A&P II - Chapter 21
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
E) lipids
Special lymphoid vessels, called lacteals, absorb dietary __________ that are not absorbed by the blood capillaries.
A) water
B) glucose
C) vitamins
D) amino acids
E) lipids
True
T/F: The lymphoid system is involved in fluid recovery, immune surveillance, and lipid absorption.
True
T/F: Red bone marrow is where all immune cells of the lymphoid system originate.
False
T/F: Lymph originates in blood capillaries that pick up tissue fluid.
B) 15%
Lymphatic vessels recover about __________ of the fluid filtered by capillaries.
A) 5%
B) 15%
C) 25%
D) 50%
E) 85%
A) protein
Lymph is similar to blood plasma, but very low in __________.
A) protein
B) carbon dioxide
C) metabolic waste
D) electrolytes
E) sodium and potassium
D) The lymphatic node pump
Which of the following forces does not help lymph to flow?
A) Rhythmic contractions of lymphatic vessels
B) The thoracic pump
C) The skeletal muscle pump
D) The lymphatic node pump
E) Arterial pulsations squeezing lymphatic vessels
D) Collecting ducts; subclavian veins
__________ are the largest of the lymphatic vessels, and they empty into the __________.
A) Lymphatic trunks; collecting ducts
B) Lymphatic trunks; subclavian arteries
C) Lymphatic trunks; subclavian veins
D) Collecting ducts; subclavian veins
E) Collecting ducts; subclavian arteries
E) Eosinophils
__________ are found especially in the mucous membrane, standing guard against parasites and allergens.
A) Monocytes
B) Lymphocytes
C) Basophils
D) Neutrophils
E) Eosinophils
A) Neutrophils
__________ employ a "respiratory burst" to produce bactericidal chemicals such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hypochlorite (HClO).
A) Neutrophils
B) Basophils
C) Cytotoxic T cells
D) Natural killer cells
E) Suppressor T cells
E) natural killer (NK) cells
Immune surveillance is a process in which __________ nonspecifically detect and destroy foreign cells and diseased host cells.
A) T lymphocytes (T cells)
B) reticular cells
C) dendritic cells
D) macrophages
E) natural killer (NK) cells
A) cytotoxic T cells
Perforin is released by __________.
A) cytotoxic T cells
B) class I MHCs
C) peptide fragments
D) viruses
E) APCs
D) Macrophages
Which of the following is not an example of lymphoid tissue?
A) Aggregated lymphoid nodules
B) MALT
C) Lymphoid nodules
D) Macrophages
E) Diffuse lymphoid tissue
A) Aggregated lymphoid nodules
Which of the following is common in the distal small intestine?
A) Aggregated lymphoid nodules
B) MALT
C) Lymphoid nodules
D) Macrophages
E) Diffuse lymphoid tissue
D) thymus
T cells achieve immunocompetence in the __________.
A) bone marrow
B) bloodstream
C) spleen
D) thymus
E) liver
C) palatine
The __________ tonsils are the largest, and their surgical removal (tonsillectomy) used to be one of the most common surgical procedures performed in children.
A) adenoid
B) lingual
C) palatine
D) pharyngeal
E) nasopharyngeal
B) thymus
The __________ show(s) a remarkable degree of degeneration (involution) with age.
A) lymph nodes
B) thymus
C) spleen
D) pharyngeal tonsils
E) appendix
A) lymph nodes
The only lymphoid organ(s) with afferent lymphatic vessels is(are) the __________.
A) lymph nodes
B) thymus
C) spleen
D) red bone marrow
E) tonsils
C) thymus
Removal of the __________ would be more harmful to a one-year-old child than an adult.
A) spleen
B) lymph node
C) thymus
D) appendix
E) palatine tonsil
True
T/F: A pathogen is a disease-causing microbe.
True
T/F: The immune system spans nearly every organ and tissue in the human body.
D) The gastric juices
Which of the following does(do) not belong to the second line of defense?
A) The macrophage system
B) Natural killer cells
C) Inflammation
D) The gastric juices
E) Interferon and the complement system
True
T/F: Mucous membranes prevent most pathogens from entering the body because of the stickiness of the mucus and the presence of lysozymes.
D) Innate immunity; adaptive immunity
__________ lacks the capacity to remember a pathogen or react differently to it in the future, whereas __________ utilizes memory cells to adapt to a given pathogen and ward it off more easily in the future.
A) Innate immunity; cytotoxicity
B) Adaptive immunity; innate immunity
C) A natural killer cell; a macrophage
D) Innate immunity; adaptive immunity
E) Natural immunity; artificial immunity
True
T/F: Adaptive immunity involves macrophages, antibodies, and interleukin.
C) granzymes
One group of proteolytic enzymes secreted by natural killer (NK) cells is __________.
A) selectins
B) cytokines
C) granzymes
D) perforins
E) interferons
D) heparin; histamine
Basophils of the blood help to get defensive leukocytes to the site quickly by releasing an anticoagulant called __________ and a vasodilator called __________.
A) bradykinin; histamine
B) selectin; prostaglandin
C) histamine; heparin
D) heparin; histamine
E) prostaglandins; selectin
C) natural killer cells
When an enemy cell is present, a(n) __________ secretes perforins, which bore a hole in the enemy cell membrane.
A) interferon
B) interleukin
C) natural killer cells
D) antibody
E) opsonization
False
T/F: Interferons are secreted in response to bacterial infections.
E) neutrophils and macrophages; opsonization
Complement C3b protein coats bacteria and stimulates phagocytosis by __________ during a process called __________.
A) lymphocytes and monocytes; opsonization
B) neutrophils and macrophages; cytolysis
C) mast cells and basophils; opsonization
D) mast cells and basophils; cytolysis
E) neutrophils and macrophages; opsonization
B) Interferons
__________ are secreted by cells infected with viruses, alerting neighboring cells and protecting them from becoming infected.
A) Complement system globulins
B) Interferons
C) Granzymes
D) Pyrogens
E) Perforins
B) Interferons
__________ are antimicrobial proteins.
A) Bradykinins
B) Interferons
C) Cytokines
D) Kinins
E) Prostaglandins
C) neutrophils and macrophages
Endogenous pyrogens are produced by __________.
A) bacteria
B) mast cells
C) neutrophils and macrophages
D) plasma cells
E) viruses
False
T/F: Pyrogens act by increasing the set point for body temperature in the thalamus.
E) fever
A pyrogen is a substance that causes __________.
A) inflammation
B) opsonization
C) complement fixation
D) cytolysis
E) fever
B) margination
The first of a series of neutrophil behaviors in inflammation is __________.
A) chemotaxis
B) margination
C) diapedesis
D) phagocytosis
E) opsonization
True
T/F: Pus is made of dead neutrophils, macrophages, and other tissue debris from a damaged tissue.
A) Impaired use
__________ is not a cardinal sign characteristic of inflammation.
A) Impaired use
B) Redness
C) Pain
D) Heat
E) Swelling
A) Cytotoxic T cells
Which of these cellular agents does not participate in inflammation?
A) Cytotoxic T cells
B) Macrophage
C) Eosinophils
D) Neutrophils
E) Endothelial cells
D) immunity is directed against a particular pathogen
One characteristic of the immune response is specificity. This means that __________.
A) immunity starts in defined organs in the body
B) immunity starts in specialized tissues in the body
C) immunity is carried on by a specific group of cells of the immune system
D) immunity is directed against a particular pathogen
E) immunity is carried on by a specific group of tissues of the immune system
False
T/F: Humoral immunity takes care of intracellular viruses, whereas cellular immunity takes care of extracellular viruses.
C) cancer cells
Cellular (cell-mediated) immunity is effective against __________.
A) allergens
B) venoms
C) cancer cells
D) extracellular viruses
E) toxins
B) artificial active
Vaccination stimulates __________ immunity.
A) natural active
B) artificial active
C) natural passive
D) artificial passive
E) innate
A) artificial passive
The serum used for emergency treatment of snakebites stimulates __________ immunity.
A) artificial passive
B) artificial active
C) natural passive
D) natural active
E) natural adaptive
False
T/F: The antigenicity of a molecule is due to specific regions of it called haptens.
A) epitope
A(n) __________ is the region of an antigen that stimulates an immune response.
A) epitope
B) disulfide bridge
C) hapten
D) major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
E) antibody monomer
A) two
Each immunoglobulin (Ig) has __________ antigen-binding site(s).
A) two
B) four
C) six
D) one
E) three
E) IgG
__________ constitutes about 80% of circulating antibodies in plasma.
A) IgD
B) IgE
C) IgA
D) IgM
E) IgG
D) IgA
Which class of immunoglobulin provides passive immunity to the newborn?
A) IgD
B) IgE
C) IgM
D) IgA
E) IgG
False
T/F: Naive T cells can synthesize antibodies.
