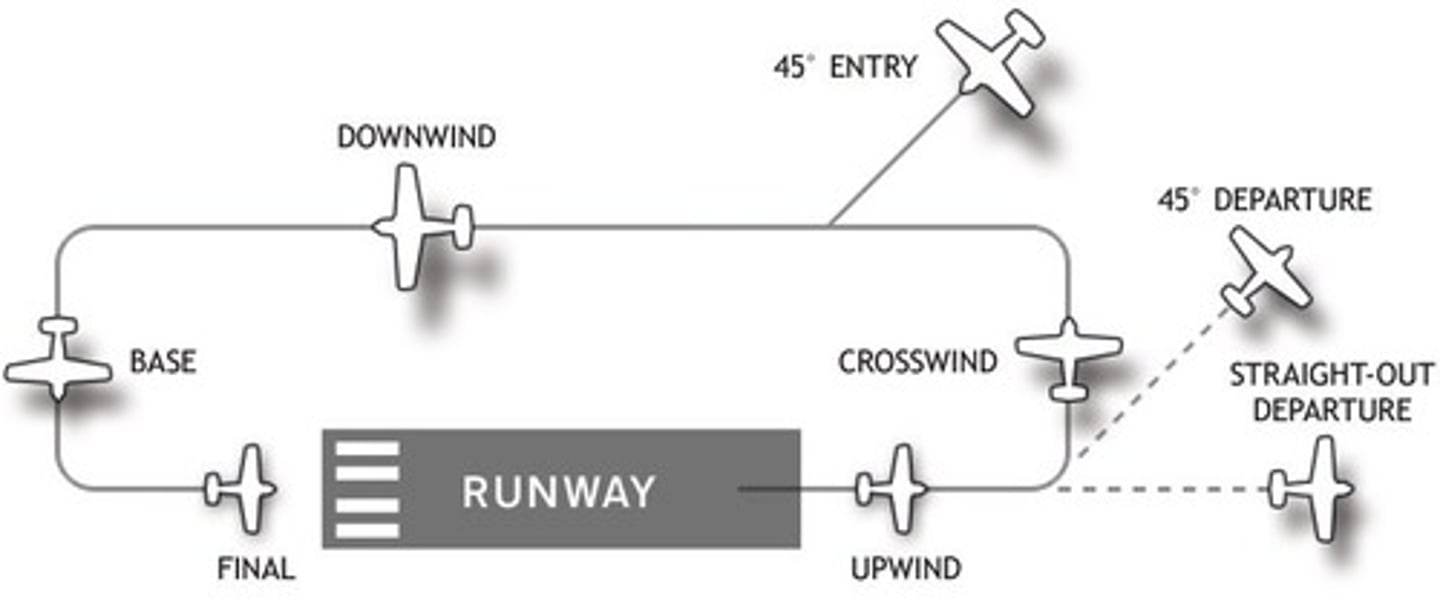
traffic pattern
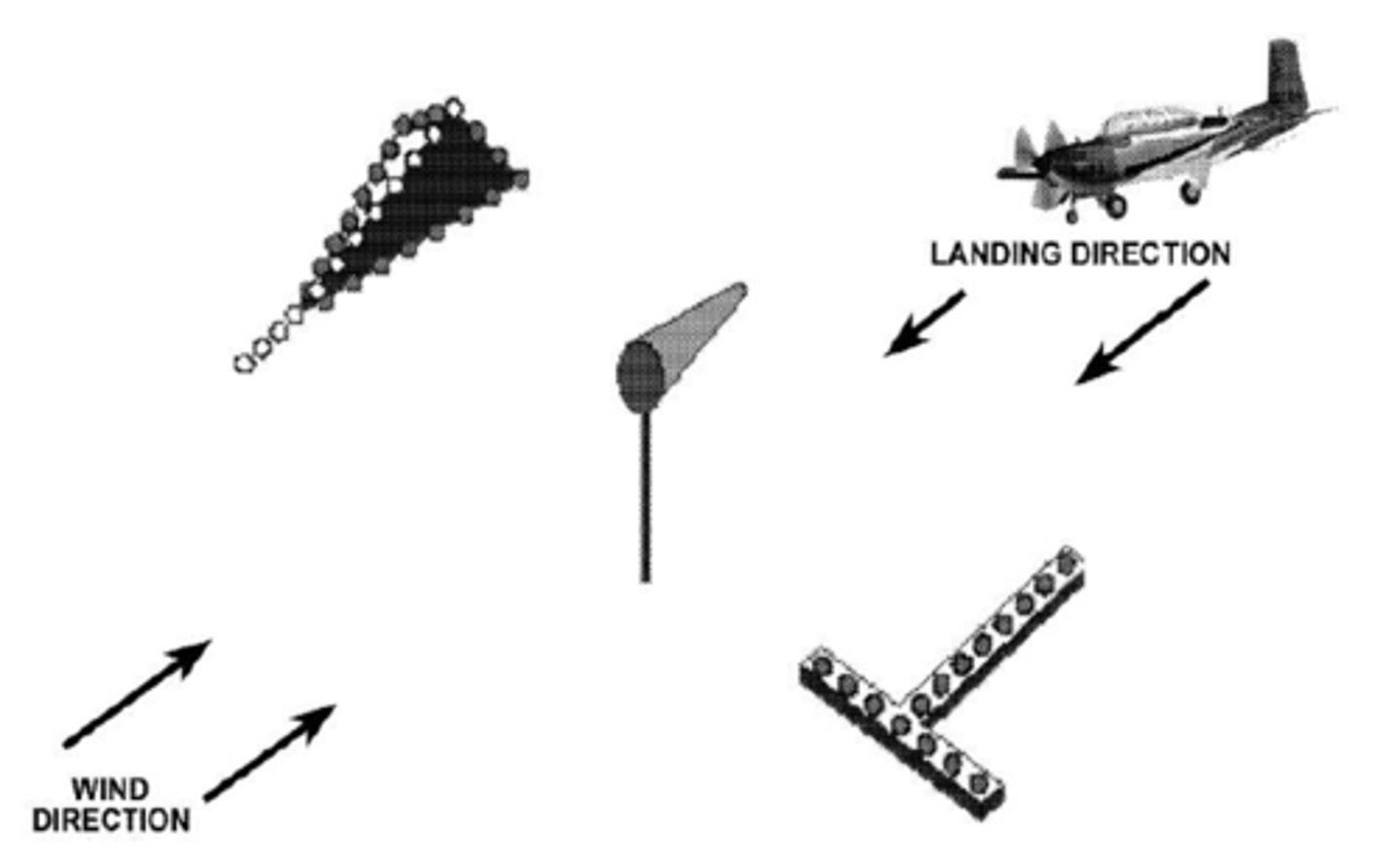
Wind indicator
Provides winds direction and velocity
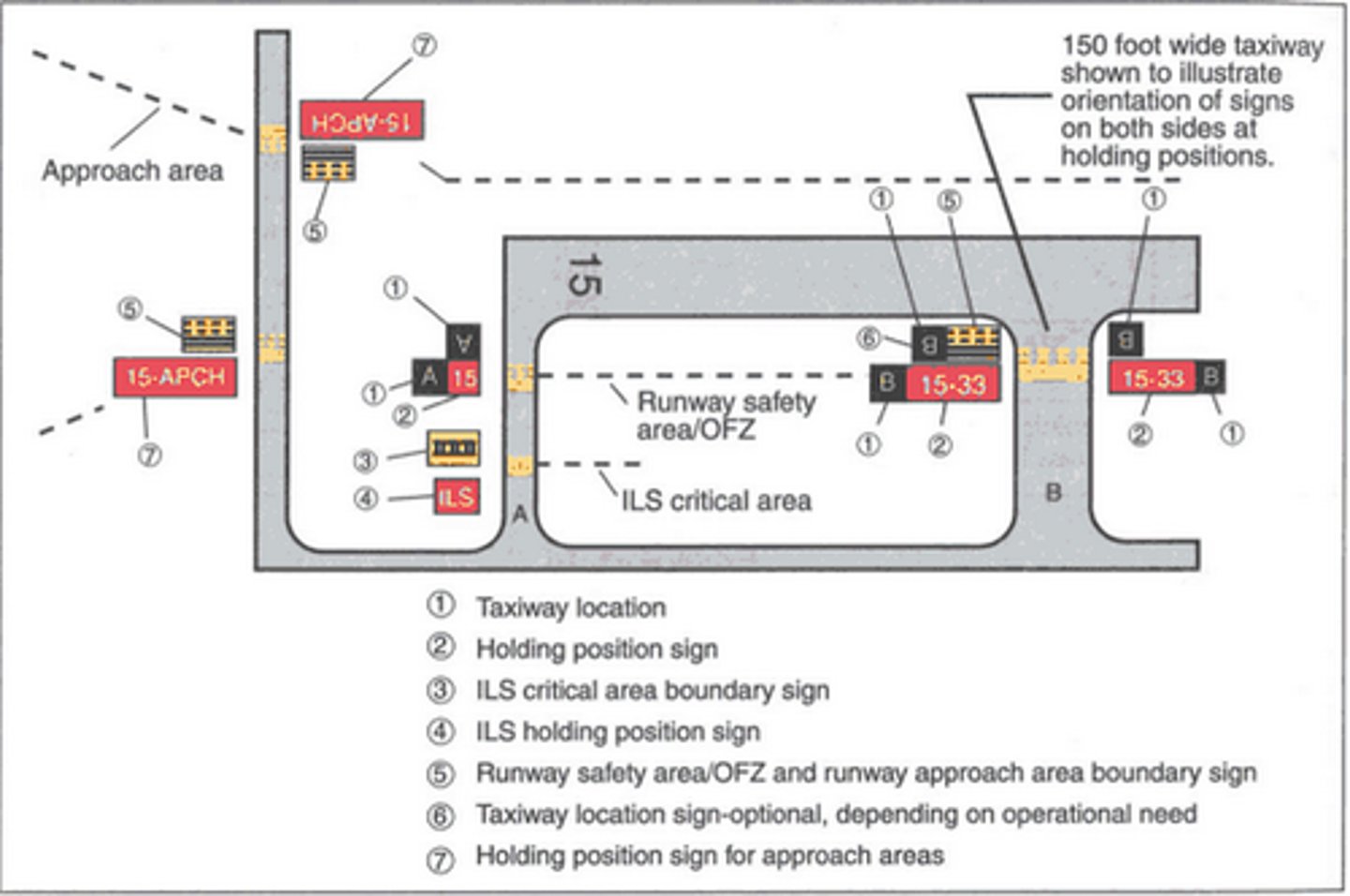
runway indicators
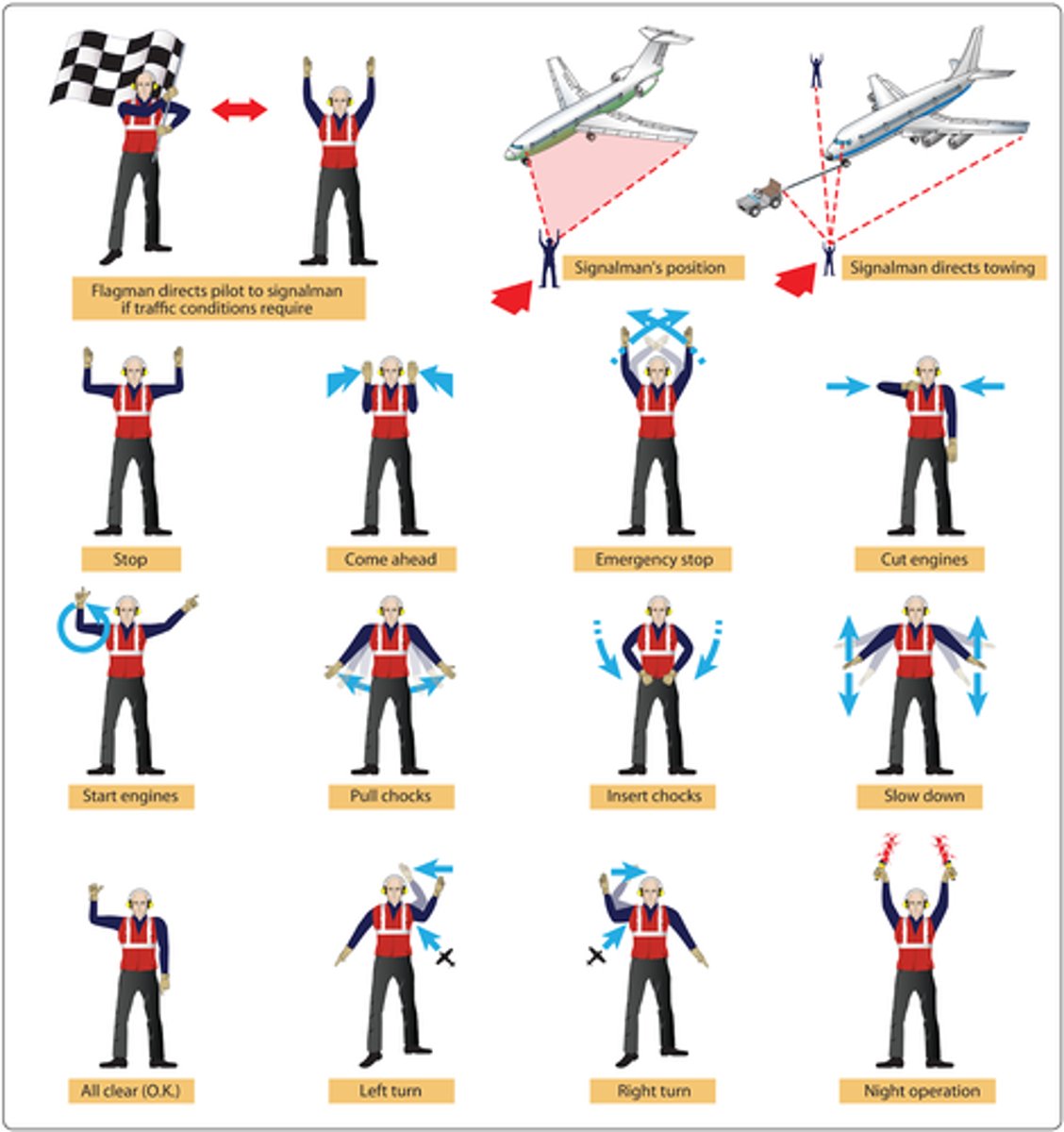
Hand signals
airport signs and markings

ATC light signals
- signals will come from control tower

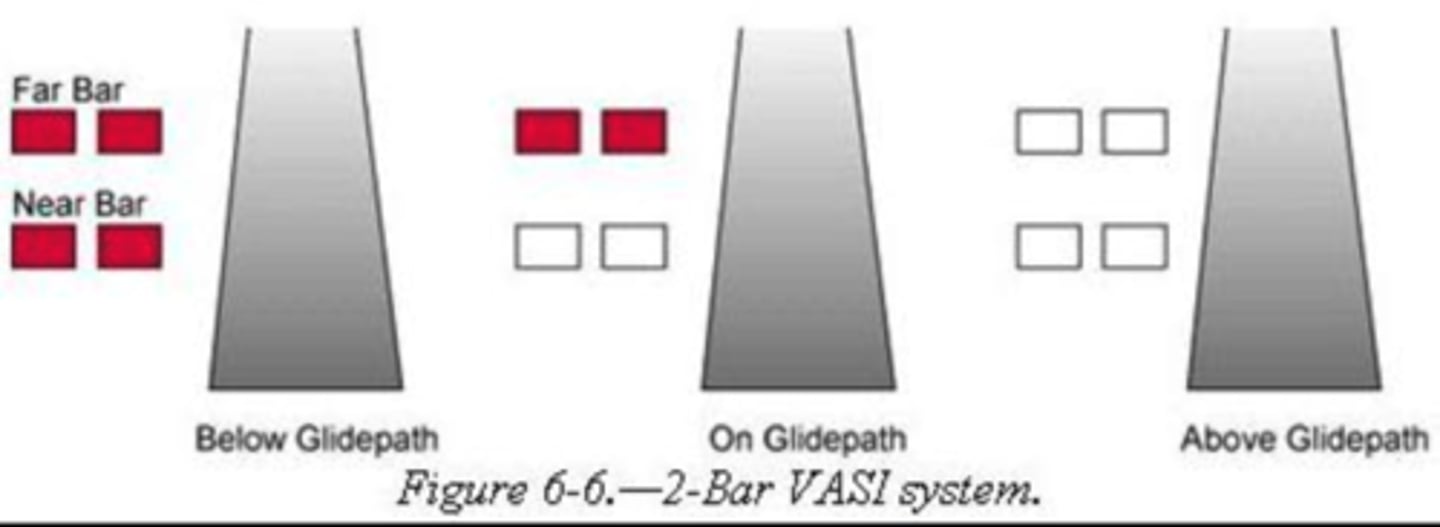
Glide path
Predetermined imaginary path to the landing strip in the horizontal plane
Each recreational or private pilot is required to have a flight review at least once
Every 24 calendar months.
Single-Pilot Resource Management (SRM)
The ability for a pilot to manage all resources effectively to ensure the outcome of the flight is successful.
Crew Resource Management (CRM)
Required more than one pilot to manage all resources effectively to ensure the outcome of the flight is successful.
Aeronautical Decision Making (ADM)
Systematic mental approach to consistently determine the best course of action in a given situation.
- recognize the change
- define problem
- chose a course of action (among pos. options)
- implement your decision
- evaluating the outcome (as expected or NOT)
I'M SAFE checklist
- Illness: Am I healthy?
- Medication: Am I still under the influence of medications?
- Stress: Am I stressed or under pressure?
- Alcohol: at least 8hr since last drink
- Fatigue: Am I tired? Have I slept enough?
- Eating/Emotion: Have I eaten and drunk enough before the flight?
