Pediatrics History & Physical (H&P) Exam MASTERY GUIDE: 376 Expert-Verified Q&A with Clinical Vignettes, Diagnostic Reasoning & SOAP Note Examples (Latest Guidelines)
1/375
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
376 Terms
Neonatal period
28 days
early childhood
1-5
late childhood
5-12

Adolescence
12-18

infancy
first year of life
What order should the pediatric exam follow?
Least invasive first
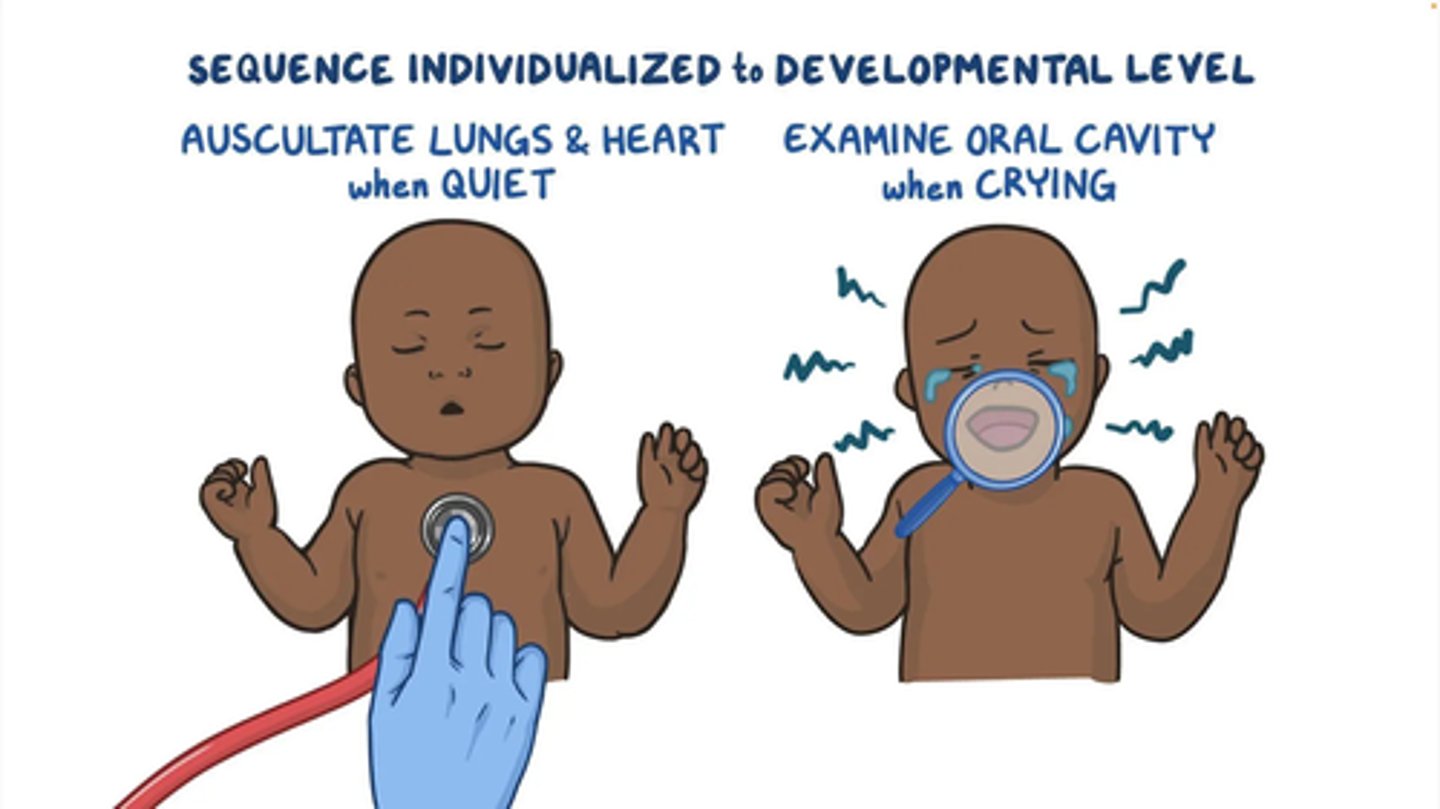
Neonatal history
Sleeping, eating, peeing, pooping, milestones
Diet for first 4 months
breast milk and formula only (no food or water)
Recommendations for amount of formula or breast milk in first month
about 3 ounces every 3 hours

Most babies are satisfied with _________ per feeding during the first month, and increase that amount by ___ ounce per month until reaching ____ ounces
3-4 oz, 1 oz, 8 oz

How often should infants void?
6-8x a day
(6 is minimum)
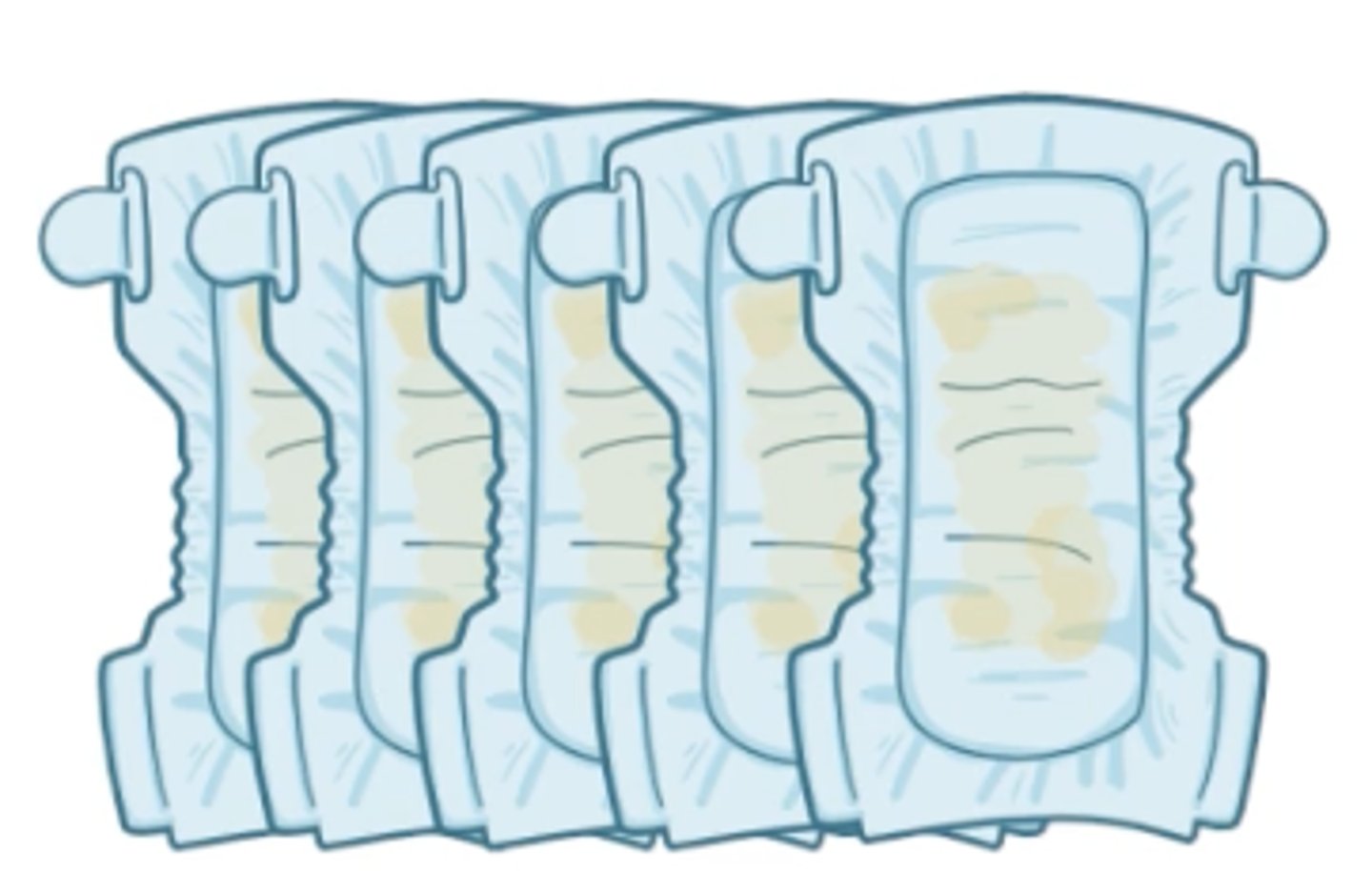
Normal bowel movements
loose, seedy, yellow stool about 4 times a day
Vitamin D supplementation for exclusively breastfed infants
400 IU daily

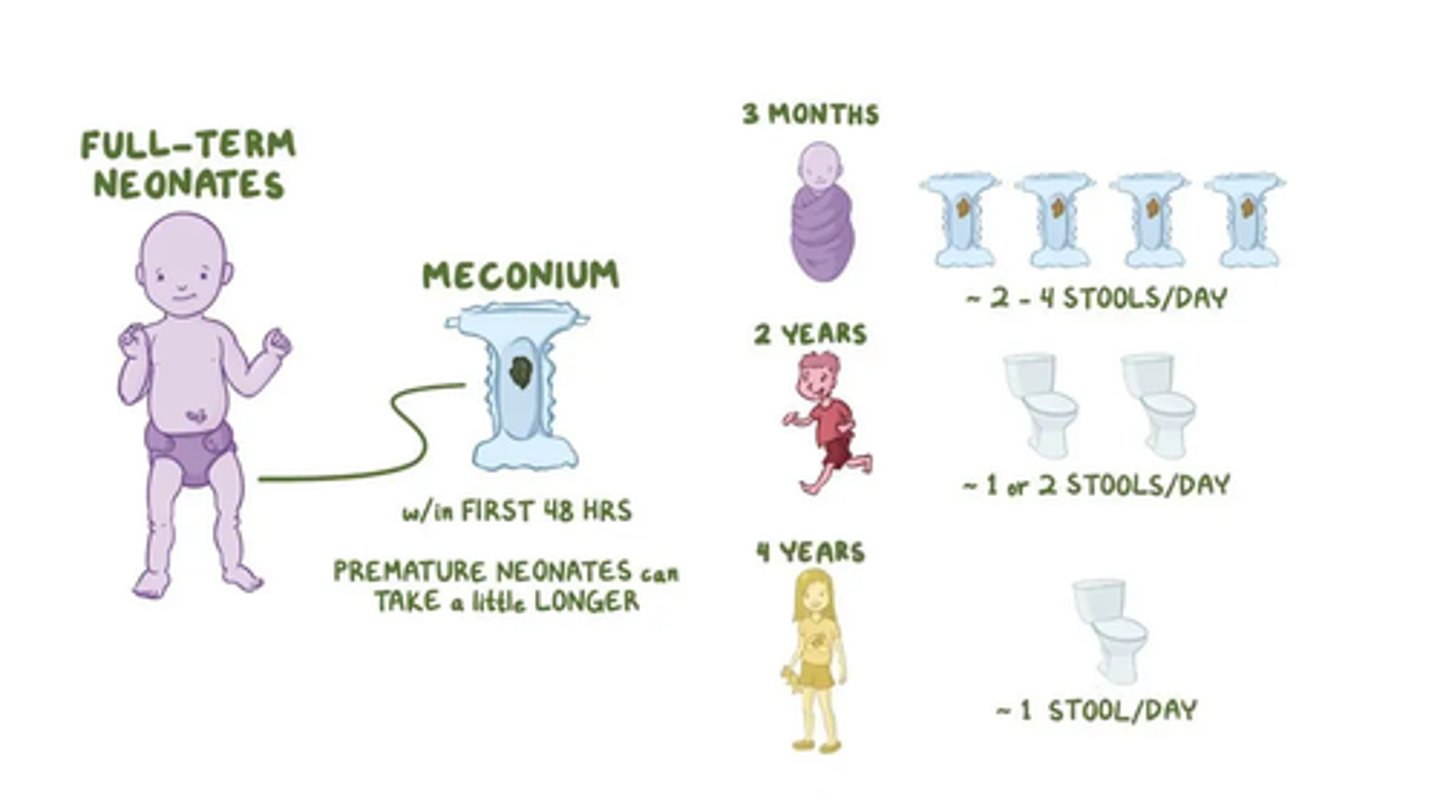
BM in first 2-3 days old
4-5 black tarry stools every 24 hours

BM first 6 weeks
1-5 yellow stools every 24 hours
BM after 6 weeks
once every 3-4 days is okay
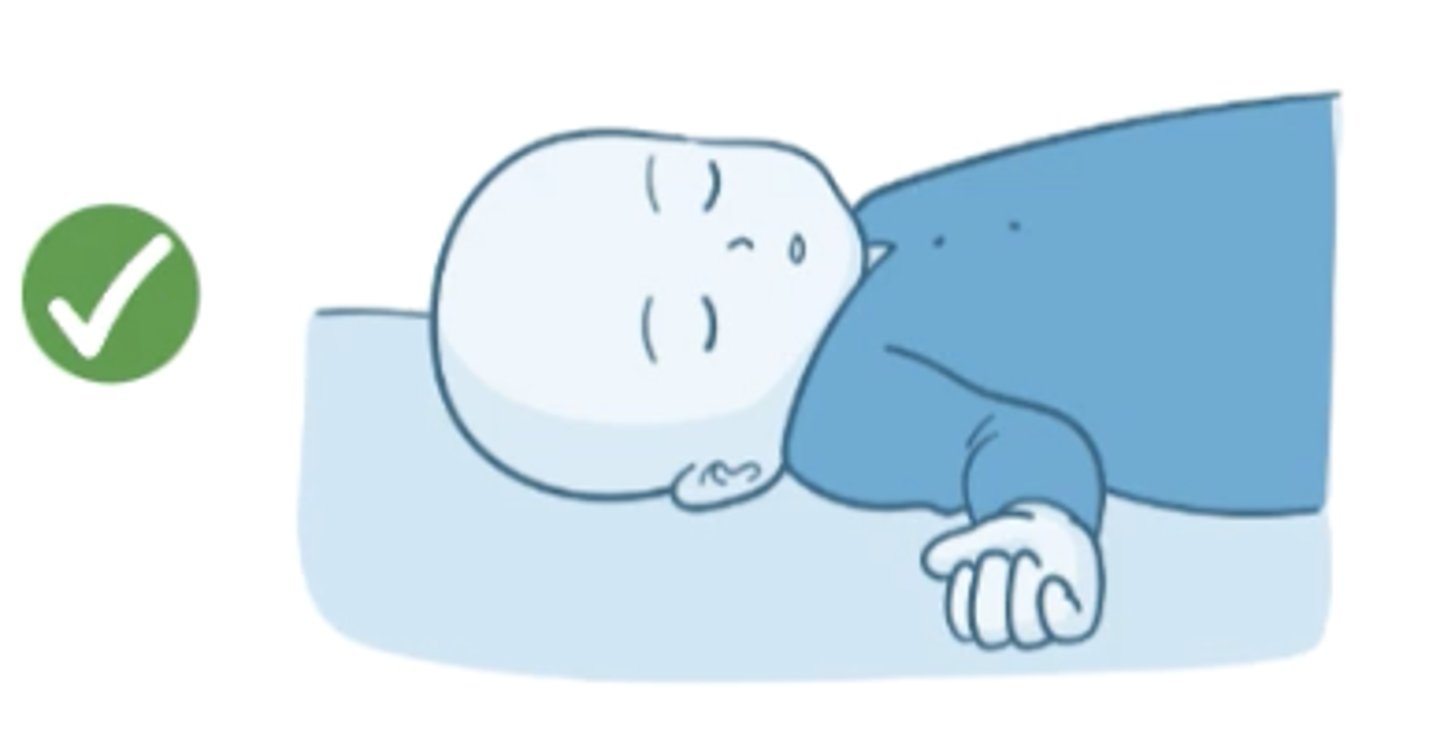
How should baby be placed to sleep?
on the back, without anything in crib, not co-sleeping

When should wellbeing of parents be assessed?
newborn through 2 month visits (at a minimum)

If parents refuse vaccines, what should you document?