C) lymphoid tissues
The majority of T cells of the naive lymphocyte pool wait for the encounter with foreign antigens in the __________.
A) plasma
B) thymus
C) lymphoid tissues
D) lymph
E) blood plasma
False
T/F: Clonal selection of T cells happens in the thymus.
D) major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein
Helper T (TH) cells recognize antigens when they are bound to a(n) __________.
A) hapten
B) immunoglobulin
C) natural killer cell
D) major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein
E) basophil
True
T/F: Interleukins are chemical signals by which immune cells communicate with each other.
D) Antibodies
Which of the following cannot act as antigen-presenting cells?
A) Dendritic cells
B) Macrophages
C) B cells
D) Antibodies
B) secrete granzymes and perforin
Cytotoxic T (TC) cells are like natural killer (NK) cells because they both __________.
A) secrete interferons
B) secrete granzymes and perforin
C) participate in the immune response
D) participate in innate immunity
E) secrete tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
True
T/F: Helper T cells respond only to epitopes attached to MHC proteins.
True
T/F: Cytotoxic T cells respond only to antigens bound to MHC-I proteins.
E) secrete fever-producing chemicals
Helper T (TH) cells do not __________.
A) secrete cytokines that stimulate clonal selection of B cells
B) secrete cytokines that stimulate clonal selection of cytotoxic T cells
C) secrete cytokines that stimulate macrophage activity
D) secrete inflammatory chemicals
E) secrete fever-producing chemicals
D) Helper T (TH) cells
__________ participate in both innate immunity and the immune response.
A) Memory T (TM) cells
B) Regulatory T (TR) cells
C) Natural killer (NK) cells
D) Helper T (TH) cells
E) Cytotoxic T (TC) cells
B) Antigen recognition -> antigen presentation -> clonal selection -> differentiation -> attack
Which is the correct sequence of events in the humoral immune response?
A) Antigen recognition -> antigen presentation -> differentiation -> clonal selection -> attack
B) Antigen recognition -> antigen presentation -> clonal selection -> differentiation -> attack
C) Antigen presentation -> antigen recognition -> clonal selection -> differentiation -> attack
D) Antigen presentation -> antigen recognition -> clonal selection -> attack -> differentiation
