GEOGRAPHY ALL YEAR 8 STUFF
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ALL YEAR EIGHT STUFF GEOGRAPHYYY
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
butlers life cycle model
describes the life cycle of a tourism factor
exploration
small number of tourists, unspoiled, few facilities
involvement
locals visit, small, facilities
development
advertised, tourists, destination
consolidation
lots of tourists and facilities
stagnation
decline as it becomes run down
rejuvenation
rebranding, more tourists
decline
no new tourists
name three factors that affect the growth of tourism
price, weather, advertising
erosion
when rocks are worn away from natural causes
hydraulic action
the erosive force of water
abrasion
the process of wearing away over time
deposition
when materials carried by wind, water or other are dropped
headland
a point of land, typically high and with a steep drop, that extends out into a body of water
bay
coastal body of water which is partially surrounded by land which leads out to sea
beach
a landform along a coastline which separates the sea from the mainland
cliffs
a steep vertical or near vertical rock face
sea wall
a structure built along the coastline to protect the land from erosion and flooding
groynes
a shore protection structure built perpendicular to the shoreline of the coast (or river), over the beach and into the shoreface
tourism
the act of travelling from a different place to visit somewhere else
regeneration
the revitalisation of an area which has experienced a decline or decay
economy
the system by which goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed within a specific region or area
conflict
when two or more opposing parties have a disagreement
precipitaion
water falling to earth from the atmosphere, as rain sleet hail, snow- an input to the drainage basin
condensation
water turning from a vapour to a liquid- results in the formation of clouds
evaporation
water turning from a liquid to gas (vapour)- an output from the drainage basin
interception
the catching of precipitation by vegetation before it reaches the ground
throughflow
water moving downhill through the soil towards a river
river flow
the volume of water moving down a river channel
transpiration
water is lost from plants and trees through the pores in the leaves, back into the atmosphere
groundwater flow
water that is deep under the ground and moves towards the river
infiltration
when water is absorbed into the upper layer of soil
surface storage
when water is stored on the surface in lakes, puddles and ponds
percolation
when water moves deeper down in the ground
water shed
the area of high land forming the edge of the drainage basin
tributary
a small river joins a large river
source
the starting point of a river
mouth
the point where a river joins a larger river
confluence
a point where 2 rivers meet
channel
where the river flows
drainage basin
the area of land drained by a river and its tributaries
infiltration rate
how quickly water is absorbed into the upper layer of the soil
permeable
a material that allows water to pass through it
impermeable
a material that does not allow water through it
pore space
the amount of ‘free space’ within a material (e.g soil, rocks)- the gaps between solid particles
meander
a bend in a river
5-80 km thick
how thick is earth’s crust
2800 km thick
how thick is earth’s mantle
2100 km thick
how thick is earth’s outer core
1300 km thick
how thick is earth’s inner core
longitude
east to west
latitude
north to south
constuctive plate boundary
new crust is created here
destructive plate boundrary
crust is destroyed here
earthquake
a sudden release of stored energy in the earth’s crust. as tectonic plates rub, it creates friction and pressure between the 2 plates. when the pressure becomes too large, plates suddenly slip, causing shaking on the surface.
volcano
an opening in the earths crust, allows hot magma and ash to escape. molten rock from mantle rises to surface, normally 1-10 km underground. pressure builds in the chamber and is released through volcanic eruption.
natural hazard
a naturally occurring event, like an earthquake or flood, that poses a threat to people, property, or the environment
mantle
the thickest layer of Earth, situated between the crust and the core, and comprises mostly solid, hot, and dense rock that behaves like a viscous fluid over long periods.
plate boundrary
the location where two or more tectonic plates meet, and it's characterised by significant geological activity like earthquakes and volcanoes.
focus
the point within the Earth where the earthquake rupture starts, and where the seismic waves originate
Richter Scale
the scale which you use to measure how big an earthquake is
magma chamber
The location beneath the vent of a volcano where molten rock (magma) is stored prior to eruption
ash cloud
the cloud of ash which comes from a volcano after it erupts
tectonic hazard
a natural event, like an earthquake or volcanic eruption, caused by the movement and interaction of the Earth's tectonic plates
crust
the planet's outermost solid shell, comprising two types: continental and oceanic, and is the layer where we live and where most natural resources are found
magma
molten rock that exists beneath the earth’s surface
main vent
the central channel or opening in a volcano through which magma, rock fragments, and volcanic gases erupt from the Earth's surface
Mid- Atlantic ridge
a divergent plate boundrary in the atlantic ocean
core
the Earth's innermost layer, a sphere composed of a solid inner core and a liquid outer core, primarily made of iron and nicke
tectonic plate
a massive, irregularly shaped slab of solid rock comprising Earth's crust and upper mantle, which move independently and are responsible for geological activity like earthquakes and volcanoes.
epicentre
the point where an earthquake starts underground
seismic waves
the shockwaves made by earthquakes
crater
a bowl- or funnel-shaped depression that usually lies directly above the vent from which volcanic material is ejected
lava flow
streams of molten rock that pour or ooze from an erupting vent
geothermal energy
all energy stored in the form of heat beneath the surface of the solid earth
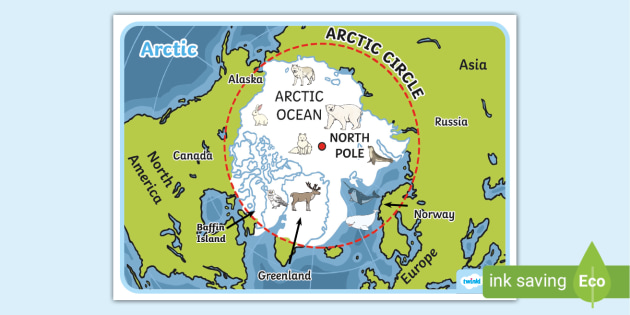
what is this a diagram of
the arctic
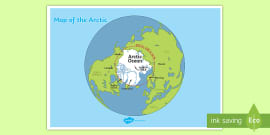
what is this a diagram of
antarctica
of the north
what does ARKITOS mean
name 1 difference between the arcitc and antarctica
arctic is an ocean surrounded by land. Antarctica is a continent surrounded by oceans
they both have extreme cold temperatures
name 1 similarity between the arctic and antarctica
Belarus, Russia, Kazakhstan
name 3 countries that used to be a part of the Soviet Union
name 3 key elements of weather
air pressure, wind direction, precipitaiton
weather
the day to day change in the atmosphere.
climate
the average weather, calculated from a period of 30 or more years
population density
the average amount of people living in one km2 of a country
population distribution
the pattern of where people live
describe the population density of Russia
in the south west it is very densly populated because of the capital city being there as well as being closer to europe. in the north east, it is very sparsely populated because there is less resources and it is colder
diaspora
the spread or migration of people from their original homeland
superpower
a very powerful or influential country that has a great deal of control over it’s neighbours
warm-water port
a port where water does not freeze in winter, which allows ships to use it throughout the year
kievan rus
a group of historic kingdoms which eventually merged to form russia
trade bloc
a group of countries that work together to trade with each other and to protect their economies from other outside countries
allys
a country that cooperates with another for military or other purposes
soviet union
a larger country which was a communist country
indigenous tribes
native animals
global warming
give 3 impacts oil drilling in the arctic could have
66 ½ degrees North
the arctic circle coordinates
66 ½ degrees south
antarctic circle
Russia is one of the world’s largest producers of oil and gas
give me 1 fact about russia’s oil and gas