Biology Keystone Module 2
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
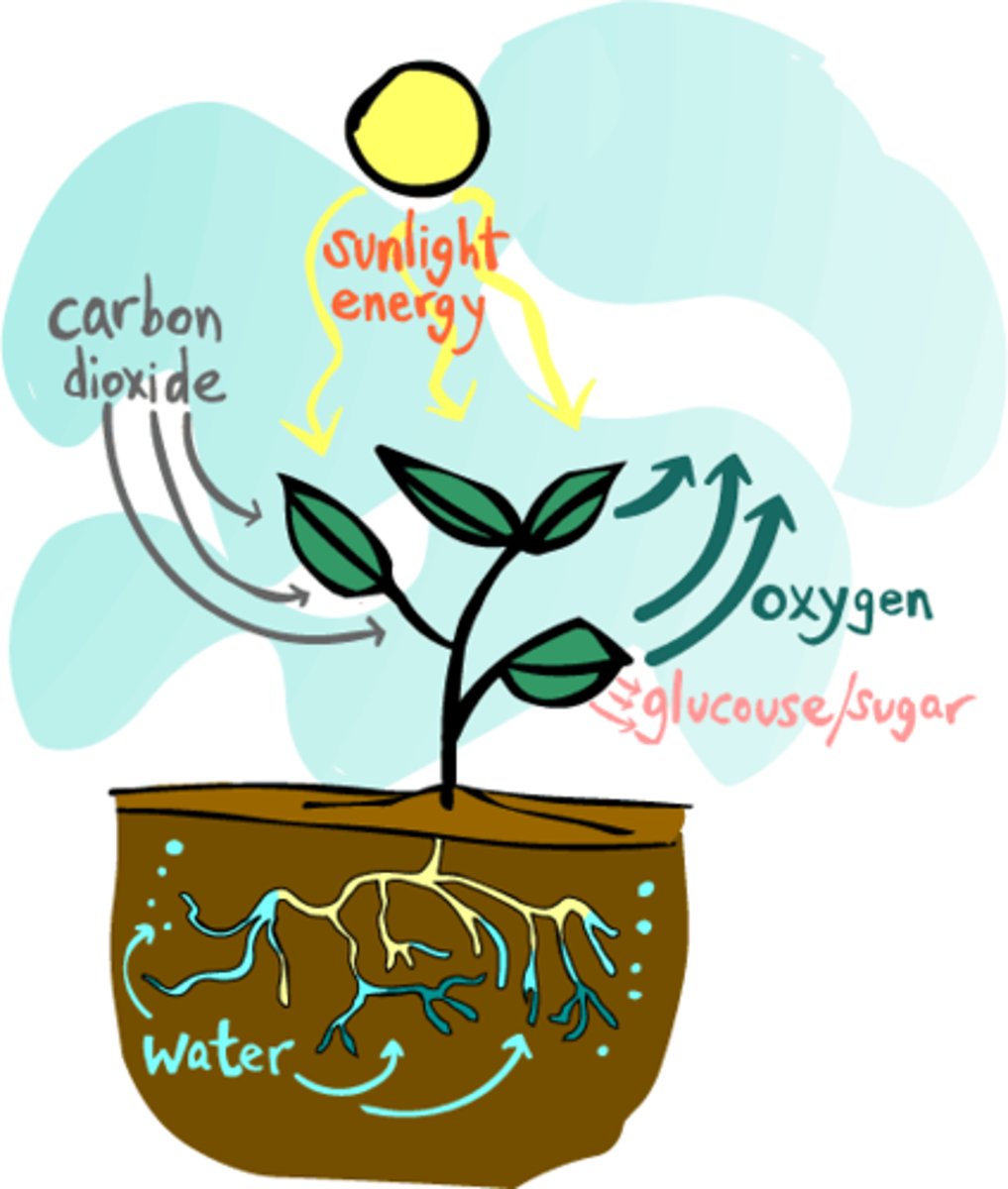
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun (and carbon dioxide and water) into chemical energy (sugar, and oxygen as a byproduct).
producer
An organism that can make its own food.

consumer
An organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms

decomposer
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms

cellular respiration
Process that releases energy (ATP, and water and carbon dioxide as a byproduct) by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen.

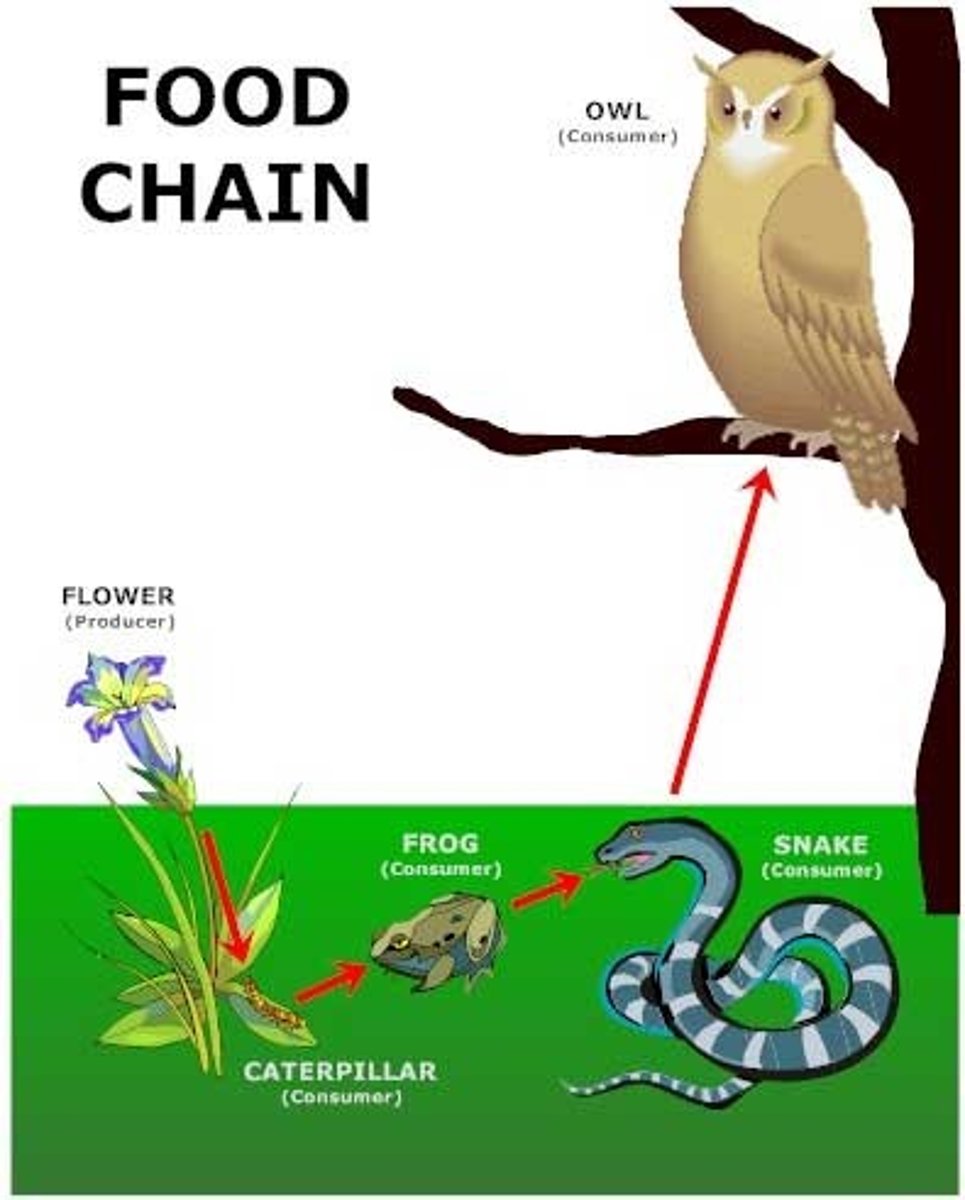
food chain
A series of events in which one organism eats another and obtains energy.
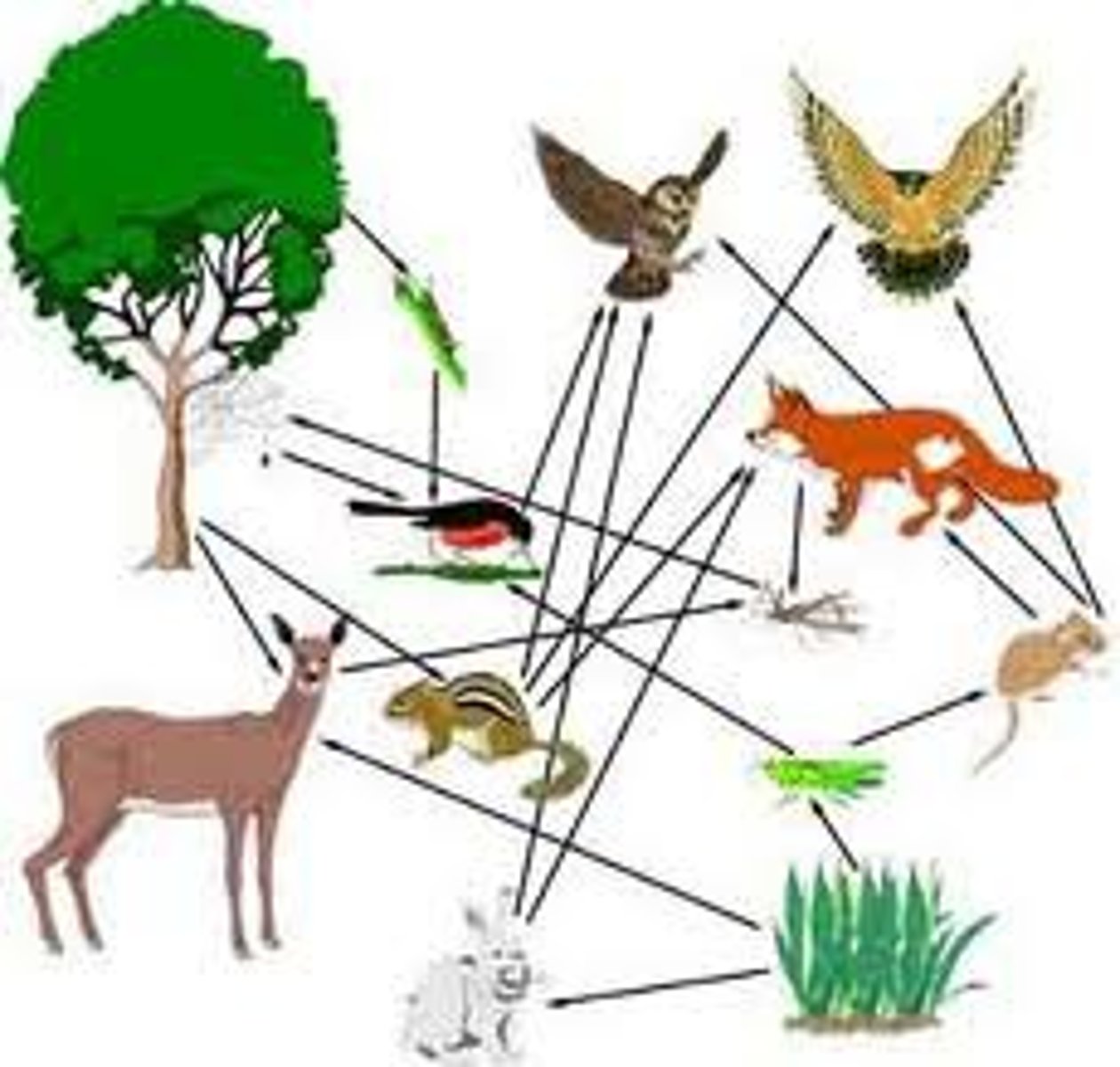
food web
A community of organisms where there are several interrelated food chains
trophic level
Each step in a food chain or food web
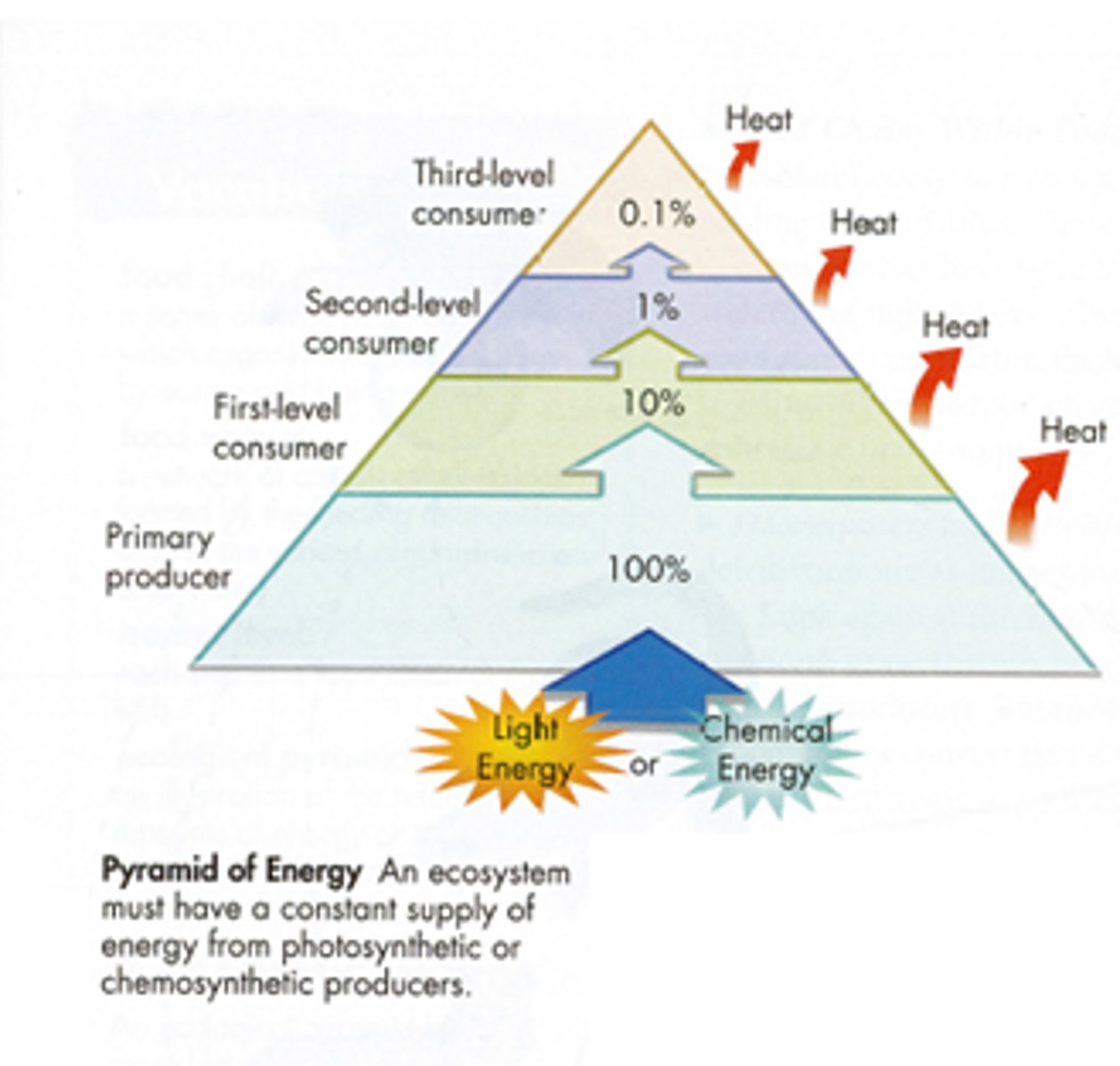
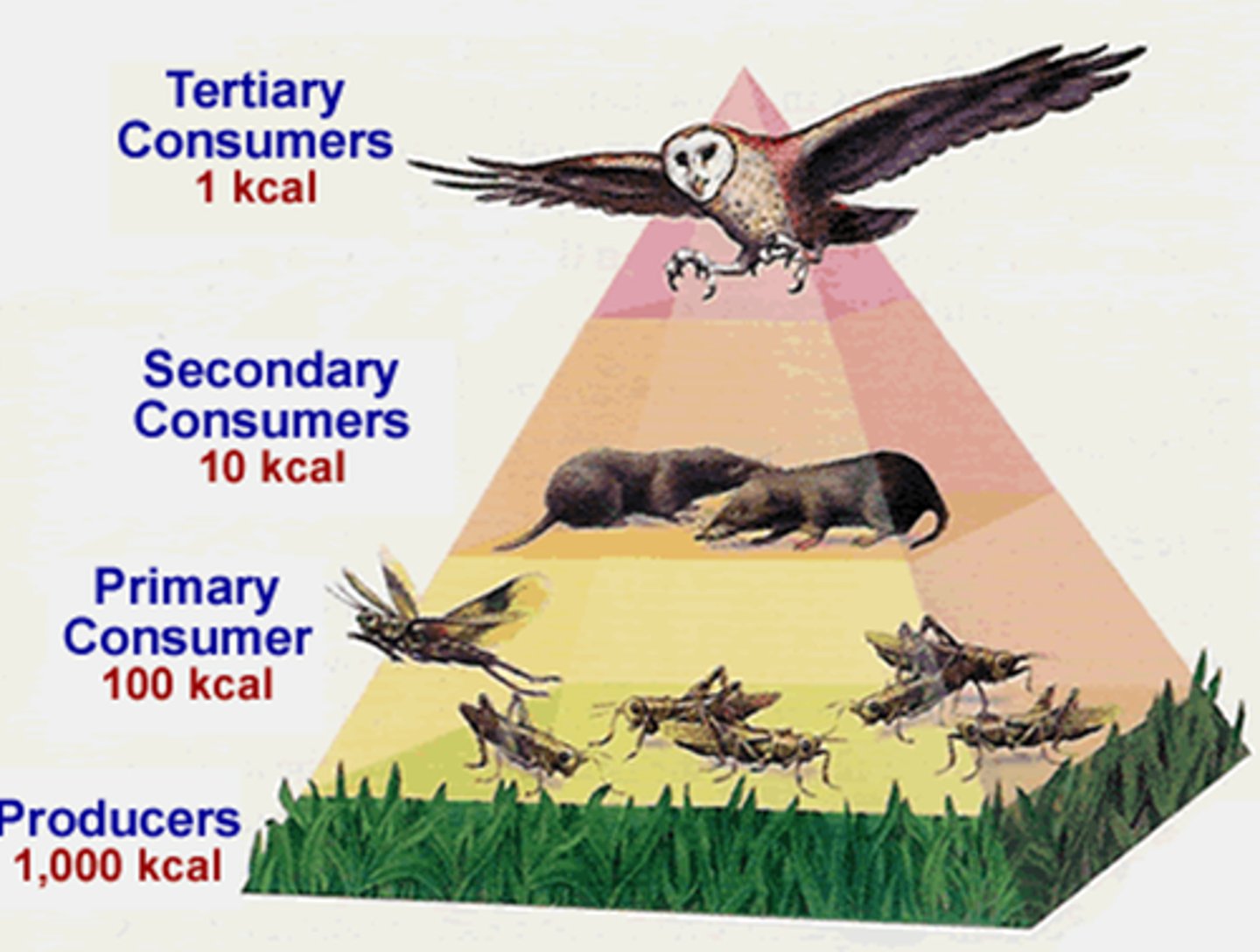
10% rule
Only 10% of the energy in one trophic level gets passed onto the next trophic level
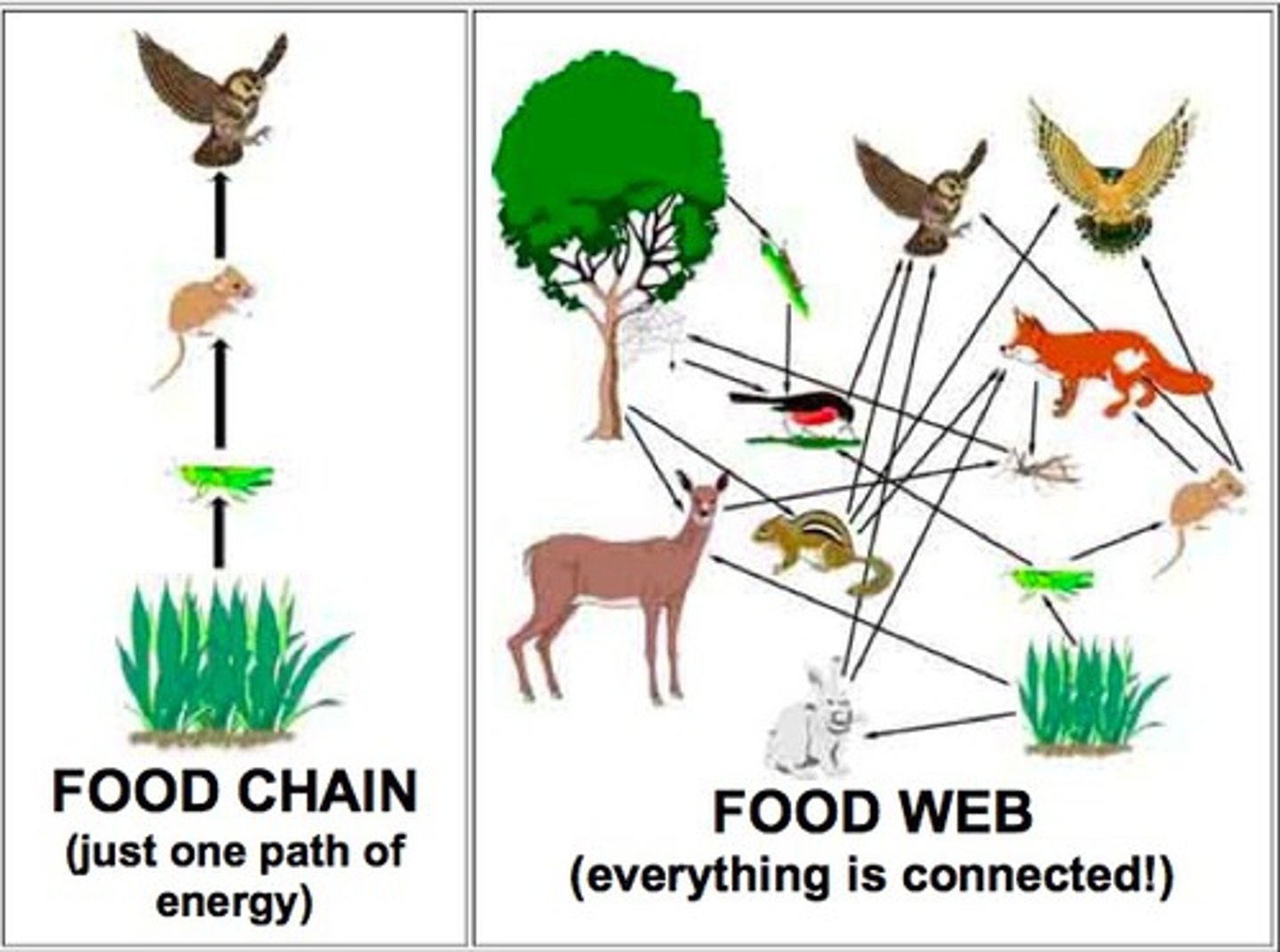
food chain vs food web
A food chain outlines who eats whom. A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem.
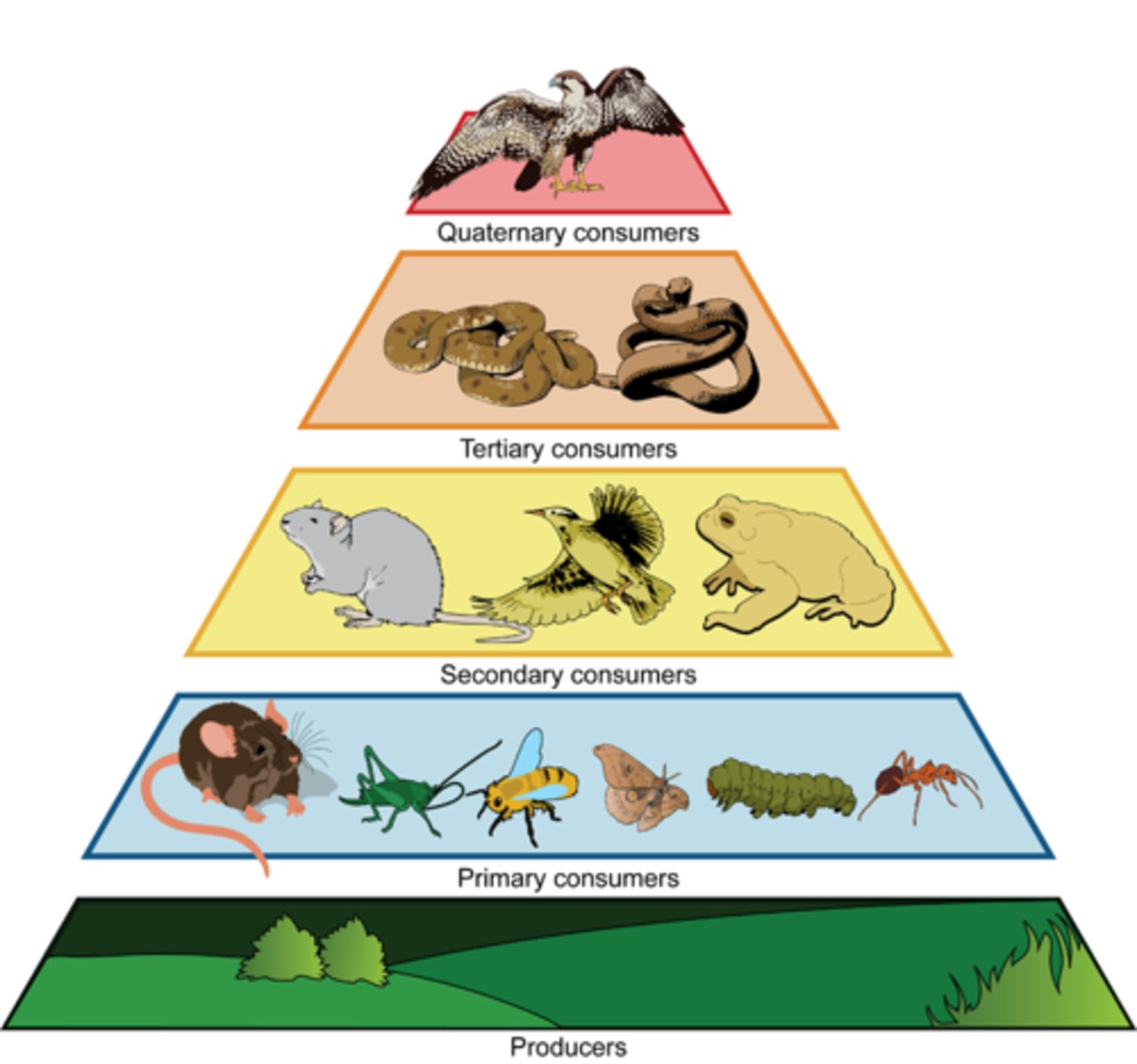
energy pyramid
A diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web
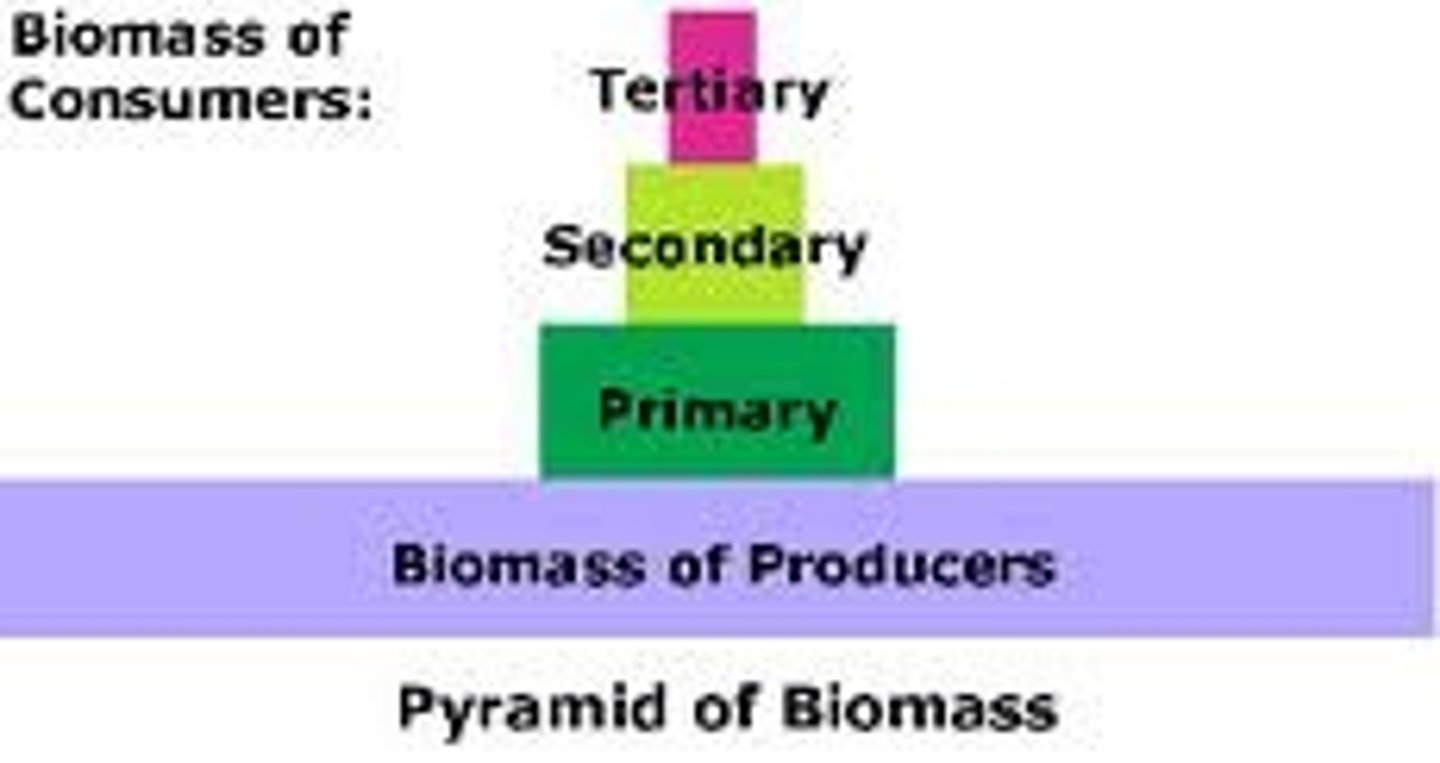
biomass pyramid
Diagram representing the biomass in each trophic level of an ecosystem
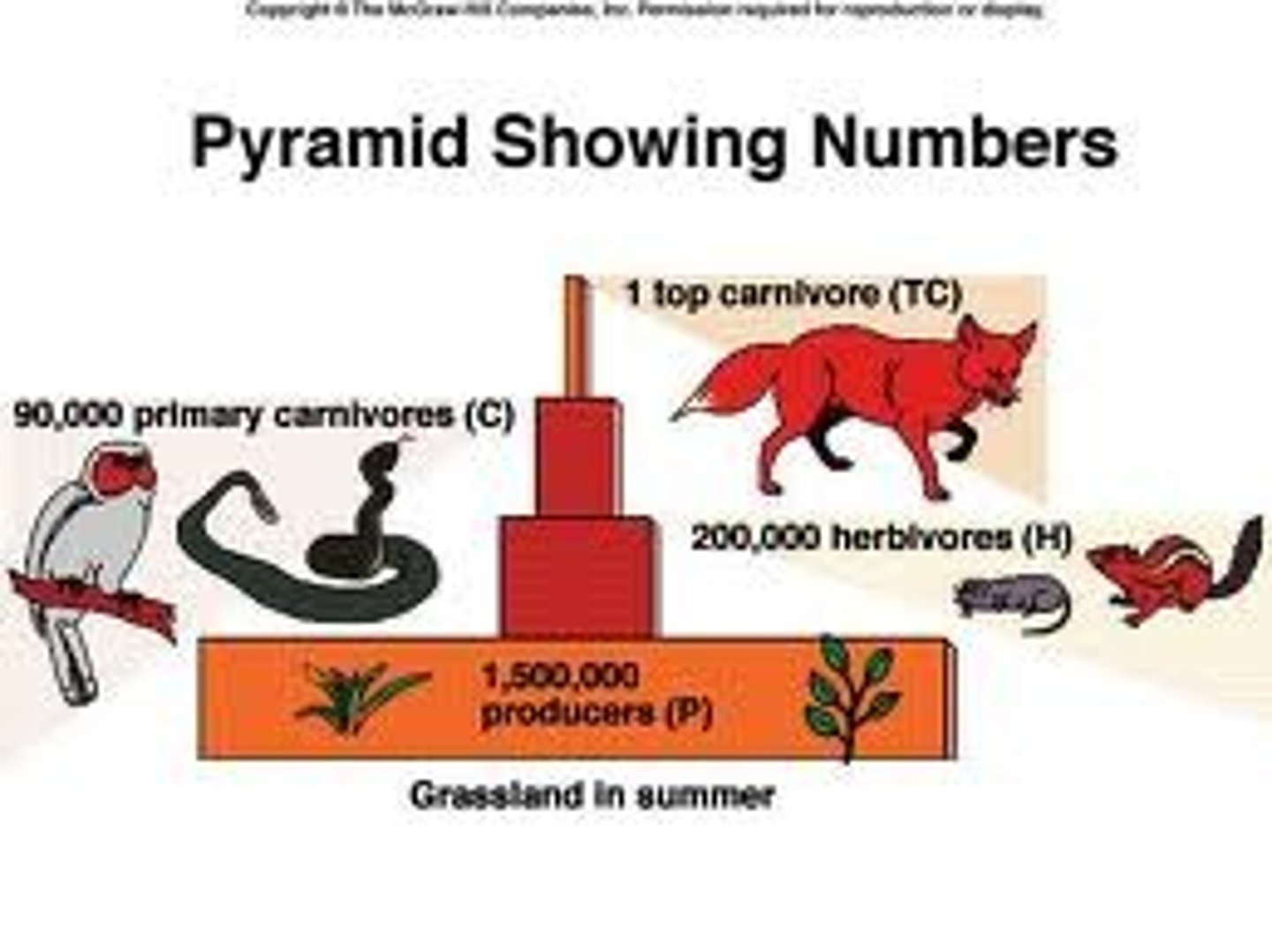
pyramid of numbers
representation of the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an ecosystem
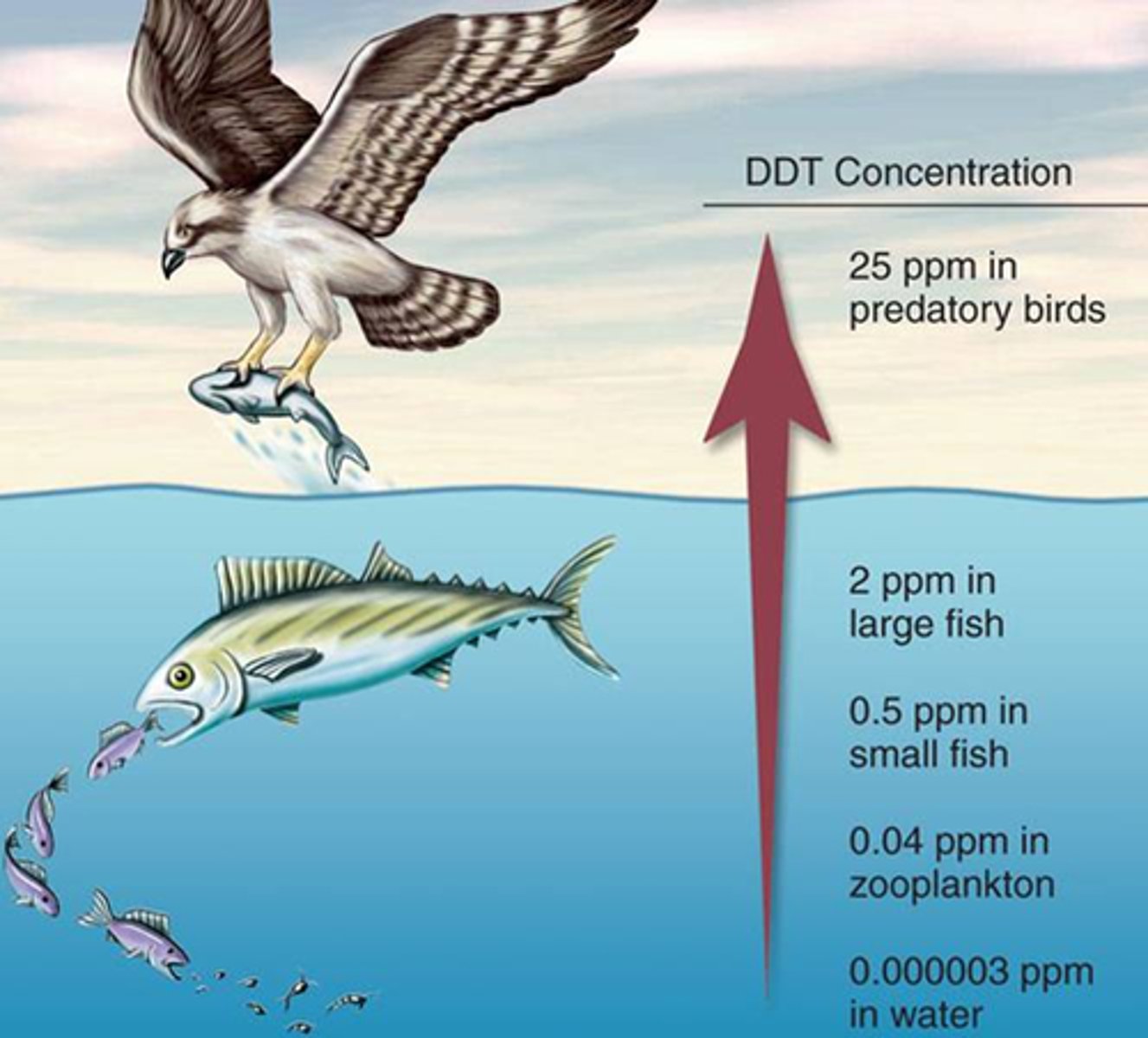
biomagnification
accumulation of pollutants at successive levels of the food chain
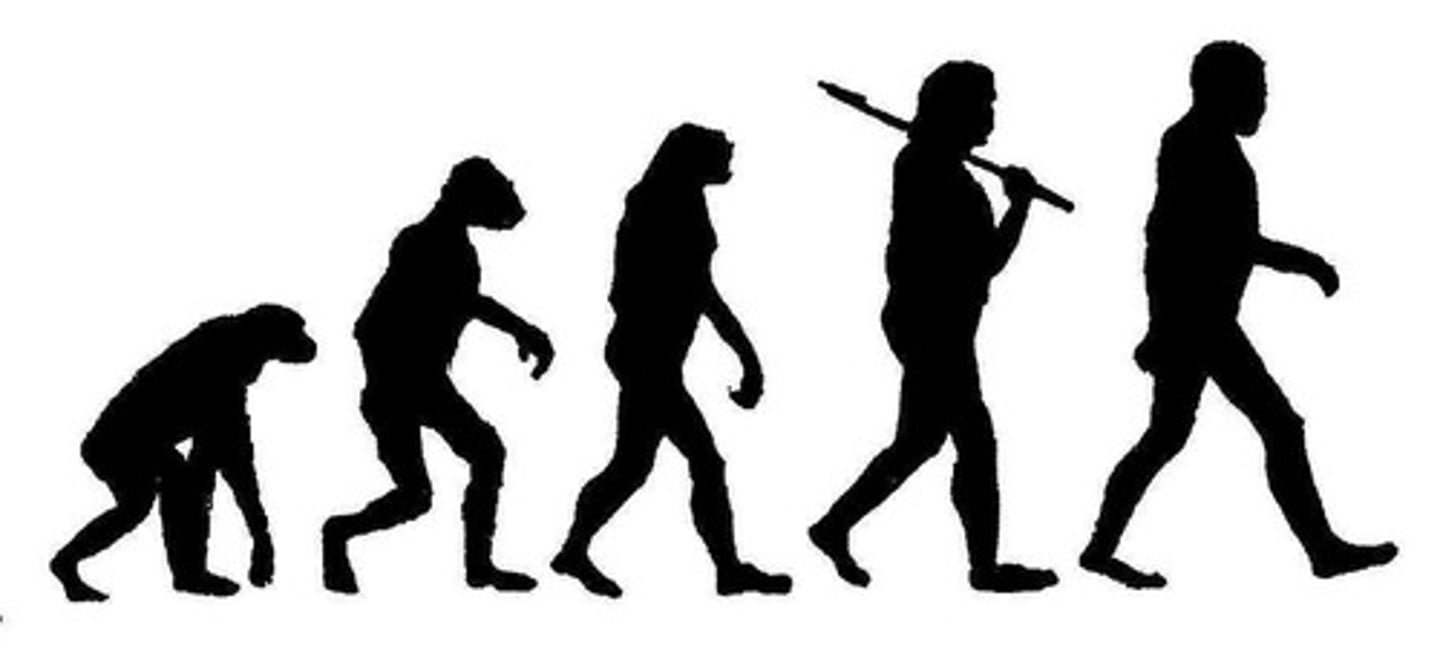
Evolution
The gradual change in a species over time
Natural Selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
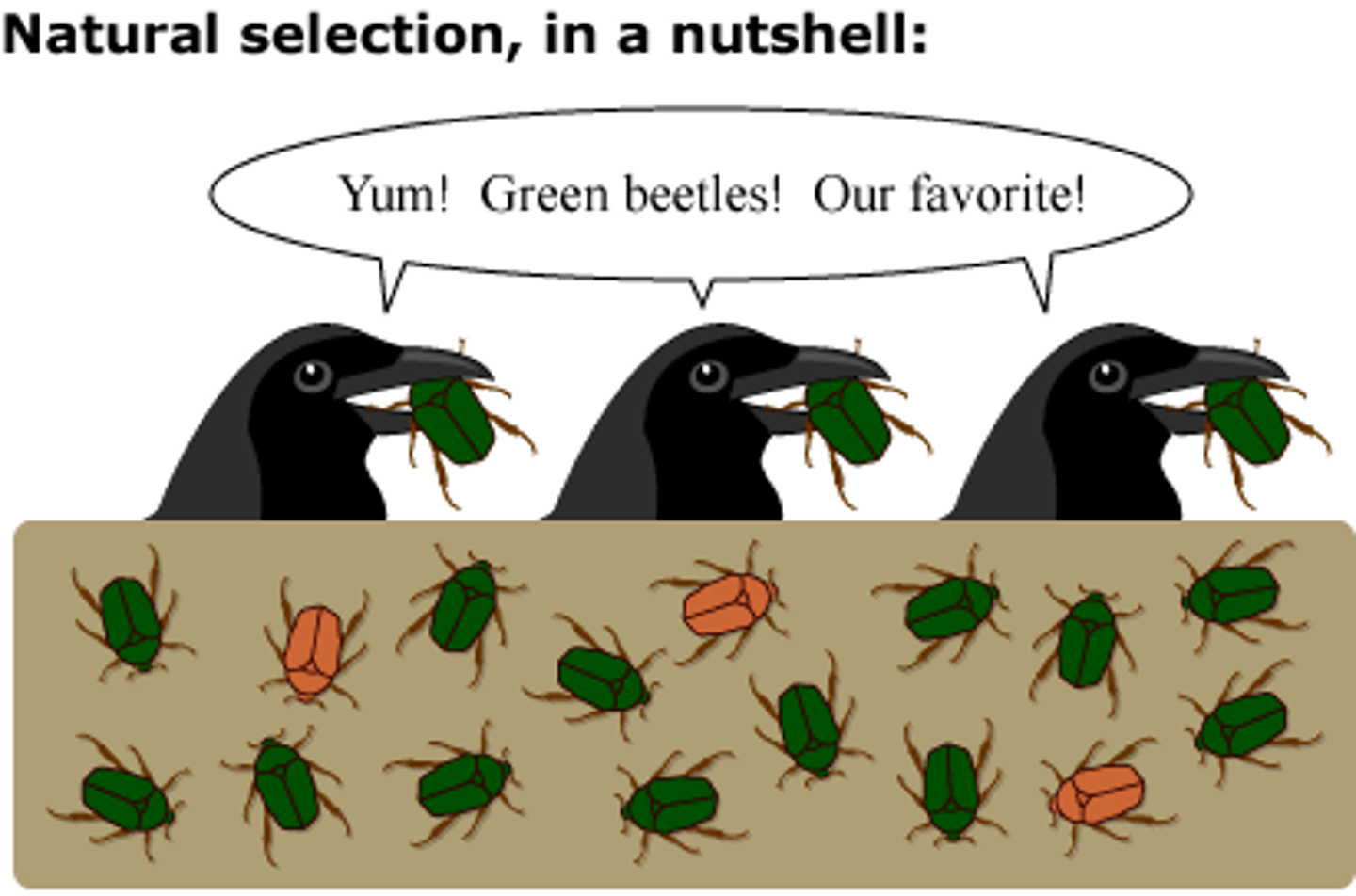
Differential Reproductive Success
better adapted individuals will more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass their traits on to the next generation