Hazardous Attitudes
Anti-authority: follow the rules
Impulsivity: think first not so fast
Invulnerability: it could happen to me
Macho: Taking chances is foolish
Resignation: I can make a difference and I am not helpless
self-critique
to be able to identify strengths and weaknesses in your drawing
learner-centered grading
During flight lessons, both you and your instructor should evaluate your performance and resolve any differences in your assessments before creating a plan for improvement
Risk Management
PAVE
- Pilot: I'M SAFE
- Aircraft: AV1ATE + ARROW
- Environment: NW KRAFT (pre-flight)
- External pressures: purpose of flight and pressure to maintain schedule
5Ps
Pilot
Passengers
Plane
Programming
Plan
Passenger Briefing
SAFETY
- safety belts
- air vents
- fire extinguisher
- emergency: doors/emergency equipment.
- talking/traffic
- questions???
If a certificated pilot changes permanent mailing address and fails to notify the FAA Airmen Certification Branch of the new address, the pilot is entitled to exercise the privileges of the pilot certificate for a period of only
30 days after the date of the move
The pilot in command is required to hold a type rating in which aircraft?
Aircraft having a gross weight of more than 12,500 pounds.
How should the 500-pound weight be shifted to balance the plank on the fulcrum?
1 inch to the left
A parachute composed of nylon, rayon, or other synthetic fibers must have been packed by a certificated and appropriately rated parachute rigger within the preceding
180 days
An approved parachute constructed of natural fibers may be carried in an aircraft for emergency use if it has been packed by an appropriately rated parachute rigger within the preceding
60 days
If an alteration or repair substantially affects an aircraft's operation in flight, that aircraft must be test flown by an appropriately-rated pilot and approved for return to service prior to being operated
with passengers aboard
When may an emergency locator transmitter (ELT) be tested?
During the first 5 minutes after the hour.
A 100-hour inspection was due at 3302.5 hours. The 100-hour inspection was actually done at 3309.5 hours. When is the next 100-hour inspection due?
3402.5 hours
Annual Inspection
check up on the entire plane and engine. 12 months
24months inspections
- transponder
- altimeter and static system on IFR aircrafts
Airworthiness Directives
- aka. recalls
- medium the FAA uses to notify unsafe aircrafts because of deign defects, maintenance, or other causes
Aircraft Transponder
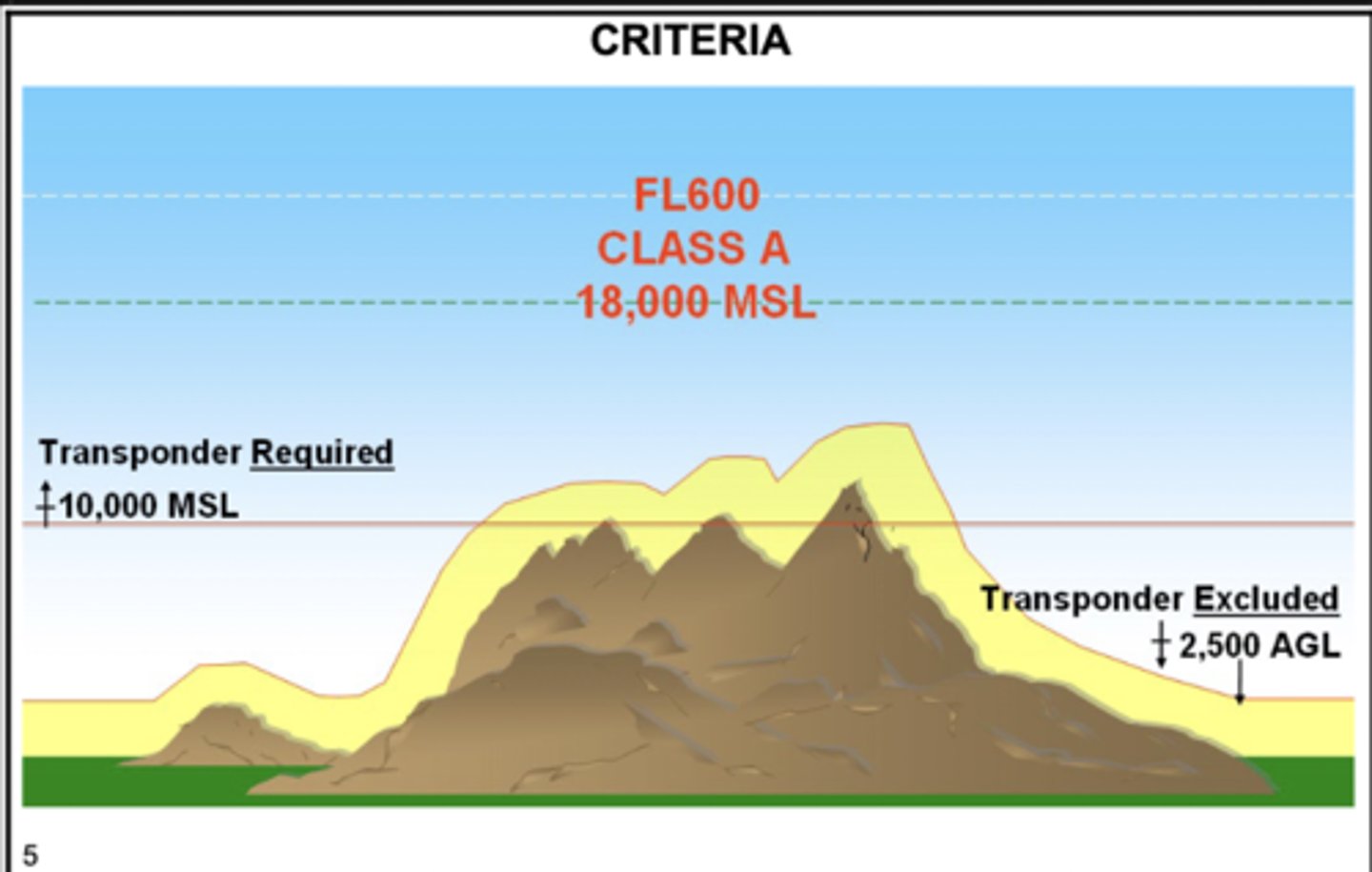
Transponder Phraseology
- 7500: hijacking
- 7600: communication failure
- 7700: MAY-DAY

Flight Plan
A predetermined plan to be followed during flight based on the latest information available on the route. It is submitted to ATC prior to takeoff
100 hour inspections
rental aircraft that are used for
- flight instruction
- hire
complex aircraft
An aircraft with
- retractable landing gear
- flaps
- controllable pitch propeller
high performance aircraft
- engine >200 horse power
FADEC
Full Authority Digital Engine Control System
What regulation allows a private pilot to perform preventive maintenance?