WHY they refused
Month 1 developmental milestones
- eye tracking
- recognize parents voice
- smile
- support head

Month 6 developmental milestones
- babbles
- recognizes name and familiar people
- rolling over
- transfers objects from hand to hand

Month 9 developmental milestones
- crawling
- pincher grasp
- feeds self with fingers
- peek a boo
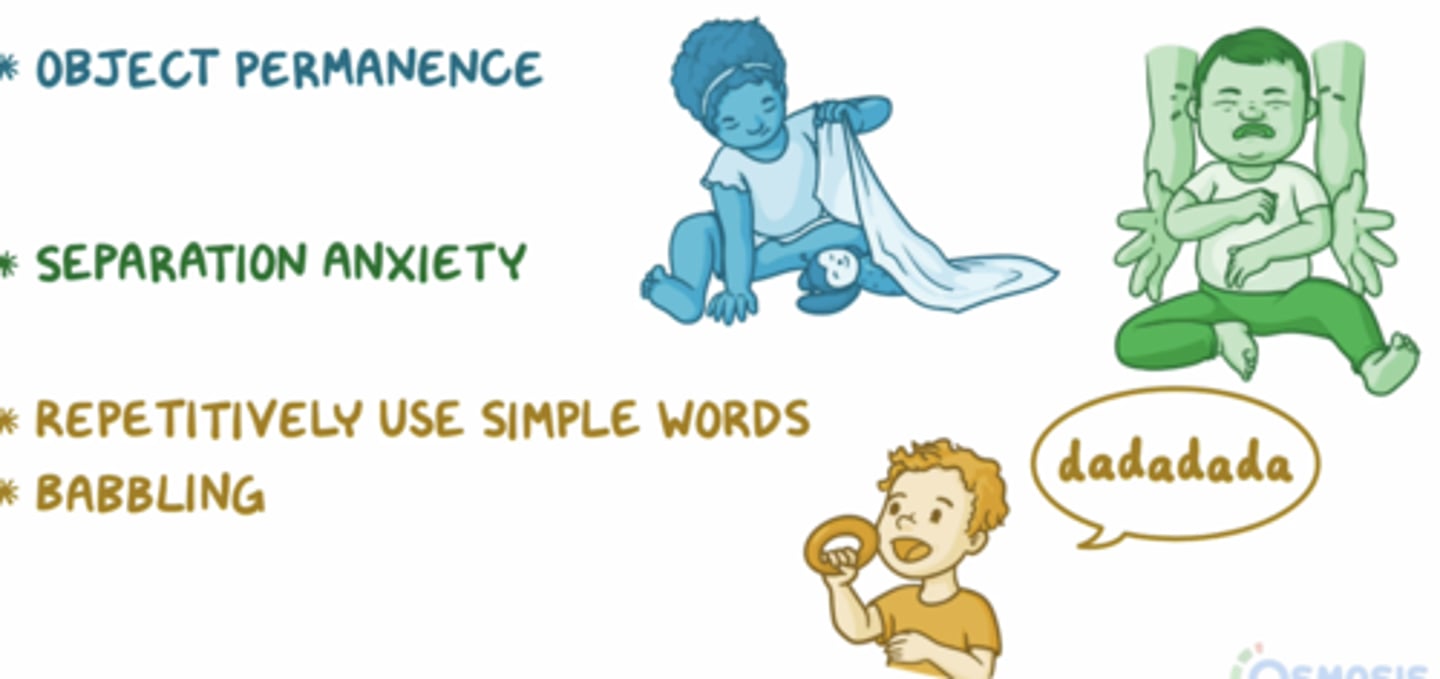
Month 12 developmental milestones
- strong parental attachment
- identifies people
- speaks a few words
- claps
- stands
- follows simple commands
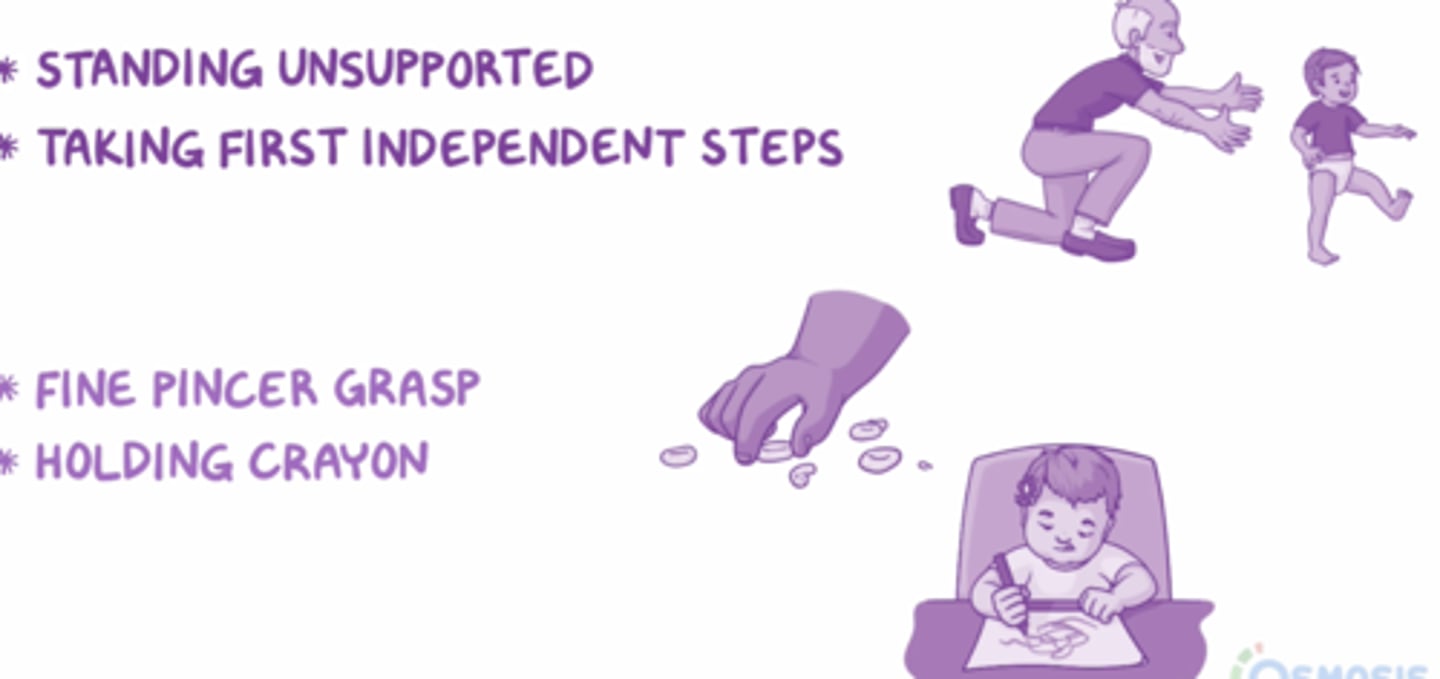
15-18 month language
use 3-5 words
2 year old language
200+ word vocabulary
1-2 word phrases
3 year old language
1500+ word vocabulary
puts 5-6 words together
6 year old language
several thousand word vocabulary
full sentences
Breastfeeding or formula is the main source of nutrition until ________
1 year (then can transition to whole milk)
APGAR Score
Preform at one 1 minute and 5 minutes and continue until score 7+
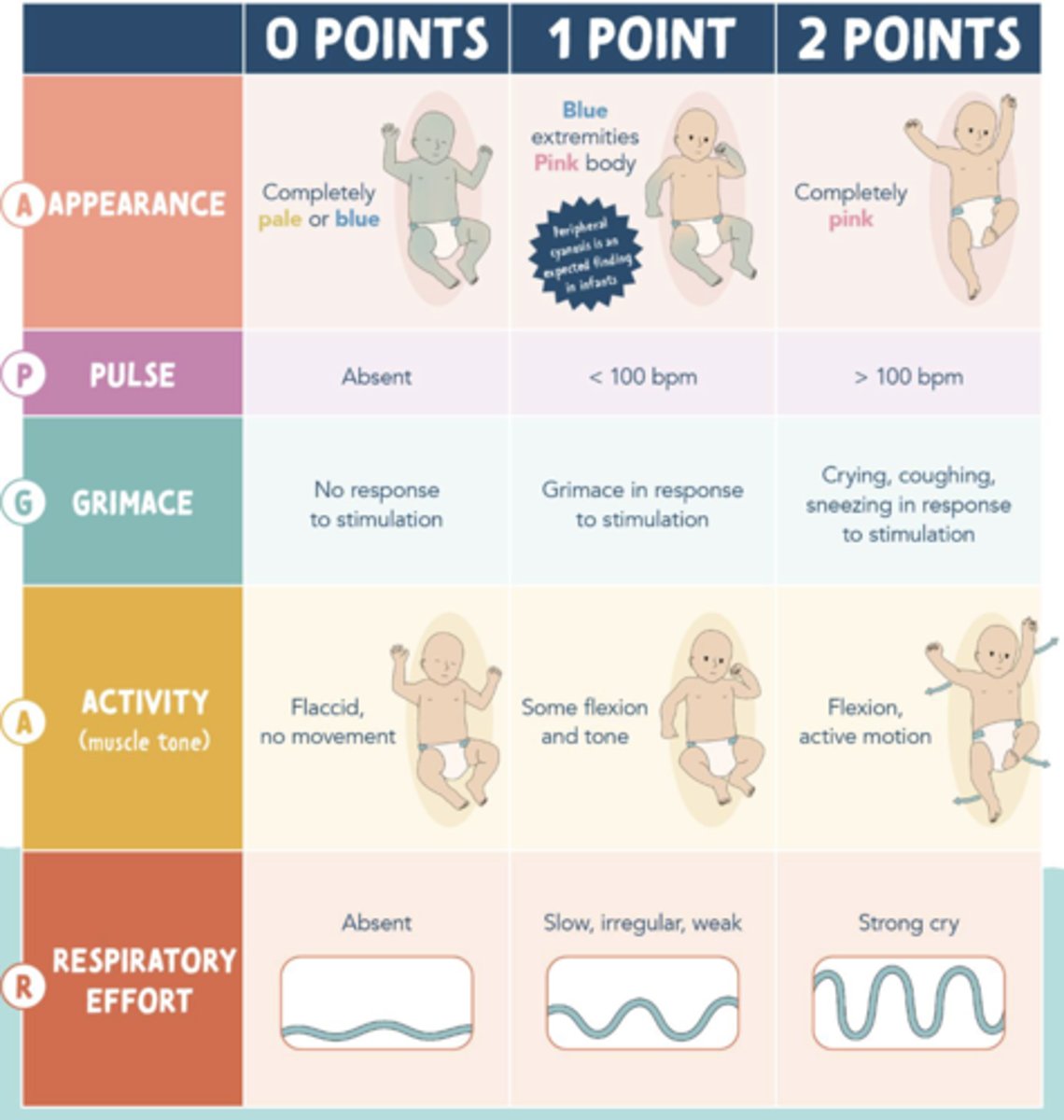
Newborn bradycardia
under 100 bpm
APGAR 1-3
critical!!
APGAR 4-6
Low - resuscitation efforts
Ballard score
assesses gestational age
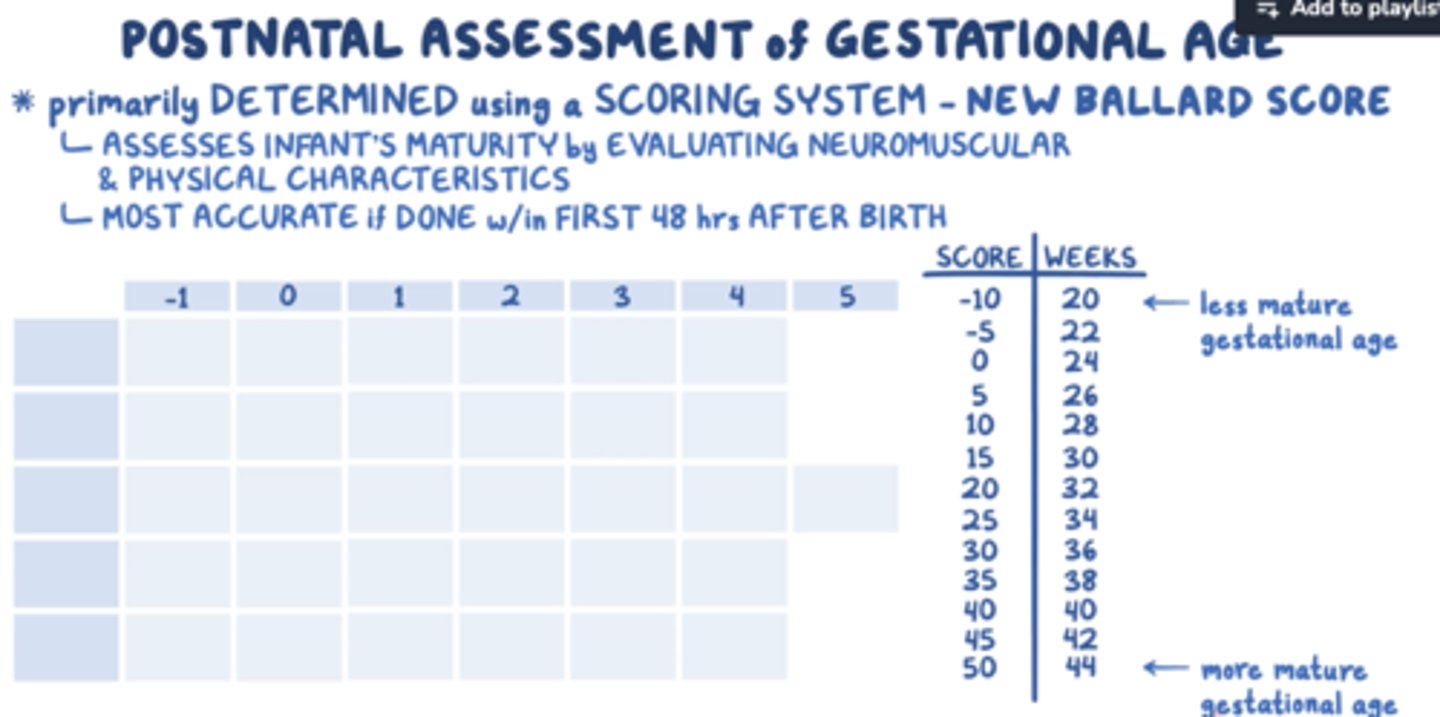
A complete newborn exam should be done within ____ hours of birth
24
preterm
under 34 weeks
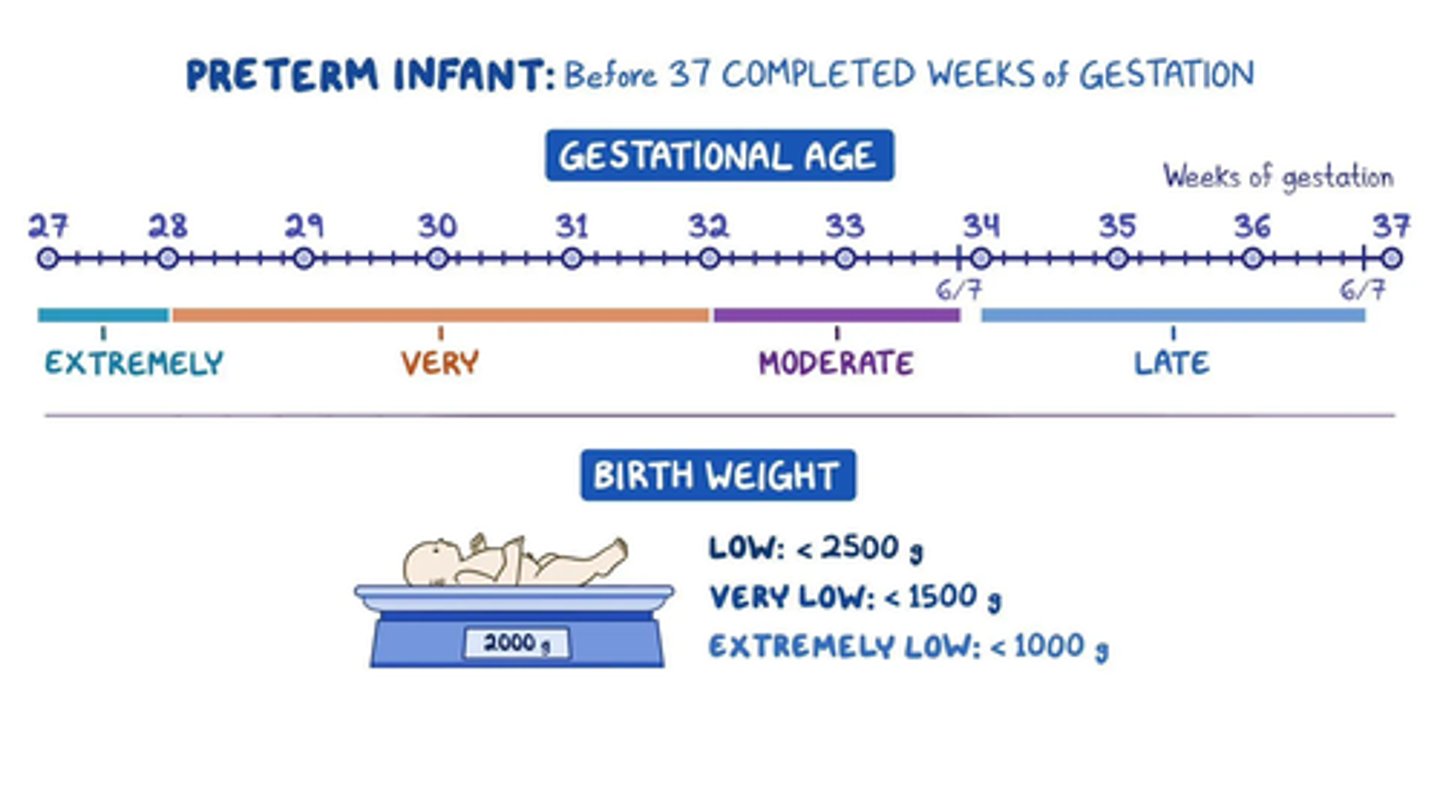
late preterm
34-36 weeks
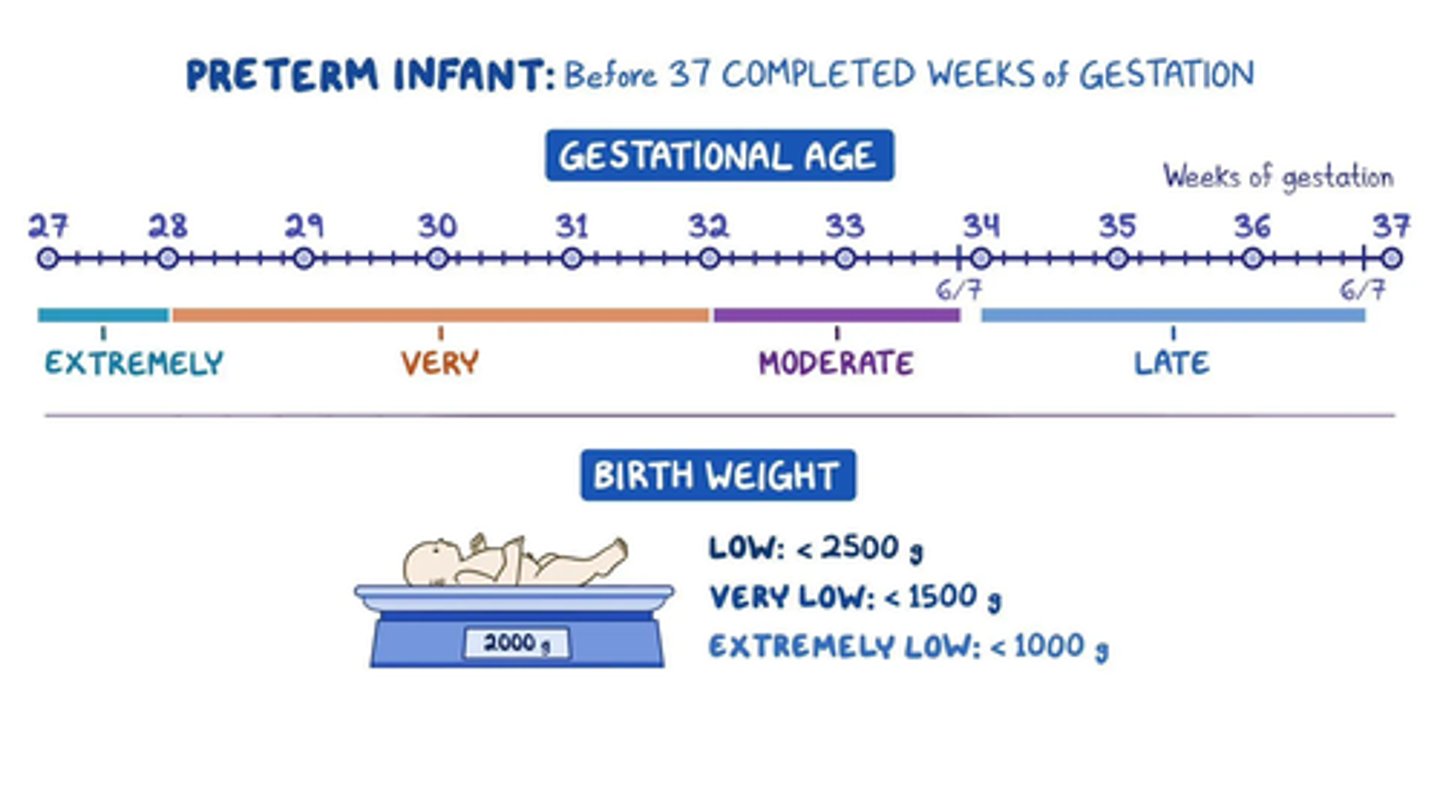
full term
37-42 weeks
post term
42+ weeks
Extremely low birth weight
less than 1000 g
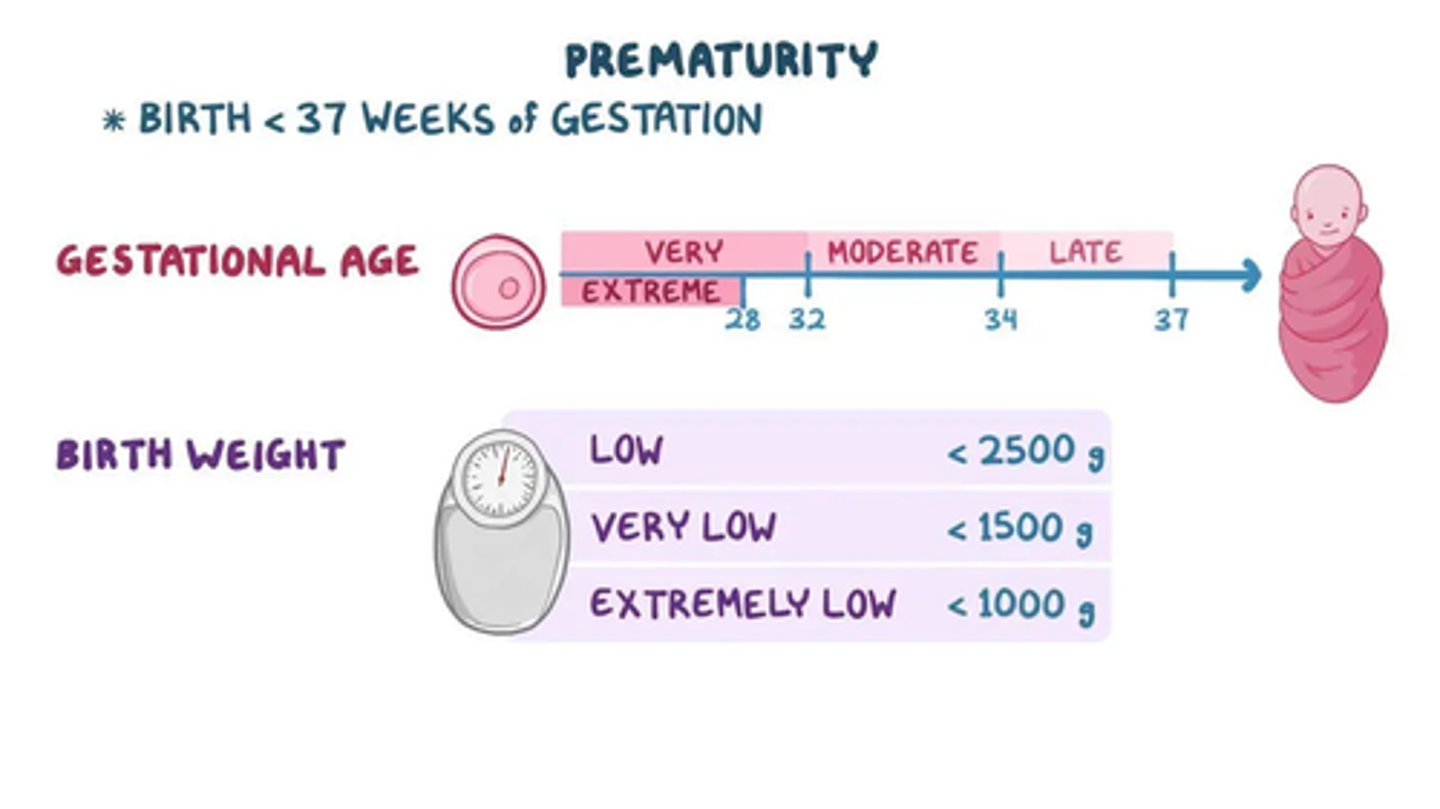
Very low birth weight
less than 1500 g
Low birthweight
1500 - 2500 grams
Normal birthweight
2500+ grams