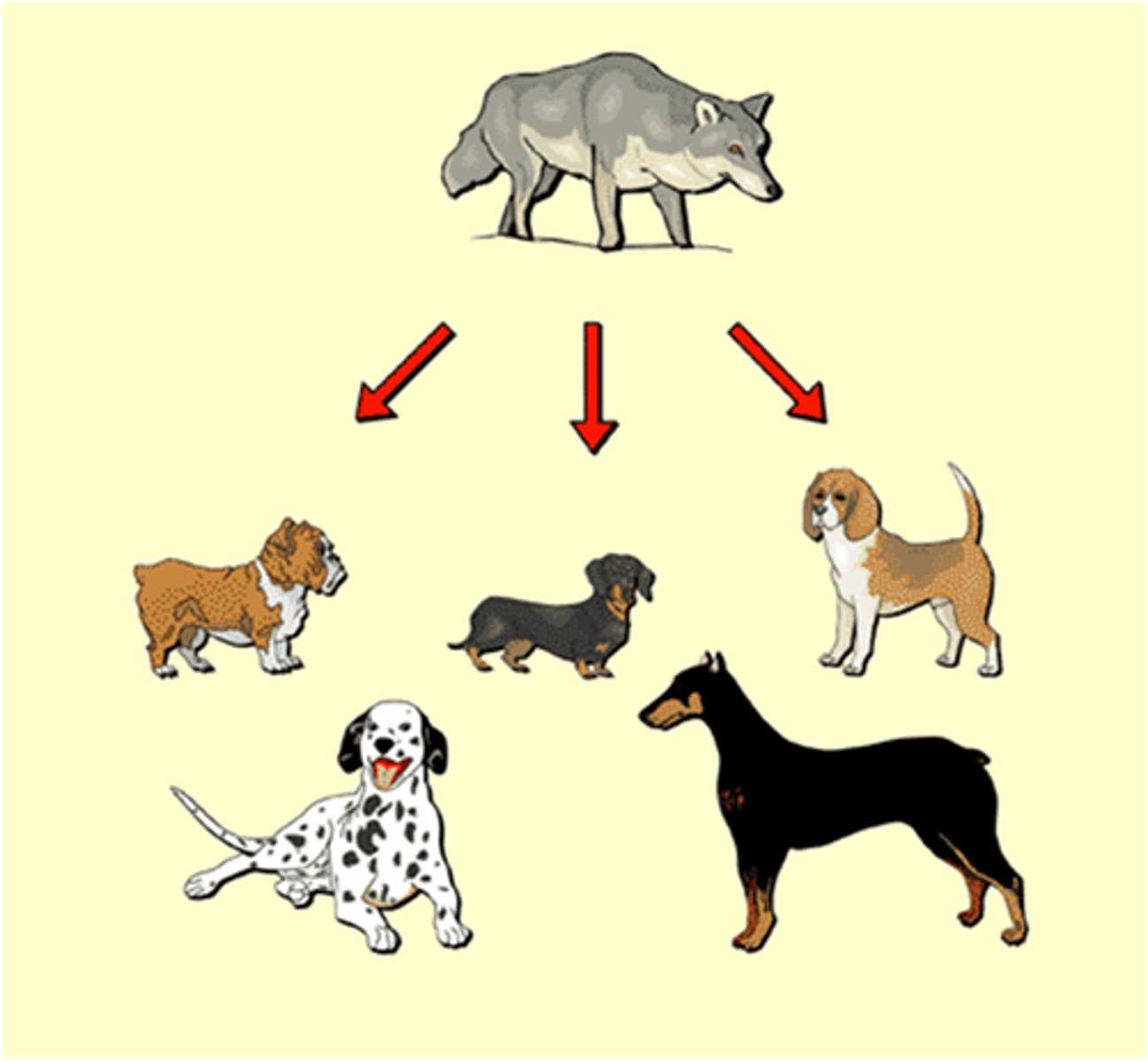
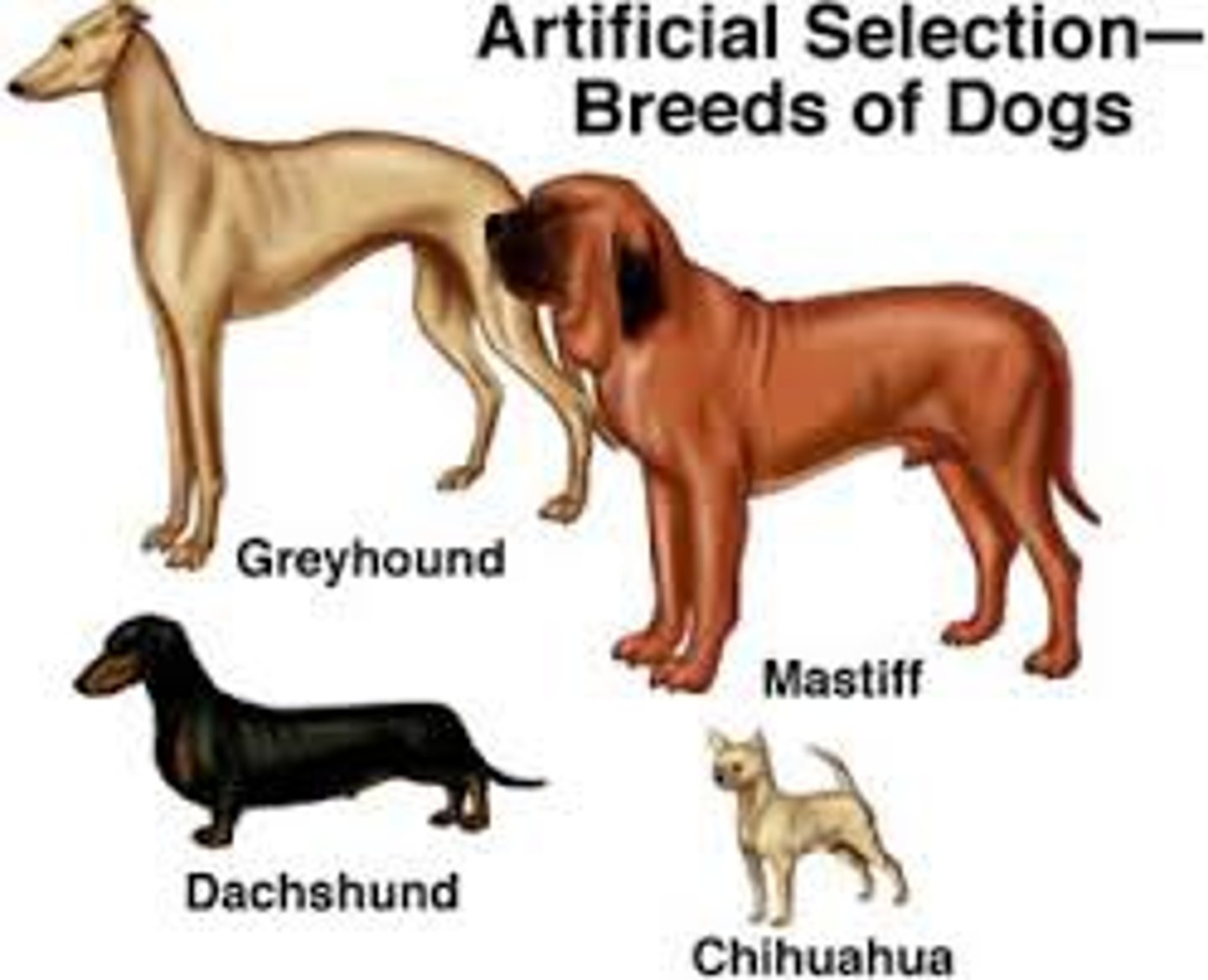
Artificial Selection
Selection by humans for breeding of useful traits from the natural variation among different organisms
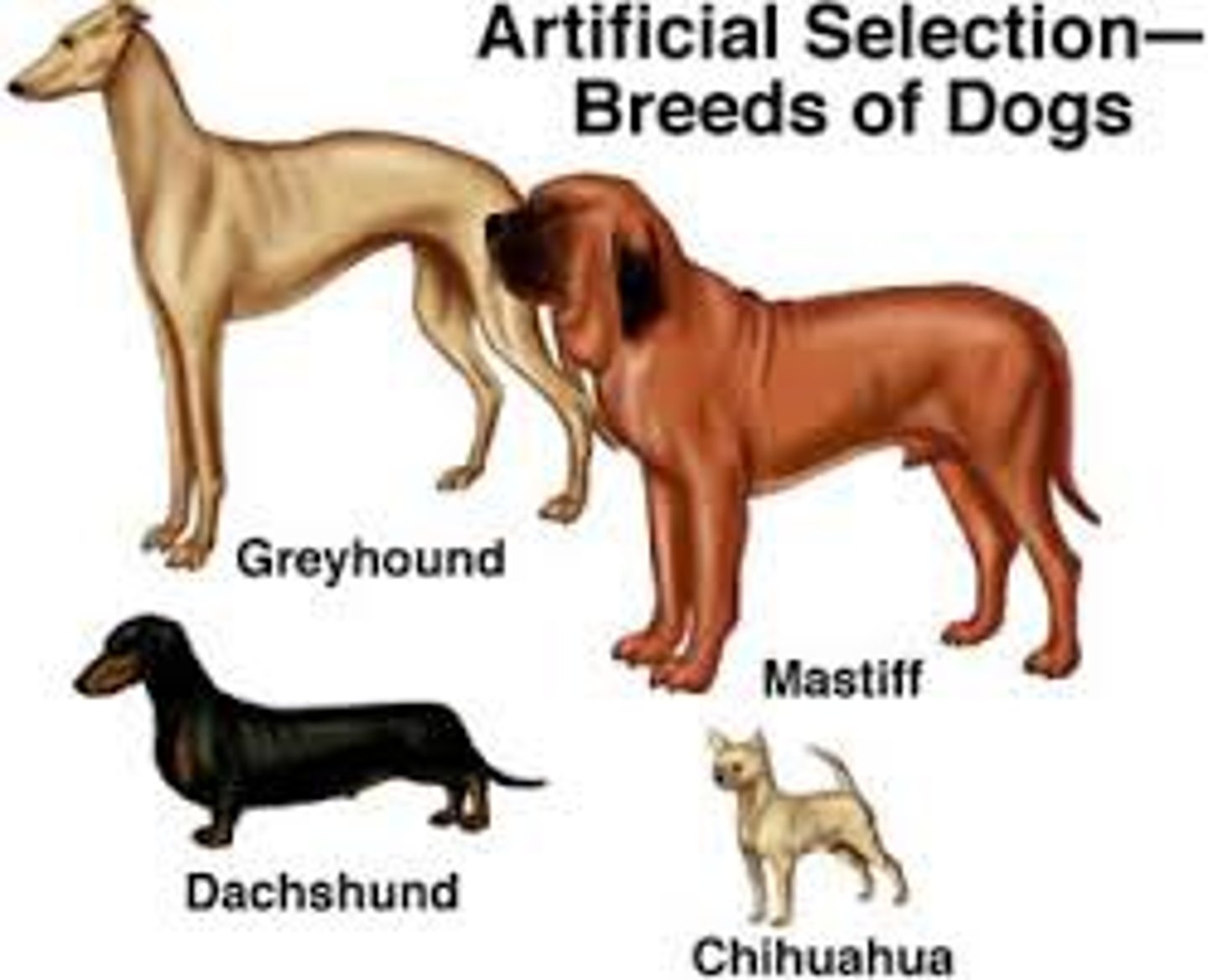
Example of Artificial Selection
dog breeding, banana breeding
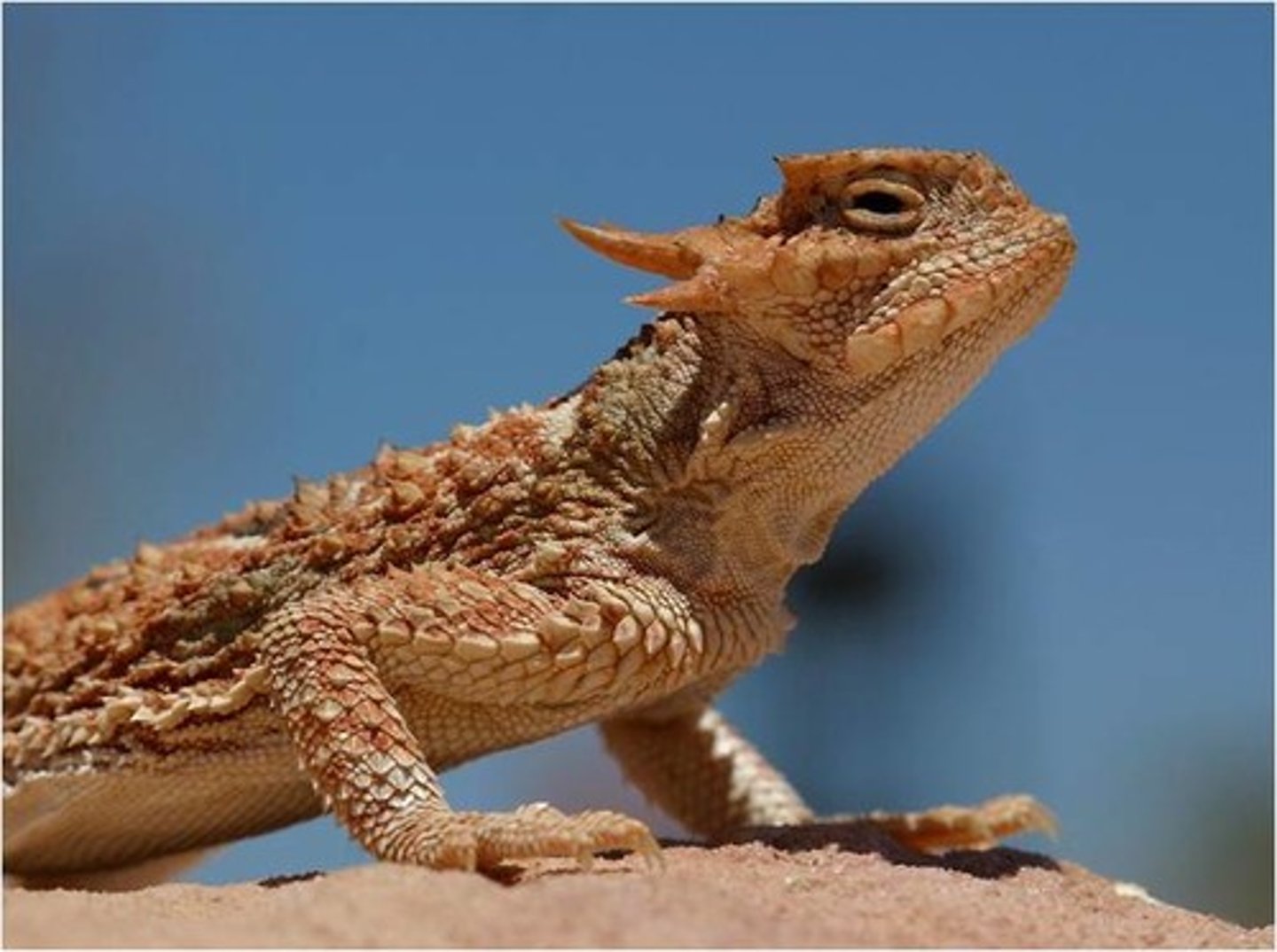
Example of Natural Selection (Lizard Activity)
Lizard population became larger, more spiky, and more drought-resistant over time due to environmental pressures