E) Antigen recognition -> differentiation -> antigen presentation -> clonal selection -> attack
B) lymph nodes
Antigen-presenting cells usually display processed antigens to T cells in the __________.
A) blood plasma
B) lymph nodes
C) thymus
D) red bone marrow
E) liver
A) Class I MHCs
Degraded self-protein fragments are presented by __________.
A) Class I MHCs
B) Cytotoxic T cells
C) Infected cells
D) Viruses
E) TCRs
False
T/F: Cytotoxic T cells degrade after coming in contact with an infected cell.
False
T/F: Most Memory B cells are found circulating in the lymph.
C) decades
Memory T cells can be up to __________ old.
A) weeks
B) days
C) decades
D) years
E) months
C) plasma cells
Before B cells secrete antibodies, they differentiate into __________.
A) stem cells
B) antigen-presenting cells
C) plasma cells
D) T cells
E) macrophages
A) plasma
IgE is produced by __________ cells.
A) plasma
B) antigen presenting
C) cytotoxic T
D) helper T
E) natural killer
True
T/F: Antibodies and complement can work together, linking innate and adaptive immunity.
D) Differentiate into memory antibodies, which upon reexposure to the same pathogen would mount a quicker attack
Which of the following is something antibodies do not do?
A) Link antigen molecules together
B) Neutralize antigens by binding to regions of an antigen that can be pathogenic
C) Bind to enemy cells, thus changing their shape so their complement-binding sites are exposed
D) Differentiate into memory antibodies, which upon reexposure to the same pathogen would mount a quicker attack
E) Bind antigen molecules of two or more enemy cells and stick them together
True
T/F: Humoral immunity produces memory by increasing the number of cells and antibodies that can fight off a pathogen in the secondary response.
False
T/F: Cellular immunity uses B cells and humoral immunity uses antibodies.
True
T/F: Cellular immunity uses MHC-I and MHC-II, but humoral immunity uses only MHC-II.
False
T/F: An allergic reaction is a form of hyposensitivity.
E) type I (acute) hypersensitivity
Most common allergies are the result of __________.
A) autoimmune diseases
B) type IV (delayed) hypersensitivity
C) type III (immune complex) hypersensitivity
D) type II (antibody-dependent cytotoxic) hypersensitivity
E) type I (acute) hypersensitivity
B) type IV (delayed) hypersensitivity