Normal newborn position
limbs semi flexed and hips abducted with spontaneous movements
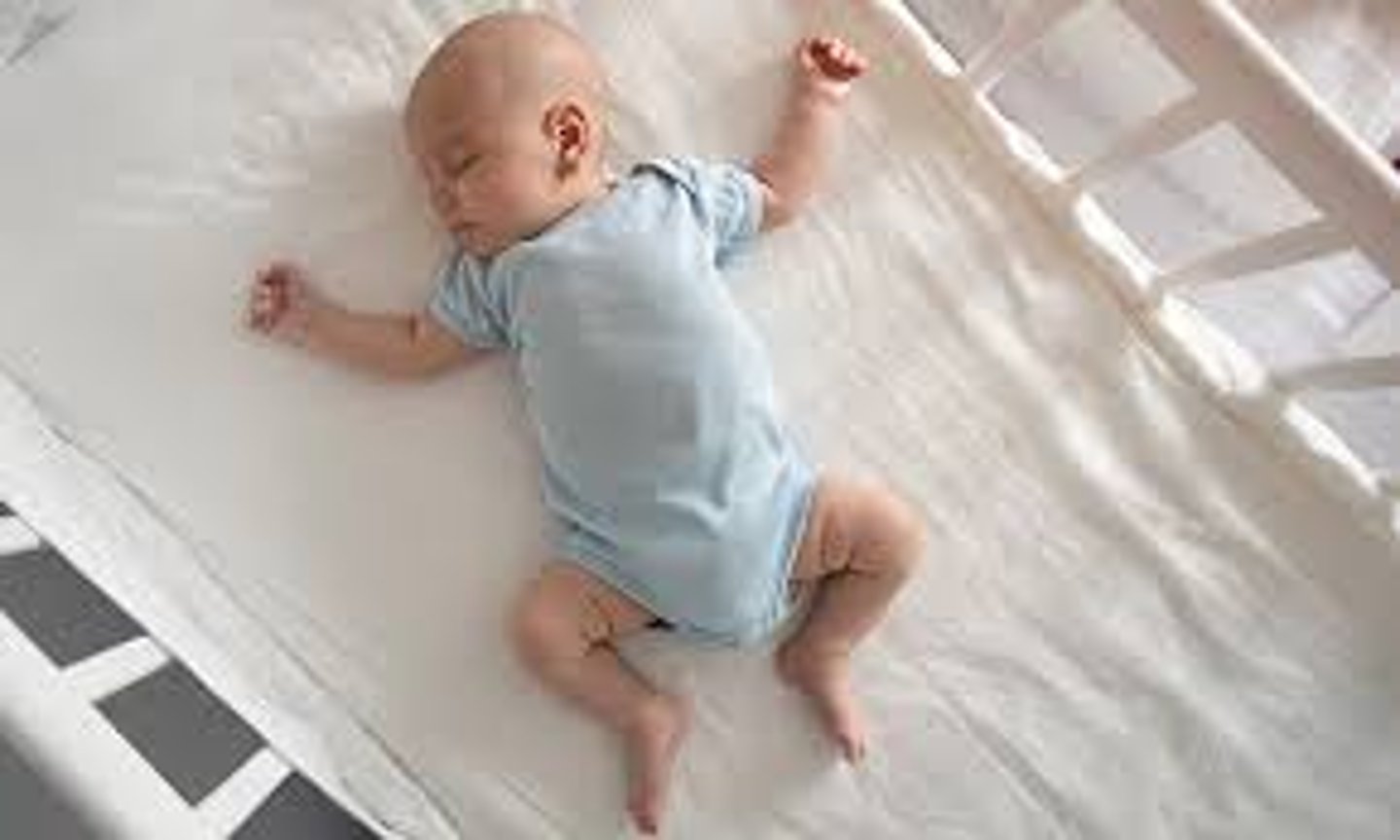

When is the best time to examine a newborn
1-2 hours after feeding
Newborn fever
100.4+
Average newborn pulse
70-190 (not below 100 if AWAKE)
Newborn RR
30-60 (sleeping rate most reliable)
newborn apnea
more than 20 seconds
1 lb = ___ kg
.45
normal length newborn
19-21 inches (48-53 cm)
It is recommended to measure head circumference until the age of _______
3 (do it three times and take the largest measurement)
(normal is 12-14 inches)
High pitched shrill cry
Children born to drug addicted mothers
Increased intracranial pressure
Low pitched hoarse cry
Infrequent and low in intensity
Assoc. with hypothyroidism, hypocalcemic tetany
Cri du chat
associated with deletion of chromosome 5
Absence of crying
Suggests severe illness, vocal cord paralysis, profound cognitive disabilities
Vernex caseosa
coating on skin when child is born
NORMAL
Lanugo
fine peachfuzz all over body
NORMAL
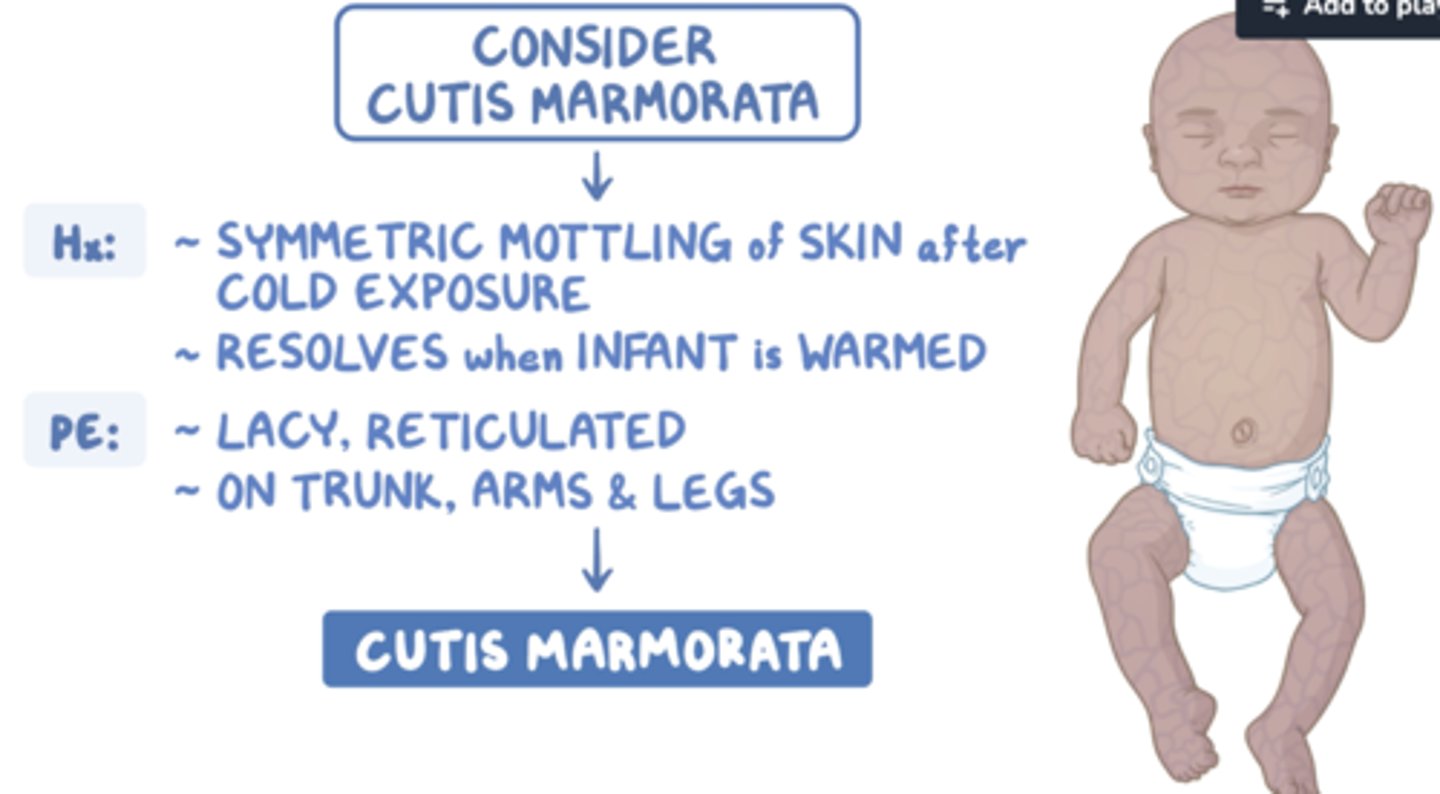
Cutis marmorata
lacy network of small BV (vasospasm/dilation) in response to cold temps -- disappears when skin warms
NORMAL
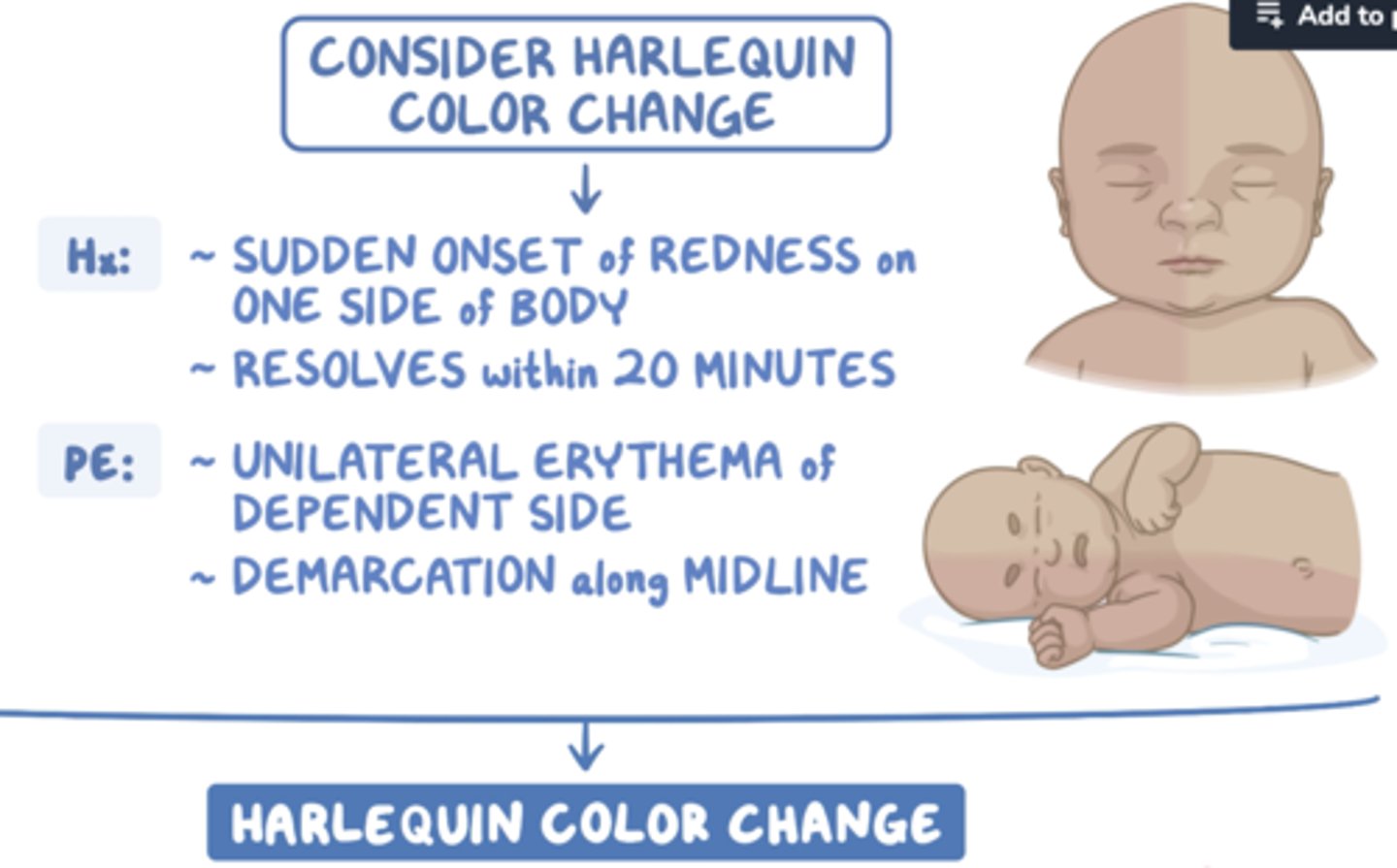
Harlequin color change
transient erythema from blood pooling (positional)
(days 2-5)
NORMAL
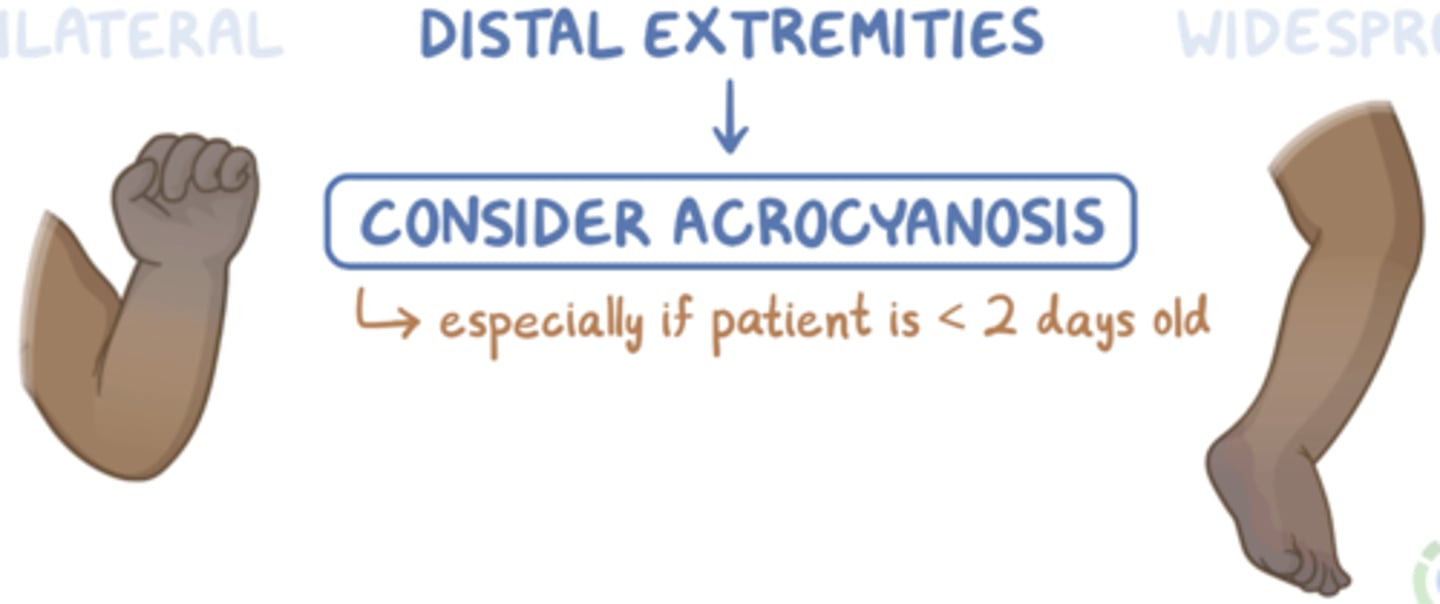
Acrocyanosis
blue cast to hands and feet when exposure to cold
(NORMAL IN FIRST 48 hours, then abnormal)
Physiologic Jaundice
Normal between 48-96 hours due to increase in RBC production and bilirubin
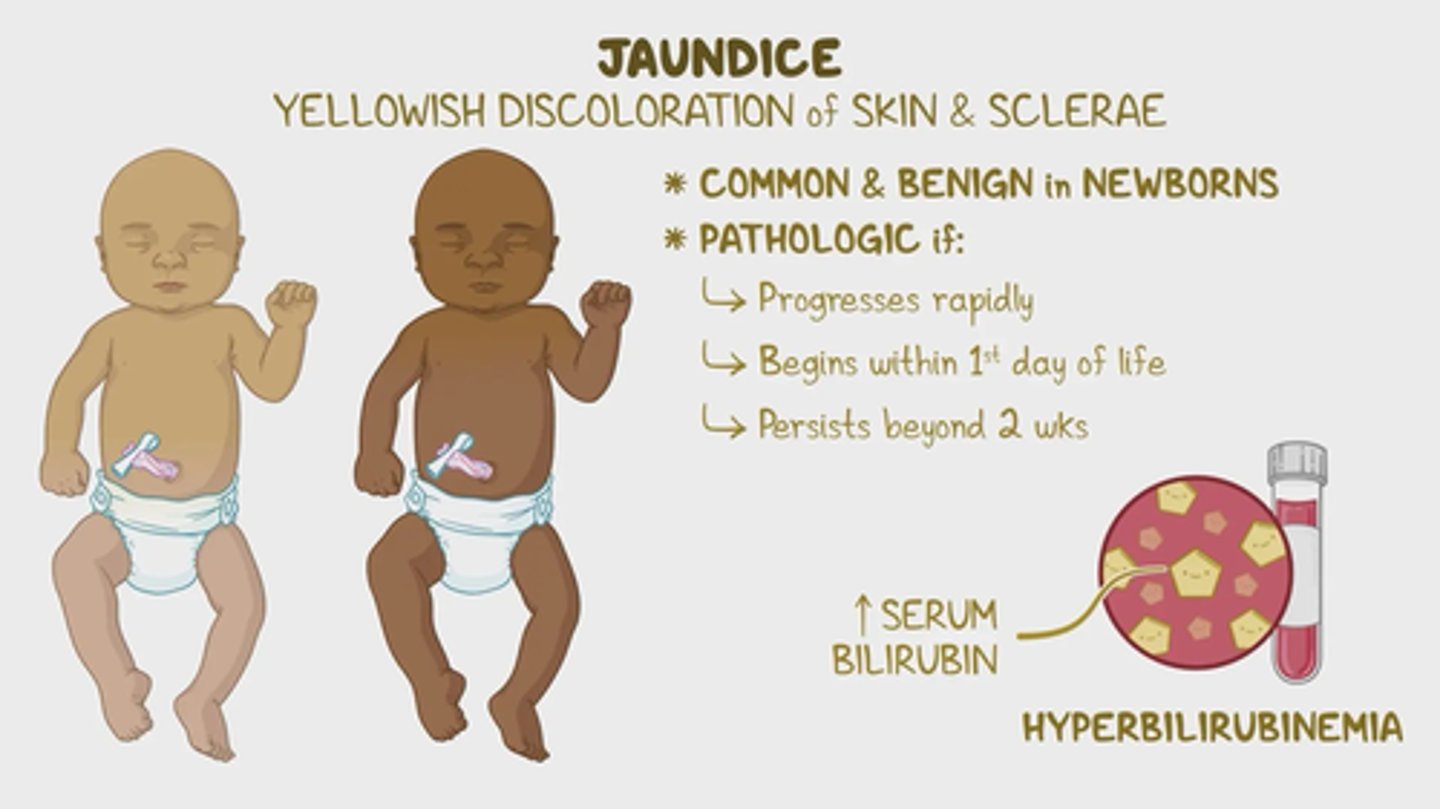
Jaundice in the first _____ hours of life is NEVER NORMAL!