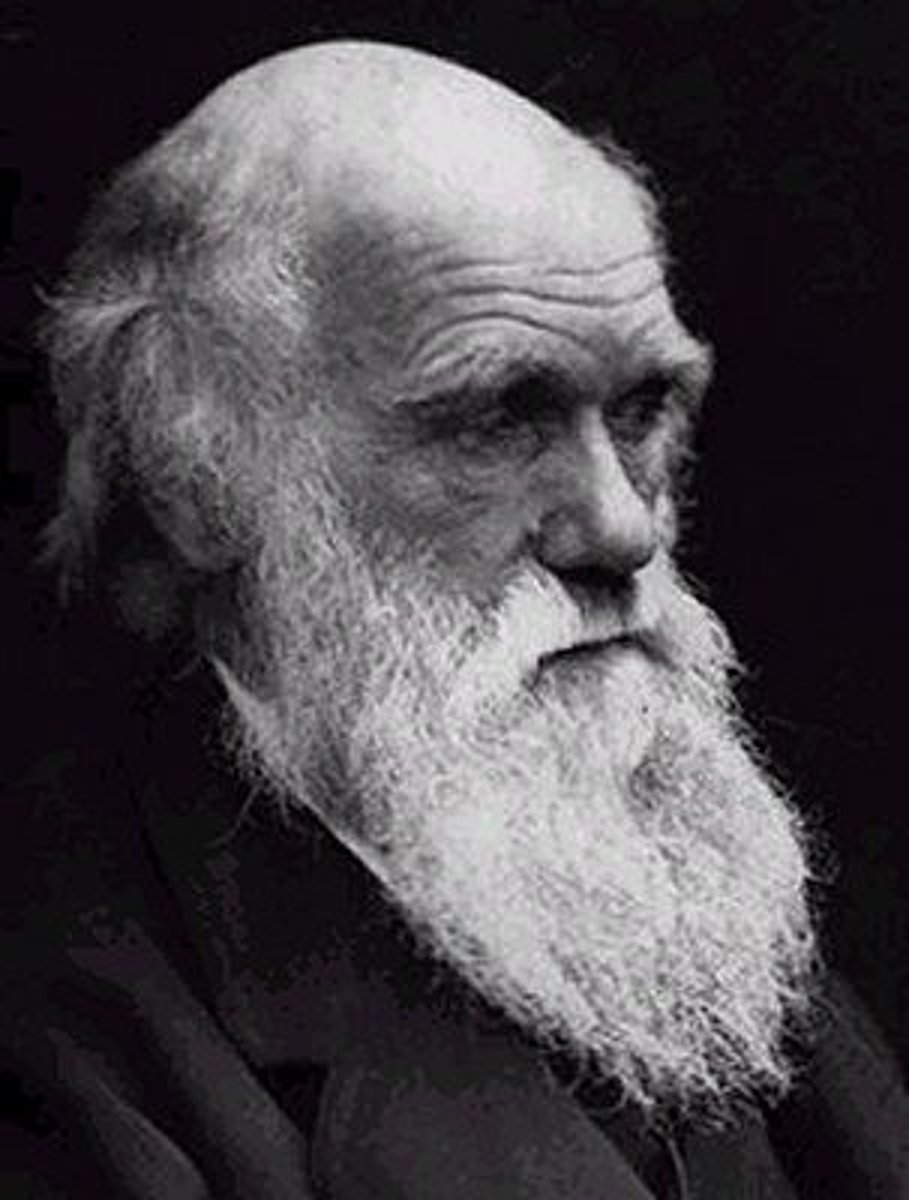
Charles Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection (1809-1882)

Heritability
the ability of a trait to be passed down from one generation to the next

Adaptations
beneficial traits (physical traits, behavior, etc.) that improve an individual's ability to survive and reproduce

Survival of the Fittest
Process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully; also called natural selection

Speciation
Formation of new species

Temporal Isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations reproduce at different times

Reproductive Isolation
condition in which a reproductive barrier keeps two species from interbreeding (fertilized egg is not viable)
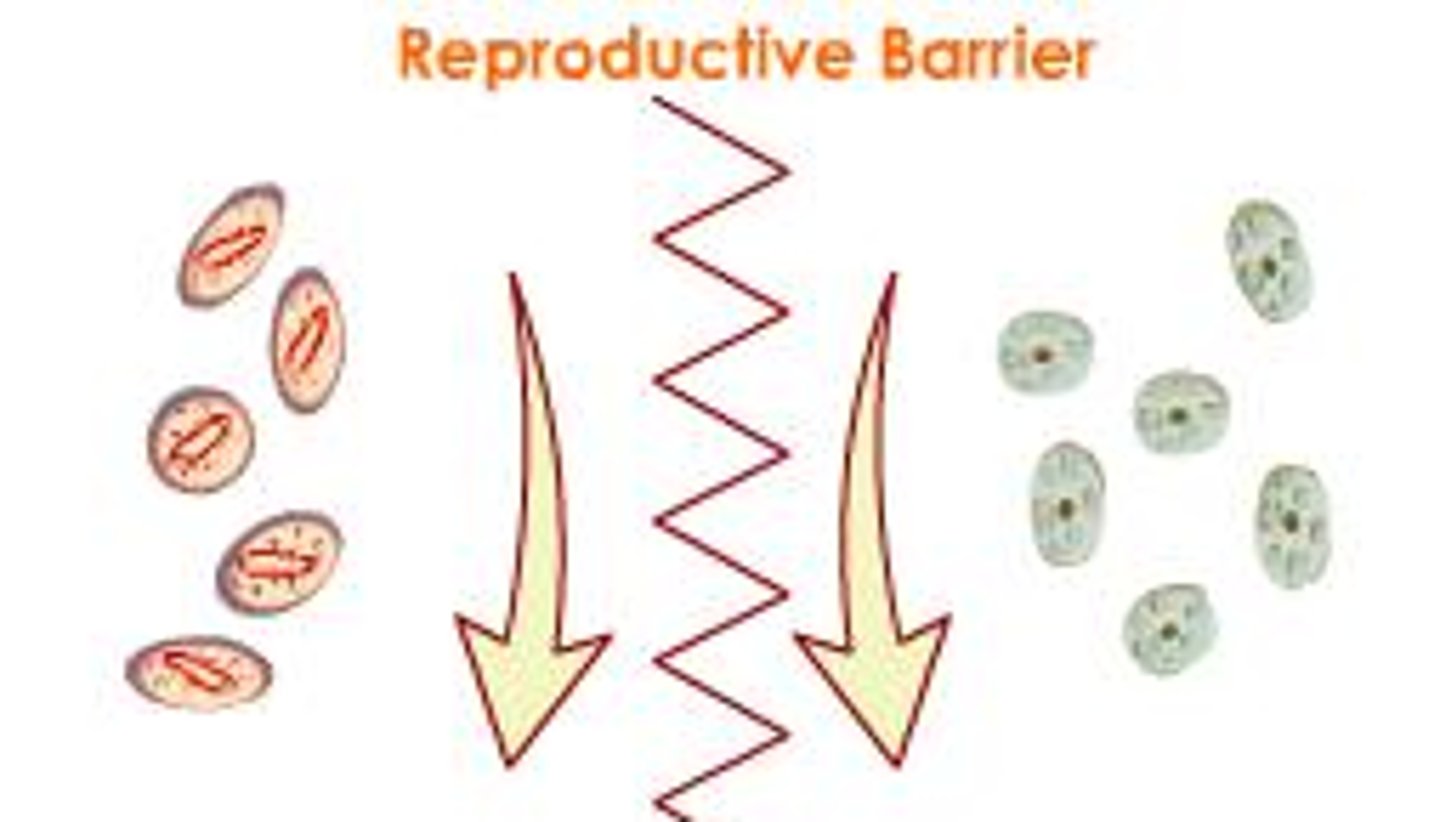
Geographic Isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations are separated physically by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or stretches of water
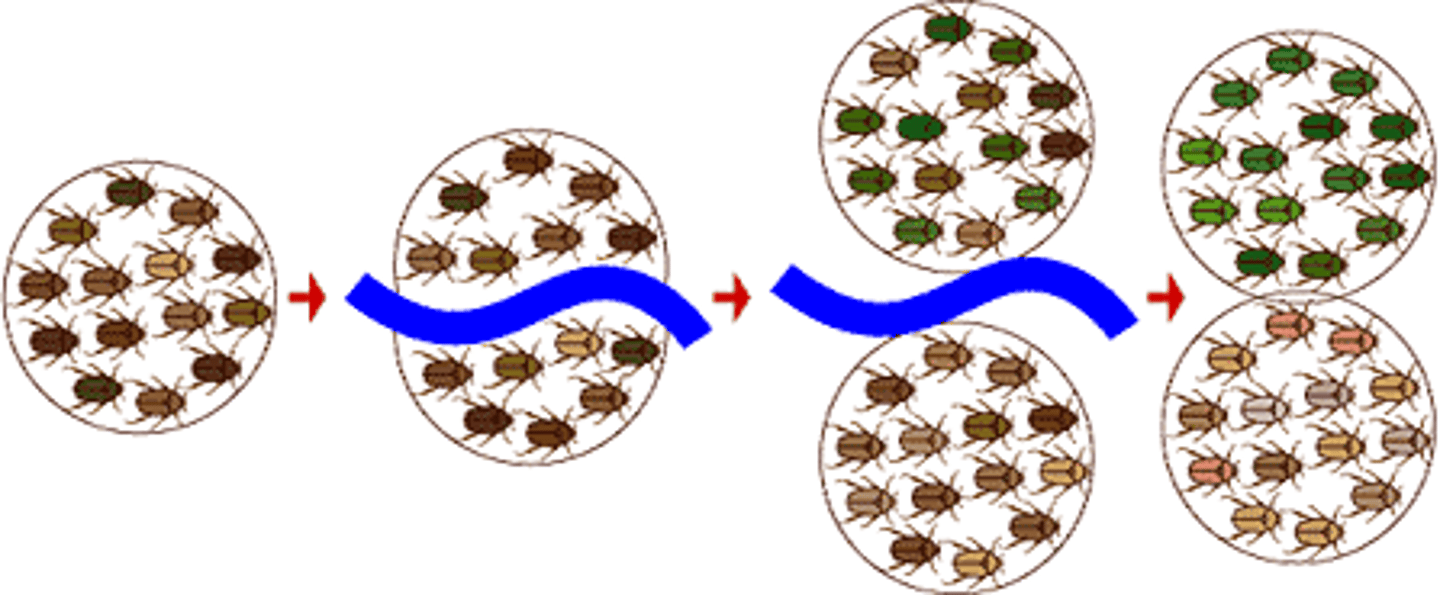
Ecological Isolation
species occur in the same area but occupy different habitats

Behavioral Isolation
isolation between populations due to differences in courtship or mating behavior

Types of Natural Selection
stabilizing selection, directional selection, disruptive selection
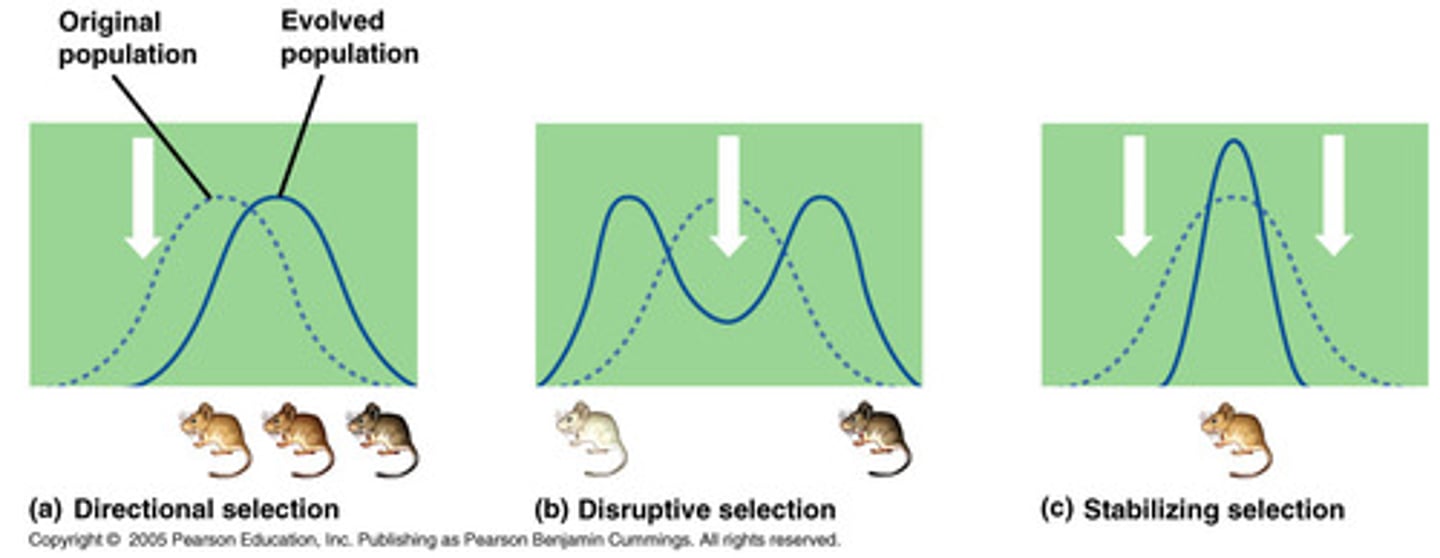
Stabilizing Selection
occurs when natural selection favors the average/intermediate/middle variation of a trait
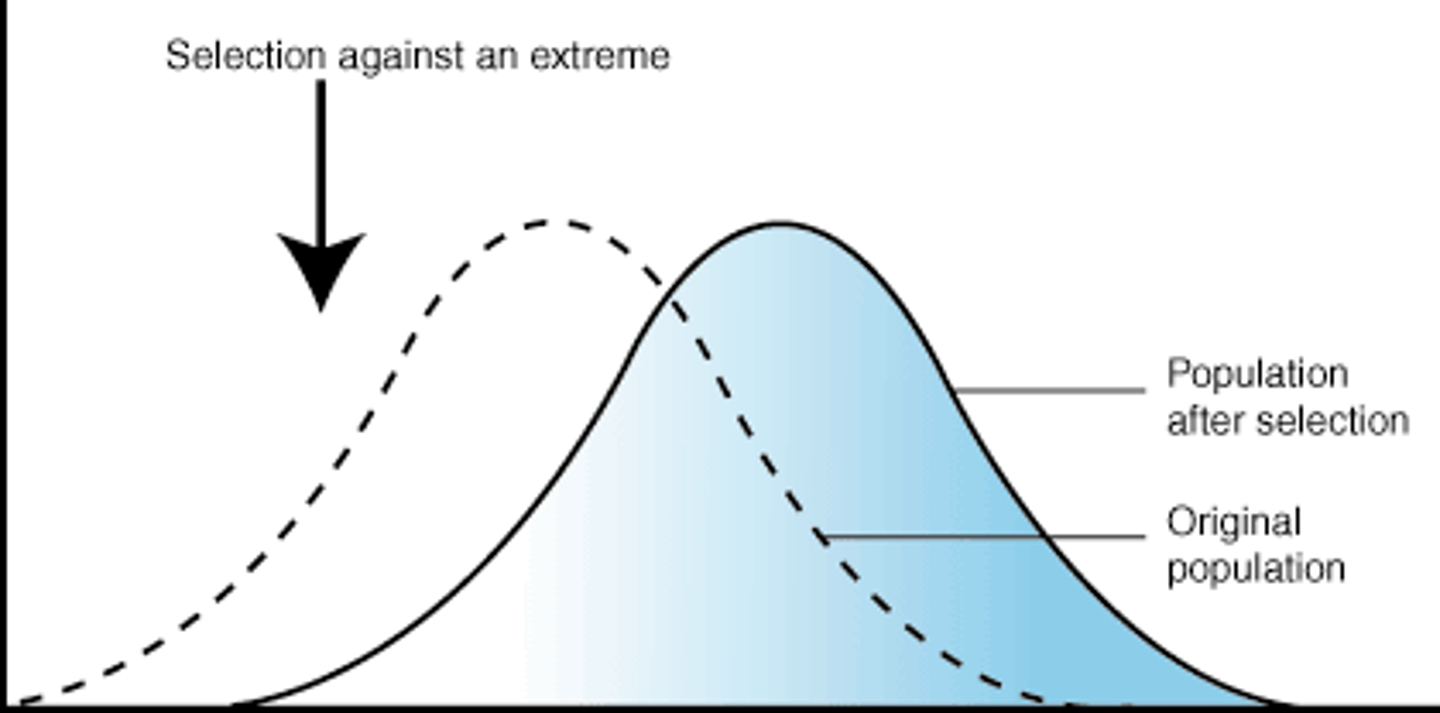
Directional Selection
occurs when natural selection favors ONE of the extreme variations of a trait
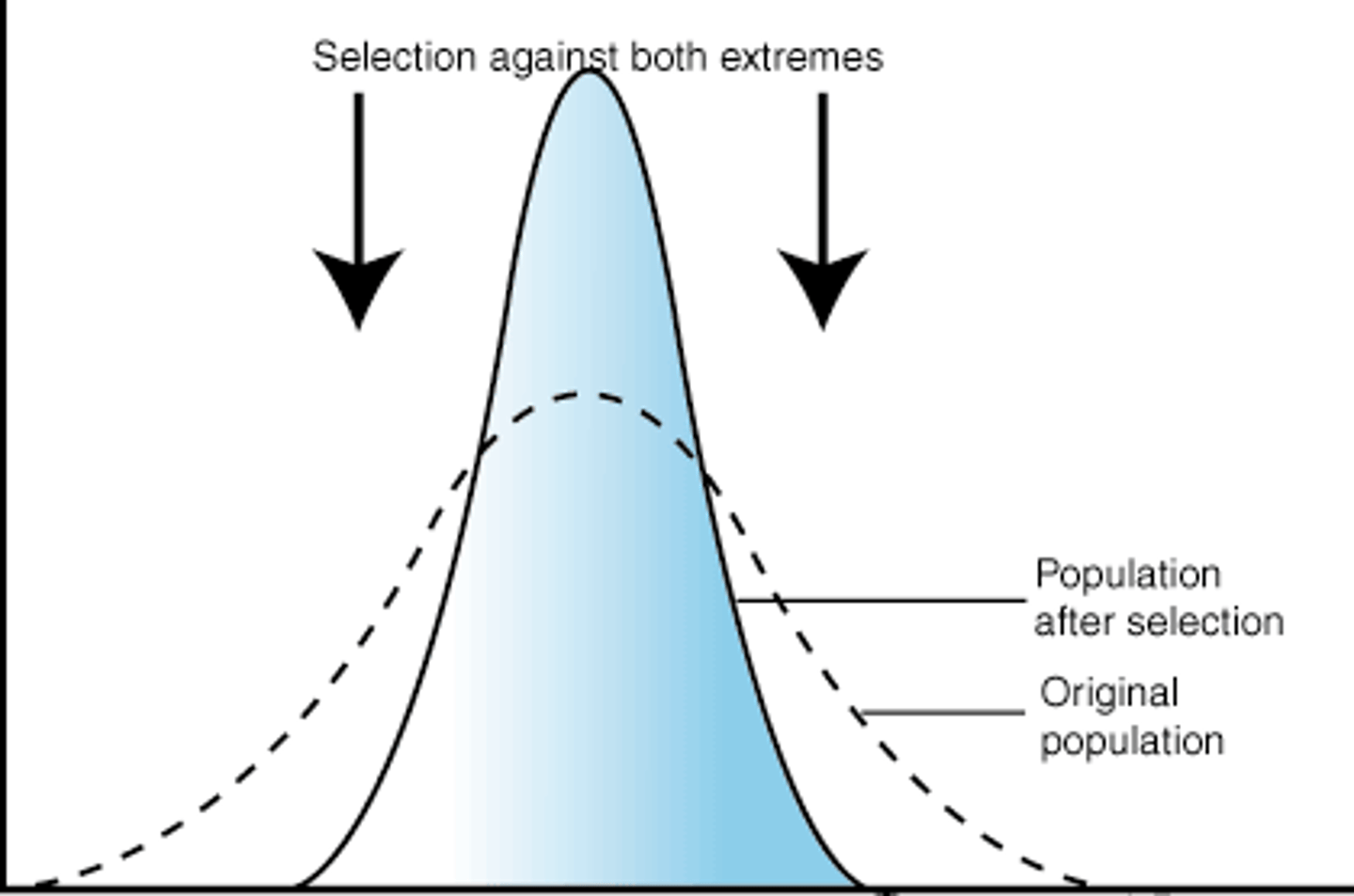
Disruptive Selection
occurs when natural selection favors BOTH extreme variations of a trait (and/or selects against the intermediate variation)
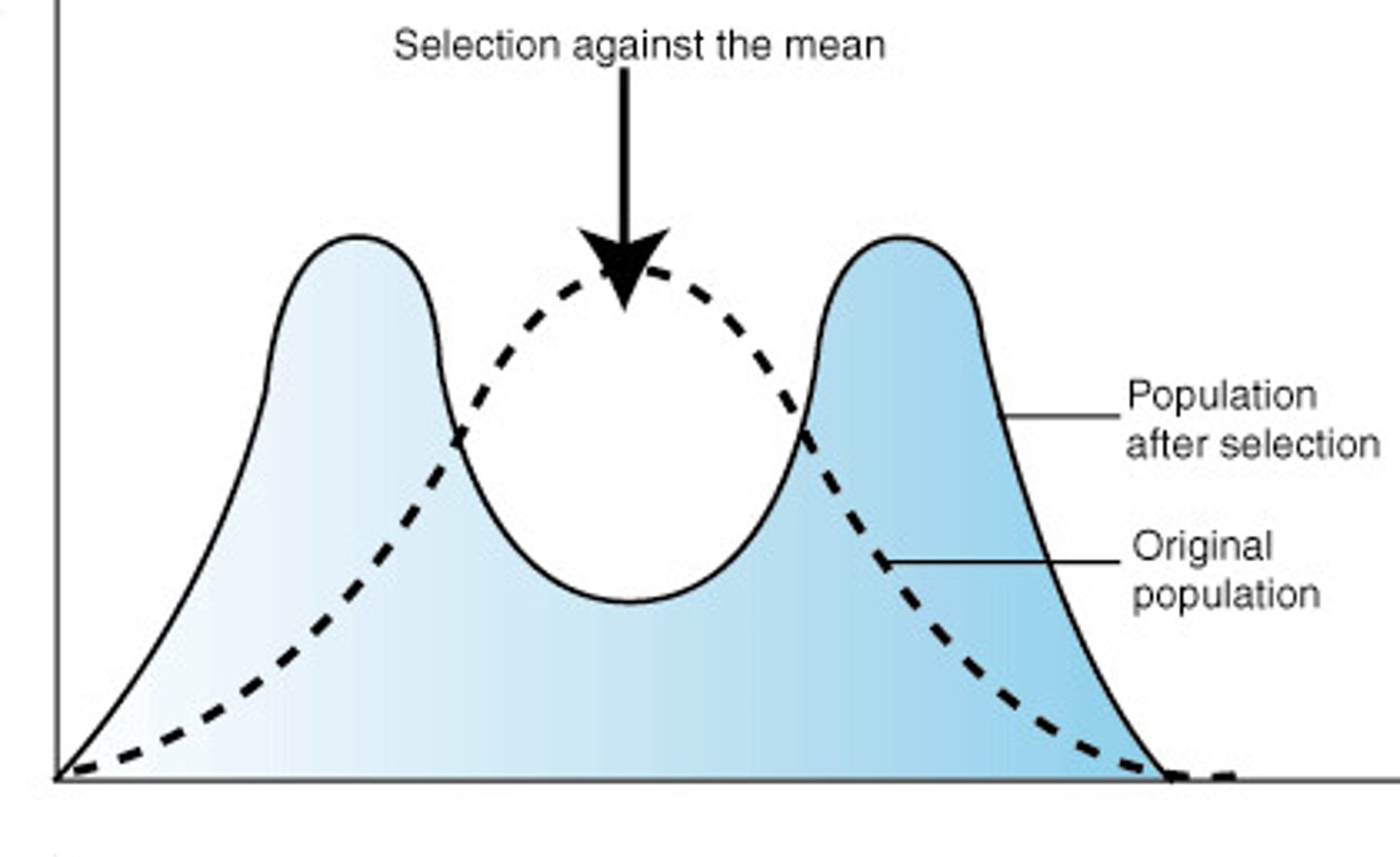
Genetic Drift
A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance
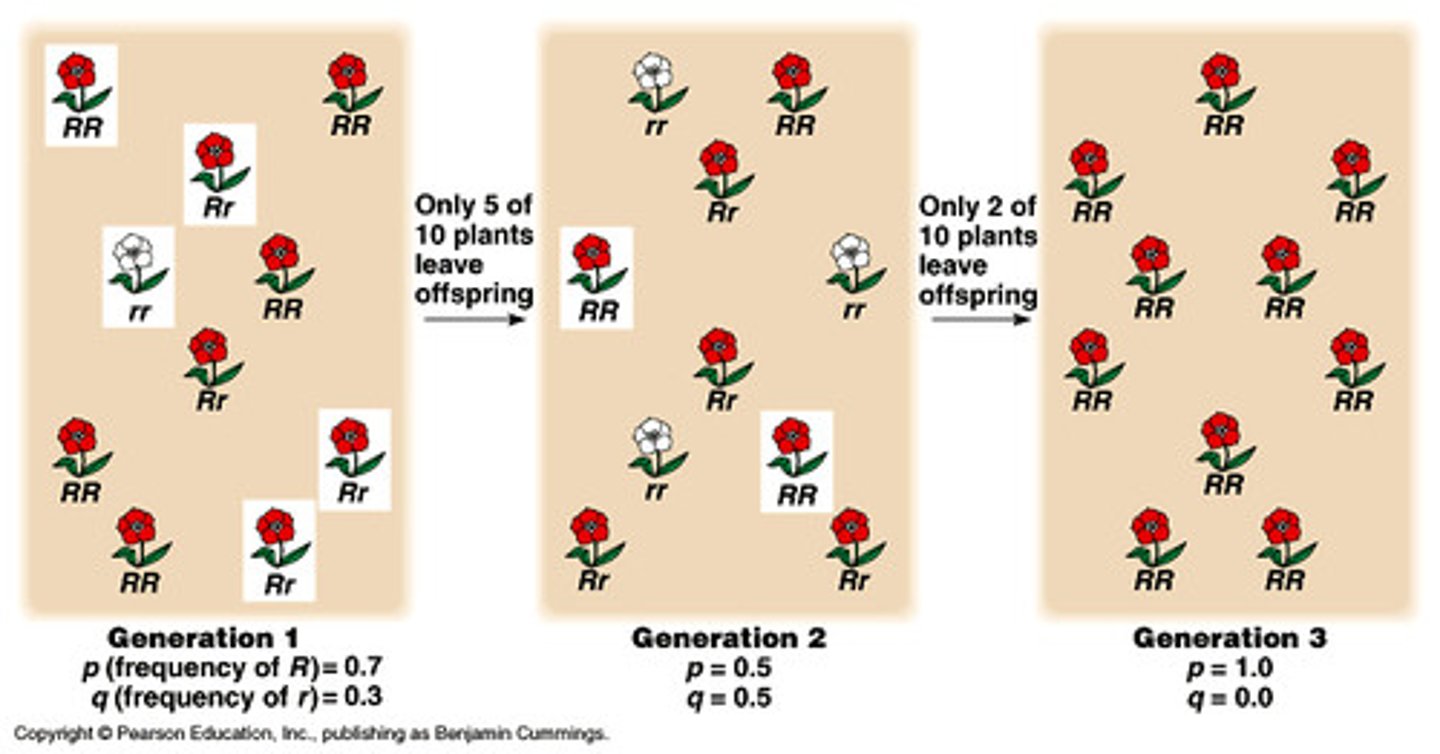
Bottleneck Effect
Genetic drift resulting from the reduction of a population, typically by a natural disaster, such that the surviving population is no longer genetically representative of the original population.