Beta cell destruction that causes type 1 diabetes mellitus is a(n) __________.
A) anaphylactic hypersensitivity
B) type IV (delayed) hypersensitivity
C) type III (immune complex) hypersensitivity
D) type II (antibody-dependent cytotoxic) hypersensitivity
E) type I (acute) hypersensitivity
B) anaphylactic shock
Bronchoconstriction, dyspnea, and widespread vasodilation are all characteristics of __________.
A) local anaphylaxis
B) anaphylactic shock
C) autoimmune disease
D) an HIV infection
E) AIDS
A) anaphylaxis
An immediate and intense type I reaction that can be treated with antihistamines is characteristic of __________.
A) anaphylaxis
B) anaphylactic shock
C) autoimmune disease
D) an HIV infection
E) AIDS
C) self-antigens
Autoimmune diseases are disorders in which the immune system fails to distinguish __________ from foreign ones.
A) self-immunoglobulins
B) self-antibodies
C) self-antigens
D) self-interleukins
E) self-complement proteins
True
T/F: Some antibodies against foreign antigens can react to similar self-antigens, causing an autoimmune disease.
A) helper T cells
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) targets mainly __________.
A) helper T cells
B) B cells
C) plasma cells
D) cytotoxic T cells
E) natural killer cells
D) 200 cells/µL
A person who is HIV-positive and has a helper T (TH) cell count lower than __________ has AIDS.
A) 20,000 cells/µL
B) 5,000 cells/µL
C) 1,000 cells/µL
D) 200 cells/µL
E) 50 cells/µL
A) A
Which of these organs shrinks significantly by adulthood?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
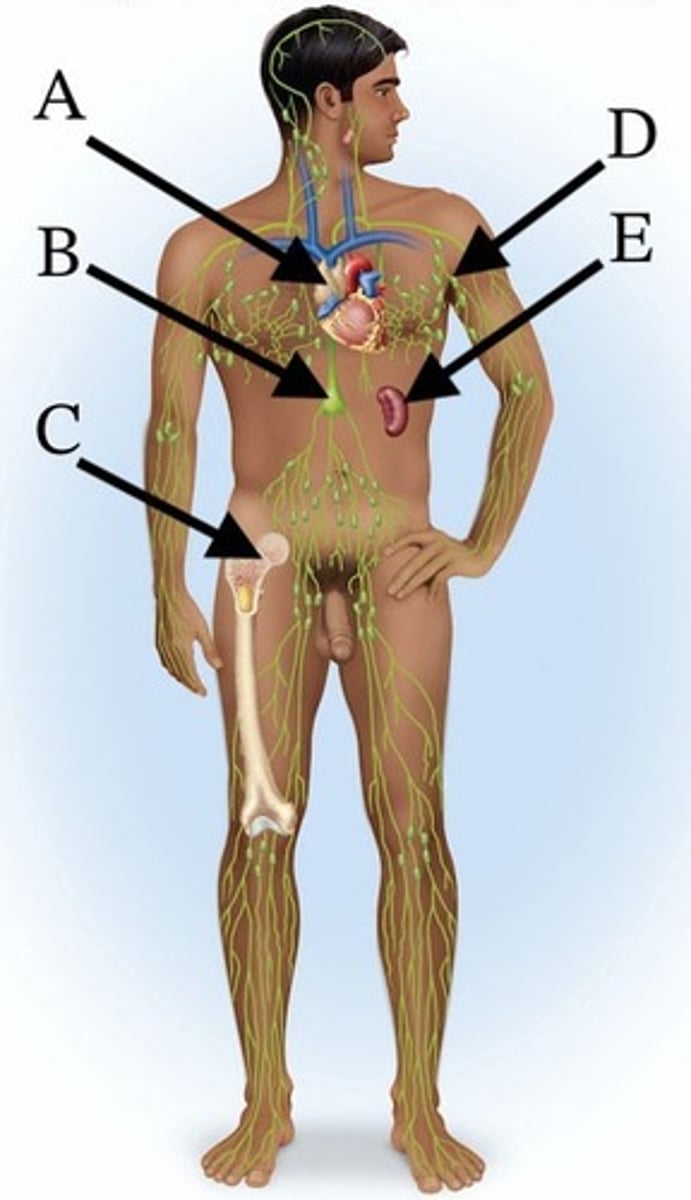
E) E
Which of these is the largest lymphoid organ in the body?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
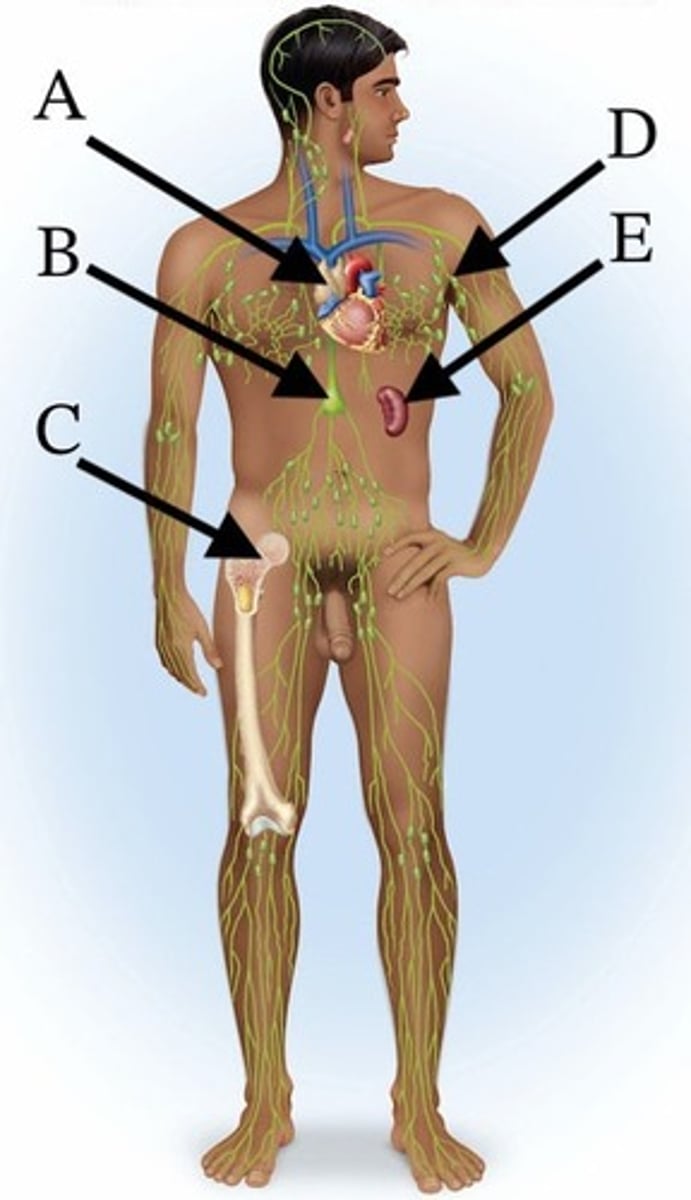
B) B
Which of these structures collects chyle?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
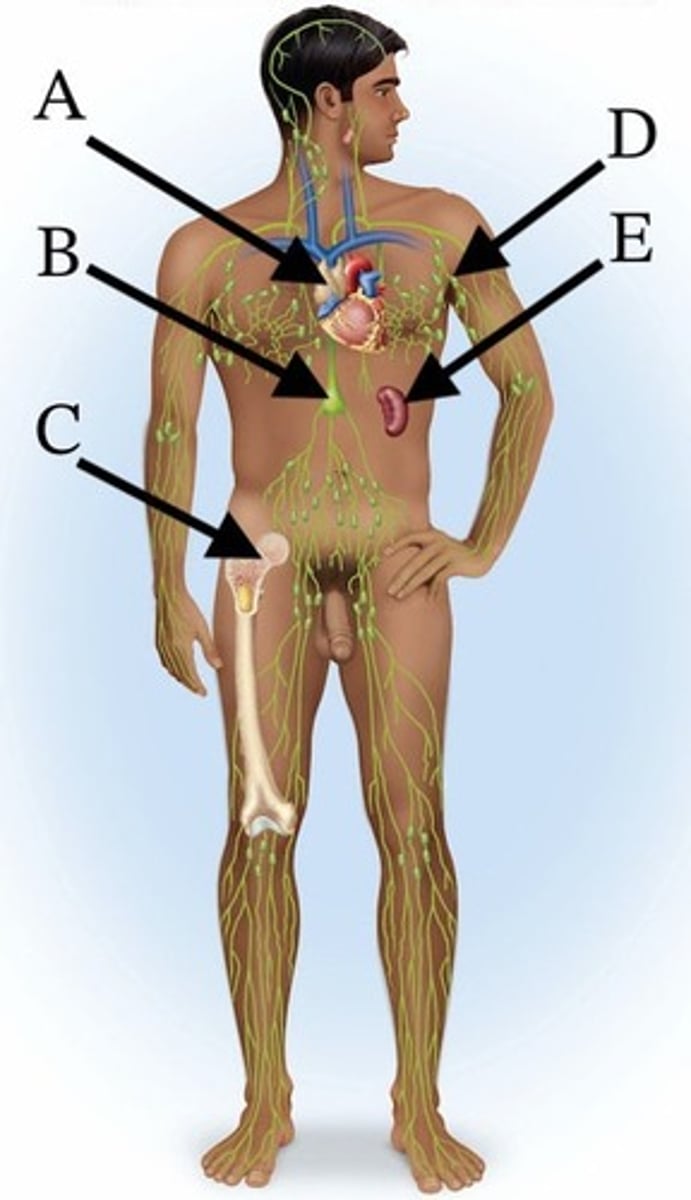
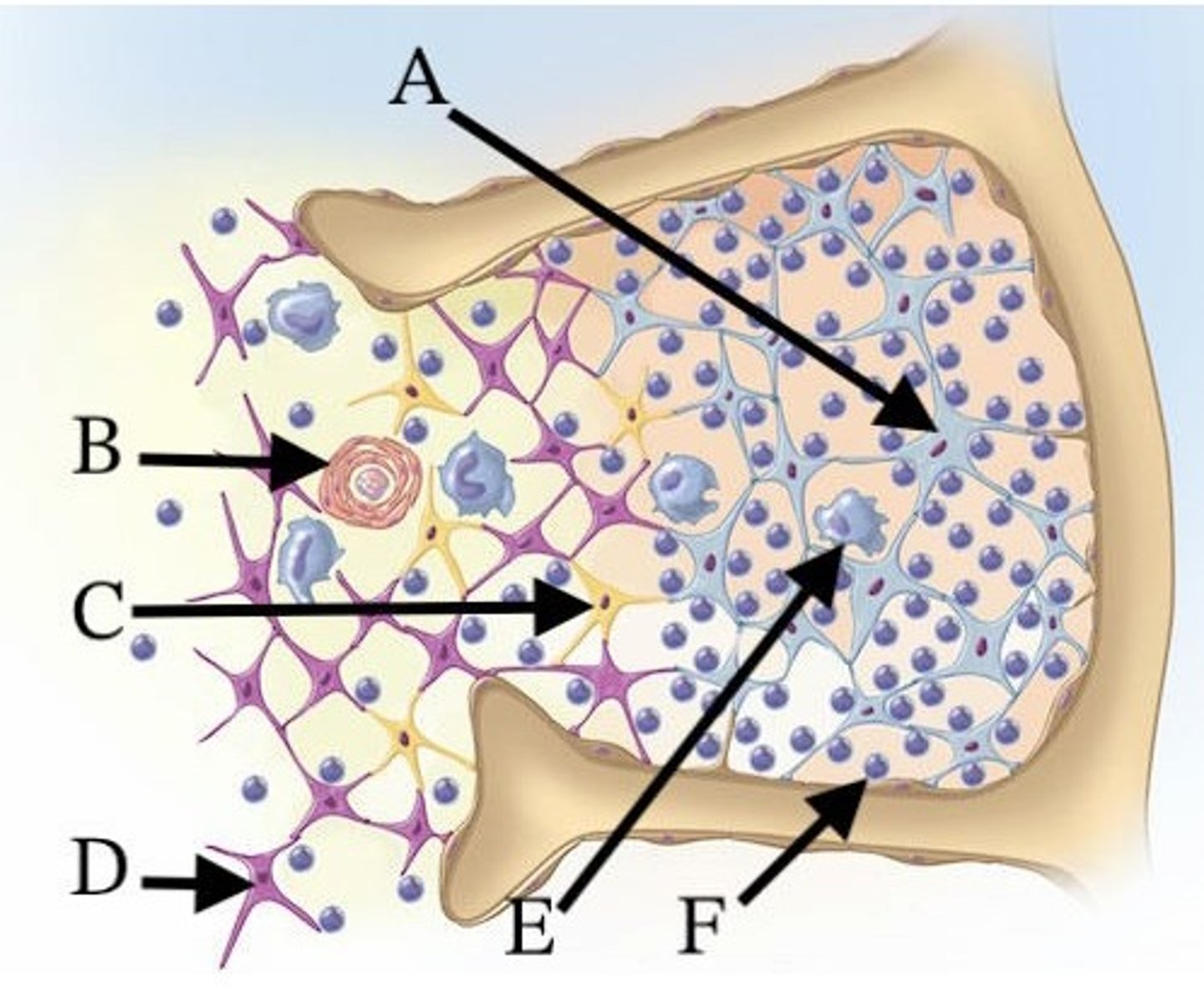
A) A
Which of these cells contributes to the formation of the blood-thymus barrier?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) E
E) F
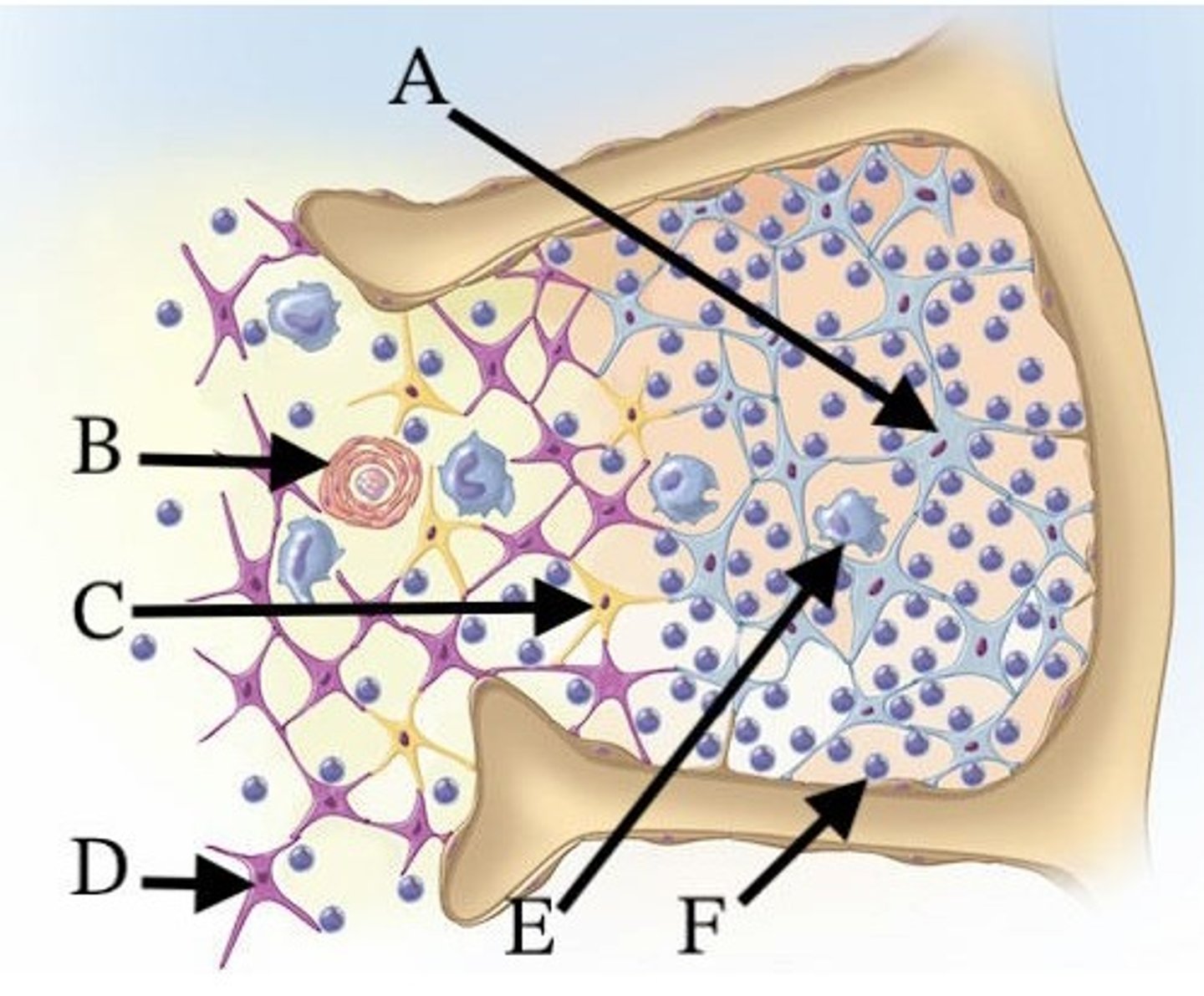
B) B
Which of these letters indicates a thymic corpuscle?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) E
E) F
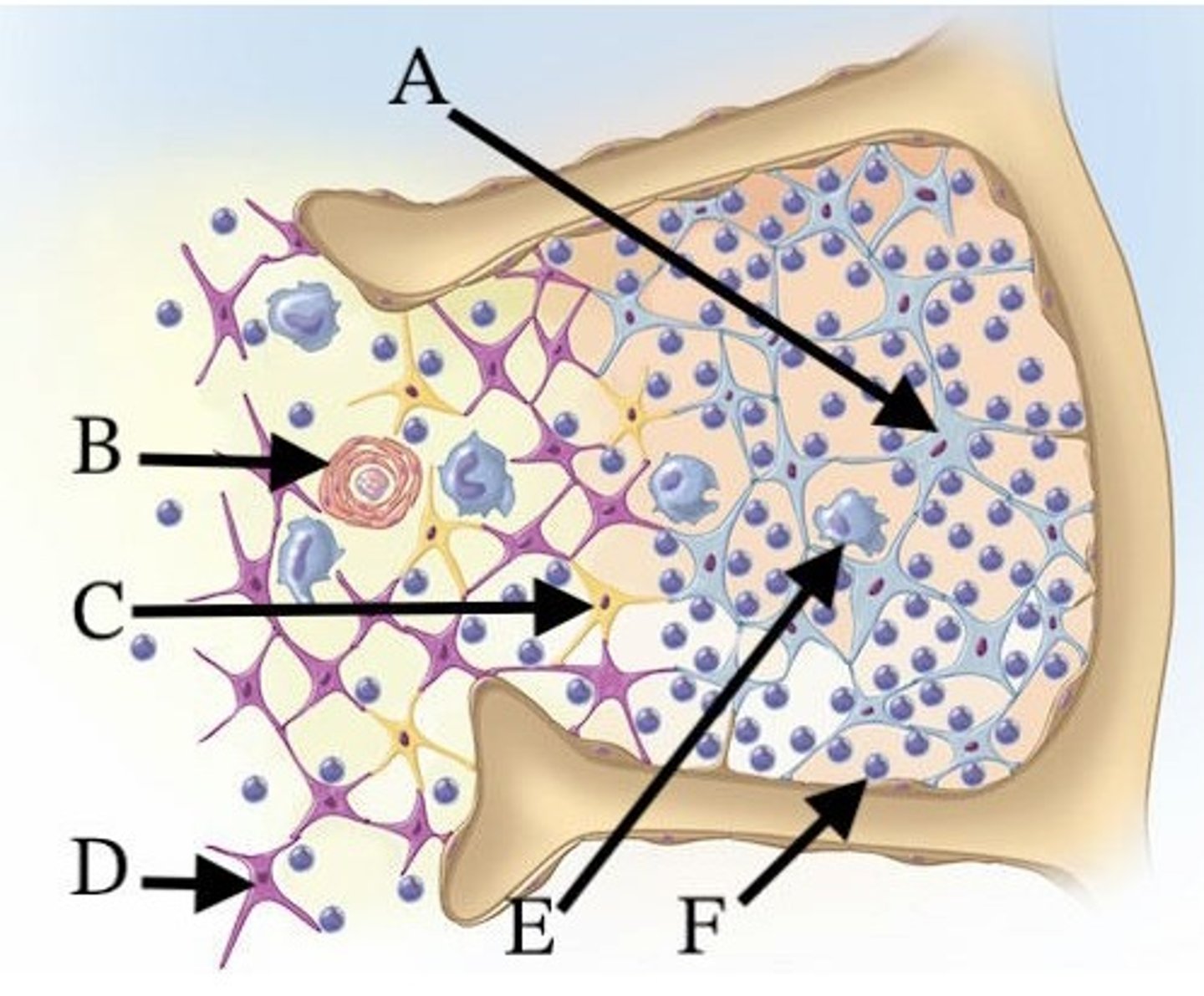
D) A, E, and F
Which cells are found in the cortex of the thymus?