24
Bilirubin levels peak _________ after birth
3-10 days
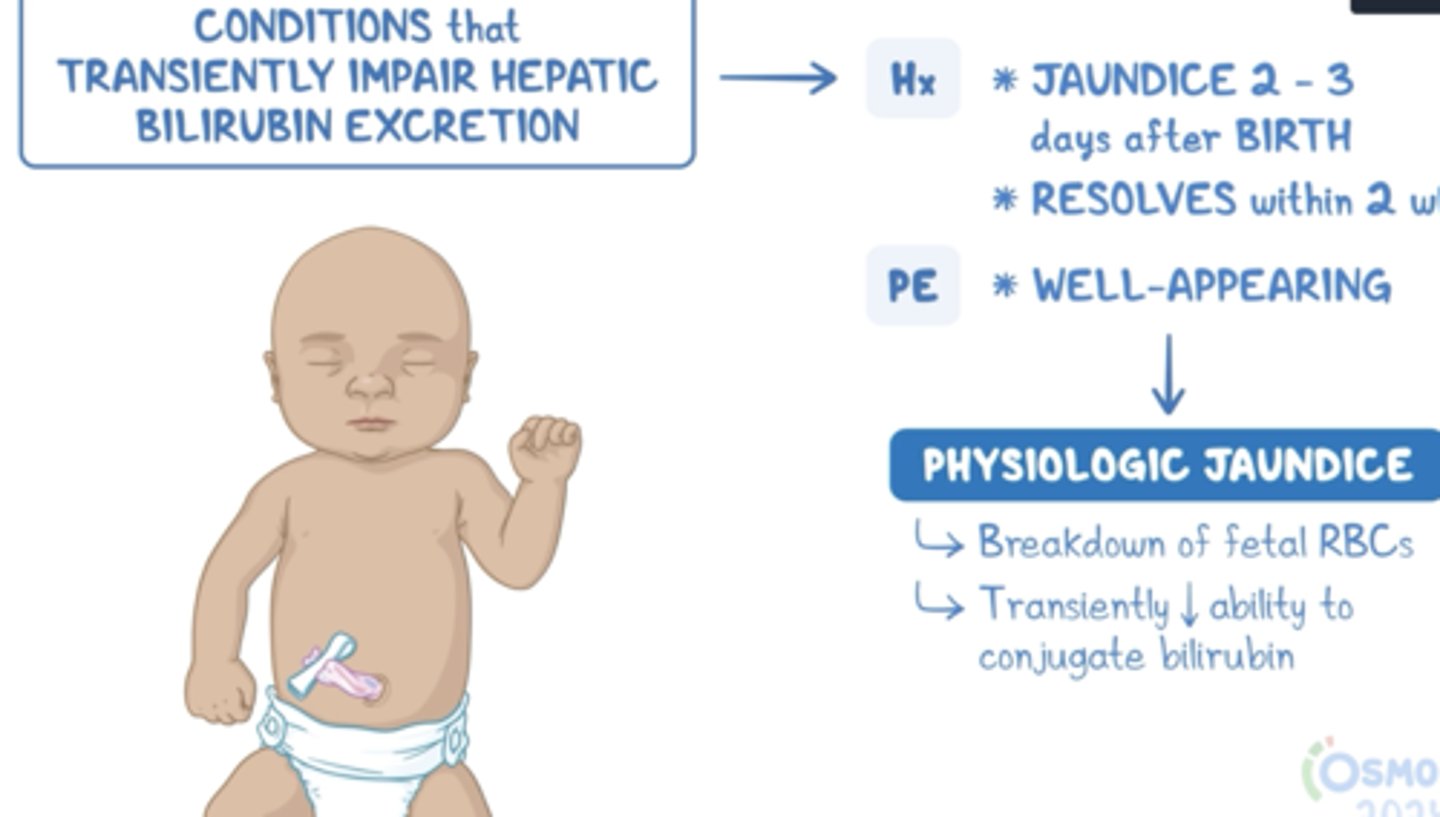
Pathologic Jaundice
- before 24 hours
- after 2 weeks
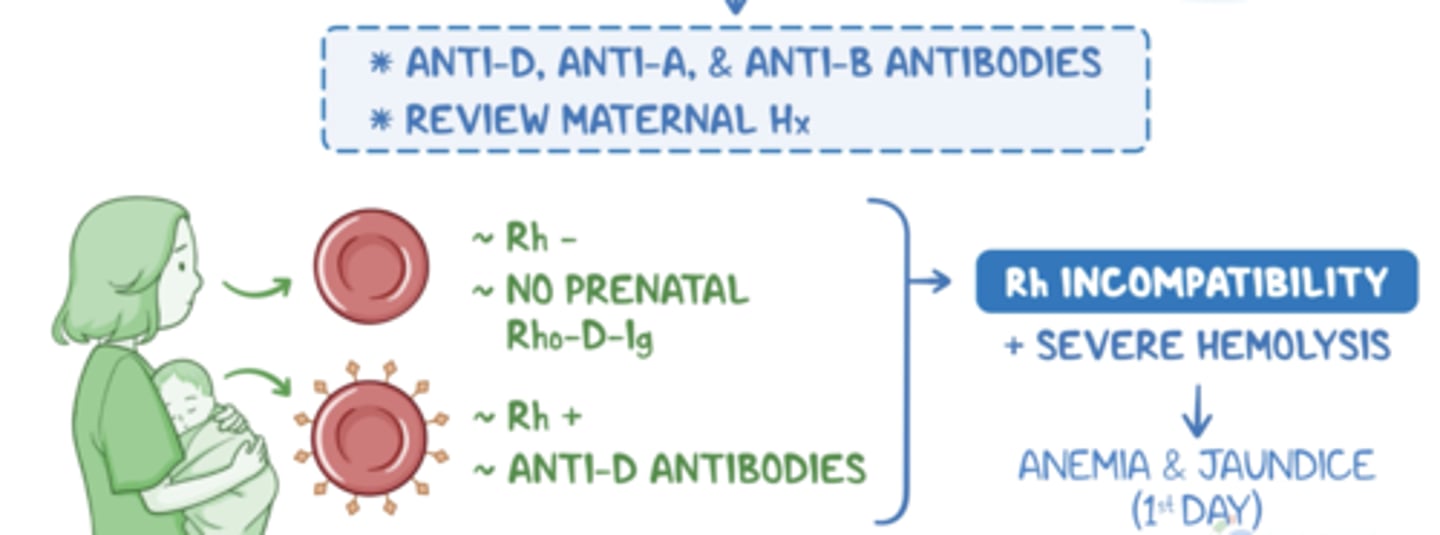
If jaundice occurs in the first 24 hours suspect...
Rapid hemolysis
- ABO
- Rh incompatibility
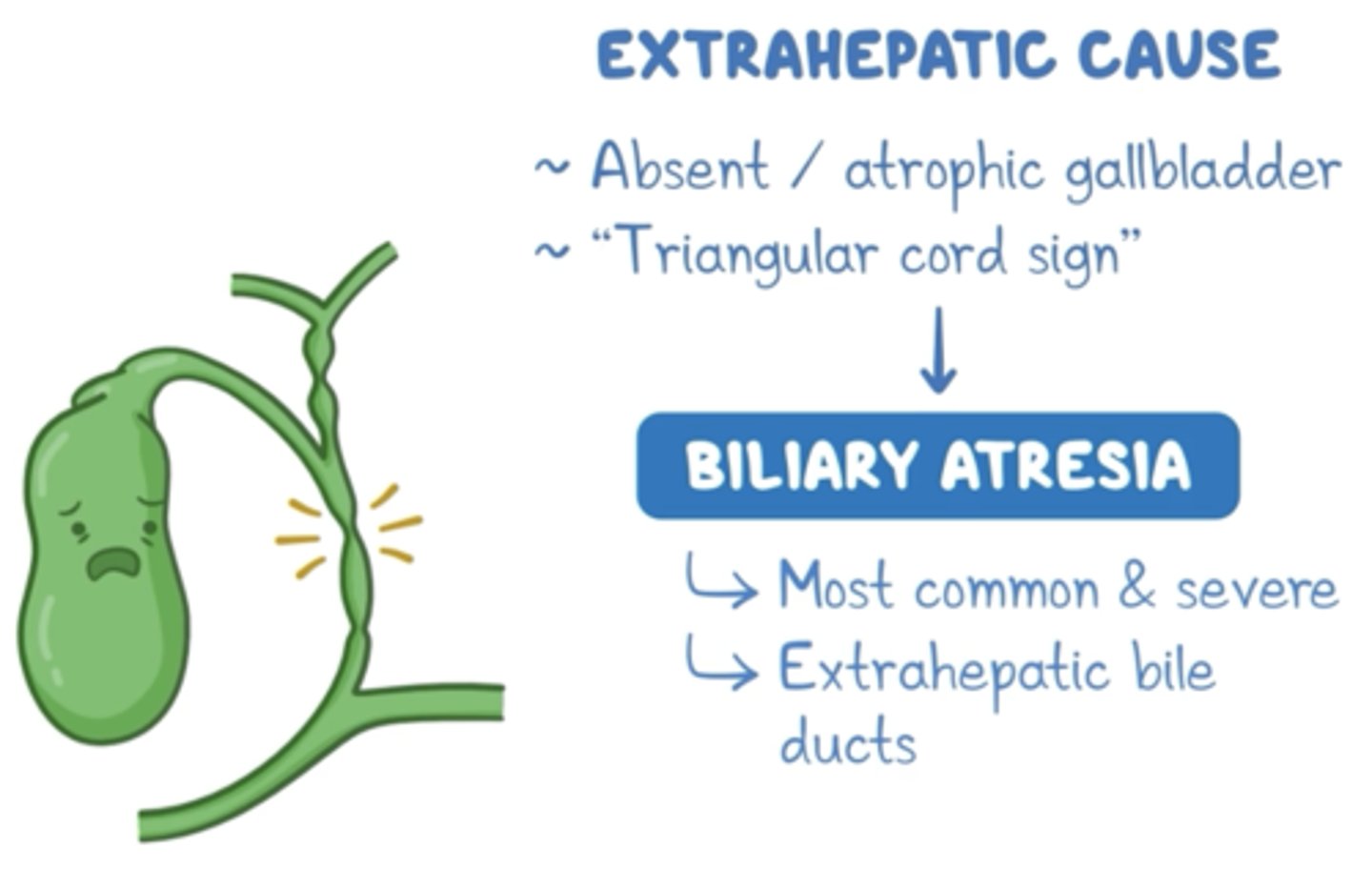
If jaundice occurs after 2 weeks suspect...
biliary obstruction or severe infection
Pathologic jaundice is associated with....