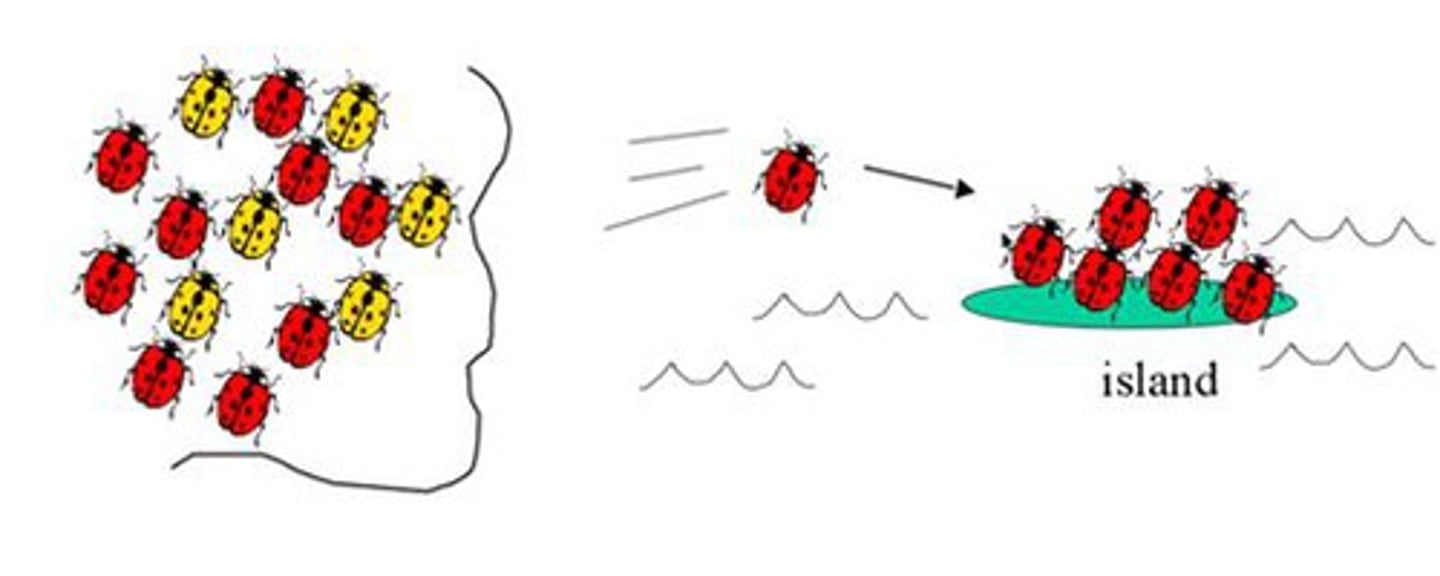
Founder Effect
Genetic drift (change in allele frequencies) as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population
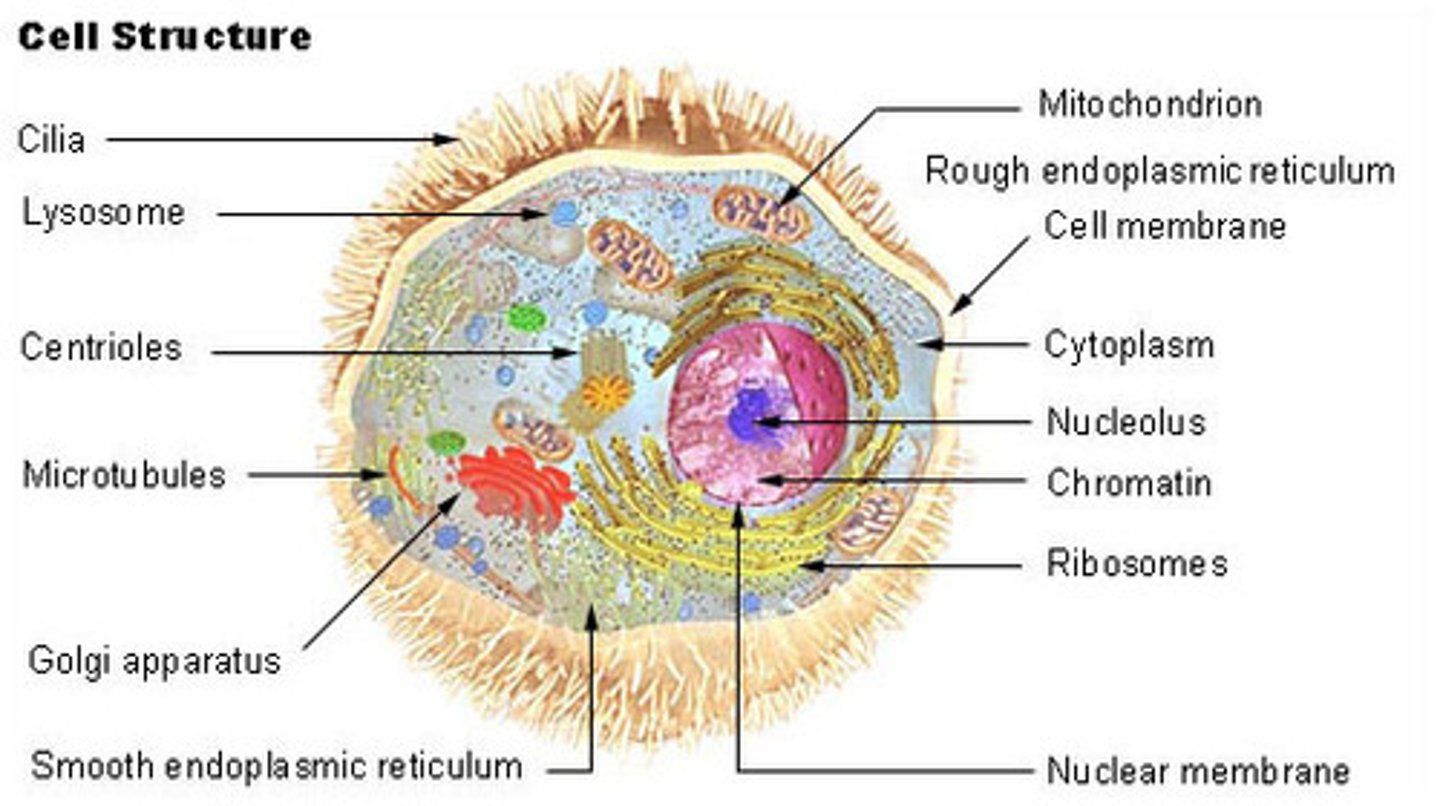
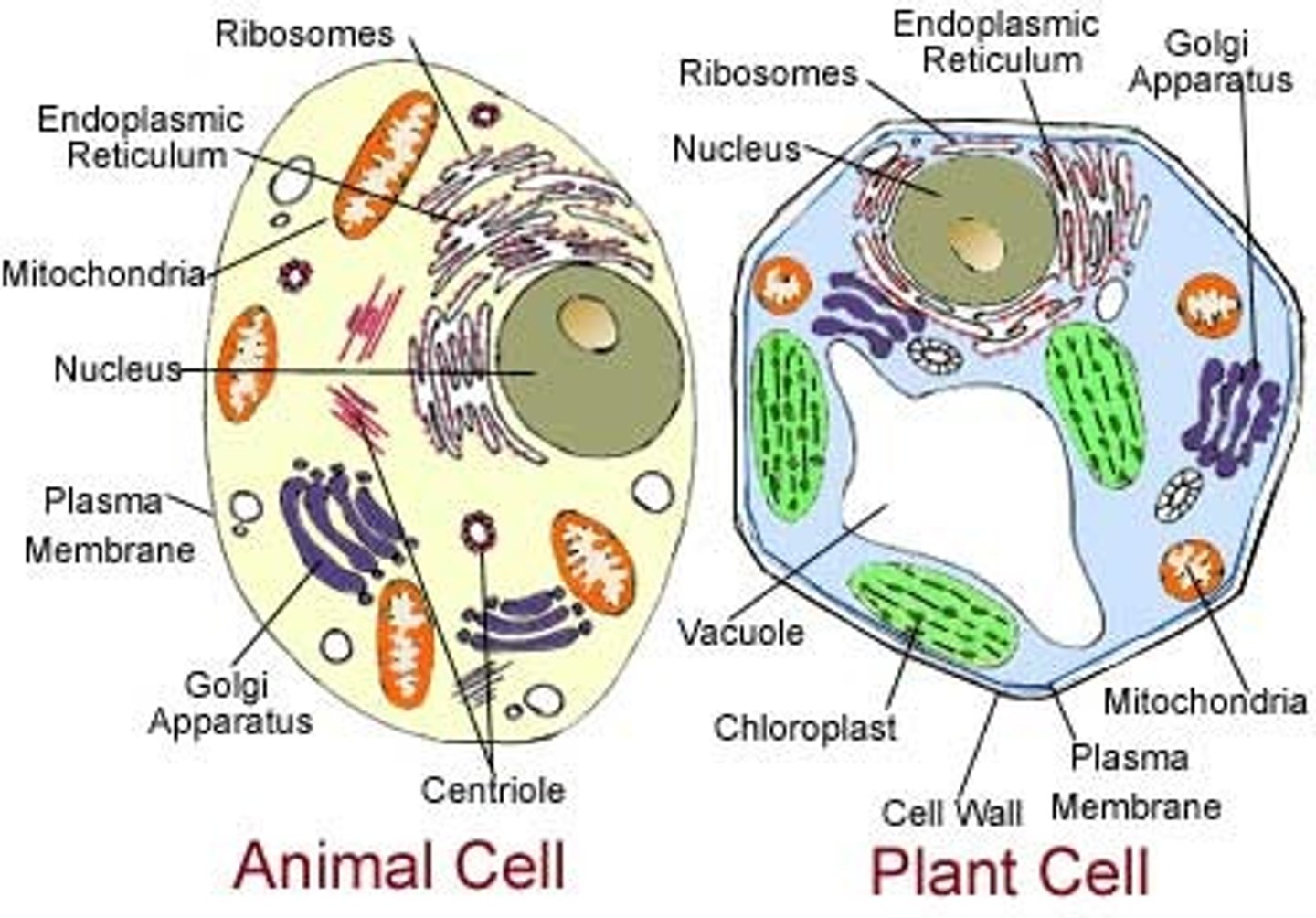
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (mitochondria, ER, Golgi, etc.)
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
Animal, Plant, Fungi, Protist
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
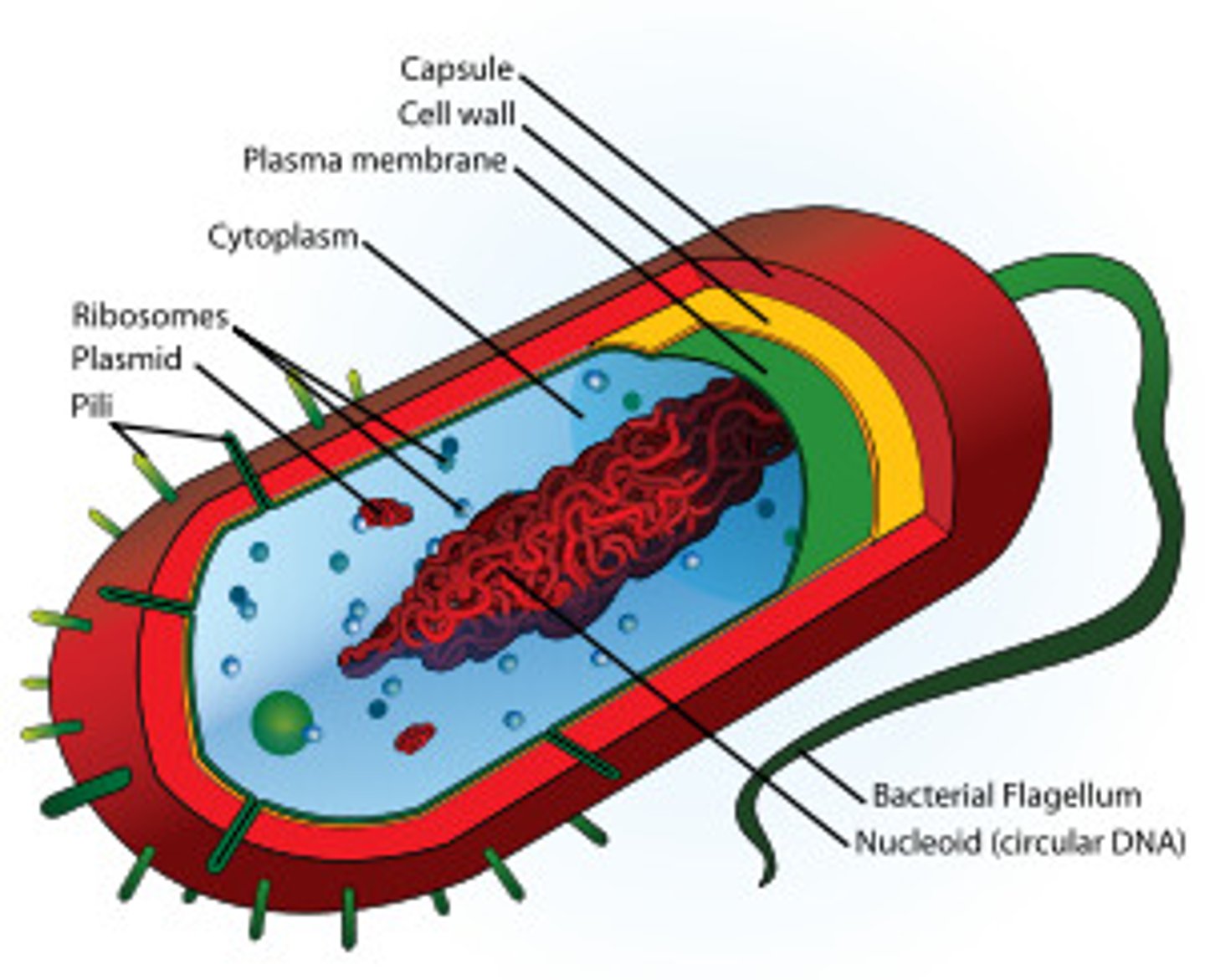
Types of Prokaryotic Cells
Bacteria, Archaea