14 CFR Part 43.3.
Except when necessary for takeoff or landing, what is the minimum safe altitude for a pilot to operate an aircraft anywhere?
An altitude allowing, if a power unit fails, an emergency landing without undue hazard to persons or property on the surface.
Slipping turn
An uncoordinated turn in which the aircraft is banked too much for the rate of turn, so the horizontal lift component is greater than the centrifugal force, pulling the aircraft toward the inside of the turn.
Skidding turn
An uncoordinated turn in which the rate of turn is too great for the angle of bank, pulling the aircraft to the outside of the turn.
Coordinated Turn
Centrifugal force and gravity react equally on the slip indicator ball, and the ball remains in the lowest part of the glass
Magnetic Dip (Magnetic Inclination)
- turn toward N/S: UNOS
- turn away from N/S: NOSE
- travel toward E/W: ANDS
Except when necessary for takeoff or landing, what is the minimum safe altitude required for a pilot to operate an aircraft over congested areas?
An altitude of 1,000 feet above the highest obstacle within a horizontal radius of 2,000 feet of the aircraft.
Except when necessary for takeoff or landing, an aircraft may not be operated closer than what distance from any person, vessel, vehicle, or structure?
500 feet
Except when necessary for takeoff or landing, what is the minimum safe altitude required for a pilot to operate an aircraft over other than a congested area?
An altitude of 500 feet AGL, except over open water or a sparsely populated area, which requires 500 feet from any person, vessel, vehicle, or structure.
Which is normally prohibited when operating a restricted category civil aircraft?
Flight over a densely populated area
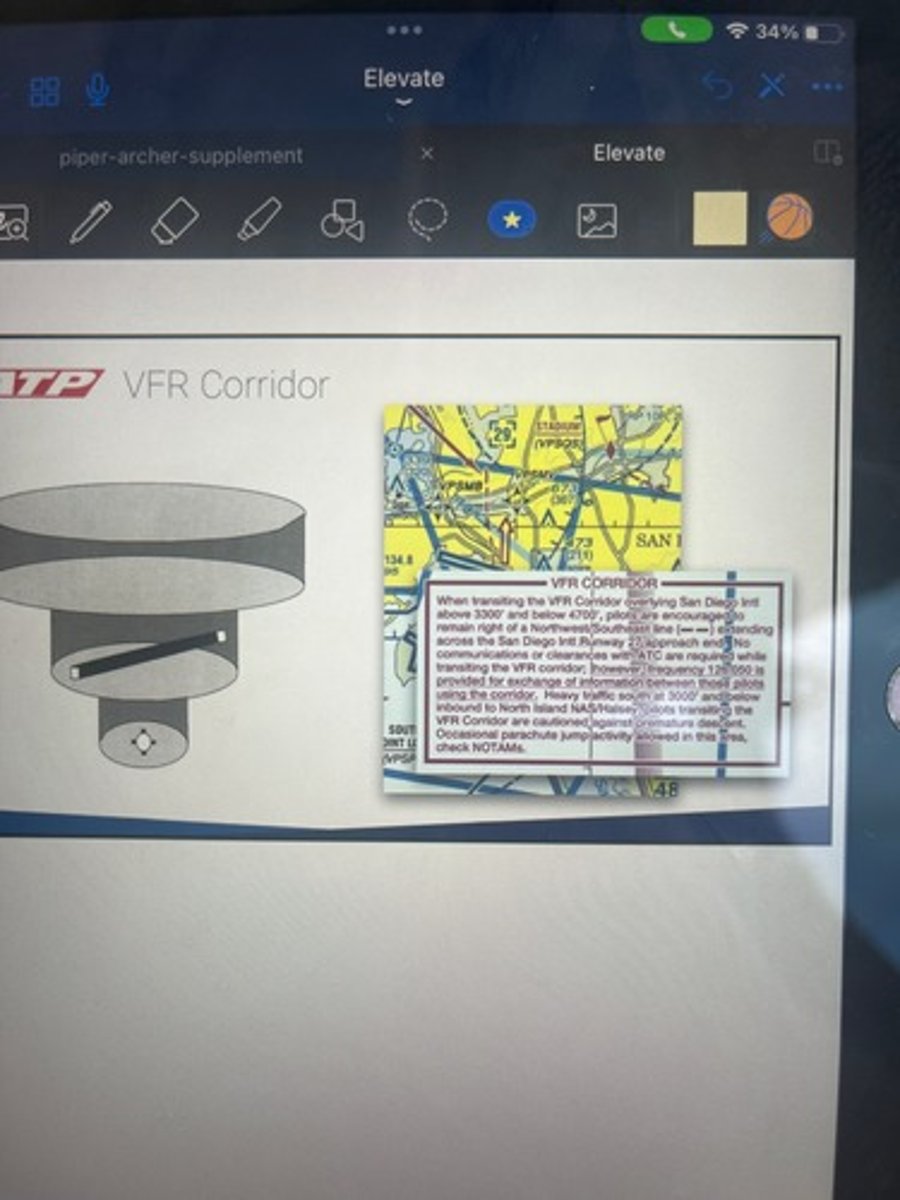
When flying in a VFR corridor designated through Class B airspace, the maximum speed authorized is
200 knots