lethargy, poor feeding, convulsions
Congenital Dermal Melanocytosis (Mongolian spots)
black and blue macules on back and butt usually resolving by age 2 (NORMAL)

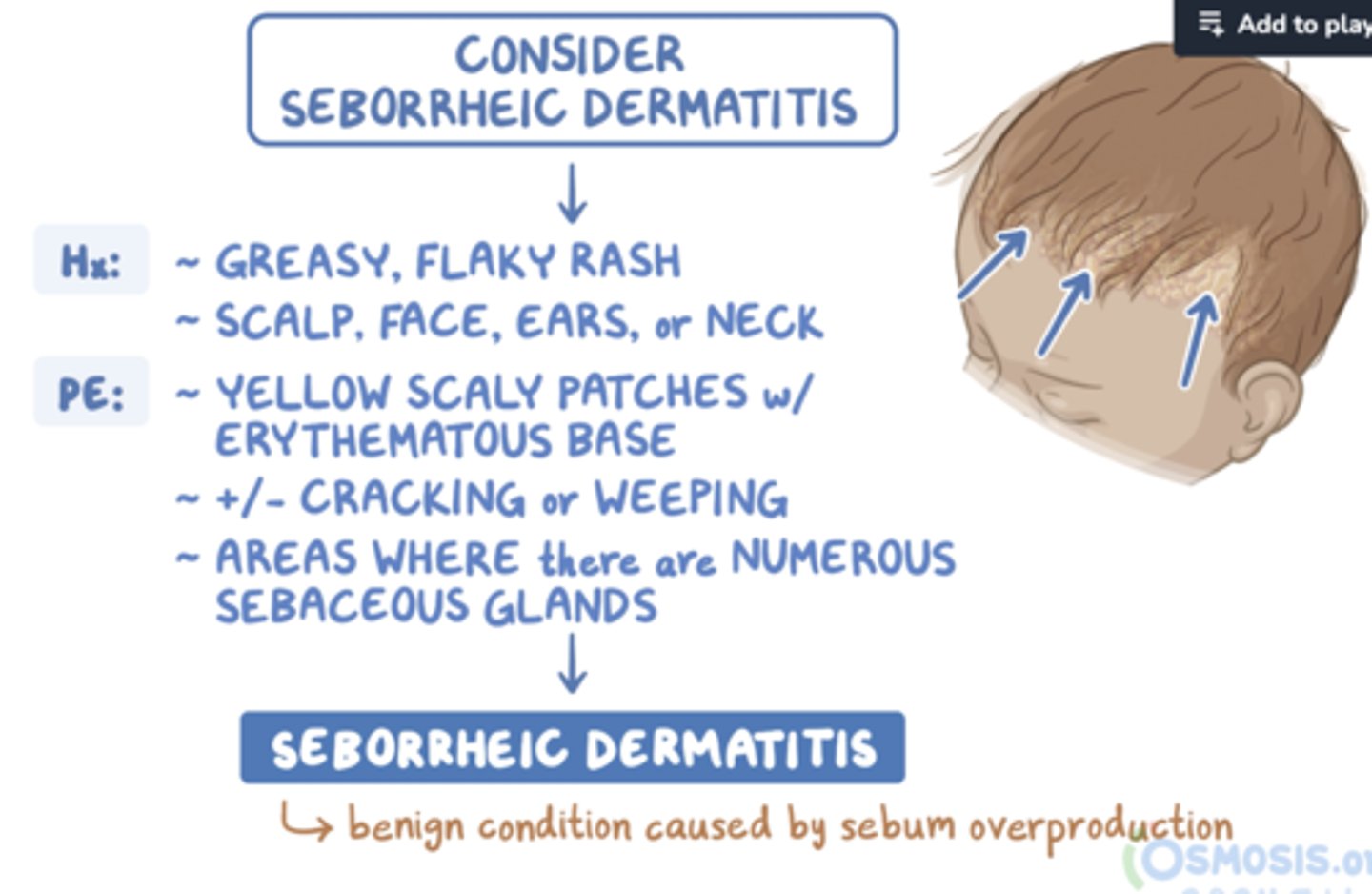
Infantile seborrheic dermatitis
cradle cap
("NORMAL")
Miliaria rubra
heat rash (obstruction of sweat glands)
scattered vesicles
("NORMAL")

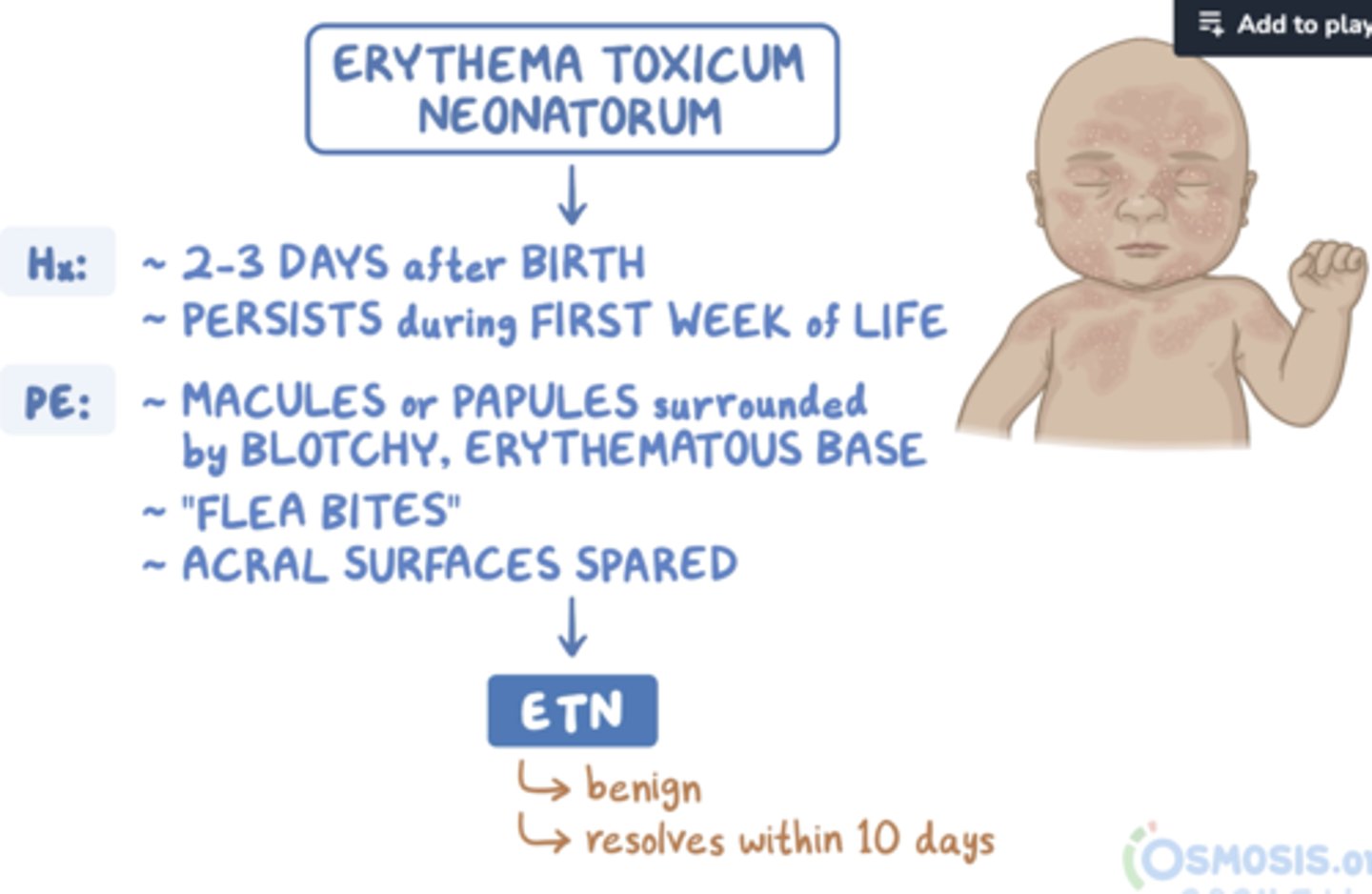
Erythema toxicum
3-5 days of life
small pustules on erythematous base
spontaneously resolve
("NORMAL")
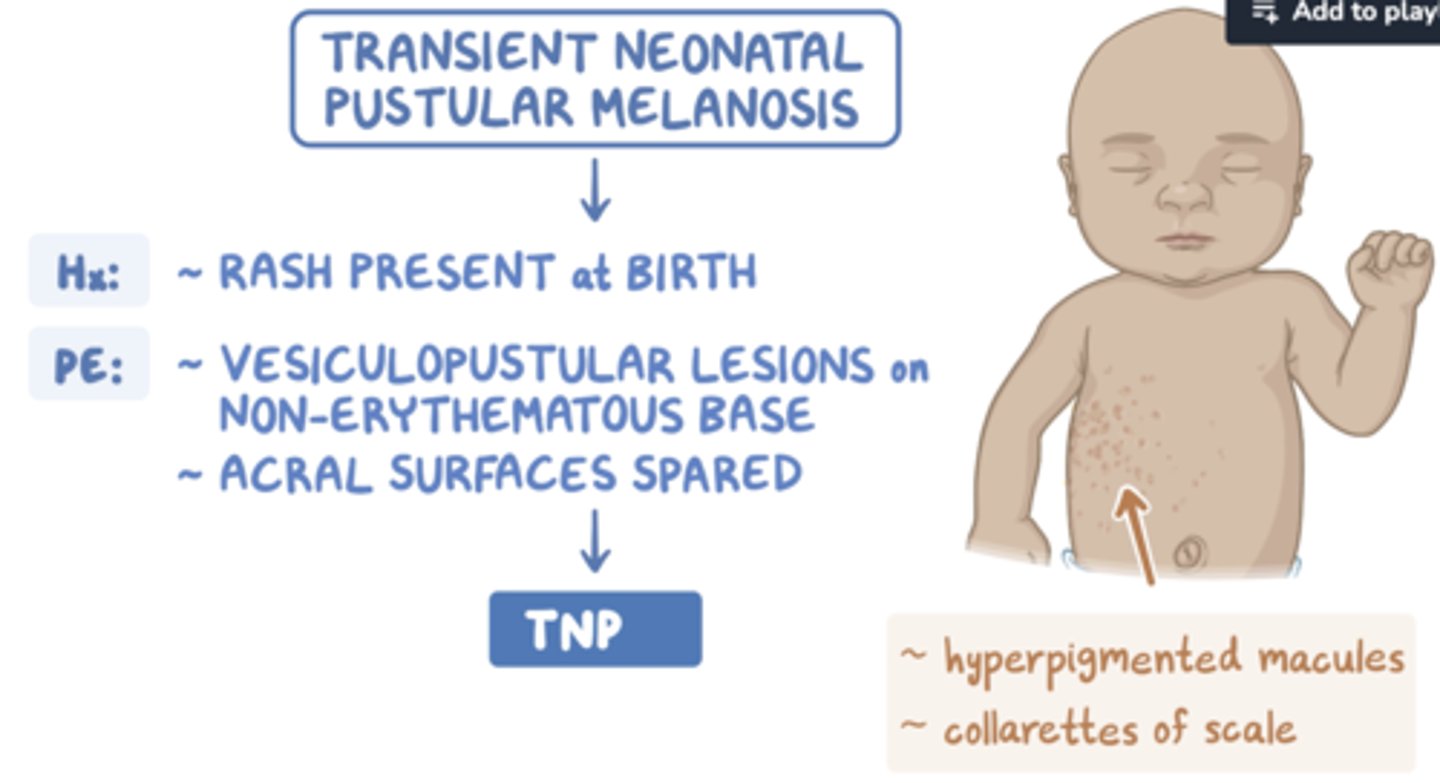
pustular melanocytosis
small pustules on brown macule base
resolves in months
("NORMAL")
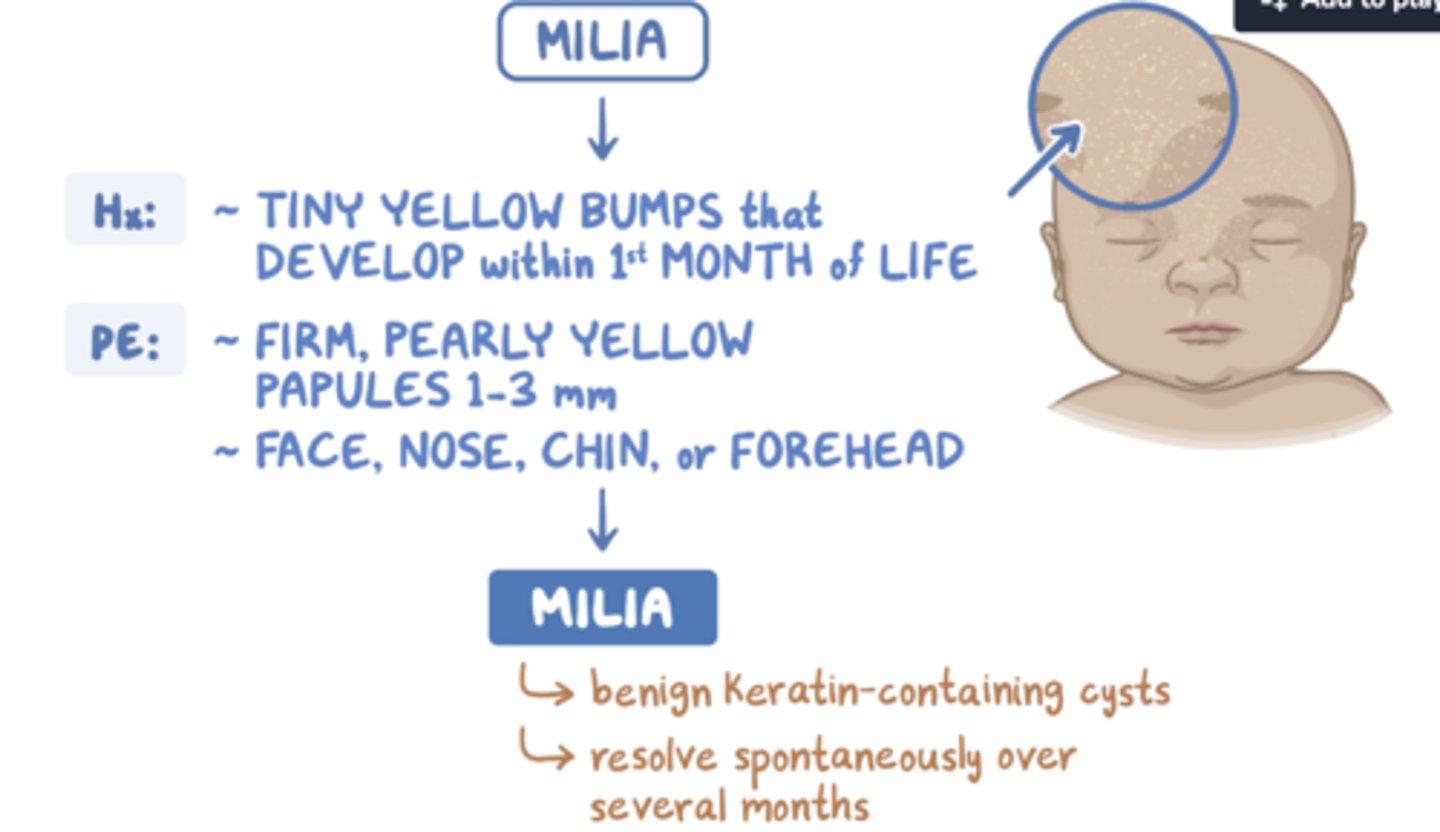
Milia
tiny white pearly pustules caused by blocked sebaceous glands
("NORMAL")
Cafe au lait spots
flat lat brown patches
(if they are large or more than 5 consider neurofibromatosis)
Nevus simplex (angle kiss)
flat, blanchable, often resolve by age 2

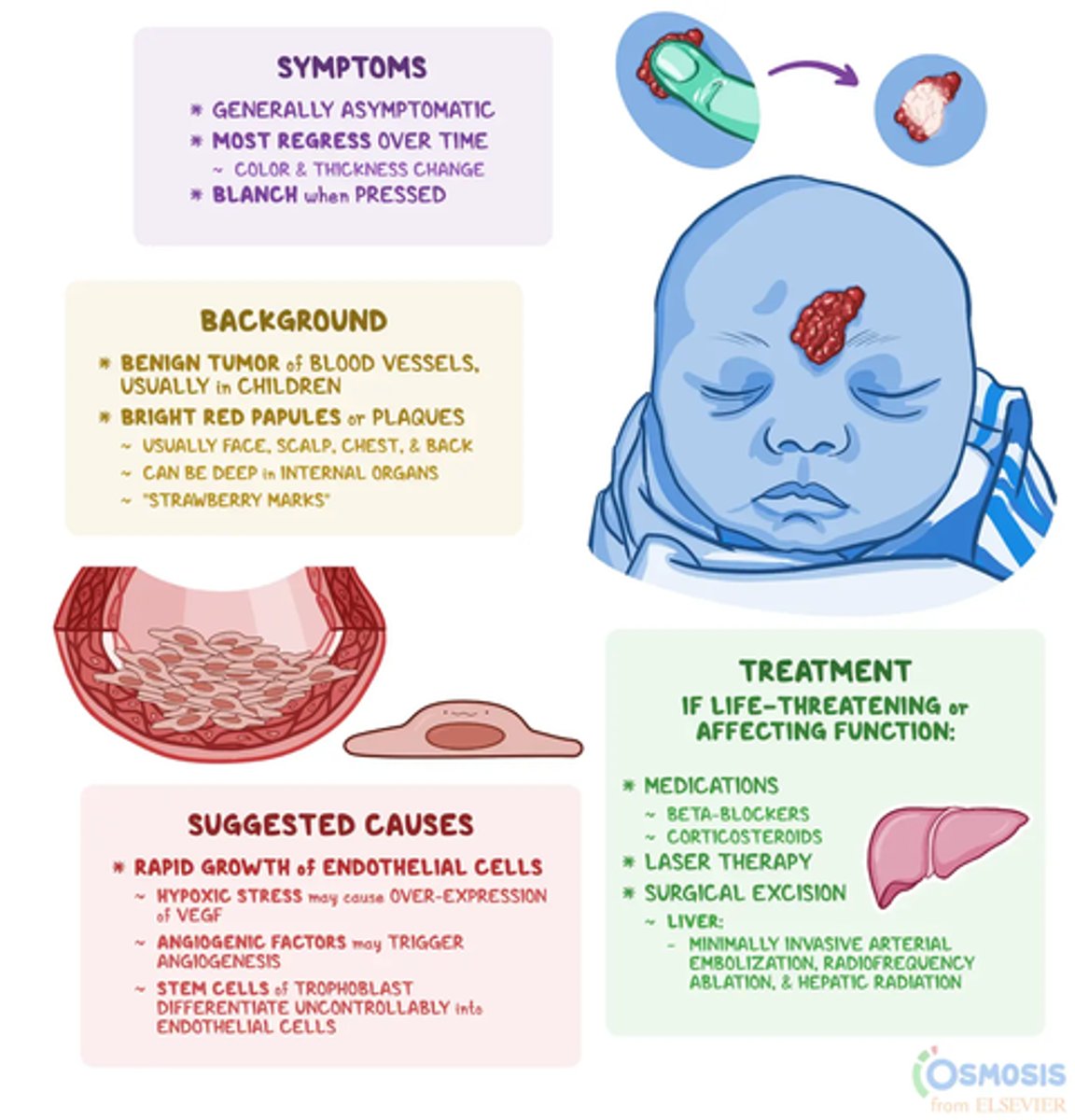
Infantile hemangioma (strawberry hemangioma)
- benign vascular tumor
- palpable bright red lesion
- develop in first 1-2 weeks
- rapidly enlarge during infancy
- resolve by age 10
Nevus Flammeus (port wine stain)
- usually unilateral
- darken over time and are permanent
- caused by capillary dilation
- present at birth
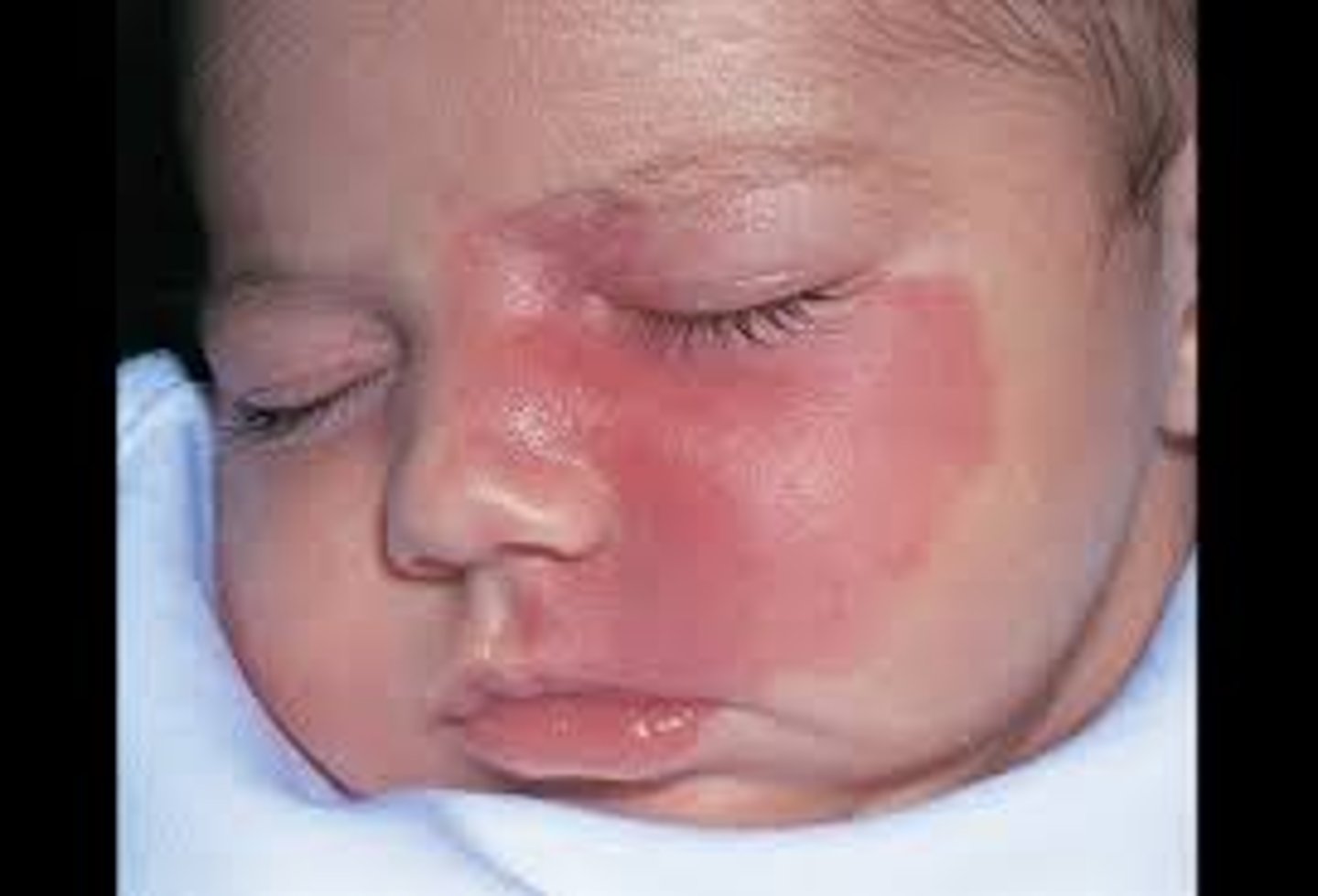
If a port wine stain involves the eye must evaluate for _______________
glaucoma
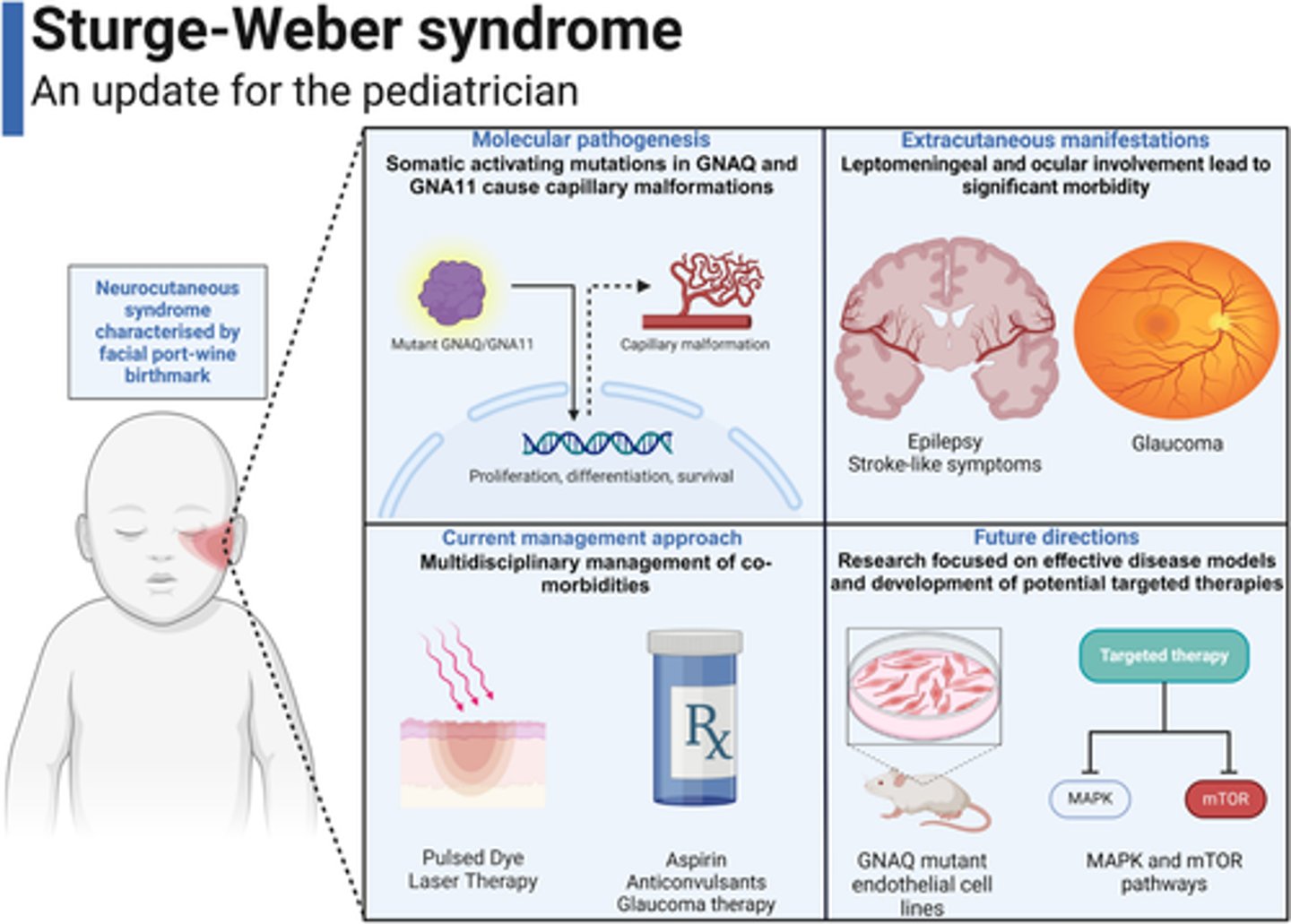
Sturge Weber Syndrome
- port wine stain in ophthalmic distribution of trigeminal nerve
- associated with seizures and glaucoma (TRIAD!)