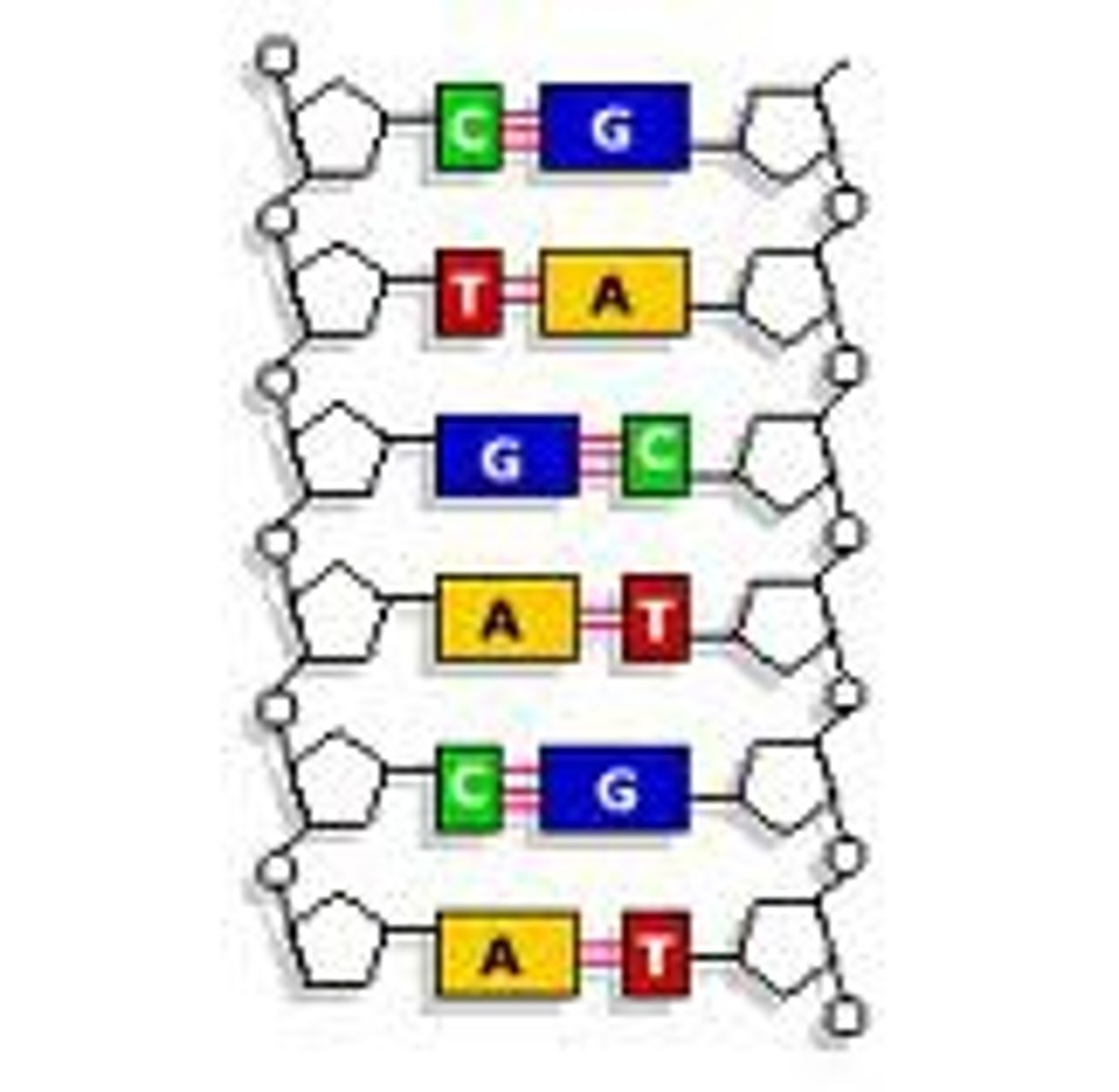
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, the carrier of genetic information.
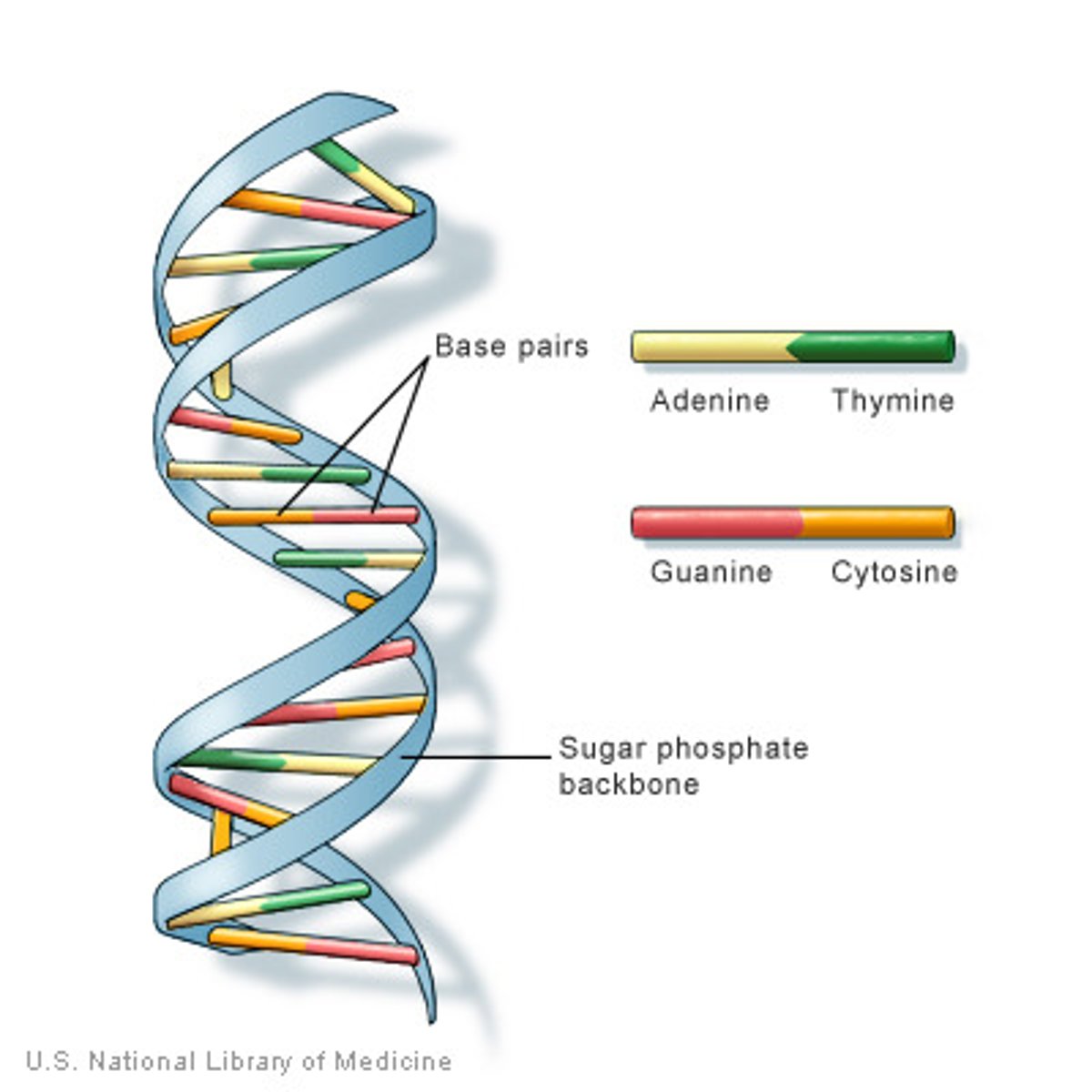
Sugar-Phosphate Backbone
The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate to which the DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases are attached
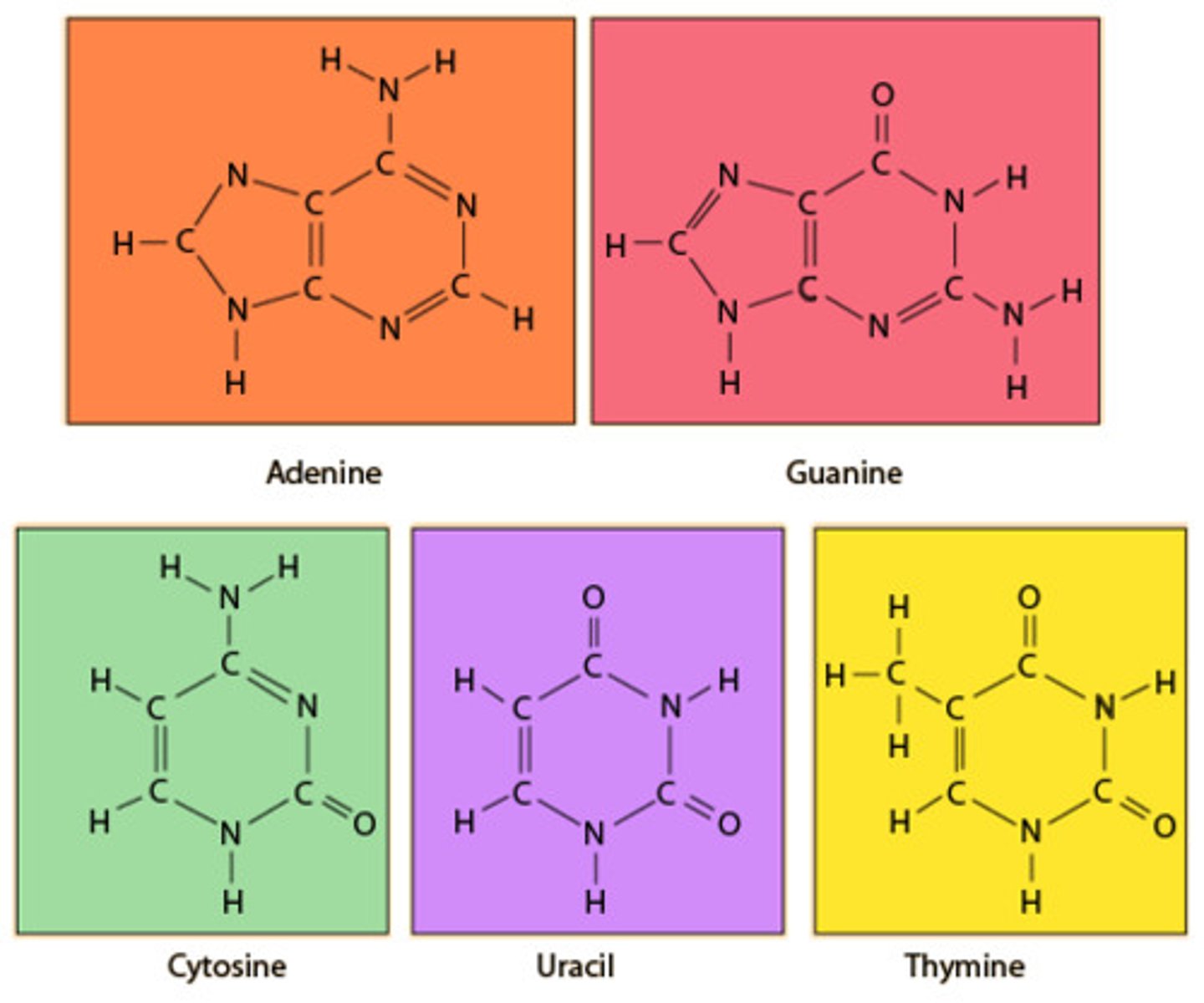
Nitrogenous Base
An organic base that contains nitrogen, such as a purine or pyrimidine; a subunit of a nucleotide in DNA and RNA (ATCG)
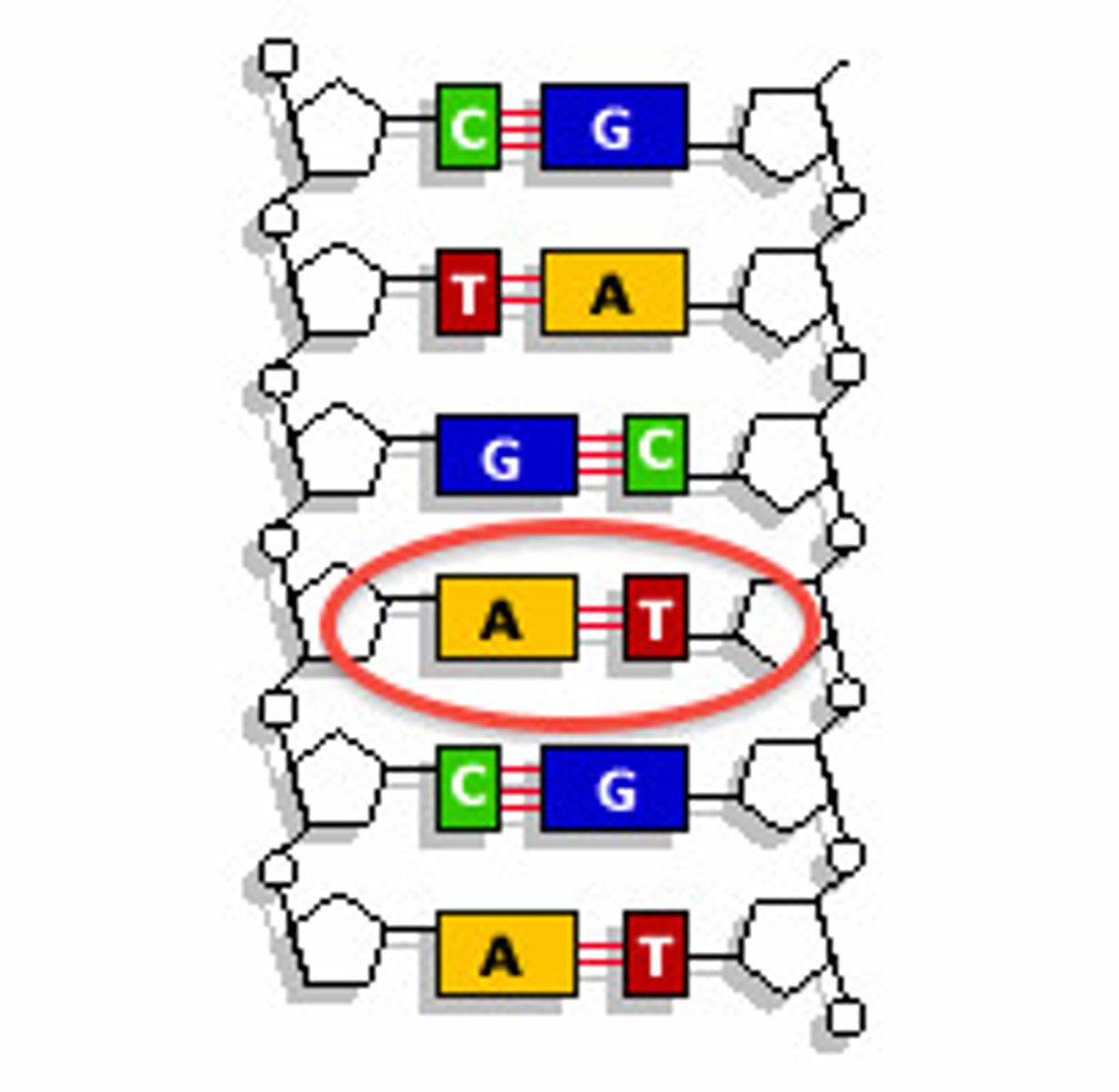
Adenine
The base that pairs with Thymine in DNA
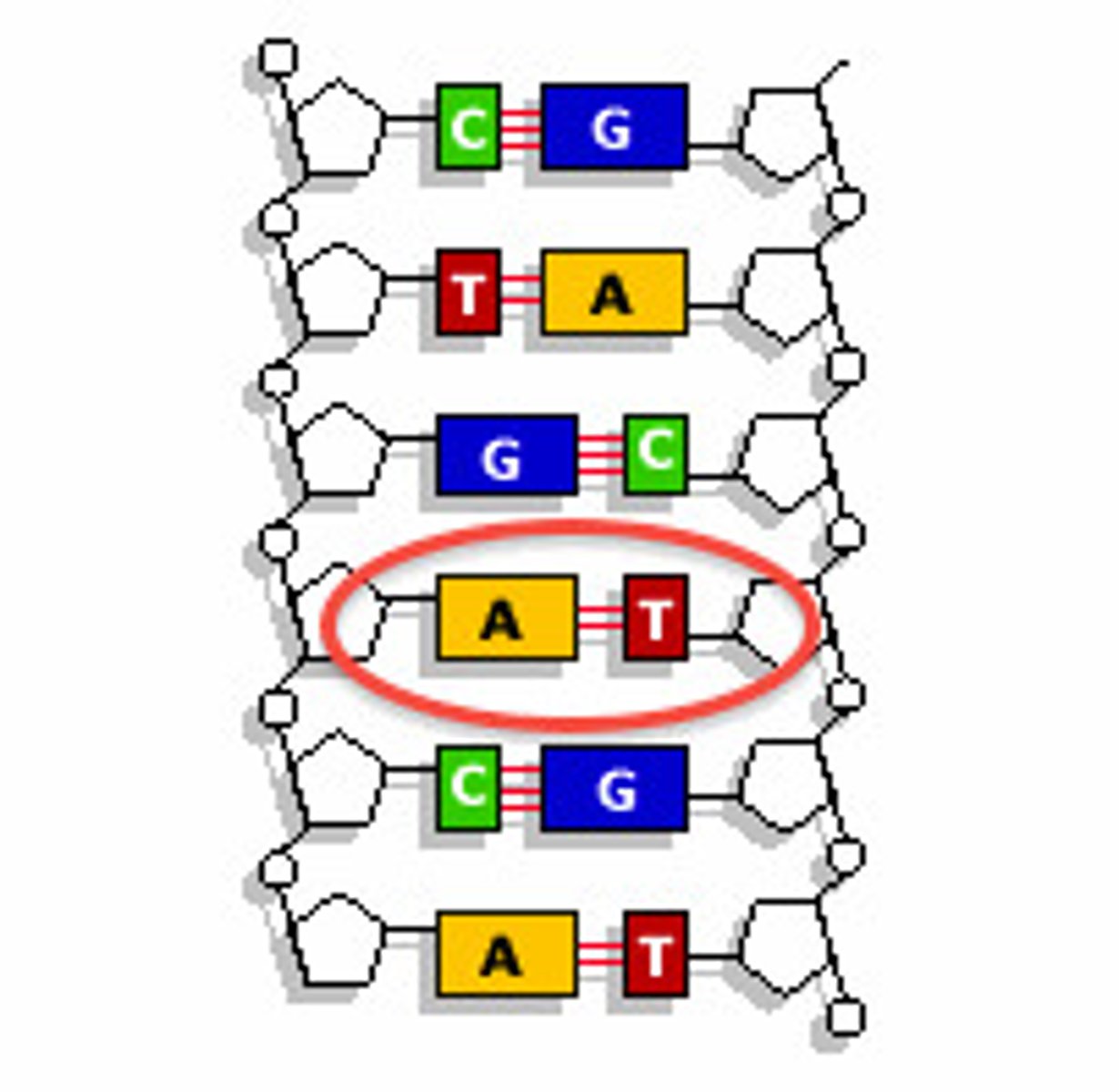
Thymine
The base that pairs with Adenine in DNA
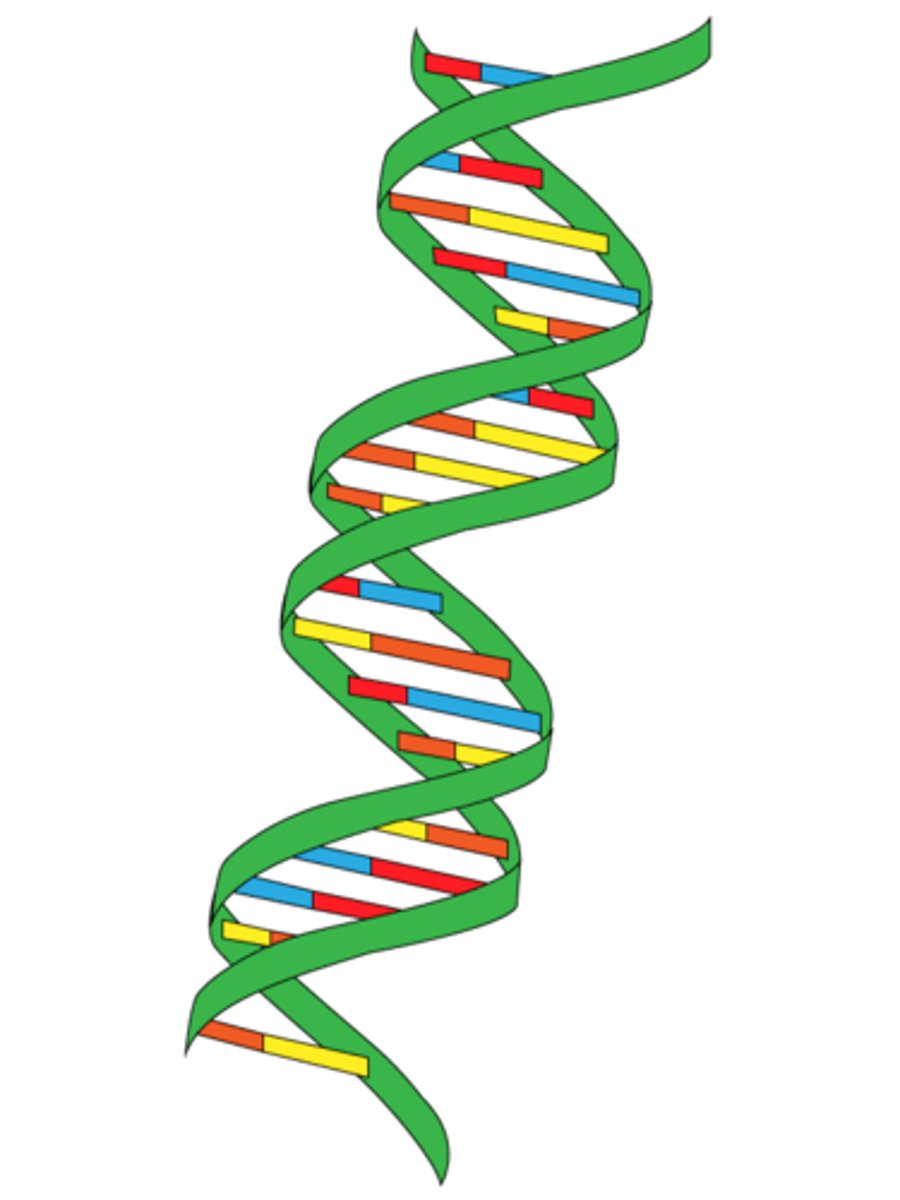
Double-Helix
two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA
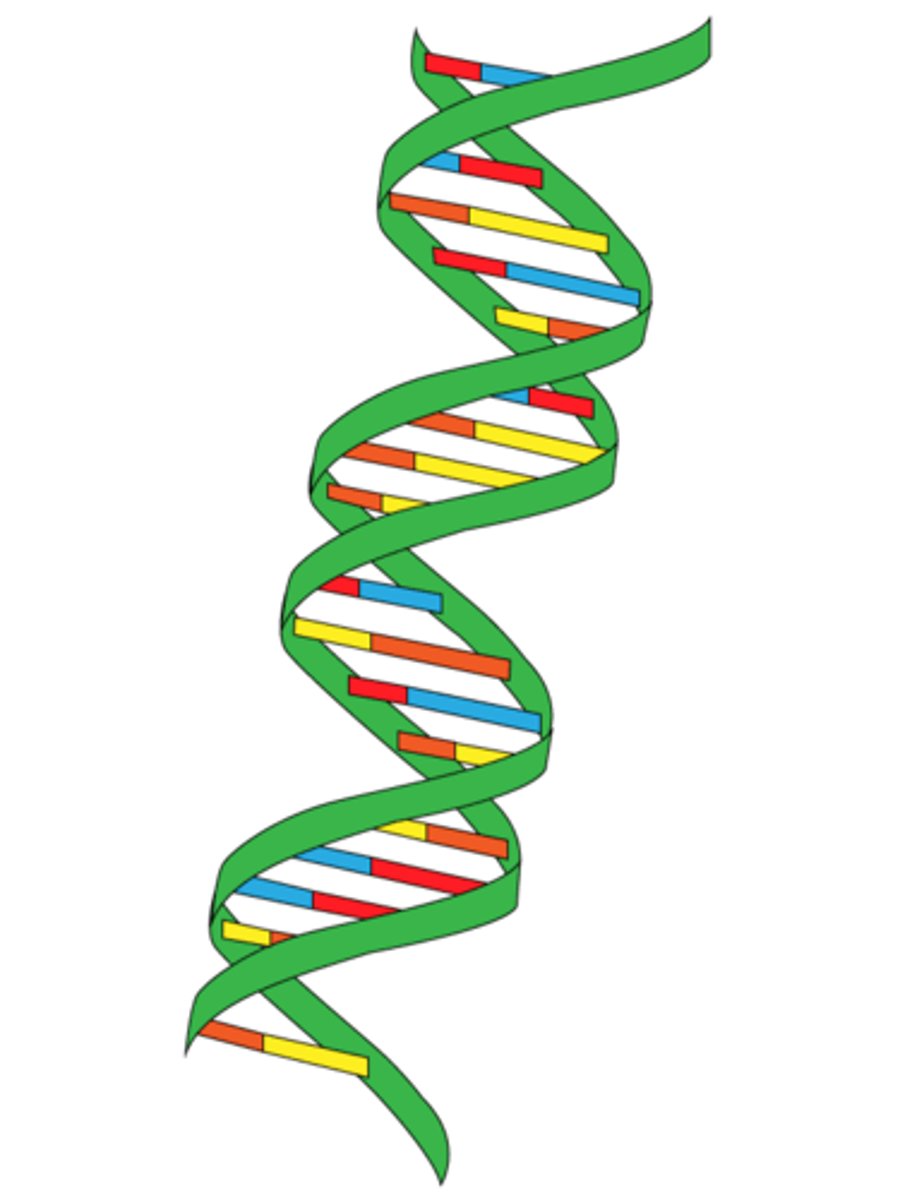
Twisted Ladder
double helix, shape of dna
Way to remember base-pair rules
Need to have their @ (AT) to put them in the group chat (GC)!

semi-conservative
Each half of an original DNA molecule serves as a template for a new strand, and the two new DNA molecules each have one old and one new strand.

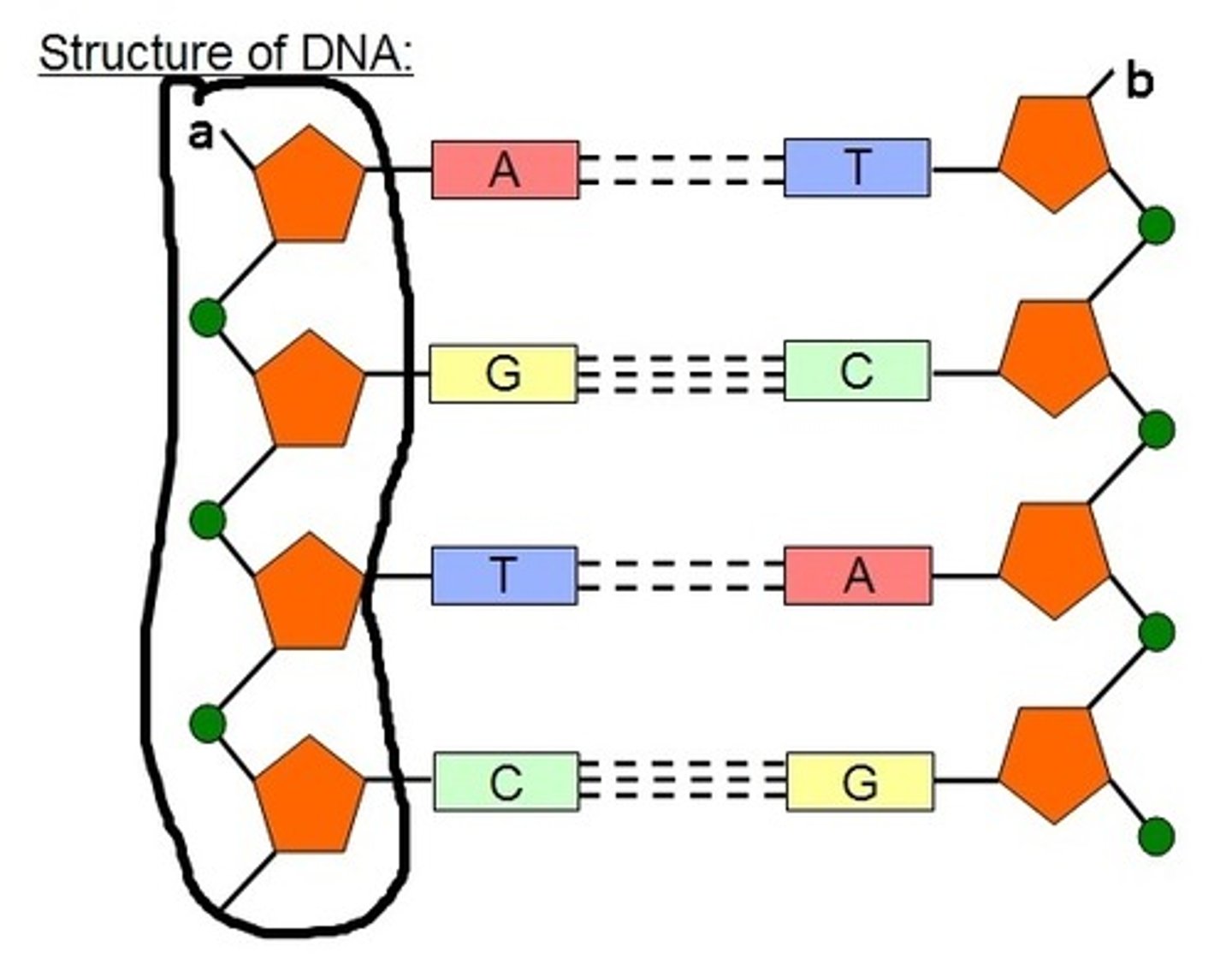
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.

Practice: What is the complementary strand of ATC GGC CGA TAT?
TAG CCG GCT ATA
genetics
The scientific study of heredity

complete dominance
a relationship in which one allele is completely dominant over another
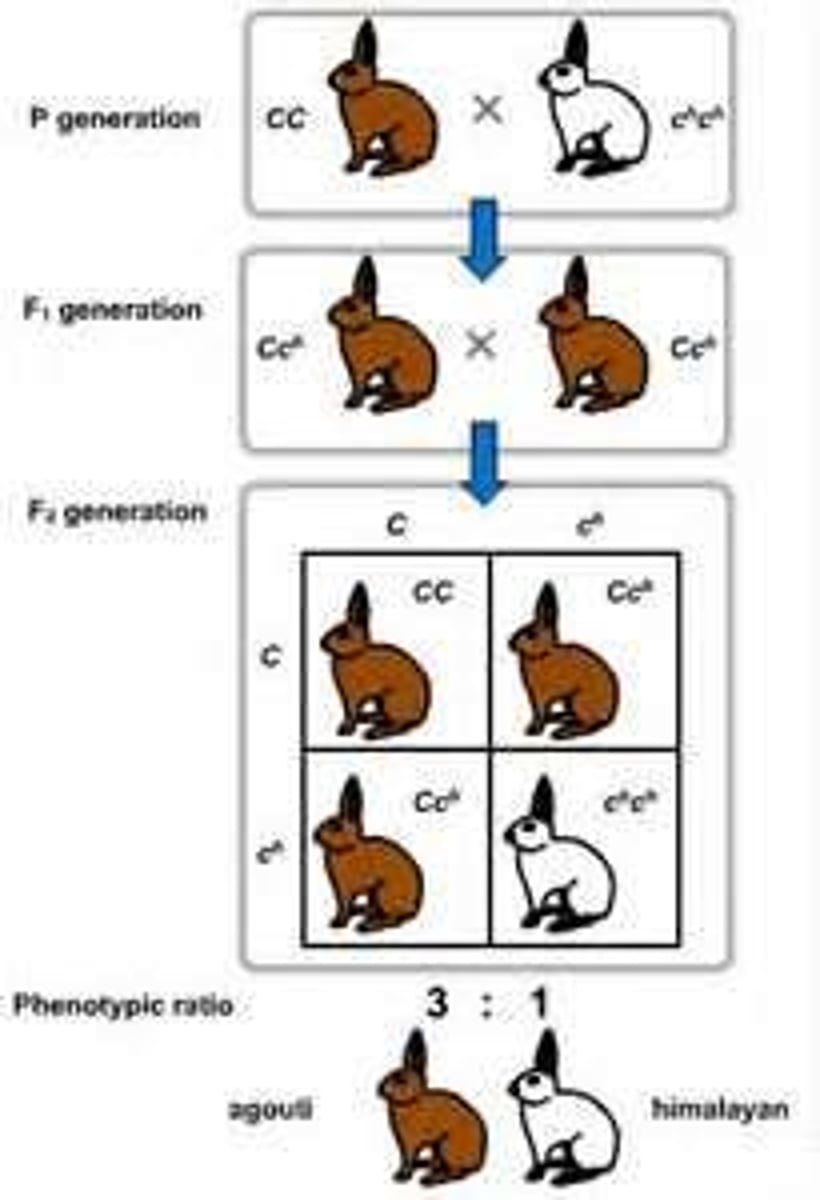
incomplete dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele - they BLEND
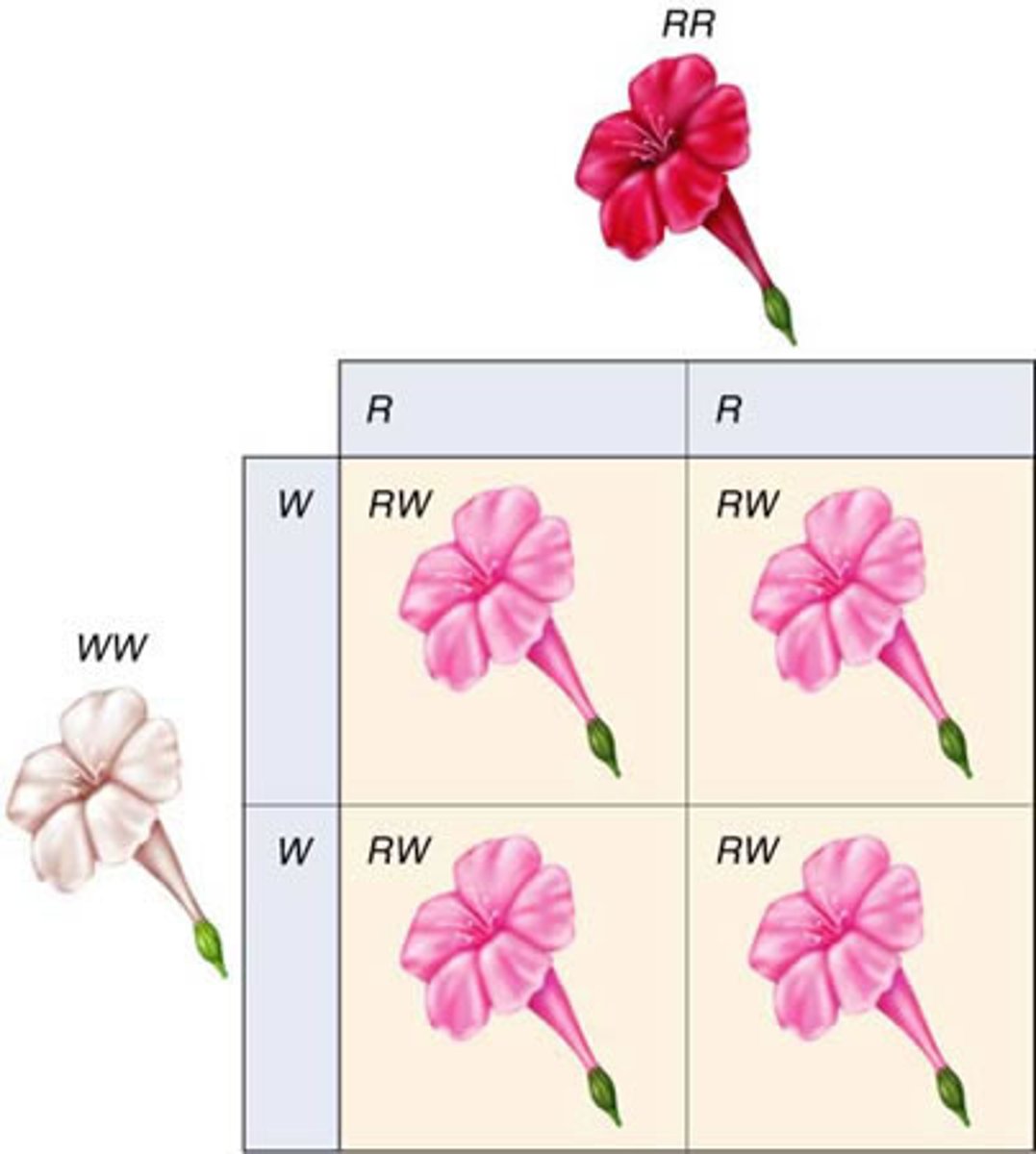
codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed
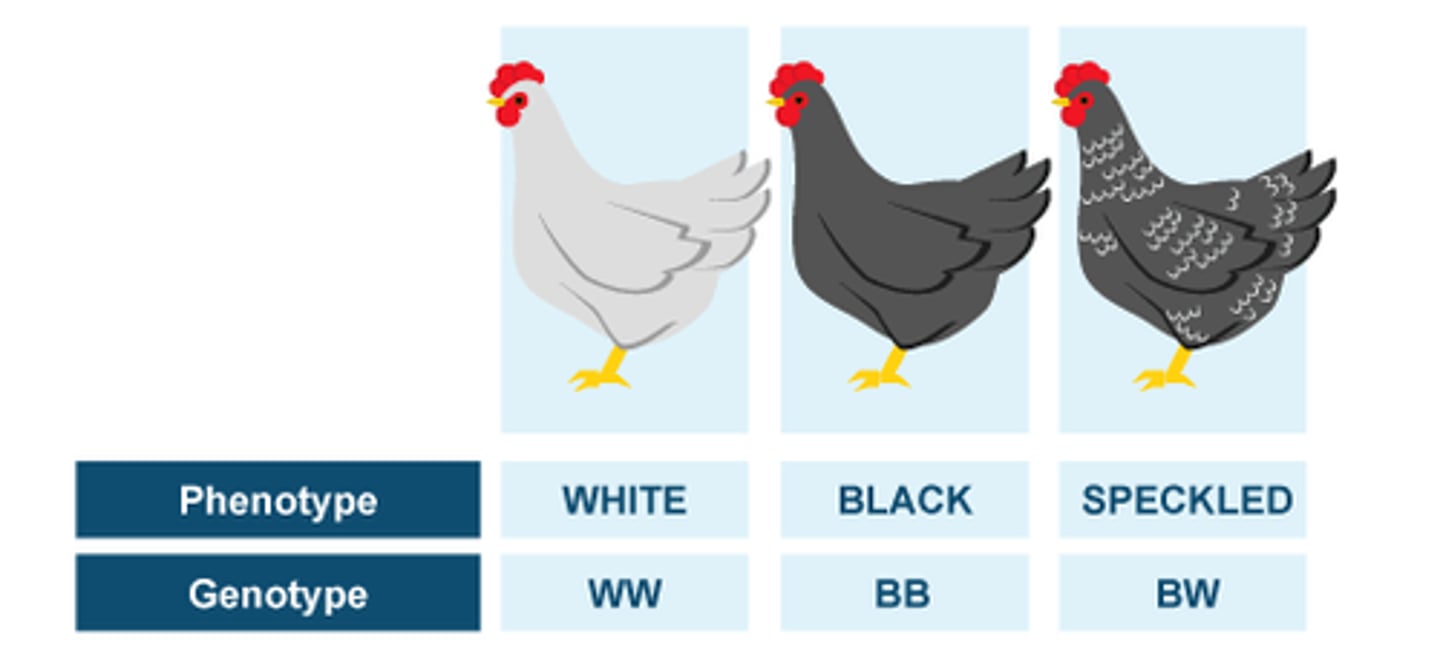
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism (allele combinations, e.g. Bb)
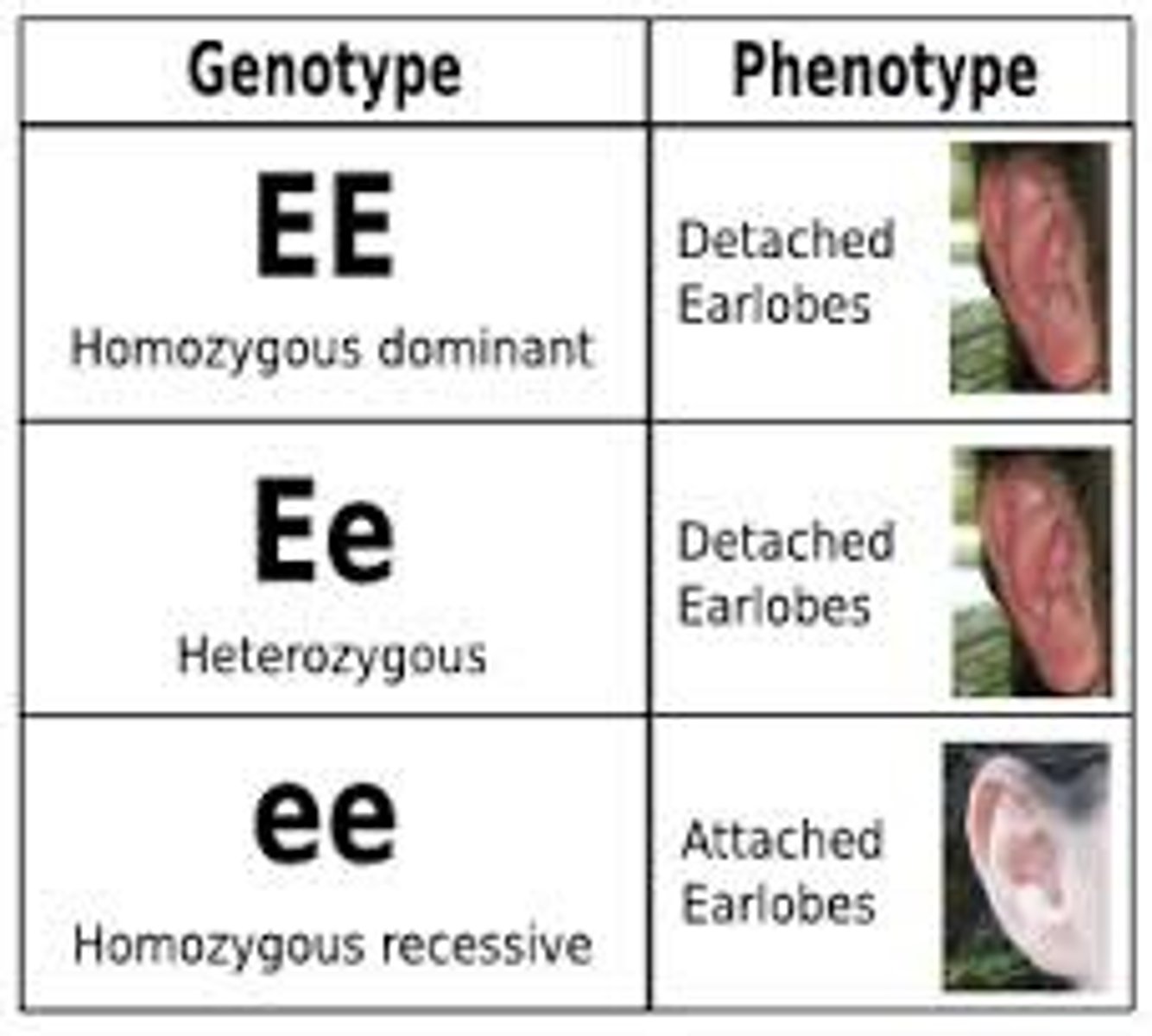
phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits. (physically what trait does an organism have, e.g. black fur)