A) A, B, and C
B) B, C, and D
C) D, E, and F
D) A, E, and F
E) A, D, and E
B) B
Which letter indicates an afferent lymphatic vessel?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
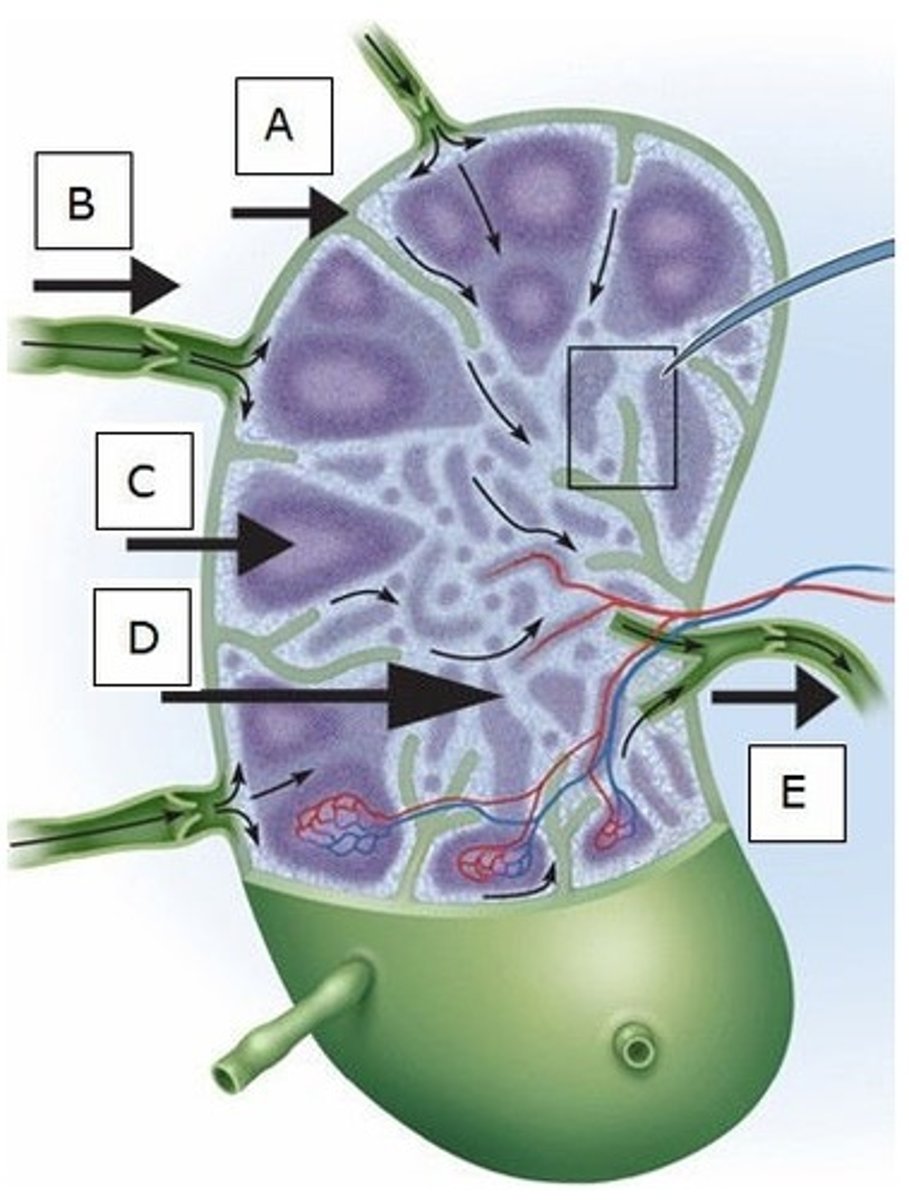
C) C
Where do B cells differentiate into plasma cells?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
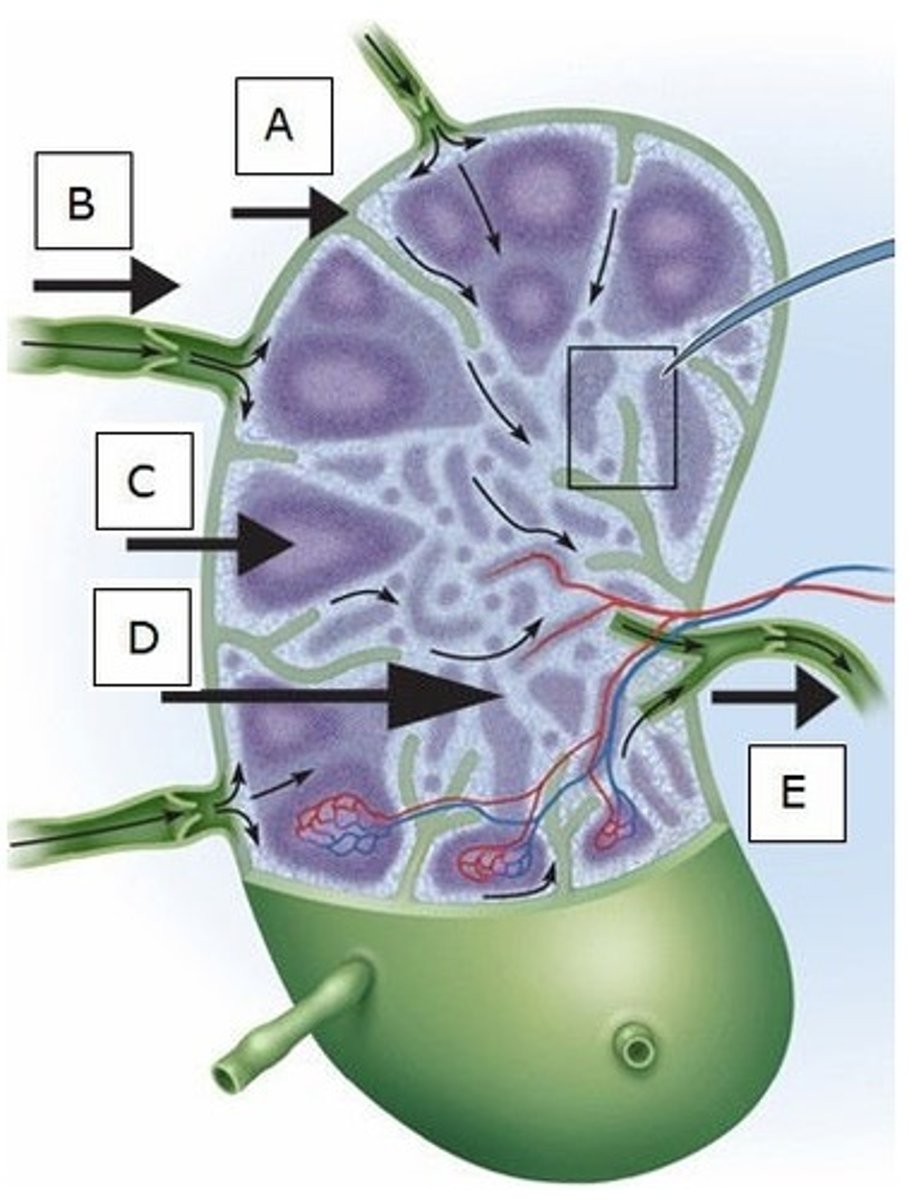
D) D
Which letter indicates a medullary cord?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
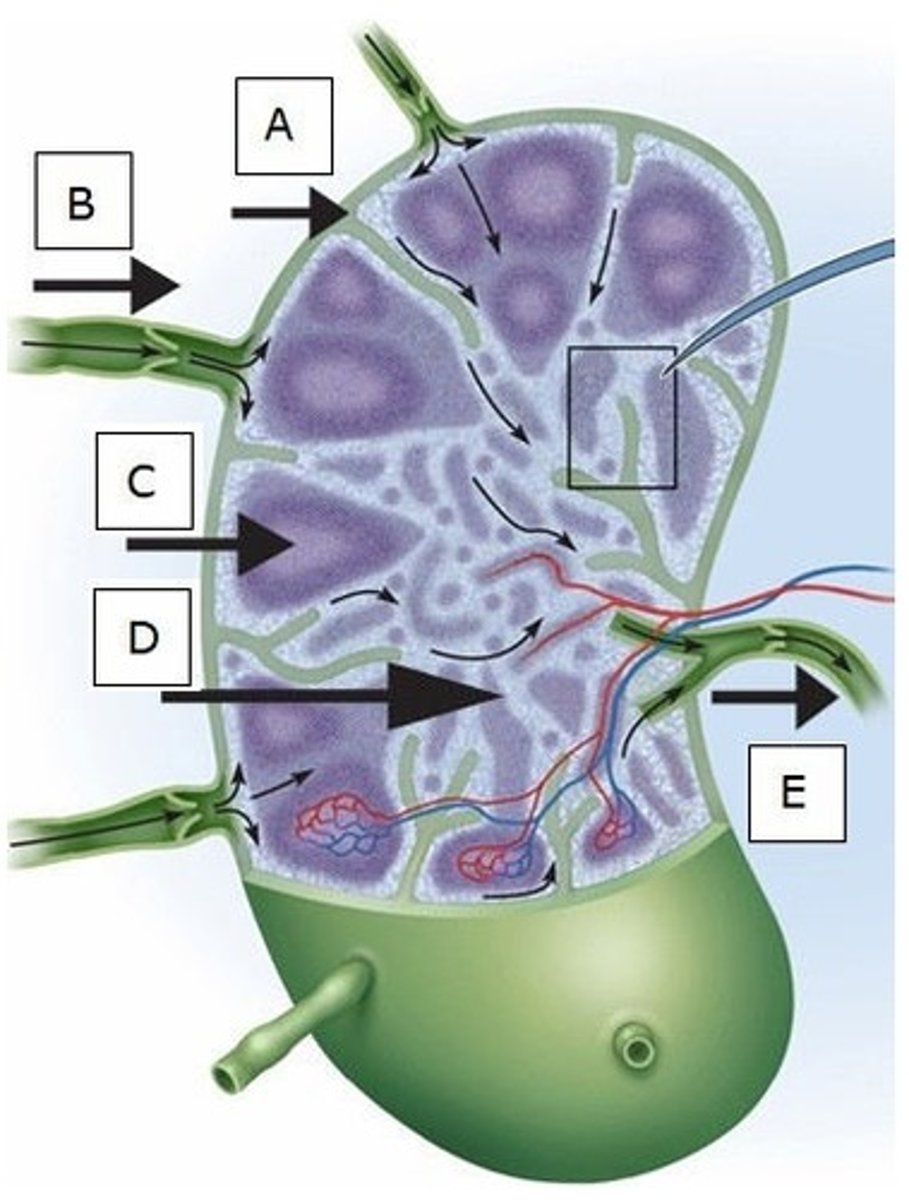
B) B