- hemangiomas of brain and meninges
- risk of developmental delay, learning disability, and hemiparesis
- refer to neuro and ophthalmology
Anterior fontanelle
Measures 3-6 cm
90% close btwn. 7-19 mo.
Posterior fontanelle
Measures 1-1.5 cm;
Closes around 2 mo
Enlargement of anterior fontanelle my indicate:
Increased intracranial pressure
Down syndrome
Hypophosphatemia
Achondroplasia
Trisomy
Congenital hypothyroidism
Intracranial tumors/lesions
Small fontanelles often seen with __________________
microcephaly
Sunken fontanelles seen with ____________
dehydration
Dilated scalp veins indicate...
long-standing increased intracranial pressure
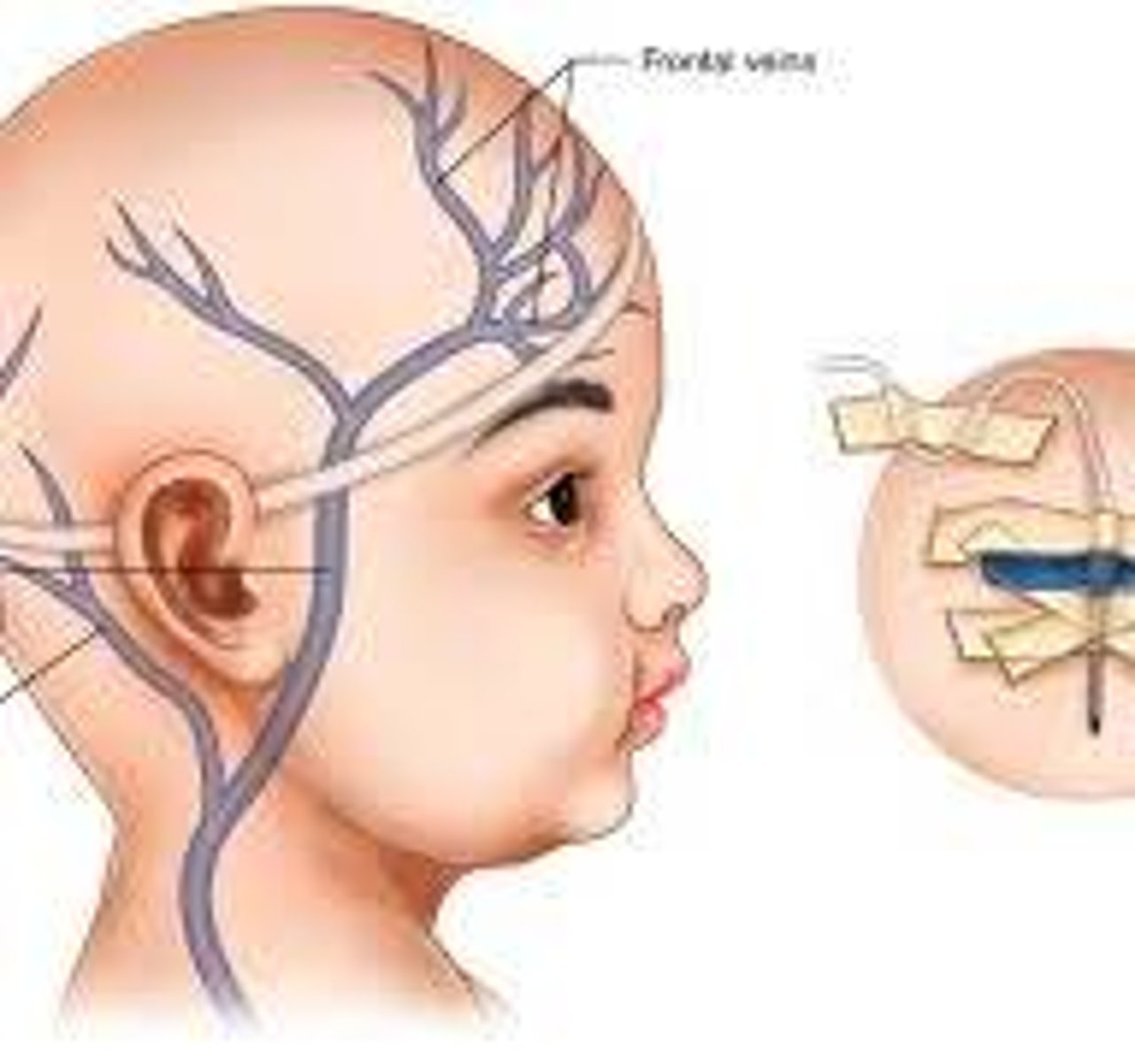
head molding
"cone head"
resolves in 2 days
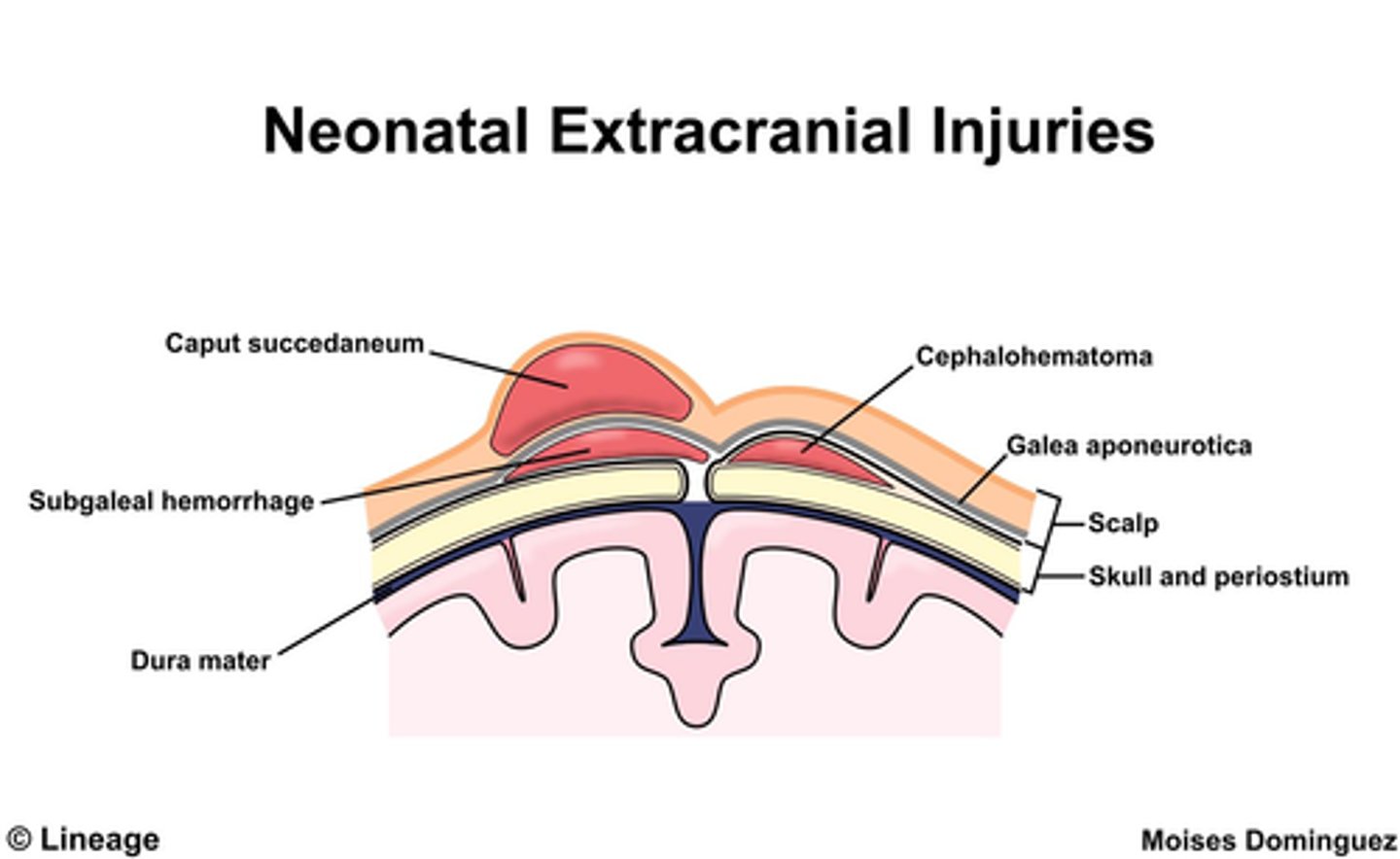
Caput Succedaneum
Pitting edema of the scalp due to pressure from vaginal canal resolving in 2-3 days (supraperiosteum)