allele
Different forms of a gene
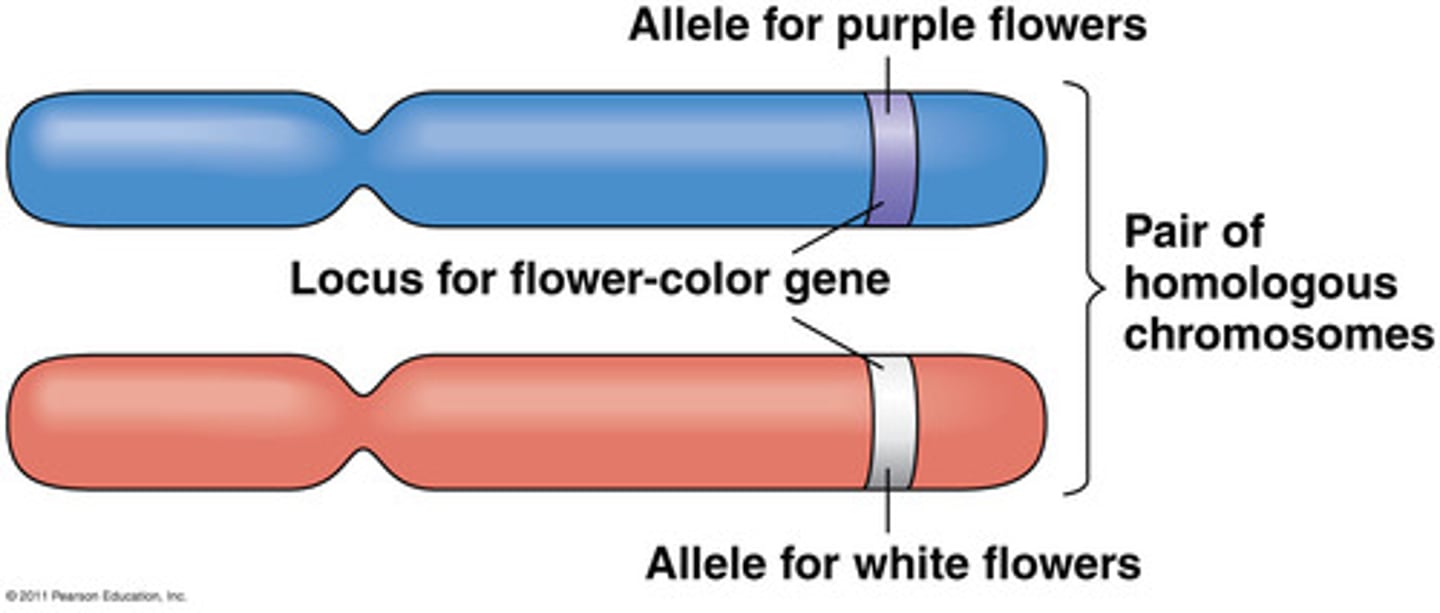
heterozygous
having two different alleles for a trait

homozygous
having two identical alleles for a trait

trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes. (e.g. fur color)
gamete
sex cell, sperm or egg

hybrid
Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits
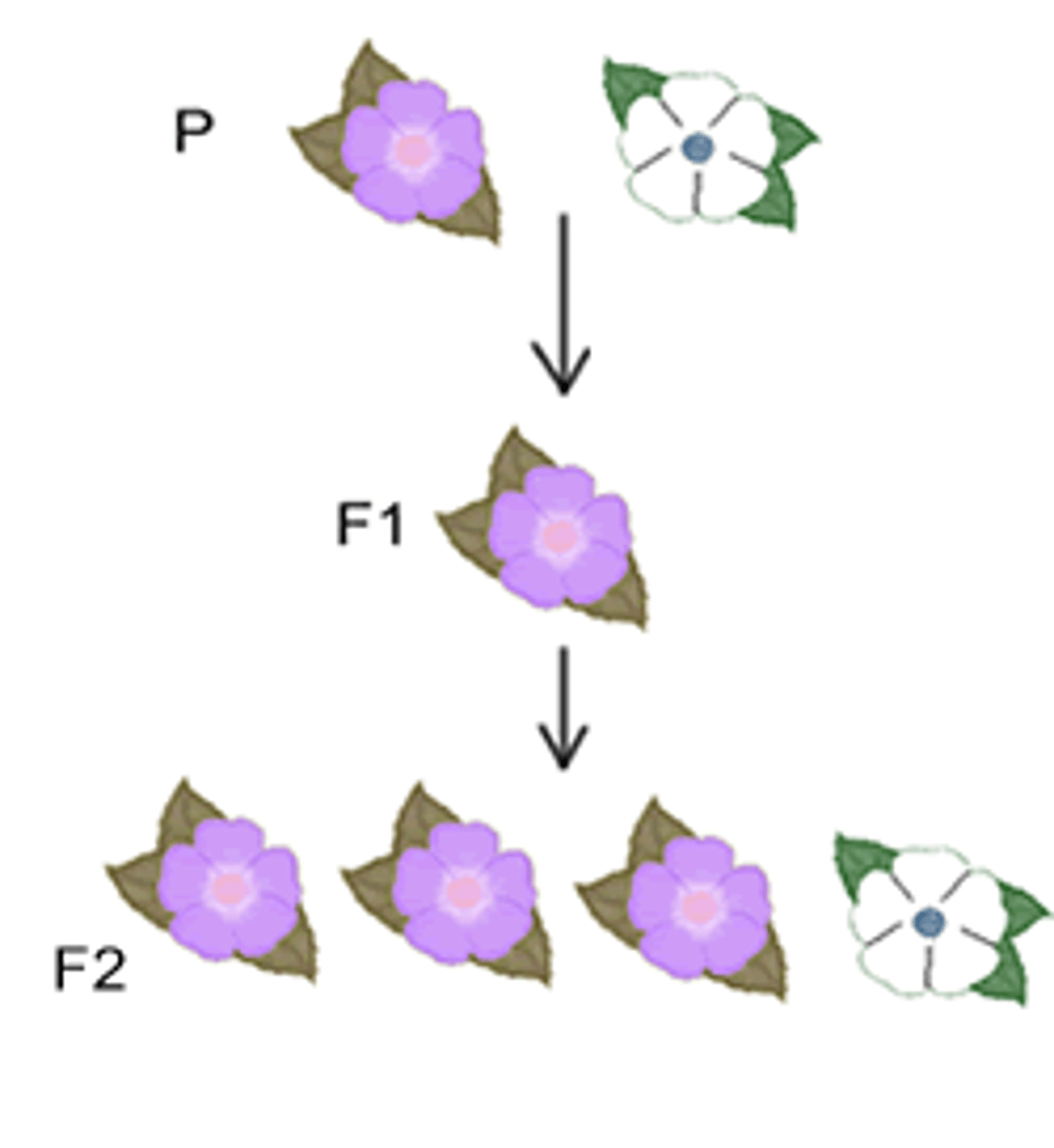
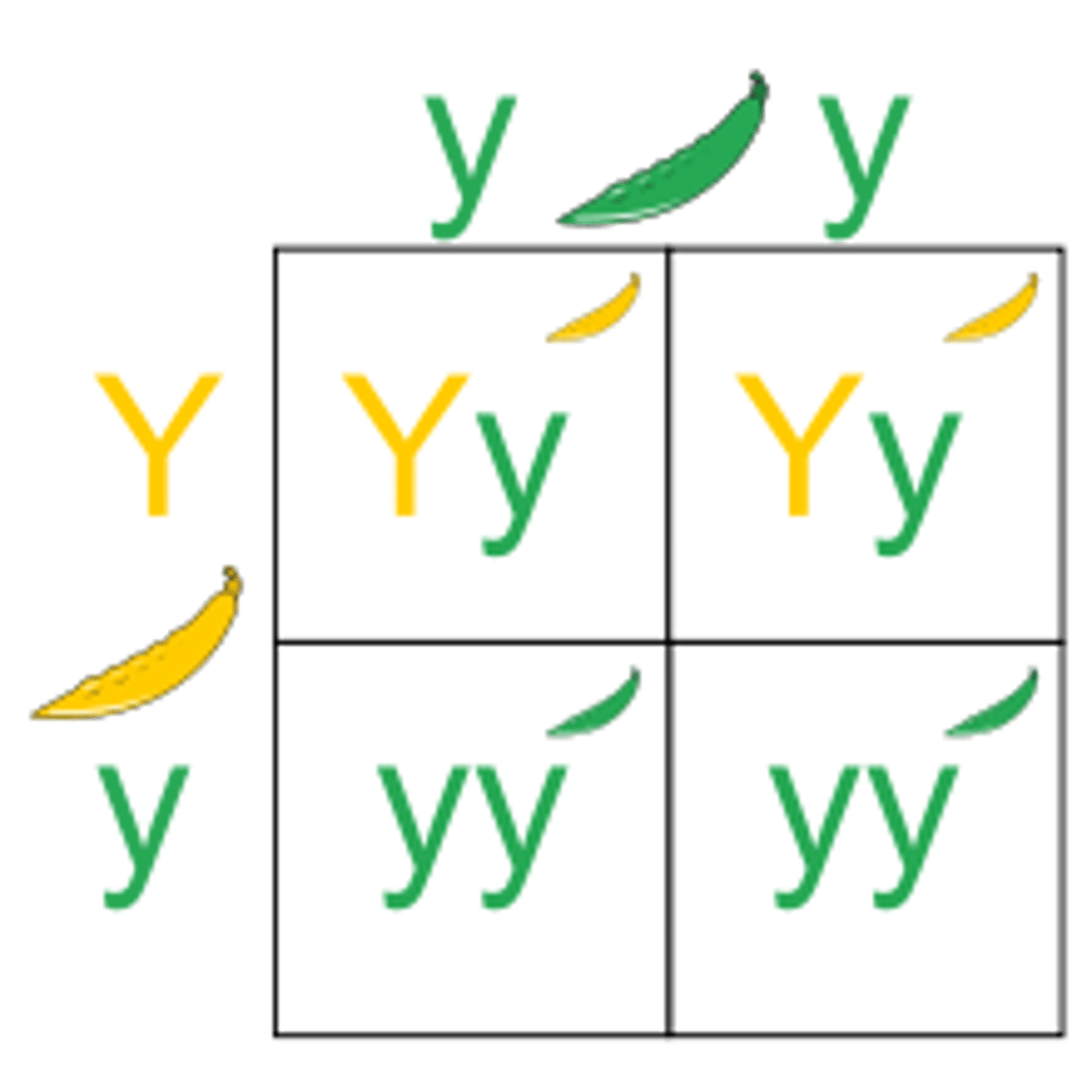
Punnett Square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
Multiple alleles
three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait (e.g. blood type ABO)

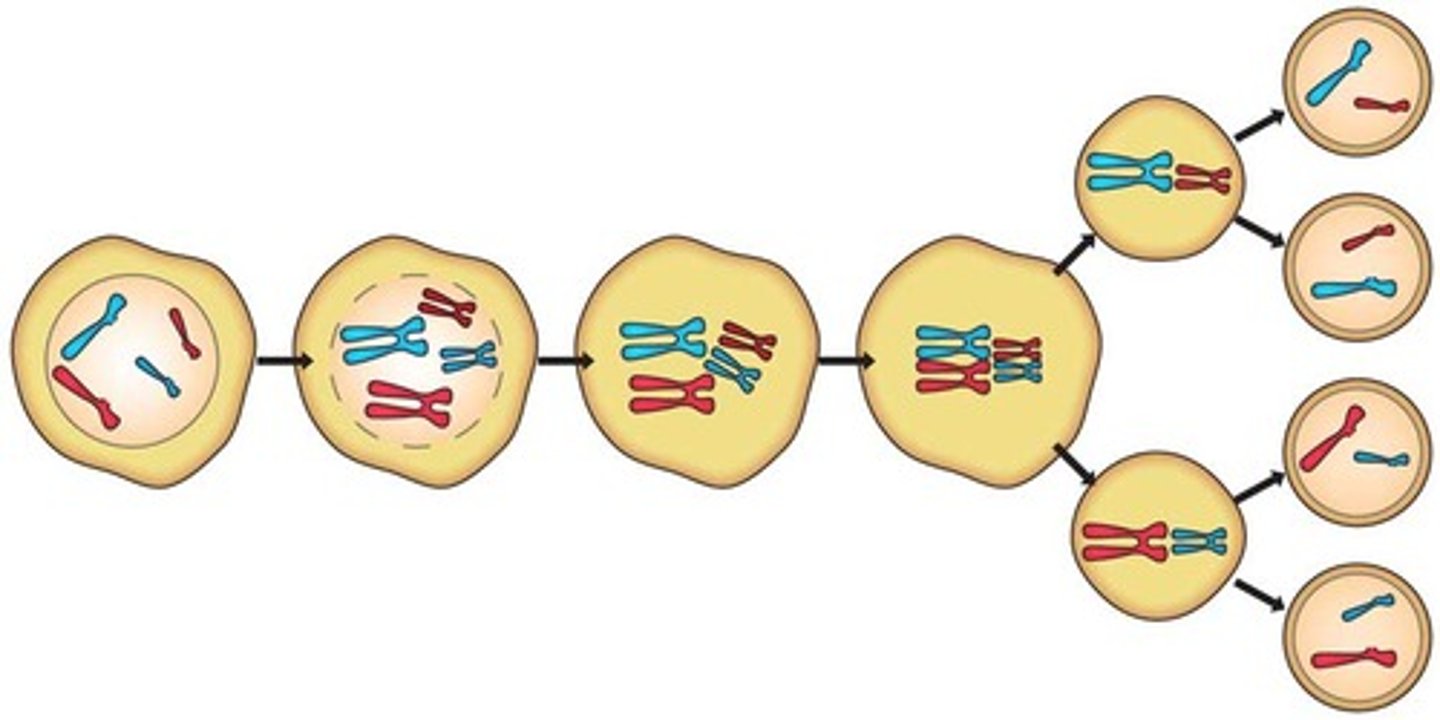
meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
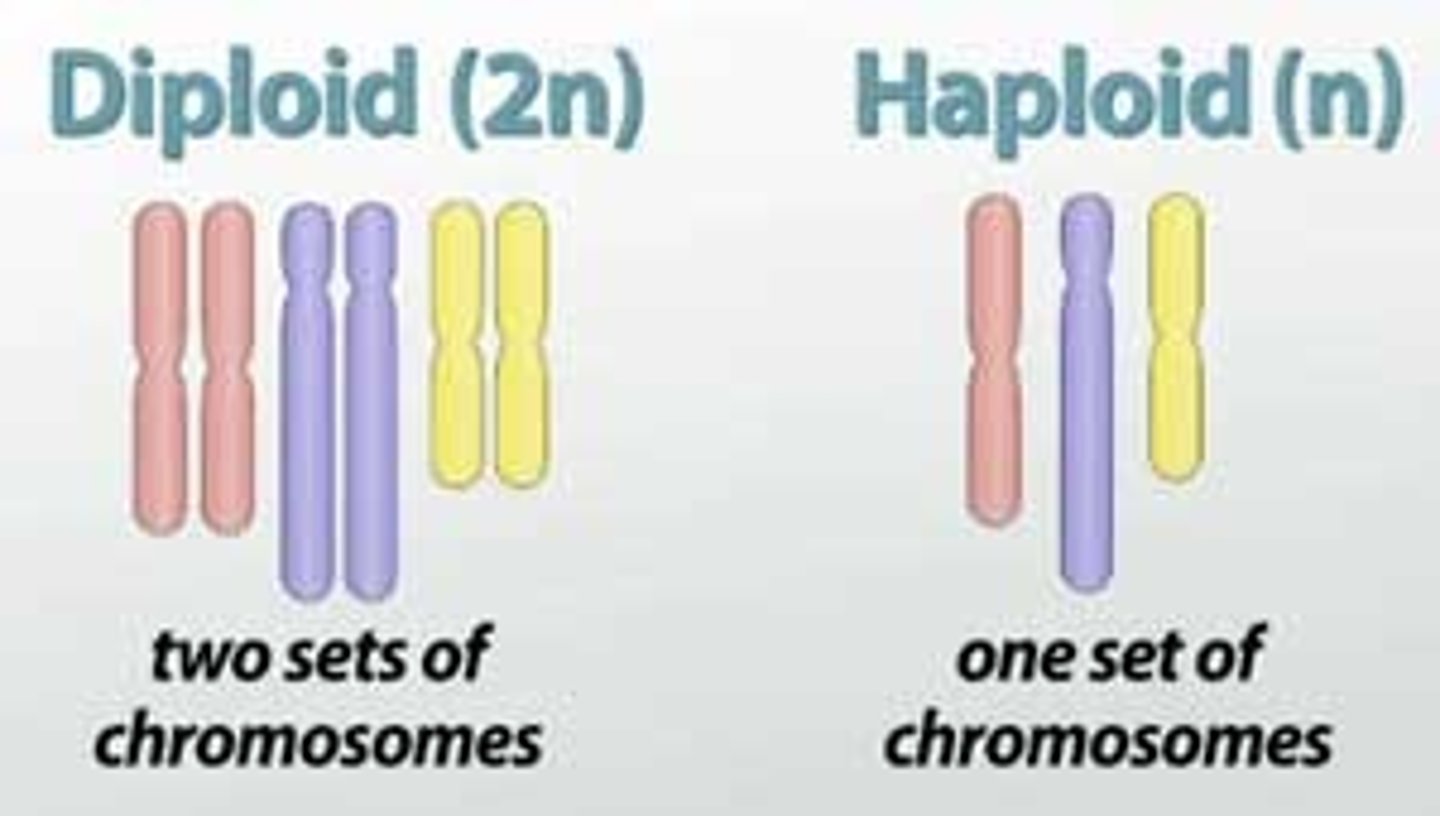
diploid
2n - containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
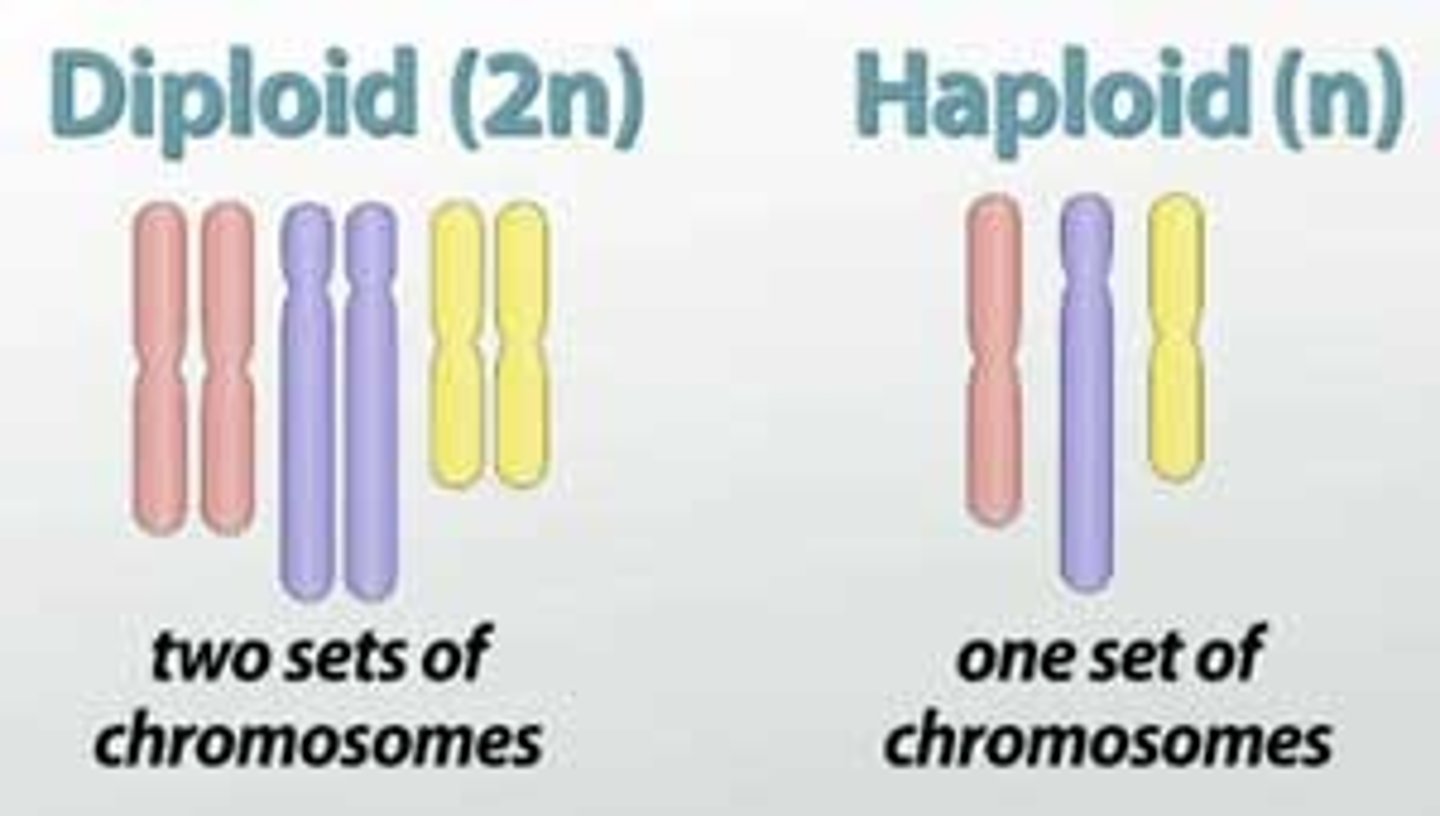
haploid
n - having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
crossing-over
Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I of meiosis LEADS TO GENETIC DIVERSITY