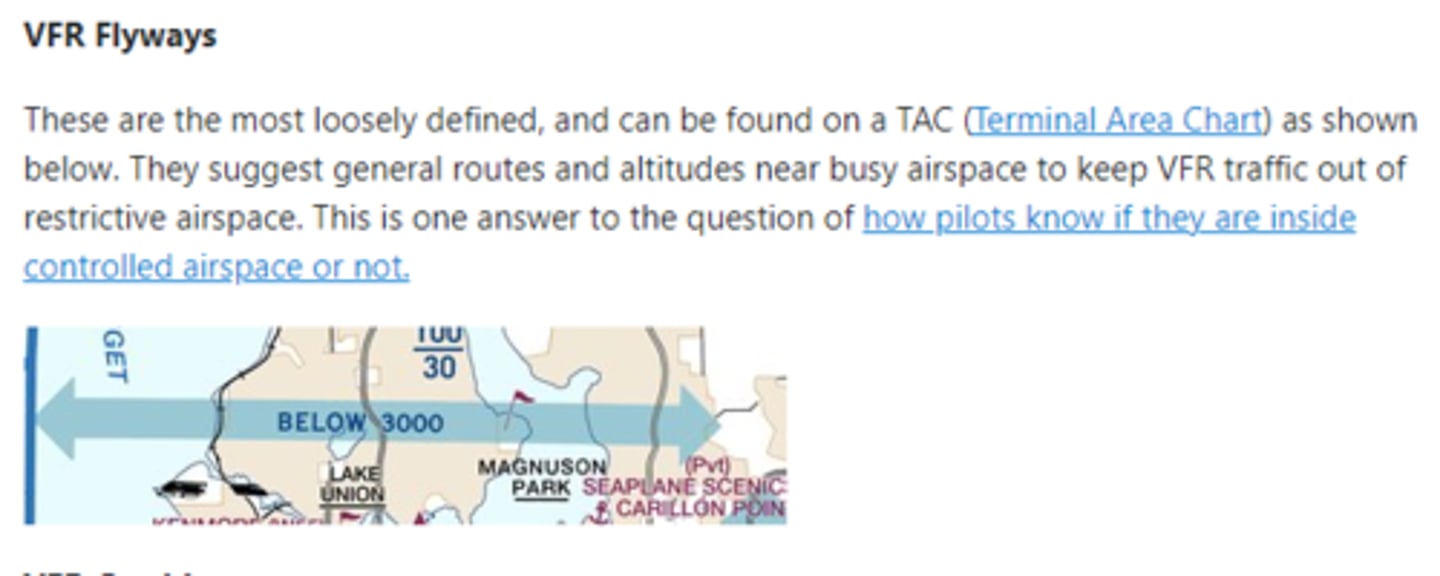
VFR Flyway
- Designed to assist pilots in planning flights under and around busy Class B airspace without actually entering Class B airspace.
VFR Corridor
- Airspace through Class B airspace with vertical / horizontal boundaries
- ATC clearance NOT required
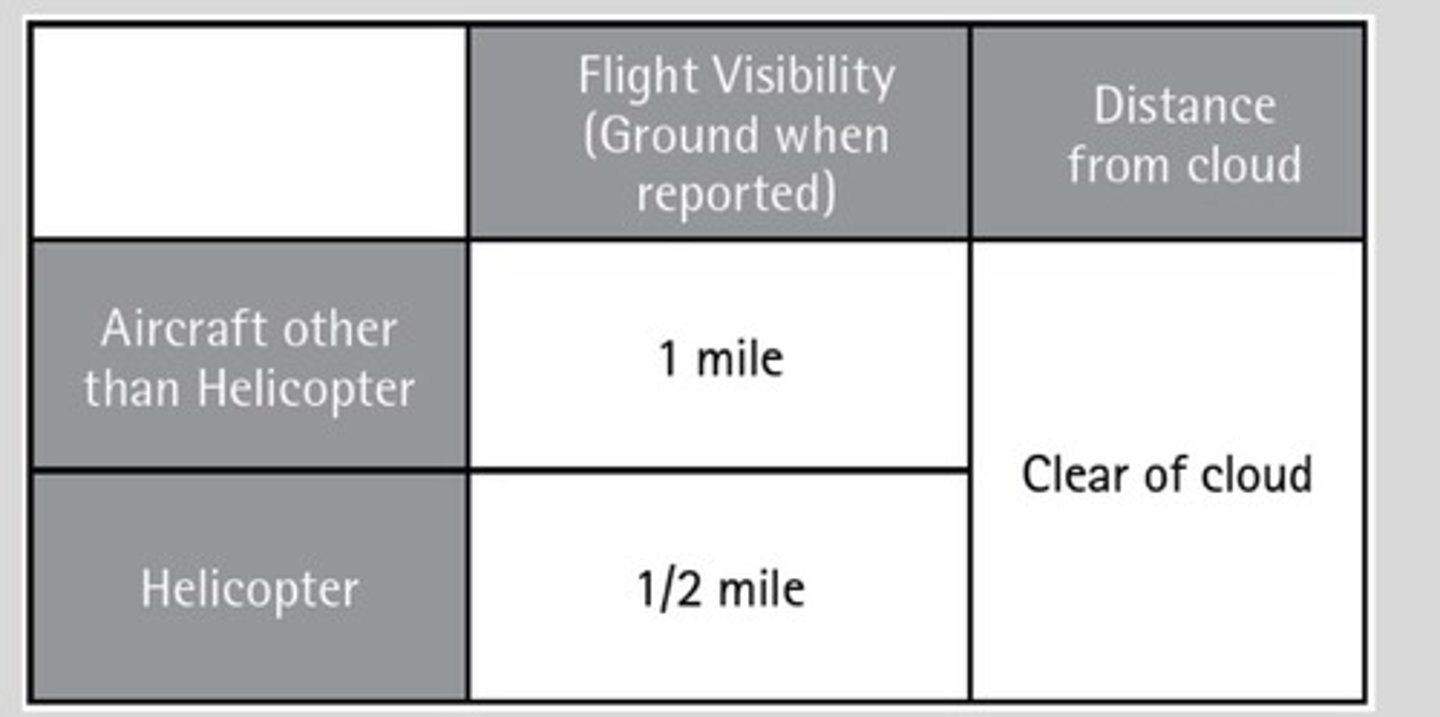
SVFR
Special Visual Flight Rules
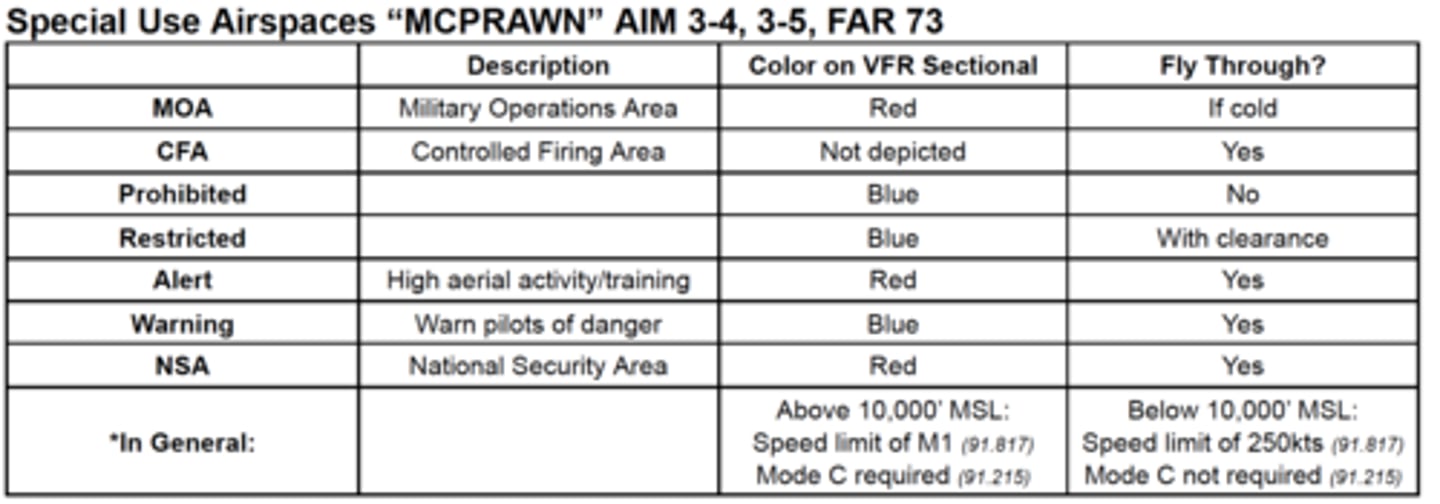
special use airspaces
TRSA
- Terminal Radar Service Area.
- Voluntary system that separates traffic to and from the primary airport.
- Provides radar services to Class D.
- gray solid ring
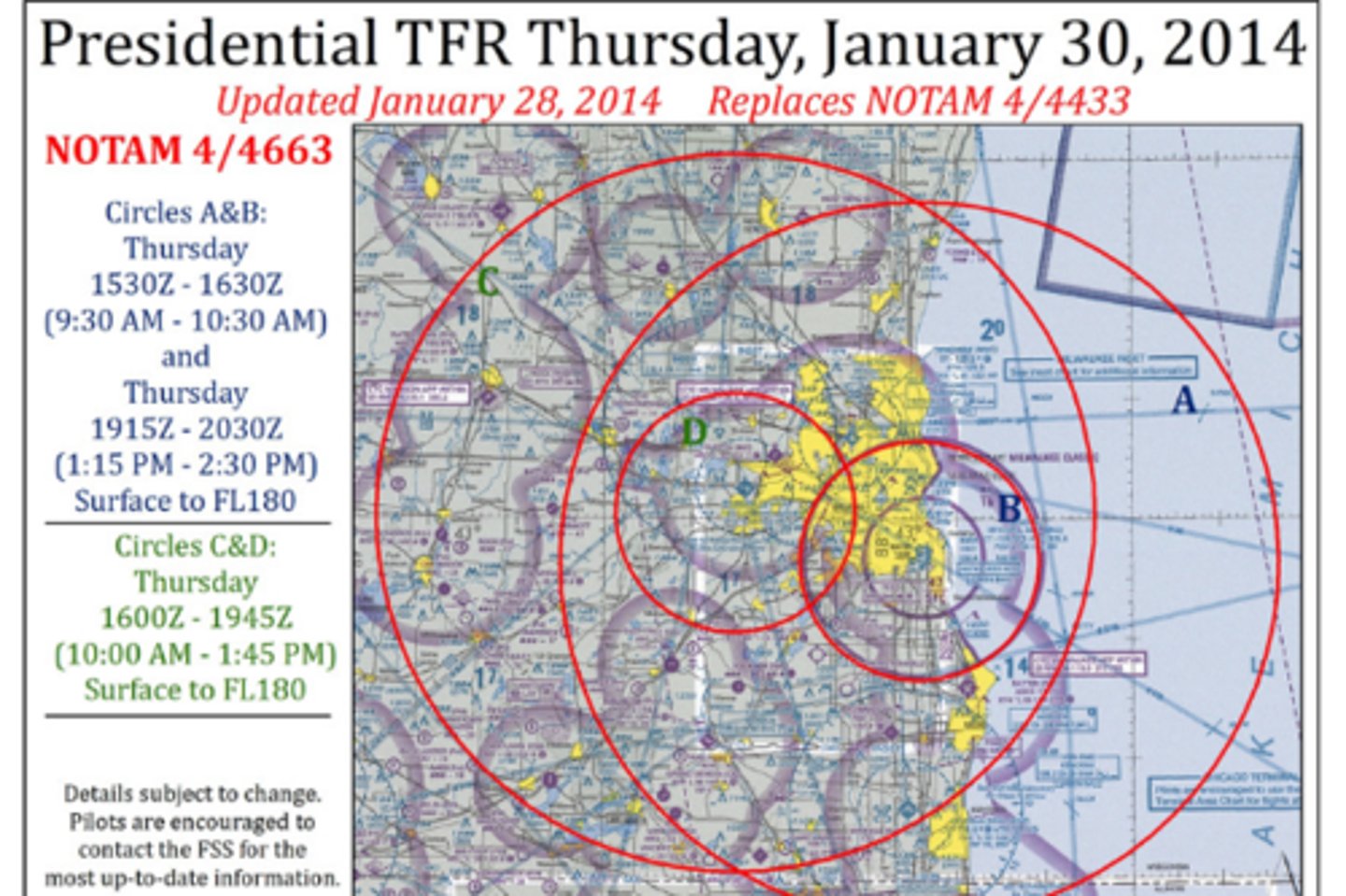
Temporary Flight Restrictions (TFR)
1. are imposed by FAA to protect persons or property on the surface or in the air from a specific hazard
2. FAA will issue a NOTAM designating the area in which a TFR applies
3. for rescue/relief aircraft operation, the restricted airspace is limited to 2,000ft AGL within a 3 nm radius.
