Reproduction
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Sexual reproduction?
The process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote.
How do offspring produced by sexual reproduction differ from each other?
They are genetically different from each other.
How many parent organisms are required for sexual reproduction?
Two parent organisms.
What process produces gametes in sexual reproduction?
Gametes are produced through meiosis.
What happens to the offspring after fertilization in sexual reproduction?
The offspring develops through mitotic cell divisions.
What genetic relationship do offspring produced by sexual reproduction have with their parents?
They share half of the DNA from each parent.
What is a disadvantage of sexual reproduction in terms of speed?
Sexual reproduction is a relatively slow reproduction process.
How does variation from sexual reproduction benefit populations?
It provides a survival advantage to the population.
What is asexual reproduction?
The process resulting in genetically identical offspring being produced from one parent.
What is the role of gametes in asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction does not involve gametes or fertilization.
What is the genetic relationship of offspring produced by asexual reproduction?
They are genetically identical to the parent and each other.
How does the speed of asexual reproduction compare to sexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction occurs much more quickly and efficiently than sexual reproduction.
What is a disadvantage of asexual reproduction regarding genetic variation?
Lack of genetic variation makes populations more vulnerable to disease or environmental change.
How do bacteria reproduce asexually?
Bacteria produce exact genetic copies of themselves in a type of asexual reproduction
What are gametes?
gametes are sex cells produced by meiosis
What are the male and female gametes in animals?
The sperm and ovum
How many chormosomes do human gamtes contain?
23 (half the number of chromosomes)
What adaptations do sperm cells have for successful fertilization?
Sperm cells have a tail for propulsion and mitochondria for energy.
Adaptations of egg cell for early embryo developmet?
Egg cells have neergy sotres within the cytoplasm
Fertilisation?
Fusion of male and female gamete to produce a zygote
Zygote after fertilisation?
The zygote divides by mitosis to develop into an embryo
Where does fertilisation occur in humans?
In the oviduct, sperm meets and egg cell.
How many chromosomes does a human zygote contain
46 chormosomes
what happens during fertilisation in plants?
A pollen tube delivers the male nucleus into the ovary, gametes fuse.
Male gamets of plants?
Male gametes are found in pollem grains
Pollination?
The transfer of pollen from the male part of a flower to the female part.
Insect-pollinated plants asapted for pollination?
Large,bright petals and produce a scent and nectar.
Role of stigma in insect-pollinated plants?
Stigma collects pollen grains.
How are wind and insect pollinated plants different?
Wind pollinated have anthers that hang outside the flower and feathery stigmas.
What happens after pollination?
The pollen tube forms to deliver the male nucleus to the egg cell in the ovary,.
What does the ovule develop into after fertilisation?
Ovule develops into a seed
what do fruits provide for seeds?
Fruits provide a mechanism for seed dispersal
Differnce between pollination and fertilisation?
Pollination is pollen landing on the stigma. fertilisation is the fusion of the male and femlae nuclei.
Three factors for germination?
water- activates enzymes for growth
oxygen- respiration to provide energy
warmth- boots enxyme activity and improves germination
Effect of carbon dioxide on germination?
none.
germination?
beginning of seed growth
what do seeds contain that develop into an embryo
a zygote
role of cotyledons during germination?
The cotyledone store food for the seedling
what happens to seed coat during germination?
water absorption splits the seed coat
first structures to emerge from gerinating seeds?
The plumle and radical
asexual reproduction in plants?
one parent involved
Offspring are exact genetic copies
can occur naturally or be controlled artificially
natural method of asexual reporduction?
runners
how do runner contribute to asexual reproduction?
they grow sideways and develop plantlets that can grow roots
The method of taking cuttings in artificial asexual reproduction?
a section of the parent plant with a new bud is cut off
function of the prostate gland?
produces fluid called semen that provides sperm cells with nutrients
role of the scrotum?
to support the testes outside the body
hormone that causes uterine wall to thicken?
oestrogen
which hormone is at it’s peak during the menstrual cycle?
peak oestrogen levels
role of FSH in the menstrual cycle?
causes an egg to start maturing in the ovary
if egg is not fertilised?
corpus leteum breaks down, progestrone levels drop, and mensutruation occurs
role of placenta in preganancy?