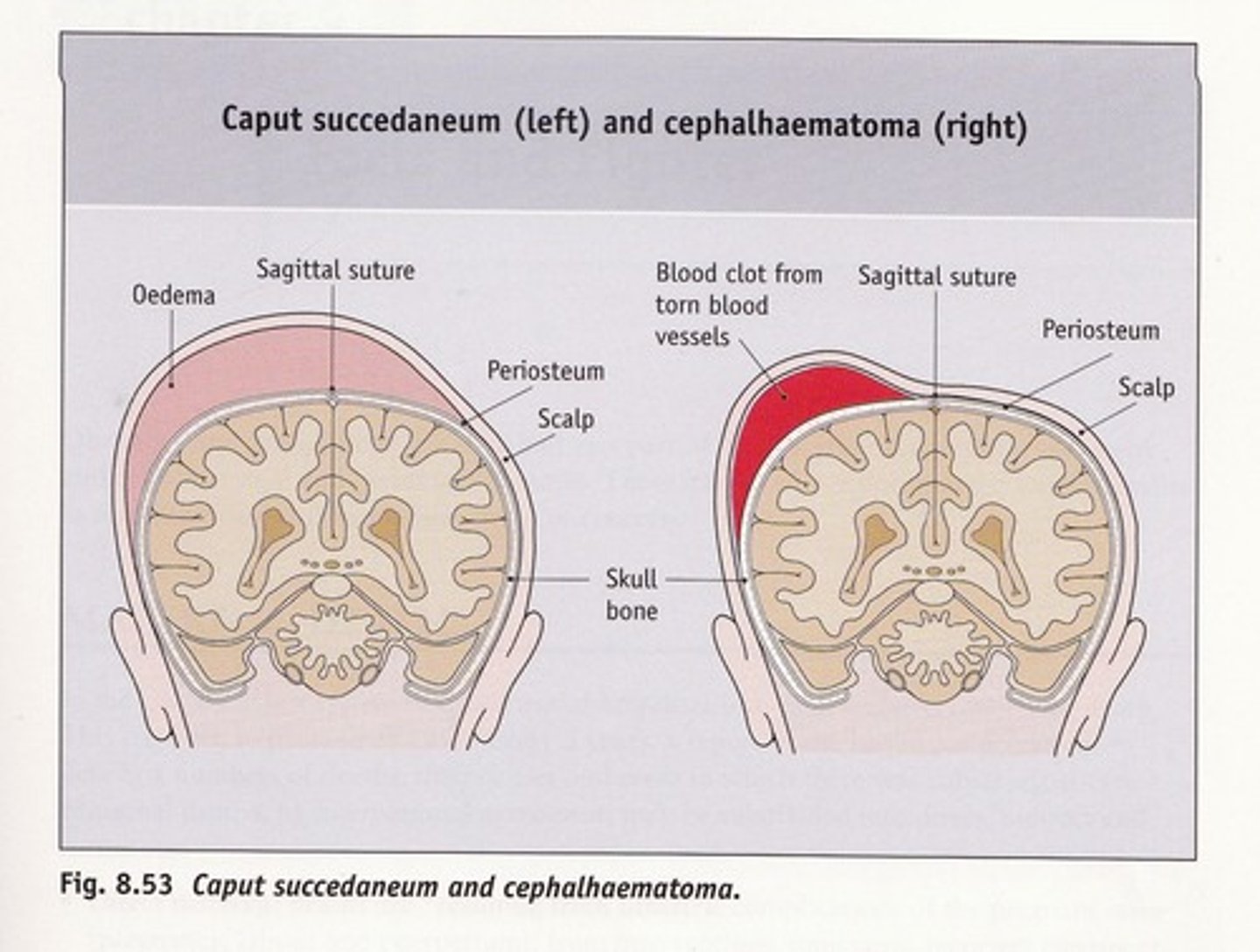
Caput Succedaneum crosses ______________________
suture lines
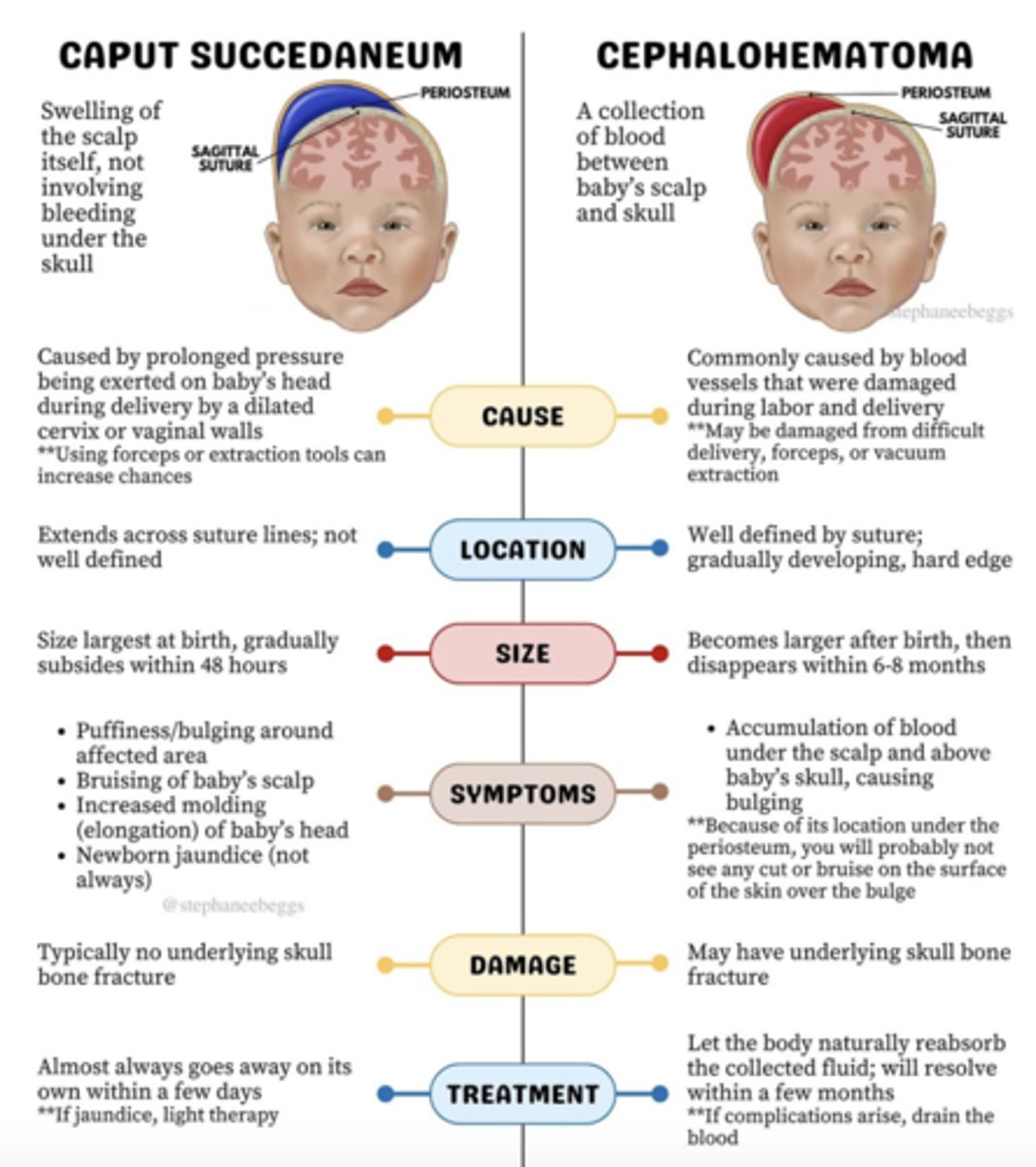
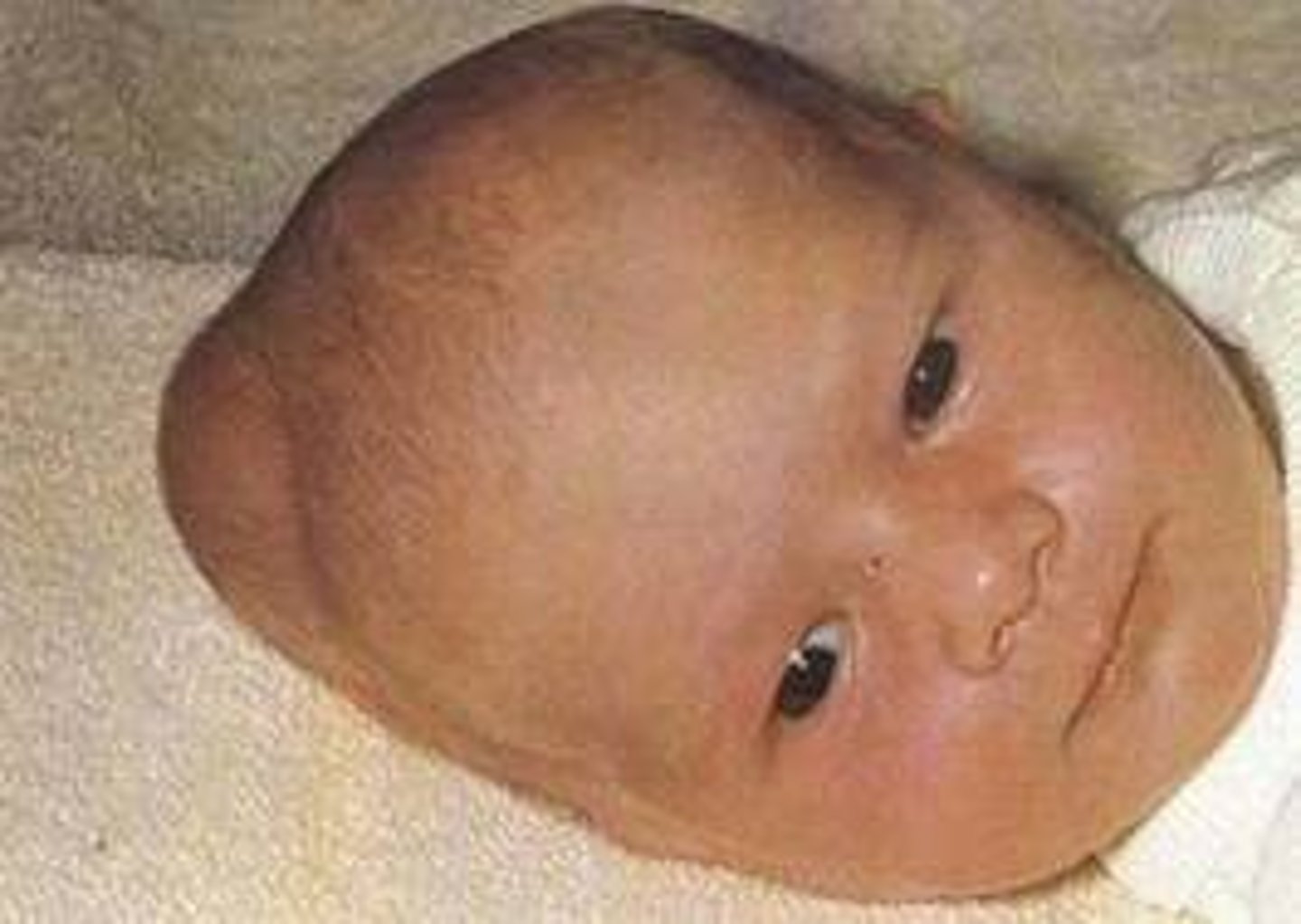
Cephalohematoma
Sub-periosteum edema
Due to an injury of blood vessels
May worsen 48 hours after birth and take 3-4 months to resolve
Often seen with forceps/vacuum delivery
Cephalohematoma increases risk of _____________________ and _________________
jaundice, sepsis
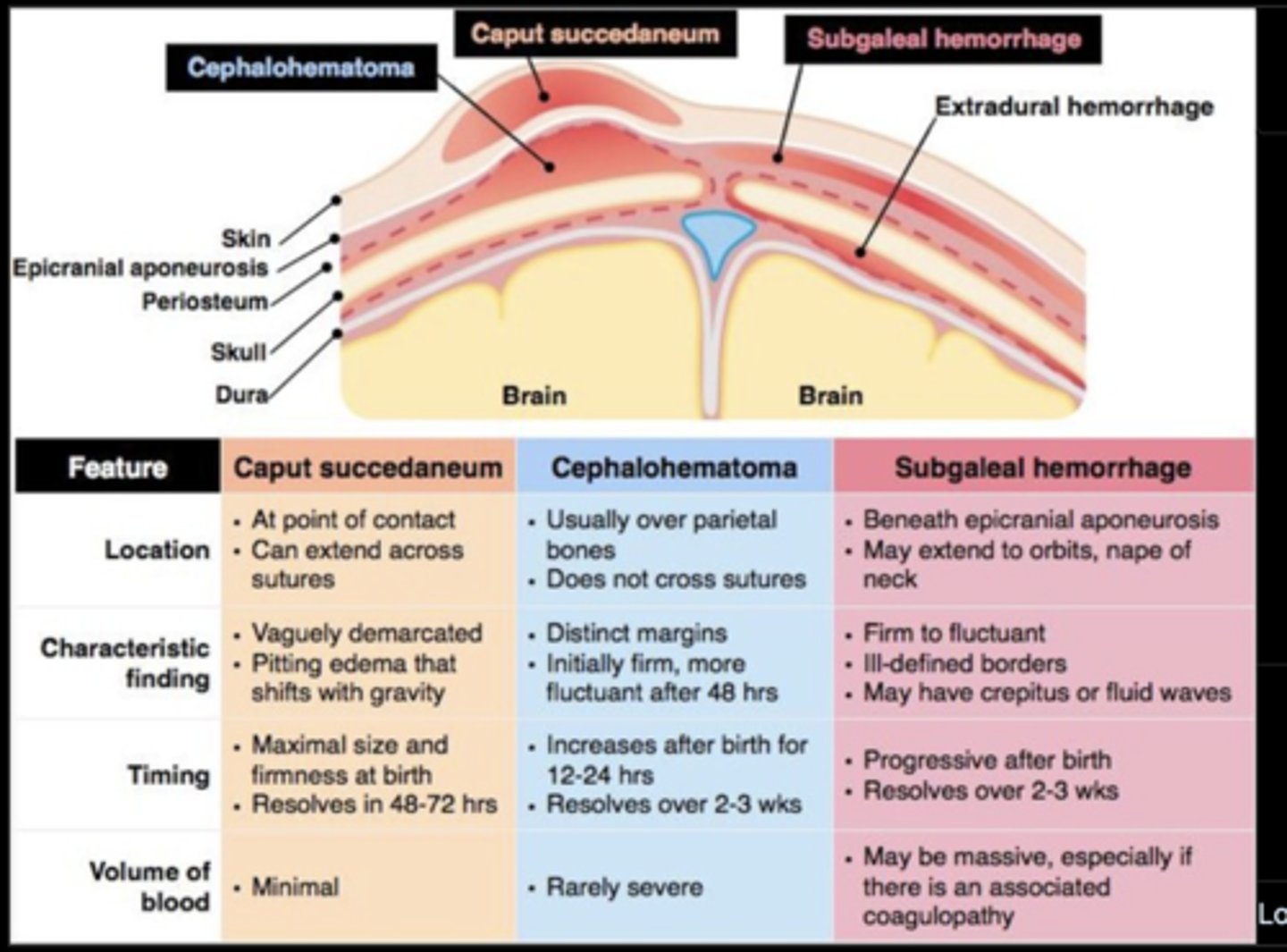
Cephalohematoma __________________ suture lines
DOES NOT CROSS!
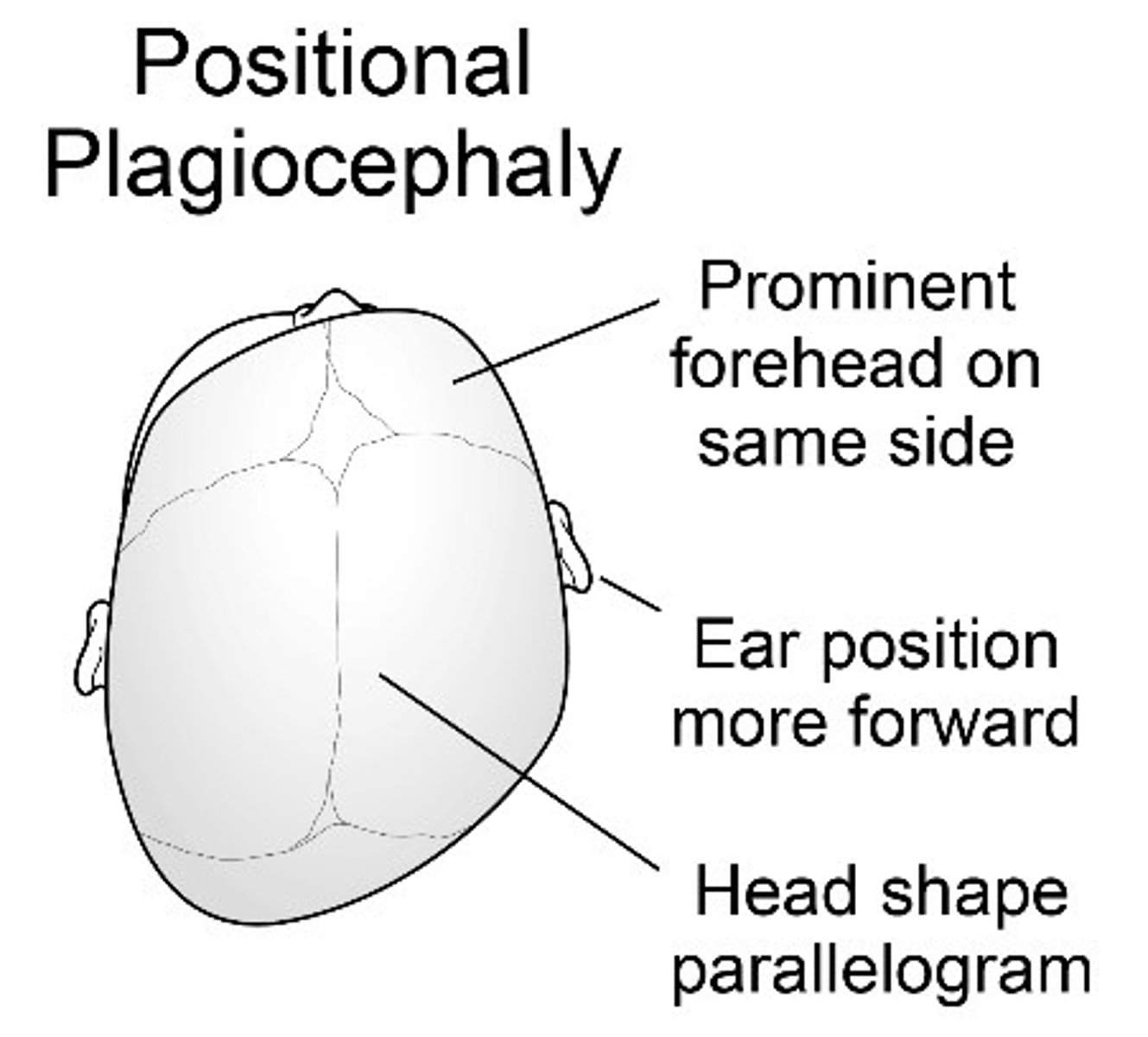
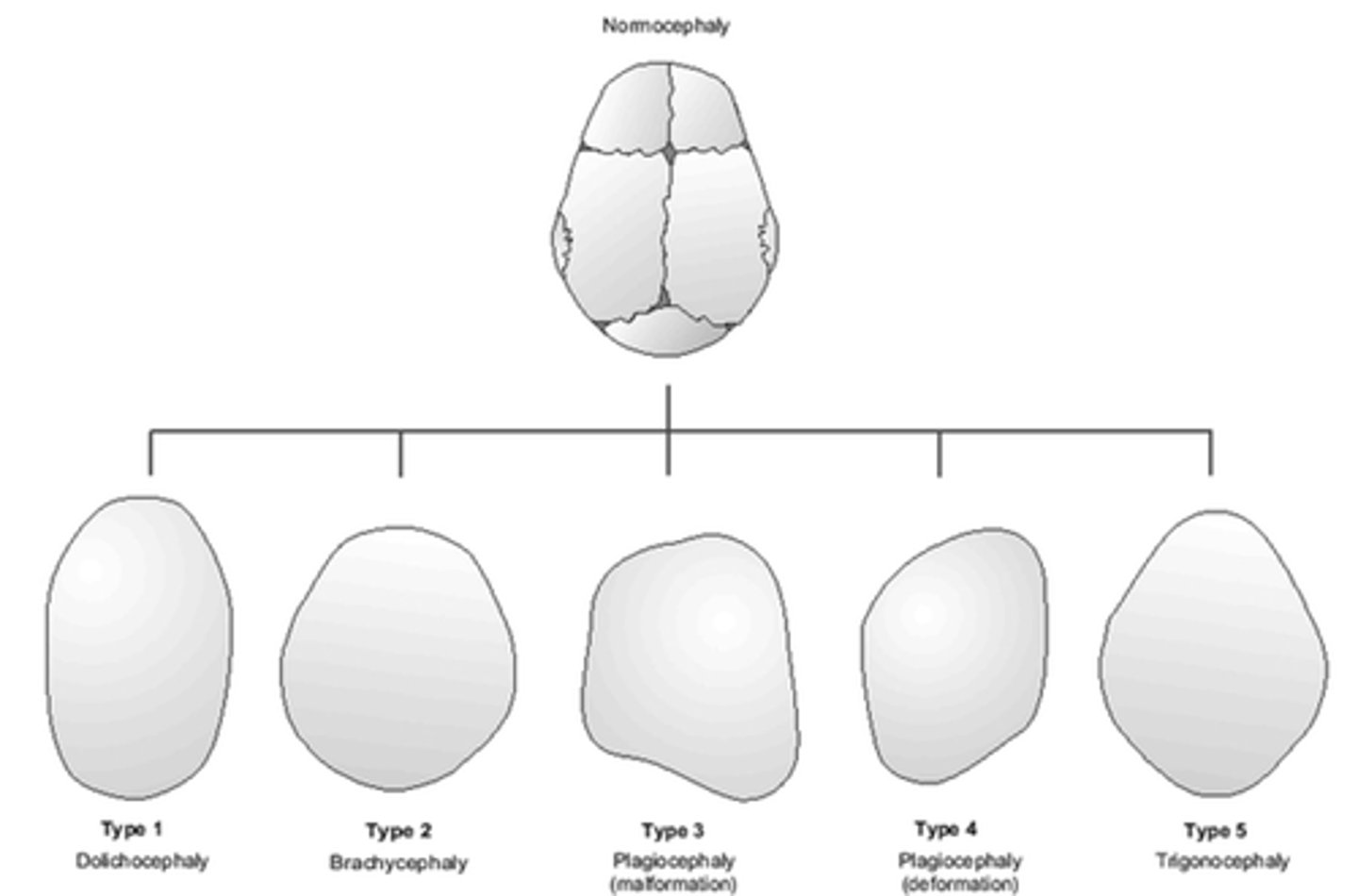
Plagiocephaly
Misshapen head
Usually from laying in one position
Flattening of occiput with a prominence of frontal region on opposite side
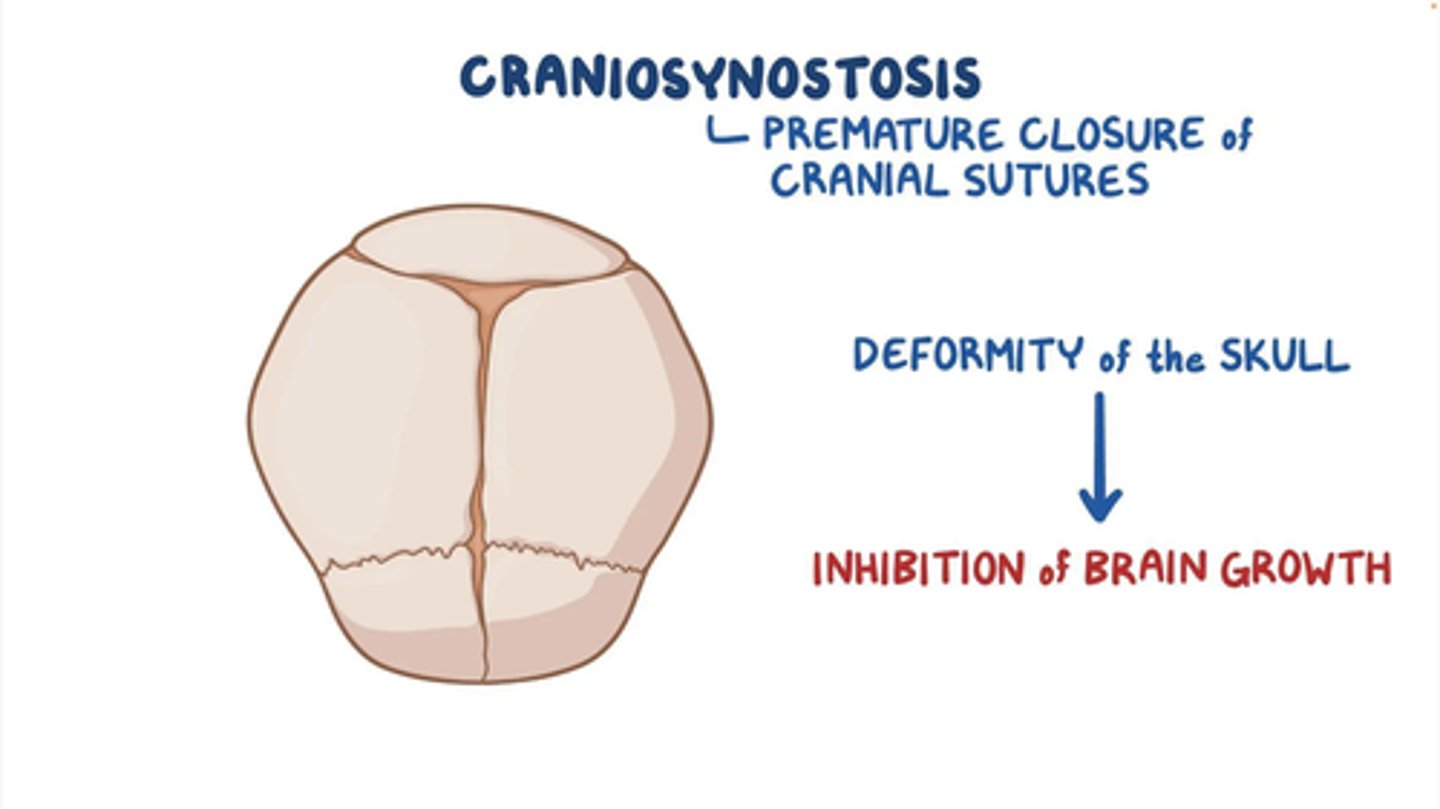
Craniosynostosis