Which of these lymphoid organs is most often infected?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B
E) B and C
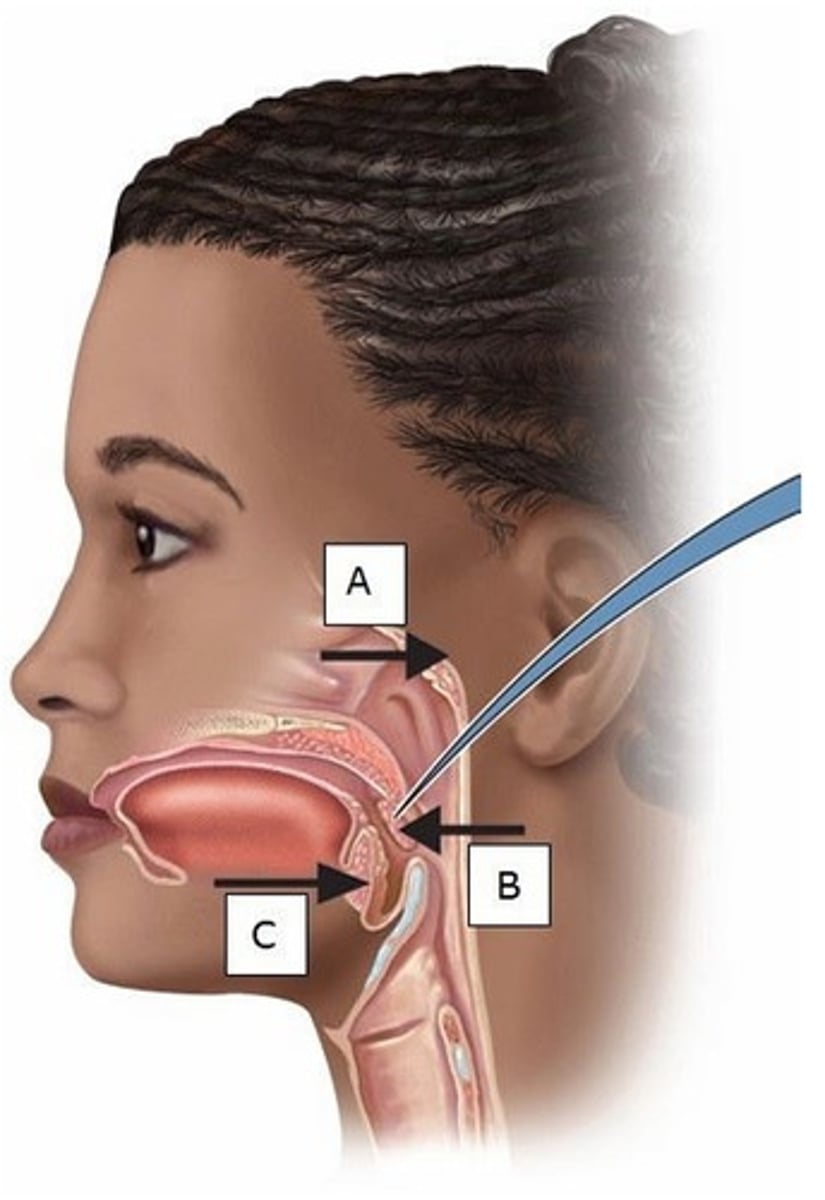
A) A
Which of these is also referred to as the adenoids?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B
E) B and C
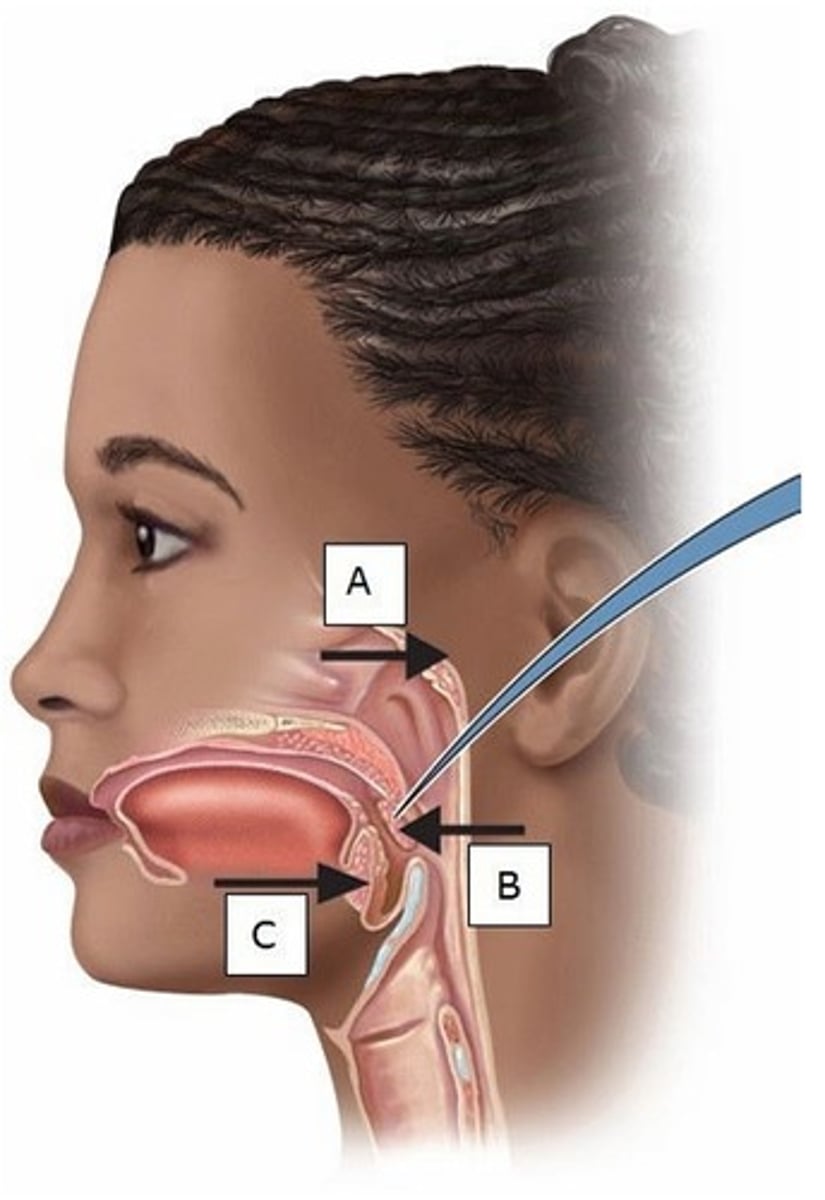
B) B
Which of these is referred to as the palatine tonsils?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B
E) B and C
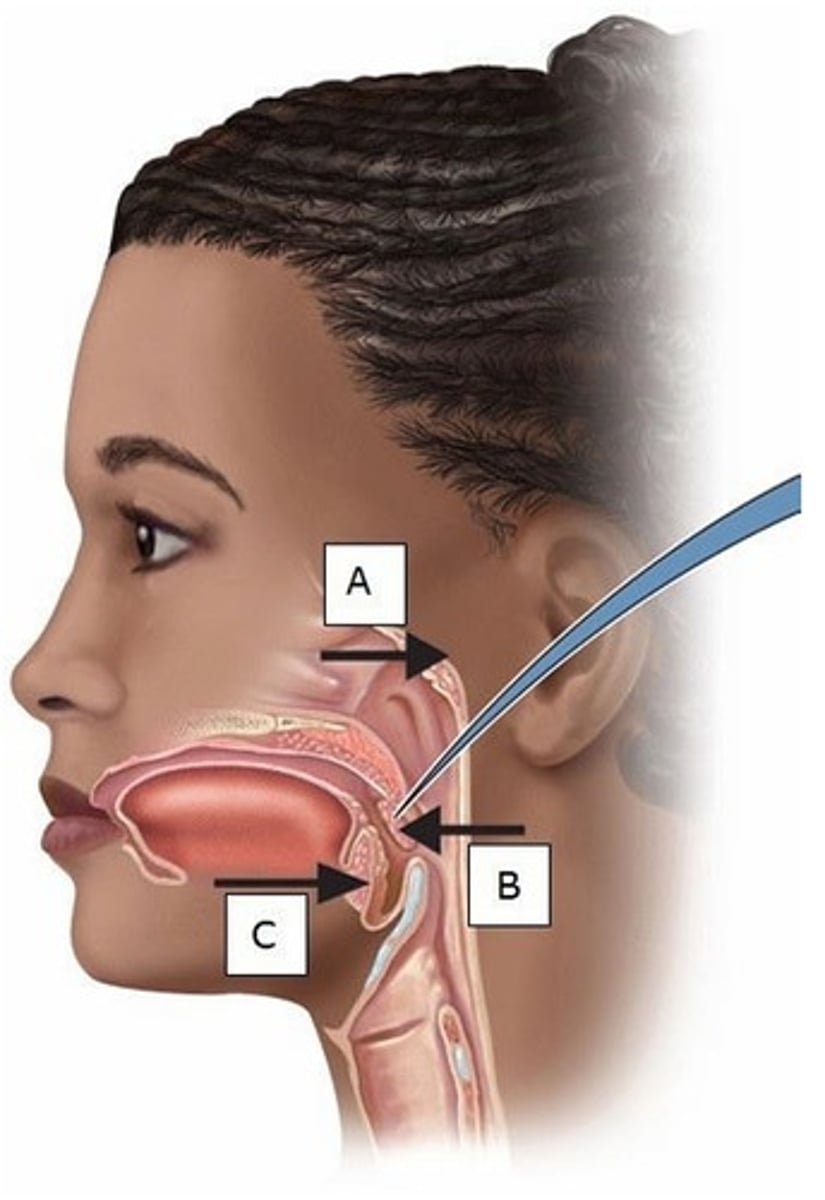
A) A
Which letter represents a Natural Killer cell?