Enables exchange of substances between mother and fetus
Connects the embryo's blood supply to the placenta via the umbilical cord
Acts as a barrier to some toxins and pathogens
What substances travel from the mother's blood to the fetus?
Oxygen, nutrients (e.g., glucose, amino acids, mineral ions)
function of amniotic fluid?
protects the embryo during development, acts as a cushioing
What are secondary sexual characteristics and how are they developed?
Changes during puberty
Controlled by hormones: oestrogen in females and testosterone in males
Examples include breast development in females and muscle growth in males
average length of menstrual cycle?
28 days
What happens to the uterine lining after menstruation finishes?
It starts to thicken again in preparation for possible implantation
What hormone is responsible for maintaining the uterine lining during pregnancy?
Progesterone
What is the role of testosterone in males during puberty?
It stimulates the growth of facial and body hair and muscle development
first structure to form after fertilisation?
The zygote
What is the significance of the umbilical cord?
It connects the embryo's blood supply to the placenta
What can pass through the placenta from the mother to the fetus?
Oxygen and nutrients
What is the effect of nicotine and alcohol on the fetus?
They can pass across the placenta, cause developmental issues or lead to miscarriage
role of amniotic sac?
contains amniotic fluid
At what age does the menstrual cycle typically start in females?
aorund 12 years
What happens to the uterine lining if the egg is fertilized?
The uterine lining is maintained for the developing fetus
hormose released when osetrogen levels peak?
LH (lutenising hormone)
What is the role of the corpus luteum after ovulation?
It produces progesterone to maintain the uterine lining
What happens to the corpus luteum if the egg is not fertilized?
It breaks down
significance of the menstrual cycle in females?
prepares body for potential pregancy each month
average duration of menstruation
5-7 days
role of the ciliated cells in the oviducts?
They help push the released ovum towards the uterus
What is the function of the cervix during pregnancy?
To keep the developing fetus in place
What is the role of hormones in the development of secondary sexual characteristics?
They control the changes that occur during puberty
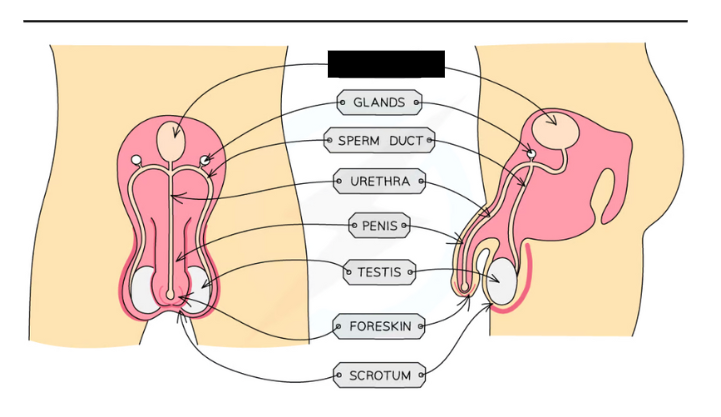
Label the structure and it’s functions
Prostate gland: Produces fluid called semen that provides sperm cells with nutrients
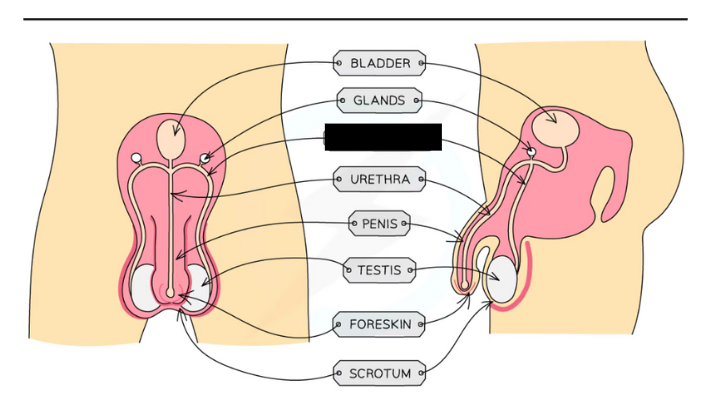
Label the structure and its functions
Sperm duct: Sperm passes through the sperm duct to be mixed with fluids produced by the glands before being passed into the urethra for ejaculation