- information can be found at:
++ 1-800-WXbrief
++ FTC NOTAM
Unless otherwise authorized, what is the maximum indicated airspeed at which a person may operate an aircraft below 10,000 feet MSL?
250 knots
Unless otherwise authorized, the maximum indicated airspeed at which aircraft may be flown when at or below 2,500 feet AGL and within 4 nautical miles of the primary airport of Class C airspace is
200 knots
Airspaces summary
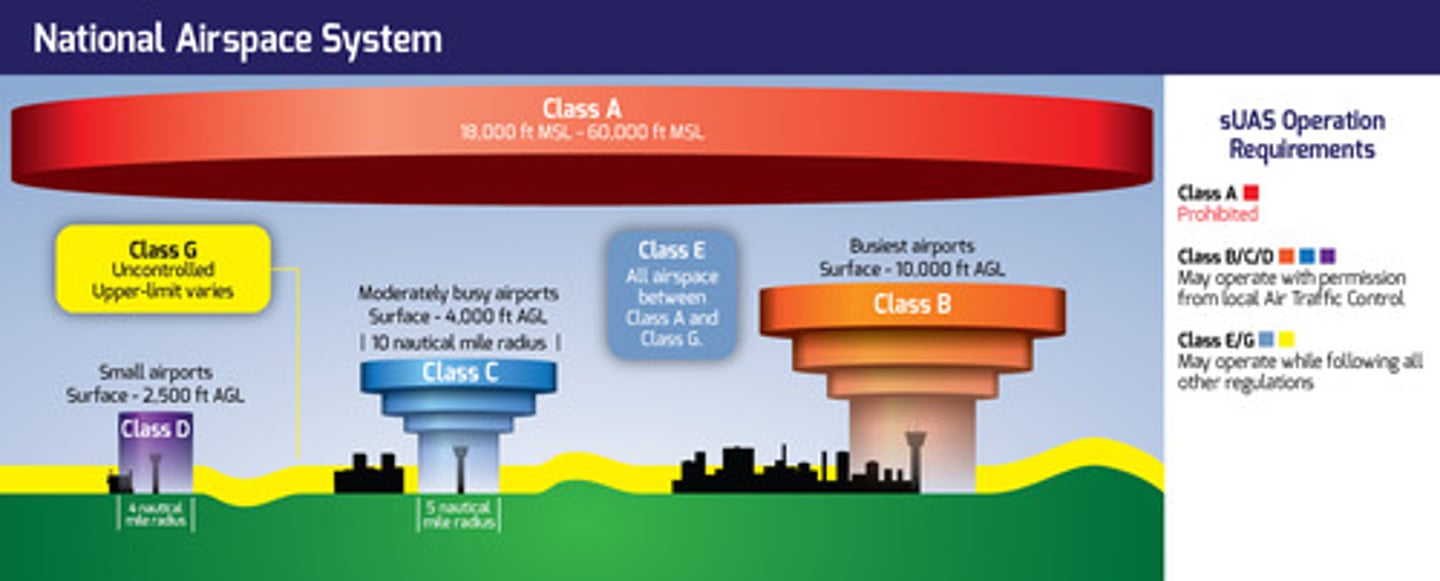
Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) Out is mandated for aircraft operations in
Class A, B, and C airspace.
When is Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) Out equipment required?
In Class E airspace above 10,000 ft. MSL, except at and below 2,500 ft. AGL.
What type of ADS-B equipment is required in Class A airspace?
ADS-B Out that operates on the frequency 1090 MHz.
Where may an aircraft's operating limitations be found if the aircraft has an Experimental or Special light-sport airworthiness certificate?
Attached to the Airworthiness Certificate.
Where may an aircraft's operating limitations be found?
The current, FAA-approved flight manual, approved manual material, markings, and placards, or any combination thereof.
Vs0
- lower limit of white arc
- Stalling speed or minimum steady flight speed in the landing configuration.
Vs1
- lower limit of green arc
- Stall Speed in Clean Configuration : 48 KIAS
Vfe
- upper limit of white arc
- Maximum flap fully extended speed
Vno
- upper limit of green arc
- Maximum structural cruising speed
Vne
- red line
- Never exceed speed
Indicated Airspeed (IAS)
Airspeed read directly from the airspeed indicator
Calibrated Airspeed (CAS)
Indicated airspeed corrector for installation and instrument errors.
True Airspeed (TAS)
Actual speed through the air. EAS corrected for nonstandard temperature and pressure
Ground Speed (GS)
True Airspeed corrected for winds; actual speed of airplane over the ground.
Pitot tube blockage
The only instrument affected is the airspeed indicator.
■ Ram air inlet clogged and drain hole open? Airspeed drops to zero.
■ Both air inlet and drain hole are clogged? The airspeed indicator will act as an altimeter (increase when climb and decrease when descending), and will no longer be reliable.
■ When suspecting a pitot blockage, consider the use of pitot heat to melt ice that may have formed in or on the pitot tube.
Prior to takeoff, the altimeter should be set to which altitude or altimeter setting?
The current local altimeter setting, if available, or the departure airport elevation.
At what altitude shall the altimeter be set to 29.92 when climbing to cruising flight level?
18,000 feet MSL.
Unless each occupant is provided with supplemental oxygen, no person may operate a civil aircraft of U.S. registry above a maximum cabin pressure altitude of
15,000 feet MSL.