genetic flow
movement of genes from one population to another
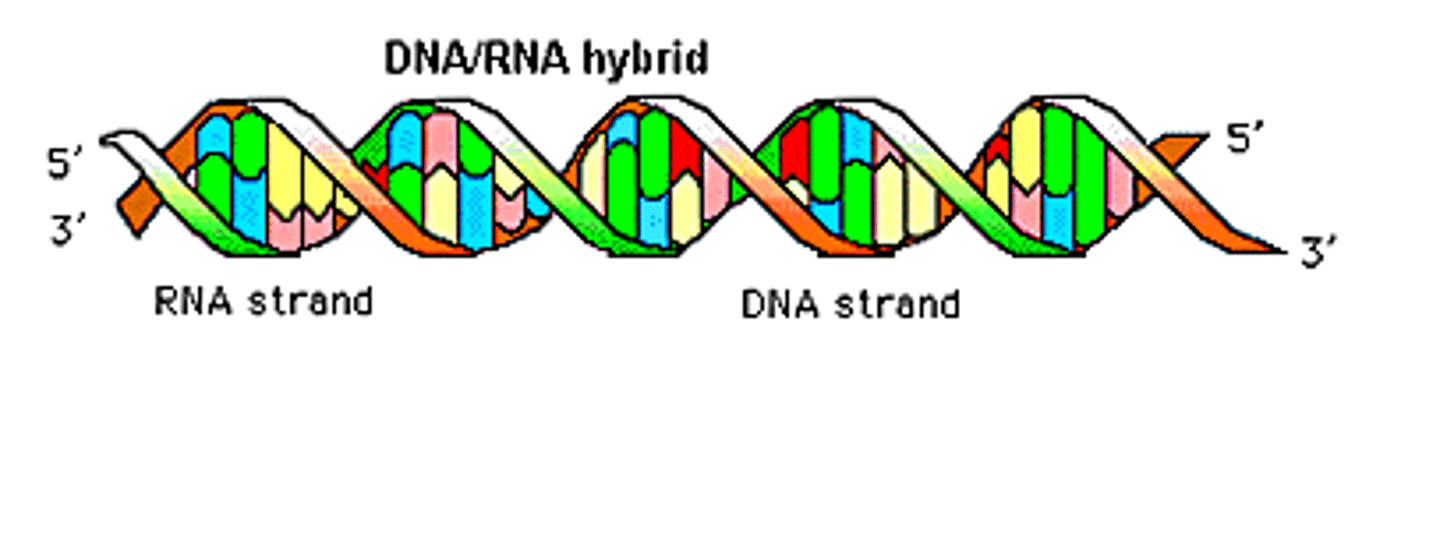
Nucleic Acid
DNA is a type of macromolecule
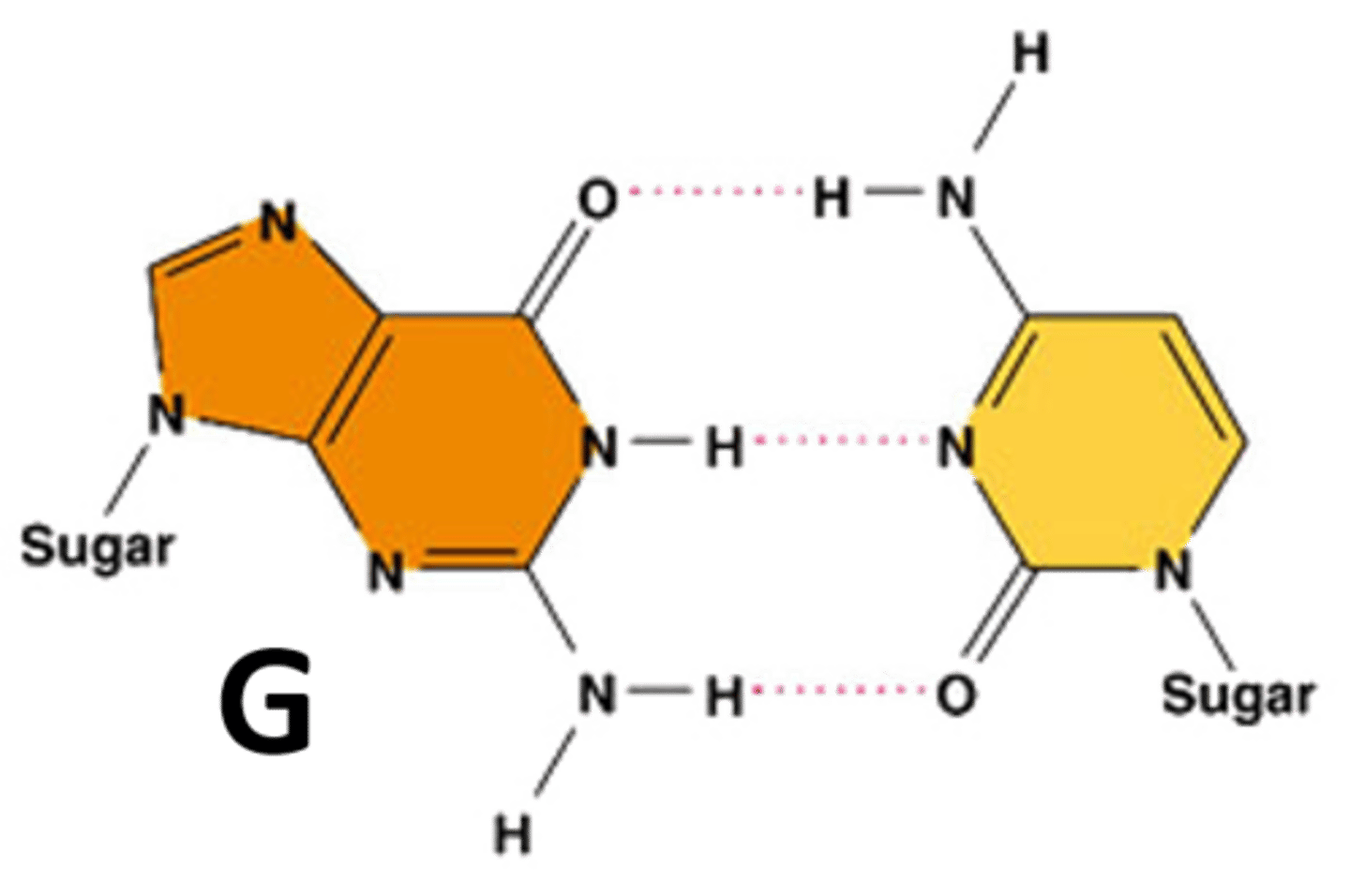
Guanine
Nitrogenous base in DNA complementary to cytosine
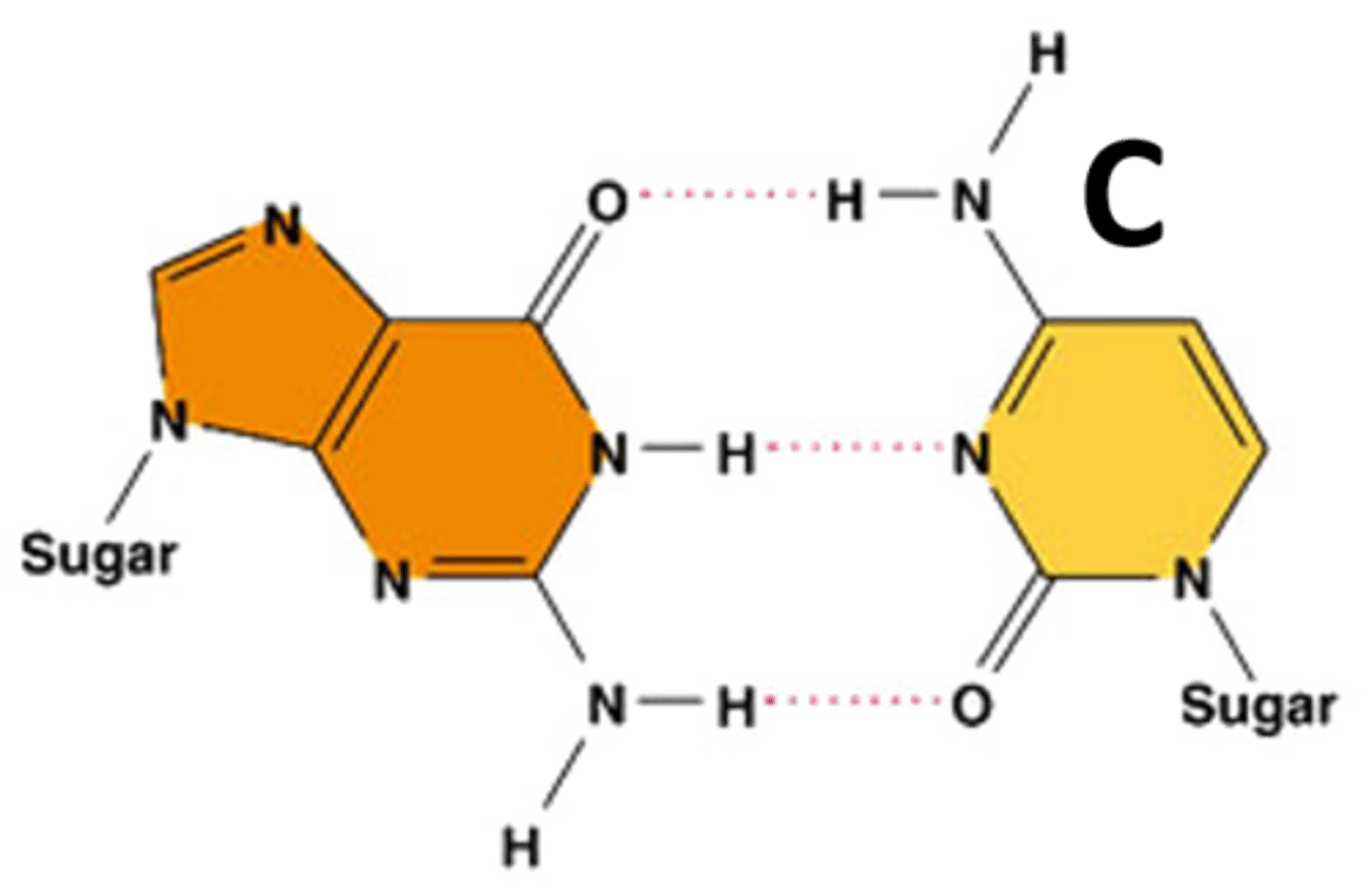
Cytosine
One of the four nitrogenous bases in DNA
Base-Pair Rules
Adenine pairs with thymine, guanine pairs with cytosine

Double Helix
DNA structure resembling a twisted ladder

Watson and Crick
Scientists who established DNA's double helix structure

Nitrogenous Bases
Form the 'rungs' of the DNA ladder connected by hydrogen bonds (A, T, C, G)
DNA Replication
Process where DNA makes a copy of itself
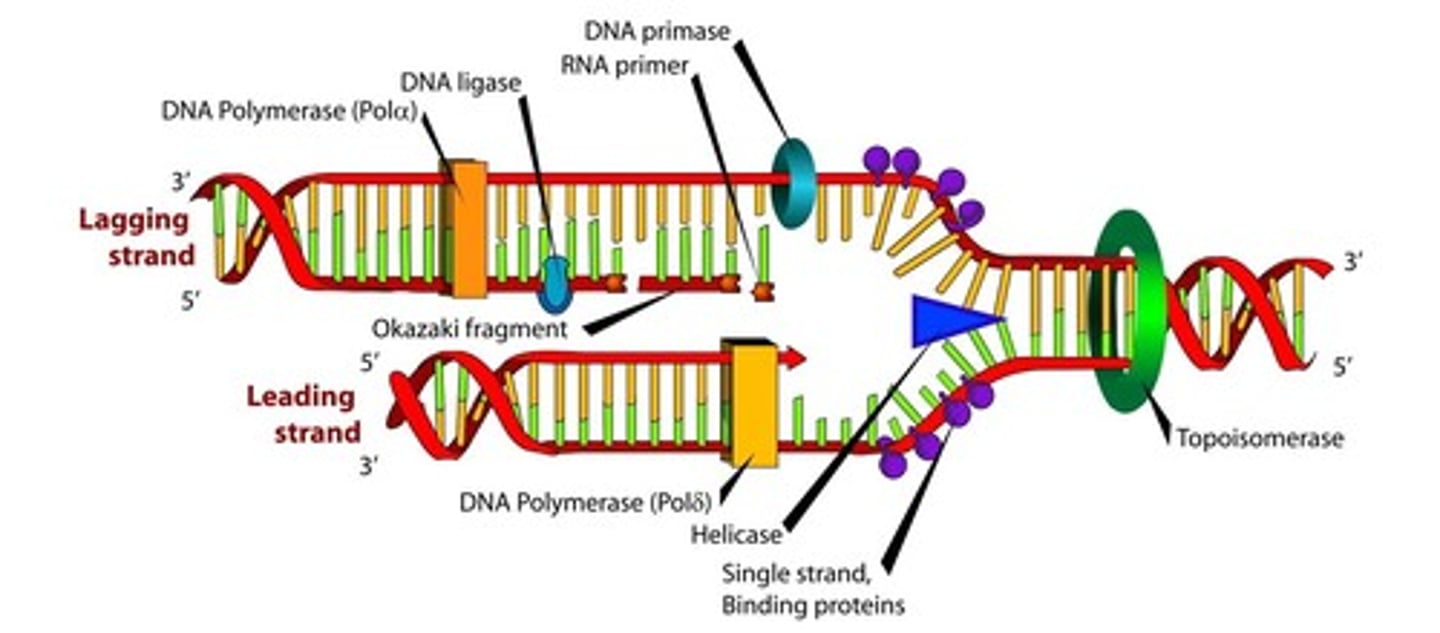
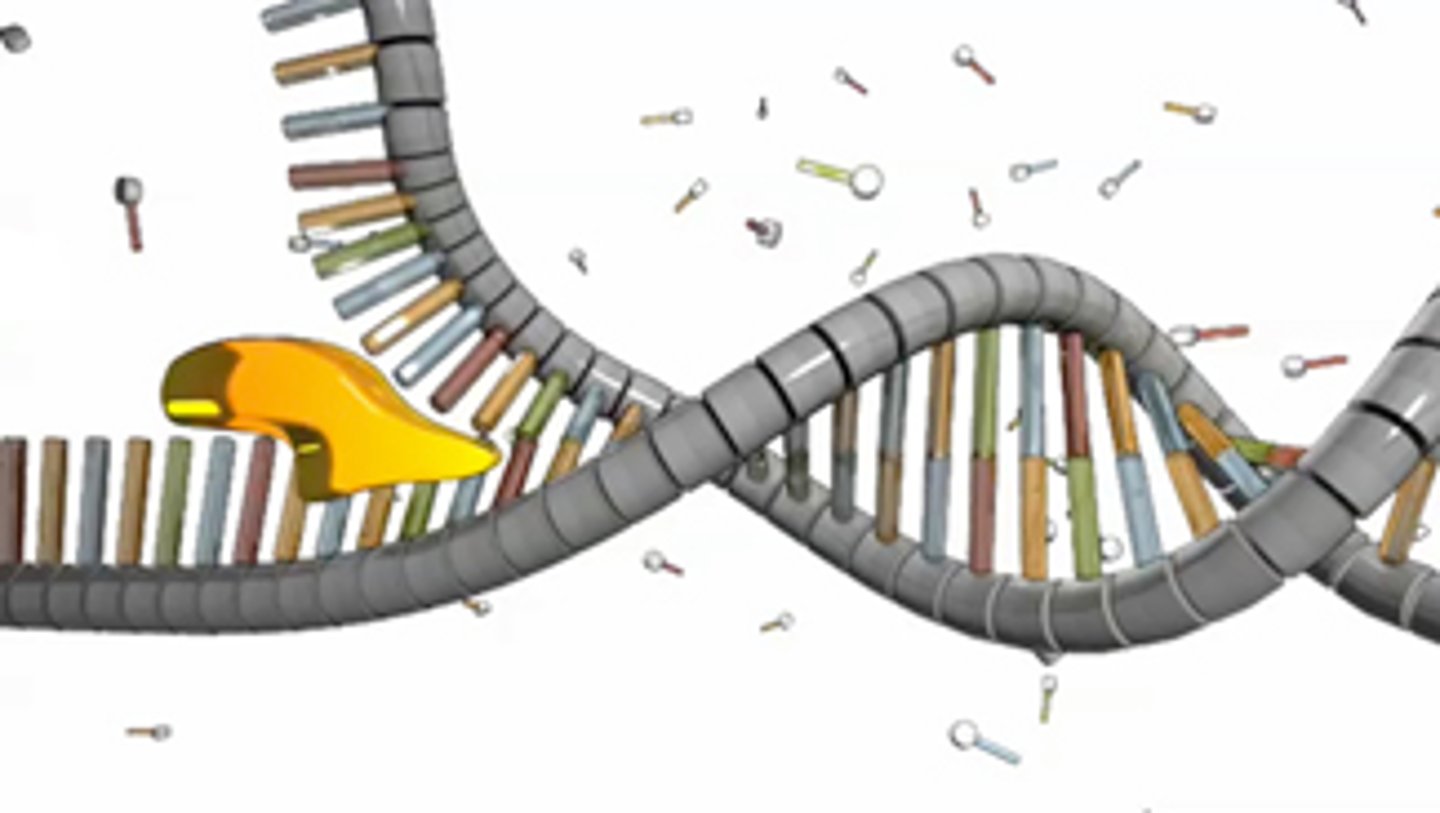
Helicase
Enzyme unzipping DNA strands during replication
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme adding free nucleotides during DNA replication

Ligase
Connects lagging strands of DNA during replication

Transcription
Process of mRNA synthesis from DNA
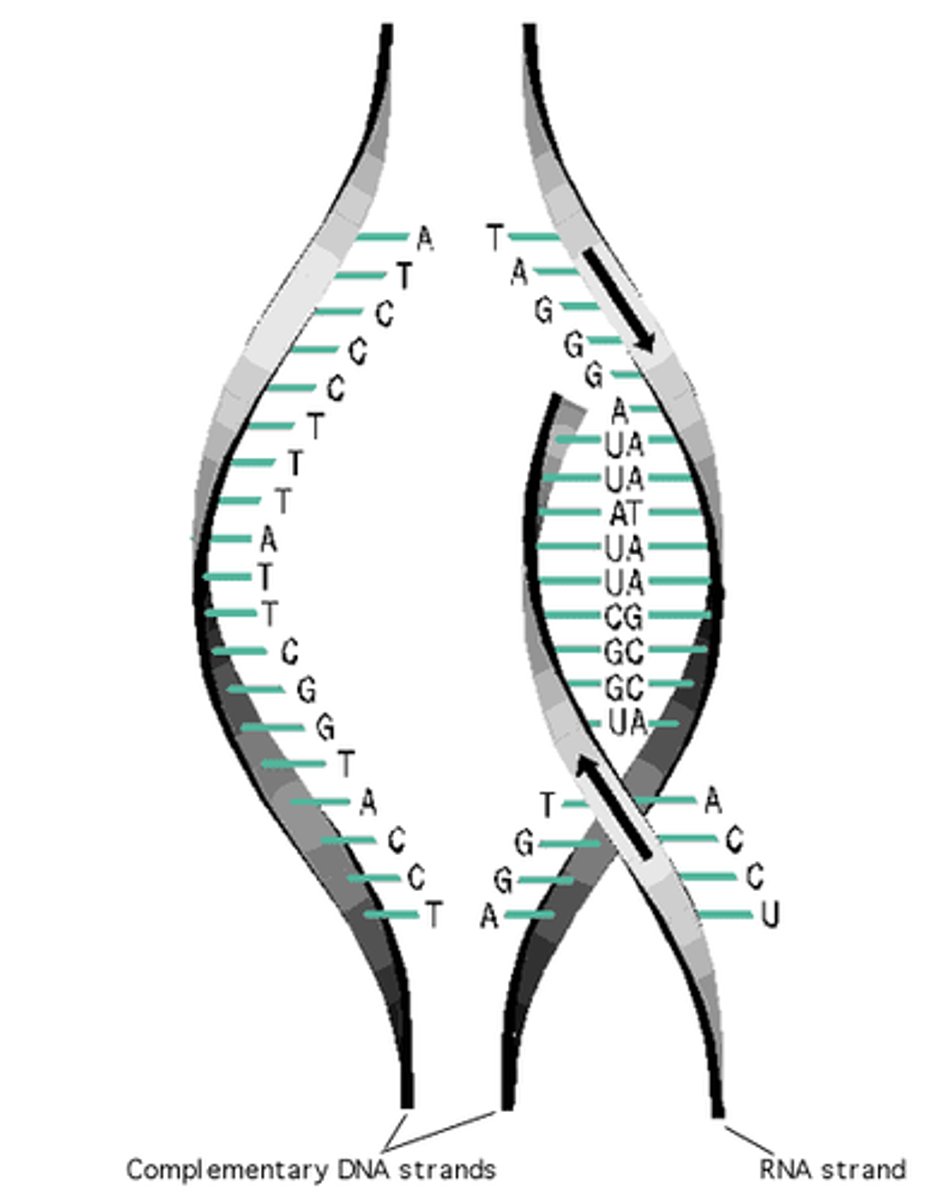
Translation
Ribosome decoding mRNA to synthesize proteins
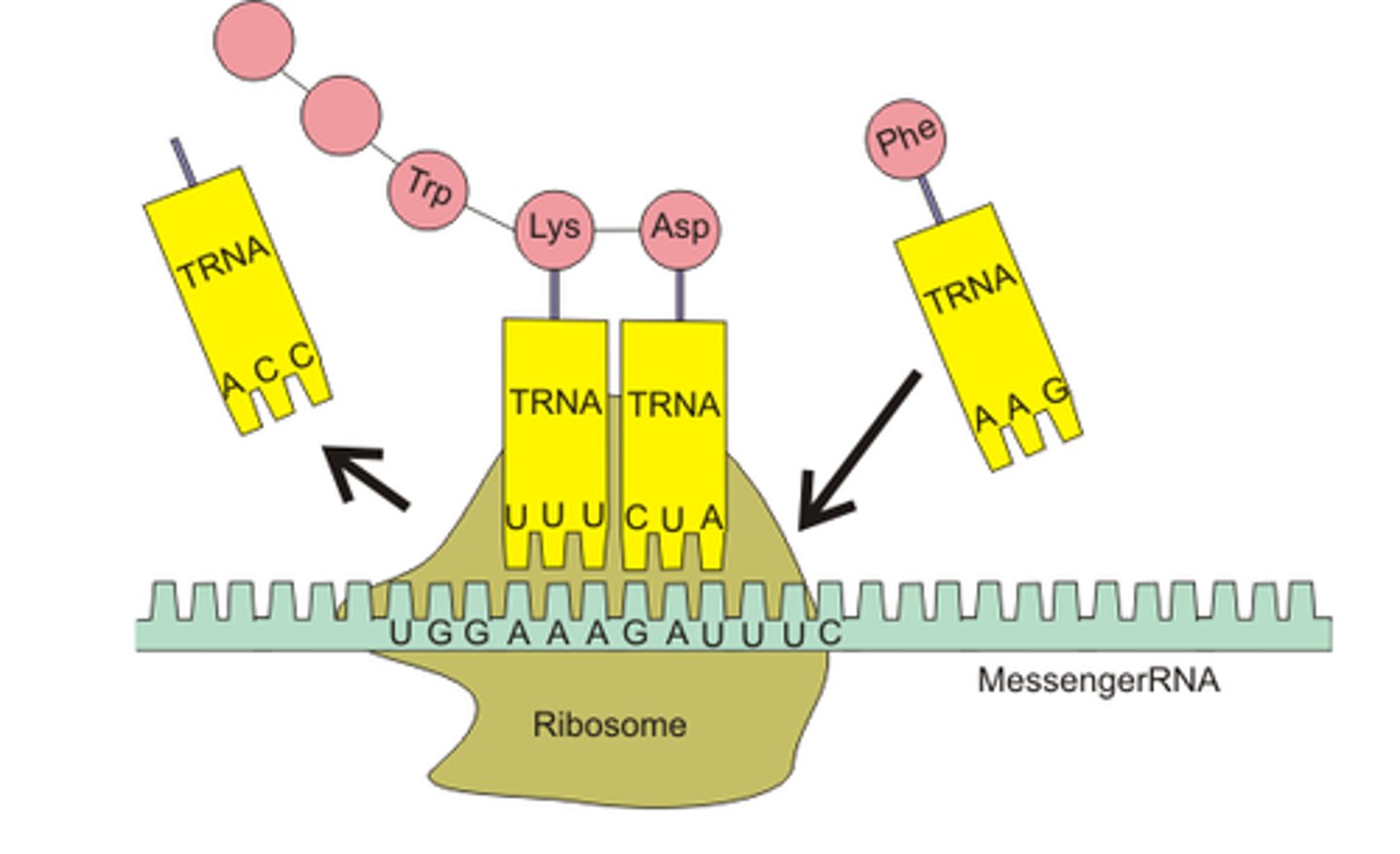
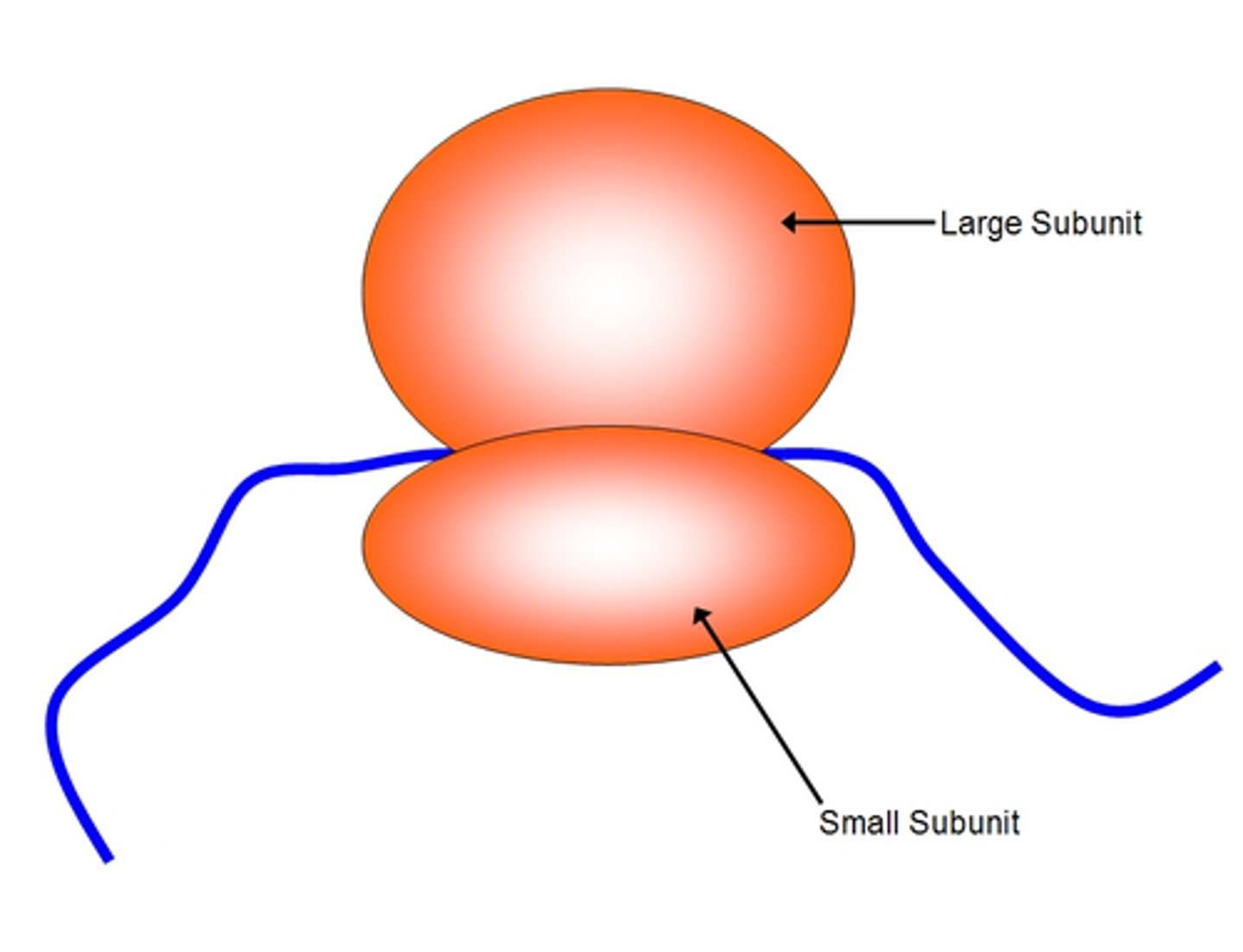
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis in the cell
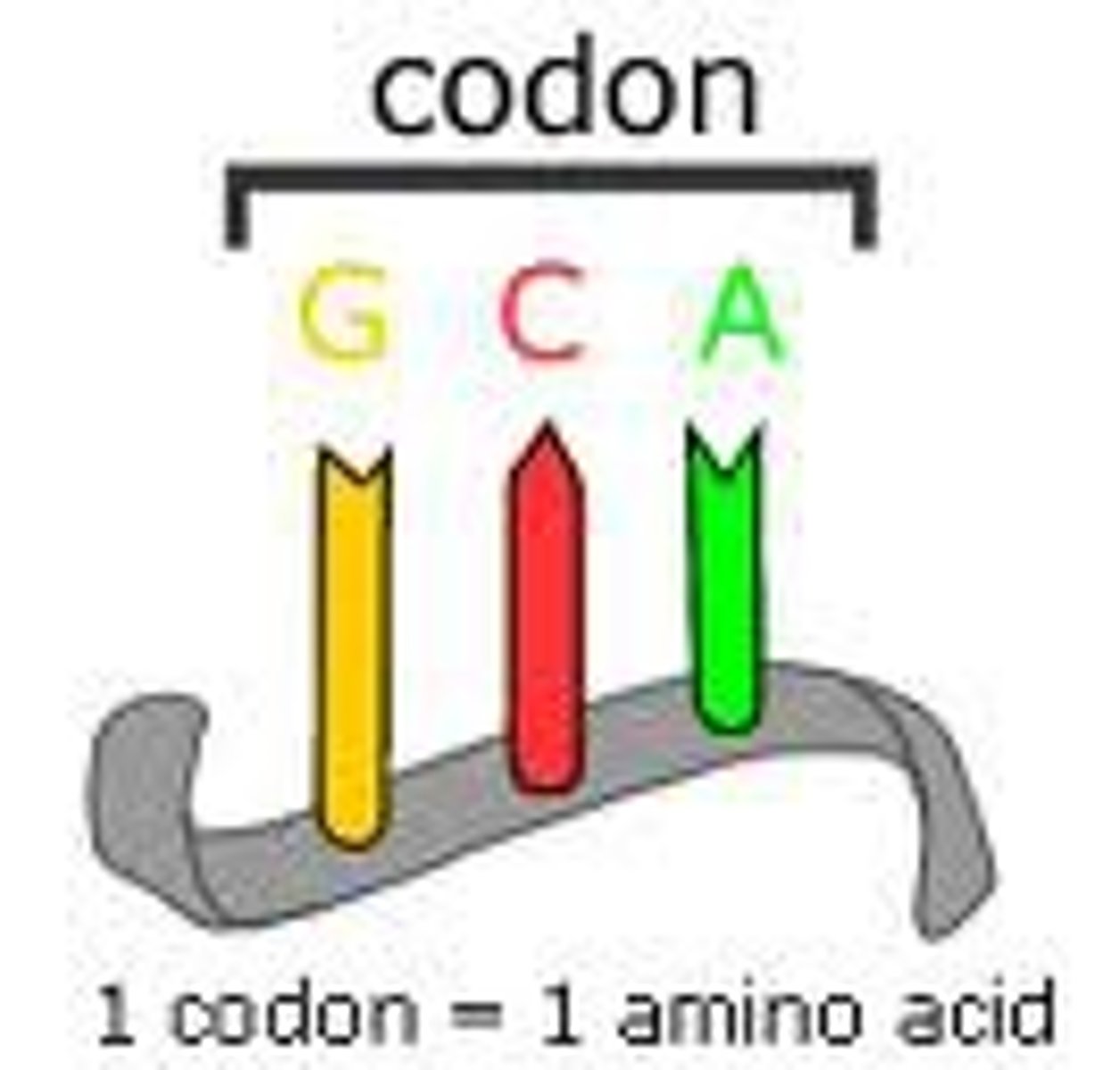
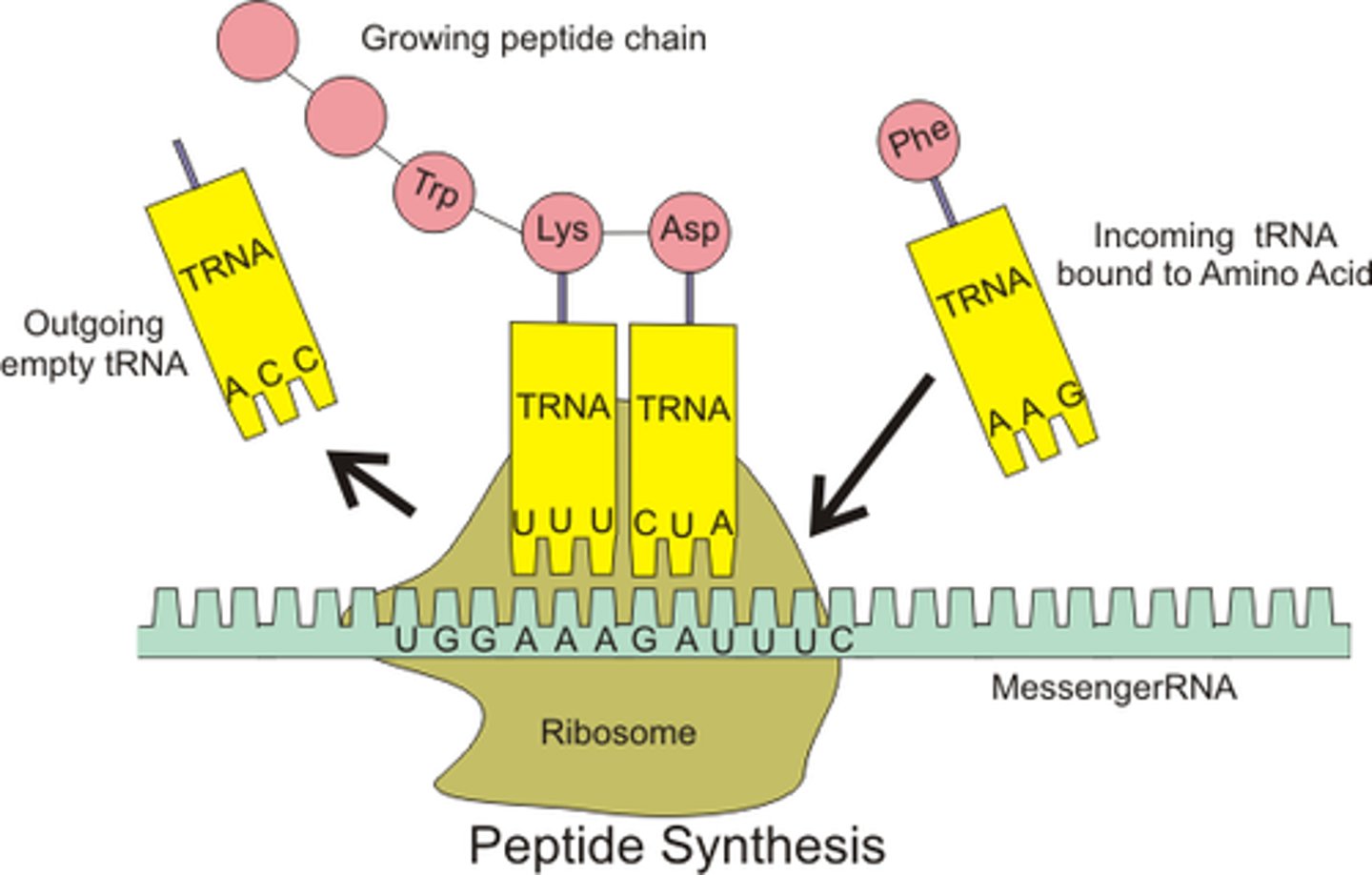
Codon
mRNA nucleotide triplet corresponding to an amino acid
Anticodon
tRNA nucleotide triplet attached to an amino acid
You have to have their ____ to put them in the ______! (Base-Pair Rules)
@ (AT); Group Chat (CG)
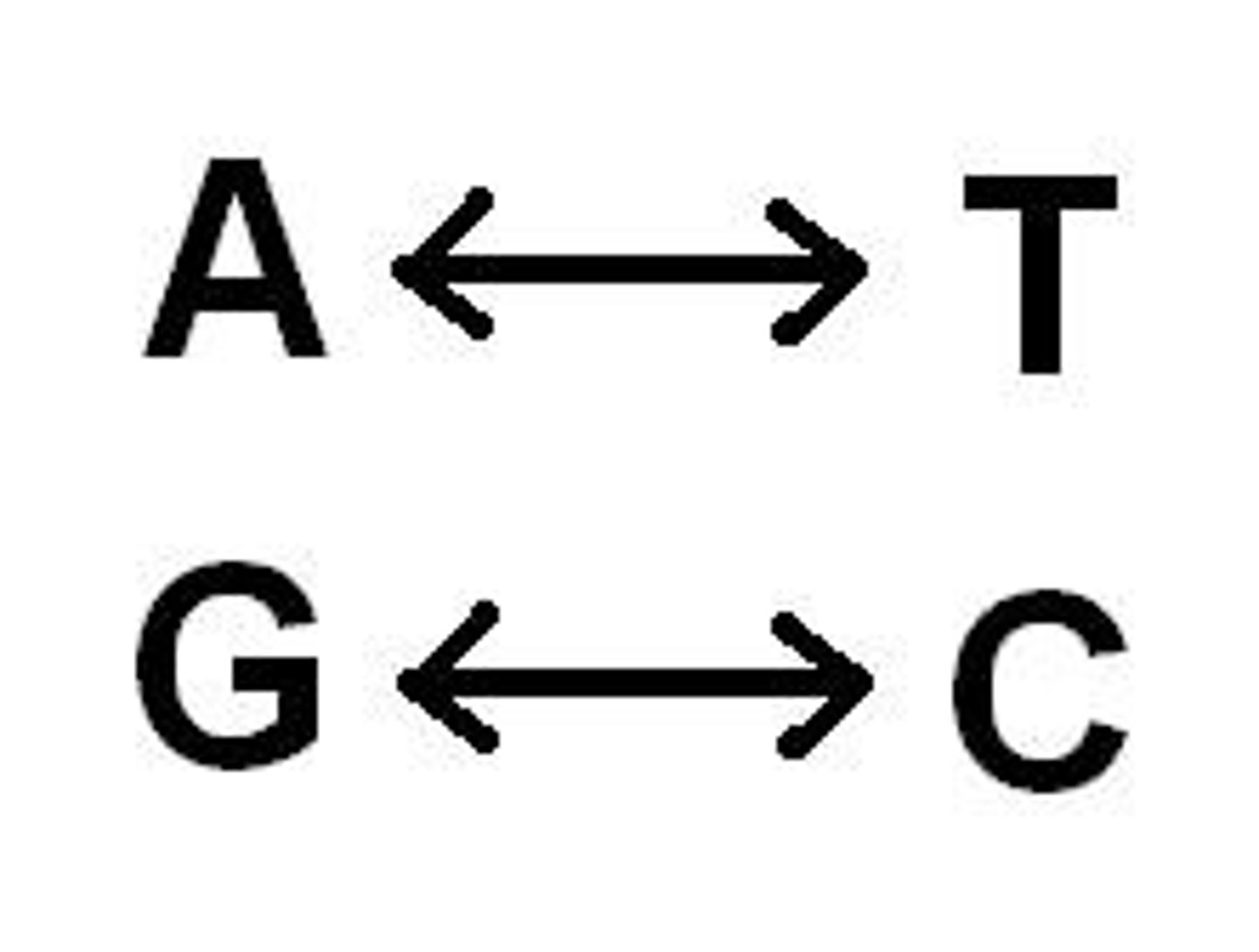
Stop Codon
codon that signals to ribosomes to stop translation