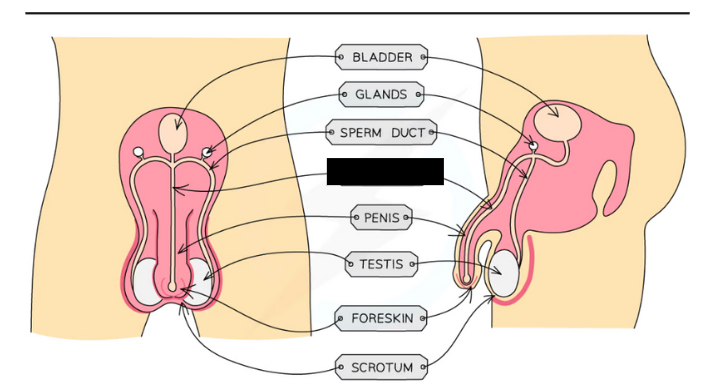
Label the structure and it’s functions
Urethra: Tube running down the centre of the penis that can carry urine or semen. A ring of muscle in the urethra prevents them from mixing
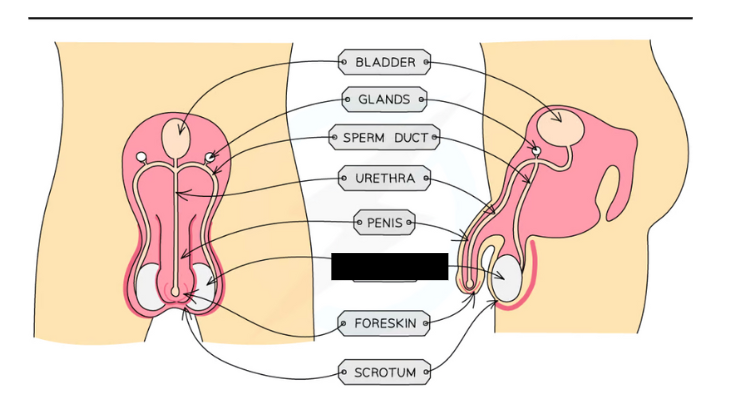
Label the structure and its functions
Testis: Contained in a bag of skin (scrotum) and produces sperm (male gamete) and testosterone (hormone)
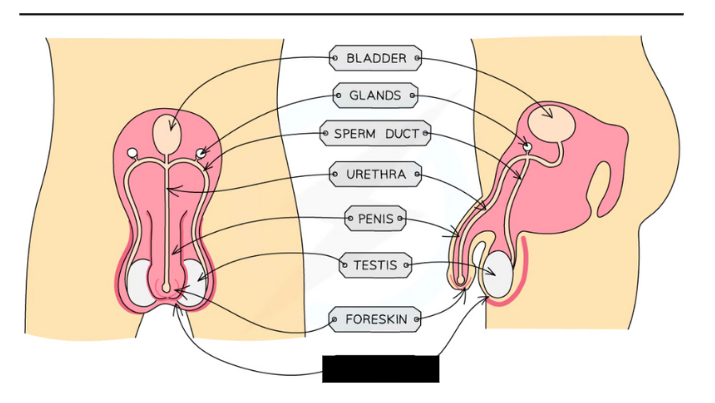
Label the structure and its functions
Scrotum: Sac supporting the testes outside the body to ensure sperm are kept at a temperature slightly lower than body temperature
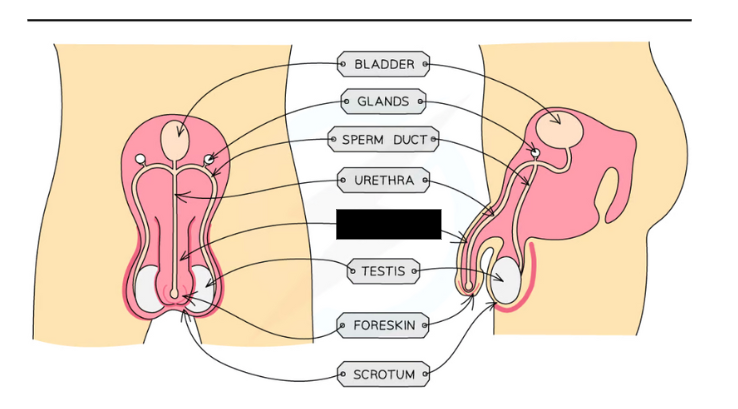
Label the structure and its function
Penis: Passes urine out of the body from the bladder and allows semen to pass into the vagina during sexual intercourse
Label the structure and its function
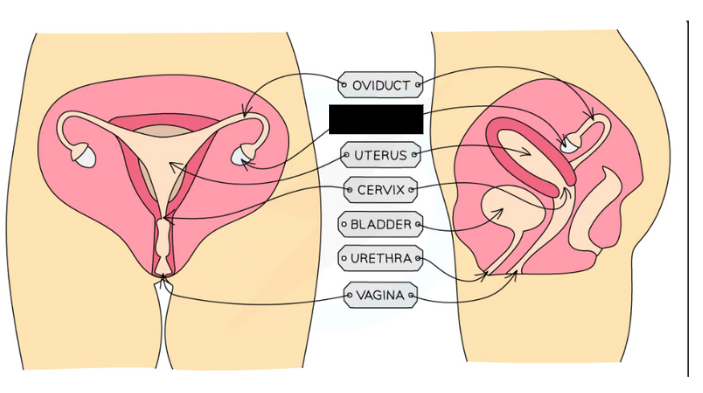
Oviducts: Connects ovary to the uterus, lined with ciliated cells to push released ovum, fertilisation occurs here
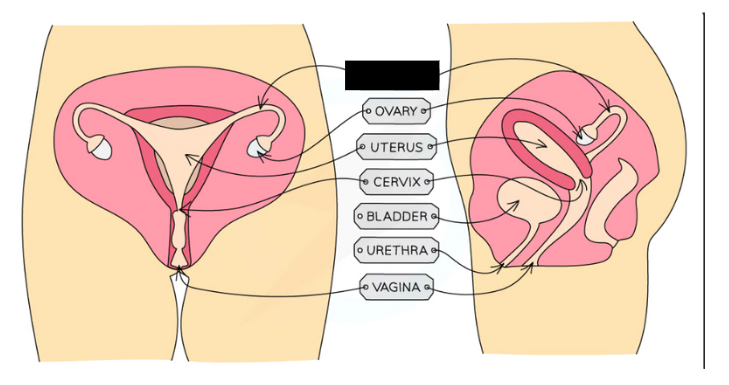
Label the structure and describe its functions
Ovaries: Contains ova (female gametes) that mature and develop when hormones are released
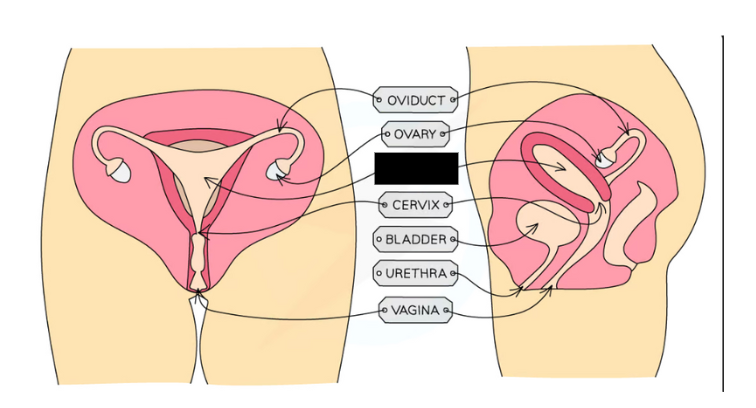
Label the structure and it’s functions
Uterus: Muscular bag with soft lining where fertilised egg (zygote) implants to develop into foetus
