the periodic table + bonding
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
what is an atom?
smallest particle of a chemical element that can exist
what is a molecule?
two or more atoms chemically bonded together
what is the relative charge and mass of a proton neutron and electron
proton relative charge = 1
proton relative mass = 1
neutron relative charge = 0
neutron relative mass = 1
electron relative charge = -1
electron relative mass = 1/1836
what is the atomic number?
number of protons/electrons
what is the mass number?
the total number of protons and neutrons
what is the nucleon number?
same as mass number ie. total number of protons and neutrons
how is the number of protons/electrons in an atom calculated
same as atomic number
how is the number of neutrons in an atom calculated?
mass number - atomic number
what is an isotope?
atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
what is the relative atomic mass?
the ratio of the average mass of one atom of an element compared with 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
how do you calculate the Ar of an element from the relative abundance of a particular isotope?
(% of isotope 1 × mass of isotope 1) + (% of isotope 2 × mass of isotope 2)/100
describe the layout of the periodic table
elements arranged in order of atomic number
hydrogen by itself
metals found left of stepped line
non-metals found right of stepped line
what is the period number of the periodic table?
tells you the number of shells of electrons
what is the group number of the periodic table?
tells you the number of electrons in the outer shell
eg. F has 7 electrons in its outer shell and is therefore in group 7
give the electronic configurations of sodium, oxygen, chlorine and magnesium
Na = 2,8,1
O = 2,6
Cl = 2,8,7
Mg = 2,8,2
Define malleable
may be hammered into shape
define ductile
may be drawn into a wire
describe the properties of metals
good conductors of heat and electricity
shiny
malleable
sonorous
ductille
form positive ions in ionic compounds
partake in ionic bonding
form basic oxides
solids at room temperature (except mercury)
describe the properties of non-metals
poor conductors
brittle
form negative ions in ionic compounds
partake in ionic and covalent bonding
form acidic oxides
why do elements in the same group have similar properties?
same number of electrons in outer shell
why are noble gases (group 0) unreactive?
they have a full outer shell of electrons
stable
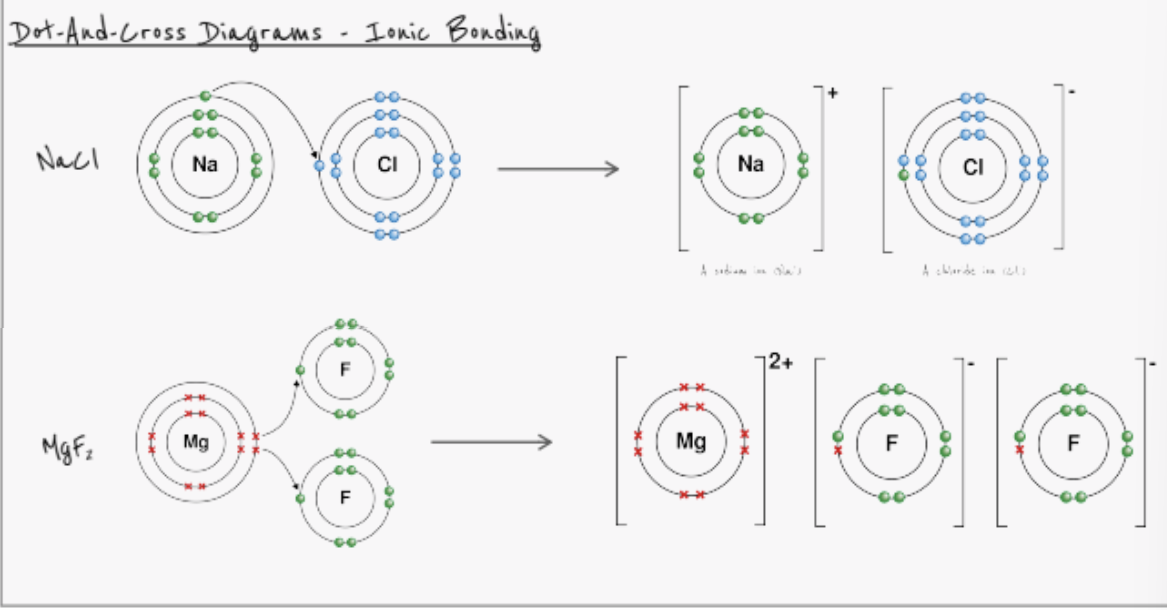
how is an ion formed?
an atom loses or gains electrons
loses electron —→ forms positive ion
gains electron —→ forms negative ion
when working out the charge on an ion, remember:
for groups 1-3, the charge on the ion is the same as the group number
eg. Mg is in group 2 and therefore forms Mg 2+
for groups 5,6,7, the charge on the ion is 8 - group number
eg. N is in group 5 8-5 = 3 , there for N 3-
what are some positive ions (cations)
H+
Ag+
Cu2+
Fe2+
Fe3+
Pb2+
Zn2+
NH4
what are some negative ions (anions)?