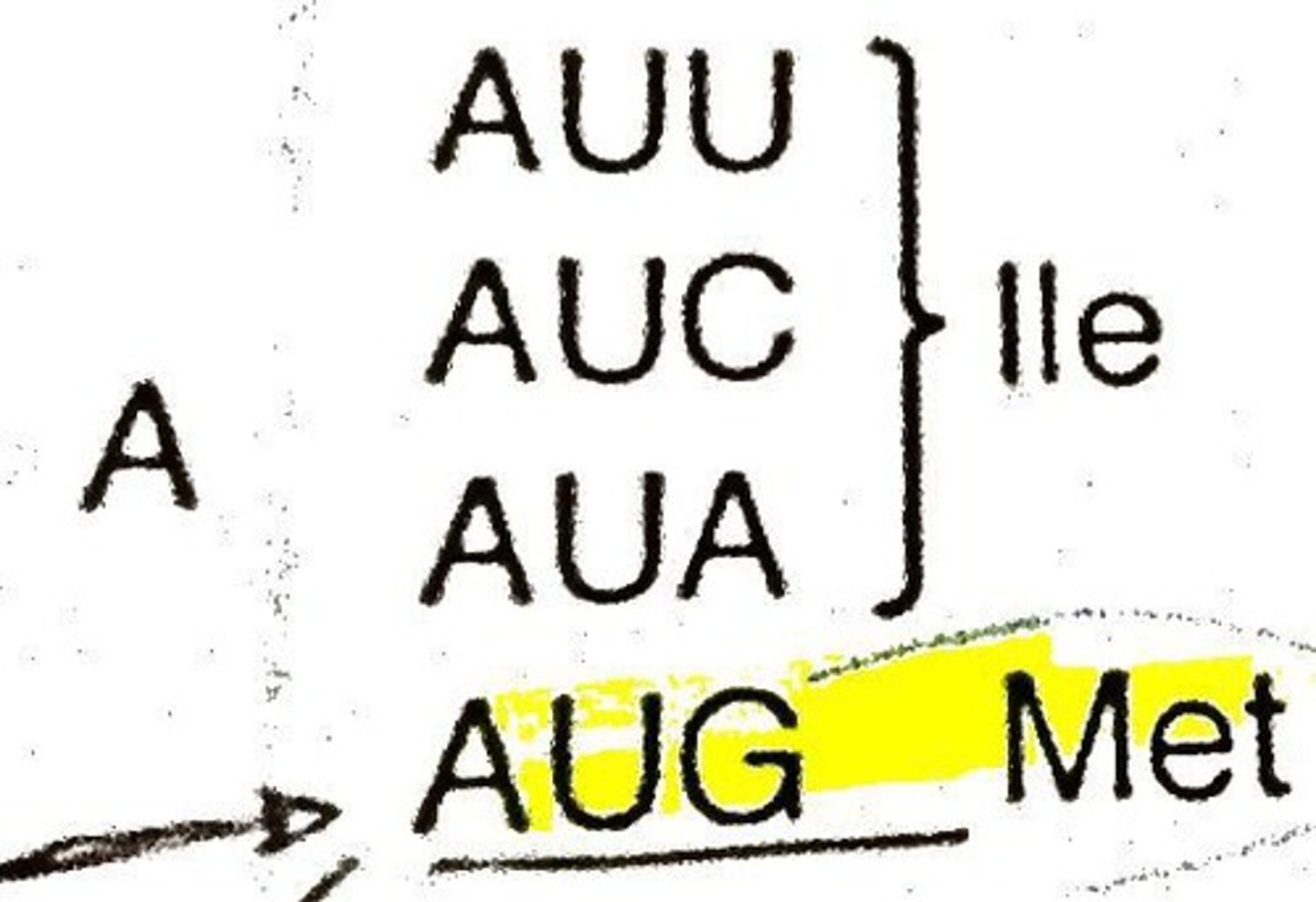
Start Codon
AUG (methionine)
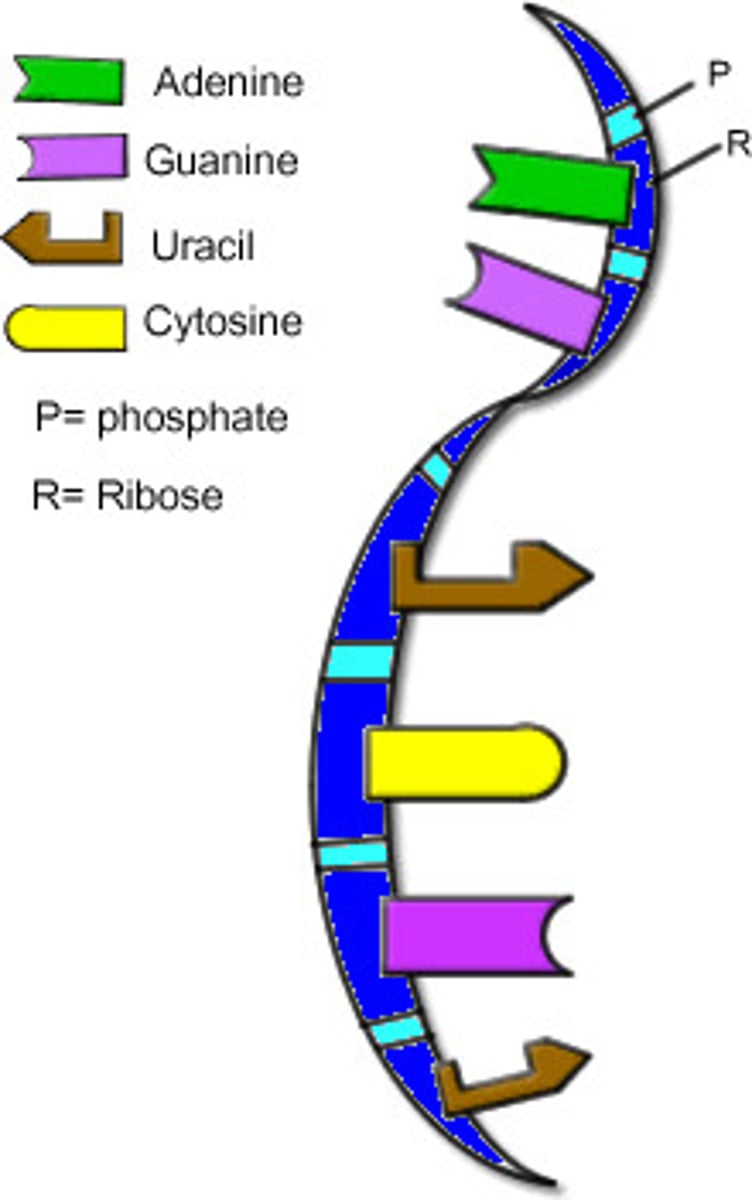
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
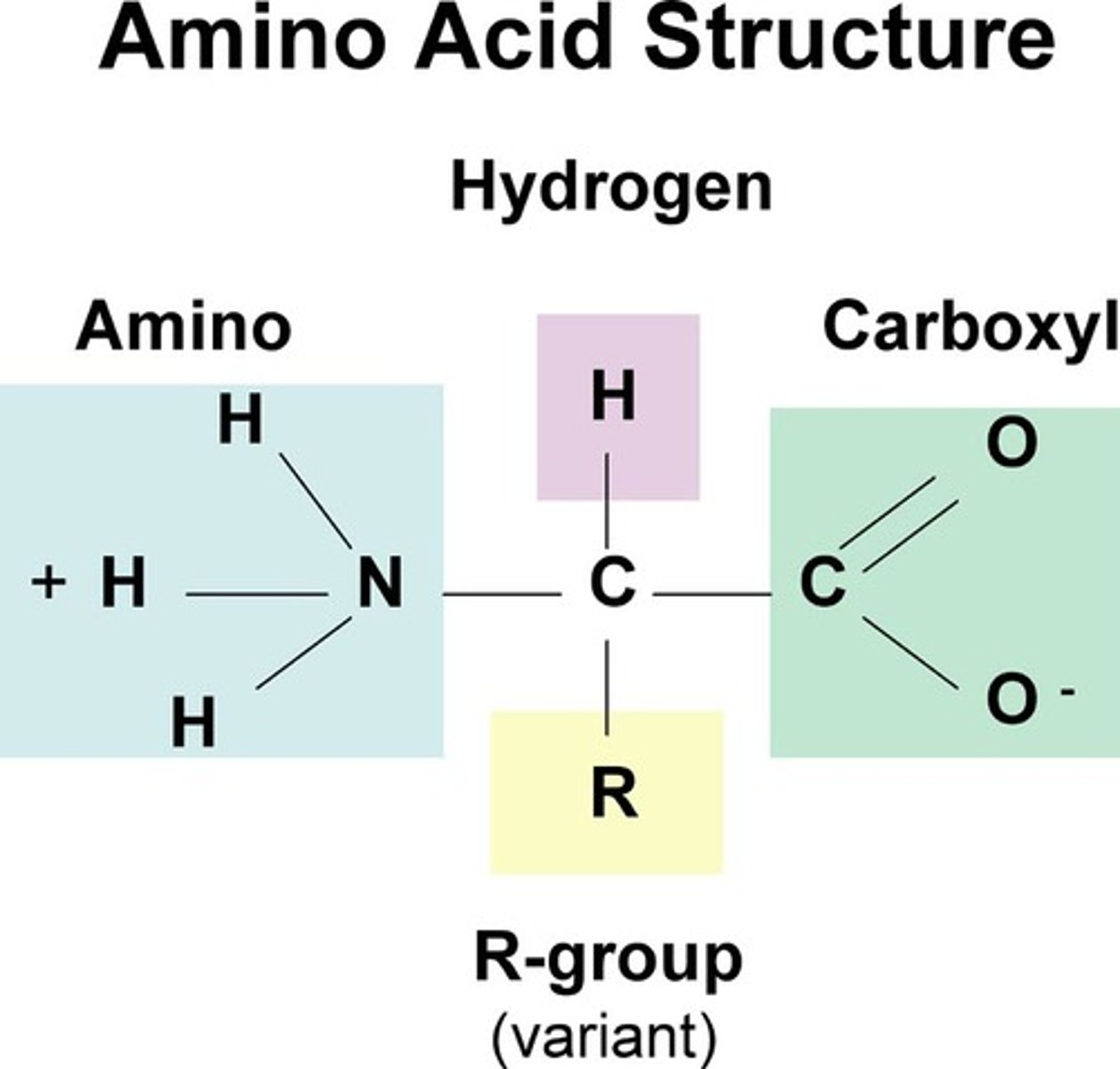
Amino Acid
Building blocks of proteins, 20 types exist.
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
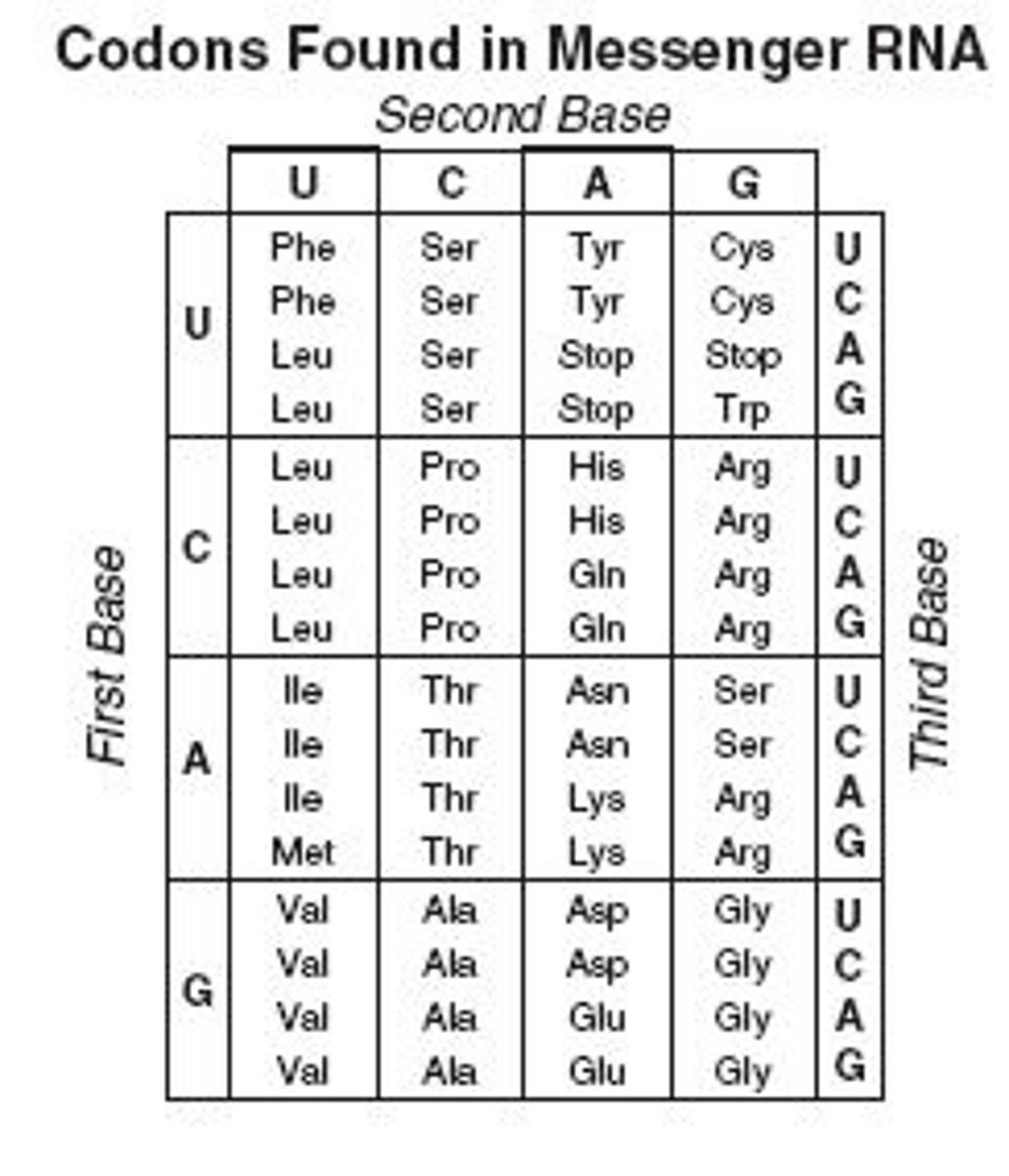
Codon Chart
shows which mRNA codon codes for a specific amino acid in translation
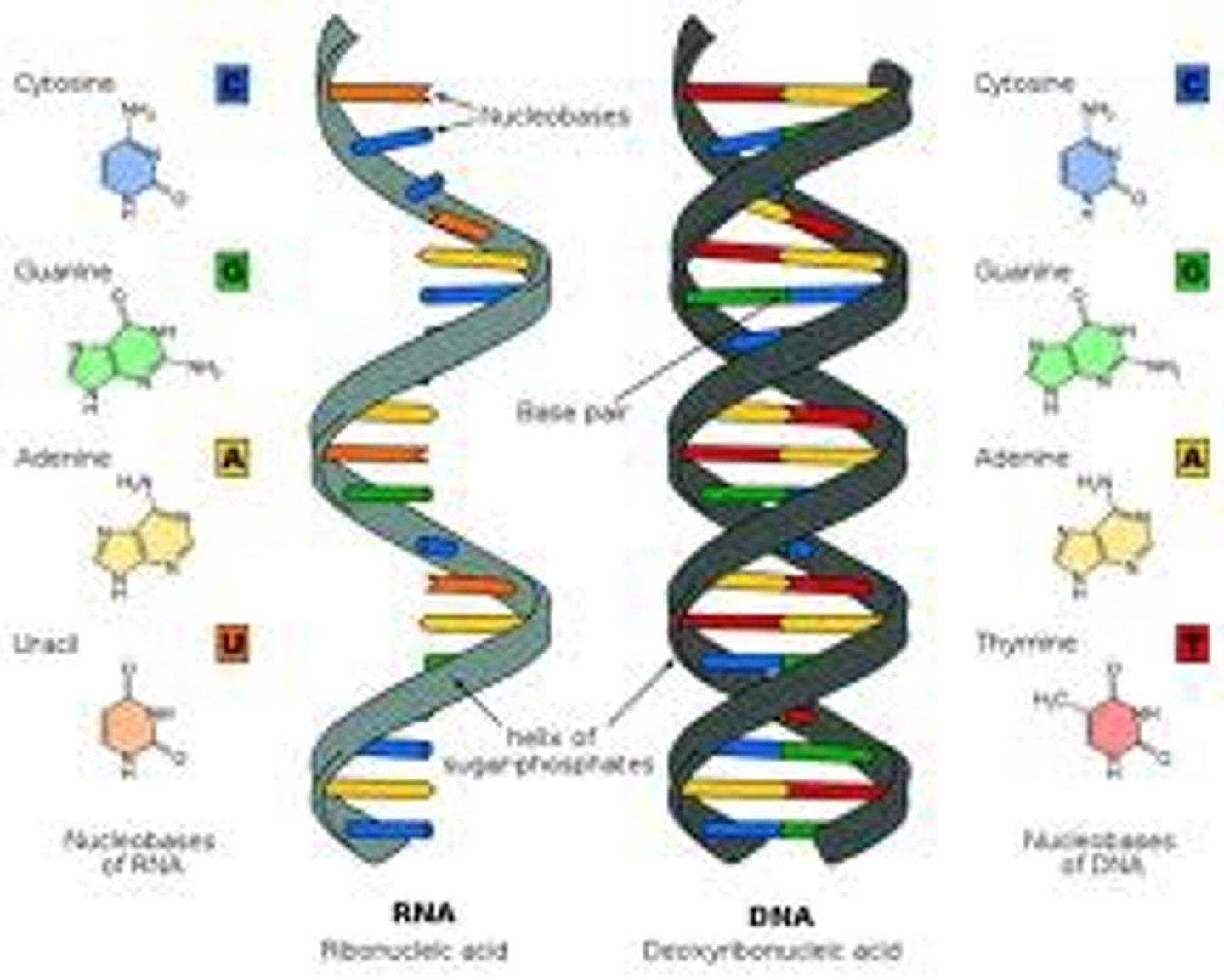
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA: 1 type. Double stranded. T instead of U. Sugar deoxyribose
RNA: 3 types (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA. 1 stranded. U instead of T. Sugar ribose
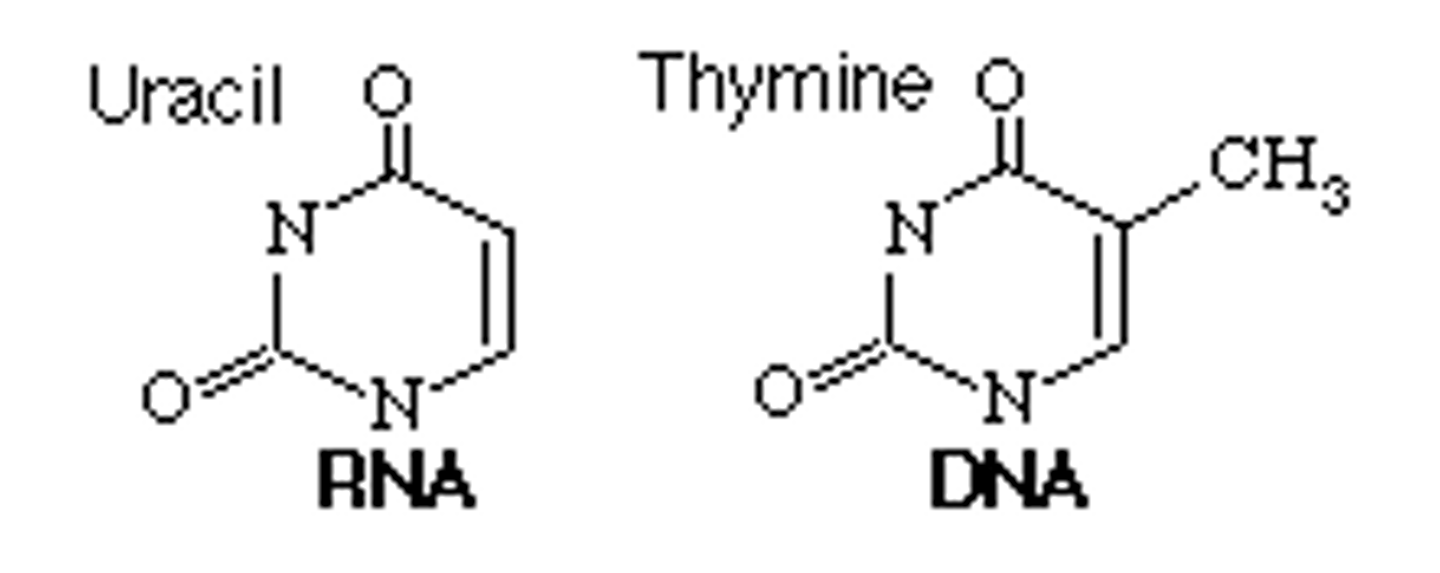
What base does RNA have instead of T?
U
Why can't DNA leave the nucleus?
It's too big - double stranded

artificial selection
selective breeding of plants and animals BY HUMANS to promote the occurrence of desirable traits in offspring (e.g. ancient banana --> modern banana)
heritability
the ability of a trait to be passed down from one generation to the next