Premature fusion of 1 or more cranial sutures, often resulting in an abnormal head shape
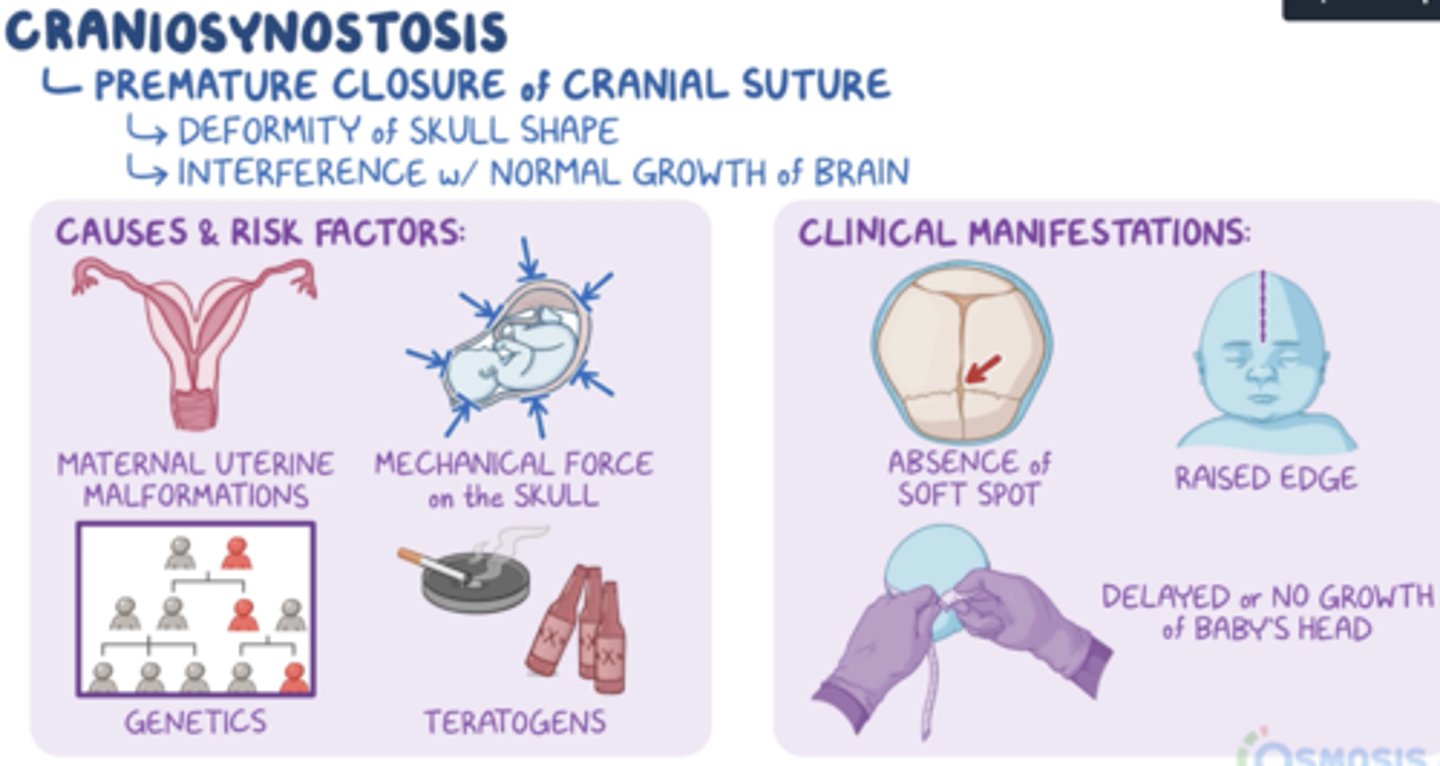
Craniosynostosis cause
>20% caused by single gene mutation or chromosomal abnormalities
In Dolichocephaly the head is disproportionately _______________
long and narrow
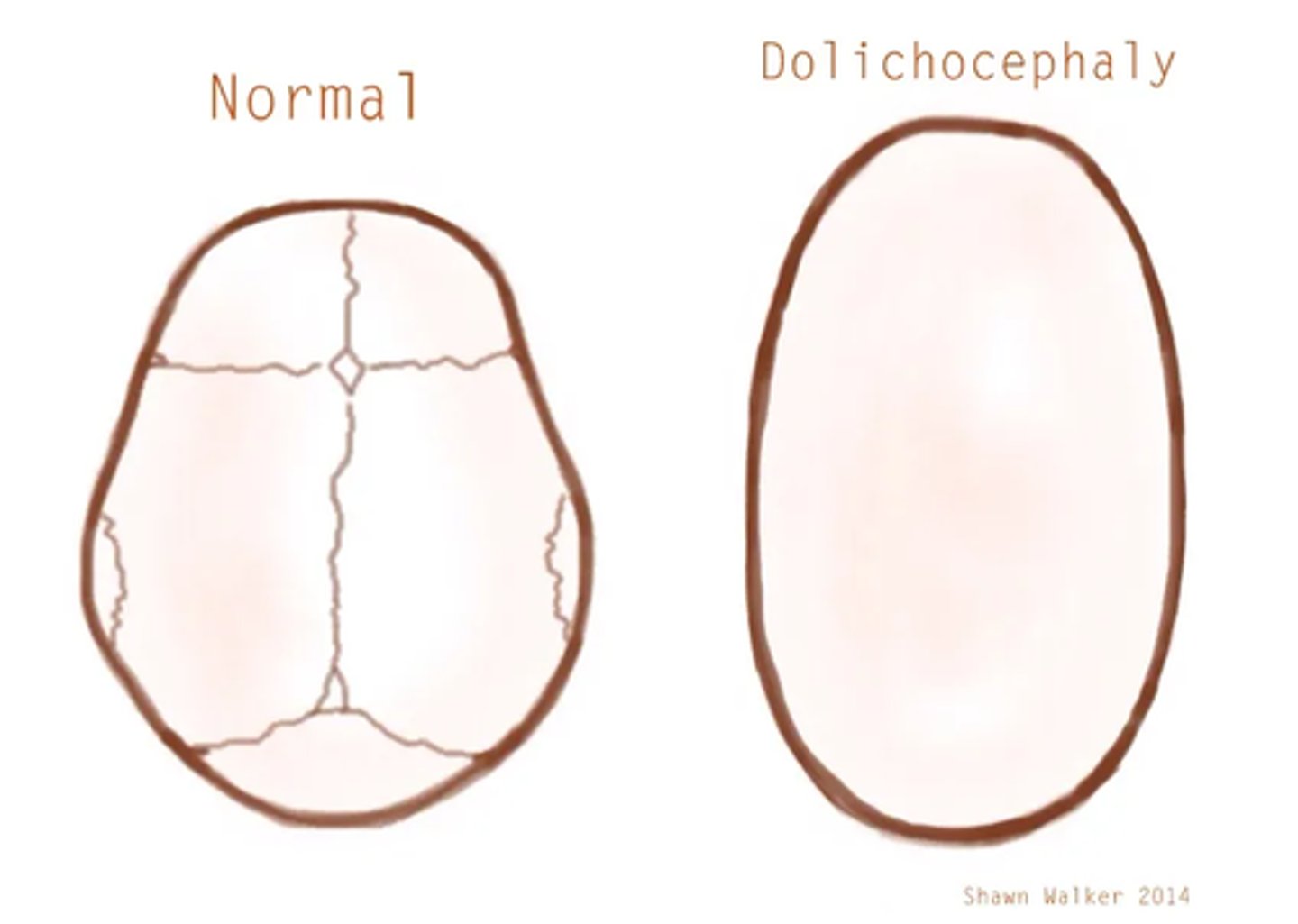
Dolichocephaly isthe result of premature fusion of the _______________ suture
sagittal
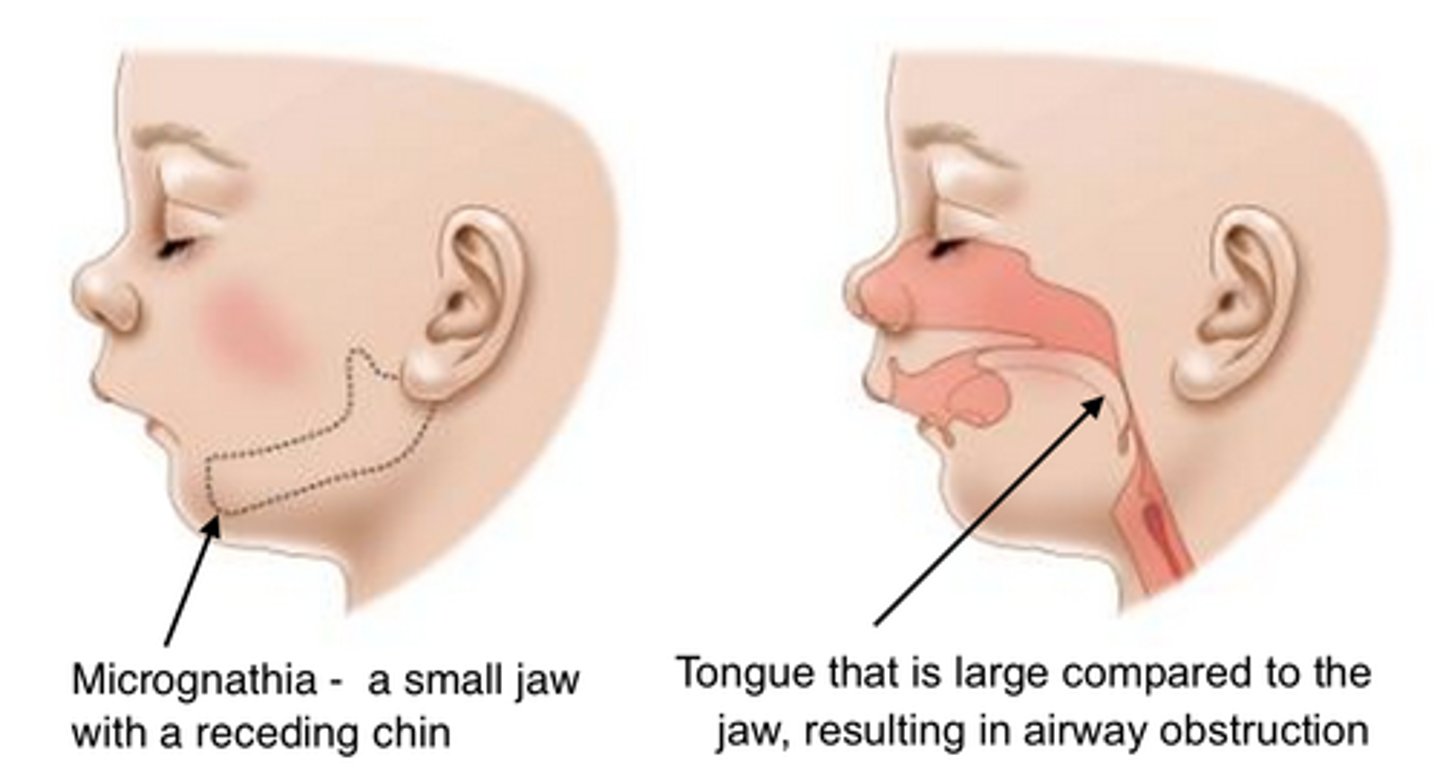
Micrognathia
Lower jaw smaller than normal
Can interfere with breathing and feeding
Can correct itself as child grows
Micrognathia is often seen with _________________________
Trisomy 13 &18
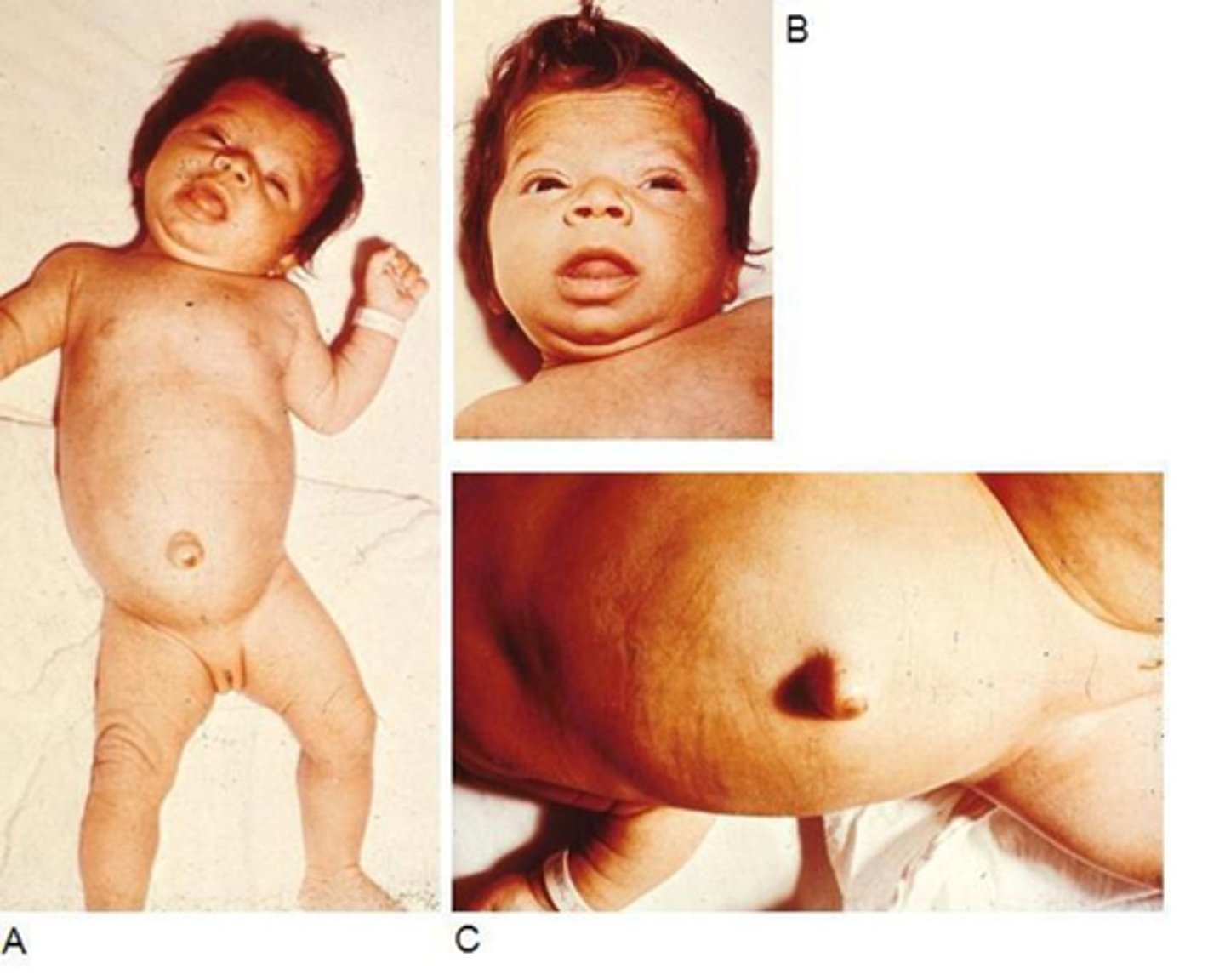
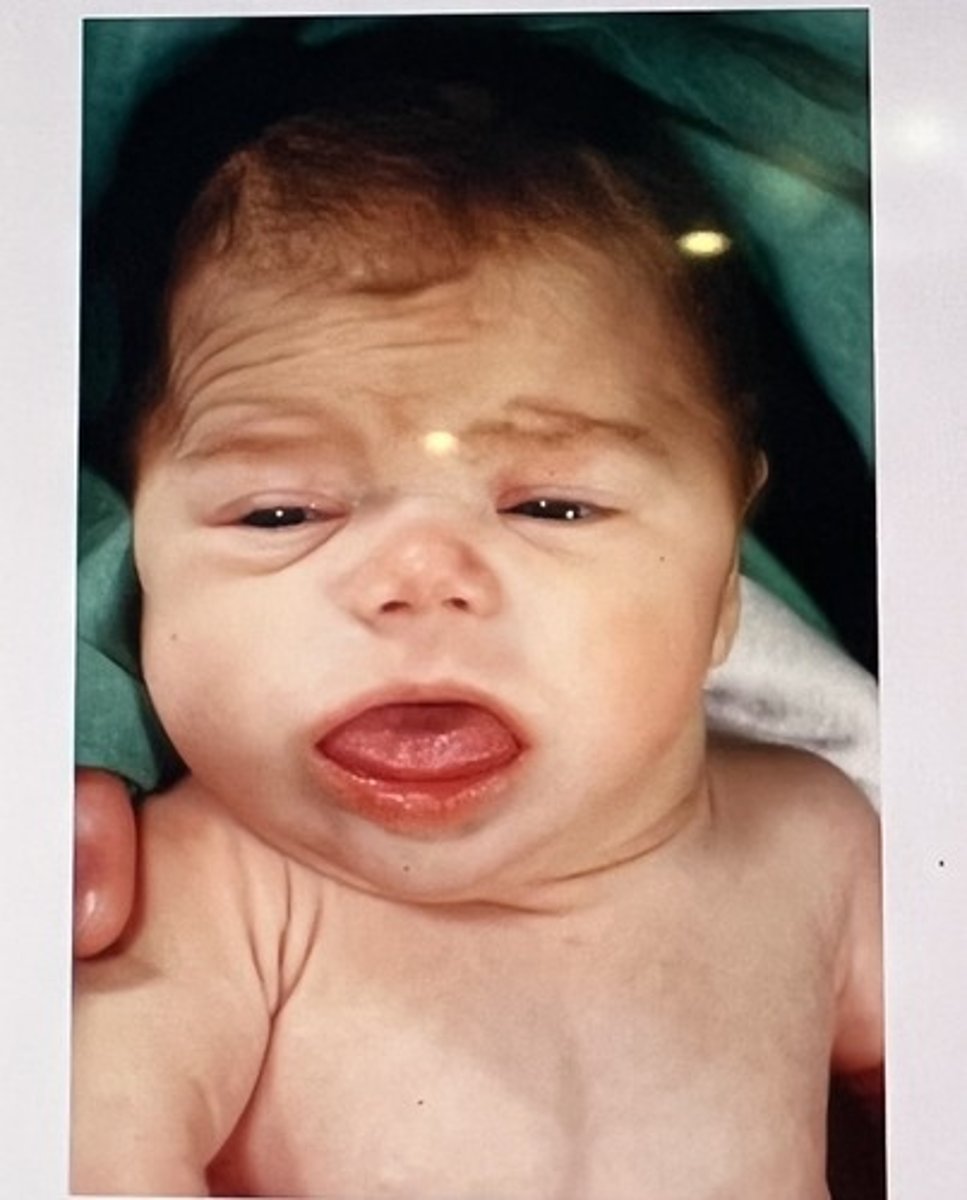
Congenital hypothyroidism facies
Course facial features
Macroglossia
Goiter
Large fontanelles
T/F: congential hypothyroidism is part of all newborn screenings
true