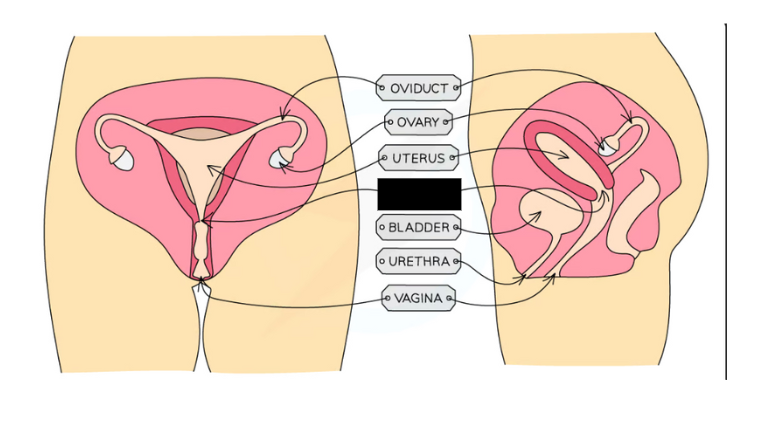
Label the structure and its functions
Cervix: Ring of muscle at the lower end of the uterus to keep the developing foetus in place during pregnancy
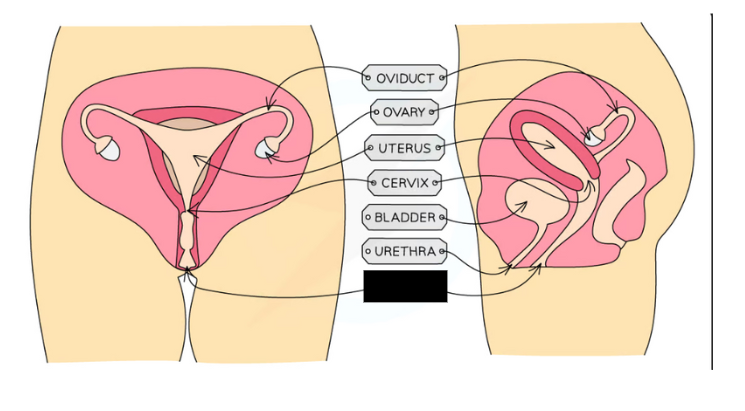
Label the structure and its functions
Vagina: Muscular tube leading to inside of woman's body, where male's penis enters and sperm are deposited during intercourse
Method for the practical on conditions for germination
Prepare 4 test tubes with 10 cress seeds on cotton wool, labeled A, B, C, and D
Tube A: Keep the cotton wool dry.
Tube B: Moisten the cotton wool with water.
Tube C: Cover the seeds and cotton wool with water and add a layer of oil on top.
Tube D: Moisten the cotton wool and place the tube in a fridge (~4°C).
Keep tubes A, B, and C at room temperature or around 20°C
After 3-5 days, ensure the cotton wool in tubes B and D stays moist
Compare the number of germinated seeds in each tube
Results of the practical
The test tubes are set up to test the necessity of water, oxygen, and warmth for germination by removing each factor in turn:
Tube A: Water is absent
Tube B: Control, all factors present
Tube C: Oxygen is blocked by oil and water layers
Tube D: Warmth is removed by refrigeration
As germination requires all three factors, only the seeds in the control tube (B) are expected to germinate