Understanding Pain and Its Mechanisms
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Pain
Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience from tissue damage.
think about how our response affects patients response
Manifestation of Pain
Wide range of sensations
ask patient to describe it to us first
burning
throbbing
tingling
prickly
itchiness
other odd - strings pulling, water running on skin, ants crawling on skin
Sensory Neurons
Neurons labeled by order in sensory chain
First Order Neurons
Transmit signals from receptors to dorsal horn.
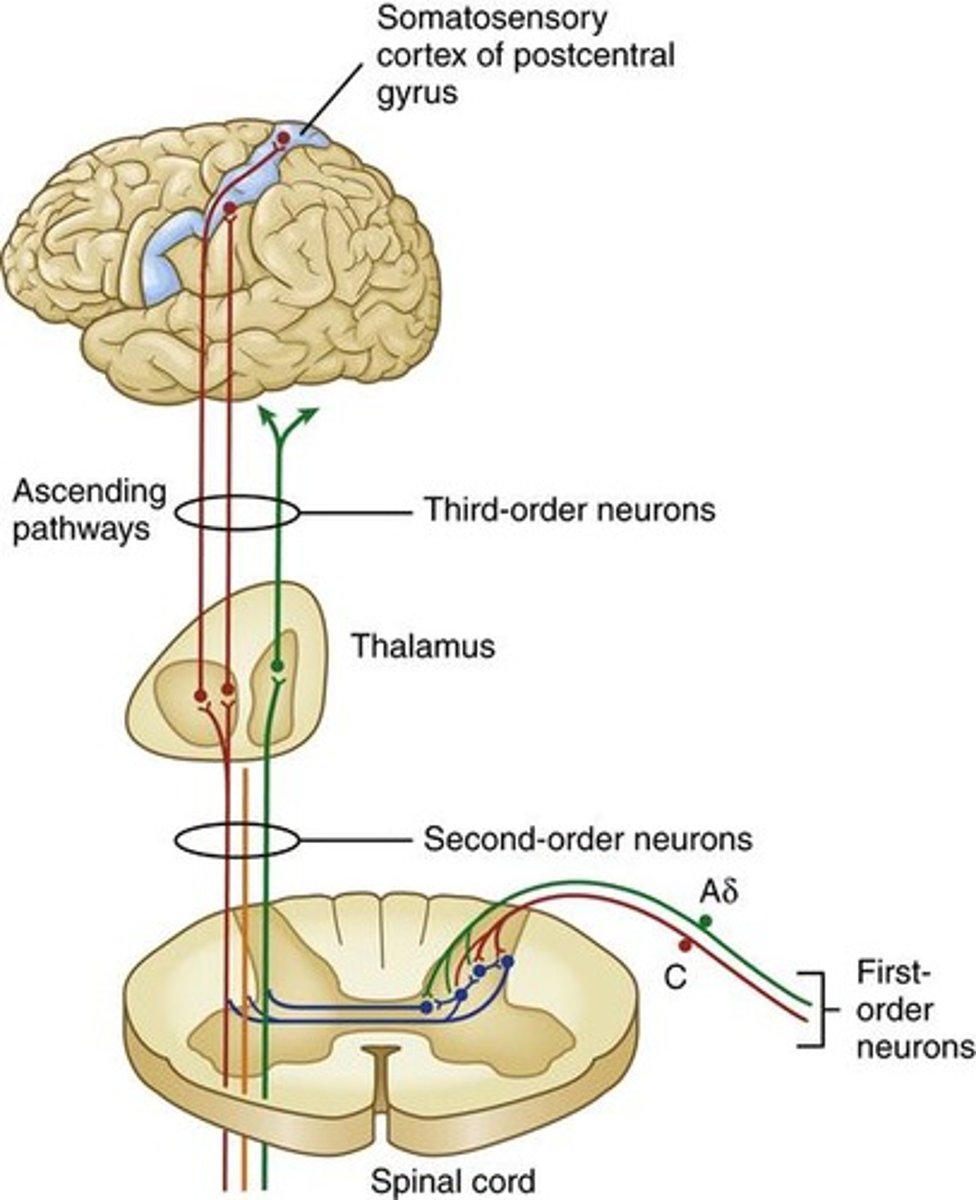
Second Order Neurons
Transmit signals from dorsal horn to thalamus.