A) A
B) D
C) E
D) A and D
E) D and E
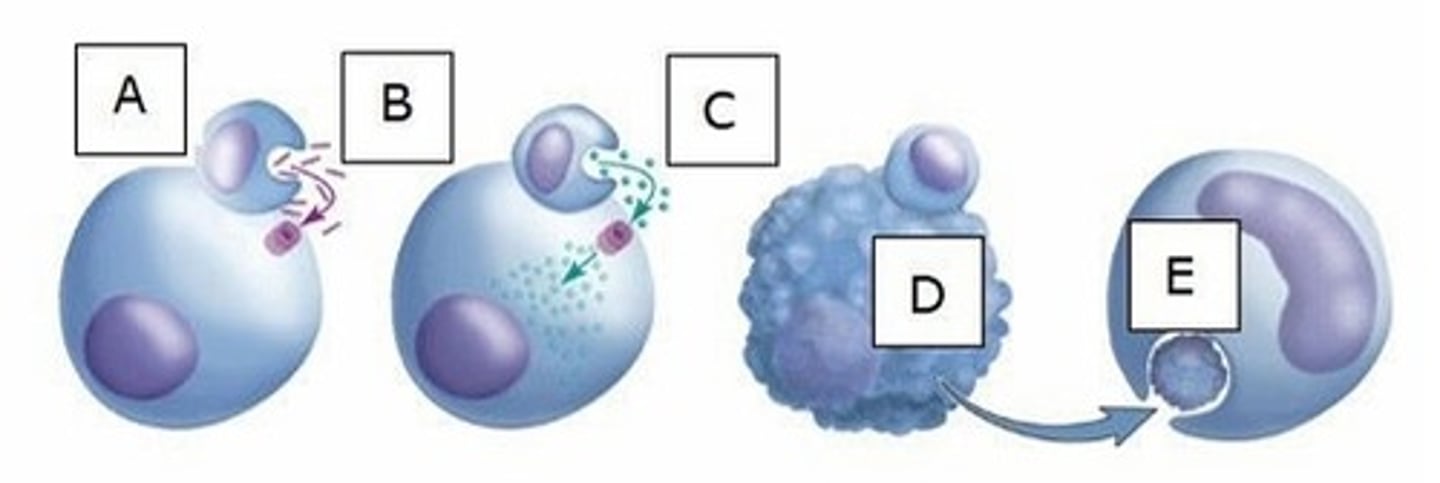
C) E
Which letter represents a macrophage?
A) A
B) D
C) E
D) A and D
E) D and E
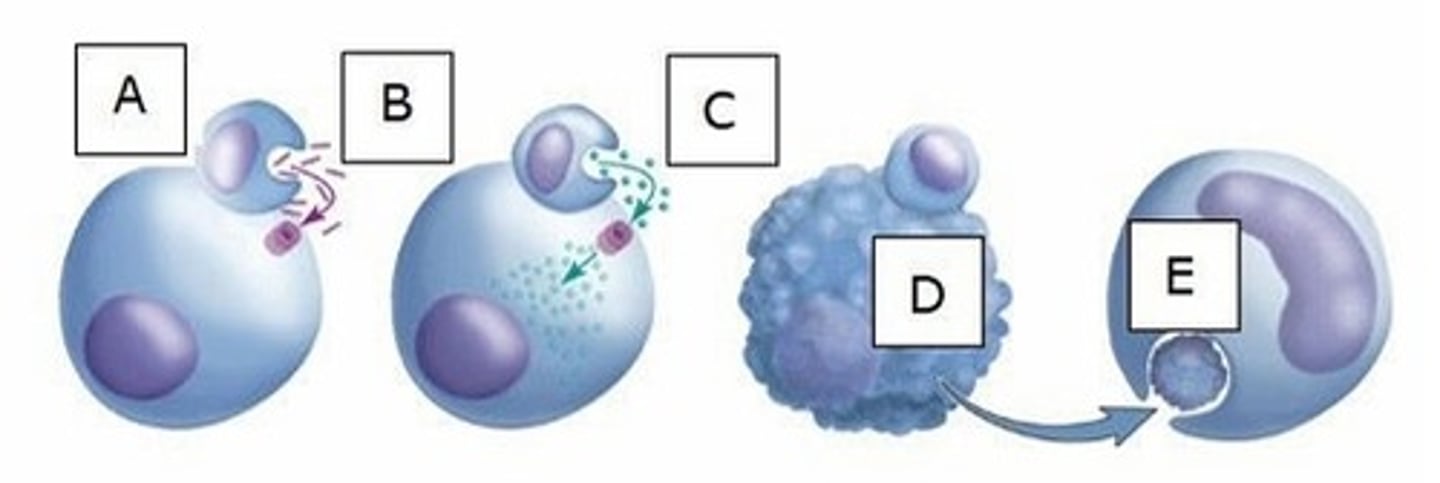
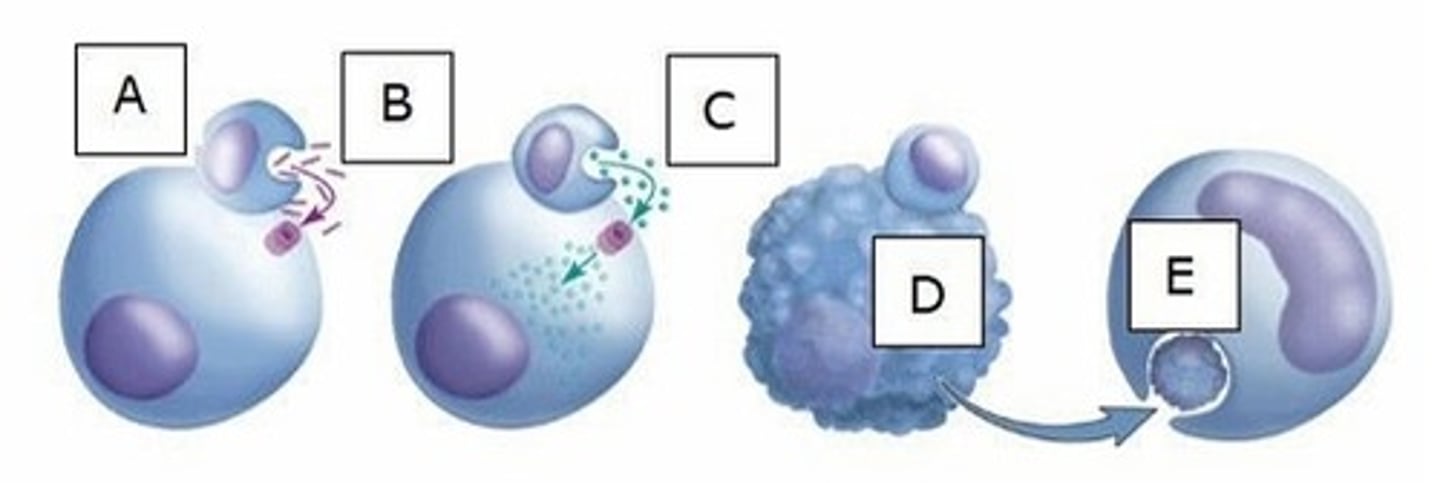
A) Perforins
What chemical does A represent?
