Connective Tissues and its types
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
connective tissue
bind, support, protect, serve as frameworks, fill spaces, store fat, produce blood cells, protect against infection, and repair tissue damage.
2. Unlike epithelial tissues, BLANK have abundant matrix, or intercellular material, throughout, and have good blood supplies (except cartilage).
fibroblast
most common cell type, and is a fixed, star-shaped cell that secretes fibers and is large in size.
wandering macrophages
scavenger cells and defend against infection.
mast cells
large and are located near blood vessels where they release heparin (anticoagulant) and histamine (promotes inflammation).
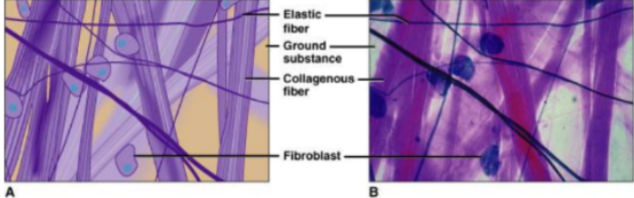
connective tissue fibers
1. Strong collagenous fibers (white fibers), made of the protein collagen, add strength for holding body parts together.
2. Elastic fibers (yellow fibers), made of the protein elastin, are stretchy and add flexibility to certain types of connective tissues.
3. Reticular fibers are thin collagenous fibers that form supportive networks in a variety of tissues.
strong collagenous fibers
(white fibers), made of the protein collagen, add strength for holding body parts together.
elastic fibers
(yellow fibers), made of the protein elastin, are stretchy and add flexibility to certain types of connective tissues.
reticular fibers
thin collagenous fibers that form supportive networks in a variety of tissues.
loose connective tissue
forms delicate, thin membranes throughout the body that bind body parts together such as skin and underlying organs.
2. The majority of the cells are fibroblasts that are separated by a gel-like ground substance that contains collagenous and elastic fibers.
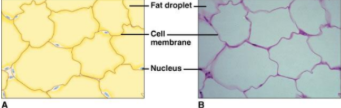
adipose tissue
1. loose connective tissue designed to store fat.
2. found beneath the skin, around joints, padding the kidneys and other internal organs, and in certain abdominal membranes.
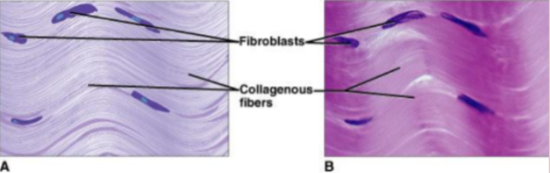
dense connective tissue
1. consists of DENSELY packed collagenous fibers and is very strong but lacks a good blood supply.
2. It is found as part of tendons and ligaments.
1. a rigid connective tissue that provides a supportive framework for various structures. It lacks a vascular system and so heals slowly.
5 types of BLANK (CCHEF)
2. Cartilage cells (chondrocytes) lie within lacunae in the gel-like fluid matrix.
3. Cartilaginous structures are enclosed within a connective tissue perichondrium.
4. The most common, hyaline cartilage, is white with abundant fine collagen fibers, is found at the ends of bones, and supports respiratory passages.
5. Elastic cartilage, with elastic fibers, provides a framework for the external ears and parts of the larynx.
6. Fibrocartilage, with many collagenous fibers, is a tough tissue that provides a shock-absorbing function in intervertebral disks, knees and pelvic girdle.
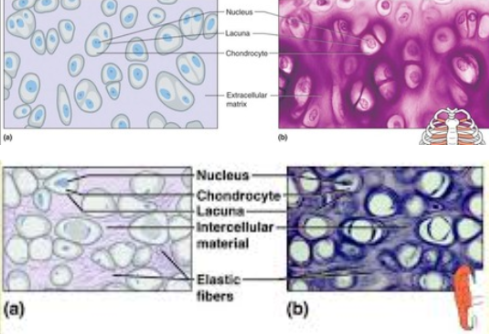
chondrocytes
Cartilage cells lie within lacunae in the gel-like fluid matrix.
perichondrium
cartilage structures are enclosed within a connective tissue BLANK.
hyaline cartilage
The most common, BLANK cartilage, is white with abundant fine collagen fibers, is found at the ends of bones, and supports respiratory passages.
elastic cartilage
BLANK cartilage with elastic fibers, provides a framework for the external ears and parts of the larynx.
fibrocartilage
cartilage, with many collagenous fibers, is a tough tissue that provides a shock-absorbing function in intervertebral disks, knees and pelvic girdle.
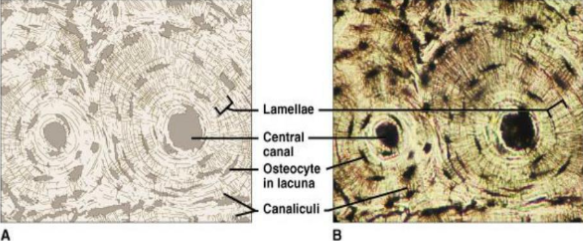
bone
1. BLANK is the most rigid connective tissue, with deposits of mineral salts and collagen within the matrix.
internally supports the body, protects, forms muscle attachments, and is the site for blood cell formation.
3. BLANK cells, called osteocytes, lie within lacunae and are arranged in concentric circles (osteons) around osteonic canals interconnected by canaliculi.
4. BLANK has a good blood supply, enabling rapid recovery after an injury.
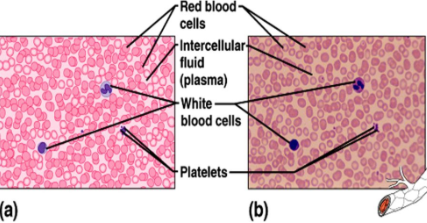
blood
composed of cells (red and white) suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma.
functions to transport substances throughout the body.