OH-
NO3-
CO3^2-
SO4²-
what is an ionic bond?
electro static force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
forms between a metal and a non-metal
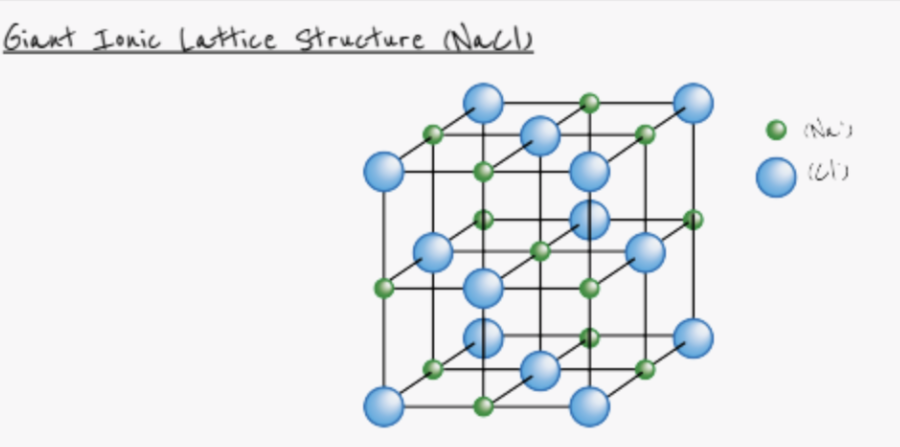
give the properties of giant ionic lattices
high melting and boiling points
conduct electricity when molten/dissolved in aqueous solution
brittle
why do ionic structures have high melting and boiling points?
form giant ionic lattices
strong electro static forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
requires lots of energy to break
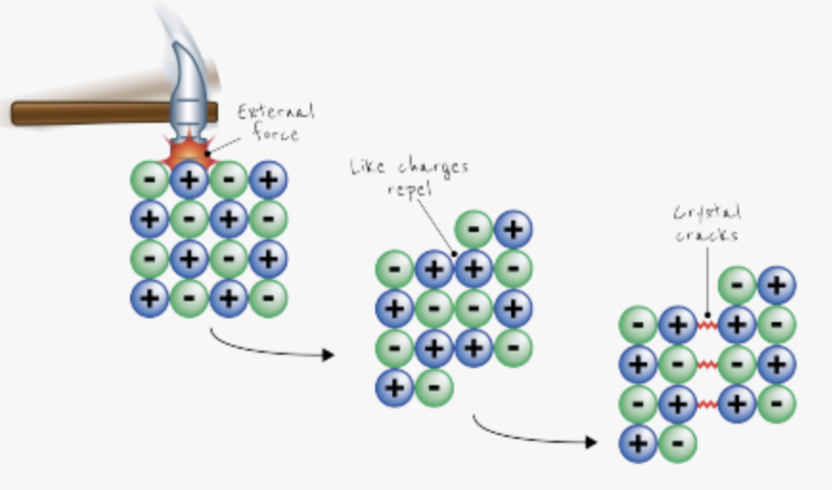
why dont ionic substances conduct electricity when solid?
ions are held tightly in fixed positions
not free to move
why do ionic substances conduct electricity when molten/dissolved?
ions are free to move
can carry electric charge
explain why ionic substances are brittle
applying force causes ions to move
like charges align and repel
lattice structure breaks apart
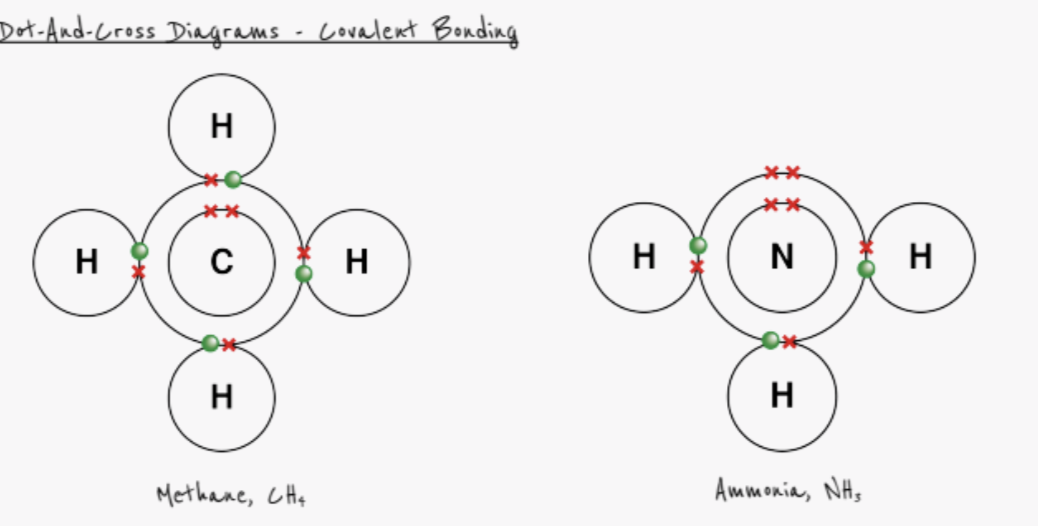
what is a covalent bond?