Third Order Neurons
Transmit signals from thalamus to cerebral cortex.
cerebral cortex interprets messages sent out
Nociceptors
Specialized nerve endings responding to damaging stimuli.
sensory receptors
activate A delta and C nerve fibers
A delta
larger and faster
relay signal to CNS
interprested as pain
C fibers
smaller and slower
relay signals to CNS
interpreted as pain
Nociception
Ability to feel pain
caputures protentially damaging signlas
relay signals to the CNS
interpret as pain
Nociception vs Pain
Nociception is objective event; pain is subjective, emotional experience.
pain results from...
modulation of nociception by a host of factors
heredity
psychosocial experience
prior pain experience
general life stress
Types of Nociceptors
Cutaneous, somatic, visceral
based on location.
most common by function
mechanical nociceptors
lightly mylenated A delta fibers
high threshold
polymodal nociceptors
unmyelinated c fibers
common noxious stimuli
Mechanical (pressure on nerve due to swelling or muscle spasm, most common in sports medicine), thermal, electrical, and chemical pain triggers.
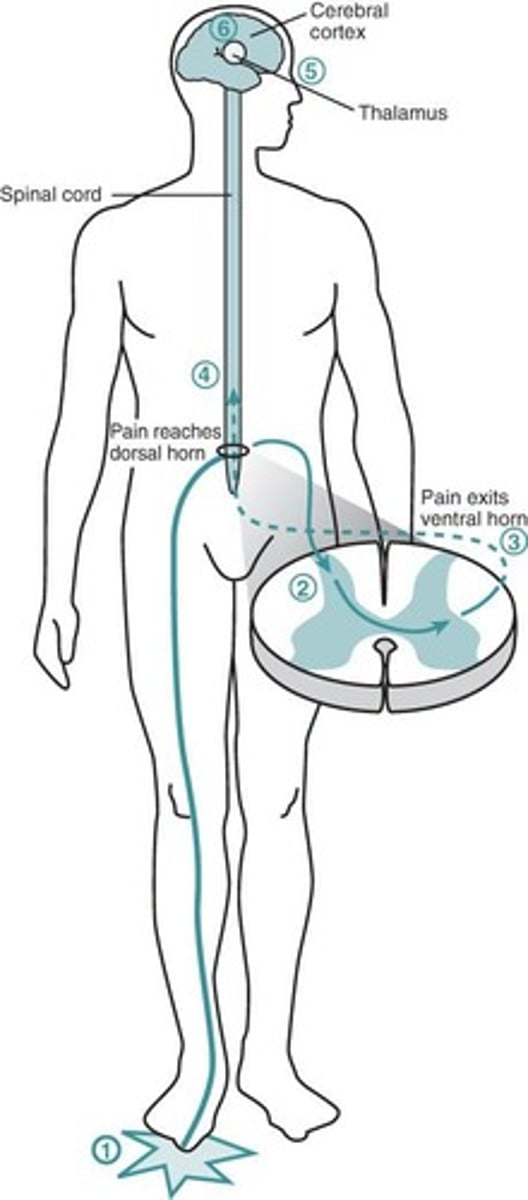
Pathway of Pain Signals
Injury site to dorsal horn via electro-chemical impulse (1st)
up spinal cord to thalamus where heat, cold, touch, and pain first become conscious (2nd)
then to cerebral cortex where the exact location and intensity of the pain are determined, person orally or physically expresses discomfort (3rd)
like a relay
Gate Control Theory
Spinal mechanism allowing one sensation at a time.
located in dorsal horn
whichever one is "louder"
inhibitory mechanism located in the substantia gelatinosa
SG inhibits T cells
Enkephalin
andogenous Opioid-like molecule blocking pain signal transmission.
found in brain, spinal cord, gut
half life only few seconds, no ciculation
thought to block gate by interfering with a delta fiber and cfiber signal transmission to t cells
released through non painful sensory stimulus
Endorphin
Endogenous morphine-like molecule reducing pain perception.
released when injured, take pain away
produced in pituitary and circulated through body
inhibits pain signal transmission and decreases chemical irritants in CNS
may be released by acupuncture and other
endorphin and enkephalin speculation
why ppl experience more pain than others
perhaps more people espeacially sensitive to pain have enkephalin or receptor deficiency
placebo effect may be increased by enkephalin and endorphin
Descending Endogenous Opiate Theory
efferent pathway
operates at supraspinal levels and spinal gate
originates from above
pain signal blocked on way out vs in
Central Control Trigger Theory
aka central biasing theory
pain is not just a simple response to injury but is influenced by the brain and spinal cord. According to this theory, signals from the body (like injury or pressure) are filtered through a "gate" in the spinal cord, and the brain can control whether those signals are felt as pain or not — kind of like a volume dial for pain.
Pain Perception
Multifaceted experience often confused with other sensations.
decrease pain means decrease neural inhibition
treat pain in order to treat other things
Pain vs Pain Perception
Pain is brain's response to noxious stimuli.
as healing progresses, noxious stimuli decline and pain sensation diminishes until minimal or absent
Variability of Pain Tolerance
Pain response varies between individuals and situations.
difficult to research because pain is subjective
hard to describe pain
Pain Management
a complex, tailored approach needed for each patient and injury.
be able to adjust from patient to patient