A) Perforins
B) Cytokines
C) Interleukins
D) Granzymes
E) Pyrogens
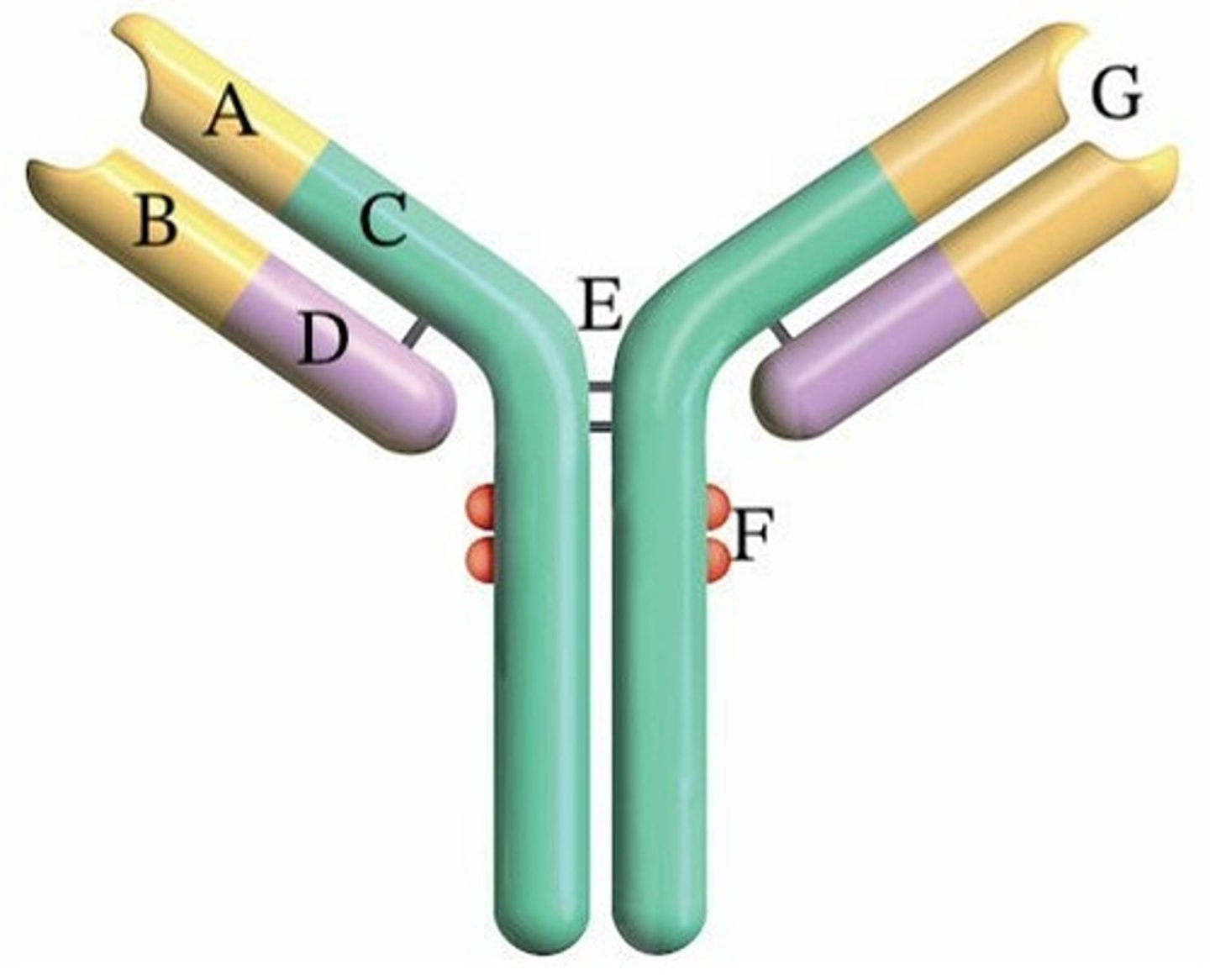
A) C and D
Which letter(s) represent(s) constant regions?
A) C and D
B) A and B
C) C
D) A
E) A and C
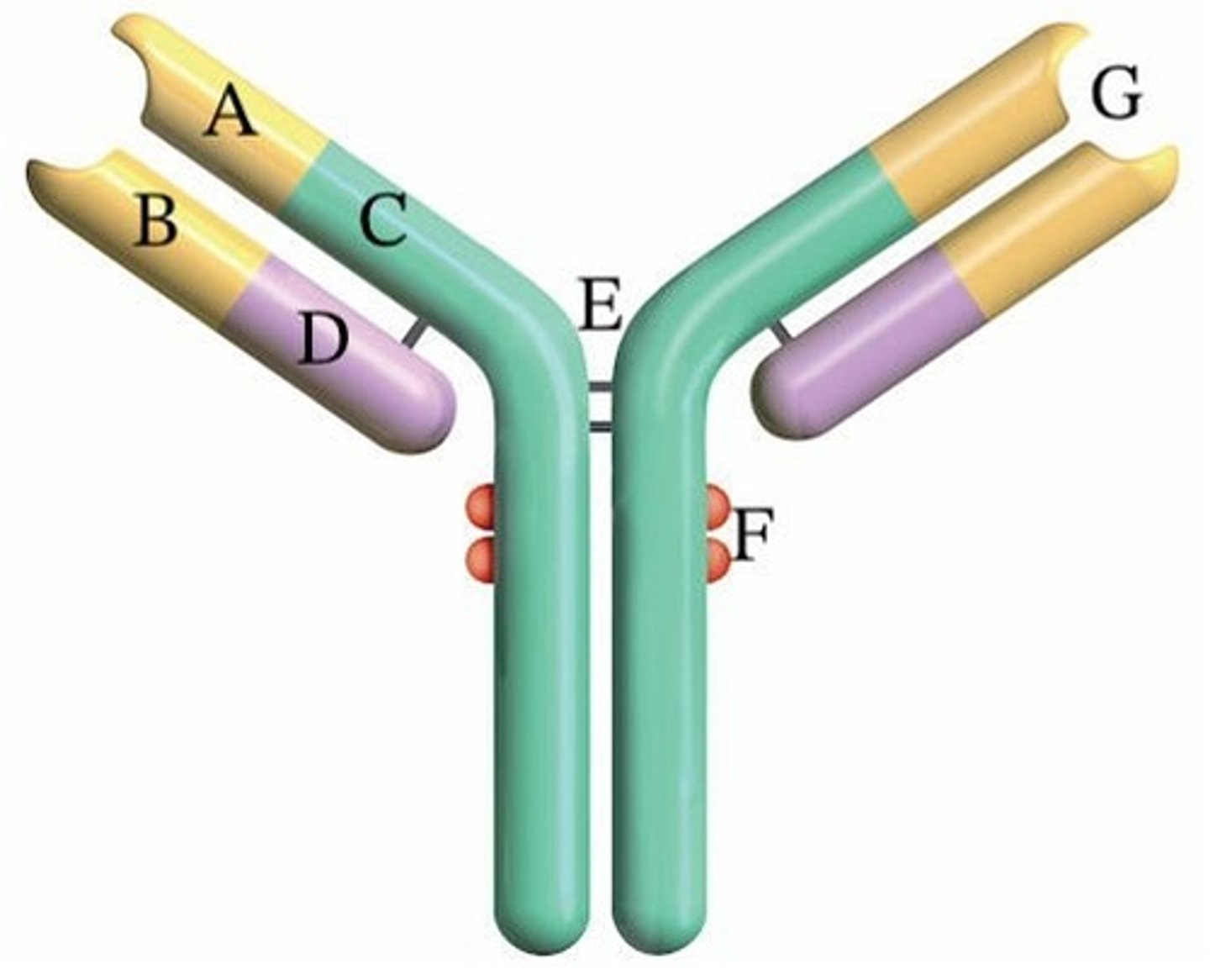
A) Disulfide
What type of bond is found at E?
A) Disulfide
B) Hydrogen
C) Ionic
D) Peptide
E) Van der Waals

C) C
Where does complement bind?
A) E
B) B
C) C
D) A
E) G