basic definition: a pair of electrons shared between two atoms
detailed definition: strong electrostatic forces of attraction between nuclei (positively charged) and shared pair of electrons (negatively charged)
form between two non-metals
what is a simple molecular substance?
small, covalently bonded molecule
H2O CO2
define intermolecular force
temporary weak attraction between different molecules
why do simple molecular substances have low melting points?
weak intermolecular forces of attraction
do not require a lot of energy to overcome
why does the boiling point of simple molecular substances increase with increasing relative molecular mass?
boiling overcomes the intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules
greater Mr = greater intermolecular forces of attraction to be overcome
more heat energy needed to overcome these forces
why dont simple molecular substances conduct electricity?
no overall electric charge
no free electrons
define giant covalent structure
large lattice of covalently bonded atoms
eg. graphite silicon dioxide
what is an allotrope?
different forms of the same element in the same physical state
give 3 allotropes of carbon
diamond
graphite
C60 fullerene
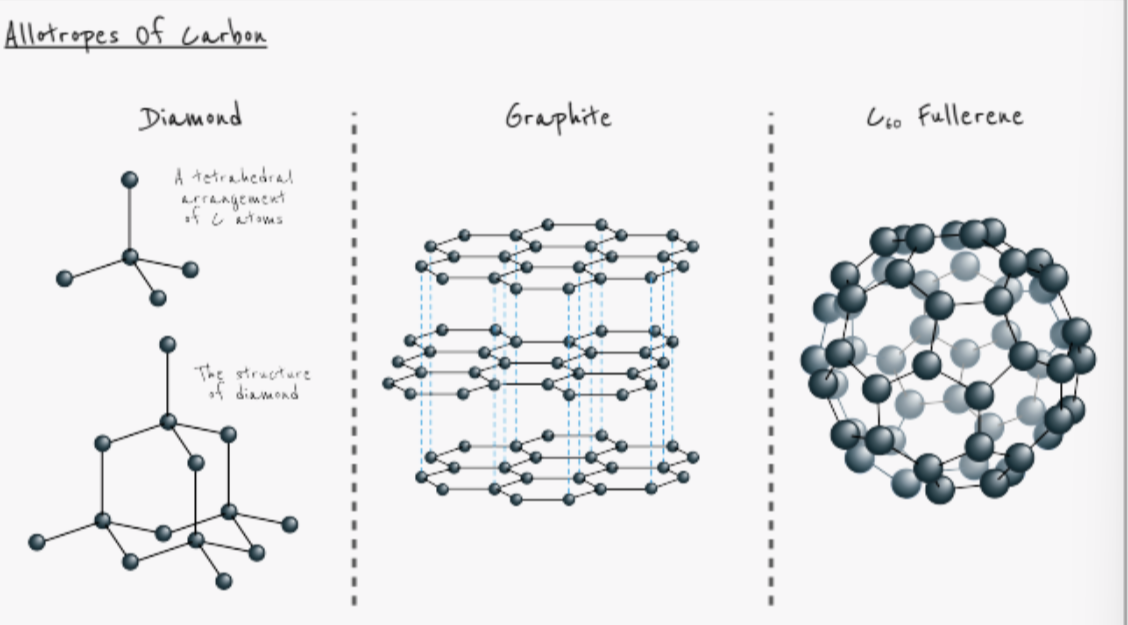
why does diamond have such a high melting point?
giant covalent structure
each carbon atom covalently bonded to 4 others
many strong covalent bonds
require lots of energy to break
why dont most covalent substances conduct electricity?
no free electrons
each electron in outer shell is bonded
why doesnt diamond conduct electricity?
no free electrons
each electron in outer shell is bonded
why does graphite have such a high melting point?
many strong covalent bonds
require lots of energy to break
why does graphite conduct electricity?
each carbon atom is only bonded to 3 others
4th electron free to move - delocalised pool of electrons
why is graphite used as lubricant?
carbon atoms are arranged in layers
layers held together by weak intermolecular forces
do not require a lot energy to break
layers slide off eachother
why does C60 fullerene have a lower melting and boiling point than graphite and diamond?
simple molecular structure
weak intermolecular forces
require little energy to break
why does C60 fullerene not conduct electricity?
although each carbon atom is only bonded to 3 others, 4th electron not free to move
stays within each C60 molecule